|
Rock Art
In archaeology, rock arts are human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also may be called cave art or parietal art. A global phenomenon, rock art is found in many culturally diverse regions of the world. It has been produced in many contexts throughout human history. In terms of technique, the four main groups are: * cave paintings, * petroglyphs, which are carved or scratched into the rock surface, * sculpted rock reliefs, and * geoglyphs, which are formed on the ground. The oldest known rock art dates from the Upper Palaeolithic period, having been found in Europe, Australia, Asia, and Africa. Anthropologists studying these artworks believe that they likely had magico-religious significance. The archaeological sub-discipline of rock art studies first developed in the late-19th century among Francophone schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often created by ''Human, Homo sapiens'', but also Denisovan, Denisovans and Neanderthal, Neanderthals; other species in the same ''Homo'' genus. Discussion around prehistoric art is important in understanding the history of ''Homo sapiens'' and how human beings have come to have unique abstract thoughts. Some point to these prehistoric paintings as possible examples of creativity, spirituality, and sentimental thinking in prehistoric humans. The oldest known are more than 40,000 years old (art of the Upper Paleolithic) and found in the caves in the district of Maros (Sulawesi, Indonesia). The oldest are often constructed from hand stencils and simple geometric shapes.M. Aubert et al., "Pleistocene cave art from Sulawesi, Indonesia", ''Nature'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
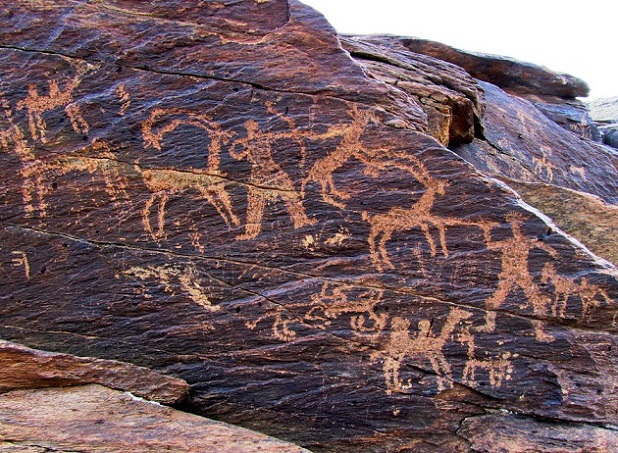
Petroglyphs
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions of the technique to refer to such images. Petroglyphs, estimated to be 20,000 years old are classified as protected monuments and have been added to the tentative list of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites. Petroglyphs are found worldwide, and are often associated with prehistoric peoples. The word comes from the Greek prefix , from meaning "stone", and meaning "carve", and was originally coined in French as . In scholarly texts, a ''petroglyph'' is a rock engraving, whereas a '' petrograph'' (or ''pictograph'') is a rock painting. In common usage, the words are sometimes used interchangeably. Both types of image belong to the wider and more general category of rock art or parietal art. Petroforms, or patterns and shapes made by many large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroglyph Jqjacobs
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions of the technique to refer to such images. Petroglyphs, estimated to be 20,000 years old are classified as protected monuments and have been added to the tentative list of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites. Petroglyphs are found worldwide, and are often associated with prehistoric peoples. The word comes from the Greek prefix , from meaning "stone", and meaning "carve", and was originally coined in French as . In scholarly texts, a ''petroglyph'' is a rock engraving, whereas a ''petrograph'' (or ''pictograph'') is a rock painting. In common usage, the words are sometimes used interchangeably. Both types of image belong to the wider and more general category of rock art or parietal art. Petroforms, or patterns and shapes made by many large ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Archéologique De Bidzar4
Site most often refers to: * Archaeological site * Campsite, a place used for overnight stay in an outdoor area * Construction site * Location, a point or an area on the Earth's surface or elsewhere * Website, a set of related web pages, typically with a common domain name It may also refer to: * Site, a National Register of Historic Places property type * SITE (originally known as ''Sculpture in the Environment''), an American architecture and design firm * Site (mathematics), a category C together with a Grothendieck topology on C * ''The Site'', a 1990s TV series that aired on MSNBC * SITE Intelligence Group, a for-profit organization tracking jihadist and white supremacist organizations * SITE Institute, a terrorism-tracking organization, precursor to the SITE Intelligence Group * Sindh Industrial and Trading Estate, a company in Sindh, Pakistan * SITE Centers, American commercial real estate company * SITE Town, a densely populated town in Karachi, Pakistan * S.I.T.E Indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stencil
Stencilling produces an image or pattern on a surface by applying pigment to a surface through an intermediate object, with designed holes in the intermediate object. The holes allow the pigment to reach only some parts of the surface creating the design. The stencil is both the resulting image or pattern and the intermediate object; the context in which ''stencil'' is used makes clear which meaning is intended. In practice, the (object) stencil is usually a thin sheet of material, such as paper, plastic, wood or metal, with lettering, letters or a design cut from it, used to produce the letters or design on an underlying surface by applying pigment through the cut-out holes in the material. The key advantage of a stencil is that it can be reused to repeatedly and rapidly produce the same letters or design. Although aerosol paint, aerosol or painting stencils can be made for one-time use, typically they are made with the intention of being reused. To be reusable, they must rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent, as a rubber additive, and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese is commonly found in labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhas At Ili
In Buddhism, Buddha (, which in classic Indic languages means "awakened one") is a title for those who are spiritually awake or enlightened, and have thus attained the supreme goal of Buddhism, variously described as awakening or enlightenment (''bodhi''), '' Nirvāṇa'' ("blowing out"), and liberation (''vimokṣa''). A Buddha is also someone who fully understands the '' Dhārma'', the true nature of all things or phenomena ('' dhārmata''), the ultimate truth. Buddhahood (Sanskrit: ''buddhatva''; or ; zh, c=成佛) is the condition and state of being a Buddha. This highest spiritual state of being is also termed ''sammā-sambodhi'' (Sanskrit: ''samyaksaṃbodhi''; "full, complete awakening") and is interpreted in many different ways across schools of Buddhism. The title of "Buddha" is most commonly used for Gautama Buddha, the historical founder of Buddhism, who is often simply known as "the Buddha". The title is also used for other sentient beings who have achieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, called charcoal burning, often by forming a charcoal kiln, the heat is supplied by burning part of the starting material itself, with a limited supply of oxygen. The material can also be heated in a closed retort. Modern charcoal briquettes used for outdoor cooking may contain many other additives, e.g. coal. The early history of wood charcoal production spans ancient times, rooted in the abundance of wood in various regions. The process typically involves stacking wood billets to form a conical pile, allowing air to enter through openings at the bottom, and igniting the pile gradually. Charcoal burners, skilled professionals tasked with managing the delicate operation, often lived in isolation to tend their wood piles . Throughout histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), iron ochre, or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as red ochre (or, in some dialects, ruddle). The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper. Earth pigments Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known as limonite, which gives them a yellow colour. A range of other minerals may also be included in the mixture:Krivovichev V. G. Mineralogical glossary. Scientific editor :uk:Булах Андрій Глібович, A. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |