Ghana Bishops' Conference on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to the east. Ghana covers an area of , spanning diverse ecologies, from
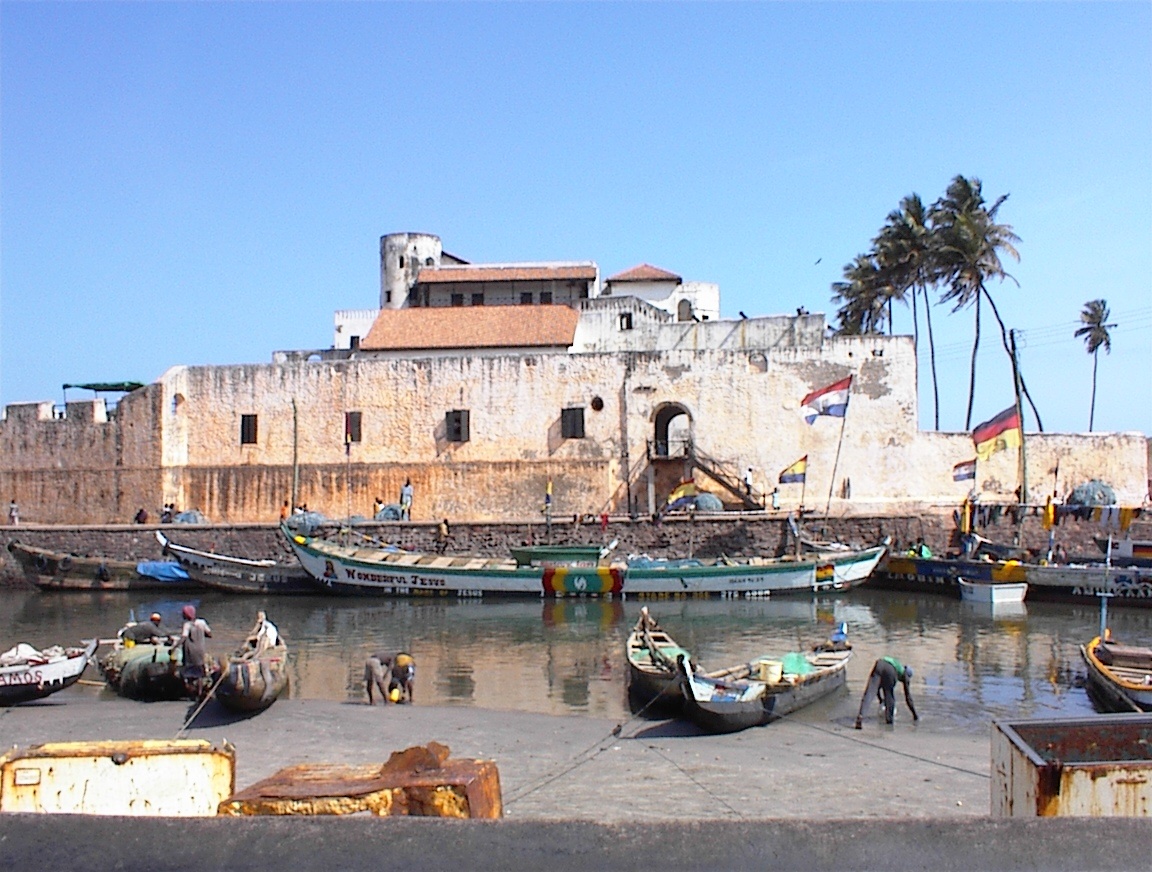 Akan trade with European states began after contact with the Portuguese in the 15th century. European contact was by the
Akan trade with European states began after contact with the Portuguese in the 15th century. European contact was by the
 After the 2000 general election,
After the 2000 general election,

A Country Study: Ghana
'' (La Verle Berry, editor).
Lcweb2.loc.gov
 Since independence, Ghana has been devoted to ideals of nonalignment and is a founding member of the
Since independence, Ghana has been devoted to ideals of nonalignment and is a founding member of the
''The Other Cold War: Canada's Military Assistance to the Developing World 1945–75''
,
 The
The 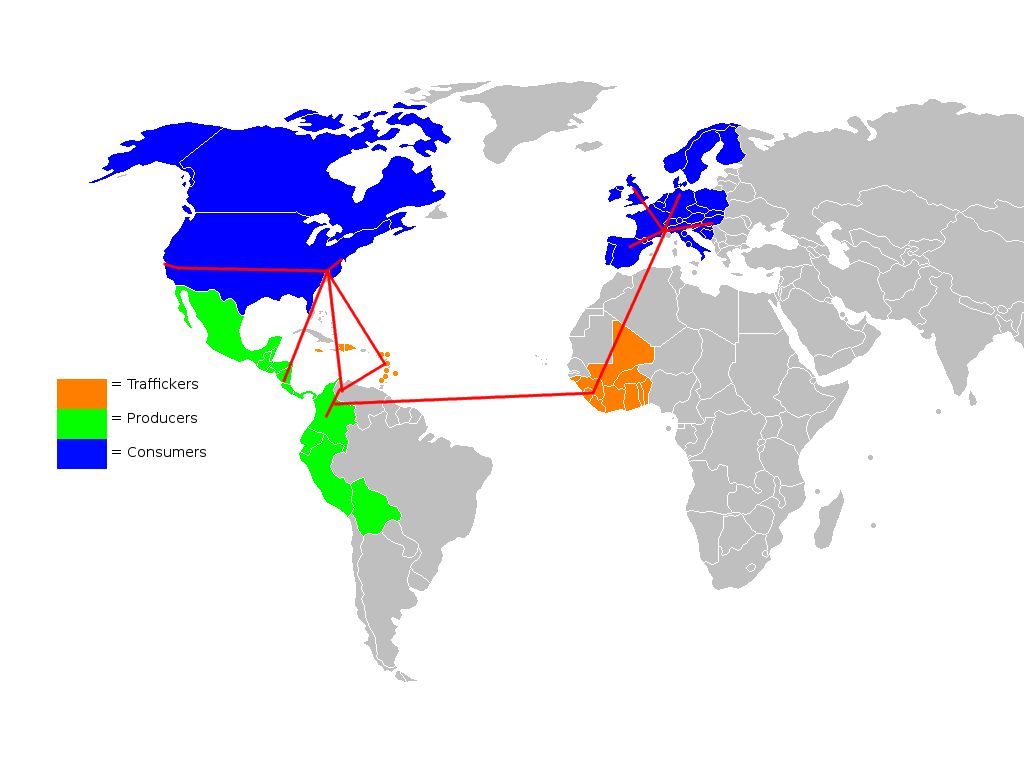 Ghana is used as a key narcotics industry transshipment point by traffickers, usually from South America as well as some from other African nations. In 2013, the UN chief of the Office on Drugs and Crime stated that "West Africa is completely weak in terms of border control and the big drug cartels from Colombia and Latin America have chosen Africa as a way to reach Europe." There is not a wide or popular knowledge about the narcotics industry and intercepted narcotics within Ghana, since it is an black market, underground economy. The social context within which narcotic trafficking, storage, transportation, and repacking systems exist in Ghana and the state's location along the Gulf of Guinea makes Ghana an attractive country for the narcotics business. The Narcotics Control Board (Ghana), Narcotics Control Board has impounded container ships at the Sekondi Naval Base in the Takoradi Harbour. These ships were carrying thousands of kilograms of cocaine, with a street value running into billions of Ghanaian cedi, Ghana cedis. However, drug seizures saw a decline in 2011. Drug cartels are using new methods in narcotics production and narcotics exportation, to avoid Ghanaian security agencies. Underdeveloped institutions, porous open borders, and the existence of established smuggling organisations contribute to Ghana's position in the narcotics industry. President Mills initiated ongoing efforts to reduce the role of airports in Ghana's drug trade.
Ghana is used as a key narcotics industry transshipment point by traffickers, usually from South America as well as some from other African nations. In 2013, the UN chief of the Office on Drugs and Crime stated that "West Africa is completely weak in terms of border control and the big drug cartels from Colombia and Latin America have chosen Africa as a way to reach Europe." There is not a wide or popular knowledge about the narcotics industry and intercepted narcotics within Ghana, since it is an black market, underground economy. The social context within which narcotic trafficking, storage, transportation, and repacking systems exist in Ghana and the state's location along the Gulf of Guinea makes Ghana an attractive country for the narcotics business. The Narcotics Control Board (Ghana), Narcotics Control Board has impounded container ships at the Sekondi Naval Base in the Takoradi Harbour. These ships were carrying thousands of kilograms of cocaine, with a street value running into billions of Ghanaian cedi, Ghana cedis. However, drug seizures saw a decline in 2011. Drug cartels are using new methods in narcotics production and narcotics exportation, to avoid Ghanaian security agencies. Underdeveloped institutions, porous open borders, and the existence of established smuggling organisations contribute to Ghana's position in the narcotics industry. President Mills initiated ongoing efforts to reduce the role of airports in Ghana's drug trade.
Pew Research Center. 4 June 2013. Sometimes elderly women in Ghana are accused of witchcraft, particularly in rural Ghana. Issues of witchcraft mainly remain as speculations based on superstitions within families. In some parts of northern Ghana, there exist what are called witch camps. These are said to house a total of around 1,000 people accused of witchcraft. The Ghanaian government has announced that it intends to close the camps.
 Ghana possesses industrial minerals, hydrocarbons and precious metals. It is an emerging designated digital economy with mixed economy hybridisation and an emerging market. It has an economic plan target known as the "Ghana Vision 2020". This plan envisions Ghana as the first African country to become a developed country between 2020 and 2029 and a Newly industrialized country, newly industrialised country between 2030 and 2039. This excludes fellow
Ghana possesses industrial minerals, hydrocarbons and precious metals. It is an emerging designated digital economy with mixed economy hybridisation and an emerging market. It has an economic plan target known as the "Ghana Vision 2020". This plan envisions Ghana as the first African country to become a developed country between 2020 and 2029 and a Newly industrialized country, newly industrialised country between 2030 and 2039. This excludes fellow
''A Country Study: Ghana''
(La Verle Berry, editor).
Lcweb2.loc.gov
The Jubilee Oil Field, which contains up to of sweet crude oil, was discovered in 2007. Ghana is believed to have up to to of petroleum in reserves, which is the fifth-largest in Africa and the 21st-to-25th-List of countries by proven oil reserves, largest proven reserves in the world. It also has up to of natural gas in reserves. The government has drawn up plans to Nationalization, nationalise petroleum and natural gas reserves to increase government revenue. In 2015, Ghana produced 88 metric tonnes of gold as per the our world in data report. As of 2019, Ghana was the 7th largest producer of gold in the world, producing ~140 tonnes that year. This record saw Ghana surpass South Africa in output for the first time, making Ghana the largest gold producer in Africa. In addition to gold, Ghana exports silver, timber, diamonds, bauxite, and manganese, and has other mineral deposits. Ghana ranks 9th in the world in diamond export and reserve size. The government has drawn up plans to Nationalization, nationalize mining industry to increase government revenue. "Shortages" of electricity in 2015 and 2016 led to dumsor ("persistent, irregular and unpredictable" electric power outages), increasing the interest in renewables. As of 2019, there is a surplus of electricity. The Judiciary of Ghana, judicial system of Ghana deals with corruption, economic malpractice and lack of economic transparency. According to Transparency International's Corruption Perceptions Index of 2018, out of 180 countries, Ghana was ranked 78th, with a score of 41 on a scale where a 0–9 score means highly corrupt, and a 90–100 score means very clean. This was based on perceived levels of public sector corruption.
 Ghana has a universal health care system, National Health Insurance Scheme (Ghana), National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS), which is strictly designated for Ghanaian people, Ghanaian nationals. Health care is variable throughout Ghana and in 2012, more than 12 million Ghanaian nationals were covered by the NHIS. Urban centres are well served and contain most of the hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies. There are more than 200 hospitals, and Ghana is a destination for medical tourism. In 2010, there were 0.1 physicians per 1,000 people and , 0.9 hospital beds per 1,000 people. In 2010, 5.2% of Ghana's GDP was spent on health.Field Listing :: Health expenditures
Ghana has a universal health care system, National Health Insurance Scheme (Ghana), National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS), which is strictly designated for Ghanaian people, Ghanaian nationals. Health care is variable throughout Ghana and in 2012, more than 12 million Ghanaian nationals were covered by the NHIS. Urban centres are well served and contain most of the hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies. There are more than 200 hospitals, and Ghana is a destination for medical tourism. In 2010, there were 0.1 physicians per 1,000 people and , 0.9 hospital beds per 1,000 people. In 2010, 5.2% of Ghana's GDP was spent on health.Field Listing :: Health expenditures
. Retrieved 24 June 2013. In 2020, the WHO announced Ghana became the second country in the WHO African Region to attain regulatory system "maturity level 3", the second-highest in the four-tiered WHO classification of National medicines regulatory systems. Life expectancy at birth in 2021 was 68.6 for a female and 63.7 for a male. In 2013, infant mortality was to 39 per 1,000 live births. Sources vary on life expectancy at birth; the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated 62 years for men and 64 years for women born in 2016. The fertility rate declined from 3.99 (2000) to 3.28 (2010) with 2.78 in urban region and 3.94 in rural region. The United Nations reports a fertility decline from 6.95 (1970) to 4.82 (2000) to 3.93 live births per woman in 2017. , the HIV/AIDS prevalence was estimated at 1.40% among adults aged 15–49.
 The education system is divided into three parts: basic education, secondary cycle, and tertiary education. "Basic education" lasts 11 years (ages 4‒15). It is divided into kindergarten (two years), primary school (two modules of three years) and junior high (three years). Junior high school ends with the Basic Education Certificate Examination. Once certified, the pupil can proceed to the secondary cycle. Hence, the pupil has the choice between general education (offered by the senior high school) and vocational education (offered by the technical senior high school or the technical and vocational institutes). Senior high school lasts 3 years and leads to the West African Senior School Certificate Examination, which is a prerequisite for enrollment in a university bachelor's degree programme. Polytechnics are open to vocational students.
A bachelor's degree requires four years of study. It can be followed by a one- or two-year master's degree programme, which can be followed by a PhD programme of at least three years. A polytechnic programme lasts two or three years. Ghana possesses colleges of education. Some of the universities are the University of Ghana, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, and University of Cape Coast.
There are more than 95% of children in school. The female and male ages 15–24 years literacy rate was 81% in 2010, with males at 82%, and females at 80%. An education system annually attracts foreign students particularly in the university sector.
Ghana has a free education six-year primary school education system beginning at age 6. The government largely funds basic education comprising public primary schools and public junior high schools. Senior high schools were subsidised by the government until September 2017/2018 academic year that senior high education became free. At the higher education level, the government funds more than 80% of resources provided to public universities, polytechnics and teacher training colleges. As part of the Free Compulsory Universal Basic Education, Fcube, the government supplies all basic education schools with all their textbooks and other educational supplies, like exercise books. Senior high schools are provided with all their textbook requirements by the government. Private schools acquire their educational material from private suppliers.
The education system is divided into three parts: basic education, secondary cycle, and tertiary education. "Basic education" lasts 11 years (ages 4‒15). It is divided into kindergarten (two years), primary school (two modules of three years) and junior high (three years). Junior high school ends with the Basic Education Certificate Examination. Once certified, the pupil can proceed to the secondary cycle. Hence, the pupil has the choice between general education (offered by the senior high school) and vocational education (offered by the technical senior high school or the technical and vocational institutes). Senior high school lasts 3 years and leads to the West African Senior School Certificate Examination, which is a prerequisite for enrollment in a university bachelor's degree programme. Polytechnics are open to vocational students.
A bachelor's degree requires four years of study. It can be followed by a one- or two-year master's degree programme, which can be followed by a PhD programme of at least three years. A polytechnic programme lasts two or three years. Ghana possesses colleges of education. Some of the universities are the University of Ghana, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, and University of Cape Coast.
There are more than 95% of children in school. The female and male ages 15–24 years literacy rate was 81% in 2010, with males at 82%, and females at 80%. An education system annually attracts foreign students particularly in the university sector.
Ghana has a free education six-year primary school education system beginning at age 6. The government largely funds basic education comprising public primary schools and public junior high schools. Senior high schools were subsidised by the government until September 2017/2018 academic year that senior high education became free. At the higher education level, the government funds more than 80% of resources provided to public universities, polytechnics and teacher training colleges. As part of the Free Compulsory Universal Basic Education, Fcube, the government supplies all basic education schools with all their textbooks and other educational supplies, like exercise books. Senior high schools are provided with all their textbook requirements by the government. Private schools acquire their educational material from private suppliers.
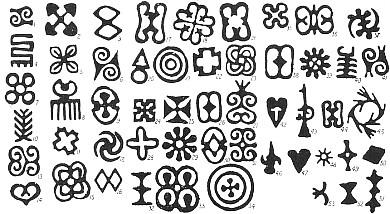 During the 13th century, Ghanaians developed their unique art of ''Adinkra symbols, adinkra'' printing. Hand-printed and hand-embroidered adinkra clothes were made and used exclusively by royalty for devotional ceremonies. Each of the motifs that make up the Text corpus, corpus of adinkra symbolism has a name and meaning derived from a proverb, a historical event, human attitude, ethology, plant life-form, or shapes of inanimate and man-made objects. The meanings of the motifs may be categorised into aesthetics, ethics, human relations, and concepts. The Adinkra symbols have a decorative function as tattoos but also represent objects that encapsulate evocative messages that convey traditional wisdom, aspects of life, or the environment. There are many symbols with distinct meanings, often linked with proverbs. In the words of Kwame Anthony Appiah, Anthony Appiah, they were one of the means in a pre-literate society for "supporting the transmission of a complex and nuanced body of practice and belief".
During the 13th century, Ghanaians developed their unique art of ''Adinkra symbols, adinkra'' printing. Hand-printed and hand-embroidered adinkra clothes were made and used exclusively by royalty for devotional ceremonies. Each of the motifs that make up the Text corpus, corpus of adinkra symbolism has a name and meaning derived from a proverb, a historical event, human attitude, ethology, plant life-form, or shapes of inanimate and man-made objects. The meanings of the motifs may be categorised into aesthetics, ethics, human relations, and concepts. The Adinkra symbols have a decorative function as tattoos but also represent objects that encapsulate evocative messages that convey traditional wisdom, aspects of life, or the environment. There are many symbols with distinct meanings, often linked with proverbs. In the words of Kwame Anthony Appiah, Anthony Appiah, they were one of the means in a pre-literate society for "supporting the transmission of a complex and nuanced body of practice and belief". Along with the ''adinkra cloth,'' Ghanaians use many cloth fabrics for their traditional attire. The different ethnic groups have their own individual cloth. The most well known is the Kente cloth. Kente is a very important national costume and clothing, and these clothes are used to make traditional and modern Kente attire. Different symbols and different colours mean different things. Kente cloth, Kente is the most famous of all the Ghanaian clothes. Kente is a ceremonial cloth hand-woven on a horizontal Loom, treadle loom and strips measuring about 4 inches wide are sewn together into larger pieces of cloths. Cloths come in various colours, sizes and designs and are worn during very important social and religious occasions. In a cultural context, kente is more important than just a cloth as it is a visual representation of history and also a form of written language through weaving. The term kente has its roots in the Akan word ''kɛntɛn'' which means a basket and the first kente weavers used raffia fibres to weave cloths that looked like kenten (a basket); and thus were referred to as ''kenten ntoma''; meaning basket cloth. The original Akan name of the cloth was ''nsaduaso'' or ''nwontoma'', meaning "a cloth hand-woven on a loom"; however, "kente" is the most frequently used term today.
Kente is also woven by the Ewe people (Ewe Kente) in the Volta Region. The main weaving centres are Agortime area and Agbozume. Agbozume has a vibrant kente market attracting patrons from all over west Africa and the diaspora.
Contemporary Ghanaian fashion includes traditional and modern styles and fabrics and has made its way into the African and global fashion scene. The cloth known as African wax prints, African print fabric was created out of Dutch wax textiles. It is believed that in the late 19th century, Dutch ships on their way to Asia stocked with machine-made textiles that mimicked Indonesian batik stopped at many West African ports on the way. The fabrics did not do well in Asia. However, in West Africa—mainly Ghana where there was an already established market for cloths and textiles—the client base grew and it was changed to include local and traditional designs, colours and patterns to cater to the taste of the new consumers. Today outside of Africa it is called "Ankara", and it has a client base well beyond Ghana and Africa as a whole. It is popular among Caribbean peoples and African Americans; celebrities such as Solange Knowles and her sister Beyoncé have been seen wearing African print attire. Many designers from countries in North America and Europe are now using African prints, and they have gained a global interest. British luxury fashion house Burberry created a collection around Ghanaian styles. American musician Gwen Stefani has repeatedly incorporated African prints into her clothing line and can often be seen wearing it. Internationally acclaimed Ghanaian-British designer Ozwald Boateng introduced African print suits in his 2012 collection.
Along with the ''adinkra cloth,'' Ghanaians use many cloth fabrics for their traditional attire. The different ethnic groups have their own individual cloth. The most well known is the Kente cloth. Kente is a very important national costume and clothing, and these clothes are used to make traditional and modern Kente attire. Different symbols and different colours mean different things. Kente cloth, Kente is the most famous of all the Ghanaian clothes. Kente is a ceremonial cloth hand-woven on a horizontal Loom, treadle loom and strips measuring about 4 inches wide are sewn together into larger pieces of cloths. Cloths come in various colours, sizes and designs and are worn during very important social and religious occasions. In a cultural context, kente is more important than just a cloth as it is a visual representation of history and also a form of written language through weaving. The term kente has its roots in the Akan word ''kɛntɛn'' which means a basket and the first kente weavers used raffia fibres to weave cloths that looked like kenten (a basket); and thus were referred to as ''kenten ntoma''; meaning basket cloth. The original Akan name of the cloth was ''nsaduaso'' or ''nwontoma'', meaning "a cloth hand-woven on a loom"; however, "kente" is the most frequently used term today.
Kente is also woven by the Ewe people (Ewe Kente) in the Volta Region. The main weaving centres are Agortime area and Agbozume. Agbozume has a vibrant kente market attracting patrons from all over west Africa and the diaspora.
Contemporary Ghanaian fashion includes traditional and modern styles and fabrics and has made its way into the African and global fashion scene. The cloth known as African wax prints, African print fabric was created out of Dutch wax textiles. It is believed that in the late 19th century, Dutch ships on their way to Asia stocked with machine-made textiles that mimicked Indonesian batik stopped at many West African ports on the way. The fabrics did not do well in Asia. However, in West Africa—mainly Ghana where there was an already established market for cloths and textiles—the client base grew and it was changed to include local and traditional designs, colours and patterns to cater to the taste of the new consumers. Today outside of Africa it is called "Ankara", and it has a client base well beyond Ghana and Africa as a whole. It is popular among Caribbean peoples and African Americans; celebrities such as Solange Knowles and her sister Beyoncé have been seen wearing African print attire. Many designers from countries in North America and Europe are now using African prints, and they have gained a global interest. British luxury fashion house Burberry created a collection around Ghanaian styles. American musician Gwen Stefani has repeatedly incorporated African prints into her clothing line and can often be seen wearing it. Internationally acclaimed Ghanaian-British designer Ozwald Boateng introduced African print suits in his 2012 collection.
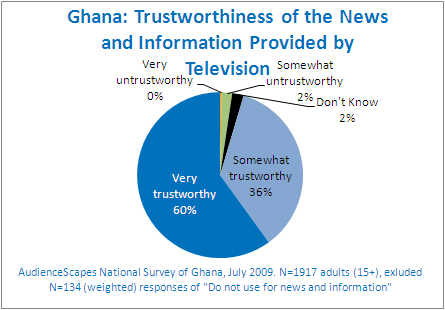 Chapter 12 of the 1992 Constitution of Ghana guarantees freedom of the press and independence of the media, while Chapter 2 prohibits censorship., ''Government of Ghana''. Post-independence, private outlets closed during the military governments, and media laws prevented criticism of government.Anokwa, K. (1997). In ''Press Freedom and Communication in Africa''. Erbio, F. & Jong-Ebot, W. (Eds.) Africa World Press. . Press freedoms were restored in 1992, and after the election in 2000 of Kufuor, the tensions between the private media and government decreased. Kufuor supported press freedom and repealed a Defamation, libel law, and maintained that the media had to act responsibly.Basic Data
Chapter 12 of the 1992 Constitution of Ghana guarantees freedom of the press and independence of the media, while Chapter 2 prohibits censorship., ''Government of Ghana''. Post-independence, private outlets closed during the military governments, and media laws prevented criticism of government.Anokwa, K. (1997). In ''Press Freedom and Communication in Africa''. Erbio, F. & Jong-Ebot, W. (Eds.) Africa World Press. . Press freedoms were restored in 1992, and after the election in 2000 of Kufuor, the tensions between the private media and government decreased. Kufuor supported press freedom and repealed a Defamation, libel law, and maintained that the media had to act responsibly.Basic Data
. pressreference.com The media have been described as "one of the most unfettered" in Africa.BBC Country Profile: Ghana
, BBC News. In 1948, the Gold Coast Film Unit was set up in the Information Services Department.
 Association football is the top spectator sport in Ghana. Ghana has won the Africa Cup of Nations four times, the FIFA U-20 World Cup once, and has participated in four FIFA World Cups (2006, 2010, 2014 and 2022) and has also won the FIFA U-17 World Cup twice. The International Federation of Football History & Statistics, International Federation of Football History and Statistics crowned Asante Kotoko SC as the International Federation of Football History & Statistics#Continental Clubs of the 20th century, African club of the 20th century.
Ghana competes in the Commonwealth Games, sending athletes in every edition since 1954 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1954 (except for the 1986 Commonwealth Games, 1986 games). Ghana has won 57 medals at the Commonwealth Games, including 15 gold, with all but one of their medals coming in athletics and boxing. The country has also produced a number of boxers, including Azumah Nelson a three-time world champion, Nana Konadu, Nana Yaw Konadu also a three-time world champion, Ike Quartey, and Joshua Clottey.
Association football is the top spectator sport in Ghana. Ghana has won the Africa Cup of Nations four times, the FIFA U-20 World Cup once, and has participated in four FIFA World Cups (2006, 2010, 2014 and 2022) and has also won the FIFA U-17 World Cup twice. The International Federation of Football History & Statistics, International Federation of Football History and Statistics crowned Asante Kotoko SC as the International Federation of Football History & Statistics#Continental Clubs of the 20th century, African club of the 20th century.
Ghana competes in the Commonwealth Games, sending athletes in every edition since 1954 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1954 (except for the 1986 Commonwealth Games, 1986 games). Ghana has won 57 medals at the Commonwealth Games, including 15 gold, with all but one of their medals coming in athletics and boxing. The country has also produced a number of boxers, including Azumah Nelson a three-time world champion, Nana Konadu, Nana Yaw Konadu also a three-time world champion, Ike Quartey, and Joshua Clottey.
The Parliament of Ghana
National Commission on Culture
Country Profile
from BBC News
Ghana
from ''Encyclopædia Britannica''
Ghana
profile from ECOWAS
News headline links
from Al Jazeera. * * Th
African Activist Archive Project
website has photographs of the All Africa People's Conference held in Accra, Ghana, 5–13 December 1958 includin
Kwame Nkrumah, Prime Minister of Ghana
addressing the conference, th
American Committee on Africa delegation
meeting with Nkrumah, and o
Patrick Duncan and Alfred Hutchinson
of South Africa at the conference. {{Coord, 8.03, N, 1.08, W, display=title Ghana 1957 establishments in Ghana Articles containing video clips Countries in Africa Economic Community of West African States Countries and territories where English is an official language Member states of the African Union Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the United Nations Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations States and territories established in 1957 West African countries
coast
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
al savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
s to tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are dense and warm rainforests with high rainfall typically found between 10° north and south of the Equator. They are a subset of the tropical forest biome that occurs roughly within the 28° latitudes (in the torrid zo ...
s. With nearly 35 million inhabitants, Ghana is the second-most populous country in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
. The capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metrop ...
is Accra
Accra (; or ''Gaga''; ; Ewe: Gɛ; ) is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , had a population of ...
; other significant cities
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
include Tema
Tema is a city on the Bight of Benin and Atlantic coast of Ghana. It is located east of the capital city; Accra, in the region of Greater Accra, and is the capital of the Tema Metropolitan District. As of 2013, Tema is the eleventh most p ...
, Kumasi
Kumasi is a city and the capital of the Kumasi Metropolitan Assembly and the Ashanti Region of Ghana. It is the second largest city in the country, with a population of 443,981 as of the 2021 census. Kumasi is located in a rain forest region ...
, Sunyani
Sunyani () is a city and the capital of the Sunyani Municipal District and the Bono Region of Ghana. The city is located about northwest of Kumasi and away from Accra. It is the sixth largest city in the country as of the 2010 census, with ...
, Ho, Cape Coast
Cape Coast is a city and the capital of the Cape Coast Metropolitan Assembly, Cape Coast Metropolitan District and the Central Region (Ghana), Central Region of Ghana, Ghana. It is located about from Sekondi-Takoradi and approximately from Ac ...
, Techiman
Techiman (Akan language, Akan: ''Takyiman'') is a city and the capital of the Techiman Municipal District, Techiman Metropolitan District and the Bono East Region of Ghana. The city is located about from Sunyani and about away from Kumasi. I ...
, Tamale
A tamale, in Spanish language, Spanish , is a traditional Mesoamerican dish made of ''masa'', a dough made from nixtamalization, nixtamalized maize, corn, which is steaming, steamed in a corn husk or Banana leaf, banana leaves. The wrapping ...
, and Sekondi-Takoradi
Sekondi-Takoradi ( ) is a city in Ghana comprising the Twin cities (geographical proximity), twin cities of Sekondi and Takoradi. It is the capital of Sekondi Takoradi Metropolitan Assembly, Sekondi-Takoradi Metropolitan District and the Weste ...
.
The earliest kingdoms to emerge in Ghana were Bonoman
Bono State (also known as Bonoman) was the first centralized Akan state, founded by the Bono people in what is now central Ghana. Bonoman is generally considered a cultural, political ancestor and origin to Akan subgroups that migrated southwar ...
in the south and the Kingdom of Dagbon
The Kingdom of Dagbon ( ) is the oldest and one of the most organised traditional kingdoms in Ghana founded by the Dagomba people (Dagbamba) in the 15th century. During its rise, it comprised, at various points, the Northern Region (Ghana), North ...
in the north, with Bonoman existing in the area during the 11th century. The Asante Empire
The Asante Empire ( Asante Twi: ), also known as the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted from 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana and also parts of Ivory Coast ...
and other Akan kingdoms in the south emerged over the centuries. Beginning in the 15th century, the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa ...
, followed by other European powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
, contested the area for trading rights, until the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
ultimately established control of the coast by the 19th century
A century is a period of 100 years or 10 decades. Centuries are numbered ordinally in English and many other languages. The word ''century'' comes from the Latin ''centum'', meaning ''one hundred''. ''Century'' is sometimes abbreviated as c.
...
. Following more than a century of colonial resistance, the current borders of the country took shape, encompassing four separate British colonial territories: Gold Coast, Ashanti, the Northern Territories, and British Togoland
British Togoland, officially the Mandate Territory of Togoland and later officially the Trust Territory of Togoland, was a territory in West Africa under the administration of the United Kingdom, which subsequently entered a union with Ghana, pa ...
. These were unified as an independent dominion within the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an International organization, international association of member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, 56 member states, the vast majo ...
. On 6 March 1957 Ghana became the first colony in Sub-Saharan Africa to achieve sovereignty—that is, gain independence. Under President Kwame Nkrumah
Francis Kwame Nkrumah (, 21 September 1909 – 27 April 1972) was a Ghanaian politician, political theorist, and revolutionary. He served as Prime Minister of the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast from 1952 until 1957, when it gained ...
, it became influential in decolonisation efforts and the Pan-African movement.
Ghana is a multi-ethnic
The term multiracial people refers to people who are mixed with two or more
races and the term multi-ethnic people refers to people who are of more than one ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mult ...
country with diverse linguistic and religious groups; while the Akan Akan may refer to:
People and languages
*Akan people, an ethnic group in Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire
*Akan languages, a language group within the wider Central Tano languages
*Kwa languages, a language group which includes Akan
*Central Tano language ...
are the largest ethnic group, they constitute a plurality. Most Ghanaians
The Ghanaian people are a nation originating in the Ghanaian Gold Coast. Ghanaians predominantly inhabit the Republic of Ghana and are the predominant cultural group and residents of Ghana, numbering 34 million people as of 2024, making up 85% ...
are Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
(71.3%); almost a fifth are Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
; a tenth practice traditional faiths or report no religion. Ghana is a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigr ...
constitutional democracy
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of Legal entity, entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
Wh ...
led by a president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
who is head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "
and he head of state
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (letter), the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads
* He (pronoun), a pronoun in Modern English
* He (kana), one of the Japanese kana (へ in hiragana and ヘ in katakana)
* Ge (Cyrillic), a Cyrillic letter cal ...
being an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...head of government
In the Executive (government), executive branch, the head of government is the highest or the second-highest official of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presid ...
. For political stability in Africa, Ghana ranked seventh in the 2012 Ibrahim Index of African Governance
The Ibrahim Index of African Governance (IIAG), established in 2007, provides an assessment of the quality of governance in African countries. The IIAG is compiled by 81 indicators and 265 variables from 54 data projects, coming from 47 independ ...
and fifth in the 2012 Fragile States Index
The Fragile States Index (FSI; formerly the Failed States Index) is an annual report mainly published and supported by the American think tank Fund for Peace. The FSI is also published by the American magazine ''Foreign Policy'' from 2005 to 201 ...
. It has maintained since 1993 one of the freest and most stable governments on the continent, and it performs relatively well in healthcare
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
, economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
growth, and human development, so that it has a significant influence in West Africa and Africa as a whole. Ghana is highly integrated in international affairs, being a founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
and the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
, and a member of the Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as CEDEAO in French and Portuguese) is a regional political and economic union of twelve countries of West Africa. Collectively, the present and former members comprise an area ...
, the Group of 24
The Intergovernmental Group of Twenty-Four on International Monetary Affairs and Development, or The Group of 24 (G-24) was established in 1971 as a chapter of the Group of 77 in order to help coordinate the positions of developing countries on ...
and the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an International organization, international association of member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, 56 member states, the vast majo ...
.
Etymology
The name ''Ghana'' comes fromWagadu
The Ghana Empire (), also known as simply Ghana, Ghanata, or Wagadu, was an ancient western-Sahelian empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali.
It is uncertain among historians when Ghana's ruling dynasty began. T ...
, an empire in west Africa from the 3rd to 12th centuries; Wagadu was termed ''Ghana'' by Arab traders involved in the trans-Saharan trade. ''Ghana'' is thought to originate from the title ''Kaya Maghan'' of the rulers of Wagadu, which translates as ''ruler of gold''. As the Gold Coast colony prepared for independence, the nation's leader and first prime minister later first president Kwame Nkrumah
Francis Kwame Nkrumah (, 21 September 1909 – 27 April 1972) was a Ghanaian politician, political theorist, and revolutionary. He served as Prime Minister of the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast from 1952 until 1957, when it gained ...
who together with five others known as The Big Six
''The Big Six'' is the ninth book of Arthur Ransome's Swallows and Amazons series of children's books, published in 1940. The book returns Dick and Dorothea Callum, known as the Ds, to the Norfolk Broads where they renew their friendship with ...
, led Ghana to independence, settled on ''Ghana'', aiming to evoke a sense of unity and liberation among the Ghanaian people
The Ghanaian people are a nation originating in the Ghanaian Gold Coast. Ghanaians predominantly inhabit the Republic of Ghana and are the predominant cultural group and residents of Ghana, numbering 34 million people as of 2024, making up 85% ...
. The name was a powerful reminder of their shared heritage and the legacy of the ancient empire that once thrived in the wider region. It encapsulated the aspirations of the Ghanaian people for self-governance, progress, and a future marked by dignity and resilience.
History
Medieval kingdoms
The earliest kingdoms to emerge in Ghana wereBonoman
Bono State (also known as Bonoman) was the first centralized Akan state, founded by the Bono people in what is now central Ghana. Bonoman is generally considered a cultural, political ancestor and origin to Akan subgroups that migrated southwar ...
in the south and the Kingdom of Dagbon
The Kingdom of Dagbon ( ) is the oldest and one of the most organised traditional kingdoms in Ghana founded by the Dagomba people (Dagbamba) in the 15th century. During its rise, it comprised, at various points, the Northern Region (Ghana), North ...
in the north, with Bonoman existing in the area during the 11th century. From the 17th century, different Akan states begun to emerge from what is believed to have been the Bonoman area, mainly based on gold trading. These states included Bonoman (Brong-Ahafo region), Adansi
Adanse or Adansi is one of the earliest Akan states, located in the southern part of present-day Ashanti Region, Ghana. Widely regarded in oral tradition as a spiritual and ancestral homeland of many Akan polities, Adansi was an early center of ...
and Asante
Asante may refer to:
*Asante people, an ethnic group in Ghana
*Asante Empire
*Asante (name)
*Asante dialect, a dialect of the Akan languages
* Asante Kotoko S.C., a Ghanaian professional association football club
*Asante (album), 1974 jazz album b ...
(Ashanti Region
The Ashanti Region is located in the southern part of Ghana and is the third largest of Regions of Ghana, 16 administrative regions, occupying a total land surface of and making up 10.2 percent of the total land area of Ghana. It is the List of ...
), Denkyira
Denkyira (also known as Denkira, Denchira, Inguira, or Dinkira) was a powerful Akan kingdom that rose to prominence in precolonial Ghana, dominating large parts of the forest zone in the south-central Gold Coast. Centered around its capital at ...
(Western North region
The Western North region is one of the six new regions of Ghana created in 2019. The region is bounded by the Ivory Coast ( Comoé District) on the west, the Central region in the southeast, and the Ashanti, Ahafo, Bono East and Bono regions ...
), Mankessim Kingdom ( Central region), Akyem
The Akyem Kingdoms (also known as Greater Akyem, Akim, Great Akim, or Akan Grande) were prominent Akan people, Akan kingdoms in precolonial Ghana, consisting of the three related states of Akyem Abuakwa, Akyem Kotoku, and Akyem Bosome. Located in ...
and Akwamu
The Akwamu Empire was a powerful Akan state that rose to prominence in the 17th century in what is now southeastern Ghana. According to oral tradition, the Akwamu traced their origins to the Twifo-Heman area, but the earliest historical records p ...
(Eastern region). By the 19th century, the territory of the southern part of Ghana was included in the Asante Kingdom. The government of the Ashanti Empire operated first as a loose network and eventually as a centralised kingdom with a specialised bureaucracy centred in the capital city of Kumasi
Kumasi is a city and the capital of the Kumasi Metropolitan Assembly and the Ashanti Region of Ghana. It is the second largest city in the country, with a population of 443,981 as of the 2021 census. Kumasi is located in a rain forest region ...
. Prior to Akan contact with Europeans, the Akan people created an economy based on principally gold and gold bar
A gold bar, also known as gold bullion or a gold ingot, is a quantity of refined metallic gold that can be shaped in various forms, produced under standardized conditions of manufacture, labeling, and record-keeping. Larger varieties of gold ...
precious metals, which were traded with other states in Africa.
The Ga-Dangme and Ewe migrated westward from south-western Nigeria. The Ewe, formerly known as Dogbo, migrated from Oyo area with their Gbe-speaking kinsmen (Adja, Fon, Phla/Phera and Ogun/Gun) and, in transition, settled at Ketou in Benin Republic, Tado in Togo, and Dogbo Nyigbo in Benin Republic, with Nortsie (a walled town in present-day Togo) as their final dispersal point. Their dispersal from Nortsie was necessitated by the high-handed rule of King Agorkorli (Agɔ Akɔli), who was the reigning monarch of the tribe at that time. The Ewe in Ghana speak three principal dialects: Anlo (along the coast), Tongu (along the Volta river) and Ewedome (in the hill country side). The Ga-Dangme occupy the Greater Accra Region and parts of the Eastern Region, while the Ewe are found in the Volta Region
Volta Region (or Volta) is one of Ghana's sixteen administrative regions, with Ho designated as its capital. It is located west of Republic of Togo and to the east of Lake Volta. Divided into 25 administrative districts, the region is multi- ...
as well as the neighbouring Togo, Benin Republic and Nigeria (around Badagry area).
European contact and colonialism
 Akan trade with European states began after contact with the Portuguese in the 15th century. European contact was by the
Akan trade with European states began after contact with the Portuguese in the 15th century. European contact was by the Portuguese people
The Portuguese people ( – masculine – or ''Portuguesas'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation Ethnic groups in Europe, indigenous to Portugal, a country that occupies the west side of the Iberian Peninsula in ...
, who came to the Gold Coast region in the 15th century to trade. The Portuguese then established the Portuguese Gold Coast
The Portuguese Gold Coast was a Portuguese colony on the West African Gold Coast (present-day Ghana) along the Gulf of Guinea.
From their seat of power at the fortress of São Jorge da Mina (established in 1482 and located in modern Elmina) ...
(Costa do Ouro), focused on the availability of gold. The Portuguese built a trading lodge at a coastal settlement called Anomansah (the perpetual drink), which they renamed São Jorge da Mina. In 1481, King John II of Portugal
John II (; ; 3 May 1455 – 25 October 1495), called the Perfect Prince (), was King of Portugal from 1481 until his death in 1495, and also for a brief time in 1477. He is known for reestablishing the power of the Portuguese monarchy, reinvigo ...
commissioned Diogo de Azambuja
Diogo de Azambuja or Diego de Azambuja (1432–1518) was a Portuguese noble and explorer.
Soldier
He was born at Montemor-o-Velho, and became a knight of the Order of Aviz in the service of the Infante Dom Pedro, son of the Regent Infante ...
to build the Elmina Castle
Elmina Castle was erected by the Portuguese in 1482 as Castelo de São Jorge da Mina (''St. George of the Mine Castle''), also known as ''Castelo da Mina'' or simply ''Mina'' (or '' Feitoria da Mina''), in present-day Elmina, Ghana, formerly t ...
, which was completed in three years. By 1598, the Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
had joined the Portuguese in the gold trade, establishing the Dutch Gold Coast
The Dutch Gold Coast or Dutch Guinea, officially Dutch possessions on the Coast of Guinea (Dutch language, Dutch: ''Nederlandse Bezittingen ter Kuste van Guinea'') was a portion of contemporary Ghana that was gradually colonized by the Dutch (et ...
(''Nederlandse Bezittingen ter Kuste van Guinea'' – 'Dutch properties at the Guinea coast') and building forts at Fort Komenda
Fort Komenda was a British fort on the Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast, currently preserved as a ruin. Because of its testimony to the Atlantic slave trade and European economic and colonial influence in West Africa, the fort was inscribed on th ...
and Kormantsi. In 1617, the Dutch captured the Elmina Castle from the Portuguese and Axim
Axim is a coastal town and the capital of Nzema East Municipal district, a district in Western Region of South Ghana. Axim lies 64 kilometers west of the port city of Sekondi-Takoradi in the Western Region, west of Cape Three Points. Axim ha ...
in 1642 ( Fort St Anthony).
European traders had joined in gold trading by the 17th century, including the Swedes
Swedes (), or Swedish people, are an ethnic group native to Sweden, who share a common ancestry, Culture of Sweden, culture, History of Sweden, history, and Swedish language, language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countries, ...
, establishing the Swedish Gold Coast (''Svenska Guldkusten''), and Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway (Danish language, Danish and Norwegian language, Norwegian: ) is a term for the 16th-to-19th-century multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (includ ...
, establishing the Danish Gold Coast
The Danish Gold Coast ( or ''Dansk Guinea'') comprised the colonies that Denmark–Norway controlled in Africa as a part of the Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast (roughly present-day southeast Ghana), which is on the Gulf of Guinea. It was coloni ...
(''Danske Guldkyst'' or ''Dansk Guinea''). European traders participated in the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
in this area. More than 30 forts and castles were built by the merchants. The Germans established the Brandenburger Gold Coast
The Brandenburger Gold Coast, later Prussian Gold Coast, was a colony of Brandenburg-Prussia, later the Kingdom of Prussia, on the Gold Coast. The Brandenburg colony existed from 1682 to 1701, after which it became a Prussian colony from 1701 ...
or Groß Friedrichsburg. In 1874, Great Britain established control over some parts of the country, assigning these areas the status of the British Gold Coast
The Gold Coast was a British Empire, British Crown colony on the Gulf of Guinea in West Africa from 1821 until its independence in 1957 as Ghana. The term Gold Coast is also often used to describe all of the four separate jurisdictions that w ...
.MacLean, Iain (2001), ''Rational Choice and British Politics: An Analysis of Rhetoric and Manipulation from Peel to Blair'', p. 76, . Military engagements occurred between British colonial powers and Akan nation-states. The Kingdom of Ashanti defeated the British some times in the 100-year-long Anglo-Ashanti wars
The Anglo-Ashanti wars were a series of five conflicts that took place between 1824 and 1900 between the Ashanti Empire—in the Akan people, Akan interior of the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast—and the British Empire and its African ...
and eventually lost with the War of the Golden Stool
The War of the Golden Stool, also known as the Yaa Asantewaa War, the Third Ashanti Expedition, the Ashanti Uprising, or variations thereof, was a campaign in 1900 during the series of conflicts between the United Kingdom and the Ashanti Empire ...
in 1900.Freeman-Grenville, G. S. P. (1975), ''Chronology of World History: A Calendar of Principal Events from 3000 BC to AD 1973'', Part 1973, Rowman & Littlefield
Rowman & Littlefield Publishing Group is an American independent academic publishing company founded in 1949. Under several imprints, the company offers scholarly books for the academic market, as well as trade books. The company also owns ...
, .
Transition to independence
In 1947, the newly formedUnited Gold Coast Convention
The United Gold Coast Convention (UGCC) was an early nationalist movement British colony of the Gold Coast (present-day Ghana) that sought independence after the Second World War. It was founded in August 1947 with the aim of self-government "i ...
led by "The Big Six" called for "self-government within the shortest possible time" following the 1946 Gold Coast legislative election. Kwame Nkrumah
Francis Kwame Nkrumah (, 21 September 1909 – 27 April 1972) was a Ghanaian politician, political theorist, and revolutionary. He served as Prime Minister of the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast from 1952 until 1957, when it gained ...
, a Ghanaian nationalist who led Ghana from 1957 to 1966 as the country's first prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
and president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
, formed the Convention People's Party
The Convention People's Party (CPP) is a socialist political party in Ghana based on the ideas of the first President of Ghana, Kwame Nkrumah. The CPP was formed in June 1949 after Nkrumah broke away from the United Gold Coast Convention (UGC ...
in 1949 with the motto "self-government now". The party initiated a "positive action" campaign involving non-violent protests, strikes and non-cooperation with the British authorities. Nkrumah was arrested and sentenced to one year imprisonment during this time. In the Gold Coast's 1951 general election, he was elected to Parliament and was released from prison. He became prime minister in 1952 and began a policy of Africanization.
At midnight on 6 March 1957, the Gold Coast, Ashanti, the Northern Territories, and British Togoland
British Togoland, officially the Mandate Territory of Togoland and later officially the Trust Territory of Togoland, was a territory in West Africa under the administration of the United Kingdom, which subsequently entered a union with Ghana, pa ...
were unified as one single independent dominion within the British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an international association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire
The B ...
under the name Ghana. This was done under the Ghana Independence Act 1957
The Ghana Independence Act 1957 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that granted the Gold Coast fully responsible government within the British Commonwealth of Nations under the name of Ghana. The Act received royal assent on 7 F ...
. The current flag of Ghana
The national flag of Ghana consists of a horizontal triband of red, yellow, and green. It replaced the British Gold Coast's Blue Ensign.
The flag, which was adopted upon the independence of the Dominion of Ghana on 6 March 1957, was designe ...
, consisting of the colours red, gold, green, and a black star, dates back to this unification. On 1 July 1960, following the Ghanaian constitutional referendum and Ghanaian presidential election, Nkrumah declared Ghana a republic and assumed the presidency. 6 March is the nation's Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event memorialization, commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or Sovereign state, statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or after the end of a milit ...
, and 1 July is celebrated as Republic Day
Republic Day is the name of a holiday in several countries to commemorate the day when they became republics.
List
January 1 January in Slovak Republic
The day of creation of Slovak republic. A national holiday since 1993. Officially calle ...
.
Nkrumah led an authoritarian
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in democracy, separation of powers, civil liberties, and ...
regime in Ghana, as he repressed political opposition and conducted elections that were not free and fair. In 1964, a constitutional amendment
A constitutional amendment (or constitutional alteration) is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly alt ...
made Ghana a one-party state
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a governance structure in which only a single political party controls the ruling system. In a one-party state, all opposition parties are either outlawed or en ...
, with Nkrumah as president for life of both the nation and its party. Nkrumah was the first African head of state to promote the concept of Pan-Africanism
Pan-Africanism is a nationalist movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all Indigenous peoples of Africa, indigenous peoples and diasporas of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atla ...
, which he had been introduced to during his studies at Lincoln University, Pennsylvania in the United States, at the time when Marcus Garvey
Marcus Mosiah Garvey Jr. (17 August 188710 June 1940) was a Jamaican political activist. He was the founder and first President-General of the Universal Negro Improvement Association and African Communities League (UNIA-ACL) (commonly known a ...
was known for his "Back to Africa Movement". He merged the teachings of Garvey, Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister, civil and political rights, civil rights activist and political philosopher who was a leader of the civil rights move ...
and the naturalised Ghanaian scholar W. E. B. Du Bois
William Edward Burghardt Du Bois ( ; February 23, 1868 – August 27, 1963) was an American sociologist, socialist, historian, and Pan-Africanist civil rights activist.
Born in Great Barrington, Massachusetts, Du Bois grew up in a relativel ...
into the formation of 1960s Ghana. Osagyefo Dr. Kwame Nkrumah, as he became known, played an instrumental part in the founding of the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
, and in establishing the Kwame Nkrumah Ideological Institute
The Kwame Nkrumah Ideological Institute (officially known as the Kwame Nkrumah Institute of Economics and Political Science or Winneba ideological Institute) was an educational body in Winneba, founded to promote socialism in Ghana as well as the ...
to teach his ideologies of communism
Communism () is a political sociology, sociopolitical, political philosophy, philosophical, and economic ideology, economic ideology within the history of socialism, socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a ...
and socialism
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
. His life achievements were recognised by Ghanaians during his centenary birthday celebration, and the day was instituted as a public holiday in Ghana ( Founders' Day).
Operation Cold Chop and aftermath
The government of Nkrumah was subsequently overthrown in a coup by theGhana Armed Forces
The Ghana Armed Forces (GAF) is the state military organisation of Ghana, consisting of the Army (GA), Navy (GN), and Ghana Air Force.
The Commander-in-Chief of the Ghana Armed Forces is the president of Ghana, who is also the supreme military ...
, codenamed "Operation Cold Chop". This occurred while Nkrumah was abroad with Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai ( zh, s=周恩来, p=Zhōu Ēnlái, w=Chou1 Ên1-lai2; 5 March 1898 – 8 January 1976) was a Chinese statesman, diplomat, and revolutionary who served as the first Premier of the People's Republic of China from September 1954 unti ...
in the People's Republic of China, on a mission to Hanoi
Hanoi ( ; ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Vietnam, second-most populous city of Vietnam. The name "Hanoi" translates to "inside the river" (Hanoi is bordered by the Red River (Asia), Red and Black River (Asia), Black Riv ...
, Vietnam, to help end the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
. The coup took place on 24 February 1966, led by Colonel Emmanuel Kwasi Kotoka and Brigadier Akwasi Afrifa. The National Liberation Council
The National Liberation Council (NLC) led the Ghanaian government from 24 February 1966 to 1 October 1969. The body emerged from a ''coup d'état'' against the Nkrumah government carried out jointly by the Ghana Police Service and Ghana Arme ...
was formed, chaired by Lieutenant General Joseph A. Ankrah.
A series of alternating military and civilian governments, often affected by economic instabilities, ruled Ghana from 1966, ending with the ascent to power of Flight Lieutenant Jerry John Rawlings
Jerry John Rawlings (born Jerry Rawlings John; 22 June 194712 November 2020) was a Ghanaian military officer, aviator, and politician who led the country briefly in 1979 and then from 1981 to 2001. He led a military junta until 1993 and then se ...
of the Provisional National Defence Council
The Provisional National Defence Council (PNDC) was the name of the Ghanaian government after the People's National Party's elected government was overthrown by Jerry Rawlings, the former head of the Armed Forces Revolutionary Council, in a coup ...
in 1981. These changes resulted in the suspension of the constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
in 1981 and the banning of political parties
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
. The economy soon declined, so Rawlings negotiated a structural adjustment plan, changing many old economic policies, and growth recovered during the mid-1980s. A new constitution restoring multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional ...
politics was promulgated in the presidential election of 1992, in which Rawlings was elected, and again in the general election of 1996.
In a tribal war in Northern Ghana
The Northern Region is one of the sixteen regions of Ghana. It is situated in the northern part of the country and ranks as the second largest of the sixteen regions. Before its division, it covered an area of 25,000 square kilometres, representi ...
in 1994, between the Konkomba and other ethnic groups, including the Nanumba, Dagomba and Gonja, between 1,000 and 2,000 people were killed and 150,000 people were displaced.
 After the 2000 general election,
After the 2000 general election, John Kufuor
John Kofi Agyekum Kufuor (born 8 December 1938) is a Ghanaian politician who served as the tenth president of Ghana from 2001 to 2009. He was the fifth chairperson of the African Union from 2007 to 2008 and his victory over John Atta Mills at t ...
of the New Patriotic Party
The New Patriotic Party (NPP; ) is a Centre-right politics, centre-right and Liberal conservatism, liberal-conservative political party in Ghana. Since the democratisation of Ghana in 1992, it has been one of the two dominant parties in Ghanaian ...
became president of Ghana on 7 January 2001 and was re-elected in 2004, thus also serving two terms (the term limit) as president of Ghana and marking the first time under the fourth republic that power was transferred from one legitimately elected head of state and head of government to another.
Nana Akufo-Addo
William Nana Addo Dankwa Akufo-Addo ( ; born 29 March 1944) is a Ghanaian politician who served as the 13th president of Ghana from January 2017 to January 2025. He previously served as Attorney General of Ghana, Attorney General from 2001 to 20 ...
, the ruling party candidate, was defeated in a very close 2008 general election by John Atta Mills
John Evans Fiifi Atta Mills (21 July 1944 – 24 July 2012) was a Ghanaian politician and legal scholar who served as the 11th president of Ghana from 2009 until his death in 2012. He was inaugurated on 7 January 2009, having defeated the govern ...
of the National Democratic Congress. Mills died of natural causes and was succeeded by Vice President John Mahama
John Dramani Mahama (; born 29 November 1958) is a Ghanaian politician who has been the 14th president of Ghana since January 2025. A member of the National Democratic Congress (Ghana), National Democratic Congress (NDC), he served as the 12th p ...
on 24 July 2012. Following the 2012 general election, Mahama became president in his own right, and Ghana was described as a "stable democracy". As a result of the 2016 general election, Nana Akufo-Addo
William Nana Addo Dankwa Akufo-Addo ( ; born 29 March 1944) is a Ghanaian politician who served as the 13th president of Ghana from January 2017 to January 2025. He previously served as Attorney General of Ghana, Attorney General from 2001 to 20 ...
became president on 7 January 2017. He was re-elected after a tightly contested election in 2020.
To combat deforestation, on 11 June 2021 Ghana inaugurated Green Ghana Day, with the aim of planting five million trees in a concentrated effort to preserve the country's rainforest cover.
Geography
Ghana is located on theGulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez i ...
, a few degrees north of the Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
. It spans an area of , and has an Atlantic coastline that stretches on the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
to its south. Dodi Island
Dodi Island is an island in Ghana, located off the shore of Lake Volta. It is a tourist destination and was a landing place for the Ghanaian former cruise ship Dodi Princess, which was used for cruises on Lake Volta, from 1991 until the vessel's ...
and Bobowasi Island
Bobowasi Island is an island in Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, ...
are near the south coast. It lies between latitudes 4°45'N and 11°N, and longitudes 1°15'E and 3°15'W. The prime meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrarily chosen meridian (geography), meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. On a spheroid, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian ...
passes through Ghana, specifically through Tema
Tema is a city on the Bight of Benin and Atlantic coast of Ghana. It is located east of the capital city; Accra, in the region of Greater Accra, and is the capital of the Tema Metropolitan District. As of 2013, Tema is the eleventh most p ...
. Ghana is geographically closer to the intersection of the Prime Meridian and the Equator than any other country, since this point, (0°, 0°), is located in the Atlantic Ocean approximately 614 km (382 mi) off the south-east coast of Ghana.
Grasslands mixed with south coastal shrublands and forests dominate Ghana, with forest extending northward from the coast and eastward for a maximum of about with locations for mining of industrial minerals and timber. Ghana is home to five terrestrial ecoregions: Eastern Guinean forests
The Eastern Guinean forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of West Africa.
Geography
The ecoregion includes the lowland forests extending from the Gulf of Guinea a few hundred kilometres inland, from western Côte d'Ivoire to ...
, Guinean forest–savanna mosaic
The Guinean forest-savanna, also known as the Guinean forest-savanna transition, is a distinctive ecological region located in West Africa. It stretches across several countries including Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, B ...
, West Sudanian savanna
The West Sudanian savanna is a tropical savanna ecoregion that extends across West Africa.
Geography
The ecoregion stretches east and west across West Africa, from the Atlantic coast of Senegal to the Mandara Mountains on Nigeria's eastern bor ...
, Central African mangroves
The Central African mangroves ecoregion consists of the largest area of mangrove swamp in Africa, located on the coasts of West Africa, mainly in Nigeria.
Location and description
These mangroves are found in fertile rivermouths and lagoons and ...
, and Guinean mangroves
The Guinean mangroves ( French: ''Mangroves guinéennes'', Portuguese: ''Mangais guineenses'') are a coastal ecoregion of mangrove swamps in rivers and estuaries near the ocean of West Africa from Senegal to Sierra Leone.
Location and descript ...
.
The White Volta
The White Volta or Nakambé ( French: ''Volta blanche'') is the headstream of the Volta River, Ghana's main waterway. The White Volta emerges in northern Burkina Faso, flows through Northern Ghana and empties into Lake Volta in Ghana. The White V ...
River and its tributary Black Volta
The Black Volta or Mouhoun ( French: ''Volta noire'') is a river that flows through Burkina Faso for approximately 1,352 km (840 mi) to the White Volta in Dagbon, Ghana, the upper end of Lake Volta. It is one of the three main parts ...
, flow south through Ghana to Lake Volta
Lake Volta (), the largest artificial reservoir in the world based on surface area, is contained behind the Akosombo Dam which generates a substantial amount of Ghana's electricity. It is completely within the country of Ghana and has a surface ...
, the world's third-largest reservoir by volume and largest by surface area, formed by the hydroelectric Akosombo Dam
The Akosombo Dam, also known as the Volta Dam, is a Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric dam on the Volta River in southeastern Ghana in the Akosombo gorge and part of the Volta River Authority. The construction of the dam flooded part of the Volta Riv ...
, completed in 1965. The Volta flows out of Lake Volta into the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez i ...
. The northernmost part of Ghana is Pulmakong and the southernmost part of Ghana is Cape Three Points
Cape Three Points is a small peninsula and a fishing village in the Ahanta West Municipal District, Ahanta West Municipal, Western Region, Ghana, Western Region of Ghana on the Atlantic Ocean. It forms the southernmost tip of Ghana. The part of th ...
.

Climate
The climate of Ghana istropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
, and there is wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the rainy season or monsoon season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least one month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used a ...
and dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
. Ghana sits at the intersection of three hydro-climatic zones. The eastern coastal belt is warm and comparatively dry, the south-west corner of Ghana is hot and humid
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
, and the north of Ghana is hot and dry.
Climate change in Ghana is having significant impacts on the people of Ghana. Increasing temperatures and changes in rainfall
Rain is a form of precipitation where water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. ...
, extreme weather
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual, severe weather, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weat ...
, drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
, wild fires, flood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
s and sea-level rise
The sea level has been rising from the end of the last ice age, which was around 20,000 years ago. Between 1901 and 2018, the average sea level rose by , with an increase of per year since the 1970s. This was faster than the sea level had e ...
are expected to negatively affect the country's infrastructure, hydropower production, food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
, water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Th ...
, and coastal and agricultural livelihood
A person's livelihood (derived from ''life-lode'', "way of life"; cf. OG ''lib-leit'') refers to their "means of securing the basic necessities (food, water, shelter and clothing) of life". Livelihood is defined as a set of activities essential ...
s such as farming and fisheries. Ghana's economy will be impacted by climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, due to its dependence on climate-sensitive sectors such as agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
, and forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests and woodlands for associated resources for human and Natural environment, environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and ...
. Diseases like malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after i ...
and cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
are predicted to increase due to changes in water conditions. Ghana signed the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (also called the Paris Accords or Paris Climate Accords) is an international treaty on climate change that was signed in 2016. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was ...
in 2016. Ghana aims to avoid 64 million metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
by 2030, compared to a business-as-usual scenario for 2020–2030. The country has committed to net zero
Global net-zero emissions is reached when greenhouse gas emissions and removals due to human activities are in balance. It is often called simply net zero. ''Emissions'' can refer to all greenhouse gases or only carbon dioxide (). Reaching net ze ...
by 2060.
Politics
Ghana is aunitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigr ...
presidential
Presidential may refer to:
* "Presidential" (song), a 2005 song by YoungBloodZ
* Presidential Airways (charter), an American charter airline based in Florida
* Presidential Airways (scheduled), an American passenger airline active in the 1980s
* ...
constitutional democracy
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of Legal entity, entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
Wh ...
with a parliamentary multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional ...
that is dominated by two parties—the National Democratic Congress (NDC) and the New Patriotic Party (NPP). Ghana alternated between civilian and military governments until January 1993, when the military government gave way to the Fourth Republic of Ghana after presidential
Presidential may refer to:
* "Presidential" (song), a 2005 song by YoungBloodZ
* Presidential Airways (charter), an American charter airline based in Florida
* Presidential Airways (scheduled), an American passenger airline active in the 1980s
* ...
and parliamentary elections
A general election is an electoral process to choose most or all members of a governing body at the same time. They are distinct from by-elections, which fill individual seats that have become vacant between general elections. General elections ...
in late 1992. The 1992 constitution of Ghana
The Constitution of Ghana is the supreme law of the Republic of Ghana. It was approved on 28 April 1992 through a national referendum after 92% support. It defines the fundamental political principles, establishing the structure, procedures, pow ...
divides powers among a commander-in-chief of the Ghana Armed Forces
The Ghana Armed Forces (GAF) is the state military organisation of Ghana, consisting of the Army (GA), Navy (GN), and Ghana Air Force.
The Commander-in-Chief of the Ghana Armed Forces is the president of Ghana, who is also the supreme military ...
(President of Ghana
The president of the Republic of Ghana is the elected head of state and head of government of Ghana, as well as commander-in-chief of the Ghana Armed Forces. The current president of Ghana is John Mahama, who won the 2024 presidential elect ...
), parliament (Parliament of Ghana
The Parliament of Ghana is the unicameral legislature of Ghana. It consists of 276 members, who are elected for four-year terms in single-seat Electoral district, constituencies using a first-past-the-post voting system.
History
Legislature, L ...
), cabinet ( Cabinet of Ghana), council of state ( Ghanaian Council of State), and an independent judiciary ( Judiciary of Ghana). The government is elected by universal suffrage
Universal suffrage or universal franchise ensures the right to vote for as many people bound by a government's laws as possible, as supported by the " one person, one vote" principle. For many, the term universal suffrage assumes the exclusion ...
after every four years."Government and Politics". A Country Study: Ghana
'' (La Verle Berry, editor).
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., serving as the library and research service for the United States Congress and the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It also administers Copyright law o ...
Federal Research Division
The Federal Research Division (FRD) is the research and analysis unit of the United States Library of Congress.
The Federal Research Division provides directed research and analysis on domestic and international subjects to agencies of the Unite ...
(November 1994). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
Lcweb2.loc.gov
Nana Akufo-Addo
William Nana Addo Dankwa Akufo-Addo ( ; born 29 March 1944) is a Ghanaian politician who served as the 13th president of Ghana from January 2017 to January 2025. He previously served as Attorney General of Ghana, Attorney General from 2001 to 20 ...
won the presidency in the general election in 2016, defeating incumbent John Mahama
John Dramani Mahama (; born 29 November 1958) is a Ghanaian politician who has been the 14th president of Ghana since January 2025. A member of the National Democratic Congress (Ghana), National Democratic Congress (NDC), he served as the 12th p ...
. He also won the 2020 election after the presidential election results were challenged at the Supreme Court by flagbearer of the NDC, John Mahama. Presidents are limited to two four-year terms in office.
The 2012 Fragile States Index
The Fragile States Index (FSI; formerly the Failed States Index) is an annual report mainly published and supported by the American think tank Fund for Peace. The FSI is also published by the American magazine ''Foreign Policy'' from 2005 to 201 ...
indicated that Ghana is ranked the 67th-least fragile state in the world and the fifth-least fragile state in Africa. Ghana ranked 112th out of 177 countries on the index. Ghana ranked as the 64th-least corrupt and politically corrupt country in the world out of all 174 countries ranked and ranked as the fifth-least corrupt and politically corrupt country in Africa out of 53 countries in the 2012 Transparency International Corruption Perception Index. Ghana was ranked seventh in Africa out of 53 countries in the 2012 Ibrahim Index of African Governance
The Ibrahim Index of African Governance (IIAG), established in 2007, provides an assessment of the quality of governance in African countries. The IIAG is compiled by 81 indicators and 265 variables from 54 data projects, coming from 47 independ ...
. The Ibrahim Index is a comprehensive measure of African government, based on variables which reflect the success with which governments deliver essential political goods to its citizens. According to 2023 V-Dem Democracy indices Ghana is ranked 67th electoral democracy worldwide and 10th electoral democracy in Africa.
Foreign relations
 Since independence, Ghana has been devoted to ideals of nonalignment and is a founding member of the
Since independence, Ghana has been devoted to ideals of nonalignment and is a founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
. Ghana favours international and regional political and economic co-operation, and is an active member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
and the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
.
Ghana has a strong relationship with the United States. Three recent U.S. presidents—Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
, George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician and businessman who was the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Bush family and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he i ...
, and Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
—and a Vice President—Kamala Harris
Kamala Devi Harris ( ; born October 20, 1964) is an American politician and attorney who served as the 49th vice president of the United States from 2021 to 2025 under President Joe Biden. She is the first female, first African American, and ...
—have made diplomatic trips to Ghana. Many Ghanaian diplomats and politicians hold positions in international organisations, including Ghanaian diplomat and former Secretary-General of the United Nations
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or UNSECGEN) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the United Nations System#Six principal organs, six principal organs of ...
Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan (8 April 193818 August 2018) was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founder a ...
, International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC) is an intergovernmental organization and International court, international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute ...
Judge Akua Kuenyehia
Akua Kuenyehia (born 1947) is a Ghanaian academic and lawyer who served as judge of the International Criminal Court (ICC) from 2003 to 2015. She also served as First Vice-president of the Court. She was one of the three female African judges at t ...
, as well as former President Jerry John Rawlings
Jerry John Rawlings (born Jerry Rawlings John; 22 June 194712 November 2020) was a Ghanaian military officer, aviator, and politician who led the country briefly in 1979 and then from 1981 to 2001. He led a military junta until 1993 and then se ...
and former President John Agyekum Kufuor
John Kofi Agyekum Kufuor (born 8 December 1938) is a Ghanaian politician who served as the tenth president of Ghana from 2001 to 2009. He was the fifth chairperson of the African Union from 2007 to 2008 and his victory over John Atta Mills at t ...
, who both served as diplomats of the United Nations. The most notable among diplomats from Ghana is the Late Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan (8 April 193818 August 2018) was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founder a ...
, who served as the 7th Secretary-General of the United Nations.
In September 2010, President John Atta Mills
John Evans Fiifi Atta Mills (21 July 1944 – 24 July 2012) was a Ghanaian politician and legal scholar who served as the 11th president of Ghana from 2009 until his death in 2012. He was inaugurated on 7 January 2009, having defeated the govern ...
visited China on an official visit. Mills and China's former President Hu Jintao
Hu Jintao (born 21 December 1942) is a Chinese retired politician who served as the general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 2002 to 2012, the president of China from 2003 to 2013, and chairman of the Central Military Comm ...
marked the 50th anniversary of diplomatic ties between the two nations, at the Great Hall of the People
The Great Hall of the People is a state building situated to the west of Tiananmen Square in Beijing. It is used for legislative and ceremonial activities by the government of the People's Republic of China. The People's Great Hall functions as ...
. China reciprocated with an official visit in November 2011, by the vice-chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress of China
The Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (NPCSC) is the permanent body of the National People's Congress (NPC), the national legislature of the People's Republic of China. It exercises the powers of the NPC when it is not in s ...
, Zhou Tienong who visited Ghana and met with Ghana's president John Mahama
John Dramani Mahama (; born 29 November 1958) is a Ghanaian politician who has been the 14th president of Ghana since January 2025. A member of the National Democratic Congress (Ghana), National Democratic Congress (NDC), he served as the 12th p ...
. China recently became one of the top investing countries of Ghana, which predominantly focus on infrastructure, natural resources, and the manufacturing sector
In macroeconomics, the secondary sector of the economy is an economic sector in the three-sector theory that describes the role of manufacturing. It encompasses industries that produce a finished, usable product or are involved in construction ...
, have promoted economic growth, job creation, and technology transfer in Ghana. However, concerns regarding the sustainability of Chinese-financed projects, environmental impacts, and the lack of transparency in their investments call for a careful assessment of these collaborations. Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad
Mahmoud Ahmadinejad (born Mahmoud Sabbaghian on 28 October 1956) is an Iranian Iranian principlists, principlist and Iranian nationalism, nationalist politician who served as the sixth president of Iran from 2005 to 2013. He is currently a mem ...
met with Mahama in 2013 to hold discussions on strengthening the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
and also co–chair a bilateral meeting between Ghana and Iran at the Ghanaian presidential palace
A presidential palace is the official residence of the president in some countries. Some presidential palaces were once the official residences to monarchs in former monarchies that were preserved during those states' transition into republics. ...
Flagstaff House Flagstaff House may refer to:
* Teen Murti Bhavan - earlier residence of Commander-in-Chief, India and later the residence of the first Prime Minister of India, Jawaharlal Nehru
* Flagstaff House, Hong Kong - earlier residence of the British Forces ...
.
The Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
(SDG) were integrated into Ghana's development agenda and the budget. According to reports, the SDGs were implemented through a decentralized planning approach. This allows for stakeholders' participation, such as in UN agencies, traditional leaders, civil society organizations, academia, and others. The 17 SDGs are a global call to action to end poverty among others, and the UN and its partners in the country are working towards achieving them. According to the President Nana Akufo-Addo
William Nana Addo Dankwa Akufo-Addo ( ; born 29 March 1944) is a Ghanaian politician who served as the 13th president of Ghana from January 2017 to January 2025. He previously served as Attorney General of Ghana, Attorney General from 2001 to 20 ...
, Ghana was "the first Sub-Saharan African country to achieve the goal of halving poverty, as contained in Goal 1 of the Millennium Development Goals
In the United Nations, the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 created following the Millennium Summit, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. These w ...
".
Military
In 1957, theGhana Armed Forces
The Ghana Armed Forces (GAF) is the state military organisation of Ghana, consisting of the Army (GA), Navy (GN), and Ghana Air Force.
The Commander-in-Chief of the Ghana Armed Forces is the president of Ghana, who is also the supreme military ...
(GAF) consisted of its headquarters, support services, three battalions of infantry and a reconnaissance squadron with armoured vehicles.Kilford, Christopher R. (2010)''The Other Cold War: Canada's Military Assistance to the Developing World 1945–75''
,
Kingston
Kingston may refer to:
Places
* List of places called Kingston, including the six most populated:
** Kingston, Jamaica
** Kingston upon Hull, England
** City of Kingston, Victoria, Australia
** Kingston, Ontario, Canada
** Kingston upon Thames, ...
, Ontario: Canadian Defence Academy Press, p. 138, . President Nkrumah aimed at rapidly expanding the GAF to support the United States of Africa
The United States of Africa is a concept of a federation of some or all of the 54 sovereign states and two disputed states on the continent of Africa. The concept takes its origin from Marcus Garvey's 1924 poem "Hail, United States of Africa". ...
ambitions. Thus, in 1961, 4th and 5th Battalions were established, and in 1964 6th Battalion was established, from a parachute
A parachute is a device designed to slow an object's descent through an atmosphere by creating Drag (physics), drag or aerodynamic Lift (force), lift. It is primarily used to safely support people exiting aircraft at height, but also serves va ...
airborne unit
Airborne forces are ground combat units carried by aircraft and airdropped into battle zones, typically by parachute drop. Parachute-qualified infantry and support personnel serving in airborne units are also known as paratroopers.
The main adv ...
originally raised in 1963. Today, Ghana is a regional power
In international relations, regional power, since the late 20thcentury, has been used for a sovereign state that exercises significant power within its geographical region.Joachim Betz, Ian Taylor"The Rise of (New) Regional Powers in Asia, ...
and regional hegemon. In his book '' Shake Hands with the Devil'', Canadian Forces
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; , FAC) are the unified Military, military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air commands referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army and the Royal Canadian Air Force. Under the ''National Defenc ...
commander Roméo Dallaire
Roméo Antonius Dallaire (born June 25, 1946) is a retired Canadian politician and military officer who was a senator from Quebec from 2005 to 2014, and a lieutenant-general in the Canadian Armed Forces. He notably was the force commander of U ...
highly rated the GAF soldiers and military personnel.
The military operation
A military operation (op) is the coordinated military actions of a state, or a non-state actor, in response to a developing situation. These actions are designed as a military plan to resolve the situation in the state or actor's favor. Operati ...
s and military doctrine
Military doctrine is the expression of how military forces contribute to campaigns, major operations, battles, and engagements. A military doctrine outlines what military means should be used, how forces should be structured, where forces shou ...
of the GAF are conceptualised in the constitution, Ghana's Law on Armed Force Military Strategy, and Kofi Annan International Peacekeeping Training Centre agreements to which GAF is attestator. GAF military operations are executed under the auspices and imperium of the Ministry of Defence
A ministry of defence or defense (see American and British English spelling differences#-ce.2C -se, spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is the part of a government responsible for matters of defence and Mi ...
. Although Ghana is relatively peaceful and is often considered being one of the least violent countries in the region, Ghana has experienced political violence in the past and 2017 has thus far seen an upward trend in incidents motivated by political grievances.
Law enforcement
 The
The Ghana Police Service
The Ghana Police Service (GPS) is the main law enforcement agency of Ghana. The service is under the control of the Ghanaian Ministry of the Interior, and employs over 30,000 officers across its 651 stations.
Organisational structure
The Ghana P ...
and the Criminal Investigation Department
The Criminal Investigation Department (CID) is the branch of a police force to which most plainclothes criminal investigation, detectives belong in the United Kingdom and many Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth nations. A force's CID is disti ...
are the main law enforcement agencies, responsible for the detection of crime, maintenance of law and order and the maintenance of internal peace and security. The Ghana Police Service has eleven specialised police units, including a Militarized police
The militarization of police (paramilitarization of police in some media) is the use of military equipment and tactics by law enforcement officers. This includes the use of armored personnel carriers (APCs), assault rifles, submachine guns, ...
Rapid deployment force
A rapid reaction force / rapid response force (RRF), quick reaction force / quick response force (QRF), immediate reaction force (IRF), rapid deployment force (RDF), or quick maneuver force (QMF) is a military or law enforcement unit capable of ...
and Ghana Police Service#Marine Police Unit, Marine Police Unit. The Ghana Police Service operates in 12 divisions: ten covering the regions of Ghana, one assigned specifically to the seaport and industrial hub of Tema
Tema is a city on the Bight of Benin and Atlantic coast of Ghana. It is located east of the capital city; Accra, in the region of Greater Accra, and is the capital of the Tema Metropolitan District. As of 2013, Tema is the eleventh most p ...
, and the twelfth being the Railways, Ports and Harbours Division. The Ghana Police Service's Marine Police Unit and Division handles issues that arise from the country's offshore oil and gas industry.
The Ghana Prisons Service and the sub-division Borstal Institute for Juveniles administers incarceration. Ghana retains and exercises the death penalty for treason, corruption, robbery, piracy, drug trafficking, rape, and homicide. The new sustainable development goals adopted by the United Nations call for the international community to come together to promote the rule of law; support equal access to justice for all; reduce corruption; and develop effective, accountable, and transparent institutions at all levels. Ghana is used as a key narcotics industry transshipment point by traffickers, usually from South America as well as some from other African nations. In 2013, the UN chief of the Office on Drugs and Crime stated that "West Africa is completely weak in terms of border control and the big drug cartels from Colombia and Latin America have chosen Africa as a way to reach Europe." There is not a wide or popular knowledge about the narcotics industry and intercepted narcotics within Ghana, since it is an black market, underground economy. The social context within which narcotic trafficking, storage, transportation, and repacking systems exist in Ghana and the state's location along the Gulf of Guinea makes Ghana an attractive country for the narcotics business. The Narcotics Control Board (Ghana), Narcotics Control Board has impounded container ships at the Sekondi Naval Base in the Takoradi Harbour. These ships were carrying thousands of kilograms of cocaine, with a street value running into billions of Ghanaian cedi, Ghana cedis. However, drug seizures saw a decline in 2011. Drug cartels are using new methods in narcotics production and narcotics exportation, to avoid Ghanaian security agencies. Underdeveloped institutions, porous open borders, and the existence of established smuggling organisations contribute to Ghana's position in the narcotics industry. President Mills initiated ongoing efforts to reduce the role of airports in Ghana's drug trade.
Ghana is used as a key narcotics industry transshipment point by traffickers, usually from South America as well as some from other African nations. In 2013, the UN chief of the Office on Drugs and Crime stated that "West Africa is completely weak in terms of border control and the big drug cartels from Colombia and Latin America have chosen Africa as a way to reach Europe." There is not a wide or popular knowledge about the narcotics industry and intercepted narcotics within Ghana, since it is an black market, underground economy. The social context within which narcotic trafficking, storage, transportation, and repacking systems exist in Ghana and the state's location along the Gulf of Guinea makes Ghana an attractive country for the narcotics business. The Narcotics Control Board (Ghana), Narcotics Control Board has impounded container ships at the Sekondi Naval Base in the Takoradi Harbour. These ships were carrying thousands of kilograms of cocaine, with a street value running into billions of Ghanaian cedi, Ghana cedis. However, drug seizures saw a decline in 2011. Drug cartels are using new methods in narcotics production and narcotics exportation, to avoid Ghanaian security agencies. Underdeveloped institutions, porous open borders, and the existence of established smuggling organisations contribute to Ghana's position in the narcotics industry. President Mills initiated ongoing efforts to reduce the role of airports in Ghana's drug trade.
Human rights
Homosexuality, Homosexual acts are prohibited by law in Ghana. According to a 2013 survey by the Pew Research Center, 96% of Ghanaians believe that homosexuality should not be accepted by society."The Global Divide on Homosexuality."Pew Research Center. 4 June 2013. Sometimes elderly women in Ghana are accused of witchcraft, particularly in rural Ghana. Issues of witchcraft mainly remain as speculations based on superstitions within families. In some parts of northern Ghana, there exist what are called witch camps. These are said to house a total of around 1,000 people accused of witchcraft. The Ghanaian government has announced that it intends to close the camps.
Economy
Group of 24
The Intergovernmental Group of Twenty-Four on International Monetary Affairs and Development, or The Group of 24 (G-24) was established in 1971 as a chapter of the Group of 77 in order to help coordinate the positions of developing countries on ...
member and Sub-Saharan African country South Africa, which is a newly industrialised country.
Ghana's economy has ties to the Renminbi, Chinese yuan renminbi along with Ghana's vast gold reserves. In 2013, the Bank of Ghana began circulating the renminbi throughout Ghanaian state-owned banks and to the Ghana public as hard currency along with the national Ghanaian cedi for second national trade currency.
Between 2012 and 2013, 38% of rural dwellers were experiencing poverty whereas only 11% of urban dwellers were. Urban areas hold greater opportunity for employment, particularly in informal trade, while nearly all (94 percent) of "rural poor households" participate in the agricultural sector.
The Volta River Authority and the Ghana National Petroleum Corporation, both state-owned, are the two major electricity producers. The Akosombo Dam
The Akosombo Dam, also known as the Volta Dam, is a Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric dam on the Volta River in southeastern Ghana in the Akosombo gorge and part of the Volta River Authority. The construction of the dam flooded part of the Volta Riv ...
, built on the Volta River in 1965, along with the Bui Dam, the Kpong Dam and several other hydroelectric dams, provide hydropower. In addition, the government sought to Nuclear power in Ghana, build the second nuclear power plant in Africa.
The Ghana Stock Exchange is the fifth largest on continental Africa and 3rd largest in Sub-Saharan Africa with a Market capitalization, market capitalisation of Ghana Cedi, GH¢ 57.2 billion or Renminbi, CN¥180.4 billion in 2012 with the South Africa JSE Limited as first. The Ghana Stock Exchange was the second best performing stock exchange in Sub-Saharan Africa in 2013.
Ghana produces high-quality Cocoa bean, cocoa. It is the second largest producer of cocoa globally and its International Cocoa Organization, ICCO membership helps in its international cocoa trade. Ghana is classified as a middle-income country. Tertiary sector of the economy, Services account for 50% of GDP, followed by manufacturing (24.1%), Primary sector of the economy, extractive industries (5%), and taxes (20.9%).
Ghana's economy is characterized by a growing manufacturing sector and the export of digital technology products. The country is also engaged in the assembly and export of automobiles and ships. Additionally, Ghana's economy benefits from a diverse range of resource-rich exports, including industrial minerals and agricultural products, with cocoa being a primary commodity. The nation is also a significant producer and exporter of petroleum and natural gas.
The information and communications technology (ICT) sector plays a crucial role in Ghana's industrial landscape, with companies such as Rlg Communications, a state-affiliated digital technology corporation, leading in the production of tablet computers, smartphones, and various consumer electronics.
Urban electric cars have been manufactured in Ghana since 2014.
Ghana announced plans to issue government debt by way of social and green bonds in autumn of 2021, making it the first African country to do so. The country, which was planning to borrow up to $5 billion in international markets, would use the proceeds from these sustainable bonds to refinance debt used for social and environmental projects and pay for educational or health. Only a few other nations have sold them so far, including Chile and Ecuador. The country will use the proceeds to forge ahead with a free secondary-school initiative started in 2017 among other programs, despite having recorded its lowest economic growth rate in 37 years in 2020.
Ghana produces and exports hydrocarbons such as sweet crude oil and natural gas. The 100%-state-owned filling station company, Ghana Oil Company, is the number one petroleum and gas filling station, and the 100%-state-owned state oil company Ghana National Petroleum Corporation oversees hydrocarbon exploration and production of petroleum and natural gas reserves. Ghana aims to further increase the output of oil to per day and gas to per day.Clark, Nancy L. "Petroleum Exploration"''A Country Study: Ghana''
(La Verle Berry, editor).
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., serving as the library and research service for the United States Congress and the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It also administers Copyright law o ...
Federal Research Division
The Federal Research Division (FRD) is the research and analysis unit of the United States Library of Congress.
The Federal Research Division provides directed research and analysis on domestic and international subjects to agencies of the Unite ...
(November 1994). ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
.'Lcweb2.loc.gov
The Jubilee Oil Field, which contains up to of sweet crude oil, was discovered in 2007. Ghana is believed to have up to to of petroleum in reserves, which is the fifth-largest in Africa and the 21st-to-25th-List of countries by proven oil reserves, largest proven reserves in the world. It also has up to of natural gas in reserves. The government has drawn up plans to Nationalization, nationalise petroleum and natural gas reserves to increase government revenue. In 2015, Ghana produced 88 metric tonnes of gold as per the our world in data report. As of 2019, Ghana was the 7th largest producer of gold in the world, producing ~140 tonnes that year. This record saw Ghana surpass South Africa in output for the first time, making Ghana the largest gold producer in Africa. In addition to gold, Ghana exports silver, timber, diamonds, bauxite, and manganese, and has other mineral deposits. Ghana ranks 9th in the world in diamond export and reserve size. The government has drawn up plans to Nationalization, nationalize mining industry to increase government revenue. "Shortages" of electricity in 2015 and 2016 led to dumsor ("persistent, irregular and unpredictable" electric power outages), increasing the interest in renewables. As of 2019, there is a surplus of electricity. The Judiciary of Ghana, judicial system of Ghana deals with corruption, economic malpractice and lack of economic transparency. According to Transparency International's Corruption Perceptions Index of 2018, out of 180 countries, Ghana was ranked 78th, with a score of 41 on a scale where a 0–9 score means highly corrupt, and a 90–100 score means very clean. This was based on perceived levels of public sector corruption.
Science and technology
Ghana launched a cellular mobile network in 1992. It was later connected to the Internet and introduced ADSL broadband services. Ghana was ranked 99th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024. The Ghana Space Science and Technology Centre (GSSTC) and Ghana Space Agency (GhsA) oversee space exploration and space programmes. GSSTC and GhsA worked to have a national security Earth observation satellite, observational satellite launched into orbit in 2015. Ghana's annual space exploration expenditure has been 1% of its GDP, to support research in science and technology. In 2012, Ghana was elected to chair the Commission on Science and Technology for Sustainable Development in the South (Comsats); Ghana has a joint effort in space exploration with the South African National Space Agency.Tourism
In 2011, tourists visiting Ghana numbered 1,087,000, with arrivals including South Americans, Asians, Europeans, and North Americans. Among the attractions and tourist destinations are waterfalls such as Kintampo waterfalls and the largest waterfall in west Africa, Wli waterfalls, the coastal palm-lined sandy beaches, caves, mountains, rivers, and reservoirs and lakes such as Lake Bosumtwi and the largest human-made lake in the world by surface area,Lake Volta
Lake Volta (), the largest artificial reservoir in the world based on surface area, is contained behind the Akosombo Dam which generates a substantial amount of Ghana's electricity. It is completely within the country of Ghana and has a surface ...
, dozens of List of castles in Ghana, forts and castles, World Heritage Sites, nature reserves and national parks. Notable castles are Cape Coast Castle Museum, Cape Coast Castle and the Elmina Castle
Elmina Castle was erected by the Portuguese in 1482 as Castelo de São Jorge da Mina (''St. George of the Mine Castle''), also known as ''Castelo da Mina'' or simply ''Mina'' (or '' Feitoria da Mina''), in present-day Elmina, Ghana, formerly t ...
. Castles mark where blood was shed in the slave trade and preserve and promote the African heritage stolen and destroyed through the slave trade. The World Heritage Site, World Heritage Convention of UNESCO named Ghana's castles and forts as World Heritage Monuments, based on the criterion: "The Castles and Forts of Ghana shaped not only Ghana's history but that of the world over four centuries as the focus of first the gold trade and then the slave trade. They are a significant and emotive symbol of European–African encounters and of the starting point of the African Diaspora."
The World Economic Forum statistics in 2010 showed that out of the world's favourite tourist destinations, Ghana was ranked 108th out of 139 countries. The country had moved two places up from the 2009 rankings. In 2011, ''Forbes'' magazine published that Ghana was ranked the 11th most friendly country in the world. The assertion was based on a survey in 2010 of a cross-section of travellers. Of all the African countries that were included in the survey, Ghana ranked highest. Tourism is the fourth highest earner of foreign exchange for the country. In 2024, Ghana ranked as the Global Peace Index, 55th most peaceful country in the world.
Up and down the coastline, surfing spots have been identified and cultivated by locals and internationals. Surfers have made trips to the country to sample the waves. Surfers carried their boards amid Traditional fishing boat, traditional fishing vessels.
According to Destination Pride—a data-driven search platform used to visualize the world's LGBTQ+ laws, rights and social sentiment—Ghana's Pride score is 22 (out of 100).
Demographics
, the United Nations reports Ghana has a population of 34,581,288. , around 29% of the population is under the age of 15, while persons aged 15–64 make up 57.8% of the population. The 2010 census reported that the largest ethnic groups are the Akan (47.3%), the Mole-Dagbani (18.5%), the Ewe (13.9%), the Ga-Dangme (7.4%), the Gurma (5.7%) and the Guan (3.7%). , the United Nations reports the median age of Ghanaian citizens is 21 years old. Ghana contributes 0.42% to the total world population. With Immigration to Ghana, recent legal immigration of skilled workers who possess Ghana Cards, there is a small population of Chinese, Malaysian, Indian, Middle Eastern and European nationals. In 2010, the Ghana Immigration Service reported many economic migrants and Illegal immigration to Ghana, Illegal immigrants inhabiting Ghana: 14.6% (or 3.1 million) of Ghana's 2010 population (predominantly Nigerians, Burkinabe citizens, Togolese citizens, and Malian citizens). In 1969, under the "Ghana Aliens Compliance Order" enacted by then Prime Minister Kofi Abrefa Busia, the Border Guard Unit deported more than 3,000,000 aliens and illegal immigrants in three months as they made up 20% of the population at the time. In 2013, there was a mass deportation of illegal miners, more than 4,000 of whom were Chinese nationals.Languages
English is the official language of Ghana. Additionally, there are eleven languages that have the status of government-sponsored languages: *Akan languages (Asante dialect, Asante Twi, Akuapem Twi, Fante dialect, Fante, Bono language, Bono which have a high degree of mutual intelligibility, and Nzema language, Nzema, which is less intelligible with the above) *Dangme language, Dangme *Ewe language, Ewe *Ga language, Ga *Gua language, Guan *Kasena language, Kasem *Mole–Dagbani languages (Dagaare and Dagbani language, Dagbanli) Of these, Asante Twi is the most widely spoken. Because Ghana is surrounded by List of countries and territories where French is an official language, French-speaking countries, French is widely taught in schools and used for commercial and international economic exchanges. Since 2005, Ghana has been an associate member of the , the global organisation that unites French-speaking countries (84 nations on six continents). In 2005, more than 350,000 Ghanaian children studied French in schools. Since then, its status has been progressively updated to a mandatory language in every junior high school, and it is in the process of becoming an official language. Ghanaian Pidgin English, also known as Kru English (or in Akan, ''kroo brofo''), is a variety of West African Pidgin English spoken in Accra and in the southern towns.Magnus Huber, ''Ghanaian Pidgin English in its West African Context'' (1999), page 139 It can be divided into two varieties, referred to as "uneducated" or "non-institutionalized" pidgin and "educated" or "institutionalized" pidgin, the former associated with uneducated or illiterate people and the latter acquired and used in institutions such as universities.Huber (1999), pp. 138–153Religion
Christianity is the largest religion in Ghana, with 71.3% of the population being members of various Christian denominations as of the 2021 census. Islam is practised by 20% of the total population. According to a 2012 report by Pew Research, 51% of Muslims are followers of Sunni Islam, while approximately 16% belong to the Ahmadiyya movement and around 8% identify with Shia Islam, while the remainder are non-denominational Muslims.Owusu-Ansah (1994), "Religion and Society". There is "no significant link between ethnicity and religion in Ghana". Ghana has around 150,000 Jehovah's Witnesses.Universal health care and life expectancy
. Retrieved 24 June 2013. In 2020, the WHO announced Ghana became the second country in the WHO African Region to attain regulatory system "maturity level 3", the second-highest in the four-tiered WHO classification of National medicines regulatory systems. Life expectancy at birth in 2021 was 68.6 for a female and 63.7 for a male. In 2013, infant mortality was to 39 per 1,000 live births. Sources vary on life expectancy at birth; the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated 62 years for men and 64 years for women born in 2016. The fertility rate declined from 3.99 (2000) to 3.28 (2010) with 2.78 in urban region and 3.94 in rural region. The United Nations reports a fertility decline from 6.95 (1970) to 4.82 (2000) to 3.93 live births per woman in 2017. , the HIV/AIDS prevalence was estimated at 1.40% among adults aged 15–49.
Education
 The education system is divided into three parts: basic education, secondary cycle, and tertiary education. "Basic education" lasts 11 years (ages 4‒15). It is divided into kindergarten (two years), primary school (two modules of three years) and junior high (three years). Junior high school ends with the Basic Education Certificate Examination. Once certified, the pupil can proceed to the secondary cycle. Hence, the pupil has the choice between general education (offered by the senior high school) and vocational education (offered by the technical senior high school or the technical and vocational institutes). Senior high school lasts 3 years and leads to the West African Senior School Certificate Examination, which is a prerequisite for enrollment in a university bachelor's degree programme. Polytechnics are open to vocational students.
A bachelor's degree requires four years of study. It can be followed by a one- or two-year master's degree programme, which can be followed by a PhD programme of at least three years. A polytechnic programme lasts two or three years. Ghana possesses colleges of education. Some of the universities are the University of Ghana, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, and University of Cape Coast.
There are more than 95% of children in school. The female and male ages 15–24 years literacy rate was 81% in 2010, with males at 82%, and females at 80%. An education system annually attracts foreign students particularly in the university sector.
Ghana has a free education six-year primary school education system beginning at age 6. The government largely funds basic education comprising public primary schools and public junior high schools. Senior high schools were subsidised by the government until September 2017/2018 academic year that senior high education became free. At the higher education level, the government funds more than 80% of resources provided to public universities, polytechnics and teacher training colleges. As part of the Free Compulsory Universal Basic Education, Fcube, the government supplies all basic education schools with all their textbooks and other educational supplies, like exercise books. Senior high schools are provided with all their textbook requirements by the government. Private schools acquire their educational material from private suppliers.
The education system is divided into three parts: basic education, secondary cycle, and tertiary education. "Basic education" lasts 11 years (ages 4‒15). It is divided into kindergarten (two years), primary school (two modules of three years) and junior high (three years). Junior high school ends with the Basic Education Certificate Examination. Once certified, the pupil can proceed to the secondary cycle. Hence, the pupil has the choice between general education (offered by the senior high school) and vocational education (offered by the technical senior high school or the technical and vocational institutes). Senior high school lasts 3 years and leads to the West African Senior School Certificate Examination, which is a prerequisite for enrollment in a university bachelor's degree programme. Polytechnics are open to vocational students.
A bachelor's degree requires four years of study. It can be followed by a one- or two-year master's degree programme, which can be followed by a PhD programme of at least three years. A polytechnic programme lasts two or three years. Ghana possesses colleges of education. Some of the universities are the University of Ghana, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, and University of Cape Coast.
There are more than 95% of children in school. The female and male ages 15–24 years literacy rate was 81% in 2010, with males at 82%, and females at 80%. An education system annually attracts foreign students particularly in the university sector.
Ghana has a free education six-year primary school education system beginning at age 6. The government largely funds basic education comprising public primary schools and public junior high schools. Senior high schools were subsidised by the government until September 2017/2018 academic year that senior high education became free. At the higher education level, the government funds more than 80% of resources provided to public universities, polytechnics and teacher training colleges. As part of the Free Compulsory Universal Basic Education, Fcube, the government supplies all basic education schools with all their textbooks and other educational supplies, like exercise books. Senior high schools are provided with all their textbook requirements by the government. Private schools acquire their educational material from private suppliers.
Culture
Food and drink
Ghanaian cuisine includes an assortment of soups and stews with varied seafoods; most Ghanaian soups are prepared with vegetables, meat, poultry or fish. Fish is important in the diet with tilapia, roasted and fried whitebait, smoked fish and crayfish, all being common components of Ghanaian dishes. Banku (dish), Banku (akple) is a common starchy food made from ground corn (maize), and cornmeal based staples kɔmi (kenkey) and banku (akple) are usually accompanied by some form of fried fish (chinam) or grilled tilapia and a very spicy condiment made from raw red and green chillies, onions and tomatoes (pepper sauce). Banku and tilapia is a combo served in most restaurants. Fufu is the most common exported Ghanaian dish and is a delicacy across the African diaspora. Rice is an established staple meal across the country, with various rice-based dishes serving as breakfast, lunch and dinner, the main variants are waakye, plain rice and stew (either kontomire or tomato gravy), fried rice and jollof rice.Literature
Clothing
 During the 13th century, Ghanaians developed their unique art of ''Adinkra symbols, adinkra'' printing. Hand-printed and hand-embroidered adinkra clothes were made and used exclusively by royalty for devotional ceremonies. Each of the motifs that make up the Text corpus, corpus of adinkra symbolism has a name and meaning derived from a proverb, a historical event, human attitude, ethology, plant life-form, or shapes of inanimate and man-made objects. The meanings of the motifs may be categorised into aesthetics, ethics, human relations, and concepts. The Adinkra symbols have a decorative function as tattoos but also represent objects that encapsulate evocative messages that convey traditional wisdom, aspects of life, or the environment. There are many symbols with distinct meanings, often linked with proverbs. In the words of Kwame Anthony Appiah, Anthony Appiah, they were one of the means in a pre-literate society for "supporting the transmission of a complex and nuanced body of practice and belief".
During the 13th century, Ghanaians developed their unique art of ''Adinkra symbols, adinkra'' printing. Hand-printed and hand-embroidered adinkra clothes were made and used exclusively by royalty for devotional ceremonies. Each of the motifs that make up the Text corpus, corpus of adinkra symbolism has a name and meaning derived from a proverb, a historical event, human attitude, ethology, plant life-form, or shapes of inanimate and man-made objects. The meanings of the motifs may be categorised into aesthetics, ethics, human relations, and concepts. The Adinkra symbols have a decorative function as tattoos but also represent objects that encapsulate evocative messages that convey traditional wisdom, aspects of life, or the environment. There are many symbols with distinct meanings, often linked with proverbs. In the words of Kwame Anthony Appiah, Anthony Appiah, they were one of the means in a pre-literate society for "supporting the transmission of a complex and nuanced body of practice and belief". Along with the ''adinkra cloth,'' Ghanaians use many cloth fabrics for their traditional attire. The different ethnic groups have their own individual cloth. The most well known is the Kente cloth. Kente is a very important national costume and clothing, and these clothes are used to make traditional and modern Kente attire. Different symbols and different colours mean different things. Kente cloth, Kente is the most famous of all the Ghanaian clothes. Kente is a ceremonial cloth hand-woven on a horizontal Loom, treadle loom and strips measuring about 4 inches wide are sewn together into larger pieces of cloths. Cloths come in various colours, sizes and designs and are worn during very important social and religious occasions. In a cultural context, kente is more important than just a cloth as it is a visual representation of history and also a form of written language through weaving. The term kente has its roots in the Akan word ''kɛntɛn'' which means a basket and the first kente weavers used raffia fibres to weave cloths that looked like kenten (a basket); and thus were referred to as ''kenten ntoma''; meaning basket cloth. The original Akan name of the cloth was ''nsaduaso'' or ''nwontoma'', meaning "a cloth hand-woven on a loom"; however, "kente" is the most frequently used term today.
Kente is also woven by the Ewe people (Ewe Kente) in the Volta Region. The main weaving centres are Agortime area and Agbozume. Agbozume has a vibrant kente market attracting patrons from all over west Africa and the diaspora.
Contemporary Ghanaian fashion includes traditional and modern styles and fabrics and has made its way into the African and global fashion scene. The cloth known as African wax prints, African print fabric was created out of Dutch wax textiles. It is believed that in the late 19th century, Dutch ships on their way to Asia stocked with machine-made textiles that mimicked Indonesian batik stopped at many West African ports on the way. The fabrics did not do well in Asia. However, in West Africa—mainly Ghana where there was an already established market for cloths and textiles—the client base grew and it was changed to include local and traditional designs, colours and patterns to cater to the taste of the new consumers. Today outside of Africa it is called "Ankara", and it has a client base well beyond Ghana and Africa as a whole. It is popular among Caribbean peoples and African Americans; celebrities such as Solange Knowles and her sister Beyoncé have been seen wearing African print attire. Many designers from countries in North America and Europe are now using African prints, and they have gained a global interest. British luxury fashion house Burberry created a collection around Ghanaian styles. American musician Gwen Stefani has repeatedly incorporated African prints into her clothing line and can often be seen wearing it. Internationally acclaimed Ghanaian-British designer Ozwald Boateng introduced African print suits in his 2012 collection.
Along with the ''adinkra cloth,'' Ghanaians use many cloth fabrics for their traditional attire. The different ethnic groups have their own individual cloth. The most well known is the Kente cloth. Kente is a very important national costume and clothing, and these clothes are used to make traditional and modern Kente attire. Different symbols and different colours mean different things. Kente cloth, Kente is the most famous of all the Ghanaian clothes. Kente is a ceremonial cloth hand-woven on a horizontal Loom, treadle loom and strips measuring about 4 inches wide are sewn together into larger pieces of cloths. Cloths come in various colours, sizes and designs and are worn during very important social and religious occasions. In a cultural context, kente is more important than just a cloth as it is a visual representation of history and also a form of written language through weaving. The term kente has its roots in the Akan word ''kɛntɛn'' which means a basket and the first kente weavers used raffia fibres to weave cloths that looked like kenten (a basket); and thus were referred to as ''kenten ntoma''; meaning basket cloth. The original Akan name of the cloth was ''nsaduaso'' or ''nwontoma'', meaning "a cloth hand-woven on a loom"; however, "kente" is the most frequently used term today.
Kente is also woven by the Ewe people (Ewe Kente) in the Volta Region. The main weaving centres are Agortime area and Agbozume. Agbozume has a vibrant kente market attracting patrons from all over west Africa and the diaspora.
Contemporary Ghanaian fashion includes traditional and modern styles and fabrics and has made its way into the African and global fashion scene. The cloth known as African wax prints, African print fabric was created out of Dutch wax textiles. It is believed that in the late 19th century, Dutch ships on their way to Asia stocked with machine-made textiles that mimicked Indonesian batik stopped at many West African ports on the way. The fabrics did not do well in Asia. However, in West Africa—mainly Ghana where there was an already established market for cloths and textiles—the client base grew and it was changed to include local and traditional designs, colours and patterns to cater to the taste of the new consumers. Today outside of Africa it is called "Ankara", and it has a client base well beyond Ghana and Africa as a whole. It is popular among Caribbean peoples and African Americans; celebrities such as Solange Knowles and her sister Beyoncé have been seen wearing African print attire. Many designers from countries in North America and Europe are now using African prints, and they have gained a global interest. British luxury fashion house Burberry created a collection around Ghanaian styles. American musician Gwen Stefani has repeatedly incorporated African prints into her clothing line and can often be seen wearing it. Internationally acclaimed Ghanaian-British designer Ozwald Boateng introduced African print suits in his 2012 collection.
Music and dance
Music incorporates types of musical instruments such as the talking drum ensembles, Akan Drum, goje fiddle and koloko lute, court music, including the Akan Seperewa, the Akan atumpan, the Ga kpanlogo styles, and log xylophones used in asonko music. African jazz was created by Guy Warren, Kofi Ghanaba. A form of secular music is highlife. Highlife originated in the 19th and 20th centuries and spread throughout West Africa. In the 1990s, a genre of music was created incorporating the influences of highlife, Afro-reggae, dancehall and Hip hop music, hip hop. This hybrid was called hiplife. There are dances for occasions. Dances for celebrations include the Adowa dance, Adowa, Kpanlogo, Azonto, Klama, Agbadza, Borborbor and Bamaya. The Nana Otafrija Pallbearing Services, also known as the Dancing Pallbearers, come from the coastal town of Prampram. The group was featured in a BBC feature story in 2017, and footage from the story became part of an Internet meme in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, COVID-19 world pandemic.Media
 Chapter 12 of the 1992 Constitution of Ghana guarantees freedom of the press and independence of the media, while Chapter 2 prohibits censorship., ''Government of Ghana''. Post-independence, private outlets closed during the military governments, and media laws prevented criticism of government.Anokwa, K. (1997). In ''Press Freedom and Communication in Africa''. Erbio, F. & Jong-Ebot, W. (Eds.) Africa World Press. . Press freedoms were restored in 1992, and after the election in 2000 of Kufuor, the tensions between the private media and government decreased. Kufuor supported press freedom and repealed a Defamation, libel law, and maintained that the media had to act responsibly.Basic Data
Chapter 12 of the 1992 Constitution of Ghana guarantees freedom of the press and independence of the media, while Chapter 2 prohibits censorship., ''Government of Ghana''. Post-independence, private outlets closed during the military governments, and media laws prevented criticism of government.Anokwa, K. (1997). In ''Press Freedom and Communication in Africa''. Erbio, F. & Jong-Ebot, W. (Eds.) Africa World Press. . Press freedoms were restored in 1992, and after the election in 2000 of Kufuor, the tensions between the private media and government decreased. Kufuor supported press freedom and repealed a Defamation, libel law, and maintained that the media had to act responsibly.Basic Data. pressreference.com The media have been described as "one of the most unfettered" in Africa.BBC Country Profile: Ghana
, BBC News. In 1948, the Gold Coast Film Unit was set up in the Information Services Department.
Architecture
There are two types of construction: the series of adjacent buildings in an enclosure around a common, and the round huts with grass roof. The round huts with grass roof architecture are situated in the northern regions, while the series of adjacent buildings are in the southern regions. Postmodern architecture and high-tech architecture buildings are in the southern regions, while heritage sites are evident in the more than 30 forts and castles in the country, such as Fort William, Ghana, Fort William and Fort Amsterdam, Ghana, Fort Amsterdam. Ghana has museums that are situated inside castles, and two are situated inside a fort. The Armed Forces Museum (Ghana), Military Museum and the National Museum of Ghana, National Museum organise temporary exhibitions. Ghana has museums that allow an in-depth look at specific regions, with a number of museums providing insight into the traditions and history of the geographical areas. The Cape Coast Castle Museum and St. Georges Castle (Elmina Castle
Elmina Castle was erected by the Portuguese in 1482 as Castelo de São Jorge da Mina (''St. George of the Mine Castle''), also known as ''Castelo da Mina'' or simply ''Mina'' (or '' Feitoria da Mina''), in present-day Elmina, Ghana, formerly t ...
) Museum offer guided tours. The Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Museum of Science and Technology provides its visitors with a look into the domain of scientific development, through exhibits of objects of scientific and technological interest.
Sports
 Association football is the top spectator sport in Ghana. Ghana has won the Africa Cup of Nations four times, the FIFA U-20 World Cup once, and has participated in four FIFA World Cups (2006, 2010, 2014 and 2022) and has also won the FIFA U-17 World Cup twice. The International Federation of Football History & Statistics, International Federation of Football History and Statistics crowned Asante Kotoko SC as the International Federation of Football History & Statistics#Continental Clubs of the 20th century, African club of the 20th century.
Ghana competes in the Commonwealth Games, sending athletes in every edition since 1954 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1954 (except for the 1986 Commonwealth Games, 1986 games). Ghana has won 57 medals at the Commonwealth Games, including 15 gold, with all but one of their medals coming in athletics and boxing. The country has also produced a number of boxers, including Azumah Nelson a three-time world champion, Nana Konadu, Nana Yaw Konadu also a three-time world champion, Ike Quartey, and Joshua Clottey.
Association football is the top spectator sport in Ghana. Ghana has won the Africa Cup of Nations four times, the FIFA U-20 World Cup once, and has participated in four FIFA World Cups (2006, 2010, 2014 and 2022) and has also won the FIFA U-17 World Cup twice. The International Federation of Football History & Statistics, International Federation of Football History and Statistics crowned Asante Kotoko SC as the International Federation of Football History & Statistics#Continental Clubs of the 20th century, African club of the 20th century.
Ghana competes in the Commonwealth Games, sending athletes in every edition since 1954 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1954 (except for the 1986 Commonwealth Games, 1986 games). Ghana has won 57 medals at the Commonwealth Games, including 15 gold, with all but one of their medals coming in athletics and boxing. The country has also produced a number of boxers, including Azumah Nelson a three-time world champion, Nana Konadu, Nana Yaw Konadu also a three-time world champion, Ike Quartey, and Joshua Clottey.
See also
*Index of Ghana-related articles *Outline of GhanaNotes
References
Further reading
* * *Birmingham, David, ''Kwame Nkrumah: Father Of African Nationalism'' (Ohio University Press, 1998) *Boafo-Arthur, Kwame, ''Ghana: One Decade of the Liberal State'' (Zed Books, 2007) *Briggs, Philip, ''Ghana (Bradt Travel Guide)'' (Bradt Travel Guides, 2010) *Clark, Gracia, ''African Market Women: Seven Life Stories from Ghana'' (Indiana University Press, 2010) *Basil Davidson, Davidson, Basil, ''Black Star: A View of the Life and Times of Kwame Nkrumah'' (James Currey, 2007) *Toyin Falola, Falola, Toyin, and Salm, Stephen J, ''Culture and Customs of Ghana'' (Greenwood, 2002) *Grant, Richard, ''Globalizing City: The Urban and Economic Transformation of Accra, Ghana'' (Syracuse University Press, 2008) *Hadjor, Kofi Buenor, ''Nkrumah and Ghana'' (Africa Research & Publications, 2003) *Hasty, Jennifer, ''The Press and Political Culture in Ghana'' (Indiana University Press, 2005) *C. L. R. James, James, C.L.R., ''Kwame Nkrumah and the Ghana Revolution'' (Allison & Busby, 1977) *Kuada, John, and Chachah Yao, ''Ghana. Understanding the People and their Culture'' (Woeli Publishing Services, 1999) *Miescher, Stephan F, ''Making Men in Ghana'' (Indiana University Press, 2005) *June Milne, Milne, June, ''Kwame Nkrumah, A Biography'' (Panaf Books, 2006) *Nkrumah, Kwame, ''Ghana: The Autobiography of Kwame Nkrumah'' (International Publishers, 1971) *Utley, Ian, ''Ghana – Culture Smart!: the essential guide to customs & culture'' (Kuperard, 2009) *Various, ''Ghana: An African Portrait Revisited'' (Peter E. Randall Publisher, 2007) *Younge, Paschal Yao, ''Music and Dance Traditions of Ghana: History, Performance and Teaching'' (Mcfarland & Co Inc., 2011) *External links
* , Government of GhanaThe Parliament of Ghana
National Commission on Culture
Country Profile
from BBC News
Ghana
from ''Encyclopædia Britannica''
Ghana
profile from ECOWAS
News headline links
from Al Jazeera. * * Th
African Activist Archive Project
website has photographs of the All Africa People's Conference held in Accra, Ghana, 5–13 December 1958 includin
Kwame Nkrumah, Prime Minister of Ghana
addressing the conference, th
American Committee on Africa delegation
meeting with Nkrumah, and o
Patrick Duncan and Alfred Hutchinson
of South Africa at the conference. {{Coord, 8.03, N, 1.08, W, display=title Ghana 1957 establishments in Ghana Articles containing video clips Countries in Africa Economic Community of West African States Countries and territories where English is an official language Member states of the African Union Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the United Nations Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations States and territories established in 1957 West African countries