|
Tetrahydrofolate
Tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA), or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative. Metabolism In humans, tetrahydrofolic acid is produced from dihydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase. This reaction is inhibited by methotrexate. It is converted into 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate by serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Many bacteria produce tetrahydrofolic acid via dihydropteroate. Humans lack the enzymes to do this, thus molecules that shut down these enzymes are effective antibacterial compounds. For example, sulfonamide antibiotics competitively binds the active site of dihydropteroate synthetase, ecluding the binding of the dihydropteroate precuror, 4-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). Functions Tetrahydrofolic acid is a cofactor in many reactions, especially in the synthesis (or anabolism) of amino acids and nucleic acids. In addition, it serves as a carrier molecule for single-carbon moieties, that is, groups containing one carbon atom e.g. methyl, methylene, methenyl, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dihydrofolate Reductase
Dihydrofolate reductase, or DHFR, is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, using NADPH as an electron donor, which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in one-carbon transfer chemistry. In humans, the DHFR enzyme is encoded by the ''DHFR'' gene. It is found in the q14.1 region of chromosome 5. There are two structural classes of DHFR, evolutionarily unrelated to each other. The former is usually just called DHFR and is found in bacterial chromosomes and animals. In bacteria, however, antibiotic pressure has caused this class to evolve different patterns of binding diaminoheterocyclic molecules, leading to many "types" named under this class, while mammalian ones remain highly similar. The latter (type II), represented by the plastid-encoded R67, is a tiny enzyme that works by forming a homotetramer. Function Dihydrofolate reductase converts dihydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate, a proton shuttle required for the de no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Folic Acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and storage. Folate is required for the body to make DNA and RNA and metabolise amino acids necessary for cell division and maturation of blood cells. As the human body cannot make folate, it is required in the diet, making it an Nutrient#Essential nutrients, essential nutrient. It occurs naturally in many foods. The recommended adult daily intake of folate in the U.S. is 400 micrograms from foods or dietary supplements. Folate in the form of folic acid is used to treat anemia caused by folic acid deficiency, folate deficiency. Folic acid is also used as a supplement by women during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) in the baby. NTDs include anencephaly and spina bifida, among other defects. Low levels in early pregna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, gestational trophoblastic disease, and osteosarcoma. Types of autoimmune diseases it is used for include psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It can be given Oral administration, by mouth or by injection. Common side effects include nausea, feeling tired, fever, increased risk of infection, leukopenia, low white blood cell counts, and ulcerative stomatitis, breakdown of the skin inside the mouth. Other side effects may include liver disease, lung disease, lymphoma, and severe skin rashes. People on long-term treatment should be regularly checked for side effects. It is not safe during breastfeeding. In those with kidney problems, lower doses may be needed. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trimethoprim
Trimethoprim (TMP) is an antibiotic used mainly in the treatment of bladder infections. Other uses include for middle ear infections and travelers' diarrhea. With sulfamethoxazole or dapsone it may be used for ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It is taken orally (swallowed by mouth). Common side effects include nausea, changes in taste, and rash. Rarely it may result in blood problems such as not enough platelets or white blood cells. Trimethoprim may cause sun sensitivity. There is evidence of potential harm during pregnancy in some animals but not humans. It works by blocking folate metabolism via dihydrofolate reductase in some bacteria, preventing creation of bacterial DNA and RNA and leading to bacterial cell death. Trimethoprim was first used in 1962. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses It is primarily used in the treatment of urinary tract infectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) Vitamin B6, (Vitamin B6) dependent enzyme () which plays an important role in cellular one-carbon pathways by catalyzing the reversible, simultaneous conversions of L-serine to glycine and tetrahydrofolate (THF) to 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH2-THF). This reaction provides the largest part of the one-carbon units available to the cell. Structure The structure of the SHMT Protein subunit, monomer is similar across prokaryotes and eukaryotes, but whereas the active enzyme is a dimer in prokaryotes, the enzyme exists as a tetramer in eukaryotic cells, though the evolutionary basis for this difference in structure is unknown. However, the evolutionary path taken by SHMT going from prokaryotic dimeric form to the eukaryotic tetrameric form can be easily seen as a sort of doubling event. In other words, the eukaryotic SHMT tetramer resembles two prokaryotic dimers that have packed together, forming wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dihydropteroate
Dihydropteroate is an important intermediate in folate biosynthesis. It is a pterin created from ''para''-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) by the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase. Bacteriostatic agents such as sulfonamides target dihydropteroate synthetase. The effect of dihydropteroate synthetase inhibition is comparable to that of dihydrofolate reductase inhibition by trimethoprim, another bacteriostatic agent. Combinations of these two drug types, such as the combination trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or TMP-SMX), are commonly used to treat recurrent urinary tract, ''Shigella'', ''Salmonella'', and ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' infections, though resistance is known. See also * Dihydrofolic acid Dihydrofolic acid (conjugate base dihydrofolate) (DHF) is a folic acid ( vitamin B9) derivative which is converted to tetrahydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase. Since tetrahydrofolate is needed to make both purines and pyrimidines, which ... References {{reflist Benzoic acids F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dihydropteroate Synthetase
Dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) is an enzyme classified under . It produces dihydropteroate in bacteria, but it is not expressed in most eukaryotes including humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide antibiotics, which compete with the PABA precursor. * (2-amino-4-hydroxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl diphosphate + 4-aminobenzoate (PABA) \rightleftharpoons diphosphate + dihydropteroate. All organisms require reduced folate cofactors for the synthesis of a variety of metabolites. Most microorganisms must synthesize folate de novo because they lack the active transport system of higher vertebrate cells that allows these organisms to use dietary folates. Proteins containing this domain include dihydropteroate synthase () as well as a group of methyltransferase enzymes including methyltetrahydrofolate, corrinoid iron-sulphur protein methyltransferase (MeTr) that catalyses a key step in the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway of carbon dioxide fixation. Dihydropteroate synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
4-aminobenzoic Acid
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as ''para''-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the ''para'' position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA is a white crystalline solid, although commercial samples can appear gray. It is slightly soluble in water. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with amino and carboxyl groups. The compound occurs extensively in the natural world. Production and occurrence In industry, PABA is prepared mainly by two routes: * Reduction of 4-nitrobenzoic acid * Hoffman degradation of the monoamide derived from terephthalic acid. Food sources of PABA include liver, brewer's yeast (and unfiltered beer), kidney, molasses, mushrooms, and whole grains. Other food sources of PABA include spinach, liver, and oat seeds. Biology Biochemistry PABA is an intermediate in the synthesis of folate by bacteria, plants, and fungi. Many bacteria, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in two optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
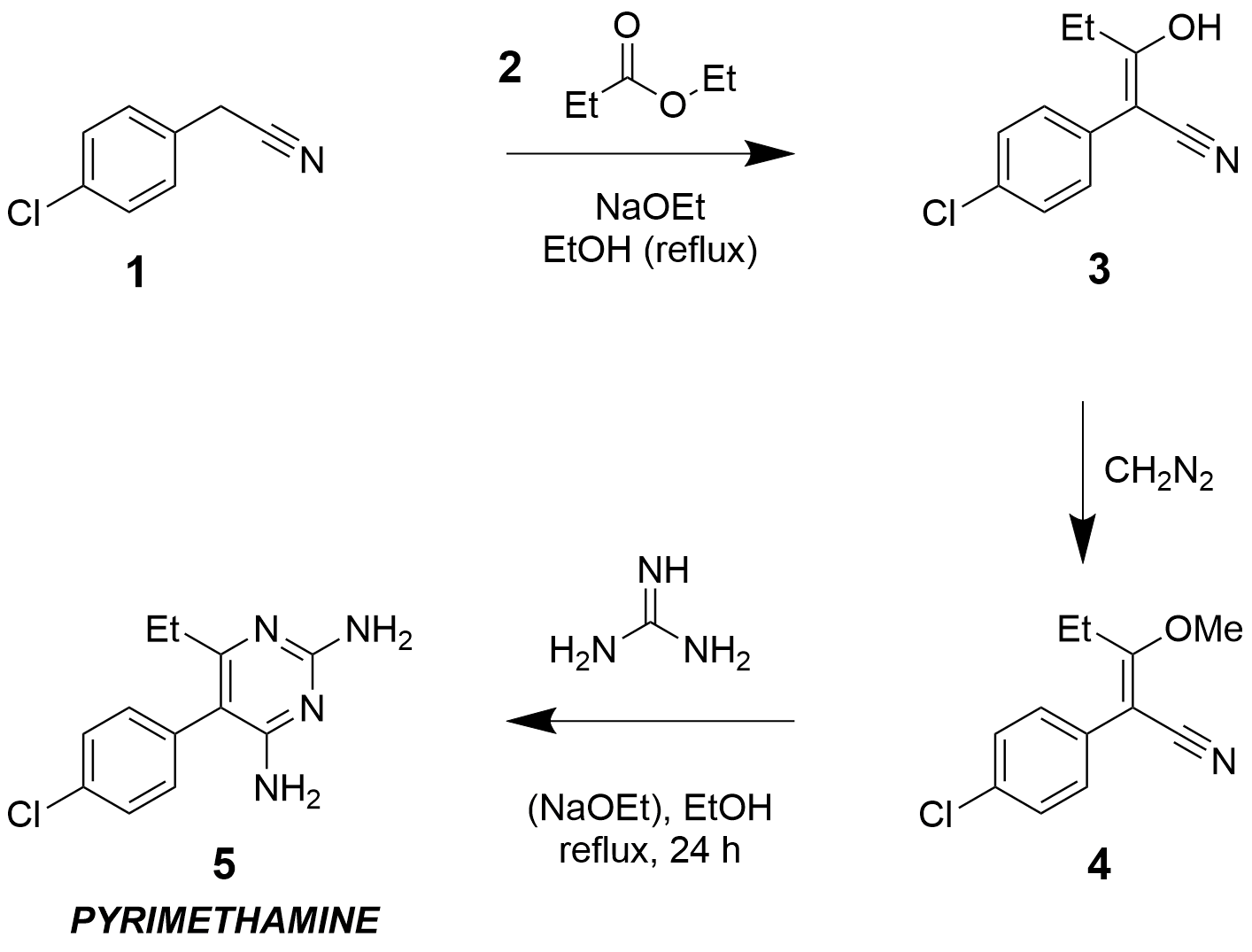
Pyrimethamine
Pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Daraprim among others, is a medication used with leucovorin (leucovorin is used to decrease side effects of pyrimethamine; it does not have intrinsic anti-parasitic activity) to treat the parasitic diseases toxoplasmosis and cystoisosporiasis. It is also used with dapsone as a second-line option to prevent Pneumocystis pneumonia, ''Pneumocystis jiroveci'' pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It was previously used for malaria but is no longer recommended due to resistance. Pyrimethamine is oral administration, taken by mouth. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, severe allergic reactions, and bone marrow suppression. It should not be used by people with folate deficiency that has resulted in anemia. There is concern that it may increase the risk of cancer. While occasionally used in pregnancy it is unclear if pyrimethamine is safe for the baby. Pyrimethamine is classified as a folic acid antagonist. It works by inhibiting f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Formiminoglutamic Acid
Formiminoglutamic acid (FIGLU; conjugate base, formiminoglutamate) is an intermediate in the catabolism of L-histidine to L-glutamic acid. It thus is also a biomarker for intracellular levels of folate. The FIGLU test is used to identify vitamin B₁₂ deficiency, folate deficiency, and liver failure or liver disease. It is elevated with folate trapping, where it is accompanied by decreased methylmalonic acid, increased folate and a decrease in homocysteine. See also * Formiminotransferase cyclodeaminase * Glutamate-1-semialdehyde * Glutamic acid * Imidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid Imidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid is an intermediate in the metabolism of histidine. It is a colorless compound that is sensitive to light in air. The compound features an imidazolone ring. Occurrence It arises via the action of urocanase on uro ... References Amidines Amino acid derivatives Glutamic acids {{Base-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dihydrofolic Acid
Dihydrofolic acid (conjugate base dihydrofolate) (DHF) is a folic acid ( vitamin B9) derivative which is converted to tetrahydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase. Since tetrahydrofolate is needed to make both purines and pyrimidines, which are building blocks of DNA and RNA, dihydrofolate reductase is targeted by various drugs to prevent nucleic acid Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ... synthesis. Interactive pathway map Further reading * References Folates {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |