Somaliland, officially the Republic of Somaliland, is an
unrecognised country in the
Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
. It is located in the southern coast of the
Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden (; ) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. ...
and bordered by
Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
to the northwest,
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
to the south and west, and
Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
to the east. Its claimed territory has an area of ,
with approximately 6.2 million people as of 2024.
The capital and largest city is
Hargeisa
Hargeisa ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland, a ''List of states with limited recognition, de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still considered internationally to be part of Somalia. It is also th ...
.
Various Somali Muslim kingdoms were established in the area during the early Islamic period, including in the 14th to 15th centuries the Zeila-based
Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, also known as the Adal Empire or Barr Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate'', ''Adal Sultanate'') (), was a medieval Sunni Muslim empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din III on th ...
.
In the early modern period, successor states to the Adal Sultanate emerged, including the
Isaaq Sultanate
The Isaaq Sultanate (, Wadaad's writing, Wadaad: , ) was a Muslims, Muslim sultanate that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa in the 18th and 19th centuries. The kingdom spanned the territories of the Isaaq clan in modern-day Somaliland and Ethiopi ...
which was established in the middle of the 18th century.
In the late 19th century, the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
signed agreements with various clans in the area, establishing the
Somaliland Protectorate
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936-1941). From 1940 ...
,
which was formally granted independence by the United Kingdom as the
State of Somaliland
Somaliland, officially the State of Somaliland (), was an independent country in the territory of the present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland, which regards itself as its legal successor. It existed on the territory of former ...
on 26 June 1960. Five days later, the State of Somaliland voluntarily united with the
Trust Territory of Somalia
The Trust Territory of Somaliland, officially the Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian Administration (), was a United Nations Trust Territory from 1950 to 1960, following the dissolution of the former British Military Administration. I ...
(the former Italian Somalia) to form the
Somali Republic
The Somali Republic (; ; ) was formed by the union of the Trust Territory of Somaliland (formerly Italian Somaliland) and the State of Somaliland (formerly British Somaliland). A government was formed by Abdullahi Issa Mohamud and Muhammad ...
.
The union of the two states proved problematic early on,
and in response to the harsh policies enacted by Somalia's Barre regime against the main clan family in Somaliland, the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
, shortly after the conclusion of the disastrous
Ogaden War
The Ogaden War, also known as the Ethio-Somali War (, ), was a military conflict between Somali Democratic Republic, Somalia and derg, Ethiopia fought from July 1977 to March 1978 over control of the sovereignty of the Ogaden region. Somalia ...
, a 10-year
war of independence
Wars of national liberation, also called wars of independence or wars of liberation, are conflicts fought by nations to gain independence. The term is used in conjunction with wars against foreign powers (or at least those perceived as foreign) ...
concluded with the
declaration of Somaliland's independence in 1991. The
Government of Somaliland regards itself as the
successor state
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th ...
to British Somaliland.
[''The New Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2002), p. 835.]
Since 1991, the territory has been governed by democratically elected governments that seek international recognition as the government of the Republic of Somaliland.
The central government maintains
informal ties with some foreign governments, who have sent delegations to Hargeisa;
Somaliland hosts
representative offices from several countries, including
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
and
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
.
However, Somaliland's self-proclaimed independence has not been officially recognised by any UN member state or international organisation.
It is the largest unrecognised state in the world by ''de facto'' controlled land area. It is a member of the
Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization
The Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO) is an international organization established to facilitate the voices of unrepresented and marginalized nations and peoples worldwide. It was formed on 11 February 1991 at the Peace Pal ...
, an advocacy group whose members consist of indigenous peoples, minorities and unrecognised or occupied territories.
Following the
Las Anod conflict that emerged in 2022, Somaliland lost control of a significant portion of its eastern territory to pro-unionist forces who established the
SSC-Khatumo administration.
Etymology
The name ''Somaliland'' is derived from two words: "
Somali" and "land". The area was named when
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
took control from the
Egyptian administration in 1884, after signing successive treaties with the ruling Somali Sultans from the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
,
Issa,
Gadabursi
The Gadabuursi ( Somali: ''Gadabuursi'', Arabic: جادابورسي), also known as ''Samaroon'' (Arabic: ''قبيلة سَمَرُون)'', is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.I. M. Lewis (1959)
The Gadabuursi ...
, and
Warsangali
The Warsangali (, ), alternatively the Mohamoud Harti, are a major Somali sub clan, part of the larger Harti branch, which belongs to the Darod clan, one of the largest Somali tribe families. In the Somali language, the name Warsangali means "b ...
clans. The British established a
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over ...
in the region referred to as
British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
. In 1960, when the protectorate became
independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in Pennsylvania, United States
* Independentes (English: Independents), a Portuguese artist ...
from Britain, it was called the
State of Somaliland
Somaliland, officially the State of Somaliland (), was an independent country in the territory of the present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland, which regards itself as its legal successor. It existed on the territory of former ...
. Five days later, on 1 July 1960, Somaliland united with the
Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian Administration (the former
Italian Somaliland
Italian Somaliland (; ; ) was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia, which was ruled in the 19th century by the Sultanate of Hobyo and the Majeerteen Sultanate in the north, and by the Hiraab Imamate and ...
). The name "Republic of Somaliland" was adopted upon the
declaration of independence
A declaration of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the territory of another state or failed state, or are breaka ...
following the
Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War (; ) is an List of ongoing armed conflicts, ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Barre during the 1980s. From 1988 to 1990, the Somali Armed ...
in 1991.
At the Grand conference in
Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
held in 1991, many names for the country were suggested, including ''Puntland'', in reference to Somaliland's location in the ancient
Land of Punt
The Land of Punt (Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pwnt#Egyptian, pwnt''; alternate Egyptian language#Egyptological pronunciation, Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') ) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. ...
and which is now the name of the
Puntland
Puntland is an autonomous state that considers itself to be part of Somalia, despite not accepting the legitimacy of Somalia's current governing administration. It was formed in 1998, and was a federal member state of Somalia from its fou ...
state in neighbouring Somalia, and ''Shankaroon'', meaning "better than five" in
Somali, in reference to the five regions of
Greater Somalia
Greater Somalia, also known as Greater Somaliland (; ), is the geographic location comprising the regions in the Horn of Africa in which ethnic Somalis live and have historically inhabited.During the Scramble for Africa at the end of the 19th cent ...
.
History
Prehistory

The area of Somaliland was inhabited around 10,000 years ago during the
Neolithic age
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wid ...
. The ancient shepherds raised cows and other livestock and created vibrant rock art paintings. During the
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
, the Doian and Hargeisan cultures flourished here.
The oldest evidence of burial customs in the
Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
comes from
cemeteries
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite, graveyard, or a green space called a memorial park or memorial garden, is a place where the remains of many dead people are buried or otherwise entombed. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek ) implies th ...
in Somaliland dating back to the
4th millennium BCE
File:4th millennium BC montage.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: The Temple of Ġgantija, one of the oldest freestanding structures in the world; Warka Vase; Bronocice pot with one of the earliest known depictions of a wheeled vehicle; K ...
.
The stone implements from the Jalelo site in the north were also characterised in 1909 as important artefacts demonstrating the archaeological universality during the Paleolithic between the East and the West.
According to linguists, the first
Afroasiatic-speaking populations arrived in the region during the ensuing
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period from the family's proposed
urheimat
In historical linguistics, the homeland or ( , from German 'original' and 'home') of a proto-language is the region in which it was spoken before splitting into different daughter languages. A proto-language is the reconstructed or historicall ...
("original homeland") in the
Nile Valley
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
,
[Zarins, Juris (1990), "Early Pastoral Nomadism and the Settlement of Lower Mesopotamia", (Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research)] or the
Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
.
The
Laas Geel
Laas Geel (), also spelled Laas Gaal, are cave formations on the rural outskirts of Hargeisa, Somalia, situated in the Maroodi Jeex region of the country. They contain some of the earliest known cave paintings of domesticated African aurochs (' ...
complex on the outskirts of Hargeisa dates back around 5,000 years, and has
rock art
In archaeology, rock arts are human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type al ...
depicting both wild animals and decorated cows.
Other
cave painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often c ...
s are found in the northern
Dhambalin
Dhambalin ("half, vertically cut mountain") is an archaeological site in the central Sahil province of Somaliland. The sandstone rock shelter contains rock art depicting various animals such as horned cattle and goats, as well as giraffes, an a ...
region, which feature one of the earliest known depictions of a hunter on horseback. The rock art is in the distinctive Ethiopian-Arabian style, dated to 1,000 to 3,000 BCE.
Additionally, between the towns of
Las Khorey
Las Qoray (, ) is a historic coastal town in the Sanaag region of Somalia.
BBC reported in 2021, "The Navy or Somalia Coast Guard is one of the military departments of Somalia, operating on the coast of Somaliland in Las Qoray, Zeila and Berbera ...
and
El Ayo
El Ayo (, ), also known as El Ayum, is a coastal town in the eastern Sanaag region of Somaliland.
History Ancient times
El Ayo is one of a series of ancient settlements in Somalia. About one mile from the town are the ruins of an old city, which ...
in eastern Somaliland lies
Karinhegane, the site of numerous cave paintings of real and mythical animals. Each painting has an inscription below it, which collectively have been estimated to be around 2,500 years old.
Antiquity and classical era

Ancient
pyramid
A pyramid () is a structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be of any polygon shape, such as trian ...
ical structures,
mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type o ...
s, ruined cities and stone walls, such as the
Wargaade Wall
Wargaade Wall, or Warqaadi, is an ancient stone construction in Wargaadhi, Hirshabelle, in Somalia. It enclosed a large settlement in the region.
Overview
Graves and unglazed sherds of pottery dating from antiquity have been found during excav ...
, are evidence of civilisations thriving in the Somali peninsula.
Ancient Somaliland had a trading relationship with
ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
and
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
dating back to at least the second millennium BCE, supporting the hypothesis that Somalia or adjacent regions were the location of the ancient
Land of Punt
The Land of Punt (Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pwnt#Egyptian, pwnt''; alternate Egyptian language#Egyptological pronunciation, Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') ) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. ...
.
The Puntites traded
myrrh
Myrrh (; from an unidentified ancient Semitic language, see '' § Etymology'') is a gum-resin extracted from a few small, thorny tree species of the '' Commiphora'' genus, belonging to the Burseraceae family. Myrrh resin has been used ...
, spices, gold, ebony, short-horned cattle, ivory and
frankincense
Frankincense, also known as olibanum (), is an Aroma compound, aromatic resin used in incense and perfumes, obtained from trees of the genus ''Boswellia'' in the family (biology), family Burseraceae. The word is from Old French ('high-quality in ...
with the Egyptians, Phoenicians,
Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
ns, Indians, Chinese and Romans through their commercial ports. An Egyptian expedition sent to Punt by the
18th dynasty
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVIII, alternatively 18th Dynasty or Dynasty 18) is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty ...
Queen
Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut ( ; BC) was the sixth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, Egypt, ruling first as regent, then as queen regnant from until (Low Chronology) and the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Thutmose II. She was Egypt's second c ...
is recorded on the temple reliefs at
Deir el-Bahari
Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri (, , ) is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part of the Theban Necropolis.
History
Deir el-Bahari, located on the west ...
, during the reign of the Puntite King Parahu and Queen Ati.
In 2015, isotopic analysis of ancient baboon mummies from Punt that had been brought to Egypt as gifts indicated that the specimens likely originated from an area encompassing eastern Somalia and the Eritrea-Ethiopia corridor.
The camel is believed to have been domesticated in the Horn region sometime between the 2nd and 3rd millennium BCE. From there, it spread to Egypt and the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
.
During the classical period, the northern
Barbara city-states of
Mosylon,
Opone,
Mundus,
Isis
Isis was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her sla ...
,
Malao,
Avalites
Avalites (also spelled Abalitês, from or ) was an ancient port city in present-day Somalia. It corresponds with what later became the city of Zeila.
According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'', Avalites was located on the Far-Side mar ...
,
Essina,
Nikon
(, ; ) is a Japanese optics and photographic equipment manufacturer. Nikon's products include cameras, camera lenses, binoculars, microscopes, ophthalmic lenses, measurement instruments, rifle scopes, spotting scopes, and equipment related to S ...
, and
Sarapion
Sarapion (, also spelled Serapion) was an ancient port city located in the Horn of Africa.
History
It was situated on a site that later became Mogadishu. Sarapion was briefly mentioned in Ptolemy's ''Geographia'' as one of the harbours a trader ...
developed a lucrative trade network, connecting with merchants from
Ptolemaic Egypt Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
*Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
,
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
,
Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
,
Parthian Persia,
Saba
Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Șaba or Șaba-Târg, the Romanian name for Shabo, a village in Ukraine
* Saba, ...
, the
Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea () was a political state of the Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassin ...
, and the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. They used the ancient Somali maritime vessel known as the ''
beden
The ''beden'' See author at . or alternate type names ''beden-seyed'' (also ''beden seyad'') and ''beden-safar'', is a fast, ancient Somali single or double-masted maritime vessel and ship, typified by its towering stern-post and powerful rudde ...
'' to transport their cargo.
After the
Roman conquest of the Nabataean Empire and the establishment of a Roman naval presence at
Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
to curb piracy, Arab and Somali merchants cooperated with the Romans to bar Indian ships from trading in the free port cities of the Arabian peninsula
[.] to protect the interests of Somali and Arab merchants in the lucrative commerce between the Red and Mediterranean Seas.
[.] However, Indian merchants continued to trade in the port cities of the Somali peninsula, which was free from Roman interference.
[.]
For centuries, Indian merchants brought large quantities of
cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, biscuits, b ...
to Somalia and Arabia from
Ceylon
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and the
Spice Islands
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for ...
. The source of the spices is said to have been the best-kept secret of Arab and Somali merchants in their trade with the Roman and Greek world; the Romans and Greeks believed the source to have been the Somali peninsula.
[.] The collaboration between Somali and Arab traders inflated the price of Indian and Chinese cinnamon in North Africa, the Near East, and Europe, and made the spice trade profitable, especially for the Somali merchants through whose hands large quantities were shipped across sea and land routes.
In 2007, more rock art sites with Sabaean and Himyarite writings in and around Hargeisa were found, but some were bulldozed by developers.
Birth of Islam and the Middle Ages

The Isaaq people traditionally claim to have descended from
Sheikh Ishaaq bin Ahmed, an
Islamic scholar
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
who purportedly traveled to Somaliland in the 12th or 13th century and married two women; one from the local
Dir clan
The Dir () is one of the largest and most prominent Somali clans in the Horn of Africa. They are also considered to be the oldest Somali stock to have inhabited the region. Its members inhabit Djibouti, Somalia, Ethiopia ( Somali, Harar, Dir ...
and the other from the neighboring
Harari people
The Harari people ( Harari: / , Gēy Usuach, "People of the City") are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group which inhabits the Horn of Africa. Members of this ethnic group traditionally reside in the walled city of Harar, simply called ''Gēy'' "the ...
.
[I.M. Lewis, ''A Modern History of the Somali'', fourth edition (Oxford: James Currey, 2002), pp. 31 & 42] He is said to have sired eight sons who are the common ancestors of the clans of the Isaaq clan-family. He remained in
Maydh
Maydh (also transliterated as Maedh, Mette, Mait or Meit) (, ) is an ancient port city in the eastern Sanaag region of Somaliland.
History
Antiquity
According to Augustus Henry Keane, Maydh represents an early center of dispersal of the Somali ...
until his death.
As the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
clan-family grew in size and numbers during the 12th century, the clan-family migrated and spread from their core area in
Mait (Maydh) and the wider
Sanaag
Sanag (, ) is an administrative region ('' gobol'') in north eastern Somaliland.[Regions of Somalia](_blank)
Sa ...
region in a southwestward expansion over a wide portion of present-day Somaliland by the 15th and 16th centuries.
As the Isaaq expanded the earlier Dir communities of Mait and the wider Sanaag region were driven westwards and to the south towards their present positions.
In this general expansion the Isaaq split up into their present component segments, however one fraction of the Habar Yunis clan, the Muse 'Arre, remains behind in Mait as the custodians of the tomb of Sheikh Ishaaq.
By the 1300s the Isaaq clans united to defend their inhabited territories and resources during clan conflicts against migrating clans.
After the war, the Isaaq clans (along with other tribes like the
Daarood) grew in numbers and territory in the northeast, causing them to began to vie with their
Oromo neighbours, who were expanding northwards themselves after the
Great Oromo Migrations, thus creating a general thrust toward the southwest. The Isaaq, along with Darood subclans pushed westwards into the plains of
Jigjiga
Jijiga (, , ''Jijiga'') is the capital city of Somali Region, Ethiopia. It became the capital of the Somali Region in 1995 after it was moved from Gode. Located in the Fafan Zone with 75 km (37 mi) west of the border with Somali ...
and further, beyond where they played a important role in the
Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, also known as the Adal Empire or Barr Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate'', ''Adal Sultanate'') (), was a medieval Sunni Muslim empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din III on th ...
's campaigns against Christian
Abyssinia
Abyssinia (; also known as Abyssinie, Abissinia, Habessinien, or Al-Habash) was an ancient region in the Horn of Africa situated in the northern highlands of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea.Sven Rubenson, The survival of Ethiopian independence, ...
. By the 16th to 17th century the movements that followed seem to have established the Isaaqs on coastal Somaliland.
Various Somali Muslim kingdoms were established in the area in the early Islamic period.
In the 14th century, the
Zeila
Zeila (, ), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila with the Biblical location of Havilah. Most modern schola ...
-based
Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, also known as the Adal Empire or Barr Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate'', ''Adal Sultanate'') (), was a medieval Sunni Muslim empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din III on th ...
battled the forces of the Ethiopian emperor
Amda Seyon I
Amda Seyon I, also known as Amda Tsiyon I ( , , "Pillar of Zion"), throne name Gebre Mesqel (ገብረ መስቀል , "Servant of the Cross"), was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1314 to 1344 and a member of the Solomonic dynasty.
He is best known ...
.
[, page 45] The
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
later occupied
Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
and environs in the 1500s.
Muhammad Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and social activist. A global cultural icon, widely known by the nickname "The Greatest", he is often regarded as the gr ...
,
Pasha
Pasha (; ; ) was a high rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. ''Pasha'' was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of ...
of
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, subsequently established a foothold in the area between 1821 and 1841.
The Sanaag region is home to the ruined Islamic city of
Maduna near
El Afweyn
El Afweyn (, ) is a town in the Sanaag region of Somaliland.
El Afweyn is a major historical town in western Sanaag region and sits at the major road connecting the cities of Burao and Erigavo. By road, the town is approximately 283 km east ...
, which is considered the most substantial and accessible ruin of its type in Somaliland.
The main feature of the ruined city is a large rectangular mosque, its 3-metre high walls still standing, which include a mihrab and possibly several smaller arched niches.
Swedish-Somali archaeologist
Sada Mire
Sada Mire (born July 1976) ( Somali: ''Sacda Mire'', Arabic: سعدة ميرة) is a Swedish-Somali archaeologist, art historian and presenter from the Arap clan, who is currently a professor of Heritage Studies at University College London. ...
dates the ruined city to the 15th–17th centuries.
Early modern sultanates

Isaaq Sultanate
In the
early modern
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
period, successor states to the Adal Sultanate began to flourish in Somaliland. These included the
Isaaq Sultanate
The Isaaq Sultanate (, Wadaad's writing, Wadaad: , ) was a Muslims, Muslim sultanate that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa in the 18th and 19th centuries. The kingdom spanned the territories of the Isaaq clan in modern-day Somaliland and Ethiopi ...
and
Habr Yunis Sultanate
The Habr Yunis Sultanate (, ) was a Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa during the 18th century. It spanned the territories of the Habr Yunis clan which is part of the wider Isaaq in modern day Somaliland and Ethiopia. The su ...
.
[British Somaliland by Ralph E. Drake-Brockman. Drake-Brockman, Ralph E. (Ralph Evelyn), 1875–1952. p. 275] The
Isaaq Sultanate
The Isaaq Sultanate (, Wadaad's writing, Wadaad: , ) was a Muslims, Muslim sultanate that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa in the 18th and 19th centuries. The kingdom spanned the territories of the Isaaq clan in modern-day Somaliland and Ethiopi ...
was a
Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the
Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
during the 18th and 19th centuries. It spanned the territories of the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
clan, descendants of the
Banu Hashim
Banu Hashim () is an Arab clan within the Quraysh tribe to which the Islamic prophet Muhammad belonged, named after Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim ibn Abd Manaf.
Members of this clan, and especially their descendants, are also referred ...
clan,
[I. M. Lewis, ''A pastoral democracy: a study of pastoralism and politics among the Northern Somali of the Horn of Africa'', (LIT Verlag Münster: 1999), p. 157.] in modern-day Somaliland and
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
. The sultanate was governed by the Rer Guled branch established by the first sultan, Sultan
Guled Abdi, of the
Eidagale
The Eidagalle (; ) is a major Somali clan of the Isaaq clan family. Members of this clan are concentrated in Somaliland and the Somali region. They are the traditional holders of the Isaaq Sultanate since the 18th century. As descendants of Is ...
clan. The sultanate is the pre-colonial predecessor to the modern Republic of Somaliland.
According to oral tradition, prior to the Guled dynasty the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
clan-family were ruled by a dynasty of the Tolje'lo branch descending from Ahmed nicknamed Tol Je'lo, the eldest son of
Sheikh Ishaaq's
Harari wife. There were eight Tolje'lo rulers in total, starting with Boqor Harun () who ruled the Isaaq Sultanate for centuries starting from the 13th century. The last Tolje'lo ruler
Garad
Garad ( Harari: ገራድ, , , Oromo: ''Garaada'') is a term used to refer to a king, Sultan or regional administrator. It was used primarily by Muslims in the Horn of Africa that were associated with Islamic states, most notably the Adal Sultanat ...
Dhuh Barar () was overthrown by a coalition of Isaaq clans. The once strong Tolje'lo clan were scattered and took refuge among the
Habr Awal
The Habr Awal, alternately known as the Zubeyr Awal (, , Full Name: '' Abd al-Raḥmān ibn ash-Ishaaq bin Ahmed, Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad)'' is one of the largest subclans of the wider Isaaq clan family, and is further divided into eight su ...
with whom they still mostly live.
The Sultan of Isaaq regularly convened ''shirs'' (meetings) where he would be informed and advised by leading elders or religious figures on what decisions to make. In the case of the
Dervish movement, Sultan
Deria Hassan had chosen not to join after receiving counsel from
Sheikh Madar
Madar Ahmed Shirwac, better known as Sheikh Madar (; 1825–1918) was a 19th-century Somalis, Somali political/religious leader, a social reformer, merchant and a jurist who is known as the founder of Hargeisa. He hailed from the Yunis Nuh divisio ...
. He addressed early tensions between the Saad Musa and Eidagale upon the former's settlement into the growing town of Hargeisa in the late 19th century. The Sultan was also responsible for organising grazing rights and, in the late 19th century, new agricultural spaces. The allocation of resources and sustainable use of them was also a matter that Sultans concerned themselves with and was crucial in this arid region. In the 1870s, at a famous meeting between
Sheikh Madar
Madar Ahmed Shirwac, better known as Sheikh Madar (; 1825–1918) was a 19th-century Somalis, Somali political/religious leader, a social reformer, merchant and a jurist who is known as the founder of Hargeisa. He hailed from the Yunis Nuh divisio ...
and Sultan Deria, it was proclaimed that hunting and tree cutting in the vicinity of Hargeisa would be banned, and that the holy relics from
Aw Barkhadle
Yusuf bin Ahmad al-Kawneyn () (b. 10th century), popularly known as Aw Barkhadle ("Blessed Father")Abdullahi, p.13 or Yusuf Al Kownayn, was an Islamic scholar and traveler based in Zeila, Somaliland. According to Dr. Enrico Cerulli, Yusuf Al K ...
would be brought and oaths would be sworn on them by the Isaaqs in the presence of the Sultan whenever internal combat broke out.
Aside from the leading Sultan of Isaaq there were numerous Akils, Garaads and subordinate Sultans alongside religious authorities that constituted the Sultanate; occasionally these would declare their independence or simply break from its authority.
The Isaaq Sultanate had 5 rulers prior to the creation of
British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
in 1884. Historically, Sultans would be chosen by a committee of several important members of the various Isaaq subclans. Sultans were usually buried at
Toon, south of Hargeisa, which was a significant site and the capital of the Sultanate during
Farah Guled
Farah Guled (, ) was a Somali ruler. He was the second Grand Sultan of the Isaaq Sultanate and also a Hajji having completed pilgrimage to Mecca.
Biography
Son of Sultan Guled, he was amongst the first generation of the Ba Ambaro branch of the e ...
's rule.
Battle of Berbera
The first engagement between Somalis of the region and the British was in 1825 and led to hostilities,
ending in the
Battle of Berbera and a subsequent trade agreement between the
Habr Awal
The Habr Awal, alternately known as the Zubeyr Awal (, , Full Name: '' Abd al-Raḥmān ibn ash-Ishaaq bin Ahmed, Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad)'' is one of the largest subclans of the wider Isaaq clan family, and is further divided into eight su ...
and the United Kingdom.
[Hertslet's Commercial Treaties: A Complete Collection of the Treaties and Conventions, and Reciprocal Regulations, at Present Subsisting Between Great Britain and Foreign Powers, and of the Laws, Decrees, and Orders in Council, Concerning the Same, So Far as They Relate to Commerce and Navigation, to the Repression and Abolition of the Slave Trade, and to the Privileges and Interests of the Subjects of the High Contracting Parties, Volume 13, pg 5] This was followed by a British treaty with the Governor of
Zeila
Zeila (, ), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila with the Biblical location of Havilah. Most modern schola ...
in 1840. An engagement was then started between the British and elders of
Habar Garhajis and
Habar Toljaala clans of the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
in 1855, followed a year later by the conclusion of the "Articles of Peace and Friendship" between the Habar Awal and
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
. These engagements between the British and Somali clans culminated in the formal treaties the British signed with the henceforth 'British Somaliland' clans, which took place between 1884 and 1886 (treaties were signed with the Habar Awal, Gadabursi, Habar Toljaala, Habar Garhajis, Esa, and the Warsangali clans), and paved the way for the British to establish a
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over ...
in the region referred to as
British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
.
[Hugh Chisholm (ed.), ''The Encyclopædia Britannica: a dictionary of arts, sciences, literature and general information'', Volume 25, (At the University press: 1911), p.383.] The British garrisoned the protectorate from
Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
and administered it as part of
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
until 1898. British Somaliland was then administered by the
Foreign Office
Foreign may refer to:
Government
* Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries
** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government
** Foreign office and foreign minister
* United ...
until 1905, and afterwards by the
Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created in 1768 from the Southern Department to deal with colonial affairs in North America (particularly the Thirteen Colo ...
.
British Somaliland

The Somaliland Campaign, also called the Anglo-Somali War or the Dervish War, was a series of military expeditions that took place between 1900 and 1920 in the
Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, pitting the
Dervishes
Dervish, Darvesh, or Darwīsh (from ) in Islam can refer broadly to members of a Sufi fraternity (''tariqah''), or more narrowly to a religious mendicant, who chose or accepted material poverty. The latter usage is found particularly in Persi ...
led by
Mohammed Abdullah Hassan
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, ...
(nicknamed the "Mad Mullah") against the
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
.
[Nicolle (1997), 5.] The British were assisted in their offensives by the
Ethiopians
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global Ethiopian diaspora, diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute #Ethnicity, several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighbor ...
and
Italians
Italians (, ) are a European peoples, European ethnic group native to the Italian geographical region. Italians share a common Italian culture, culture, History of Italy, history, Cultural heritage, ancestry and Italian language, language. ...
. During the
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
(1914–1918), Hassan also received aid from the
Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
,
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
and, for a time, from the Emperor
Iyasu V of Ethiopia. The conflict ended when the British
aerially bombed the Dervish capital of
Taleh
Taleh (, ) is a historical town in Sool region of Somalia. The town served as the capital of the pre-independence Dervish movement.Laurence, p.47.
The Dalyare fort and the Taleh complex built between 1909 and 1910 are among the least disfigur ...
in February 1920.
The Fifth Expedition of the
Somaliland campaign
The Somaliland campaign, also called the Anglo-Somali War or the Dervish rebellion, was a series of military expeditions that took place between 1900 and 1920 in modern-day Somaliland. The British were assisted in their offensives by the Ethiop ...
in 1920 was the final
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
expedition against the
Dervish
Dervish, Darvesh, or Darwīsh (from ) in Islam can refer broadly to members of a Sufi fraternity (''tariqah''), or more narrowly to a religious mendicant, who chose or accepted material poverty. The latter usage is found particularly in Persi ...
forces of
Mohammed Abdullah Hassan
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, ...
, the
Somali religious leader. Although most of the combat took place in January of the year, British troops had begun preparations for the assault as early as November 1919. The British forces included elements of the
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
and the
Somaliland Camel Corps
The Somaliland Camel Corps (SCC) was a British Colonial Auxiliary Forces unit which was raised in British Somaliland. It existed from 1914 until 1944.
Beginnings and the Dervish rebellion
In 1888, after signing successive treaties with the the ...
. After three weeks of battle, Hassan's Dervishes were defeated, bringing an effective end to their 20-year resistance.
It was one of the bloodiest and longest militant movements in sub-Saharan Africa during the colonial era, one that overlapped with World War I. The battles between various sides over two decades killed nearly a third of Somaliland's population and ravaged the local economy.
The Italian conquest of British Somaliland was a military campaign in East Africa, which took place in August 1940 between forces of
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
and those of several British and
Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
countries. The Italian attack was part of the
East African campaign.
Anti-colonial resistance
Burao Tax Revolt and RAF bombing

The people of Burao clashed with the British in 1922. They revolted in opposition to a new tax that was imposed upon them, rioting and attacking British government officials. This led to a shootout between the British and Burao residents in which Captain Allan Gibb, a Dervish war veteran and district commissioner, was shot and killed. The British requested Sir
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
, then
Secretary of State for the Colonies
The secretary of state for the colonies or colonial secretary was the Cabinet of the United Kingdom's government minister, minister in charge of managing certain parts of the British Empire.
The colonial secretary never had responsibility for t ...
, to send troops from
Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
and Air Force bombers Burao the revolting clans' livestock. The RAF planes arrived at Burao within two days and proceeded to bomb the town with incendiaries, effectively burning the entire settlement to the ground.
[Correspondence between Governor of British Somaliland and Secretary of State for the Colonies. Colonial Office, 26 March 1922.]
Telegram from
Sir Geoffrey Archer, Governor of British Somaliland to
Sir Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
the
Secretary of State for the Colonies
The secretary of state for the colonies or colonial secretary was the Cabinet of the United Kingdom's government minister, minister in charge of managing certain parts of the British Empire.
The colonial secretary never had responsibility for t ...
:
I deeply regret to inform that during an affray at Burao yesterday between Rer Sugulleh and Akils of other tribes Captain Gibb was shot dead. Having called out Camel corps company to quell the disturbance, he went forward himself with his interpreter, whereupon fire opened on him by some Rer segulleh riflemen and he was instantly killed..Miscreants then disappeared under the cover of darkness.
To meet the situation created by the Murder of Gibb, we require two aeroplanes for about fourteen days. I have arranged with resident, Aden, for these. And made formal application, which please confirm. It is proposed they fly via Perim, confining sea crossing to 12 miles. We propose to inflict fine of 2,500 camels on implicated sections, who are practically isolated and demand surrender of man who killed Gibbs. He is known. Fine to be doubled in failure to comply with latter conditions and aeroplanes to be used to bomb stock on grazing grounds.
Sir Winston Churchill reporting on the Burao incident at the
House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
:
On 25th February the Governor of Somaliland telegraphed that an affray between tribesmen had taken place at Burao on the previous day, in the course of which Captain Allan Gibb, D.S.O., D.C.M., the District Commissioner at Burao, had been shot dead. Captain Gibb had advanced with his interpreter to quell the disturbance, when 1954 fire was opened upon him by some riflemen, and he was instantly killed. The murderers escaped under cover of falling darkness.
Captain Gibb was an officer of long and valued service in Somaliland, whose loss I deeply regret. From the information available, his murder does not appear to have been premeditated, but it inevitably had a disturbing effect upon the surrounding tribes, and immediate dispositions of troops became necessary to ensure the apprehension and punishment of those responsible for the murder. On 27th February the Governor telegraphed that, to meet the situation which had arisen, he required two aeroplanes for purposes of demonstration, and suggested that two aeroplanes from the Royal Air Force Detachment at Aden should fly over to Berber a from Aden. He also telegraphed that in certain circumstances it might become necessary to ask for reinforcements of troops to be sent to the Protectorate.
James Lawrence author of ''Imperial Rearguard: Wars of Empire'' writes
ibb
Ibb () is a city in Yemen, the capital of Ibb Governorate, located about northeast of Mocha and south of Sana'a. A market town and administrative centre developed during the Ottoman Empire, it is one of the most important medium-sized cities i ...
.was murdered by rioters during a protest against taxation at Burao. Governor Archer immediately called for aircraft which were at Burao within two days. The inhabitants of the native township were turned out of their houses, and the entire area was razed by a combination of bombing, machine-gun fire and burning.
After the RAF aircraft bombed Burao to the ground, the leaders of the rebellion acquiesced, agreeing to pay a fine for Gibb's death, but they refused to identify and apprehend the accused individuals. Most of the men responsible for Gibb's shooting evaded capture. In light of the failure to implement the taxation without provoking a violent response, the British abandoned the policy altogether.
1945 Sheikh Bashir Rebellion
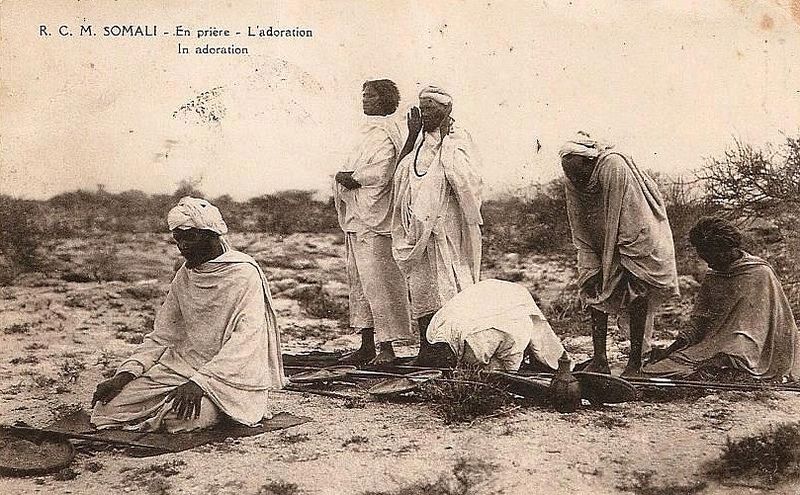

The 1945 Sheikh Bashir Rebellion was a rebellion waged by tribesmen of the
Habr Je'lo
The Habr Je'lo (), , Full Name: ''Mūsa ibn ash-Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad,'' historically known as the Habr Toljaala () is a major Northern Somali clan of the wider Isaaq family. Its members form the Habr Habusheed () confederation along with t ...
clan in the former
British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
protectorate against British authorities in July 1945 led by
Sheikh Bashir
Sheikh Bashir Sheikh Yusuf Sheikh Hassan (, , born c. 1905) was a Somali religious leader famed for leading the 1945 Sheikh Bashir Rebellion against the British colonial authority in Somaliland.
Biography
Sheikh Bashir was born in 1905 in Tal ...
, a
Somali religious leader.
On 2 July, Sheikh Bashir collected 25 of his followers in the town of
Wadamago
Wadamago () is a historic town in Aynabo District, in the Sool region of Somaliland.
Etymology
The name Wadamago () stems from the phrase ''Wadaamo go, meaning ''wadaan breaker'' in Somali. A wadaan is a hand made bucket that is made up of ...
and transported them on a lorry to the vicinity of
Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
, where he distributed arms to half of his followers. On the evening of 3 July, the group entered Burao and opened fire on the police guard of the central prison in the city, which was filled with prisoners arrested for previous demonstrations. The group also attacked the house of the district commissioner of
Burao District, Major Chambers, resulting in the death of Major Chamber's police guard before escaping to Bur Dhab, a strategic mountain south-east of Burao, where Sheikh Bashir's small unit occupied a fort and took up a defensive position in anticipation of a British counterattack.
The British campaign against Sheikh Bashir's troops proved abortive after several defeats as his forces kept moving from place to place and avoiding any permanent location. No sooner had the expedition left the area, than the news travelled fast among the Somali nomads across the plain. The war had exposed the British administration to humiliation. The government came to a conclusion that another expedition against him would be useless; that they must build a railway, make roads and effectively occupy the whole of the protectorate, or else abandon the interior completely. The latter course was decided upon, and during the first months of 1945, the advance posts were withdrawn, and the British administration confined to the coast town of
Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
.
Sheikh Bashir settled many disputes among the tribes in the vicinity, which kept them from raiding each other. He was generally thought to settle disputes through the use of Islamic
Sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
and gathered around him a strong following.
The British administration recruited Indian and South African troops, led by police general James David, to fight against Sheikh Bashir and had intelligence plans to capture him alive. The British authorities mobilised a police force, and eventually on 7 July found Sheikh Bashir and his unit in defensive positions behind their fortifications in the mountains of Bur Dhab. After clashes Sheikh Bashir and his second-in-command, Alin Yusuf Ali, nicknamed Qaybdiid, were killed. A third rebel was wounded and was captured along with two other rebels. The rest fled the fortifications and dispersed. On the British side the police general leading the British troops as well as a number of Indian and South African troops perished in the clashes, and a policeman was injured.
After his death, Sheikh Bashir was widely hailed by locals as a martyr and was held in great reverence. His family took quick action to remove his body from the place of his death at Geela-eeg mountain, about 20 miles from
Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
.
State of Somaliland (Independence)

Initially the
British government
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. planned to delay
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over ...
of
British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
independence in favour of a gradual transfer of power. The arrangement would allow local politicians to gain more political experience in running the protectorate before official independence. However, strong pan-Somali nationalism and a landslide victory in the earlier elections encouraged them to demand independence and unification with the
Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian Administration (the former
Italian Somaliland
Italian Somaliland (; ; ) was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia, which was ruled in the 19th century by the Sultanate of Hobyo and the Majeerteen Sultanate in the north, and by the Hiraab Imamate and ...
).
In May 1960, the British government stated that it would be prepared to grant independence to the then
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over ...
of British Somaliland, with the intention that the territory would unite with the Italian-administered Trust Territory of Somaliland.
The Legislative Council of British Somaliland passed a resolution in April 1960 requesting independence and union with the Trust Territory of Somaliland, which was scheduled to gain independence on 1 July that year. The legislative councils of both territories agreed to this proposal following a joint conference in
Mogadishu
Mogadishu, locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Ocean for millennia and has ...
.
On 26 June 1960, the former British Somaliland protectorate briefly obtained independence as the State of Somaliland, with the Trust Territory of Somaliland following suit five days later.
During its brief period of independence, the
State of Somaliland
Somaliland, officially the State of Somaliland (), was an independent country in the territory of the present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland, which regards itself as its legal successor. It existed on the territory of former ...
garnered recognition from thirty-five sovereign states.
However, the United States merely acknowledged Somaliland's independence:
The United States did not extend formal recognition to Somaliland, but Secretary of State Herter sent a congratulatory message dated June 26 to the Somaliland Council of Ministers.
The following day, on 27 June 1960, the newly convened Somaliland Legislative Assembly approved a bill that would formally allow for the union of the State of Somaliland with the Trust Territory of Somaliland on 1 July 1960.
Somali Republic (union with Somalia)
On 1 July 1960, the
State of Somaliland
Somaliland, officially the State of Somaliland (), was an independent country in the territory of the present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland, which regards itself as its legal successor. It existed on the territory of former ...
and the
Trust Territory of Somaliland
The Trust Territory of Somaliland, officially the Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian Administration (), was a United Nations Trust Territory from 1950 to 1960, following the dissolution of the former British Military Administration. I ...
(the former
Italian Somaliland
Italian Somaliland (; ; ) was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia, which was ruled in the 19th century by the Sultanate of Hobyo and the Majeerteen Sultanate in the north, and by the Hiraab Imamate and ...
) united as planned to form the
Somali Republic
The Somali Republic (; ; ) was formed by the union of the Trust Territory of Somaliland (formerly Italian Somaliland) and the State of Somaliland (formerly British Somaliland). A government was formed by Abdullahi Issa Mohamud and Muhammad ...
.
Inspired by
Somali nationalism, the northerners were initially enthusiastic about the union. A government was formed by
Abdullahi Issa, with
Aden Abdullah Osman Daar
Aden Abdulle Osman Da’ar (, ) (9 December 1908 – 8 June 2007), popularly known as Aden Adde, was a Somali politician who served as the first president of the Somali Republic from 1 July 1960 to 6 July 1967. as
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
and
Abdirashid Ali Shermarke
Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke (, ) (8 June 1919 – 15 October 1969), was the first Prime Minister of Somalia from 12 July 1960 to 14 June 1964 and the second President of Somalia from 6 July 1967, until his assassination on October 15, 1969. as
Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
(later becoming president, from 1967 to 1969). On 20 July 1961 and through a popular
referendum
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate (rather than their Representative democracy, representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either bin ...
, the Somali people ratified a new constitution, which was first drafted in 1960.
[Greystone Press Staff, ''The Illustrated Library of The World and Its Peoples: Africa, North and East'', (Greystone Press: 1967), p.338] The constitution had little support in the former Somaliland and was believed to favour the south. Many northerners boycotted the referendum in protest, and over 60% of those who voted in the north were against the new constitution. Regardless, the referendum passed, and Somaliland became quickly dominated by southerners. As result, dissatisfaction became widespread in the north, and support for the union plummeted. British-trained Somaliland officers attempted a
revolt to end the union in December 1961. Their uprising failed, and Somaliland continued to be marginalised by the south during the next decades.
In 1967,
Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal
Mohamed Haji Ibrahim Egal (, ; August 15, 1928 – May 3, 2002) was a Somali politician who served as the president of Somaliland from 1993 to his death in 2002. He previously served as the prime minister of the State of Somaliland between 26 ...
became Prime Minister, a position to which he was appointed by Shermarke. Shermarke was assassinated two years later by one of his own bodyguards. His murder was quickly followed by a military coup d'état on 21 October 1969 (the day after his funeral), in which the
Somalian Army seized power without encountering armed opposition. The putsch was spearheaded by Major General
Mohamed Siad Barre
Mohammed Siad Barre (, Osmanya script: , ''Muhammad Ziād Barīy''; 6 October 1919 – 2 January 1995) was a Somali military officer, politician, and revolutionary who served as the third president of Somalia from 21 October 1969 to 26 Ja ...
, who at the time commanded the army.
[Moshe Y. Sachs, ''Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations'', Volume 2, (Worldmark Press: 1988), p.290.] The new regime would go on to rule Somalia for the next 22 years.
Somali National Movement, Barre persecution
The
moral authority
Moral authority is authority premised on principles, or fundamental truths, which are independent of written, or positive laws. As such, moral authority necessitates the existence of and adherence to truth. Because truth does not change the princip ...
of Barre's government was gradually eroded, as many Somalis became disillusioned with life under military rule. By the mid-1980s, resistance movements supported by Ethiopia's communist
Derg
The Derg or Dergue (, ), officially the Provisional Military Administrative Council (PMAC), was the military junta that ruled Ethiopia, including present-day Eritrea, from 1974 to 1987, when they formally "Civil government, civilianized" the ...
administration had sprung up across the country, which led to the
Somaliland War of Independence
The Somaliland War of Independence () was a rebellion waged by the Somali National Movement (SNM) against the ruling military junta in Somali Democratic Republic, Somalia led by General Siad Barre lasting from its founding on 6 April 1981 and en ...
. Barre responded by ordering punitive measures against those he perceived as locally supporting the guerrillas, especially in the northern regions. The clampdown included bombing of cities, with the northwestern administrative centre of Hargeisa, a
Somali National Movement
The Somali National Movement (, ) was one of the first and most important Guerrilla warfare, organized guerilla groups and Mujahideen groups that opposed the Siad Barre regime in the 1980s to the 1990s, as well as being the main anti-government f ...
(SNM) stronghold, among the targeted areas in 1988.
The bombardment was led by General
Mohammed Said Hersi Morgan, Barre's son-in-law.
In May 1988, the SNM launched a
major offensive on the cities of Hargeisa and
Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
,
then the second and third largest cities of
Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
.
The SNM captured Burao on 27 May within two hours,
while the SNM entered Hargeisa on 29 May, overrunning most of the city apart from its airport by 1 June.
According to Abou Jeng and other scholars, the Barre regime rule was marked by a targeted brutal persecution of the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
clan.
Mohamed Haji Ingiriis and
Chris Mullin
Christopher Paul Mullin (born July 30, 1963) is an American former professional basketball player, executive and coach. He is a five time NBA All-Star and four time All-NBA Team member. He is also two-time Olympic Gold medalist and a two-time ...
state that the clampdown by the Barre regime against the Hargeisa-based Somali National Movement targeted the Isaaq clan, to which most members of the SNM belonged. They refer to the clampdown as the
Isaaq Genocide
The Isaaq genocide (; ), also known as the Hargeisa Holocaust, was the systematic, state-sponsored genocide of Isaaq civilians between 1987 and 1989 by the Somali Democratic Republic, under the dictatorship of Siad Barre, during the Somalilan ...
or "Hargeisa Holocaust".
A United Nations investigation concluded that the crime of genocide was .
The number of civilian casualties is estimated to be between 50,000 and 100,000 according to various sources,
while some reports estimate the total civilian deaths to be upwards of 200,000 Isaaq civilians.
Along with the deaths, Barre regime bombarded and razed the second and third largest cities in Somalia, Hargeisa and
Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
, respectively.
This displaced an estimated 400,000 local residents to
Hart Sheik in Ethiopia;
another 400,000 individuals were also internally displaced.
The counterinsurgency by the Barre regime against the SNM targeted the rebel group's civilian base of support, escalating into a genocidal onslaught against the Isaaq clan. This led to anarchy and violent campaigns by fragmented militias, which then wrested power at a local level.
The Barre regime's persecution was not limited to the Isaaq, as it targeted other clans such as the
Hawiye
The Hawiye (; ) are one of the principal and largest of the Somali clans, tracing their lineage back to Sheikh Ahmed Bin Abdulrahman Bin Uthman, also known as Sheikh Hawiye, the eponymous figure of the clan. They are considered the earliest do ...
.
The Barre regime collapsed in January 1991. Thereafter, as the political situation in Somaliland stabilised, the displaced people returned to their homes, the militias were demobilised or incorporated into the army, and tens of thousands of houses and businesses were reconstructed from rubble.
Restoration of sovereignty (end of the unity with Somalia)

Although the SNM at its inception had a unionist constitution, it eventually began to pursue independence, looking to secede from the rest of Somalia.
Under the leadership of
Abdirahman Ahmed Ali Tuur
Abdirahman Ahmed Ali Tuur (, ) (var. "Tur", "Tour", meaning "Hunchback") (November 6, 1931 - November 8, 2003) was a Somali politician who served as the first President of Somaliland from 1991 to 1993. Tuur previously served as the Chairman of ...
, the local administration declared the northwestern Somali territories independent at a conference held in
Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
between 27 April 1991 and 15 May 1991.
Tuur then became the newly established Somaliland polity's first President, but subsequently renounced the separatist platform in 1994 and began instead to publicly seek and advocate reconciliation with the rest of Somalia under a power-sharing
federal system of governance.
A brief armed conflict had begun in January 1992 against rebels against Tuur in the period that he was in power, lasting until August 1992, when it was settled by a conference at the town of Sheikh.
Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal
Mohamed Haji Ibrahim Egal (, ; August 15, 1928 – May 3, 2002) was a Somali politician who served as the president of Somaliland from 1993 to his death in 2002. He previously served as the prime minister of the State of Somaliland between 26 ...
was appointed as Tuur's successor in 1993 by the Grand Conference of National Reconciliation in
Borama
Borama (, ) is the largest city of the northwestern Awdal region of Somaliland. The commercial seat of the province, it is situated near the border with Ethiopia.
During the Middle Ages, Borama was ruled by the Adal Sultanate. It later formed a ...
, which met for four months, leading to a gradual improvement in security, as well as a consolidation of the new territory.
[Lewis, ''A Modern History'', pp. 282–286] Another armed conflict between the Somaliland government, now under Egal, and rebels began, as militias of the Eidagalley clan occupied Hargeisa airport for some time. Conflict re-erupted when troops of the government attacked the airport to drive out the Eidagalley militias in October 1994, sparking a new war that would spread out of Hargeisa and last until around April 1995, with a rebel defeat. Around the same time, Djiboutian-backed forces of the Issa-dominated United Somali Front attempted and failed to carve out Issa-inhabited areas of Somaliland.
Egal was reappointed in 1997, and remained in power until his death on 3 May 2002. The vice-president,
Dahir Riyale Kahin
Dahir Riyale Kahin (, ; born 12 March 1952) is a Somaliland politician who was President of Somaliland from 2002 to 2010. He previously served as a senior officer in the National Security Service in Somalia, and he was Vice President of Somal ...
, who was during the 1980s the highest-ranking
National Security Service (NSS) officer in
Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
in Siad Barre's government, was sworn in as president shortly afterward.
[Human Rights Watch (Organization), Chris Albin-Lackey, ''Hostages to peace: threats to human rights and democracy in Somaliland'', (Human Rights Watch: 2009), p.13.] In 2003, Kahin became the first elected president of Somaliland.
The
war in southern Somalia between
Islamist insurgents on the one hand, and the
Federal Government of Somalia
The Federal Government of Somalia (FGS; , DFS; ) is the internationally recognised government of Somalia, and the longest running attempt to create a central government in Somalia since the collapse of the Somali Democratic Republic in 1991. It ...
and its
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
allies on the other, has for the most part not directly affected Somaliland, which, like neighbouring
Puntland
Puntland is an autonomous state that considers itself to be part of Somalia, despite not accepting the legitimacy of Somalia's current governing administration. It was formed in 1998, and was a federal member state of Somalia from its fou ...
, has remained relatively stable.
2001 constitutional referendum
In August 2000, Egal's government distributed thousands of copies of the proposed constitution throughout Somaliland for consideration and review by the people. One critical clause of the 130 individual articles of the constitution would ratify Somaliland's self-declared independence and final separation from Somalia, restoring the nation's independence for the first time since 1960. In late March 2001, Egal set the date for the referendum on the Constitution for 31 May 2001.
99.9% of eligible voters took part in the referendum and 97.1% of them voted in favour of the constitution.
Government and politics
Constitution
The
Constitution of Somaliland
The Constitution of the Republic of Somaliland (; ) is the supreme source of national law of Somaliland, an unrecognised state considered to be part of Somalia by the international community, adopted by the Houses of the Parliament of Somali ...
defines the political system; the Republic of Somaliland is a
unitary state
A unitary state is a (Sovereign state, sovereign) State (polity), state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or ...
and
Presidential Republic
A presidential, strong-president, or single-executive system (sometimes also congressional system) is a form of government in which a head of government (usually titled " president") heads an executive branch that derives its authority and l ...
, based on peace, co-operation, democracy and a
multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional ...
.
President and cabinet
The executive is led by an elected
president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
, whose government includes a vice-president and a Council of Ministers.
The Council of Ministers, who are responsible for the normal running of government, are nominated by the President and approved by the Parliament's House of Representatives.
The President must approve bills passed by the Parliament before they come into effect.
Presidential elections are confirmed by the
National Electoral Commission of Somaliland.
The President can serve a maximum of two five-year terms. The official residence and administrative headquarters of the President is the
Somaliland Presidential Palace or State House in the capital city of
Hargeisa
Hargeisa ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland, a ''List of states with limited recognition, de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still considered internationally to be part of Somalia. It is also th ...
.
Parliament

Legislative power is held by the
Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
, which is
bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature that is divided into two separate Deliberative assembly, assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate ...
. Its upper house is the
House of Elders House of Elders could refer to:
* House of Elders (Afghanistan)
* House of Elders (Somaliland)
See also
* Elder (disambiguation)
* Eldership (disambiguation)
* Council of Elders (disambiguation) Council of Elders may refer to:
* Council of El ...
, chaired by
Suleiman Mohamoud Adan
Suleiman Mohamoud Adan (, ), also known as Saleebaan Gaal is a Somaliland politician and the current speaker of Somaliland House of Elders since 28 August 2004.
Biography
Suleiman Mohamoud Adan Yusuf was born in 1937. He belongs to the Solom ...
, and the lower house is the
House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
,
chaired by
Yasin Haji Mohamoud
Yasin Haji Mohamoud Hiir () also known as Faratoon (Faraton) is a Somaliland politician, who is currently the speaker of Somaliland's Lower House of Parliament (House of Representatives).
Prior to his election as a member of Somaliland's Hou ...
. Each house has 82 members. Members of the House of Elders are elected indirectly by local communities for six-year terms. The House of Elders shares power in passing laws with the House of Representatives, and also has the role of solving internal conflicts, and exclusive power to extend the terms of the President and representatives under circumstances that make an election impossible. Members of the House of Representatives are directly elected by the people for five-year terms. The House of Representatives shares voting power with the House of Elders, though it can pass a law that the House of Elders rejects if it votes for the law by a two-thirds majority and has absolute power in financial matters and confirmation of Presidential appointments (except for the
Chief Justice of the Supreme Court).
Law

The judicial system is divided into district courts (which deal with matters of family law and succession, lawsuits for amounts up to 3 million
SLSH, criminal cases punishable by up to 3 years' imprisonment or 3 million SL fines, and crimes committed by juveniles), regional courts (which deal with lawsuits and criminal cases not within the jurisdiction of district courts, labour and employment claims, and local government elections), regional appeals courts (which deal with all appeals from the district and regional courts), and the
Supreme court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
(which deals with issues between courts and in government, and reviews its own decisions), which is the highest court and also functions as the Constitutional Court.
[d]
Somaliland nationality law
Somaliland is in the Horn of Africa in which inhabitants were initially governed by various kinship networks. Upon contact with Europeans, treaties were signed in the area to secure rights to trade in the territory in exchange for protection of ...
defines who is a Somaliland citizen,
as well as the procedures by which one may be
naturalised
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-national of a country acquires the nationality of that country after birth. The definition of naturalization by the International Organization for Migration of the ...
into Somaliland citizenship or
renounce it.
The Somaliland government continues to apply the 1962 penal code of the Somali Republic. As such, homosexual acts are illegal in the territory.
Parties and elections

The ''guurti'' worked with rebel leaders to set up a new government, and was incorporated into the governance structure, becoming the Parliament's
House of Elders House of Elders could refer to:
* House of Elders (Afghanistan)
* House of Elders (Somaliland)
See also
* Elder (disambiguation)
* Eldership (disambiguation)
* Council of Elders (disambiguation) Council of Elders may refer to:
* Council of El ...
.
The government became in essence a , with seats in the Upper and Lower houses proportionally allocated to clans according to a predetermined formula, although not all clans are satisfied with their representation. In 2002, after several extensions of this interim government, Somaliland transitioned to multi-party democracy.
The election was limited to three parties, in an attempt to create ideology-based elections rather than clan-based elections.
As of December 2014, Somaliland has three
political parties
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
: the
Peace, Unity, and Development Party
The Kulmiye Peace, Unity and Development Party (; ), also known as simply Kulmiye (), is a political party in Somaliland. The party was founded by Ahmed Mohamed Mohamoud, Ahmed Mohamed Mohamoud "Silanyo" in May 2002, ahead of the first 2002 Somal ...
, the
Justice and Development Party, and
Wadani. Under the Somaliland Constitution, a maximum of three political parties at the national level is allowed.
The minimum age required to vote is 15.
Freedom House
Freedom House is a nonprofit organization based in Washington, D.C. It is best known for political advocacy surrounding issues of democracy, Freedom (political), political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, wi ...
ranks the Somaliland government as partly free.
Seth Kaplan (2011) argues that in contrast to southern Somalia and adjacent territories, Somaliland, the secessionist northwestern portion of Somalia, has built a more democratic mode of governance from the bottom up, with virtually no foreign assistance.
Specifically, Kaplan suggests that Somaliland has the most democratic political system in the Horn of Africa because it has been largely insulated from the extremist elements in the rest of Somalia and has viable electoral and legislative systems as well as a robust private sector-dominated economy, unlike neighbouring authoritarian governments. He largely attributes this to Somaliland's integration of customary laws and tradition with modern state structures, which he indicates most post-colonial states in Africa and the Middle East have not had the opportunity to do. Kaplan asserts that this has facilitated cohesiveness and conferred greater governmental legitimacy in Somaliland, as has the territory's comparatively homogeneous population, relatively equitable income distribution, a common fear of the south, and absence of interference by outside forces, which has obliged local politicians to observe a degree of accountability.
Foreign relations
Somaliland has political contacts with its neighbours
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
and
Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
,
non-UN member state
Republic of China (Taiwan)
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
,
as well as with South Africa,
Sweden,
and the United Kingdom.
On 17 January 2007, the European Union (EU) sent a delegation for foreign affairs to discuss future co-operation.
The
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
(AU) has also sent a foreign minister to discuss the future of international acknowledgment, and on 29 and 30 January 2007, the ministers stated that they would discuss acknowledgement with the organisation's member states.
In early 2006, the
National Assembly for Wales
The Senedd ( ; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, Its role is to scrutinise the Welsh Government and legislate on devolve ...
extended an official invitation to the Somaliland government to attend the royal opening of the
Senedd building
The Senedd building (), in Cardiff, houses the debating chamber and three committee rooms of the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; ; formerly the National Assembly for Wales). The Senedd building was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 1 March 2006, Saint ...
in
Cardiff
Cardiff (; ) is the capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of Wales. Cardiff had a population of in and forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area officially known as the City and County of Ca ...
. The move was seen as an act of recognition by the Welsh Assembly of the breakaway government's legitimacy. The
Foreign and Commonwealth Office
The Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO) is the ministry of foreign affairs and a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, ministerial department of the government of the United Kingdom.
The office was created on 2 ...
made no comment on the invitation. Wales is home to a significant Somali
expatriate
An expatriate (often shortened to expat) is a person who resides outside their native country.
The term often refers to a professional, skilled worker, or student from an affluent country. However, it may also refer to retirees, artists and ...
community from Somaliland.
In 2007, a delegation led by President Kahin was present at the
Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting
The Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM; or) is a wiktionary:biennial, biennial summit meeting of the List of current heads of state and government, governmental leaders from all Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth nations. ...
in
Kampala
Kampala (, ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Uganda. The city proper has a population of 1,875,834 (2024) and is divided into the five political divisions of Kampala Central Division, Kampala, Kawempe Division, Kawempe, Makindy ...
, Uganda. Although Somaliland has applied to join the
Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
under
observer status
Observer status is a privilege granted by some organizations to non-members to give them an ability to participate in the organization's activities. Observer status is often granted by intergovernmental organizations (IGO) to non-member parties and ...
, its application is still pending.
On 24 September 2010,
Johnnie Carson, Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs, stated that the United States would be modifying its strategy in Somalia and would seek deeper engagement with the governments of Somaliland and Puntland while continuing to support the Somali Transitional Government.
Carson said the US would send aid workers and diplomats to Puntland and Somaliland and alluded to the possibility of future development projects. However, Carson emphasised that the US would not extend formal recognition to either region.

The then-UK Minister for Africa,
Henry Bellingham MP, met President Silanyo of Somaliland in November 2010 to discuss ways in which to increase the UK's engagement with Somaliland.
President Silanyo said during his visit to London:
Recognition of Somaliland by the UK was also supported by the
UK Independence Party
The UK Independence Party (UKIP, ) is a Eurosceptic, right-wing populist political party in the United Kingdom. The party reached its greatest level of success in the mid-2010s, when it gained two members of parliament (both through defect ...
, which came third in the popular vote at the
2015 general election, though only electing a single MP. The former leader of UKIP,
Nigel Farage
Nigel Paul Farage ( ; born 3 April 1964) is a British politician and broadcaster who has been Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) for Clacton (UK Parliament constituency), Clacton and Leader of Reform UK since 20 ...
, met with Ali Aden Awale, Head of the Somaliland UK Mission on Somaliland's national day, 18 May, in 2015, to express UKIP's support for Somaliland.
In 2011, Somaliland and the neighbouring Puntland region each entered a security-related
memorandum of understanding with the
Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
. Following the framework of an earlier agreement signed between the Transitional Federal Government and Seychelles, the memorandum is
On 1 July 2020, Somaliland and
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
signed an agreement to set up representative offices to promote cooperation between the two countries.
Cooperation between the two polities on education, maritime security, and medicine began in 2009, and Taiwanese staff entered Somaliland in February 2020 to prepare for the representative office.
As of 2023, Taiwan's Ministry of Foreign Affairs refers to Somaliland as a country.
[
On 1 January 2024, a memorandum of understanding was signed between Ethiopia and Somaliland, where Ethiopia will lease the port of ]Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
on the Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden (; ) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. ...
, and a 20-kilometre stretch of Gulf of Aden coastline, for 20 years, in exchange for eventual recognition of Somaliland as an independent state and a stake in the Ethiopian Airlines
Ethiopian Airlines (), formerly ''Ethiopian Air Lines'' (EAL), is the flag carrier of Ethiopia, and is wholly owned by the country's government. EAL was founded on 21 December 1945 and commenced operations on 8 April 1946, expanding to intern ...
. If this agreement is honoured, Ethiopia would become the first United Nations member state to recognise the breakaway nation.
Border disputes
 Somaliland continues to claim the entire area of the former
Somaliland continues to claim the entire area of the former British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
which gained independence in 1960 in the name of State of Somaliland
Somaliland, officially the State of Somaliland (), was an independent country in the territory of the present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland, which regards itself as its legal successor. It existed on the territory of former ...
.State of Somaliland
Somaliland, officially the State of Somaliland (), was an independent country in the territory of the present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland, which regards itself as its legal successor. It existed on the territory of former ...
.
Puntland
Puntland is an autonomous state that considers itself to be part of Somalia, despite not accepting the legitimacy of Somalia's current governing administration. It was formed in 1998, and was a federal member state of Somalia from its fou ...
, a federal member state of Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
, disputes the Harti
Harti () is a Somali clan that traces its lineage back to Saleh Abdi Harti. They are a sub-clan of the larger Darod clan. Notable sub-clans within Harti include the Majeerteen, Warsangali, Warsengeli, Dishishe, and the Dhulbahante. They predomi ...
-inhabited territory in the former British Somaliland protectorate based on kinship. In 1998, the northern Darod clans established the state, and the Dhulbahante
The Dhulbahante, (, ) are a Somali sub-clan, part of the Harti branch of the larger Darod clan. They primary reside in and around their traditional territories of Nugaal, as well as Doollo. The clan's progenitor is buried at Badweyn.
The cur ...
and Warsangali
The Warsangali (, ), alternatively the Mohamoud Harti, are a major Somali sub clan, part of the larger Harti branch, which belongs to the Darod clan, one of the largest Somali tribe families. In the Somali language, the name Warsangali means "b ...
clans wholly participated in its foundation.Borama
Borama (, ) is the largest city of the northwestern Awdal region of Somaliland. The commercial seat of the province, it is situated near the border with Ethiopia.
During the Middle Ages, Borama was ruled by the Adal Sultanate. It later formed a ...
Conference, when they were replaced in importance by the Gadabursi. The Dhulbahante
The Dhulbahante, (, ) are a Somali sub-clan, part of the Harti branch of the larger Darod clan. They primary reside in and around their traditional territories of Nugaal, as well as Doollo. The clan's progenitor is buried at Badweyn.
The cur ...
and Warsangali
The Warsangali (, ), alternatively the Mohamoud Harti, are a major Somali sub clan, part of the larger Harti branch, which belongs to the Darod clan, one of the largest Somali tribe families. In the Somali language, the name Warsangali means "b ...
clans established two separate administrations in the early 1990s. First, the former was to hold the Boocame I conference in May 1993, while the later held a conference in Hadaaftimo in September 1992. In both conferences the desire to remain part of Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
was expressed.
Tensions between Puntland and Somaliland escalated into violence several times between 2002 and 2009. In October 2004, and again in April and October 2007, armed forces of Somaliland and Puntland clashed near the town of Las Anod
Las Anod (; ) is the administrative capital of the Sool region, currently controlled by Khatumo State forces aligned with Somalia.
Territorial dispute
The city is disputed by Puntland and Somaliland. The former bases its claim due to the kins ...
, the capital of Sool region. In October 2007, Somaliland troops took control of the town.Sanaag
Sanag (, ) is an administrative region ('' gobol'') in north eastern Somaliland.[Regions of Somalia](_blank)
Sa ...
on 10 July 2008, along with positions east of the town. The defence forces completed their operations on 9 July 2008 after the Maakhir and Puntland militia in the area left their positions.Sanaag
Sanag (, ) is an administrative region ('' gobol'') in north eastern Somaliland.[Regions of Somalia](_blank)
Sa ...
was formed with the goal to establish its own regional administration (Sool, Sanaag and Cayn, or SSC).Khatumo State
SSC-Khaatumo (), officially known as the SSC-Khaatumo State of Somalia (), is a federal member state in northern Somalia, with its capital in Las Anod. It includes parts of the Sool, Sanaag and Cayn regions (combined under the acronym "SSC") ...
, which was established in 2012. The local administration and its constituents does not recognise the Somaliland government's claim to sovereignty or to its territory.Aynabo
Aynaba, also spelt Ainabo, Ainaba or Aynabo (, ) is a major town in western Sool region of Somaliland as well as the administrative seat of the Aynaba District.
Overview
Aynaba is situated on a busy tarmac road connecting Somaliland's major ci ...
, an agreement was signed with the Somaliland government that stipulated the amendment of Somaliland's constitution and integrating the organisation into the Somaliland government.Dhulbahante
The Dhulbahante, (, ) are a Somali sub-clan, part of the Harti branch of the larger Darod clan. They primary reside in and around their traditional territories of Nugaal, as well as Doollo. The clan's progenitor is buried at Badweyn.
The cur ...
community.
Military
 The
The Somaliland Armed Forces
The Somaliland National Armed Forces (; ) are the military services of the Republic of Somaliland. The Somaliland National Armed Forces consist of the Somaliland National Army, the Somaliland Coast Guard, the Somaliland Police Force, the Somalil ...
are the main military command in Somaliland. Along with the Somaliland Police and all other internal security forces, they are overseen by Somaliland's Ministry of Defence
A ministry of defence or defense (see American and British English spelling differences#-ce.2C -se, spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is the part of a government responsible for matters of defence and Mi ...
. The current head of Somaliland's Armed Forces is the Minister of Defence, Abdiqani Mohamoud Aateye.howitzer
The howitzer () is an artillery weapon that falls between a cannon (or field gun) and a mortar. It is capable of both low angle fire like a field gun and high angle fire like a mortar, given the distinction between low and high angle fire break ...
s and mobile rocket launcher
A rocket launcher is a weapon that launches an unguided, rocket-propelled projectile.
History
The earliest rocket launchers documented in imperial China consisted of arrows modified by the attachment of a rocket motor to the shaft a few i ...
s. Its armoured vehicles and tanks are mostly of Soviet design, though there are some ageing Western vehicles and tanks in its arsenal. The Somaliland Navy (often referred to as a Coast Guard by the Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American not-for-profit organization, not-for-profit news agency headquartered in New York City.
Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association, and produces news reports that are dist ...
), despite a crippling lack of equipment and formal training, has apparently had some success at curbing both piracy and illegal fishing
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) is an issue around the world. Fishing industry observers believe IUU occurs in most fisheries, and accounts for up to 30% of total catches in some important fisheries.
Illegal fishing takes pl ...
within Somaliland waters.
Human rights
According to the 2023 Freedom House
Freedom House is a nonprofit organization based in Washington, D.C. It is best known for political advocacy surrounding issues of democracy, Freedom (political), political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, wi ...
report, Somaliland has seen a consistent erosion of political rights and civic space. Public figures and journalists face pressure from authorities. Minority clans are subject to economic and political marginalisation, and violence against women remains a serious problem.
Administrative divisions
 The Republic of Somaliland is divided into six administrative regions:
The Republic of Somaliland is divided into six administrative regions: Awdal
Awdal (, ) is an administrative region (''Administrative divisions of Somaliland, gobol'') in western Somaliland. It was separated from Woqooyi Galbeed and became a province in 1984 and is the most northwesterly province of Somaliland. To the e ...
, Sahil, Maroodi Jeeh, Togdheer
Togdheer (, ) is an administrative region (''Administrative divisions of Somaliland, gobol'') in central Somaliland. Togdheer is bordered by Maroodi Jeex to the west, Sahil, Somaliland, Saaxil to the north, Sanaag to the northeast, Sool, Somalia ...
, Sanaag
Sanag (, ) is an administrative region ('' gobol'') in north eastern Somaliland.[Regions of Somalia](_blank)
Sa ...
and Sool. The regions are divided into eighteen administrative districts.
Regions and districts
The following regions are taken from ''Michael Walls: State Formation in Somaliland: Bringing Deliberation to Institutionalism'' from 2011, ''Somaliland: The Strains of Success'' from 2015 and ActionAID, a humanitarian organisation currently active in Somaliland.[State Formation in Somaliland: Bringing Deliberation to Institutionalism. Michael Walls, Planning Unit, UCL February 2011](_blank)
/ref>Somaliland protectorate
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936-1941). From 1940 ...
; however, the Siad Barre
Mohammed Siad Barre (, Osmanya script: , ''Muhammad Ziād Barīy''; 6 October 1919 – 2 January 1995) was a Somali military officer, politician, and revolutionary who served as the third president of Somalia from 21 October 1969 to 26 Janu ...
era boundaries subsist as the de facto boundaries.
Geography
Location and habitat
 Somaliland is situated in the northwest of recognised Somalia. It lies between 08°N and 11°30'N, and between 42°30'E and 49°00'E.
Somaliland is situated in the northwest of recognised Somalia. It lies between 08°N and 11°30'N, and between 42°30'E and 49°00'E.Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
to the west, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
to the south, and Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
to the east. Somaliland has an coastline with the majority lying along the Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden (; ) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. ...
.Awdal
Awdal (, ) is an administrative region (''Administrative divisions of Somaliland, gobol'') in western Somaliland. It was separated from Woqooyi Galbeed and became a province in 1984 and is the most northwesterly province of Somaliland. To the e ...
, Sahil and Maroodi Jeex
Marodi Jeh (, ), formerly known as Woqooyi Galbeed (lit. ''North West'') is an administrative region ('' gobol'') in western Somaliland. It is the most populous region of the country. It is bordered by Awdal to the west, Sahil to the north, To ...
regions are fertile and mountainous, while Togdheer
Togdheer (, ) is an administrative region (''Administrative divisions of Somaliland, gobol'') in central Somaliland. Togdheer is bordered by Maroodi Jeex to the west, Sahil, Somaliland, Saaxil to the north, Sanaag to the northeast, Sool, Somalia ...
is mostly semi-desert
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of sem ...
with little fertile greenery around. The Awdal region is also known for its offshore islands, coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s and mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
s.
A scrub-covered, semi-desert plain referred as the '' Guban'' lies parallel to the Gulf of Aden littoral. With a width of in the west to as little as in the east, the plain is bisected by watercourses that are essentially beds of dry sand except during the rainy seasons. When the rains arrive, the Guban's low bushes and grass clumps transform into lush vegetation.[Hadden, Robert Lee. 2007]
"The Geology of Somalia: A Selected Bibliography of Somalian Geology, Geography and Earth Science."
Engineer Research and Development Laboratories, Topographic Engineering Center This coastal strip is part of the Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands
The Djibouti xeric shrublands is an ecoregion defined by One Earth, consisting of a semi-desert strip on or near the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden coasts in Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti and Somalia. This ecoregion lies mainly between sea level and ...
ecoregion.
Cal Madow
Cal Madow (also Calmadow, Al Madow, Al Medu, or Al Mado; ; ) is a mountain range in Somalia. It stretches across the area of Sanaag. Its peak sits at almost in Shimbiris, northwest of Erigavo. Cal Madow was a tourist destination in the late 198 ...
is a mountain range in the eastern part of the country. Extending from the northwest of Erigavo
Erigavo (, ), also spelled as Erigabo, is the capital and largest city of the Sanaag region of Somaliland.
Etymology
The name ''Ceerigaabo'' is made up of two parts: ''Ceeri'' which describes a place water collects, and ''gaabo'' (''gaaban'') ...
to several kilometres west of the city of Bosaso
Bosaso (, ), historically known as Bender Qassim is a city in the northeastern Bari province ('' gobol'') of Somalia. It is the seat of the Bosaso District. Located on the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden, the municipality serves as the region ...
in neighbouring Somalia, it features Somaliland's highest peak Peak or The Peak may refer to:
Basic meanings Geology
* Mountain peak
** Pyramidal peak, a mountaintop that has been sculpted by erosion to form a point Mathematics
* Peak hour or rush hour, in traffic congestion
* Peak (geometry), an (''n''-3)-d ...
, Shimbiris
Mount Shimbiris is the highest peak in Somaliland. It has an elevation of above sea level. It is located in the Ogo Mountains range in the Sanaag region. SRTM
The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is an international research effort th ...
, which sits at an elevation of about .Haud
The Haud (also Hawd) (, ), formerly known as the Hawd Reserve Area, is a plateau situated in the Horn of Africa consisting of thorn-bush and grasslands. The region includes the southern part of Somaliland as well as the northern and eastern part ...
, an important grazing area for livestock.Cal Madow
Cal Madow (also Calmadow, Al Madow, Al Medu, or Al Mado; ; ) is a mountain range in Somalia. It stretches across the area of Sanaag. Its peak sits at almost in Shimbiris, northwest of Erigavo. Cal Madow was a tourist destination in the late 198 ...
mountain range.
File:Somalia (Somaliland)(168).jpg, upThe Somaliland countryside
File:Almadow Overview.JPG, upView of the Cal Madow
Cal Madow (also Calmadow, Al Madow, Al Medu, or Al Mado; ; ) is a mountain range in Somalia. It stretches across the area of Sanaag. Its peak sits at almost in Shimbiris, northwest of Erigavo. Cal Madow was a tourist destination in the late 198 ...
Mountains, home to numerous endemic species
File:Somaliland (6790659460) (2).jpg, Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
beach
File:Sacadin.jpg, Sacadin, Zeila Archipelago
Climate
 Somaliland is located north of the
Somaliland is located north of the equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
. It is semi-arid. The average daily temperatures range from . The sun passes vertically overhead twice a year, in April and in August or September. Somaliland consists of three main topographic zones: a coastal plain (Guban), the coastal range (Ogo), and a plateau (Hawd). The coastal plain is a zone with high temperatures and low rainfall. Summer temperatures in the region easily average over . However, temperatures come down during the winter, and both human and livestock populations increase dramatically in the region.
The coastal range (Ogo) is a high plateau to the immediate south of Guban. Its elevation ranges from above sea level in the West to in the East. Rainfall is heavier there than in Guban, although it varies considerably within the zone. The plateau (Hawd) region lies to the south of Ogo range. It is generally more heavily populated during the wet season, when surface water is available. It is also an important area for grazing. Somalilanders recognise four seasons in the year; GU and Hagaa comprise spring and summer in that order, and Dayr and Jiilaal correspond to autumn and winter, respectively.
Wildlife
Economy
 Somaliland has the fourth-lowest GDP per capita in the world, and there are huge socio-economic challenges for Somaliland, with an unemployment rate between 60 and 70% among youth, if not higher. According to ILO, illiteracy exists up to 70% in several areas of Somaliland, especially among females and the elder population.
Since Somaliland is unrecognised, international donors have found it difficult to provide aid. As a result, the government relies mainly upon tax receipts and
Somaliland has the fourth-lowest GDP per capita in the world, and there are huge socio-economic challenges for Somaliland, with an unemployment rate between 60 and 70% among youth, if not higher. According to ILO, illiteracy exists up to 70% in several areas of Somaliland, especially among females and the elder population.
Since Somaliland is unrecognised, international donors have found it difficult to provide aid. As a result, the government relies mainly upon tax receipts and remittance
A remittance is a non-commercial transfer of money by a foreign worker, a member of a diaspora community, or a citizen with familial ties abroad, for household income in their home country or homeland.
Money sent home by migrants competes ...
s from the large Somali diaspora
The Somali diaspora or Qurbajoogta refers to Somalis who were born in Greater Somalia and reside in areas of the world that they were not born in. The civil war in Somalia greatly increased the size of the Somali diaspora, as many Somalis moved fr ...
, which contribute significantly to the Somaliland economy.[Daniel Harris with Marta Foresti 2011]
Somaliland's progress on governance: A case of blending the old and the new
. London: Overseas Development Institute
ODI Global (formerly Overseas Development Institute) is a global affairs think tank, founded in 1960. Its mission is "to inspire people to act on injustice and inequality through collaborative research and ideas that matter for people and the ...
Remittances come to Somaliland through money transfer companies, the largest of which is Dahabshiil,World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
estimates that remittances worth approximately US$1 billion reach Somalia annually from émigrés working in the Gulf states, Europe and the United States. Analysts say that Dahabshiil may handle around two-thirds of that figure and as much as half of it reaches Somaliland alone.non-governmental organisations
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
, religious groups, the international community (especially the diaspora), and the growing private sector. Local and municipal governments have been developing key public service provisions such as water in Hargeisa and education, electricity, and security in Berbera.Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
, opened a branch in Hargeisa and became the first bank in the country since the 1990 collapse of the Commercial and Savings Bank of Somalia.
Monetary and payment system
 The
The Somaliland shilling
The Somaliland shilling (, ; abbreviation: Sl.Sh. or SLSH; symbol: Slash (punctuation), /-) is the official currency of the Republic of Somaliland, an List of states with limited recognition, unrecognised state in the Horn of Africa, recognised i ...
, which cannot easily be exchanged outside of Somaliland on account of the nation's lack of recognition, is regulated by the Bank of Somaliland, the central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
, which was established constitutionally in 1994.
The most popular and used payment system in the country is the ZAAD service, which is a mobile money transfer service that was launched in Somaliland in 2009 by the largest mobile operator Telesom
Telesom is a private telecommunication company established in 2002 by local entrepreneurs in Hargeisa, Somaliland. It is the leading provider of ICT services in the country and offers a wide range of products including voice and mobile broadband, ...
.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications companies serving Somaliland include Telesom
Telesom is a private telecommunication company established in 2002 by local entrepreneurs in Hargeisa, Somaliland. It is the leading provider of ICT services in the country and offers a wide range of products including voice and mobile broadband, ...
,Somtel
Somtel (, ) is a telecommunications company headquartered in Hargeisa, Somaliland.
Regions
Somtel provides services in both Somaliland and Somalia.
Background
Somtel provides mobile voice and data services to customers, including Mobile Money ...
, Telcom Telcom may refer to:
* Telephone company, a provider of telecommunications services, such as telephony and data communications
* Telcom (Ireland), a telecommunications company
* Telcom (Somalia), a telecommunications network operator
* Telcom (c ...
and NationLink.
Agriculture
 Livestock is the backbone of Somaliland's economy. Sheep, camels, and cattle are shipped from the Berbera port and sent to Gulf Arab countries, such as Saudi Arabia.
Livestock is the backbone of Somaliland's economy. Sheep, camels, and cattle are shipped from the Berbera port and sent to Gulf Arab countries, such as Saudi Arabia.Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, with as many as 10,000 heads of sheep and goats sold daily in the markets of Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
and Yirowe, many of whom shipped to Gulf states via the port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
of Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
.quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mining, open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock (geology), rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some juri ...
ing represents the extent of current operations, despite the presence of diverse quantities of mineral deposits.
Tourism
The rock art
In archaeology, rock arts are human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type al ...
and caves at Laas Geel
Laas Geel (), also spelled Laas Gaal, are cave formations on the rural outskirts of Hargeisa, Somalia, situated in the Maroodi Jeex region of the country. They contain some of the earliest known cave paintings of domesticated African aurochs (' ...
, situated on the outskirts of Hargeisa, are a popular local tourist attraction. Totaling ten caves, they were discovered by a French archaeological team in 2002 and are believed to date back around 5,000 years. The government and locals keep the cave painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often c ...
s safe and only a restricted number of tourists are allowed entry.War Memorial
A war memorial is a building, monument, statue, or other edifice to celebrate a war or victory, or (predominating in modern times) to commemorate those who died or were injured in a war.
Symbolism
Historical usage
It has ...
in the city centre. Natural attractions are very common around the region. The Naasa Hablood
Naasa Hablood (), also known as the Virgin's Breast Mountain, are twin hills situated in Maroodi Jeex, Somaliland. Located on the outskirts of the city of Hargeisa, they are made of granite and sand. The hills were dubbed ''Naasa Hablood'' () due ...
are twin hills located on the outskirts of Hargeisa that Somalis in the region consider to be a majestic natural landmark.Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
also houses historic and impressive Ottoman architectural buildings. Another equally famous historic city is Zeila
Zeila (, ), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila with the Biblical location of Havilah. Most modern schola ...
. Zeila was once part of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, a dependency of Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and a major trade city during the 19th century. The city has been visited for its old colonial landmarks, offshore mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
s and coral reefs, towering cliffs, and beach. The nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic culture of Somaliland has also attracted tourists. Most nomads live in the countryside.
Transport
 Bus services operate in
Bus services operate in Hargeisa
Hargeisa ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland, a ''List of states with limited recognition, de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still considered internationally to be part of Somalia. It is also th ...
, Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
, Gabiley
Gabiley (, ), also known as Gebiley, is a city in the Maroodi Jeex region of Somaliland.
Gabiley is located 58 km west of Hargeisa, the capital of Somaliland. It is in the center of the Gabiley district, bounded on the north by the Gulf of ...
, Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
and Borama
Borama (, ) is the largest city of the northwestern Awdal region of Somaliland. The commercial seat of the province, it is situated near the border with Ethiopia.
During the Middle Ages, Borama was ruled by the Adal Sultanate. It later formed a ...
. There are also road transportation services between the major towns and adjacent villages, which are operated by different types of vehicles. Among these are taxis, four-wheel drive
A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case pr ...
s, minibus
A minibus, microbus, or minicoach is a passenger-carrying motor vehicle that is designed to carry more people than a multi-purpose vehicle or minivan, but fewer people than a full-size bus. In the United Kingdom, the word "minibus" is us ...
es and light goods vehicles (LGV).African Express Airways
African Express Airways is a Somali-owned Kenyan airline with its head office at Jomo Kenyatta International Airport in Embakasi, Nairobi, Kenya.
Services
African Express Airways is a short-haul airline, which caters to business and leisure tr ...
and Ethiopian Airlines
Ethiopian Airlines (), formerly ''Ethiopian Air Lines'' (EAL), is the flag carrier of Ethiopia, and is wholly owned by the country's government. EAL was founded on 21 December 1945 and commenced operations on 8 April 1946, expanding to intern ...
also fly from airports in Somaliland to Djibouti City
Djibouti (also called Djibouti City and Jibuti in early Western texts) is the capital city of the Djibouti, Republic of Djibouti. It is located in the coastal Djibouti Region on the Gulf of Tadjoura.
Djibouti has a population of around 780,000 ...
, Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; ,) is the capital city of Ethiopia, as well as the regional state of Oromia. With an estimated population of 2,739,551 inhabitants as of the 2007 census, it is the largest city in the country and the List of cities in Africa b ...
, Dubai
Dubai (Help:IPA/English, /duːˈbaɪ/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''doo-BYE''; Modern Standard Arabic, Modern Standard Arabic: ; Emirati Arabic, Emirati Arabic: , Romanization of Arabic, romanized: Help:IPA/English, /diˈbej/) is the Lis ...
and Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), alternatively transliterated as Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; , ), is a List of governorates of Saudi Arabia, governorate and the largest city in Mecca Province, Saudi Arabia, and the country's second largest city after Riyadh, located ...
, and offer flights for the Hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
and Umrah
The Umrah () is an Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, the holiest city for Muslims, located in the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia. It can be undertaken at any time of the year, in contrast to the '' Ḥajj'' (; "pilgrimage"), which has specific d ...
pilgrimages via the Egal International Airport
Egal International Airport (), ( ) is an airport in Hargeisa, the capital of Somaliland, named after Somaliland's second president Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal, the airport underwent major renovations in 2012–2013. In 2002 the airport handled ...
in Hargeisa. Other major airports in the region include the Berbera Airport.
Ports
 In June 2016, the Somaliland government signed an agreement with
In June 2016, the Somaliland government signed an agreement with DP World
DP World is a multinational logistics company based in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It specialises in cargo logistics, port terminal operations, maritime services and free trade zones. Formed in 2005 by the merger of Dubai Ports Authority and ...
to manage the strategic port of Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
with the aim of enhancing productive capacity and acting as an alternative port for landlocked Ethiopia.
Oil exploration
In 1958, the first test well was dug by Standard Vacuum (Exxon Mobil and Shell) in Dhagax Shabeel, Saaxil region. These wells were selected without field data or seismic testing and were solely based on the geological makeup of the region. Three of the four test wells were successful in producing of light crude oil.
In August 2012, the Somaliland government awarded Genel Energy a licence to explore oil within its territory. Results of a surface seep study completed early in 2015 confirmed the outstanding potential offered in the SL-10B, SL-13, and Oodweyne blocks, with estimated oil reserves of 1 billion barrels each.Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
's CPC Corporation
The CPC Corporation () is a state-owned petroleum, natural gas, and gasoline company in Taiwan and is the core of the Taiwanese petrochemicals industry.
History Early history
CPC was founded on 1 June 1946 in Shanghai as Chinese Petroleum Corpo ...
, on the SL10B/13 block neary Aynaba.
Demographics
There has not been an official census conducted in Somaliland since the Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
census in 1975, while the results from a 1986 census were never released into public domain. A population estimate was conducted by UNFPA
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) is a UN agency aimed at improving reproductive and maternal health worldwide. Its work includes developing national healthcare strategies and protocols, increasing access to birth control, and leadin ...
in 2014 primarily for the purpose of distributing United Nations funding among the regions and to offer a reliable population estimate in lieu of a census. This population estimate puts the combined population of the regions of Somaliland at 3.5 million. The Somaliland government estimates that there are 6,200,000 residents as of 2024,Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
, Darod
The Darod (, ) is a Somali clan. The forefather of this clan is Sheikh Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti, more commonly known as Darod. The clan primarily settles the apex of the Horn of Africa and its peripheries, the Somali hinterlands adjacent ...
and Dir made up 66%, 19% and 16% of the population, respectively.
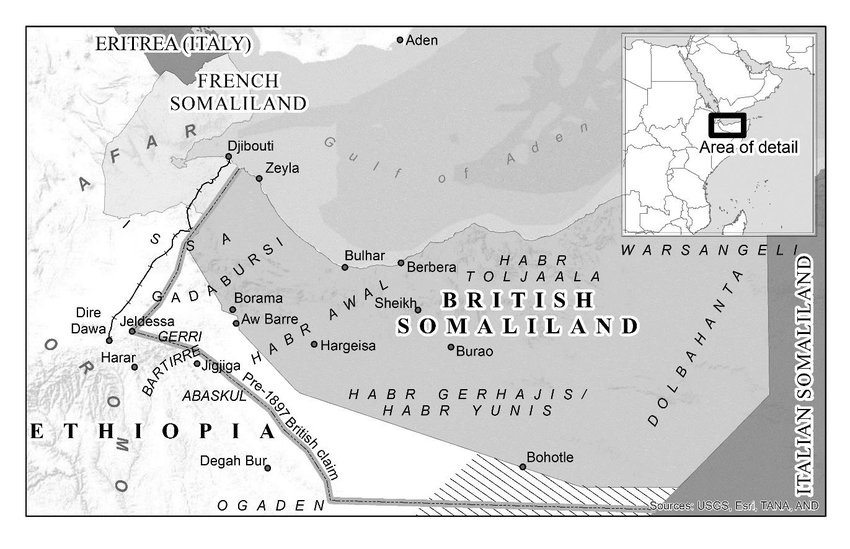
 The largest clan family in Somaliland is the
The largest clan family in Somaliland is the Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
,Hargeisa
Hargeisa ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland, a ''List of states with limited recognition, de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still considered internationally to be part of Somalia. It is also th ...
, Burao
Burao, also spelt Bur'o or Bur'ao (; , , ), is the capital of the Togdheer region and the second largest city in Somaliland. Burao was the site of the Somaliland Declaration of Independence, declaration of an independent Somaliland on 18 May 19 ...
, Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
, Erigavo
Erigavo (, ), also spelled as Erigabo, is the capital and largest city of the Sanaag region of Somaliland.
Etymology
The name ''Ceerigaabo'' is made up of two parts: ''Ceeri'' which describes a place water collects, and ''gaabo'' (''gaaban'') ...
and Gabiley
Gabiley (, ), also known as Gebiley, is a city in the Maroodi Jeex region of Somaliland.
Gabiley is located 58 km west of Hargeisa, the capital of Somaliland. It is in the center of the Gabiley district, bounded on the north by the Gulf of ...
– are predominantly Isaaq.Gadabursi
The Gadabuursi ( Somali: ''Gadabuursi'', Arabic: جادابورسي), also known as ''Samaroon'' (Arabic: ''قبيلة سَمَرُون)'', is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.I. M. Lewis (1959)
The Gadabuursi ...
of the Dir clan
The Dir () is one of the largest and most prominent Somali clans in the Horn of Africa. They are also considered to be the oldest Somali stock to have inhabited the region. Its members inhabit Djibouti, Somalia, Ethiopia ( Somali, Harar, Dir ...
Harti
Harti () is a Somali clan that traces its lineage back to Saleh Abdi Harti. They are a sub-clan of the larger Darod clan. Notable sub-clans within Harti include the Majeerteen, Warsangali, Warsengeli, Dishishe, and the Dhulbahante. They predomi ...
of the Darod
The Darod (, ) is a Somali clan. The forefather of this clan is Sheikh Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti, more commonly known as Darod. The clan primarily settles the apex of the Horn of Africa and its peripheries, the Somali hinterlands adjacent ...
. Other small clans are often not accounted for in such estimates, however, clans including Gabooye, Gahayle, Jibrahil, Magaadle, Fiqishini, and Akisho settle in Somaliland.
Somaliland in addition has an estimated 600,000
Clan groups
 The
The Gadabursi
The Gadabuursi ( Somali: ''Gadabuursi'', Arabic: جادابورسي), also known as ''Samaroon'' (Arabic: ''قبيلة سَمَرُون)'', is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.I. M. Lewis (1959)
The Gadabuursi ...
subclan of the Dir are the predominant clan of the Awdal
Awdal (, ) is an administrative region (''Administrative divisions of Somaliland, gobol'') in western Somaliland. It was separated from Woqooyi Galbeed and became a province in 1984 and is the most northwesterly province of Somaliland. To the e ...
region,[Samatar, Abdi I. (2001) "Somali Reconstruction and Local Initiative: Amoud University," , p. 132.]Zeila District
Zeila District () is a district in western Somaliland. Its capital is at Zeila.
Demographics
The town of Zeila is primarily inhabited by people from the Somali ethnic group, with the Gadabuursi subclan of the Dir especially well represented. Th ...
.Habr Awal
The Habr Awal, alternately known as the Zubeyr Awal (, , Full Name: '' Abd al-Raḥmān ibn ash-Ishaaq bin Ahmed, Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad)'' is one of the largest subclans of the wider Isaaq clan family, and is further divided into eight su ...
subclan of the Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory.
The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend ...
form the majority of the population living in both the northern and western portions of the Maroodi Jeex
Marodi Jeh (, ), formerly known as Woqooyi Galbeed (lit. ''North West'') is an administrative region ('' gobol'') in western Somaliland. It is the most populous region of the country. It is bordered by Awdal to the west, Sahil to the north, To ...
region, including the cities and towns of northern Hargeisa
Hargeisa ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland, a ''List of states with limited recognition, de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still considered internationally to be part of Somalia. It is also th ...
, Berbera
Berbera (; , ) is the capital of the Sahil, Somaliland, Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country, located approximately 160 km from the national capital, Hargeisa. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of t ...
, Gabiley
Gabiley (, ), also known as Gebiley, is a city in the Maroodi Jeex region of Somaliland.
Gabiley is located 58 km west of Hargeisa, the capital of Somaliland. It is in the center of the Gabiley district, bounded on the north by the Gulf of ...
, Madheera, Wajaale
Tog Wajaale (also known as Wajaale, Wajale, Tug Wajale, Togwajaale) is a city on the border of Somaliland and Ethiopia. Tog Wajaale is the main border crossing for goods coming in and out of Somaliland, primarily from the port city of Berbera, So ...
, , Bulhar">/nowiki>
Primary schools
* Number of Pr ...
, Bulhar and Kalabaydh. The
.
.
have a sizeable presence among the population inhabiting the southern and eastern portions of
. The
region. The
.
. The clan also has a significant presence in the
.
region districts.
.
district.
Many people in Somaliland speak at least two of the three national languages:
, Arabic and English, although the rate of bilingualism is lower in rural areas. Article 6 of the Constitution of 2001 designates the official language of Somaliland to be Somali,
though Arabic is a mandatory subject in school and is used in mosques around the region and English is spoken and taught in schools.
, the nation's most populous ethnic group. It is a member of the
languages.
which is the main dialect spoken in Somalia.
.
.
also has a noticeable presence.
Though traces of pre-Islamic traditional religion exist in Somaliland, Islam is dominant to the Somali sense of national identity. Many of the Somali social norms come from their religion. For example, most Somali women wear a
when they are in public. In addition, religious Somalis abstain from pork and
). Muslims generally congregate on Friday afternoons for a sermon and group prayer.
. The promotion of any religion other than Islam is illegal, and the state promotes Islamic tenets and discourages behaviour contrary to .
Somaliland has very few Christians. In 1913, during the early part of the colonial era, there were virtually no Christians in the Somali territories, with about 100–200 followers coming from the schools and orphanages of the handful of
missions in the British Somaliland protectorate.
The small number of Christians in the region today mostly come from similar Catholic institutions in
.
Somaliland falls within the Episcopal Area of the Horn of Africa as part of Somalia, under the
. However, there are no current congregations in the territory.
is designated to serve the area as part of Somalia. However, since 1990 there has been no Bishop of Mogadishu, and the Bishop of Djibouti acts as Apostolic Administrator.
also indicates that there are no Adventist members.
While 40.5% of households in Somaliland have access to improved water sources, almost a third of households lie at least an hour away from their primary source of drinking water. 1 in 11 children die before their first birthday, and 1 in 9 die before their fifth birthday.
The UNICEF multiple indicator cluster survey (MICS) in 2006 found that 94.8% of women in Somaliland had undergone some form of
in 2018 the Somaliland government issued a fatwa condemning the two most severe forms of FGM, but no laws are present to punish those responsible for the practice.
Somaliland has an urban literacy rate of 59% and a rural literacy rate of 47%, according to a 2015
assessment.
. Other smaller clans include: Jibraahil, Akisho, and others.
The
s, and have a central role in Somali culture and politics. Clans are
and are often divided into sub-clans, sometimes with many sub-divisions.
. To extend ties of alliance, marriage is often to another
from a different clan. Thus, for example, a 1954 study observed that in 89 marriages contracted by men of the
clan, 55 (62%) were with women of Dhulbahante sub-clans other than those of their husbands; 30 (33.7%) were with women of surrounding clans of other clan families (
1).
and poetry have been described as the twin pillars of Somali culture. Somali poetry is mainly oral, with both male and female poets. They use things that are common in the Somali language as metaphors. Almost all Somalis are
. Most Somalis do not belong to a specific mosque or sect and can pray in any mosque they find.
Celebrations come in the form of religious festivities. Two of the most important are
, which marks the end of the fasting month. Families get dressed up to visit one another, and money is donated to the poor. Other holidays include 26 June and 18 May, which celebrate British Somaliland's independence and the Somaliland region's establishment, respectively; the latter, however, is not recognised by the international community.
ic culture, where one's possessions are frequently moved, there is little reason for the
to be highly developed. Somalis embellish and decorate their woven and wooden milk jugs (''haamo''; the most decorative jugs are made in
) as well as wooden headrests. Traditional dance is also important, though mainly as a form of courtship among young people. One such dance known as ''Ciyaar Soomaali'' is a local favourite.
art. The custom of applying henna dates back to antiquity. During special occasions, a Somali woman's hands and feet are expected to be covered in decorative
. Girls and women usually apply or decorate their hands and feet in henna on festive celebrations like
or weddings. The henna designs vary from very simple to highly intricate. Somali designs vary, with some more modern and simple while others are traditional and intricate. Traditionally, only women apply it as
, as it is considered a feminine custom. Henna is not only applied on the hands and feet but is also used as a
. Somali men and women alike use henna as a dye to change their hair colour. Women are free to apply henna on their hair as most of the time they are wearing a
.
, track, field, and basketball.
.
* Hoehne, Markus V. 2009: Mimesis and mimicry in dynamics of state and identity formation in northern Somalia, ''Africa'' 79/2, pp. 252–281.
''International Business Times''. 18 September 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
*
* Bradbury, Mark, ''Becoming Somaliland'' (James Currey, 2008)
* Michael Schoiswohl: ''Status and (Human Rights) Obligations of Non-Recognized'' De Facto ''Regimes in International Law: The Case of 'Somaliland (Martinus Nijhoff, Leiden 2004),
*
 The area of Somaliland was inhabited around 10,000 years ago during the
The area of Somaliland was inhabited around 10,000 years ago during the  Ancient
Ancient  The people of Burao clashed with the British in 1922. They revolted in opposition to a new tax that was imposed upon them, rioting and attacking British government officials. This led to a shootout between the British and Burao residents in which Captain Allan Gibb, a Dervish war veteran and district commissioner, was shot and killed. The British requested Sir
The people of Burao clashed with the British in 1922. They revolted in opposition to a new tax that was imposed upon them, rioting and attacking British government officials. This led to a shootout between the British and Burao residents in which Captain Allan Gibb, a Dervish war veteran and district commissioner, was shot and killed. The British requested Sir  The 1945 Sheikh Bashir Rebellion was a rebellion waged by tribesmen of the
The 1945 Sheikh Bashir Rebellion was a rebellion waged by tribesmen of the  Initially the
Initially the  Although the SNM at its inception had a unionist constitution, it eventually began to pursue independence, looking to secede from the rest of Somalia. Under the leadership of
Although the SNM at its inception had a unionist constitution, it eventually began to pursue independence, looking to secede from the rest of Somalia. Under the leadership of  Legislative power is held by the
Legislative power is held by the  The judicial system is divided into district courts (which deal with matters of family law and succession, lawsuits for amounts up to 3 million SLSH, criminal cases punishable by up to 3 years' imprisonment or 3 million SL fines, and crimes committed by juveniles), regional courts (which deal with lawsuits and criminal cases not within the jurisdiction of district courts, labour and employment claims, and local government elections), regional appeals courts (which deal with all appeals from the district and regional courts), and the
The judicial system is divided into district courts (which deal with matters of family law and succession, lawsuits for amounts up to 3 million SLSH, criminal cases punishable by up to 3 years' imprisonment or 3 million SL fines, and crimes committed by juveniles), regional courts (which deal with lawsuits and criminal cases not within the jurisdiction of district courts, labour and employment claims, and local government elections), regional appeals courts (which deal with all appeals from the district and regional courts), and the  The ''guurti'' worked with rebel leaders to set up a new government, and was incorporated into the governance structure, becoming the Parliament's
The ''guurti'' worked with rebel leaders to set up a new government, and was incorporated into the governance structure, becoming the Parliament's  The then-UK Minister for Africa, Henry Bellingham MP, met President Silanyo of Somaliland in November 2010 to discuss ways in which to increase the UK's engagement with Somaliland. President Silanyo said during his visit to London:
Recognition of Somaliland by the UK was also supported by the
The then-UK Minister for Africa, Henry Bellingham MP, met President Silanyo of Somaliland in November 2010 to discuss ways in which to increase the UK's engagement with Somaliland. President Silanyo said during his visit to London:
Recognition of Somaliland by the UK was also supported by the  Somaliland continues to claim the entire area of the former
Somaliland continues to claim the entire area of the former  The
The  Somaliland has the fourth-lowest GDP per capita in the world, and there are huge socio-economic challenges for Somaliland, with an unemployment rate between 60 and 70% among youth, if not higher. According to ILO, illiteracy exists up to 70% in several areas of Somaliland, especially among females and the elder population.
Since Somaliland is unrecognised, international donors have found it difficult to provide aid. As a result, the government relies mainly upon tax receipts and
Somaliland has the fourth-lowest GDP per capita in the world, and there are huge socio-economic challenges for Somaliland, with an unemployment rate between 60 and 70% among youth, if not higher. According to ILO, illiteracy exists up to 70% in several areas of Somaliland, especially among females and the elder population.
Since Somaliland is unrecognised, international donors have found it difficult to provide aid. As a result, the government relies mainly upon tax receipts and  The
The  Livestock is the backbone of Somaliland's economy. Sheep, camels, and cattle are shipped from the Berbera port and sent to Gulf Arab countries, such as Saudi Arabia. The country is home to some of the largest livestock markets, known in Somali as ''seylad'', in the
Livestock is the backbone of Somaliland's economy. Sheep, camels, and cattle are shipped from the Berbera port and sent to Gulf Arab countries, such as Saudi Arabia. The country is home to some of the largest livestock markets, known in Somali as ''seylad'', in the  Bus services operate in
Bus services operate in  In June 2016, the Somaliland government signed an agreement with
In June 2016, the Somaliland government signed an agreement with 
 The largest clan family in Somaliland is the
The largest clan family in Somaliland is the  The
The  Eastern Sool region residents mainly hail from the
Eastern Sool region residents mainly hail from the  While 40.5% of households in Somaliland have access to improved water sources, almost a third of households lie at least an hour away from their primary source of drinking water. 1 in 11 children die before their first birthday, and 1 in 9 die before their fifth birthday.
The UNICEF multiple indicator cluster survey (MICS) in 2006 found that 94.8% of women in Somaliland had undergone some form of
While 40.5% of households in Somaliland have access to improved water sources, almost a third of households lie at least an hour away from their primary source of drinking water. 1 in 11 children die before their first birthday, and 1 in 9 die before their fifth birthday.
The UNICEF multiple indicator cluster survey (MICS) in 2006 found that 94.8% of women in Somaliland had undergone some form of 
 In the
In the  Popular sports in Somaliland include
Popular sports in Somaliland include