|
Giardia
''Giardia'' ( or ) is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates between a binucleated motile trophozoite and an infective, metabolically inert, environmentally resistant tetranucleate cyst. Cysts are transmitted between hosts through the fecal-oral route, contaminated water and/or food. ''Giardia'' were first seen by the Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1681 under the light microscope. The genus is named after French zoologist Alfred Mathieu Giard. Characteristics ''Giardia'' trophozoites are 12–15 μm long and 5–9 μm wide and have a shape of a pear bisected lengthwise. Like other diplomonads, ''Giardia'' has two transcriptionally operational nuclei that contain an equal number of well-defined chromosomes and replicate synchronously with the cell division. The cytoskeleton of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giardia Duodenalis
''Giardia duodenalis'', also known as ''Giardia intestinalis'' and ''Giardia lamblia'', is a flagellated Parasitism, parasitic protozoan microorganism of the genus ''Giardia'' that colonizes the small intestine, causing a diarrheal condition known as giardiasis. The parasite attaches to the intestinal epithelium by a ventral disc (''syn''. sucker (zoology), adhesive disc or sucker), and reproduction, reproduces via Fission (biology)#Binary_fission, binary fission. ''G. duodenalis'' is a non-invasive parasite, that does not spread to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, but remains confined to the lumen (anatomy), lumen of the small intestine. The parasite exists in two forms; Trophozoite, trophozoites and Microbial cyst, cysts. The microorganism can undergo encystation, transforming into a dormant Microbial cyst, cyst that enables it to survive outside of its Host (biology), host. ''Giardia'' trophozoites are Anaerobic organism, anaerobic, and absorb their nutrients from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
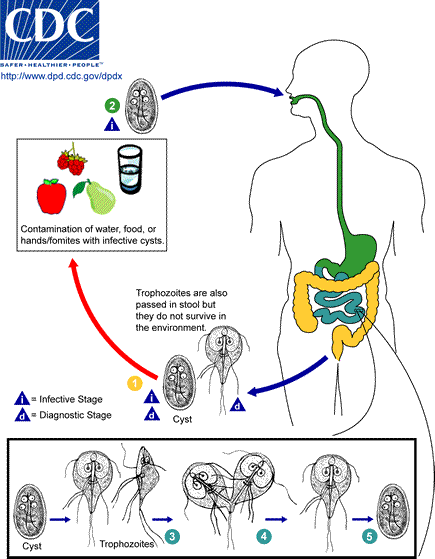
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by the protist enteropathogen ''Giardia duodenalis'' (also known as ''G. lamblia'' and ''G. intestinalis''), especially common in children and travellers. Infected individuals experience steatorrhea, a type diarrhea with fatty sticky stool; abdominal pain, weight loss, and weakness due to dehydration and malabsorption. Less common symptoms include skin rash, hives and joint swelling. Symptoms usually begin one to three weeks after exposure and, without treatment, may last two to six weeks or longer. Some infected individuals experience mild or no symptoms and remain infection carries for a long time. Giardiasis spreads via feca-oral route, when ''Giardia'' cysts excreted with faeces contaminate food or water that is later consumed orally. The disease can also spread between people and between people and animals, mainly via pets. Cysts may survive for nearly three months in cold water. The microscopic identification of ''Giardia'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giardia Agilis
''Giardia'' ( or ) is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates between a binucleated motile trophozoite and an infective, metabolically inert, environmentally resistant tetranucleate cyst. Cysts are transmitted between hosts through the fecal-oral route, contaminated water and/or food. ''Giardia'' were first seen by the Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1681 under the light microscope. The genus is named after French zoologist Alfred Mathieu Giard. Characteristics ''Giardia'' trophozoites are 12–15 μm long and 5–9 μm wide and have a shape of a pear bisected lengthwise. Like other diplomonads, ''Giardia'' has two transcriptionally operational nuclei that contain an equal number of well-defined chromosomes and replicate synchronously with the cell division. The cytoskeleton of ''Giarida'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomonad
The diplomonads (Greek for "two units") are a group of flagellates, most of which are parasitic. They include ''Giardia duodenalis'', which causes giardiasis in humans. They are placed among the metamonads, and appear to be particularly close relatives of the retortamonads. Morphology Most diplomonads are double cells: they have two nuclei, each with four associated flagella, arranged symmetrically about the body's main axis. Like the retortamonads, they lack both mitochondria and Golgi apparatuses. However, they are now known to possess modified mitochondria, in the case of ''G. duodenalis'', called mitosomes. These are not used in ATP synthesis the way mitochondria are, but are involved in the maturation of iron-sulfur proteins. Possible sexual reproduction in ''Giardia'' The common intestinal parasite ''Giardia duodenalis'' (synonyms ''Giardia lamblia'', ''G. intestinalis'') was once considered to be a descendant of a protist lineage that predated the emergence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giardia Microti
''Giardia microti'' is a species of Diplomonad parasitic protozoan. Its hosts mainly consist of rodents in the family Cricetidae, which includes voles, mice, rats and muskrats, although they have also been detected from fish. Recorded hosts ''Giardia microti'' has been recorded as a parasite of the following animals: The species is the dominant parasite in the genera ''Microtus'' and '' Myodes.'' Phylogeny ''Giardia microti'' is believed to be the sister taxon In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and ... of the '' Giardia intestinalis'' group. References External links First record of ''Giardia microti'' - Kofoid & Christiansen, 1915 Endoparasites Metamonads Taxa described in 1915 {{Parasite-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosome
A mitosome (also called a ''crypton'' in early literature) is a mitochondrion-related organelle (MRO) found in a variety of parasitic unicellular eukaryotes, such as members of the supergroup Excavata. The mitosome was first discovered in 1999 in ''Entamoeba histolytica,'' an intestinal parasite of humans, and mitosomes have also been identified in several species of Microsporidia and in '' Giardia intestinalis''. The mitosome has been detected only in anaerobic or microaerophilic eukaryotes which do not have fully developed mitochondria, and hence do not have the capability of gaining energy from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. The functions of mitosomes, while varied, have not yet been well characterized, but they may be associated with sulfate metabolism and biosynthesis of phospholipids and Fe–S clusters. Mitosomes, like other MROs, likely evolved from mitochondria, based on similarities in structure, function, and biochemical signaling pathways, and may have conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophozoite
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the ''Giardia'' group. The complementary form of the trophozoite state is the thick-walled microbial cyst, cyst form. They are often different from the cyst stage, which is a protective, dormant form of the protozoa. Trophozoites are often found in the host's body fluids and tissues and in many cases, they are the form of the protozoan that causes disease in the host. In the protozoan, ''Entamoeba histolytica'' it invades the intestinal mucosa of its host, causing dysentery, which aid in the trophozoites traveling to the liver and leading to the production of hepatic abscesses. Life cycle stages ''Plasmodium falciparium'' The causative organism of malaria is a protozoan, ''Plasmodium falciparium'', that is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito, ''Anopheles'' mosquito. Malaria is reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, several derivations of the term "flagellate" (such as " dinoflagellate" and " choanoflagellate") are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and microscopic animals, a flagellate is an organism with one or more flagella. Some cells in other animals may be flage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have Multinucleate, many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long strands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are Nuclear organization, structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |