Enzymology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An enzyme () is a
An enzyme () is a 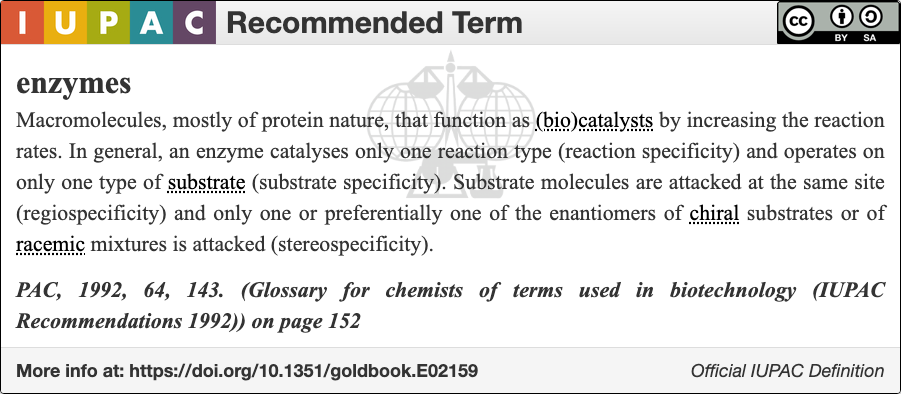 Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the
Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the
 Enzymes are generally
Enzymes are generally


 As with all catalysts, enzymes do not alter the position of the chemical equilibrium of the reaction. In the presence of an enzyme, the reaction runs in the same direction as it would without the enzyme, just more quickly. For example,
As with all catalysts, enzymes do not alter the position of the chemical equilibrium of the reaction. In the presence of an enzyme, the reaction runs in the same direction as it would without the enzyme, just more quickly. For example,
 Since the tight control of enzyme activity is essential for
Since the tight control of enzyme activity is essential for
 An enzyme () is a
An enzyme () is a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
that acts as a biological catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
by accelerating chemical reactions
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an energy change as new products ...
. The molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry ...
upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that can be offered to a market to satisfy the desire or need of a customer.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
...
. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis
Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by an "enzyme", a biological molecule. Most enzymes are proteins, and most such processes are chemical reactions. Within the enzyme, generally catalysis occurs at a localized site, calle ...
in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
s depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties.
Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types.
Other biocatalysts include catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to Catalysis, catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozy ...
s. They are sometimes described as a ''type'' of enzyme rather than being ''like'' an enzyme, but even in the decades since ribozymes' discovery in 1980–1982, the word ''enzyme'' alone often means the protein type specifically (as is used in this article). A third category of biocatalysts is constituted by those biomolecular condensates that have catalytic ability.
An enzyme's specificity comes from its unique three-dimensional structure.
 Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the
Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction rate
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per u ...
by lowering its activation energy
In the Arrhenius model of reaction rates, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be available to reactants for a chemical reaction to occur. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in kilojoules per mole (k ...
. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase
Orotidine is a nucleoside formed by attaching orotic acid to a ribose ring via a β-N1- glycosidic bond. It is found in bacteria, fungi and plants. It was first isolated in 1951 from the fungus '' Neurospora'' by A. Michael Michelson, William D ...
, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium
Equilibrium may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Equilibrium'' (film), a 2002 science fiction film
* '' The Story of Three Loves'', also known as ''Equilibrium'', a 1953 romantic anthology film
* "Equilibrium" (''seaQuest 2032'')
* ''Equilibr ...
of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many therapeutic drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
s and poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
s are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
and pH, and many enzymes are (permanently) denatured when exposed to excessive heat, losing their structure and catalytic properties.
Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.
Etymology and history
By the late 17th and early 18th centuries, the digestion ofmeat
Meat is animal Tissue (biology), tissue, often muscle, that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted and farmed other animals for meat since prehistory. The Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of vertebrates, including chickens, sheep, ...
by stomach secretions and the conversion of starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
to sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
s by plant extracts and saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which ...
were known but the mechanisms by which these occurred had not been identified.
French chemist Anselme Payen
Anselme Payen (; 6 January 1795 – 12 May 1871) was a French chemist known for discovering the enzyme diastase, and the carbohydrate cellulose.
Biography
Payen was born in Paris. He began studying science with his father when he was a 13-yea ...
was the first to discover an enzyme, diastase
A diastase (; from Greek διάστασις, "separation") is any one of a group of enzymes that catalyses the breakdown of starch into maltose. For example, the diastase α-amylase degrades starch to a mixture of the disaccharide maltose; the ...
, in 1833. A few decades later, when studying the fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
of sugar to alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
by yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
, Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur (, ; 27 December 1822 – 28 September 1895) was a French chemist, pharmacist, and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, Fermentation, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization, the la ...
concluded that this fermentation was caused by a vital force contained within the yeast cells called "ferments", which were thought to function only within living organisms. He wrote that "alcoholic fermentation is an act correlated with the life and organization of the yeast cells, not with the death or putrefaction of the cells."
In 1877, German physiologist Wilhelm Kühne (1837–1900) first used the term ''enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
'', which comes , to describe this process. The word ''enzyme'' was used later to refer to nonliving substances such as pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. It is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pe ...
, and the word ''ferment'' was used to refer to chemical activity produced by living organisms.
Eduard Buchner
Eduard Buchner (; 20 May 1860 – 13 August 1917) was a German chemist and Zymurgy, zymologist, awarded the 1907 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation.
Biography
Early years
Buchner was born in Mun ...
submitted his first paper on the study of yeast extracts in 1897. In a series of experiments at the University of Berlin
The Humboldt University of Berlin (, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin, Germany.
The university was established by Frederick William III on the initiative of Wilhelm von Humbol ...
, he found that sugar was fermented by yeast extracts even when there were no living yeast cells in the mixture. He named the enzyme that brought about the fermentation of sucrose "zymase
Zymase (also known as alcoholase) is an obsolete term for an enzyme complex that catalyzes the fermentation of sugar into ethanol and carbon dioxide. It occurs naturally in yeasts. Zymase activity varies among yeast strains.
Zymase is also the ...
". In 1907, he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
for "his discovery of cell-free fermentation". Following Buchner's example, enzymes are usually named according to the reaction they carry out: the suffix ''-ase
The suffix -ase is used in biochemistry to form names of enzymes. The most common way to name enzymes is to add this suffix onto the end of the substrate, ''e.g.'' an enzyme that breaks down peroxides may be called peroxidase; the enzyme that pr ...
'' is combined with the name of the substrate (e.g., lactase
Lactase () is an enzyme produced by many organisms and is essential to the complete digestion of whole milk. It breaks down the sugar lactose into its component parts, galactose and glucose. Lactase is found in the brush border of the small ...
is the enzyme that cleaves lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from (Genitive case, gen. ), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ''-o ...
) or to the type of reaction (e.g., DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create t ...
forms DNA polymers).
The biochemical identity of enzymes was still unknown in the early 1900s. Many scientists observed that enzymatic activity was associated with proteins, but others (such as Nobel laureate Richard Willstätter) argued that proteins were merely carriers for the true enzymes and that proteins ''per se'' were incapable of catalysis. quoted in In 1926, James B. Sumner showed that the enzyme urease
Ureases (), functionally, belong to the superfamily of amidohydrolases and phosphotriesterases. Ureases are found in numerous Bacteria, Archaea, fungi, algae, plants, and some invertebrates. Ureases are nickel-containing metalloenzymes of high ...
was a pure protein and crystallized it; he did likewise for the enzyme catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting ...
in 1937. The conclusion that pure proteins can be enzymes was definitively demonstrated by John Howard Northrop
John Howard Northrop (July 5, 1891 – May 27, 1987) was an American biochemist who, with James Batcheller Sumner and Wendell Meredith Stanley, won the 1946 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. The award was given for these scientists' isolation, crys ...
and Wendell Meredith Stanley, who worked on the digestive enzymes pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. It is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pe ...
(1930), trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
and chymotrypsin. These three scientists were awarded the 1946 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
The discovery that enzymes could be crystallized eventually allowed their structures to be solved by x-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ...
. This was first done for lysozyme
Lysozyme (, muramidase, ''N''-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase; systematic name peptidoglycan ''N''-acetylmuramoylhydrolase) is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. It is a glycoside hydrolase ...
, an enzyme found in tears, saliva and egg white
Egg white is the clear liquid (also called the albumen or the glair/glaire) contained within an egg. In chickens, it is formed from the layers of secretions of the anterior section of the hen's oviduct during the passage of the egg. It forms a ...
s that digests the coating of some bacteria; the structure was solved by a group led by David Chilton Phillips and published in 1965. This high-resolution structure of lysozyme marked the beginning of the field of structural biology
Structural biology deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every level of organization.
Early structural biologists throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries we ...
and the effort to understand how enzymes work at an atomic level of detail.
Classification and nomenclature
Enzymes can be classified by two main criteria: eitheramino acid sequence
Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthe ...
similarity (and thus evolutionary relationship) or enzymatic activity.
Enzyme activity. An enzyme's name is often derived from its substrate or the chemical reaction it catalyzes, with the word ending in ''-ase''. Examples are lactase
Lactase () is an enzyme produced by many organisms and is essential to the complete digestion of whole milk. It breaks down the sugar lactose into its component parts, galactose and glucose. Lactase is found in the brush border of the small ...
, alcohol dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) () are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to N ...
and DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create t ...
. Different enzymes that catalyze the same chemical reaction are called isozyme
In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. di ...
s.
The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB) is an international non-governmental organisation concerned with biochemistry and molecular biology. Formed in 1955 as the International Union of Biochemistry (IUB), the union ...
have developed a nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. (The theoretical field studying nomenclature is sometimes referred to as ''onymology'' or ''taxonymy'' ). The principl ...
for enzymes, the EC numbers (for "Enzyme Commission"). Each enzyme is described by "EC" followed by a sequence of four numbers which represent the hierarchy of enzymatic activity (from very general to very specific). That is, the first number broadly classifies the enzyme based on its mechanism while the other digits add more and more specificity.
The top-level classification is:
*EC 1, Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually ut ...
s: catalyze oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
/reduction reactions
*EC 2, Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved ...
s: transfer a functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
(''e.g.'' a methyl or phosphate group)
*EC 3, Hydrolase
In biochemistry, hydrolases constitute a class of enzymes that commonly function as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond:
:\ce \quad \xrightarrowtext\quad \ce
This typically results in dividing a larger molecule into s ...
s: catalyze the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of various bonds
*EC 4, Lyase
In biochemistry, a lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking (an elimination reaction) of various chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis (a substitution reaction) and oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidatio ...
s: cleave various bonds by means other than hydrolysis and oxidation
*EC 5, Isomerase
In biochemistry, isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which chemical bond, bonds are Bond cleavage, broken and formed. The general form ...
s: catalyze isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
ization changes within a single molecule
*EC 6, Ligase
In biochemistry, a ligase is an enzyme that can catalyze the joining ( ligation) of two molecules by forming a new chemical bond. This is typically via hydrolysis of a small pendant chemical group on one of the molecules, typically resulting i ...
s: join two molecules with covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
s.
*EC 7, Translocase
Translocase is a general term for a protein that assists in moving another molecule, usually across a cell membrane. These Enzyme, enzymes catalyze the movement of ions or molecules across membranes or their separation within membranes. The reactio ...
s: catalyze the movement of ions or molecules across membranes, or their separation within membranes.
These sections are subdivided by other features such as the substrate, products, and chemical mechanism. An enzyme is fully specified by four numerical designations. For example, hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that irreversibly phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important p ...
(EC 2.7.1.1) is a transferase (EC 2) that adds a phosphate group (EC 2.7) to a hexose sugar, a molecule containing an alcohol group (EC 2.7.1).
Sequence similarity. EC categories do not reflect sequence similarity. For instance, two ligases of the same EC number that catalyze exactly the same reaction can have completely different sequences. Independent of their function, enzymes, like any other proteins, have been classified by their sequence similarity into numerous families. These families have been documented in dozens of different protein and protein family databases such as Pfam.
Non-homologous isofunctional enzymes. Unrelated enzymes that have the same enzymatic activity have been called ''non-homologous isofunctional enzymes''. Horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
may spread these genes to unrelated species, especially bacteria where they can replace endogenous genes of the same function, leading to hon-homologous gene displacement.
Structure
globular protein
In biochemistry, globular proteins or spheroproteins are spherical ("globe-like") proteins and are one of the common protein types (the others being fibrous, disordered and membrane proteins). Globular proteins are somewhat water-soluble (form ...
s, acting alone or in larger complexes. The sequence of the amino acids specifies the structure which in turn determines the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Although structure determines function, a novel enzymatic activity cannot yet be predicted from structure alone. Enzyme structures unfold ( denature) when heated or exposed to chemical denaturants and this disruption to the structure typically causes a loss of activity. Enzyme denaturation is normally linked to temperatures above a species' normal level; as a result, enzymes from bacteria living in volcanic environments such as hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
s are prized by industrial users for their ability to function at high temperatures, allowing enzyme-catalysed reactions to be operated at a very high rate.
Enzymes are usually much larger than their substrates. Sizes range from just 62 amino acid residues, for the monomer
A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Chemis ...
of 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase, to over 2,500 residues in the animal fatty acid synthase
Fatty acid synthase (FAS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''FASN'' gene.
Fatty acid synthase is a multi-enzyme protein that catalyzes fatty acid synthesis. It is not a single enzyme but a whole enzymatic system composed of two ide ...
. Only a small portion of their structure (around 2–4 amino acids) is directly involved in catalysis: the catalytic site. This catalytic site is located next to one or more binding site
In biochemistry and molecular biology, a binding site is a region on a macromolecule such as a protein that binds to another molecule with specificity. The binding partner of the macromolecule is often referred to as a ligand. Ligands may includ ...
s where residues orient the substrates. The catalytic site and binding site together compose the enzyme's active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding s ...
. The remaining majority of the enzyme structure serves to maintain the precise orientation and dynamics of the active site.
In some enzymes, no amino acids are directly involved in catalysis; instead, the enzyme contains sites to bind and orient catalytic cofactors. Enzyme structures may also contain allosteric sites where the binding of a small molecule causes a conformational change
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors.
A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. Its shape can change in response to changes in its environment or othe ...
that increases or decreases activity.
A small number of RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
-based biological catalysts called ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to Catalysis, catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozy ...
s exist, which again can act alone or in complex with proteins. The most common of these is the ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
which is a complex of protein and catalytic RNA components.
Mechanism
Substrate binding
Enzymes must bind their substrates before they can catalyse any chemical reaction. Enzymes are usually very specific as to what substrates they bind and then the chemical reaction catalysed. Specificity is achieved by binding pockets with complementary shape, charge andhydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are n ...
/hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
characteristics to the substrates. Enzymes can therefore distinguish between very similar substrate molecules to be chemoselective, regioselective
In organic chemistry, regioselectivity is the preference of chemical bonding or breaking in one direction over all other possible directions. It can often apply to which of many possible positions a reagent will affect, such as which proton a str ...
and stereospecific.
Some of the enzymes showing the highest specificity and accuracy are involved in the copying and expression of the genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
. Some of these enzymes have " proof-reading" mechanisms. Here, an enzyme such as DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create t ...
catalyzes a reaction in a first step and then checks that the product is correct in a second step. This two-step process results in average error rates of less than 1 error in 100 million reactions in high-fidelity mammalian polymerases. Similar proofreading mechanisms are also found in RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Using the e ...
, aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its pre ...
s and ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
s.
Conversely, some enzymes display enzyme promiscuity
Enzyme promiscuity is the ability of an enzyme to catalyze an unexpected side reaction in addition to its main reaction. Although enzymes are remarkably specific catalysts, they can often perform side reactions in addition to their main, native cat ...
, having broad specificity and acting on a range of different physiologically relevant substrates. Many enzymes possess small side activities which arose fortuitously (i.e. neutrally), which may be the starting point for the evolutionary selection of a new function.
"Lock and key" model
To explain the observed specificity of enzymes, in 1894Emil Fischer
Hermann Emil Louis Fischer (; 9 October 1852 – 15 July 1919) was a German chemist and List of Nobel laureates in Chemistry, 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fisch ...
proposed that both the enzyme and the substrate possess specific complementary geometric shapes that fit exactly into one another. This is often referred to as "the lock and key" model. This early model explains enzyme specificity, but fails to explain the stabilization of the transition state that enzymes achieve.
Induced fit model
In 1958, Daniel Koshland suggested a modification to the lock and key model: since enzymes are rather flexible structures, the active site is continuously reshaped by interactions with the substrate as the substrate interacts with the enzyme. As a result, the substrate does not simply bind to a rigid active site; the amino acid side-chains that make up the active site are molded into the precise positions that enable the enzyme to perform its catalytic function. In some cases, such as glycosidases, the substratemolecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
also changes shape slightly as it enters the active site. The active site continues to change until the substrate is completely bound, at which point the final shape and charge distribution is determined.
Induced fit may enhance the fidelity of molecular recognition in the presence of competition and noise via the conformational proofreading mechanism.
Catalysis
Enzymes can accelerate reactions in several ways, all of which lower theactivation energy
In the Arrhenius model of reaction rates, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be available to reactants for a chemical reaction to occur. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in kilojoules per mole (k ...
(ΔG‡, Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (or Gibbs energy as the recommended name; symbol is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of Work (thermodynamics), work, other than Work (thermodynamics)#Pressure–v ...
)
# By stabilizing the transition state:
#* Creating an environment with a charge distribution complementary to that of the transition state to lower its energy
# By providing an alternative reaction pathway:
#* Temporarily reacting with the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate to provide a lower energy transition state
# By destabilizing the substrate ground state:
#* Distorting bound substrate(s) into their transition state form to reduce the energy required to reach the transition state
#* By orienting the substrates into a productive arrangement to reduce the reaction entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
change (the contribution of this mechanism to catalysis is relatively small)
Enzymes may use several of these mechanisms simultaneously. For example, protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
s such as trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
perform covalent catalysis using a catalytic triad
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acid residues that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, aminoac ...
, stabilize charge build-up on the transition states using an oxyanion hole
An oxyanion hole is a pocket in the active site of an enzyme that stabilizes transition state negative charge on a deprotonation, deprotonated oxygen or alkoxide. The pocket typically consists of backbone amides or positively charged residues. Sta ...
, complete hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
using an oriented water substrate.
Dynamics
Enzymes are not rigid, static structures; instead they have complex internal dynamic motions – that is, movements of parts of the enzyme's structure such as individual amino acid residues, groups of residues forming a protein loop or unit ofsecondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta ...
, or even an entire protein domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's Peptide, polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that Protein folding, folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded Protein tertiary structure, thre ...
. These motions give rise to a conformational ensemble of slightly different structures that interconvert with one another at equilibrium
Equilibrium may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Equilibrium'' (film), a 2002 science fiction film
* '' The Story of Three Loves'', also known as ''Equilibrium'', a 1953 romantic anthology film
* "Equilibrium" (''seaQuest 2032'')
* ''Equilibr ...
. Different states within this ensemble may be associated with different aspects of an enzyme's function. For example, different conformations of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase are associated with the substrate binding, catalysis, cofactor release, and product release steps of the catalytic cycle, consistent with catalytic resonance theory In chemistry, catalytic resonance theory was developed to describe the kinetics of reaction acceleration using dynamic catalyst surfaces. Catalytic reactions occur on surfaces that undergo variation in surface binding energy and/or entropy, exhibiti ...
. The transitions between the different conformations during the catalytic cycle involve internal viscoelatic motion that is facilitated by high- strain regions where amino acids are rearranged.
Substrate presentation
Substrate presentation is a process where the enzyme is sequestered away from its substrate. Enzymes can be sequestered to the plasma membrane away from a substrate in the nucleus or cytosol. Or within the membrane, an enzyme can be sequestered into lipid rafts away from its substrate in the disordered region. When the enzyme is released it mixes with its substrate. Alternatively, the enzyme can be sequestered near its substrate to activate the enzyme. For example, the enzyme can be soluble and upon activation bind to a lipid in the plasma membrane and then act upon molecules in the plasma membrane.Allosteric modulation
Allosteric sites are pockets on the enzyme, distinct from the active site, that bind to molecules in the cellular environment. These molecules then cause a change in the conformation or dynamics of the enzyme that is transduced to the active site and thus affects the reaction rate of the enzyme. In this way, allosteric interactions can either inhibit or activate enzymes. Allosteric interactions with metabolites upstream or downstream in an enzyme's metabolic pathway causefeedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
regulation, altering the activity of the enzyme according to the flux
Flux describes any effect that appears to pass or travel (whether it actually moves or not) through a surface or substance. Flux is a concept in applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications in physics. For transport phe ...
through the rest of the pathway.
Cofactors
Some enzymes do not need additional components to show full activity. Others require non-protein molecules called cofactors to be bound for activity. Cofactors can be eitherinorganic
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''.
Inor ...
(e.g., metal ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s and iron–sulfur clusters) or organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
s (e.g., flavin and heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prostheti ...
). These cofactors serve many purposes; for instance, metal ions can help in stabilizing nucleophilic species within the active site. Organic cofactors can be either coenzyme
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or Metal ions in aqueous solution, metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalysis, catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can ...
s, which are released from the enzyme's active site during the reaction, or prosthetic groups, which are tightly bound to an enzyme. Organic prosthetic groups can be covalently bound (e.g., biotin
Biotin (also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. ...
in enzymes such as pyruvate carboxylase).
An example of an enzyme that contains a cofactor is carbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) () form a family of enzymes that catalyst, catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the Dissociation (chemistry), dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate a ...
, which uses a zinc cofactor bound as part of its active site. These tightly bound ions or molecules are usually found in the active site and are involved in catalysis. For example, flavin and heme cofactors are often involved in redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is t ...
reactions.
Enzymes that require a cofactor but do not have one bound are called ''apoenzymes'' or ''apoproteins''. An enzyme together with the cofactor(s) required for activity is called a ''holoenzyme'' (or haloenzyme). The term ''holoenzyme'' can also be applied to enzymes that contain multiple protein subunits, such as the DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create t ...
s; here the holoenzyme is the complete complex containing all the subunits needed for activity.
Coenzymes
Coenzymes are small organic molecules that can be loosely or tightly bound to an enzyme. Coenzymes transport chemical groups from one enzyme to another. Examples includeNADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an ade ...
, NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require N ...
and adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known ...
(ATP). Some coenzymes, such as flavin mononucleotide
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN), or riboflavin-5′-phosphate, is a biomolecule produced from riboflavin (vitamin B2) by the enzyme riboflavin kinase and functions as the prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases, including NADH dehydrogenase, as ...
(FMN), flavin adenine dinucleotide
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox-active coenzyme associated with various proteins, which is involved with several enzymatic reactions in metabolism. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group, which ma ...
(FAD), thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), and tetrahydrofolate (THF), are derived from vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, ...
s. These coenzymes cannot be synthesized by the body '' de novo'' and closely related compounds (vitamins) must be acquired from the diet. The chemical groups carried include:
* the hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen (H−), a hydrogen ion with two electrons. In modern usage, this is typically only used for ionic bonds, but it is sometimes (and has been more frequently in the past) applied to all che ...
ion (H−), carried by NAD or NADP+
* the phosphate group, carried by adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known ...
* the acetyl group, carried by coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the Fatty acid metabolism#Synthesis, synthesis and Fatty acid metabolism#.CE.B2-Oxidation, oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvic acid, pyruvate in the citric ac ...
* formyl, methenyl or methyl groups, carried by folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
and
* the methyl group, carried by S-adenosylmethionine
Since coenzymes are chemically changed as a consequence of enzyme action, it is useful to consider coenzymes to be a special class of substrates, or second substrates, which are common to many different enzymes. For example, about 1000 enzymes are known to use the coenzyme NADH.
Coenzymes are usually continuously regenerated and their concentrations maintained at a steady level inside the cell. For example, NADPH is regenerated through the pentose phosphate pathway
The pentose phosphate pathway (also called the phosphogluconate pathway and the hexose monophosphate shunt or HMP shunt) is a metabolic pathway parallel to glycolysis. It generates NADPH and pentoses (five-carbon sugars) as well as ribose 5-ph ...
and ''S''-adenosylmethionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. This continuous regeneration means that small amounts of coenzymes can be used very intensively. For example, the human body turns over its own weight in ATP each day.
Thermodynamics
carbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) () form a family of enzymes that catalyst, catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the Dissociation (chemistry), dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate a ...
catalyzes its reaction in either direction depending on the concentration of its reactants:
The rate of a reaction is dependent on the activation energy
In the Arrhenius model of reaction rates, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be available to reactants for a chemical reaction to occur. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in kilojoules per mole (k ...
needed to form the transition state
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked w ...
which then decays into products. Enzymes increase reaction rates by lowering the energy of the transition state. First, binding forms a low energy enzyme-substrate complex (ES). Second, the enzyme stabilises the transition state such that it requires less energy to achieve compared to the uncatalyzed reaction (ES‡). Finally the enzyme-product complex (EP) dissociates to release the products.
Enzymes can couple two or more reactions, so that a thermodynamically favorable reaction can be used to "drive" a thermodynamically unfavourable one so that the combined energy of the products is lower than the substrates. For example, the hydrolysis of ATP is often used to drive other chemical reactions.
Kinetics
Enzyme kinetics is the investigation of how enzymes bind substrates and turn them into products. The rate data used in kinetic analyses are commonly obtained fromenzyme assay
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods for measuring enzymatic activity. They are vital for the study of enzyme kinetics and enzyme inhibition.
Enzyme units
The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with a ...
s. In 1913 Leonor Michaelis
Leonor Michaelis (16 January 1875 – 8 October 1949) was a German biochemist, physical chemist, and physician. He is known for his work with Maud Menten on enzyme kinetics in 1913, as well as for work on enzyme inhibition, pH and quinones.
...
and Maud Leonora Menten proposed a quantitative theory of enzyme kinetics, which is referred to as Michaelis–Menten kinetics
In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics, named after Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten, is the simplest case of enzyme kinetics, applied to enzyme-catalysed reactions involving the transformation of one substrate into one product. It takes th ...
. The major contribution of Michaelis and Menten was to think of enzyme reactions in two stages. In the first, the substrate binds reversibly to the enzyme, forming the enzyme-substrate complex. This is sometimes called the Michaelis–Menten complex in their honor. The enzyme then catalyzes the chemical step in the reaction and releases the product. This work was further developed by G. E. Briggs and J. B. S. Haldane, who derived kinetic equations that are still widely used today.
Enzyme rates depend on solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Solu ...
conditions and substrate concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', ...
. To find the maximum speed of an enzymatic reaction, the substrate concentration is increased until a constant rate of product formation is seen. This is shown in the saturation curve on the right. Saturation happens because, as substrate concentration increases, more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex. At the maximum reaction rate (''V''max) of the enzyme, all the enzyme active sites are bound to substrate, and the amount of ES complex is the same as the total amount of enzyme.
''V''max is only one of several important kinetic parameters. The amount of substrate needed to achieve a given rate of reaction is also important. This is given by the Michaelis–Menten constant (''K''m), which is the substrate concentration required for an enzyme to reach one-half its maximum reaction rate; generally, each enzyme has a characteristic ''K''M for a given substrate. Another useful constant is ''k''cat, also called the ''turnover number'', which is the number of substrate molecules handled by one active site per second.
The efficiency of an enzyme can be expressed in terms of ''k''cat/''K''m. This is also called the specificity constant and incorporates the rate constants for all steps in the reaction up to and including the first irreversible step. Because the specificity constant reflects both affinity and catalytic ability, it is useful for comparing different enzymes against each other, or the same enzyme with different substrates. The theoretical maximum for the specificity constant is called the diffusion limit and is about 108 to 109 (M−1 s−1). At this point every collision of the enzyme with its substrate will result in catalysis, and the rate of product formation is not limited by the reaction rate but by the diffusion rate. Enzymes with this property are called '' catalytically perfect'' or ''kinetically perfect''. Example of such enzymes are triose-phosphate isomerase, carbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) () form a family of enzymes that catalyst, catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the Dissociation (chemistry), dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate a ...
, acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee, HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme th ...
, catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting ...
, fumarase
Fumarase (or fumarate hydratase) is an enzyme () that catalyzes the reversible Hydration reaction, hydration/Dehydration reaction, dehydration of fumarate to malate. Fumarase comes in two forms: mitochondrial and cytosolic. The mitochondrial iso ...
, β-lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide Multiple drug resistance, multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem ...
, and superoxide dismutase
Superoxide dismutase (SOD, ) is an enzyme that alternately catalyzes the dismutation (or partitioning) of the superoxide () anion radical into normal molecular oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (). Superoxide is produced as a by-product of oxy ...
. The turnover of such enzymes can reach several million reactions per second. But most enzymes are far from perfect: the average values of and are about and , respectively.
Michaelis–Menten kinetics relies on the law of mass action
In chemistry, the law of mass action is the proposition that the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the activities or concentrations of the reactants. It explains and predicts behaviors of solutions in dy ...
, which is derived from the assumptions of free diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
and thermodynamically driven random collision. Many biochemical or cellular processes deviate significantly from these conditions, because of macromolecular crowding
The phenomenon of macromolecular crowding alters the properties of molecules in a solution when high concentrations of macromolecules such as proteins are present. Such conditions occur routinely in living cells; for instance, the cytosol of ''Es ...
and constrained molecular movement. More recent, complex extensions of the model attempt to correct for these effects.
Inhibition
Enzyme reaction rates can be decreased by various types of enzyme inhibitors.Types of inhibition
Competitive
Acompetitive inhibitor
Competitive inhibition is interruption of a chemical pathway owing to one chemical substance inhibiting the effect of another by competing with it for binding or bonding. Any metabolic or chemical messenger system can potentially be affected b ...
and substrate cannot bind to the enzyme at the same time. Often competitive inhibitors strongly resemble the real substrate of the enzyme. For example, the drug methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which catalyzes the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate. The similarity between the structures of dihydrofolate and this drug are shown in the accompanying figure. This type of inhibition can be overcome with high substrate concentration. In some cases, the inhibitor can bind to a site other than the binding-site of the usual substrate and exert an allosteric effect to change the shape of the usual binding-site.
Non-competitive
A non-competitive inhibitor binds to a site other than where the substrate binds. The substrate still binds with its usual affinity and hence Km remains the same. However the inhibitor reduces the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme so that Vmax is reduced. In contrast to competitive inhibition, non-competitive inhibition cannot be overcome with high substrate concentration.Uncompetitive
An uncompetitive inhibitor cannot bind to the free enzyme, only to the enzyme-substrate complex; hence, these types of inhibitors are most effective at high substrate concentration. In the presence of the inhibitor, the enzyme-substrate complex is inactive. This type of inhibition is rare.Mixed
A mixed inhibitor binds to an allosteric site and the binding of the substrate and the inhibitor affect each other. The enzyme's function is reduced but not eliminated when bound to the inhibitor. This type of inhibitor does not follow the Michaelis–Menten equation.Irreversible
An irreversible inhibitor permanently inactivates the enzyme, usually by forming acovalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
to the protein. Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
and aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
are common drugs that act in this manner.
Functions of inhibitors
In many organisms, inhibitors may act as part of afeedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
mechanism. If an enzyme produces too much of one substance in the organism, that substance may act as an inhibitor for the enzyme at the beginning of the pathway that produces it, causing production of the substance to slow down or stop when there is sufficient amount. This is a form of negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused ...
. Major metabolic pathways such as the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
make use of this mechanism.
Since inhibitors modulate the function of enzymes they are often used as drugs. Many such drugs are reversible competitive inhibitors that resemble the enzyme's native substrate, similar to methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
above; other well-known examples include statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
s used to treat high cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
, and protease inhibitors
Protease inhibitors (PIs) are medications that act by interfering with protease, enzymes that cleave proteins. Some of the most well known are antiviral drugs widely used to treat HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C and COVID-19. These protease inhibitors pre ...
used to treat retroviral infections such as HIV. A common example of an irreversible inhibitor that is used as a drug is aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
, which inhibits the COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes that produce the inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
messenger prostaglandin
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiology, physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every Tissue (biology), tissue in humans and ot ...
. Other enzyme inhibitors are poisons. For example, the poison cyanide
In chemistry, cyanide () is an inorganic chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom.
Ionic cyanides contain the cyanide anion . This a ...
is an irreversible enzyme inhibitor that combines with the copper and iron in the active site of the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV (was , now reclassified as a translocasEC 7.1.1.9 is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria, archaea, and the mitochondria of eukaryotes.
It is the last enzyme in the Cellular respir ...
and blocks cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cell ...
.
Factors affecting enzyme activity
As enzymes are made up of proteins, their actions are sensitive to change in many physio chemical factors such as pH, temperature, substrate concentration, etc. The following table shows pH optima for various enzymes.Biological function
Enzymes serve a wide variety of functions inside living organisms. They are indispensable forsignal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
and cell regulation, often via kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
s and phosphatase
In biochemistry, a phosphatase is an enzyme that uses water to cleave a phosphoric acid Ester, monoester into a phosphate ion and an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. Because a phosphatase enzyme catalysis, catalyzes the hydrolysis of its Substrate ...
s. They also generate movement, with myosin
Myosins () are a Protein family, family of motor proteins (though most often protein complexes) best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are adenosine triphosphate, ATP- ...
hydrolyzing adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known ...
(ATP) to generate muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in musc ...
, and also transport cargo around the cell as part of the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
. Other ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, ATP hydrolase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or ...
s in the cell membrane are ion pumps involved in active transport
In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellula ...
. Enzymes are also involved in more exotic functions, such as luciferase
Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words ''luciferin'' and ''luciferase'' ...
generating light in fireflies
The Lampyridae are a family of elateroid beetles with more than 2,000 described species, many of which are light-emitting. They are soft-bodied beetles commonly called fireflies, lightning bugs, or glowworms for their conspicuous production ...
. Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es can also contain enzymes for infecting cells, such as the HIV integrase and reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobi ...
, or for viral release from cells, like the influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
virus neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glycosidic linkag ...
.
An important function of enzymes is in the digestive systems of animals. Enzymes such as amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large ...
s and protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
s break down large molecules (starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
or protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, respectively) into smaller ones, so they can be absorbed by the intestines. Starch molecules, for example, are too large to be absorbed from the intestine, but enzymes hydrolyze the starch chains into smaller molecules such as maltose
}
Maltose ( or ), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the tw ...
and eventually glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
, which can then be absorbed. Different enzymes digest different food substances. In ruminant
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microb ...
s, which have herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat n ...
diets, microorganisms in the gut produce another enzyme, cellulase
Cellulase (; systematic name 4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase) is any of several enzymes produced chiefly by fungi, bacteria, and protozoans that catalyze cellulolysis, the decomposition of cellulose and of some related polysaccharides:
: Endo ...
, to break down the cellulose cell walls of plant fiber.
Metabolism
Several enzymes can work together in a specific order, creatingmetabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
s. In a metabolic pathway, one enzyme takes the product of another enzyme as a substrate. After the catalytic reaction, the product is then passed on to another enzyme. Sometimes more than one enzyme can catalyze the same reaction in parallel; this can allow more complex regulation: with, for example, a low constant activity provided by one enzyme but an inducible high activity from a second enzyme.
Enzymes determine what steps occur in these pathways. Without enzymes, metabolism would neither progress through the same steps and could not be regulated to serve the needs of the cell. Most central metabolic pathways are regulated at a few key steps, typically through enzymes whose activity involves the hydrolysis of ATP. Because this reaction releases so much energy, other reactions that are thermodynamically unfavorable can be coupled to ATP hydrolysis, driving the overall series of linked metabolic reactions.
Control of activity
There are five main ways that enzyme activity is controlled in the cell.Regulation
Enzymes can be either activated or inhibited by other molecules. For example, the end product(s) of a metabolic pathway are often inhibitors for one of the first enzymes of the pathway (usually the first irreversible step, called committed step), thus regulating the amount of end product made by the pathways. Such a regulatory mechanism is called a negative feedback mechanism, because the amount of the end product produced is regulated by its own concentration. Negative feedback mechanism can effectively adjust the rate of synthesis of intermediate metabolites according to the demands of the cells. This helps with effective allocations of materials and energy economy, and it prevents the excess manufacture of end products. Like other homeostatic devices, the control of enzymatic action helps to maintain a stable internal environment in living organisms.Post-translational modification
Examples ofpost-translational modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biolog ...
include phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
, myristoylation and glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not ...
. For example, in the response to insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
, the phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
of multiple enzymes, including glycogen synthase
Glycogen synthase (UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase) is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase () that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and (1,4--D-glucosyl)n to yield UD ...
, helps control the synthesis or degradation of glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
and allows the cell to respond to changes in blood sugar
The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis.
For a 70 kg (1 ...
. Another example of post-translational modification is the cleavage of the polypeptide chain. Chymotrypsin, a digestive protease, is produced in inactive form as chymotrypsinogen in the pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
and transported in this form to the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
where it is activated. This stops the enzyme from digesting the pancreas or other tissues before it enters the gut. This type of inactive precursor to an enzyme is known as a zymogen
In biochemistry, a zymogen (), also called a proenzyme (), is an inactive precursor of an enzyme. A zymogen requires a biochemical change (such as a hydrolysis reaction revealing the active site, or changing the configuration to reveal the activ ...
or proenzyme.
Quantity
Enzyme production ( transcription andtranslation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
of enzyme genes) can be enhanced or diminished by a cell in response to changes in the cell's environment. This form of gene regulation
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are wide ...
is called enzyme induction. For example, bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics such as penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
because enzymes called beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapene ...
s are induced that hydrolyse the crucial beta-lactam ring within the penicillin molecule. Another example comes from enzymes in the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
called cytochrome P450 oxidase
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherich ...
s, which are important in drug metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set o ...
. Induction or inhibition of these enzymes can cause drug interaction In pharmaceutical sciences, drug interactions occur when a drug's mechanism of action is affected by the concomitant administration of substances such as foods, beverages, or other drugs. A popular example of drug–food interaction is the effect ...
s. Enzyme levels can also be regulated by changing the rate of enzyme degradation. The opposite of enzyme induction is enzyme repression Enzyme Repressor
An enzyme repressor is a type of regulatory protein that controls the activity of enzymes, typically by binding to specific sites on DNA or directly to the enzyme itself. These repressors play a crucial role in cellular processe ...
.
Subcellular distribution
Enzymes can be compartmentalized, with different metabolic pathways occurring in differentcellular compartment
Cellular compartments in cell biology comprise all of the closed parts within the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell, usually surrounded by a single or double lipid layer membrane. These compartments are often, but not always, defined as membrane ...
s. For example, fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s are synthesized by one set of enzymes in the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
, endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
and Golgi and used by a different set of enzymes as a source of energy in the mitochondrion
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cell (biology), cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine tri ...
, through β-oxidation. In addition, trafficking
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations. More broadly, soc ...
of the enzyme to different compartments may change the degree of protonation
In chemistry, protonation (or hydronation) is the adding of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), usually denoted by H+, to an atom, molecule, or ion, forming a conjugate acid. (The complementary process, when a proton is removed from a Brø ...
(e.g., the neutral cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
and the acidic lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
) or oxidative state (e.g., oxidizing periplasm
The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the ''periplasmic space'' in Gram-negative (more accurately "diderm") bacteria. Using cryo-electron micros ...
or reducing cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
) which in turn affects enzyme activity. In contrast to partitioning into membrane bound organelles, enzyme subcellular localisation may also be altered through polymerisation of enzymes into macromolecular cytoplasmic filaments.
Organ specialization
Inmulticellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s, cells in different organs and tissues have different patterns of gene expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, ...
and therefore have different sets of enzymes (known as isozyme
In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. di ...
s) available for metabolic reactions. This provides a mechanism for regulating the overall metabolism of the organism. For example, hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that irreversibly phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important p ...
, the first enzyme in the glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
pathway, has a specialized form called glucokinase expressed in the liver and pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
that has a lower affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Pa ...
for glucose yet is more sensitive to glucose concentration. This enzyme is involved in sensing blood sugar
The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis.
For a 70 kg (1 ...
and regulating insulin production.
Involvement in disease
homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
, any malfunction (mutation, overproduction, underproduction or deletion) of a single critical enzyme can lead to a genetic disease. The malfunction of just one type of enzyme out of the thousands of types present in the human body can be fatal. An example of a fatal genetic disease due to enzyme insufficiency is Tay–Sachs disease
Tay–Sachs disease is an Genetic disorder, inherited fatal lysosomal storage disease that results in the destruction of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. The most common form is infantile Tay–Sachs disease, which becomes apparent arou ...
, in which patients lack the enzyme hexosaminidase.
One example of enzyme deficiency is the most common type of phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also r ...
. Many different single amino acid mutations in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) () is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of the aromatic side-chain of phenylalanine to generate tyrosine. PAH is one of three members of the biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases, a clas ...
, which catalyzes the first step in the degradation of phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
, result in build-up of phenylalanine and related products. Some mutations are in the active site, directly disrupting binding and catalysis, but many are far from the active site and reduce activity by destabilising the protein structure, or affecting correct oligomerisation. This can lead to intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability (in the United Kingdom), and formerly mental retardation (in the United States), Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010).Archive is a generalized neurodevelopmental ...
if the disease is untreated. Another example is pseudocholinesterase deficiency, in which the body's ability to break down choline ester drugs is impaired.
Oral administration of enzymes can be used to treat some functional enzyme deficiencies, such as pancreatic insufficiency and lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is caused by a lessened ability or a complete inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Humans vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pain ...
.
Another way enzyme malfunctions can cause disease comes from germline mutation
A germline mutation, or germinal mutation, is any detectable variation within germ cells (cells that, when fully developed, become sperm and Egg cell, ova). Mutations in these cells are the only mutations that can be passed on to offspring, when e ...
s in genes coding for DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is cons ...
enzymes. Defects in these enzymes cause cancer because cells are less able to repair mutations in their genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
s. This causes a slow accumulation of mutations and results in the development of cancers. An example of such a hereditary cancer syndrome is xeroderma pigmentosum
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a genetic disorder in which there is a decreased ability to repair DNA damage such as that caused by ultraviolet (UV) light. Symptoms may include a severe sunburn after only a few minutes in the sun, freckling in su ...
, which causes the development of skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
s in response to even minimal exposure to ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of th ...
.
Evolution
Similar to any other protein, enzymes change over time throughmutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
s and sequence divergence. Given their central role in metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
, enzyme evolution plays a critical role in adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the p ...
. A key question is therefore whether and how enzymes can change their enzymatic activities alongside. It is generally accepted that many new enzyme activities have evolved through gene duplication
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene ...
and mutation of the duplicate copies although evolution can also happen without duplication. One example of an enzyme that has changed its activity is the ancestor of methionyl aminopeptidase (MAP) and creatine amidinohydrolase ( creatinase) which are clearly homologous but catalyze very different reactions (MAP removes the amino-terminal methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
in new proteins while creatinase hydrolyses creatine
Creatine ( or ) is an organic compound with the nominal formula . It exists in various tautomers in solutions (among which are neutral form and various zwitterionic forms). Creatine is found in vertebrates, where it facilitates recycling of ...
to sarcosine
Sarcosine, also known as ''N''-methylglycine, or monomethylglycine, is a amino acid with the formula CH3N(H)CH2CO2H. It exists at neutral pH as the zwitterion CH3N+(H)2CH2CO2−, which can be obtained as a white, water-soluble powder. Like some ...
and urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
). In addition, MAP is metal-ion dependent while creatinase is not, hence this property was also lost over time. Small changes of enzymatic activity are extremely common among enzymes. In particular, substrate binding specificity (see above) can easily and quickly change with single amino acid changes in their substrate binding pockets. This is frequently seen in the main enzyme classes such as kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
s.
Artificial (in vitro) evolution is now commonly used to modify enzyme activity or specificity for industrial applications (see below).
Industrial applications
Enzymes are used in thechemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies and other organizations that develop and produce industrial, specialty and other chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, the chemical industry converts raw materials ( oil, natural gas, air, ...
and other industrial applications when extremely specific catalysts are required. Enzymes in general are limited in the number of reactions they have evolved to catalyze and also by their lack of stability in organic solvent
A solvent (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for p ...
s and at high temperatures. As a consequence, protein engineering is an active area of research and involves attempts to create new enzymes with novel properties, either through rational design or ''in vitro'' evolution. These efforts have begun to be successful, and a few enzymes have now been designed "from scratch" to catalyze reactions that do not occur in nature.
See also
* Industrial enzymes *List of enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system:
:Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase)
* Dehydrogenase
* Luciferase
* DMSO reduct ...
* Molecular machine
Molecular machines are a class of molecules typically described as an assembly of a discrete number of molecular components intended to produce mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli, mimicking macromolecular devices such as switch ...
Enzyme databases
* BRENDA * ExPASy * IntEnz *KEGG
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) is a collection of databases dealing with genomes, biological pathways, diseases, drugs, and chemical substances. KEGG is utilized for bioinformatics research and education, including data analysis ...
* MetaCyc
References
Further reading
;General * , A biochemistry textbook available free online through NCBI Bookshelf. ;Etymology and history * , A history of early enzymology. ;Enzyme structure and mechanism * ;Kinetics and inhibition *External links
* {{Authority control Biomolecules Catalysis Metabolism Process chemicals