eukaryotes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya,
File:Gram-negative Bacteria and Paramecium forming cyst.jpg,
The eukaryotes are a diverse lineage, consisting mainly of microscopic organisms. Multicellularity in some form has evolved independently at least 25 times within the eukaryotes. Complex multicellular organisms, not counting the aggregation of amoebae to form slime molds, have evolved within only six eukaryotic lineages:
 Mitochondria are organelles in eukaryotic cells. The mitochondrion is commonly called "the powerhouse of the cell", for its function providing energy by oxidising sugars or fats to produce the energy-storing molecule ATP. Mitochondria have two surrounding membranes, each a phospholipid bilayer, the inner of which is folded into invaginations called cristae where aerobic respiration takes place.
Mitochondria contain their own DNA, which has close structural similarities to bacterial DNA, from which it originated, and which encodes rRNA and tRNA genes that produce RNA which is closer in structure to bacterial RNA than to eukaryote RNA.
Some eukaryotes, such as the metamonads ''
Mitochondria are organelles in eukaryotic cells. The mitochondrion is commonly called "the powerhouse of the cell", for its function providing energy by oxidising sugars or fats to produce the energy-storing molecule ATP. Mitochondria have two surrounding membranes, each a phospholipid bilayer, the inner of which is folded into invaginations called cristae where aerobic respiration takes place.
Mitochondria contain their own DNA, which has close structural similarities to bacterial DNA, from which it originated, and which encodes rRNA and tRNA genes that produce RNA which is closer in structure to bacterial RNA than to eukaryote RNA.
Some eukaryotes, such as the metamonads ''
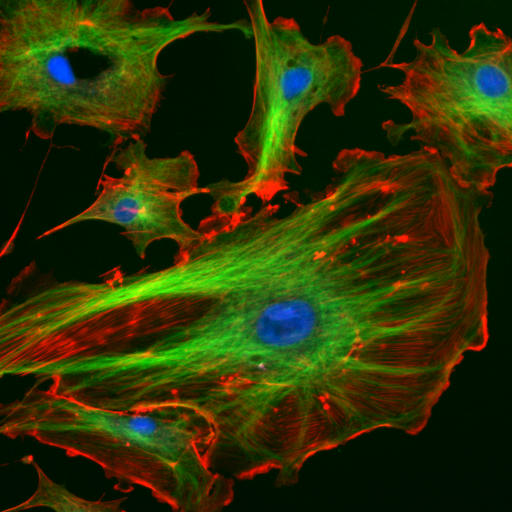 The cytoskeleton provides stiffening structure and points of
attachment for motor structures that enable the cell to move, change shape, or transport materials. The motor structures are
The cytoskeleton provides stiffening structure and points of
attachment for motor structures that enable the cell to move, change shape, or transport materials. The motor structures are
 Eukaryotes have a life cycle that involves
Eukaryotes have a life cycle that involves
 The origin of the eukaryotic cell, or ''eukaryogenesis'', is a milestone in the evolution of life, since eukaryotes include all complex cells and almost all multicellular organisms. The last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA) is the hypothetical origin of all living eukaryotes, and was most likely a biological population, not a single individual. The LECA is believed to have been a protist with a nucleus, at least one centriole and flagellum, facultatively aerobic mitochondria, sex ( meiosis and syngamy), a dormant cyst with a cell wall of
The origin of the eukaryotic cell, or ''eukaryogenesis'', is a milestone in the evolution of life, since eukaryotes include all complex cells and almost all multicellular organisms. The last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA) is the hypothetical origin of all living eukaryotes, and was most likely a biological population, not a single individual. The LECA is believed to have been a protist with a nucleus, at least one centriole and flagellum, facultatively aerobic mitochondria, sex ( meiosis and syngamy), a dormant cyst with a cell wall of
 The Neoarchean fossil '' Thuchomyces'' shares similarities with eukaryotes, specifically fungi. It especially resembles the problematic fossil ''Diskagma'', with hyphae and multiple differentiated layers. However, it is over 600 million years older than all other possible eukaryotes, and many of its "eukaryote features" are not specific to the clade, meaning it is almost certainly a microbial mat instead.
Structures proposed to represent "large colonial organisms" have been found in the black shales of the Palaeoproterozoic such as the Francevillian B Formation, in
The Neoarchean fossil '' Thuchomyces'' shares similarities with eukaryotes, specifically fungi. It especially resembles the problematic fossil ''Diskagma'', with hyphae and multiple differentiated layers. However, it is over 600 million years older than all other possible eukaryotes, and many of its "eukaryote features" are not specific to the clade, meaning it is almost certainly a microbial mat instead.
Structures proposed to represent "large colonial organisms" have been found in the black shales of the Palaeoproterozoic such as the Francevillian B Formation, in
"Eukaryotes"
( Tree of Life Web Project) * {{Authority control Articles containing video clips
organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s, plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s, fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s: the Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and the Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes.
The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal kingdom Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (also spelled Palaeoproterozoic) is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic eon, and also the longest era of the Earth's geological history, spanning from (2.5–1.6 Ga). It is further sub ...
, likely as flagellated cells. The leading evolutionary theory is they were created by symbiogenesis between an anaerobic Promethearchaeati archaean and an aerobic proteobacterium, which formed the mitochondria. A second episode of symbiogenesis with a cyanobacterium created the plants, with chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s.
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
, and the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins ...
. Eukaryotes may be either unicellular or multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
. In comparison, prokaryotes are typically unicellular. Unicellular eukaryotes are sometimes called protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s. Eukaryotes can reproduce both asexually through mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
and sexually through meiosis and gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
fusion (fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give ...
).
Etymology
The word ''eukaryote'' is derived from the Greek words "eu" (εὖ) meaning "true" or "good" and "karyon" (κάρυον) meaning "nut" or "kernel", referring to the nucleus of a cell.Diversity
Eukaryotes areorganism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s that range from microscopic single cells, such as picozoans under 3 micrometres across, to animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s like the blue whale, weighing up to 190 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s and measuring up to long, or plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s like the coast redwood, up to tall. Many eukaryotes are unicellular; the informal grouping called protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s includes many of these, with some multicellular forms like the giant kelp up to long. The multicellular eukaryotes include the animals, plants, and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, but again, these groups too contain many unicellular species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
. Eukaryotic cells are typically much larger than those of prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s—the bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and the archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
—having a volume of around 10,000 times greater. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s, but, as many of them are much larger, their collective global biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
(468 gigatons) is far larger than that of prokaryotes (77 gigatons), with plants alone accounting for over 81% of the total biomass of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
.
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s (small cylindrical cells, bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, on left) and a single-celled eukaryote, '' Paramecium''
File:California Redwood National Park (216450575).jpeg, Coast redwood
File:Anim1754 - Flickr - NOAA Photo Library (rotated).jpg, Blue whale
animals
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a ...
, symbiomycotan fungi, brown algae
Brown algae (: alga) are a large group of multicellular algae comprising the class (biology), class Phaeophyceae. They include many seaweeds located in colder waters of the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate ...
, red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest Phylum, phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 Genus, genera amidst ongoing taxon ...
, green algae
The green algae (: green alga) are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants ...
, and land plants. Eukaryotes are grouped by genomic similarities, so that groups often lack visible shared characteristics.
Distinguishing features
Nucleus
The defining feature of eukaryotes is that their cells have a well-defined, membrane-bound nuclei, distinguishing them fromprokaryotes
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' ...
that lack such a structure. Eukaryotic cells have a variety of internal membrane-bound structures, called organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
s, and a cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
which defines the cell's organization and shape. The nucleus stores the cell's DNA, which is divided into linear bundles called chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s; these are separated into two matching sets by a microtubular spindle during nuclear division, in the distinctively eukaryotic process of mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
.
Biochemistry
Eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes in multiple ways, with unique biochemical pathways such as sterane synthesis. The eukaryotic signatureprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s have no homology to proteins in other domains of life, but appear to be universal among eukaryotes. They include the proteins of the cytoskeleton, the complex transcription machinery, the membrane-sorting systems, the nuclear pore
The nuclear pore complex (NPC), is a large protein complex giving rise to the nuclear pore. A great number of nuclear pores are studded throughout the nuclear envelope that surrounds the eukaryote cell nucleus. The pores enable the nuclear tran ...
, and some enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s in the biochemical pathways.
Internal membranes
Eukaryote cells include a variety of membrane-bound structures, together forming the endomembrane system. Simple compartments, called vesicles andvacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water ...
s, can form by budding off other membranes. Many cells ingest food and other materials through a process of endocytosis, where the outer membrane invaginates and then pinches off to form a vesicle. Some cell products can leave in a vesicle through exocytosis.
The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane known as the nuclear envelope, with nuclear pore
The nuclear pore complex (NPC), is a large protein complex giving rise to the nuclear pore. A great number of nuclear pores are studded throughout the nuclear envelope that surrounds the eukaryote cell nucleus. The pores enable the nuclear tran ...
s that allow material to move in and out. Various tube- and sheet-like extensions of the nuclear membrane form the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
, which is involved in protein transport and maturation. It includes the rough endoplasmic reticulum, covered in ribosomes which synthesize proteins; these enter the interior space or lumen. Subsequently, they generally enter vesicles, which bud off from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. In most eukaryotes, these protein-carrying vesicles are released and their contents further modified in stacks of flattened vesicles ( cisternae), the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins ...
.
Vesicles may be specialized; for instance, lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
s contain digestive enzymes that break down biomolecule
A biomolecule or biological molecule is loosely defined as a molecule produced by a living organism and essential to one or more typically biological processes. Biomolecules include large macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids ...
s in the cytoplasm.
Mitochondria
Giardia
''Giardia'' ( or ) is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates be ...
'' and '' Trichomonas'', and the amoebozoan '' Pelomyxa'', appear to lack mitochondria, but all contain mitochondrion-derived organelles, like hydrogenosomes or mitosomes, having lost their mitochondria secondarily. They obtain energy by enzymatic action in the cytoplasm. It is thought that mitochondria developed from prokaryotic cells which became endosymbiont
An endosymbiont or endobiont is an organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism. Typically the two organisms are in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship. Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria (called rhizobia), whi ...
s living inside eukaryotes.
Plastids
Plants and various groups ofalgae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
have plastids as well as mitochondria. Plastids, like mitochondria, have their own DNA and are developed from endosymbionts, in this case cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
. They usually take the form of chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s which, like cyanobacteria, contain chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
and produce organic compounds (such as glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
) through photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
. Others are involved in storing food. Although plastids probably had a single origin, not all plastid-containing groups are closely related. Instead, some eukaryotes have obtained them from others through secondary endosymbiosis or ingestion. The capture and sequestering of photosynthetic cells and chloroplasts, kleptoplasty, occurs in many types of modern eukaryotic organisms.
Cytoskeletal structures
 The cytoskeleton provides stiffening structure and points of
attachment for motor structures that enable the cell to move, change shape, or transport materials. The motor structures are
The cytoskeleton provides stiffening structure and points of
attachment for motor structures that enable the cell to move, change shape, or transport materials. The motor structures are microfilament
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other ...
s of actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
and actin-binding proteins, including α- actinin, fimbrin, and filamin are present in submembranous cortical layers and bundles. Motor proteins of microtubules, dynein and kinesin, and myosin of actin filaments, provide dynamic character of the network.
Many eukaryotes have long slender motile cytoplasmic projections, called flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many pr ...
, or multiple shorter structures called cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
. These organelles are variously involved in movement, feeding, and sensation. They are composed mainly of tubulin, and are entirely distinct from prokaryotic flagella. They are supported by a bundle of microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter bet ...
s arising from a centriole, characteristically arranged as nine doublets surrounding two singlets. Flagella may have hairs ( mastigonemes), as in many stramenopile
The stramenopiles, also called heterokonts, are protists distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, an ...
s. Their interior is continuous with the cell's cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
.
Centrioles are often present, even in cells and groups that do not have flagella, but conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
s and flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s have neither. They generally occur in groups that give rise to various microtubular roots. These form a primary component of the cytoskeleton, and are often assembled over the course of several cell divisions, with one flagellum retained from the parent and the other derived from it. Centrioles produce the spindle during nuclear division.
Cell wall
The cells of plants, algae, fungi and most chromalveolates, but not animals, are surrounded by a cell wall. This is a layer outside thecell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
, providing the cell with structural support, protection, and a filtering mechanism. The cell wall also prevents over-expansion when water enters the cell.
The major polysaccharides
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
making up the primary cell wall of land plants are cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
, hemicellulose
A hemicellulose (also known as polyose) is one of a number of heteropolymers (matrix polysaccharides), such as arabinoxylans, present along with cellulose in almost all embryophyte, terrestrial plant cell walls. Cellulose is crystalline, strong, an ...
, and pectin. The cellulose microfibrils are linked together with hemicellulose, embedded in a pectin matrix. The most common hemicellulose in the primary cell wall is xyloglucan.
Sexual reproduction
sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
, alternating between a haploid phase, where only one copy of each chromosome is present in each cell, and a diploid phase, with two copies of each chromosome in each cell. The diploid phase is formed by fusion of two haploid gametes, such as eggs and spermatozoa, to form a zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
; this may grow into a body, with its cells dividing by mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
, and at some stage produce haploid gametes through meiosis, a division that reduces the number of chromosomes and creates genetic variability. There is considerable variation in this pattern. Plants have both haploid and diploid multicellular phases. Eukaryotes have lower metabolic rates and longer generation times than prokaryotes, because they are larger and therefore have a smaller surface area to volume ratio.
The evolution of sexual reproduction may be a primordial characteristic of eukaryotes. Based on a phylogenetic analysis, Dacks and Roger
Roger is a masculine given name, and a surname. The given name is derived from the Old French personal names ' and '. These names are of Germanic languages">Germanic origin, derived from the elements ', ''χrōþi'' ("fame", "renown", "honour") ...
have proposed that facultative sex was present in the group's common ancestor. A core set of genes that function in meiosis is present in both '' Trichomonas vaginalis'' and '' Giardia intestinalis'', two organisms previously thought to be asexual. Since these two species are descendants of lineages that diverged early from the eukaryotic evolutionary tree, core meiotic genes, and hence sex, were likely present in the common ancestor of eukaryotes. Species once thought to be asexual, such as ''Leishmania
''Leishmania'' () is a genus of parasitic protozoans, single-celled eukaryotic organisms of the trypanosomatid group that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. The parasites are transmitted by sandflies of the genus '' Phlebotomus'' ...
'' parasites, have a sexual cycle. Amoebae, previously regarded as asexual, may be anciently sexual; while present-day asexual groups could have arisen recently.
Evolution
History of classification
In antiquity, the two lineages ofanimal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s and plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s were recognized by Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
and Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; ; c. 371 – c. 287 BC) was an ancient Greek Philosophy, philosopher and Natural history, naturalist. A native of Eresos in Lesbos, he was Aristotle's close colleague and successor as head of the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum, the ...
. The lineages were given the taxonomic rank
In biology, taxonomic rank (which some authors prefer to call nomenclatural rank because ranking is part of nomenclature rather than taxonomy proper, according to some definitions of these terms) is the relative or absolute level of a group of or ...
of kingdom by Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
in the 18th century. Though he included the fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
with plants with some reservations, it was later realized that they are quite distinct and warrant a separate kingdom. The various single-cell eukaryotes were originally placed with plants or animals when they became known. In 1818, the German biologist Georg A. Goldfuss coined the word '' Protozoa'' to refer to organisms such as ciliates, and this group was expanded until Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; ; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, natural history, naturalist, eugenics, eugenicist, Philosophy, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biology, marine biologist and artist ...
made it a kingdom encompassing all single-celled eukaryotes, the Protista
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants o ...
, in 1866. The eukaryotes thus came to be seen as four kingdoms:
* Kingdom Protista
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants o ...
* Kingdom Plantae
* Kingdom Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
* Kingdom Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
The protists were at that time thought to be "primitive forms", and thus an evolutionary grade, united by their primitive unicellular nature. Understanding of the oldest branchings in the tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythology, mythological, religion, religious, and philosophy, philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The ...
only developed substantially with DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The ...
, leading to a system of domains rather than kingdoms as top level rank being put forward by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler, and Mark Wheelis in 1990, uniting all the eukaryote kingdoms in the domain "Eucarya", stating, however, that eukaryotes' will continue to be an acceptable common synonym". In 1996, the evolutionary biologist Lynn Margulis proposed to replace kingdoms and domains with "inclusive" names to create a "symbiosis-based phylogeny", giving the description "Eukarya (symbiosis-derived nucleated organisms)".
Phylogeny
By 2014, a rough consensus started to emerge from the phylogenomic studies of the previous two decades. The majority of eukaryotes can be placed in one of two large clades dubbed Amorphea (similar in composition to the unikont hypothesis) and the Diphoda (formerly bikonts), which includes plants and most algal lineages. A third major grouping, the Excavata, has been abandoned as a formal group as it was found to beparaphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
. The proposed phylogeny below includes two groups of excavates ( Discoba and Metamonada), and incorporates the 2021 proposal that picozoans are close relatives of rhodophytes. The Provora are a group of microbial predators discovered in 2022.
Origin of eukaryotes
chitin
Chitin (carbon, C8hydrogen, H13oxygen, O5nitrogen, N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cell ...
or cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
, and peroxisomes.
An endosymbiotic union between a motile anaerobic archaean and an aerobic alphaproteobacterium gave rise to the LECA and all eukaryotes with mitochondria. A second, much later endosymbiosis with a cyanobacterium gave rise to the ancestor of plants, with chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s.
The presence of eukaryotic biomarkers in archaea points towards an archaeal origin. The genomes of Promethearchaeati archaea have plenty of eukaryotic signature protein genes, which play a crucial role in the development of the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
and complex cellular structures characteristic of eukaryotes. In 2022, cryo-electron tomography demonstrated that Promethearchaeati archaea have a complex actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
-based cytoskeleton, providing the first direct visual evidence of the archaeal ancestry of eukaryotes.
Fossils
The timing of the origin of eukaryotes is hard to determine, but the discovery of ''Qingshania magnificia'', the earliest multicelluar eukaryote from North China which lived 1.635 billion years ago, suggests that the crown group eukaryotes originated from the latePaleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (also spelled Palaeoproterozoic) is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic eon, and also the longest era of the Earth's geological history, spanning from (2.5–1.6 Ga). It is further sub ...
( Statherian). The earliest unequivocal unicellular eukaryotes, '' Tappania plana'', '' Shuiyousphaeridium macroreticulatum'', ''Dictyosphaera macroreticulata'', ''Germinosphaera alveolata'', and ''Valeria lophostriata'' from North China, lived approximately 1.65 billion years ago.
Some acritarchs are known from at least 1.65 billion years ago, and a fossil, '' Grypania'', which may be an alga, is as much as 2.1 billion years old. The "problematic" fossil '' Diskagma'' has been found in paleosol
In Earth science, geoscience, paleosol (''palaeosol'' in Great Britain and Australia) is an ancient soil that formed in the past. The definition of the term in geology and paleontology is slightly different from its use in soil science.
In geo ...
s 2.2 billion years old.
 The Neoarchean fossil '' Thuchomyces'' shares similarities with eukaryotes, specifically fungi. It especially resembles the problematic fossil ''Diskagma'', with hyphae and multiple differentiated layers. However, it is over 600 million years older than all other possible eukaryotes, and many of its "eukaryote features" are not specific to the clade, meaning it is almost certainly a microbial mat instead.
Structures proposed to represent "large colonial organisms" have been found in the black shales of the Palaeoproterozoic such as the Francevillian B Formation, in
The Neoarchean fossil '' Thuchomyces'' shares similarities with eukaryotes, specifically fungi. It especially resembles the problematic fossil ''Diskagma'', with hyphae and multiple differentiated layers. However, it is over 600 million years older than all other possible eukaryotes, and many of its "eukaryote features" are not specific to the clade, meaning it is almost certainly a microbial mat instead.
Structures proposed to represent "large colonial organisms" have been found in the black shales of the Palaeoproterozoic such as the Francevillian B Formation, in Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
, dubbed the " Francevillian biota" which is dated at 2.1 billion years old. However, the status of these structures as fossils is contested, with other authors suggesting that they might represent pseudofossils. The oldest fossils that can unambiguously be assigned to eukaryotes are from the Ruyang Group of China, dating to approximately 1.8-1.6 billion years ago. Fossils that are clearly related to modern groups start appearing an estimated 1.2 billion years ago, in the form of red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest Phylum, phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 Genus, genera amidst ongoing taxon ...
, though recent work suggests the existence of fossilized filamentous algae in the Vindhya basin dating back perhaps to 1.6 to 1.7 billion years ago.
The presence of steranes, eukaryotic-specific biomarkers, in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
n shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of Clay mineral, clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g., Kaolinite, kaolin, aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4) and tiny f ...
s previously indicated that eukaryotes were present in these rocks dated at 2.7 billion years old, but these Archaean biomarkers have been rebutted as later contaminants. The oldest valid biomarker records are only around 800 million years old. In contrast, a molecular clock analysis suggests the emergence of sterol biosynthesis as early as 2.3 billion years ago. The nature of steranes as eukaryotic biomarkers is further complicated by the production of sterol
A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on ...
s by some bacteria.
Whenever their origins, eukaryotes may not have become ecologically dominant until much later; a massive increase in the zinc composition of marine sediments has been attributed to the rise of substantial populations of eukaryotes, which preferentially consume and incorporate zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
relative to prokaryotes, approximately a billion years after their origin (at the latest).
See also
* Eukaryote hybrid genome * List of sequenced eukaryotic genomes * ''Parakaryon myojinensis
''Parakaryon myojinensis'', also known as the Myojin parakaryote, is a highly unusual species of single-celled organism known only from a single specimen, described in 2012. It has features of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but is apparently ...
''
* Vault (organelle)
References
External links
"Eukaryotes"
( Tree of Life Web Project) * {{Authority control Articles containing video clips
Eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
Biology terminology