Patna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Patna (; ,
 The
The
File:Sir Charles D'Oyly - Street in Patna - Google Art Project.jpg, Street in Patna, 1825 (British, active in India)
File:Golghar at Bankipur, near Patna, 1814-15.jpg, Golghar at Bankipore, near Patna, 1814–15
 Patna is on the southern bank of the river
Patna is on the southern bank of the river
 Patna has a
Patna has a
 Since the 17th century, Patna has been a centre of international trade and an agricultural and textile hub, including a major silk and calico market. After gaining independence in 1947, the economy remained relatively stable, including growth in produce and manufacturing of vegetable oil. From the 1980s onwards, the economy experienced fluctuations. When liberalisation came to India in the 1990s, Patna did not attract significant global funds or foreign investment which proved a setback for the economy. Although the city had several fertiliser plants and sugar mills, due to a weakened ecosystem, many companies incurred losses and were eventually forced to close or leave the state.
The economy of Patna has seen sustained growth since 2005, in particular from the
Since the 17th century, Patna has been a centre of international trade and an agricultural and textile hub, including a major silk and calico market. After gaining independence in 1947, the economy remained relatively stable, including growth in produce and manufacturing of vegetable oil. From the 1980s onwards, the economy experienced fluctuations. When liberalisation came to India in the 1990s, Patna did not attract significant global funds or foreign investment which proved a setback for the economy. Although the city had several fertiliser plants and sugar mills, due to a weakened ecosystem, many companies incurred losses and were eventually forced to close or leave the state.
The economy of Patna has seen sustained growth since 2005, in particular from the
File:SBI Patna.JPG, State Bank of India- Patna Regional office at East Gandhi Maidan Marg
File:Software Technology Park of India, Patna..jpg, Software Technology Park of India, Patna
File:RBI Patna.JPG, Reserve Bank of India's regional office at South Gandhi Maidan Marg, Patna
 Groundwater fulfills the basic needs of the people, administered by Patna Jal Parishad under Patna Municipal Corporation. The public water supply system comprises 98 tube wells that pump water directly to the distribution mains. Around 23 overhead reservoirs of which only the ones at Agam Kuan, Gulzarbagh Press, Guru Gobind Singh Hospital and High Court serve the city. The sewerage system in Patna was set up in 1936. At present, there are four sewage treatment plants at Saidpur, Beur, Pahari and Karmali Chak. In 2019, the central government has started the process ''Nirmal Ganga'', which is to build new sewerage infrastructure at Patna's Karmalichak as well as in Barh, Naugachia and Sultanganj. The new infrastructure will be capable of preventing the flow of 67 million litre of sewage into Ganga.
As of 2011, the city's electricity consumption is about 601 kWh per capita, even though the actual demand is much higher. Electricity supply to the city is regulated and distributed by the South Bihar Power Distribution Company Limited managed by
Groundwater fulfills the basic needs of the people, administered by Patna Jal Parishad under Patna Municipal Corporation. The public water supply system comprises 98 tube wells that pump water directly to the distribution mains. Around 23 overhead reservoirs of which only the ones at Agam Kuan, Gulzarbagh Press, Guru Gobind Singh Hospital and High Court serve the city. The sewerage system in Patna was set up in 1936. At present, there are four sewage treatment plants at Saidpur, Beur, Pahari and Karmali Chak. In 2019, the central government has started the process ''Nirmal Ganga'', which is to build new sewerage infrastructure at Patna's Karmalichak as well as in Barh, Naugachia and Sultanganj. The new infrastructure will be capable of preventing the flow of 67 million litre of sewage into Ganga.
As of 2011, the city's electricity consumption is about 601 kWh per capita, even though the actual demand is much higher. Electricity supply to the city is regulated and distributed by the South Bihar Power Distribution Company Limited managed by
"Ola! City taps app & go habit"
, ''The Telegraph'' (Calcutta), 18 May 2016 Patna is about 70.02KM away from
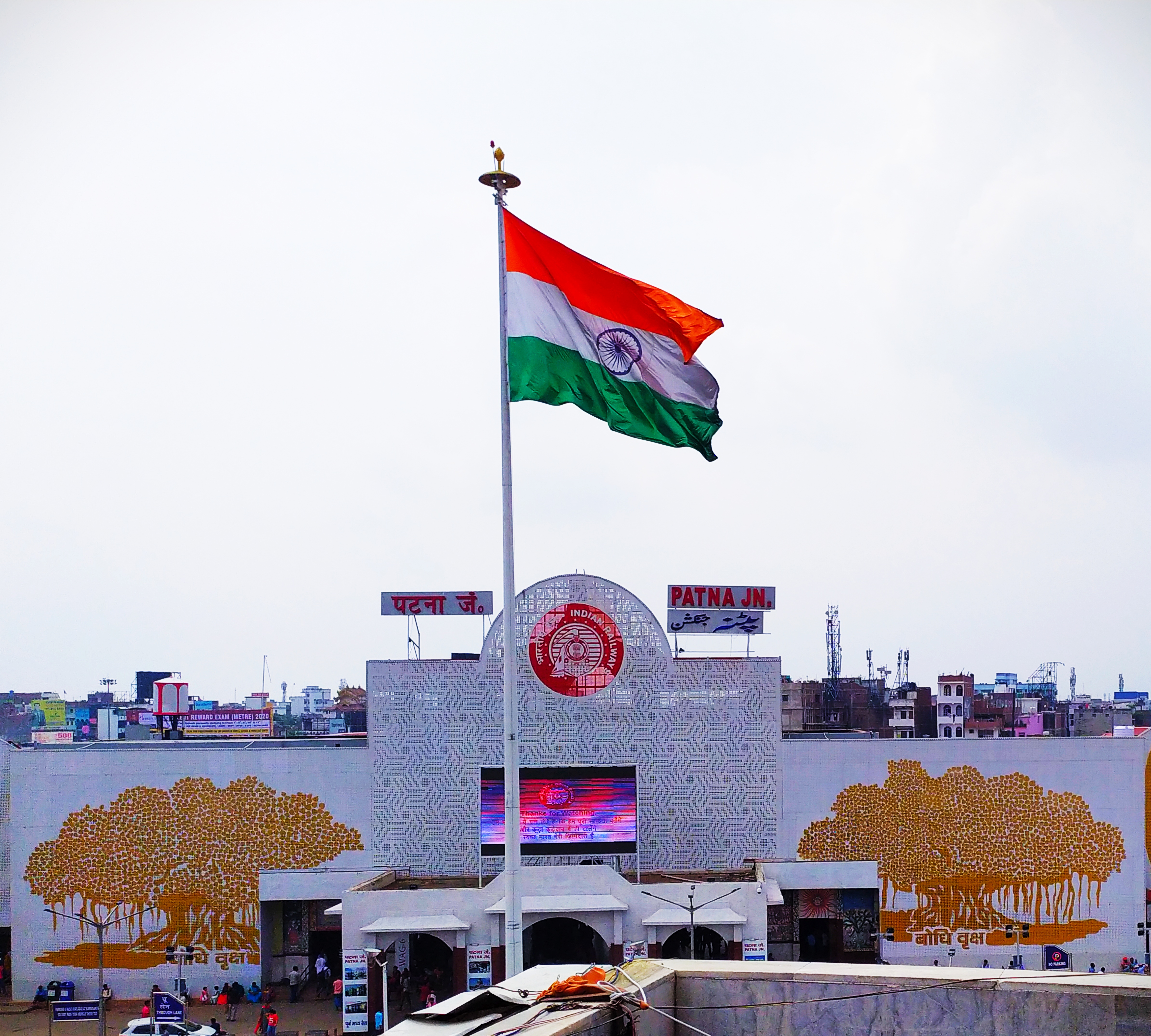 Patna is served by several railway stations within. The Patna Junction railway station is the main railway station of the city, and one of the busiest railway stations in India. Patna lies in between
Patna is served by several railway stations within. The Patna Junction railway station is the main railway station of the city, and one of the busiest railway stations in India. Patna lies in between
 The
The
 Patna's native language is Magahi or Magadhi a language derived from the ancient
Patna's native language is Magahi or Magadhi a language derived from the ancient
File:Durga Puja 2014 Patna 05.JPG, A

 Patna is home to many tourist attractions and it saw about 2.4 million tourists (including day visitors) in 2005. Tourists visiting the city accounted for 41% of the total number of tourists visiting
Patna is home to many tourist attractions and it saw about 2.4 million tourists (including day visitors) in 2005. Tourists visiting the city accounted for 41% of the total number of tourists visiting
 Schools in Patna are either government-run schools or private schools. The schools are affiliated to Bihar School Examination Board (BSEB), Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE), National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), or the
Schools in Patna are either government-run schools or private schools. The schools are affiliated to Bihar School Examination Board (BSEB), Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE), National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), or the
"The Private School Revolution in Bihar: Findings from a survey in Patna Urban"
Under the 10+2+3/4 plan, students complete ten years of schooling and then enroll in schools that have a higher secondary facility and are affiliated to the Bihar State Intermediate Board, the All-India Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE), the NIOS or the CBSE, where they select one of three streams: arts, commerce, or science. This is followed by either a general degree course in a chosen field of study or a professional degree course, such as law, engineering, and medicine. Patna has important government educational institutions like Patna University, Anugrah Narayan College, Chanakya National Law University, Aryabhatta Knowledge University, Indian Institute of Technology Patna, Bakhtiyarpur College of Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Patna, Patna Science College, Patna Women's College, Patna Law College, Bihar Veterinary College, J.D. Women's College, Birla Institute of Technology, Patna, Patna Medical College Hospital, Rajendra Memorial Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Nalanda Medical College Hospital, Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Mahavir Cancer Sansthan, All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna, National Institute of Fashion Technology Patna, Chandragupta Institute of Management, Development Management Institute, National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology, Patliputra University. Patna University was established in 1917 and is the seventh oldest modern university in the Indian Sub-continent. Patna also has a variety of other universities, as well as many primary and secondary schools.
 As in the rest of India,
As in the rest of India,
File:Cricket (2305682483).jpg, A game of cricket in progress
File:Kankarbagh Indoor Stadium.png, Kankarbagh Indoor Stadium at
Official website of Patna district
Official website of the Municipal Corporation of Patna
The Portuguese on the Bay of Bengal
{{Authority control Patna Cities and towns in Patna district Indian capital cities Holy cities Metropolitan cities in India Populated places established in the 5th century BC
ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
: ''Paṭanā''), historically known as Pāṭaliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. According to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. Covering and over 2.5 million people, its urban agglomeration is the 18th largest in India. Patna also serves as the seat of Patna High Court
The Patna High Court of Judicature at Patna (commonly known as Patna High Court) is the High Courts of India, High Court of the Indian state, state of Bihar. It was established on 3 February 1916 by British colonial government and was later aff ...
. The Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
and Jain pilgrimage centres of Vaishali, Rajgir, Nalanda
Nalanda (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: , ) was a renowned Buddhism, Buddhist ''mahavihara'' (great monastery) in medieval Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha (modern-day Bihar), eastern India. Widely considered to be am ...
, Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gayā is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple complex, situated in the Gaya district in the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Bihar. It is famous for being the place where Gautam ...
and Pawapuri
Pawapuri, or Pavapuri (also called Apapapuri, meaning "the sinless town"), is a holy site for Jainism, Jains located in the Nalanda district of Bihar state in East India, eastern India. It is located about 19 kilometres from Rajgir and 101 kilo ...
are nearby and Patna City is a sacred city for Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
s as the tenth Sikh Guru
The Sikh gurus (Punjabi language, Punjabi: ਸਿੱਖ ਗੁਰੂ; Hindi: सिख गुरु) are the spiritual masters of Sikhism, who established the religion over the course of about two and a half centuries, beginning in 1469. The year ...
, Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; born Gobind Das; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708) was the tenth and last human Sikh gurus, Sikh Guru. He was a warrior, poet, and philosopher. In 1675, at the age of nine he was formally installed as the leader of the ...
was born here. The modern city of Patna is mainly on the southern bank of the river Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
. The city also straddles the rivers Son, Gandak and Punpun. The city is approximately in length and wide.
One of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world, Patna was founded in 490 BCE by the king of Magadha. Ancient Patna, known as Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
, was the capital of the Magadha Empire throughout the Haryanka, Nanda, Mauryan
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
, Shunga, Gupta, and Pala dynasties. Pataliputra was a seat of learning and fine arts. It was home to many astronomers and scholars including Aryabhata
Aryabhata ( ISO: ) or Aryabhata I (476–550 CE) was the first of the major mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. His works include the '' Āryabhaṭīya'' (which mentions that in 3600 ' ...
, Vātsyāyana
Vātsyāyana (Sanskrit : वात्स्यायन) was an ancient Indian philosopher, known for authoring the ''Kama Sutra''. He lived in India during the second or third century CE, probably in Pataliputra (modern day Patna in Bihar).
He ...
and Chanakya
Chanakya (ISO 15919, ISO: ', चाणक्य, ), according to legendary narratives preserved in various traditions dating from the 4th to 11th century CE, was a Brahmin who assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta Maurya, Chandragup ...
. During the Maurya
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
period (around 300 BCE) its population was about 400,000. Patna served as the seat of power, and political and cultural centre of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
during the Maurya
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
and Gupta empires. With the fall of the Gupta Empire, Patna lost its glory. The British revived it again in the 17th century as a centre of international trade. Following the partition of Bengal presidency in 1912, Patna became the capital of Bihar and Orissa Province.
Until the 19th century, it was a major trading and commercial hub in India. After independence there were a few downturns but its economy was still stable. After the separation of Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in East India, eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north ...
from Bihar, it lost its glory. As per the Directorate of Economics and Statistics (Government of Bihar), Nominal GDP of Patna District was estimated at INR 63,176.55 crores in 2011-12. As of 2011-12, Patna already recorded per capita gross domestic product of 1,08,657, way ahead of many other Indian cities and state capitals. Using figures for assumed average annual growth, Patna is the 21st fastest growing city in the world and 5th fastest growing city in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
according to a study by the City Mayors Foundation. Patna registered an average annual growth of 3.72% during 2006–2010. As of 2011-12, the GDP per capita of Patna is ₹1,08,657, and its GDP growth rate is 7.29 per cent. In June 2009, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
ranked Patna second in India (after Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
) for ease of starting a business.
Etymology
The name of this city has changed with time. One of the oldest cities of India, there are several theories regarding the origin of the modern name Patna ( Bengali: পাটনা;Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
: पटना; Kaithi
Kaithi (), also called Kayathi (), Kayasthi (), or Kayastani, is a Brahmic script historically used across parts of Northern and Eastern India. It was prevalent in regions corresponding to modern-day Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Jharkhand. The s ...
: 𑂣𑂗𑂢𑂰; Gurmukhi
Gurmukhī ( , Shahmukhi: ) is an abugida developed from the Laṇḍā scripts, standardized and used by the second Sikh guru, Guru Angad (1504–1552). Commonly regarded as a Sikh script, Gurmukhi is used in Punjab, India as the official scrip ...
: ਪਟਨਾ; Urdu: پٹنہ). It is etymologically
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
derived from ''Patan'' (Devanagari: पटन), the name of the Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
goddess, Patan Devi. Patan Devi Mandir is still in old Patna near Gulzarbagh mandi along with another, Patan Devi Mandir, near Takht Sri Patna Sahib. Many believe Patna derived its name from Patli, a tree variety that was found in abundance in the historic city. It is also seen on the state tourism's logo. The place is mentioned in Chinese traveller Fa Hien's records as Pa-lin-fou. The city has been known by various names through more than 2,000 years of existence – Pataligrama, Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
, Kusumapura, Kusumdhwaja Pushpapuram, Padmavathi, Azimabad and the present-day Patna. Legend ascribes the origin of Patna to the mythological King Putraka who created Patna by magic for his queen Patali, literally "trumpet flower", which gives it its ancient name Pataligrama. It is said that in honour of the queen's firstborn, the city was named Pataliputra. ''Gram'' is Sanskrit for village and ''Putra'' means son. Legend also says that the Emerald Buddha
The Emerald Buddha ( , or , ) is an image of the meditating Gautama Buddha seated in a Meditation attitude, meditative posture, made of a semi-precious green stone (jasper rather than emerald or jade), clothed in gold, and about tall. The imag ...
was created in Patna (then Pataliputra) by Nagasena in 43 BCE.
History
Ancient Era
Traditional Buddhist literature attributes foundation of Patna 490 BCE as Ajatashatru, the king of Magadha, wanted to shift his capital from the hilly Rajagrha (today Rajgir) to a strategically chosen place to better combat the Licchavis of Vaishali. He chose the site on the bank of the Ganges and fortified the area.Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist lege ...
travelled through this place in the last year of his life. He prophesied a great future for this place even as he predicted its ruin due to flood, fire, and feud. According to Dieter Schlingloff, the Buddhist accounts may have presented the grandeur of Patna as a prophecy and that its wooden fortifications, unlike other early historic Indian cities, indicate that it might be much older than thought but only archaeological excavation and C14 dates of its wooden palisades which is presently lacking may establish this.
Mauryan Empire
Megasthenes, the Indo-Greek historian and ambassador to the court of Chandragupta Maurya, gave one of the earliest accounts of the city. He wrote that the city was on the confluence of the rivers ''Ganga'' and ''Arennovoas'' (Sonabhadra – Hiranyawah) and was long and wide. Megasthenes, the Greek ambassador to India, described the city as the greatest city on earth during its heyday. The Shungas ultimately retained control of Pataliputra and ruled for almost 100 years. The Shungas were followed by the Kanvas and eventually by the Guptas. Some Chinese travellers came to India in pursuit of knowledge and recorded their observations aboutPataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
in their travelogues. One such famous account was recorded by a Chinese Buddhist traveller Fa Hien, who visited India between 399 and 414 CE, and stayed here for many months translating Buddhist texts. When the Chinese Buddhist Monk Faxian
Faxian (337–), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized as Fa-hien and Fa-hsien, was a Han Chinese, Chinese Chinese Buddhism, Buddhist bhikkhu, monk and translator who traveled on foot from Eastern Jin dynasty, Jin China to medieval India t ...
visited the city in 400 A.D, he found the people to be rich and prosperous; they practised virtue and justice. He found that the nobles and householders of the city had constructed several hospitals in which the poor of all countries, the needy, the crippled, and the diseased, could get treatment. They could receive every kind of help gratuitously. Physicians would inspect the diseases and order them food, drink, and medicines.
Gupta and Pala empire
In the years that followed, many dynasties ruled the Indian subcontinent from the city, including theGupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian ...
and the Pala kings. With the disintegration of the Gupta empire, Patna passed through uncertain times. Bakhtiar Khilji captured Bihar in the 12th century and destroyed everything, and Patna lost its prestige as the political and cultural centre of India.
Mughal Empire
 The
The Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
was a period of unremarkable provincial administration from Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
. The most remarkable period during the Middle Ages was under the Afghan
Afghan or Afgan may refer to:
Related to Afghanistan
*Afghans, historically refers to the Pashtun people. It is both an ethnicity and nationality. Ethnicity wise, it refers to the Pashtuns. In modern terms, it means both the citizens of Afghanist ...
emperor Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri (born Farid al-Din Khan; 1472 or 1486 – 22 May 1545), also known by his title Sultan Adil (), was the ruler of Bihar from 1530 to 1540, and Sultan of Hindustan from 1540 until his death in 1545. He defeated the Mughal Empire, ...
, who revived Patna in the middle of the 16th century. He built a fort and founded a town on the banks of the Ganges. Sher Shah's fort in Patna does not survive, although the Sher Shah Suri mosque, built in Afghan architectural style, does. Mughal emperor Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
reached Patna in 1574 to crush the rebellious Afghan Chief Daud Khan. One of the navratnas from Akbar's court, his official historian and author of "Ain-i-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' (), or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document regarding the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl, in the Persian language. It forms ...
" Abul Fazl refers to Patna as a flourishing centre for paper, stone and glass industries. He also refers to the high quality of numerous strains of rice grown in Patna, famous as Patna rice in Europe. By 1620, the city of Patna was being described as the "chiefest mart towne of all Bengala" (i.e. largest town in Bengal) in northern India, "the largest town in Bengal and the most famous for trade". This was before the founding of the city of Calcutta. Mughal Emperor
The emperors of the Mughal Empire, who were all members of the Timurid dynasty (House of Babur), ruled the empire from its inception on 21 April 1526 to its dissolution on 21 September 1857. They were supreme monarchs of the Mughal Empire in ...
Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
acceded to the request of his favourite grandson, Prince Muhammad Azim, to rename Patna as Azimabad, in 1704 while Azim was in Patna as the subedar
Subedar ( ) is a military rank in the militaries of South Asia roughly equivalent to that of a warrant officer. Historically classed in the British Indian Army as a Viceroy's commissioned officer, the rank was retained in the Indian Army an ...
. Patna or Azimabad did see some violent activities, according to Phillip Mason, writing in the book "The Men Who Ruled India". "Aurangzeb had restored the poll tax (Jazia) on unbelievers, which had to be compounded for. In Patna, Peacock, the factory's chief, was not sufficiently obedient. He was seized, forced to walk through the town bare-headed and bare-footed, and subjected to many other indignities before he paid up and was released." Little changed during this period other than the name. With the decline of the Mughal empire, Patna moved into the hands of the Nawabs of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal (, ) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa which constitute the mod ...
, who levied a heavy tax on the populace but allowed it to flourish as a commercial centre. The mansions of the Maharaja of Tekari Raj dominated the Patna riverfront in 1811–12. In 1750, the future Nawab of Bengal, Siraj ud-Daulah
Mir Syed Jafar Ali Khan Mirza Muhammad Siraj-ud-Daulah (1733 – 2 July 1757), commonly known as Siraj-ud-Daulah or Siraj ud-Daula, was the last independent Nawab of the Bengal Subah. The end of his reign marked the start of the rule of th ...
revolted against his grandfather, Alivardi Khan
Alivardi Khan (1671 – 9 April 1756) was the fourth Nawab of Bengal from 1740 to 1756. He toppled the Nasiri dynasty of Nawabs by defeating Sarfaraz Khan in 1740 and assumed power himself.
During much of his reign Alivardi encountered frequen ...
, and seized Patna, but quickly surrendered and was forgiven. Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; born Gobind Das; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708) was the tenth and last human Sikh gurus, Sikh Guru. He was a warrior, poet, and philosopher. In 1675, at the age of nine he was formally installed as the leader of the ...
(22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), the tenth Guru of the Sikhs, was born as Gobind Rai in Patna to Guru Teg Bahadur, the ninth Guru of the Sikhs, and his wife Mata Gujri. His birthplace, Patna Sahib, is one of the most sacred sites of pilgrimage for Sikhs.
Portuguese Empire
As trade grew, settlements of the Portuguese empire expanded to the Bengal Gulf. Since at least 1515, the Portuguese were in Bengal as traders, and later in 1521, an embassy was sent to Gaur to create factories in the region. The Bengal Sultan after 1534 allowed the Portuguese to develop several settlements as Chitagoong e Satgaon. In 1535 the Portuguese were allied with the Bengal sultan and held the Teliagarhi pass 280 km from Patna helping to avoid the invasion by the Mughals. By then, several of the products came from Patna, and the Portuguese sent in traders, establishing a factory there in 1580 at least. The products were shipped out down the river until other Portuguese ports as Chittagoon e Satgaoon, and from there to the rest of the empire.British Empire
During the 17th century, Patna became a centre of international trade. In 1620, the EnglishEast India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
established a factory
A factory, manufacturing plant or production plant is an industrial facility, often a complex consisting of several buildings filled with machinery, where workers manufacture items or operate machines which process each item into another. Th ...
in Patna for trading in calico and silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
. Soon it became a trading centre for saltpetre
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula . It is a potassium salt of nitric acid. This salt consists of potassium cations and nitrate anions , and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate ...
. Francois Bernier, in ''Travels in the Mogul Empire'' (1656–1668), says, ". It was carried down the Ganges with great facility, and the Dutch and English sent large cargoes to many parts of the Indies, and Europe". This trade encouraged other Europeans, principally the French, Danes, Dutch, and Portuguese, to compete in the lucrative business. Peter Mundy
Peter Mundy (born-1597 ~ 1667) was a seventeenth-century English factor, merchant trader, traveller and writer. He was the first Englishman to record, in his ''Itinerarium Mundi'' ('Itinerary of the World'), tasting ''Tea, Chaa'' (tea) in China ...
, writing in 1632, described Patna as "the greatest mart of the eastern region". After the decisive Battle of Buxar
The Battle of Buxar was fought between 22 and 23 October 1764, between the forces of the British East India Company, under the command of Major Hector Munro, against the combined armies of Balwant Singh, Maharaja of the Benaras State; Mir Qa ...
of 1764, as per the treaty of Allahabad East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
was given the right to collect a tax of this former Mughal province by the Mughal emperor. Patna was annexed by the company in 1793 to its territory when Nizamat (Mughal suzerainty) was abolished, and the British East India Company took control of the province of Bengal-Bihar. Patna, however, continued as a trading centre. In 1912, when the Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal until 1937, later the Bengal Province, was the largest of all three presidencies of British India during Company rule in India, Company rule and later a Provinces o ...
was partitioned, Patna became the capital of the British province of Bihar and Orissa. However, in 1936 Orissa
Odisha (), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is a state located in Eastern India. It is the eighth-largest state by area, and the eleventh-largest by population, with over 41 million inhabitants. The state also has the thir ...
became a separate entity with its capital. To date, a major population of Bengalis lives in Patna particularly.
Indian Independence Movement
People from Patna were greatly involved in theIndian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events in South Asia with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British colonial rule. It lasted until 1947, when the Indian Independence Act 1947 was passed.
The first nationalistic ...
. Most notable movements were the Champaran movement against the Indigo
InterGlobe Aviation Limited (d/b/a IndiGo), is an India, Indian airline headquartered in Gurgaon, Haryana, India. It is the largest List of airlines of India, airline in India by passengers carried and fleet size, with a 64.1% domestic market ...
plantation and the 1942 Quit India Movement. National leaders who came from the city include Swami Sahajanand Saraswati; the first President of the Constituent Assembly of India
Constituent Assembly of India was partly elected and partly nominated body to frame the Constitution of India. It was elected by the Provincial assemblies of British India following the Provincial Assembly elections held in 1946 and nominated ...
, Dr. Rajendra Prasad; ''Bihar Vibhuti'' (Anugrah Narayan Sinha
Anugrah Narayan Sinha (18 June 1887 – 5 July 1957), known as ''Honorary titles of Indian leaders, Bihar Vibhuti'', was an Indian nationalist politician, participant in Champaran Satyagraha, Gandhian & one of the architects of modern Bihar, wh ...
); Basawon Singh (Sinha); and ''Loknayak'' (Jayaprakash Narayan
Jayaprakash Narayan Srivastava (; 11 October 1902 – 8 October 1979), also known as JP and ''Lok Nayak'' (Hindi for "People's leader"), was an Indian politician, theorist and Indian independence activist, independence activist. He is mai ...
).
Post-Independence
Patna remained the capital ofBihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
after India gained independence in 1947, even as Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
was partitioned again in 2000 when Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in East India, eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north ...
became a separate state of the Indian union. On 27 October 2013, six people were killed and 85 others were injured in a series of co-ordinated bombings at an election rally for BJP candidate Narendra Modi
Narendra Damodardas Modi (born 17 September 1950) is an Indian politician who has served as the Prime Minister of India, prime minister of India since 2014. Modi was the chief minister of Gujarat from 2001 to 2014 and is the Member of Par ...
. On 3 October 2014, 33 people were killed and 26 injured in a stampede at Gandhi Maidan during Vijaya Dashmi celebrations.
Geography
Topography
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
. The total area of Patna is . The municipal area constitutes . The suburban area covers . It has an average elevation of . A characteristic feature of the geography of Patna is its confluence of major rivers.
During the British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
, Patna was part of the Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal until 1937, later the Bengal Province, was the largest of all three presidencies of British India during Company rule in India, Company rule and later a Provinces o ...
. After Nalanda district
Nalanda district is one of the thirty-eight Districts of Bihar, districts of the state of Bihar in India. Bihar Sharif is the administrative headquarters of this district. The districts is home to the ancient Nalanda Mahavihara a UNESCO World He ...
was carved out of Patna district in 1976, Patna was purged of all hilly regions. It is an alluvial, flat expanse of land. The land in the district is fertile and is almost entirely cultivated, with no forest cover. Alluvial soil is ideal for cultivating rice, sugarcane, and other food grains. The area under cultivation is studded with mango orchards and bamboo groves. In the fields along the banks of river Ganges, weeds such as ammannia, citriculari, hygrophile and sesbania grow. But palmyra, date palm, and mango orchards are found near habitations. Dry stretches of shrubbery are sometimes seen in the villages far from the rivers. Trees commonly found are bel, siris, jack fruit, and the red cotton tree. Patna is unique in having four large rivers in its vicinity. It is the largest riverine city in the world. The topography of Patna city is saucer shaped as per Patna City Development Plan prepared in 2006. The bridge over the river Ganges, named Mahatma Gandhi Setu, is 5575m long. It is the longest river bridge in India.
Patna comes under India's seismic zone-IV, indicating its vulnerability to major earthquakes
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they c ...
, but earthquakes have not been common in recent history. Patna also falls in the risk zone for floods and cyclones.
Climate
 Patna has a
Patna has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
under the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: (Cwa) with sweltering summers from late March to June, the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
season from late June to late September and chilly winter nights and foggy or sunny days from November to February. Highest temperature ever recorded was in the year 1966, the lowest ever was on 9 January 2013, and highest rainfall was in the year 1997.
The table below details historical monthly averages for climate variables.
Air pollution
Pollution is a major concern in Patna. According to the CAG report, tabled in theBihar Legislative Assembly
The Bihar Legislative Assembly, also known as the Bihar Vidhan Sabha, is the lower house of the bicameral Bihar Legislature of the state of Bihar in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is ...
in April 2015, respirable suspended particulate matter (RSPM) level ( PM-10) in Patna was 355, three-and-a-half times higher than the prescribed limit of 100 micro-gram per cubic metre, primarily due to high vehicular and industrial emissions and construction activities in the city. In May 2014, a World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
survey declared Patna the second most air polluted city in India, only after Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, with the survey calculating the airborne particulate matter in the state capital's ambient air ( PM-2.5) to be 149 micro-grams, six times more than the safe limit, which is 25 micro-grams. Severe air pollution in the city has caused a rise in pollution-related respiratory ailments, such as lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged ...
, asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, dysentery
Dysentery ( , ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehyd ...
and diarrhoea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
. The dense smog in Patna during winter season results in major air and rail traffic disruptions every year.
Patna has been ranked 10th best "National Clean Air City" (under Category 1 >10L Population cities) in India according to 'Swachh Vayu Survekshan 2024 Results'
Economy
 Since the 17th century, Patna has been a centre of international trade and an agricultural and textile hub, including a major silk and calico market. After gaining independence in 1947, the economy remained relatively stable, including growth in produce and manufacturing of vegetable oil. From the 1980s onwards, the economy experienced fluctuations. When liberalisation came to India in the 1990s, Patna did not attract significant global funds or foreign investment which proved a setback for the economy. Although the city had several fertiliser plants and sugar mills, due to a weakened ecosystem, many companies incurred losses and were eventually forced to close or leave the state.
The economy of Patna has seen sustained growth since 2005, in particular from the
Since the 17th century, Patna has been a centre of international trade and an agricultural and textile hub, including a major silk and calico market. After gaining independence in 1947, the economy remained relatively stable, including growth in produce and manufacturing of vegetable oil. From the 1980s onwards, the economy experienced fluctuations. When liberalisation came to India in the 1990s, Patna did not attract significant global funds or foreign investment which proved a setback for the economy. Although the city had several fertiliser plants and sugar mills, due to a weakened ecosystem, many companies incurred losses and were eventually forced to close or leave the state.
The economy of Patna has seen sustained growth since 2005, in particular from the fast-moving consumer goods
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), also known as consumer packaged goods (CPG) or convenience goods, are products that are sold quickly and at a relatively low cost. Examples include non-durable household goods such as packaged foods, beve ...
industry, the service sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the ...
, and Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, or the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period during which technology transfer initiatives resulted in a significant increase in crop yields. These changes in agriculture initially emerged in Developed country , devel ...
businesses. In 2009, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
ranked Patna as the second best city in India to start a business. In 2010, Patna was ranked 21st fastest-growing city in the world and fifth fastest-growing city in India, and was forecast to grow at an average annual rate of 3.72% through 2020.
Its largest exports are grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
, sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
, sesame
Sesame (; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a plant in the genus '' Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for ...
, and Patna rice, a local medium-grained variety. There are several sugar mills in and around Patna. Patna has been described as an important business and luxury brand centre of eastern India.
The major business districts of the city are Bander Bagicha, Exhibition Road
Exhibition Road is a street in South Kensington, London which is home to several major museums and academic establishments, including the Victoria and Albert Museum, the Science Museum, London, Science Museum and the Natural History Museum, Lon ...
, Gandhi Maidan Marg, Frazer Road, Indrapuri and Maurya Lok.
Many manufacturing companies, including Hero Cycles, Britannia Industries
Britannia Industries Limited is an Indian Multinational corporation, multinational food products company, which sells biscuits, breads and dairy products. Founded in 1892, it is one of India's oldest existing companies and currently part of t ...
, PepsiCo
PepsiCo, Inc. is an American multinational corporation, multinational food, snack, and beverage corporation headquartered in Harrison, New York, in the hamlet of Purchase, New York, Purchase. PepsiCo's business encompasses all aspects of the f ...
, Sonalika Tractors and UltraTech Cement have established their manufacturing plants in the Patna metropolitan area. One of the world's largest leather clusters is in Fatuha, in Patna. Patna is also emerging as an information technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
hub, including Tata Consultancy Services
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) is an Indian Multinational corporation, multinational technology company specializing in information technology services and consulting. Headquartered in Mumbai, it is a part of the Tata Group and operates in 150 ...
, which started operations in 2019 at a new Patna facility.
Demographics
With an estimated population of 1.68 million in 2011, Patna is the 19th most populous city in India and with over 2 million people, its urban agglomeration is the 18th largest in India. Residents of Patna are referred to by the demonym Patnaite. According to 2011 census data, Patna city had a population of 1,684,222 (before the expansion of the city limits) within thecorporation
A corporation or body corporate is an individual or a group of people, such as an association or company, that has been authorized by the State (polity), state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law as ...
limits, with 893,399 men and 790,823 women. This was a 22.3% increase compared to 2001 figures. 11.32% of the population was under six years of age, with 102,208 boys and 88,288 girls. The overall literacy rate
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was ...
is 83.37%, with the male literacy rate being 87.35% and female 79.89%. The sex ratio of Patna is 885 females per 1,000 males. The child sex ratio of girls is 877 per 1000 boys. The urban agglomeration had a population of 2,049,156, of which 1,087,285 are male and 961,871 are females with 82.73% literacy. Patna is the second largest city (in terms of population) in eastern India
East India is a region consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha
and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
The states of Bihar and West Bengal lie on the Indo-Gangetic plain. Jharkhan ...
.
Roughly 0.25% of Patna's population lives in slums, which makes Patna the city with the lowest percentage of people living in slums in India. Like other fast-growing cities in the developing world, Patna suffers from major urbanisation
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also ...
problems including unemployment, poor public health, and poor civic and educational standards for a large section of the population. In 2015, the National Sample Survey Organisation revealed that, for females in India, Patna had the highest unemployment rate at 34.6%, and for males, it was the second highest with a rate of 8% in 2011–12.
Religion and language
According to the 2011 census of India, 86.39% of Patna's residents practiceHinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
. Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
is the second most popular at 12.27%. Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
, Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
, and Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
are among the other minority religions. 0.01% practice other religions and 0.49% no particular religion.
Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
and Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
are official languages of the state of Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
, but many other languages are also spoken. The native language is Magadhi or Magahi
Magahi (), also known as Magadhi (), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal states of eastern India, and in the Terai region of Nepal. Magadhi Prakrit was the ancestor of Magahi, from which the latter's name de ...
, named after Magadha, the ancient name of South Bihar, and is most widely spoken. Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
is spoken by 65.94% of the population, 18.04% Magahi, 9.67% Urdu, 3.19% Bhojpuri
Bhojpuri may refer to:
* Bhojpuri language, an Indo-Aryan language of India and Nepal
* Bhojpuri grammar, grammatical rules of the language
* Bhojpuri nouns, nouns of the language
* Bhojpuri people, people who speak the language
* Bhojpuri region ...
and 1.79% Maithili as their first language.
Administration
The Patna sub-division (Tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluk, or taluka () is a local unit of administrative division in India and Pakistan. It is a subdistrict of the area within a Zila (country subdivision), district including the designated populated place that ser ...
) is one of the 6 Tehsils of the Patna district. It is headed by an IAS or state Civil service officer of the rank of Sub Divisional Magistrate
A sub-divisional magistrate, also known as assistant collector, sub collector, revenue divisional officer, or assistant commissioner, is the administrative head of a Subdivision (India), sub-division in an Indian district, exercising Executive (g ...
(SDM). The SDM of Patna Tehsil reports to the District Magistrate
The district magistrate, also known as the district collector or deputy commissioner, is a career civil servant who serves as the executive head of a district's administration in India. The specific name depends on the state or union territo ...
(DM) of Patna District.
Blocks
The Patna Tehsil is divided into 3Block
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
s, each headed by a Block Development Officer (BDO). The list of Blocks is as follows:
# Patna
# Sampatchak
# Phulwari Sharif
Government
Civic administration
The civic administration of Patna is run by several government agencies and has overlapping structural divisions. At least five administrative definitions of the city are available; listed in ascending order of area: Patna division, Patna district (also the Patna Police area), the Patna Metropolitan Region (also known as Patna Planning area), "Greater Patna" or PRDA area, which adds to the PMC a few areas just adjacent to it and Patna Municipal Corporation area. The Patna Municipal Corporation, or PMC, oversees and manages the civic infrastructure of the city's 75 wards, which accommodates a population of 1.7 million as per 2011 Census. The municipal corporation consists of democratically elected members; each ward elects a Councillor to the PMC. The PMC is in charge of the civic and infrastructure needs of the metropolis. As Patna's apex body, the corporation discharges its functions through the mayor-in-council, which comprises a mayor, a deputy mayor, and other elected members of the PMC. The Mayor is usually chosen through indirect election by the councillors from among themselves. The functions of the PMC include water supply, drainage and sewerage, sanitation, solid waste management, street lighting, and building regulation. The Municipal Commissioner is the chief Executive Officer and head of the executive arm of the Municipal Corporation. All executive powers are vested in the Municipal Commissioner who is anIndian Administrative Service
The Indian Administrative Service (IAS) is the Public administration, administrative arm of the All India Services of Government of India. The IAS is one of the three All India Services along with the Indian Police Service (IPS) and the Indian ...
(IAS) officer appointed by the state government
A state government is the government that controls a subdivision of a country in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonom ...
. Although the Municipal Corporation is the legislative body that lays down policies for the governance of the city, it is the Commissioner who is responsible for the execution of the policies. The Commissioner is appointed for a fixed term as defined by state statute. The powers of the Commissioner are those provided by statute and those delegated by the Corporation or the Standing Committee. As of June 2017, the BJP won PMC Mayor seat; the mayor is Sita Sahu, while the deputy mayor is Vinay Kumar Pappu. The Patna Municipal Corporation was ranked 4th out of 21 Cities for best governance & administrative practices in India in 2014. It scored 3.6 on 10 compared to the national average of 3.3. The revenue district of Patna comes under the jurisdiction of a District Collector
The district magistrate, also known as the district collector or deputy commissioner, is a career civil servant who serves as the executive head of a district's administration in India. The specific name depends on the state or union territo ...
(District Magistrate). The Collectors are in charge of the general administration, property records and revenue collection for the Central Government, and oversee the national elections held in the city. The Bihar Urban Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (BUIDCO) and the Patna Metropolitan Area Authority, are responsible for the statutory planning
Urban planning (also called city planning in some contexts) is the process of developing and designing land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportati ...
and development of the Patna Metropolitan Region. Patna Metropolitan Area Authority was established in 2016. It is the superseding agency for the former Patna Regional Development Authority (PRDA), which was dissolved in 2006. In addition to the city government, numerous commissions and state authorities—including the Ministry of Tourism, the Bihar Health Department, the Bihar Water Resources Department, National Ganga River Basin Authority, Bihar State Pollution Control Board and the Bihar Public Service Commission—play a role in the life of Patnaites. As the capital of Bihar, Patna plays a major role 8n both state politics and central politics.
In October 2016, the Bihar cabinet approved the Patna Master Plan 2031, which envisages the development of a new airport at Bihta. As of August 2015, the area of Patna city (along with its urban agglomeration) is . Patna Master 2031 is the second master plan of the city that has been passed ever, after the last plan was approved for 1961-1981. Patna master plan covers six urban local bodies - Patna Municipal Corporation, Danapur Nagar Parishad, Phulwarisharif Nagar Parishad, Khagaul Nagar Parishad, Maner Nagar Panchayat and Fatuha Nagar Parishad. The new master plan proposed to increase the area of Patna city to to transform it as a metropolitan city. 5 satellite towns have also been proposed in the master plan at Bihta, Naubatpur, Punpun, Fatuha and Khusrupur.
Patna has been selected as one of the hundred Indian cities to be developed as a smart city
A smart city is an urban area that uses digital technology to collect data and operate services. Data is collected from citizens, devices, buildings, or cameras. Applications include traffic and transportation systems, power plants, utilities ...
under Government of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union t ...
's flagship Smart Cities Mission
Smart Cities Mission was an urban renewal and retrofitting program by the Government of India with the mission to develop smart cities across the country, making them citizen-friendly and sustainable. The Union Ministry of Urban Development ...
. With the grade of a Smart City, Patna will have highly up-to-date and radical provisions like uninterrupted electric supply, first-rate traffic and transport system, superior health care and many other prime utilities. Under this scheme, the city will use digital technology that will act as the integral mechanism of the aforesaid facilities and thereby further elevate the lifestyle of the citizens. A special purpose vehicle company named the Patna Smart City Limited has been formed to implement the smart city projects. On 22 November 2017, Eptisa Servicios de Ingenieria SL of Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
was chosen as the project management consultant.
Politics
As the seat of theGovernment of Bihar
Bihar Government is the State governments of India, state government of the States and territories of India, Indian state of Bihar and its nine Divisions of Bihar, divisions which consist of Districts of Bihar, districts. It consists of an execut ...
, The city has several federal facilities, including the Raj Bhavan: Governor's house, the Bihar Legislative Assembly
The Bihar Legislative Assembly, also known as the Bihar Vidhan Sabha, is the lower house of the bicameral Bihar Legislature of the state of Bihar in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is ...
; the state secretariat, which is housed in the Patna Secretariat; and the Patna High Court
The Patna High Court of Judicature at Patna (commonly known as Patna High Court) is the High Courts of India, High Court of the Indian state, state of Bihar. It was established on 3 February 1916 by British colonial government and was later aff ...
. The Patna High Court is one of the oldest High Court in India. The Patna High Court has jurisdiction over the state of Bihar. Patna also has lower courts; the Small Causes Court for civil matters, and the Sessions Court for criminal cases. The Patna Police, commanded by Senior Superintendent of Police, is overseen by the Bihar Government's Home Department. The Patna district elects two representatives to India's lower house, the Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of Parliament of India which is Bicameralism, bicameral, where the upper house is Rajya Sabha. Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha, Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by a ...
, and 14 representatives to the state legislative assembly. The capital city of Patna has 8 State Legislative Assembly constituencies, which form two constituencies of the Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of Parliament of India which is Bicameralism, bicameral, where the upper house is Rajya Sabha. Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha, Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by a ...
(the lower house
A lower house is the lower chamber of a bicameral legislature, where the other chamber is the upper house. Although styled as "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has come to wield more power or otherwise e ...
of the Parliament of India).

Utility services
 Groundwater fulfills the basic needs of the people, administered by Patna Jal Parishad under Patna Municipal Corporation. The public water supply system comprises 98 tube wells that pump water directly to the distribution mains. Around 23 overhead reservoirs of which only the ones at Agam Kuan, Gulzarbagh Press, Guru Gobind Singh Hospital and High Court serve the city. The sewerage system in Patna was set up in 1936. At present, there are four sewage treatment plants at Saidpur, Beur, Pahari and Karmali Chak. In 2019, the central government has started the process ''Nirmal Ganga'', which is to build new sewerage infrastructure at Patna's Karmalichak as well as in Barh, Naugachia and Sultanganj. The new infrastructure will be capable of preventing the flow of 67 million litre of sewage into Ganga.
As of 2011, the city's electricity consumption is about 601 kWh per capita, even though the actual demand is much higher. Electricity supply to the city is regulated and distributed by the South Bihar Power Distribution Company Limited managed by
Groundwater fulfills the basic needs of the people, administered by Patna Jal Parishad under Patna Municipal Corporation. The public water supply system comprises 98 tube wells that pump water directly to the distribution mains. Around 23 overhead reservoirs of which only the ones at Agam Kuan, Gulzarbagh Press, Guru Gobind Singh Hospital and High Court serve the city. The sewerage system in Patna was set up in 1936. At present, there are four sewage treatment plants at Saidpur, Beur, Pahari and Karmali Chak. In 2019, the central government has started the process ''Nirmal Ganga'', which is to build new sewerage infrastructure at Patna's Karmalichak as well as in Barh, Naugachia and Sultanganj. The new infrastructure will be capable of preventing the flow of 67 million litre of sewage into Ganga.
As of 2011, the city's electricity consumption is about 601 kWh per capita, even though the actual demand is much higher. Electricity supply to the city is regulated and distributed by the South Bihar Power Distribution Company Limited managed by Bihar State Power Holding Company Limited
Bihar State Power Holding Company Limited (BSPHCL), formerly Bihar State Electricity Board (BSEB) is a state-owned electricity regulation board operating within the state of Bihar in India. BSEB was established in 1958 as a statutory corporation ...
(the holding company and a successor company of erstwhile Bihar State Electricity Board). The city forms the Patna Electric Supply Undertaking (PESU) Circle, which is further divided into two wings namely Patna East (consists Kankarbagh
''Kankarbagh'', or ''Kankarbagh Colony'', is a neighborhood and residential area in Patna, Bihar, India. It is one of the largest colonies in Asia and the second largest in terms of population.
Overview
Established back in 1916, Kankarbagh is ...
, Patna City, Gulzarbagh, Bankipore, Rajendra Nagar Divisions) and Patna West (Consists Danapur, New Capital, Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
, Gardanibagh, Dak Bungalow divisions).
Direct–to–home (DTH) is available via DD Free Dish, Airtel digital TV
Airtel Digital TV is an Indian subscription based satellite television provider owned by Bharti Telemedia Limited, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Bharti Airtel. It launched DTH satellite television service in India on 9 October 2008.
Airtel D ...
, Dish TV, Tata Sky, Videocon d2h, Sun Direct and Reliance Digital TV. Cable companies include Darsh Digital Network Pvt. Ltd., SITI Maurya Cablenet Pvt. Ltd etc. The Conditional Access System for cable television was implemented in March 2013.
Patna comes under the Patna Telecom District of the Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (commonly known as BSNL) () is an Indian Public Sector Undertakings in India, central public sector undertaking, under the ownership of Department of Telecommunications, which is part of the Ministry of Communicatio ...
(BSNL), India's state-owned telecom and internet services provider. Both Global System for Mobile Communications
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a family of standards to describe the protocols for second-generation ( 2G) digital cellular networks, as used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and mobile broadband modems. GSM is also ...
(GSM) and Code division multiple access
Code-division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. CDMA is an example of channel access method, multiple access, where several transmitters can send information simultaneously over ...
(CDMA) mobile services are available. Apart from telecom, BSNL also provides broadband internet service. Among private enterprises, Bharti Airtel
Bharti Airtel Limited is an Indian Multinational corporation, multinational Telecommunications in India, telecommunications company based in New Delhi. It operates in 18 countries across South Asia and Africa, as well as the Channel Islands. ...
, Reliance Jio, Reliance GSM/CDMA, Idea Cellular
Idea Cellular was an Indian telecommunications company based at Mumbai, Maharashtra. It was an integrated GSM operator and had 220.00 million subscribers as of June 2018.
In 2018 Idea Cellular merged with Vodafone India into Vodafone ...
, Aircel, Tata Teleservices ( Tata DoCoMo, Virgin Mobile
Virgin Mobile is a wireless communications brand used by seven independent brand-licensees worldwide. Virgin Mobile branded wireless communications services are available in Ireland, Canada, Colombia, Chile, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emi ...
and Tata Indicom), Telenor
Telenor ASA ( or ) is a Norwegian majority state-owned multinational telecommunications company headquartered at Fornebu in Bærum, close to Oslo. It is one of the world's largest mobile telecommunications companies with operations worldwi ...
(Formerly Uninor & Now Acquired by Bharti Airtel), Vodafone
Vodafone Group Public Limited Company () is a British Multinational company, multinational telecommunications company. Its registered office and global headquarters are in Newbury, Berkshire, England. It predominantly operates Service (economic ...
and Videocon Telecom are the leading telephone and cell phone service providers in the city.
Patna was the second Indian city, after Bangalore
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kar ...
, which offered free WiFi connectivity to its citizens in February 2014. By surpassing the previous record-holder, Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Patna's WiFi zone is the world's longest free WiFi zone, which covers a 20-km stretch from NIT Patna on Ashok Rajpath to Danapur.
Transport
Roads
Patna is about 100 km south of national East – West Highway corridor. The NH 30, NH 31 and NH 2 passes through the city. The Ashok Rajpath, Patna- Danapur Road, Bailey Road, Harding Road andKankarbagh
''Kankarbagh'', or ''Kankarbagh Colony'', is a neighborhood and residential area in Patna, Bihar, India. It is one of the largest colonies in Asia and the second largest in terms of population.
Overview
Established back in 1916, Kankarbagh is ...
old bypass Road are the major corridors. Patna was one of the first places in India to use horse-drawn trams for public transport
Transport (in British English) or transportation (in American English) is the intentional Motion, movement of humans, animals, and cargo, goods from one location to another. Mode of transport, Modes of transport include aviation, air, land tr ...
. Public transportation is provided for by buses
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a motor vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van, but fewer than the average rail transport. It is most commonly used ...
, auto rickshaw
An auto rickshaw is a motorized version of the pulled rickshaw or cycle rickshaw. Most have three wheels and do not tilt. They are known by many other terms in various countries, including three-wheeler, Adaidaita Sahu, Keke-napep, Maruwa, auto, ...
s and local trains. Auto rickshaws are said to be the lifeline of the city. BSRTC has started City bus service on all major routes of Patna. App based cab service is available within city.Piyush Kumar Tripathi"Ola! City taps app & go habit"
, ''The Telegraph'' (Calcutta), 18 May 2016 Patna is about 70.02KM away from
Chhapra
Chhapra (ISO 15919, ISO: ''Chaparā'') is a city and headquarters of the Saran District in the Indian state of Bihar. It is situated near the junction of the Ghaghara River and the Ganges River.
Chhapra grew in importance as a river-based mar ...
Air transport
Patna Airport known as Lok Nayak Jayaprakash Narayan International Airport is classified as a restricted international airport. The arrival of several low-cost carriers and a number of new destinations have caused a growth in air traffic in recent years, as has an improvement in the situation with regard to law and order. For the period April to December 2009 the airport ranked first in a survey of 46 airports in the country in terms of percentage growth of domestic passengers as well as domestic aircraft movement. The Airport Authority of India (AAI) has proposed to develop a civil enclave at Bihta Air Force Station to serve as the new airport for Patna. The military airfield lies southwest of Patna, in Bihta.Railways
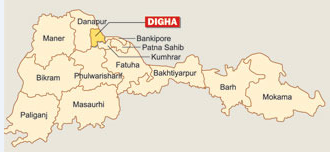
 Patna is served by several railway stations within. The Patna Junction railway station is the main railway station of the city, and one of the busiest railway stations in India. Patna lies in between
Patna is served by several railway stations within. The Patna Junction railway station is the main railway station of the city, and one of the busiest railway stations in India. Patna lies in between New Delhi
New Delhi (; ) is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the Delhi, National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the Government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Parliament ...
and Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
on Howrah–Delhi main line, which is one of the busiest rail routes in India. Patna Junction is directly connected to most of the major cities in India. The city has four additional major railway stations: (adjacent to Kankarbagh
''Kankarbagh'', or ''Kankarbagh Colony'', is a neighborhood and residential area in Patna, Bihar, India. It is one of the largest colonies in Asia and the second largest in terms of population.
Overview
Established back in 1916, Kankarbagh is ...
), (near Bailey road), (near western outskirts) and (in Patna City area). Danapur is the divisional headquarters of East Central Railway zone
The East Central Railway (abbreviated ECR) is one of the 19 railway zones in India. It is headquartered at and comprises , , , and divisions.
History
First set up on 8 September 1996 with headquarters at Hajipur, Bihar, East Central R ...
's Danapur railway division
Danapur railway division is one of the five railway divisions under the jurisdiction of East Central Railway zone of the Indian Railways. It is located in Danapur of the Indian state of Bihar. The other railway divisions are Sonpur, Samastipu ...
. Patna is well connected with Gaya, Jehanabad
Jehanabad is a city in Nagar parishad, Nagar Parishad and is the headquarters of Jehanabad district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Bihar.
Demographics
According to the Indian census of 2011, the Jehanabad had a popula ...
, Bihar Sharif, Rajgir, Islampur, Jamalpur Junction and Munger through daily passenger and express train services. India's longest road-cum-rail bridge, Digha–Sonpur Bridge, across the Ganges River
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
, connects Digha, Patna to Pahleja Ghat in Sonpur. The bridge was completed in 2015, and is long, therefore the second longest rail-cum-road bridge in India, after Bogibeel Bridge in Assam.
The city is served by several major road highways and state highways, including National Highways
National Highways (NH), formerly Highways England and before that the Highways Agency, is a State-owned enterprise, government-owned company charged with operating, maintaining and improving Roads in England, motorways and major A roads in Eng ...
19, 30, 31, and 83. Pataliputra Bus Terminal is an upcoming ISBT. Asia's longest river bridge, the Mahatma Gandhi Setu (built 1982), is in Patna and connects the city to Hajipur across the Ganga. In recent times, the bridge has been witnessing major traffic chaos and accidents due to excessive numbers of vehicles passing over it and regularly overloading the structure. A new six lane road bridge across the Ganges parallel to Mahatma Gandhi Setu is proposed which would connect Kacchi Dargah in Patna City to Bidupur in Vaishali district
Vaishali district is a district in the Indian state of Bihar. It is a part of Tirhut division. Vaishali is known for being the birthplace of Mahavira of the Jain religion. Hajipur, its largest city and district headquarters, is known for its ba ...
, which will be the longest bridge in India after completion.
Patna is well connected with roads to various major cities of Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
like Hajipur, Munger, Jamalpur, Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur, historically known as Champapuri, Champa Nagari, is a city in the Indian state of Bihar, situated on the southern bank of the Ganges river. It is the Bihar#Government and administration, third largest city of Bihar by population and ...
, Gaya Motihari, and Purnia.
Patna is east from Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, northeast from Mumbai
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12 ...
, north from Hyderabad
Hyderabad is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India. With an average altitude of , much ...
and northwest from Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
. Luxury bus service between Patna and several neighbouring cities is provided by the Bihar State Tourism Development Corporation and the Bihar State Road Transport Corporation. Auto rickshaws are a popular mode of transportation. Prepaid auto services operated by an all-women crew was started in 2013 in Patna, which is the first of its kind in India. Radio Taxi services are available within city limits and surrounding areas. There are also private options such as Ola Cabs.
Metro
Patna Metro is an under-constructionrapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT) or heavy rail, commonly referred to as metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport that is generally built in urban areas. A grade separation, grade separated rapid transit line below ground su ...
system for the city. It would be owned and operated by state run Patna Metro Rail Corporation. It will be constructed on Public Private Partnership (PPP) mode, estimated to cost . It will have 5 lines with a total planned length of , which will be built in 3 phases. Patna Monorail Project covering the municipal area is also underway. Recently the central government approved Patna metro rail project comprising two corridors (Danapur - Khemnichak and Patna Junction - Pataliputra Bus Terminal). Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
– navigable throughout the year – was the principal river highway across the vast Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, easte ...
. Vessels capable of accommodating five hundred merchants were known to ply this river in the ancient period; it served as a major trade route, as goods were transported from Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
to the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
and further, to ports in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and Southeast Asia. The role of the Ganges as a channel for trade was enhanced by its natural links – it embraces all the major rivers and streams in both north and south Bihar. In recent times, Inland Waterways Authority of India has declared the stretch of river Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
between Allahabad
Prayagraj (, ; ISO 15919, ISO: ), formerly and colloquially known as Allahabad, is a metropolis in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.The other five cities were: Agra, Kanpur, Kanpur (Cawnpore), Lucknow, Meerut, and Varanasi, Varanasi (Benar ...
and Haldia National Inland Waterway and has taken steps to restore and maintain its navigability. The National Waterway-1, the longest Waterway in India, stretches 1620 km in the River Ganga from Allahabad to Haldia via Varanasi
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tradition of I ...
, Munger, Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur, historically known as Champapuri, Champa Nagari, is a city in the Indian state of Bihar, situated on the southern bank of the Ganges river. It is the Bihar#Government and administration, third largest city of Bihar by population and ...
passes through Patna. This National Waterways has fixed terminal at Patna.
Culture
Magadhi Prakrit
Magadhi Prakrit (''Māgadhī'') is of one of the three Dramatic Prakrits, the written languages of Ancient India following the decline of Pali. It was a vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan language, replacing earlier Vedic Sanskrit.
History and over ...
, which was created in the ancient kingdom of Magadha, the core of which was the area of Patna south of the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
. It is believed to be the language spoken by Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist lege ...
. Patna has a vibrant Bengali culture too with many Bengali stalwarts including the first Chief Minister of post-independence West Bengal, Bidhan Chandra Ray, being born here. The numerous Bengali speaking Patnaites have contributed massively into fine arts, culture, education and history of Bihar in general and Patna in particular. However, Magahi was the official language of the Mauryan
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
court, in which the edicts of Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
were composed.
The name ''Magahi'' is directly derived from the name Magadhi Prakrit, and educated speakers of Magahi prefer to call it "Magadhi" rather than "Magahi".Jain Dhanesh, Cardona George, ''The Indo-Aryan Languages'', pp449
Patna has many buildings adorned with Indo-Islamic and Indo-Saracenic architectural motifs. Several well-maintained major buildings from the colonial period have been declared "heritage structures"; others are in various stages of decay. Established in 1917 as the Bihar's first museum, the Patna Museum (पटना संग्रहालय) houses large collections that showcase Indian natural history and Indian art. The Khuda Bakhsh Oriental Library and Sinha Library are historic public libraries of Patna.
Several theatres are in or near the central part of the city, including the Bhartiya Nritya Kala Mandir, the Rabindra Parishad, Premchand Rangshala and the Kalidas Rangalaya, which is home to the Bihar art theatre. Kalidas Rangalaya also hosts the Patliputra Natya Mahotsav, a dance festival. But in the last two decades, the popularity of commercial theatres in the city has declined.
The Patna School of Painting or Patna Qalaam, some times also called Company style, is an offshoot of the well-known Mughal Miniature school of painting, which flourished in Bihar during the early 18th to the mid-20th centuries. The practitioners of this art form were descendants of Hindu artisans of Mughal painting who facing persecution under the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb and who found refuge, via Murshidabad, in Patna during the late 18th century. The Patna painters differed from the Mughal painters, whose subjects included only royalty and court scenes, in that they included as subjects bazaar scenes, scenes of Indian daily life, local dignitaries, festivals and ceremonies, and nature scenes. The paintings were executed in watercolours on paper and on mica, but the style was generally of a hybrid and undistinguished quality. It is this school of painting that inspired the formation of the College of Arts and Crafts, Patna, under the leadership of Shri Radha Mohan, which is an important centre of fine arts in Bihar.
Bihar Government is promoting its art and culture through Madhubani arts to educate people about Bihar's rich cultural diversity.
Some well known dishes of Bihari cuisine include (paratha
Paratha (, also parantha/parontah) is a flatbread native to the Indian subcontinent, with earliest reference mentioned in early medieval Sanskrit, India. It is one of the most popular flatbreads in the Indian subcontinent and the Middle East.
...
s stuffed with roasted gram flour), "" (a spiced drink with roasted gram flour as main ingredient), (spicy mashed potatoes), fish curry, Bihari kebab
Kebab ( , ), kebap, kabob (alternative North American spelling), kebob, or kabab (Kashmiri spelling) is a variety of roasted meat dishes that originated in the Middle East.
Kebabs consist of cut up ground meat, sometimes with vegetables an ...
, , malpua, dal pitha (Similar to momos), ( fox nut) and (a type of snack).
Street foods such as samosa
A samosa () () (Hindi: समोसा) ( Persian: سمبوسه) is a fried South Asian and West Asian snack. It is a pastry with a savory filling that mostly consists of vegetables like spiced potatoes, onions, and peas, but can also include ...
, chaat, jalebi, litti chokha, phuchka (a deep-fried crêpe with tamarind sauce), South Indian and Chinese cuisine are favourite among Patnaites. Taj Hotel Patna is under construction at Budh Marg Lodipur.
Bihari Women have traditionally worn cotton sari
A sari (also called sharee, saree or sadi)The name of the garment in various regional languages include:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* is a drape (cloth) and a women's garment in the Indian subcontinent. It consists of an un-sti ...
but shalwar kameez
Shalwar kameez (also salwar kameez and less commonly shalwar qameez) is a traditional combination dress worn by men and women in South Asia, and Central Asia.
'' Shalwars'' are trousers which are atypically wide at the waist and narrow to a ...
and other western attire are gaining acceptance among younger women. Western attire has gained wide acceptance among the urban men, although the traditional dhoti
The dhoti is an ankle-length breechcloth, wrapped around the waist and the legs, in resemblance to the shape of trousers. The dhoti is a garment of ethnic wear for men in the Indian subcontinent. The dhoti is fashioned out of a rectangular p ...
and kurta
A ''kurta'' is a loose collarless shirt or tunic worn in many regions of South Asia, (subscription required) Quote: "A loose shirt or tunic worn by men and women." Quote: "Kurta: a loose shirt without a collar, worn by women and men from South ...
are seen during festivals. Chhath
Chhath is an ancient Hindu festival, native to eastern India and southern Nepal. It is celebrated especially in the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, and Eastern Uttar Pradesh; and Koshi, Gandaki, Bagmati, Lumbini and Madhesh province ...
, also called Dala Chhath, is a major ancient festival in Bihar. It is celebrated twice a year: once in the summer, called the Chaiti Chhath, and once about a week after Deepawali, called the Kartik Chhath. Durga Puja, held in September–October, is Patna's another important festival; it is an occasion for glamorous celebrations. Among the city's other festivals, are Saraswati Puja, Eid, Holi
Holi () is a major Hindu festival celebrated as the Festival of Colours, Love and Spring.The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) p. 874 "Holi /'həʊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...".Yudit Greenberg, Encyclopedia of Love in World ...
, Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a Religion, religious and Culture, cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by coun ...
, Vishwakarma Puja, Makar Sankranti
Makar(a) Sankrānti (), () also referred to as Uttarāyana, Makara, or simply Sankrānti, is a Hinduism, Hindu observance and a mid-winter harvest festival in India and Nepal. It is typically celebrated on 14 January annually (15 January on a ...
, Raksha Bandhan
Raksha Bandhan Quote: m Hindi ''rakśābandhan'' held on the full moon of the month of Savan, when sisters tie a talisman (rakhi q.v.) on the arm of their brothers and receive small gifts of money from them. is a popular and traditionally Hin ...
and Rath Yatra. Cultural events include the Patna Book Fair, Patna Sahib Mahotsav, the Patna Film Festival, Bihar Diwas, Rajgir Mahotsav, Vaishali Mahotsav and the Sonepur Cattle Fair in neighbouring towns.
murti
In the Hinduism, Hindu tradition, a ''murti'' (, ) is a devotional image, such as a statue or icon, of a Hindu deities, deity or Hindu saints, saint used during ''Puja (Hinduism), puja'' and/or in other customary forms of actively expressing d ...
, or representation, of the goddess Durga
Durga (, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around combating evils and demonic ...
shown during the Durga Puja
Durga Puja (ISO 15919, ISO: , ), also known as Durgotsava or Shaaradotsava, is an annual festival originating in the Indian subcontinent which pays homage to the Hinduism, Hindu goddess Durga, and is also celebrated because of Durga's victo ...
festival
File:People Celebrating Chhath Festival.jpg, People Celebrating Chhath Festival the 2nd Day at Morning a tribute to the rising holy God Sun
Tourism

 Patna is home to many tourist attractions and it saw about 2.4 million tourists (including day visitors) in 2005. Tourists visiting the city accounted for 41% of the total number of tourists visiting
Patna is home to many tourist attractions and it saw about 2.4 million tourists (including day visitors) in 2005. Tourists visiting the city accounted for 41% of the total number of tourists visiting Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
although Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gayā is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple complex, situated in the Gaya district in the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Bihar. It is famous for being the place where Gautam ...
was the most popular destination for foreign visitors. The cultural heritage of Bihar is reflected in its many ancient monuments. Kumhrar
Kumhrar or Kumrahar is the area of Patna where remains of the ancient city of Pataliputra were excavated by the Archaeological Survey of India starting from 1913. It is located 5 km east of Patna Railway Station.
Archaeological remains ...
and Agam Kuan are the sites of the ruins of the Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
n Pataliputra. Didarganj Yakshi remains as an example of Mauryan art.
Takht Sri Patna Sahib is one of the Five Takhts of Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
and consecrates the birthplace of the tenth Guru of the Sikhs, Gobind Singh. There are five other Gurdwaras in Patna that are related to different Sikh Guru
The Sikh gurus (Punjabi language, Punjabi: ਸਿੱਖ ਗੁਰੂ; Hindi: सिख गुरु) are the spiritual masters of Sikhism, who established the religion over the course of about two and a half centuries, beginning in 1469. The year ...
s; these are Gurdwara Pahila Bara, Gurdwara Gobind Ghat, Gurdwara Guru ka Bagh,
Gurdwara Bal Leela, Gurdwara Handi Sahib, and Prakash Punj. Padri Ki Haveli, High Court, Golghar, Sultan Palace, and Secretariat Building are examples of British architecture. Gandhi Maidan is a historic ground in Patna where several freedom movement rallies took place. Newly built Buddha Smriti Park near Patna Junction is also becoming a major tourist attraction
A tourist attraction is a place of interest that tourists visit, typically for its inherent or exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure and amusement.
Types
Places of natural beaut ...
.
The Patna Planetarium (Indira Gandhi Planetarium) is in Patna's Indira Gandhi Science Complex. It claims to be one of the largest planetariums in Asia and to attract a large number of tourists. The Sanjay Gandhi Jaivik Udyan (Patna Zoo) is at Bailey Road, Raj Bhawan, Rajbanshi Nagar, and includes over 300 mammals, 300 birds, and 450 species of reptiles as of January 2019.
In 2015, the Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
government has built a state-of-the-art art landmark museum in Patna at a cost of approximately 530 crores on a site of 13.9 acres at Bailey Road. 5 firms were shortlisted for the architectural design, of which the Japanese firm Maki and Associates was chosen. It is now completed and opened for all. Completed in May 2018, the Sabhyata Dwar
The Sabhyata Dwar or Civilization Gate is a sandstone arch monument located on the banks on River Ganga in the city of Patna in the States of India, Indian state of Bihar. The Sabhyata Dwar is built with a Mauryan art#Architecture, Mauryan-styl ...
was built with Mauryan-style architecture. It was opened to the general public in December 2018.
In 2014, the Bihar government laid the foundation of Samrat Ashok International Convention Centre. It is expected to use more steel than used in raising Eiffel Tower
The Eiffel Tower ( ; ) is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower from 1887 to 1889.
Locally nicknamed "''La dame de fe ...
and Indira Gandhi International Airport
Indira Gandhi International Airport is the primary international airport serving New Delhi, the capital of India, and the National Capital Region (NCR). The airport, spread over an area of ,
. Construction of Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam Science City began in February 2019. The Eco Park is in Jawaharlal Nehru Marg. It has more than 3,000 varieties of plants and includes several theme parks, a restaurant, and a boat trip zone.
Education
 Schools in Patna are either government-run schools or private schools. The schools are affiliated to Bihar School Examination Board (BSEB), Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE), National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), or the
Schools in Patna are either government-run schools or private schools. The schools are affiliated to Bihar School Examination Board (BSEB), Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE), National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), or the Central Board of Secondary Education
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) is a national-level board of education in India for public and private schools, controlled and managed by the Government of India. Established in 1929 by a resolution of the government, the Board ...
(CBSE) boards. A number of Bengali medium schools also thrive in Patna. Hindi and English are the primary languages of instruction. A 2012 survey found 1,574 schools: of these, 78% were private unaided schools (most of them at an affordable cost), 21% were government schools and 1% were private aided.Baladevan Rangaraju, Professor James Tooley, Dr Pauline Dixon"The Private School Revolution in Bihar: Findings from a survey in Patna Urban"
Under the 10+2+3/4 plan, students complete ten years of schooling and then enroll in schools that have a higher secondary facility and are affiliated to the Bihar State Intermediate Board, the All-India Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE), the NIOS or the CBSE, where they select one of three streams: arts, commerce, or science. This is followed by either a general degree course in a chosen field of study or a professional degree course, such as law, engineering, and medicine. Patna has important government educational institutions like Patna University, Anugrah Narayan College, Chanakya National Law University, Aryabhatta Knowledge University, Indian Institute of Technology Patna, Bakhtiyarpur College of Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Patna, Patna Science College, Patna Women's College, Patna Law College, Bihar Veterinary College, J.D. Women's College, Birla Institute of Technology, Patna, Patna Medical College Hospital, Rajendra Memorial Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Nalanda Medical College Hospital, Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Mahavir Cancer Sansthan, All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna, National Institute of Fashion Technology Patna, Chandragupta Institute of Management, Development Management Institute, National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology, Patliputra University. Patna University was established in 1917 and is the seventh oldest modern university in the Indian Sub-continent. Patna also has a variety of other universities, as well as many primary and secondary schools.
Nalanda University
Nālandā University (informally NU; or ISO: Nālandā Vishwavidyalaya) is a central research university located in the ancient city of Rajgir in the state of Bihar, India. Designated as an Institute of National Importance (INI) and excelle ...
(also known as Nalanda International University) is an established university in Rajgir, around from Patna. The University, created as a revival of an ancient centre of learning at Nalanda
Nalanda (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: , ) was a renowned Buddhism, Buddhist ''mahavihara'' (great monastery) in medieval Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha (modern-day Bihar), eastern India. Widely considered to be am ...
, began its first academic session on 1 September 2014. It attracts students from across the globe.
Sports
cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
is popular in Patna and is played on grounds and in streets throughout the city. There are several sports grounds across the city. The Bihar Cricket Association, which regulates cricket in Bihar, is based in the city. Tournaments, especially those involving cricket, basketball, football, badminton, and table tennis, are regularly organised on an inter-locality or inter-club basis.
Moin-ul-Haq Stadium, which has a capacity of 25,000, has served as the venue for two one-day international cricket matches and several national sports events. It was home to the Bihar cricket team. Due to negligence and lack of maintenance, the stadium is in a dilapidated state and no international match has been played here since 1996. In 2013, it was announced by the Chief Minister of Bihar
The chief minister of Bihar serves as the head of the Government of Bihar, overseeing its administration and governance within the constitutional framework of India. While the Governor of Bihar holds the ceremonial role of the constitutional h ...
Nitish Kumar that an international cricket stadium will be constructed at Rajgir.
The Patna Golf Club was established on 21 March 1916, and is one of the oldest golf courses in India. It has 18 holes in a historic setting in and around Bailey Road, a course.
Patna hosted the first ever woman's Kabaddi world cup. It was held at the Patliputra Sports Complex
The Patliputra Stadium at the Patliputra Sports Complex is a multi-purpose stadium in Kankarbagh, Patna, Bihar. The first Women World Cup Kabaddi Championship was held here in its inaugural year, in which 16 countries had participated. It also ...
, Kankarbagh
''Kankarbagh'', or ''Kankarbagh Colony'', is a neighborhood and residential area in Patna, Bihar, India. It is one of the largest colonies in Asia and the second largest in terms of population.
Overview
Established back in 1916, Kankarbagh is ...
from 1 to 4 March 2012. Hosts India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
won the World Cup defeating Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
in the finals. Patna also hosts the seven league matches of Pro Kabaddi League with its home team as Patna Pirates at the Patliputra Sports Complex.
Other famous sports complexes of Patna are Bihar Military Police's Mithilesh Stadium, East Central Railway zone
The East Central Railway (abbreviated ECR) is one of the 19 railway zones in India. It is headquartered at and comprises , , , and divisions.
History
First set up on 8 September 1996 with headquarters at Hajipur, Bihar, East Central R ...
's indoor stadium at Digha etc.
Patliputra Sports Complex
The Patliputra Stadium at the Patliputra Sports Complex is a multi-purpose stadium in Kankarbagh, Patna, Bihar. The first Women World Cup Kabaddi Championship was held here in its inaugural year, in which 16 countries had participated. It also ...
during Pro Kabaddi League match
Media
The beginning of the 20th century was marked by a number of notable new publications. A monthly magazine named ''Bharat Ratna'' was started in Patna in 1901. It was followed by ''Ksahtriya Hitaishi'', ''Aryavarta'' from Dinapure, Patna, ''Udyoga'' and ''Chaitanya Chandrika''. ''Udyog'' was edited by Vijyaanand Tripathy, a famous poet of the time and ''Chaitanya Chandrika'' by Krishna Chaitanya Goswami, a literary figure of that time. The literary activity was not confined to Patna alone but to many districts of Bihar.Ahmad Qeyamuddin, ''Patna Through the ages: Glimpses of History, Society and Economy, Commonwealth Publishers'', New Delhi, 1988 Magahi Parishad, established in Patna in 1952, pioneered Magadhi journalism in Bihar. It started the monthly journal, ''Magadhi'', which was later renamed ''Bihan''. Many national media agencies, including thePress Trust of India
The Press Trust of India Ltd., commonly known as PTI, is the largest news agency in India. It is headquartered in New Delhi and is a nonprofit cooperative among more than 450 Indian newspapers. It has over 500 full-time employees , including abo ...
and Doordarshan's regional offices, are based in the city. ''The Hindu
''The Hindu'' is an Indian English-language daily newspaper owned by The Hindu Group, headquartered in Chennai, Tamil Nadu. It was founded as a weekly publication in 1878 by the Triplicane Six, becoming a daily in 1889. It is one of the India ...
'', ''The Times of India
''The Times of India'' (''TOI'') is an Indian English-language daily newspaper and digital news media owned and managed by the Times Group. It is the List of newspapers in India by circulation, third-largest newspaper in India by circulation an ...
'', ''Hindustan Times
''Hindustan Times'' is an Indian English language, English-language daily newspaper based in Delhi. It is the flagship publication of HT Media Limited, an entity controlled by the Birla family, and is owned by Shobhana Bhartia, the daughter o ...
'', ''The Economic Times
''The Economic Times'' is an Indian English-language business-focused daily newspaper. Owned by The Times Group, ''The Economic Times'' began publication in 1961 and it is sold in all major cities in India. As of 2012, it is the world's secon ...
'' and ''The Telegraph
''The Telegraph'', ''Daily Telegraph'', ''Sunday Telegraph'' and other variant names are often names for newspapers. Newspapers with these titles include:
Australia
* The Telegraph (Adelaide), ''The Telegraph'' (Adelaide), a newspaper in Adelaid ...
'' are the five principal English-language daily newspapers which have Patna editions. '' The Pioneer'' and ''The Indian Express
''The Indian Express'' is an English-language Indian daily newspaper founded in 1932 by P. Varadarajulu Naidu. It is headquartered in Noida, owned by the ''Indian Express Group''. It was later taken over by Ramnath Goenka. In 1999, eight y ...
'', though not printed in the city, are other English-language daily newspapers available in the city. The city's Hindi newspapers include '' Hindustan Dainik'', '' Dainik Jagran'', '' Dainik Bhaskar'', ''Prabhat Khabar
is a Hindi-language daily newspaper published in Jharkhand, Bihar and West Bengal, with circulation in some other states in India, including parts of Orissa. It was founded in August 1984 in Ranchi, in Bihar. With the formation of Jharkhand ...
'', '' Aaj'' and '' Rashtriya Sahara'', all of which have editions from Patna. There are also daily Urdu newspapers like Qaumi Tanzeem, Farooqi Tanzeem, and Qaumi Duniya Daily published in Patna. There is also the Hindi and English mixed newspaper tabloid Inext.
Patna has several AM and FM radio stations, including many state-owned channels. The city hosts several radio stations, including the state-owned All India Radio
All India Radio (AIR), also known as Akashvani (), is India's state-owned public broadcasting, public radio broadcaster. Founded in 1936, it operates under the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India), Ministry of Information and Broa ...
's Vividh Bharati, and FM 105. The All India Radio, Patna (officially Akashvani Patna Kendra) was established in 1948.
Patna is served by several private channels.
Private FM stations
Notable people
See also
* Patan *List of cities in Bihar by population
Bihar is administratively divided into 9 divisions and 38 districts. For the administration of urban areas, Bihar has 19 Municipal Corporation (India), municipal corporations, 89 nagar parishads (city councils), and 154 nagar panchayats (town co ...
* Patna Lok Sabha constituency
* Largest Indian Cities by GDP
References
Further reading
* * * * * * *Nas Margens do Hindustão : o estado da India e a expansão mongol ca.1570-1640. Por Jorge Flores *External links
Official website of Patna district
Official website of the Municipal Corporation of Patna
The Portuguese on the Bay of Bengal
{{Authority control Patna Cities and towns in Patna district Indian capital cities Holy cities Metropolitan cities in India Populated places established in the 5th century BC