Dublin County Mid (Dáil Constituency) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dublin is the capital and largest city of
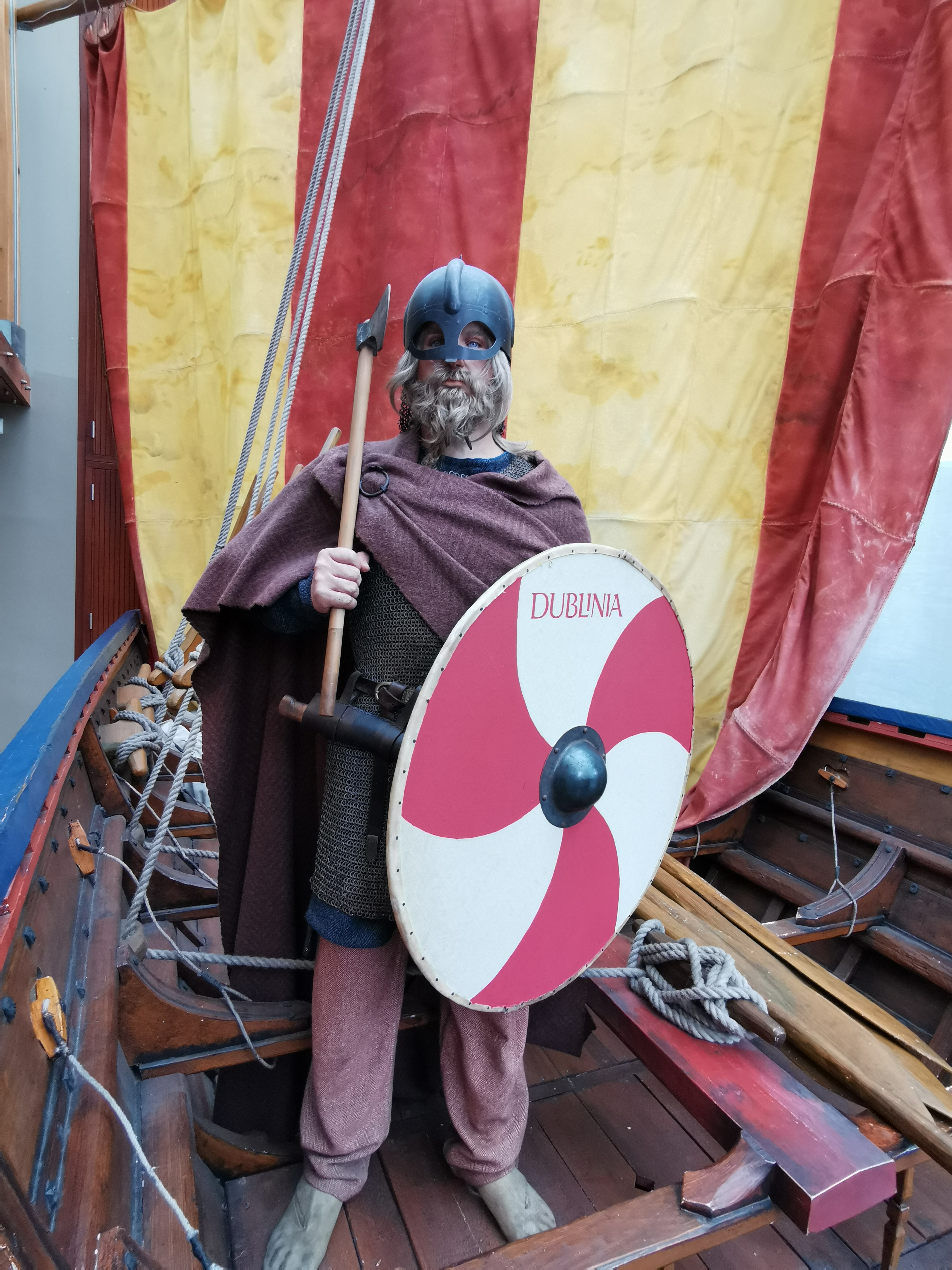

 Dublin celebrated its 'official' millennium in 1988, meaning the Irish government recognised 988 as the year in which the city was settled and that this first settlement would later become the city of Dublin.
It is now thought the Viking settlement of about 841 was preceded by a Christian ecclesiastical settlement known as ''Duibhlinn'', from which ''Dyflin'' took its name. Evidence indicating that Anglo-Saxons occupied Dublin before the Vikings arrived in 841 has been found in an archaeological dig in Temple Bar.
Beginning in the 9th and 10th centuries, there were two settlements which later became modern Dublin. The subsequent Scandinavian settlement centred on the
Dublin celebrated its 'official' millennium in 1988, meaning the Irish government recognised 988 as the year in which the city was settled and that this first settlement would later become the city of Dublin.
It is now thought the Viking settlement of about 841 was preceded by a Christian ecclesiastical settlement known as ''Duibhlinn'', from which ''Dyflin'' took its name. Evidence indicating that Anglo-Saxons occupied Dublin before the Vikings arrived in 841 has been found in an archaeological dig in Temple Bar.
Beginning in the 9th and 10th centuries, there were two settlements which later became modern Dublin. The subsequent Scandinavian settlement centred on the

 Dublin was the heart of the area known as
Dublin was the heart of the area known as
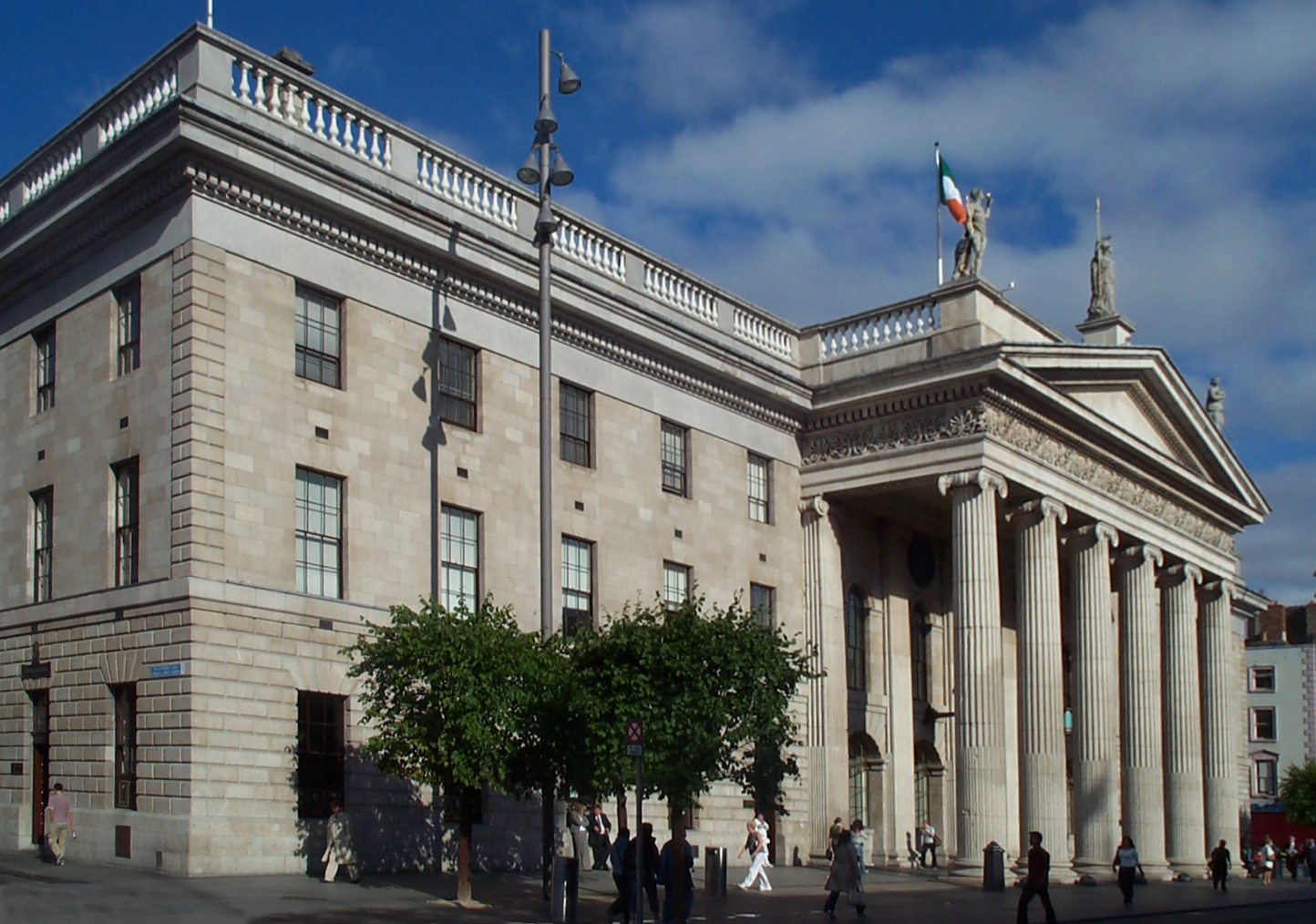 Dublin suffered a period of political and economic decline during the 19th century following the
Dublin suffered a period of political and economic decline during the 19th century following the

 As the capital city, Dublin is the seat of the national parliament of Ireland, the
As the capital city, Dublin is the seat of the national parliament of Ireland, the
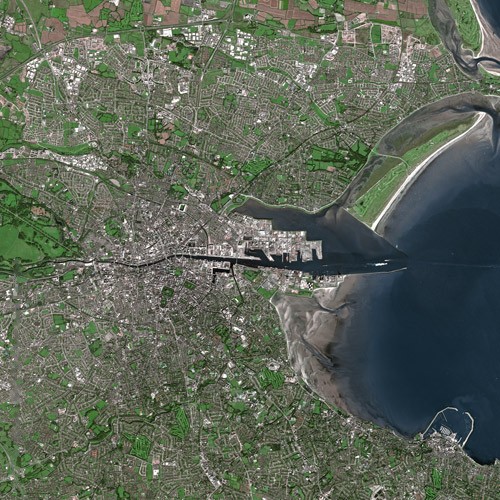 Dublin is situated at the mouth of the
Dublin is situated at the mouth of the
 Dublin has dozens of suburbs; northside suburbs include
Dublin has dozens of suburbs; northside suburbs include 
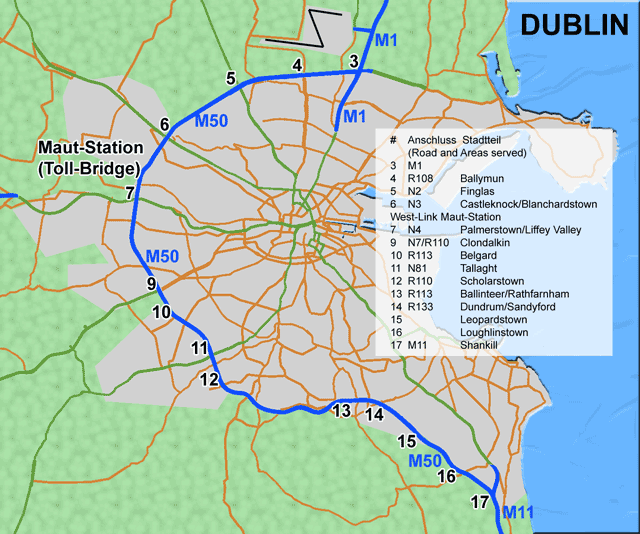 The road network in Ireland is primarily focused on Dublin. The M50 motorway, a semi-
The road network in Ireland is primarily focused on Dublin. The M50 motorway, a semi-
 The 2011 census indicated that 5.9% of commuters in Dublin cycled. A 2013 report by Dublin City Council on traffic flows crossing the canals in and out of the city found that just under 10% of all traffic was made up of cyclists, representing an increase of 14.1% over 2012 and an 87.2% increase over 2006 levels. The increase was attributed to measures such as the Dublinbikes bike rental scheme, the provision of cycle lanes, public awareness campaigns to promote cycling and the introduction of the 30 km/h city centre speed limit.
Dublin City Council began installing cycle lanes and tracks throughout the city in the 1990s, and the city had over of specific on- and off-road tracks for cyclists. In 2011, the city was ranked 9th of major world cities on the ''Copenhagenize Index of Bicycle-Friendly Cities''. The same index showed a fall to 15th in 2015, and Dublin was outside the top 20 in 2017.
The 2011 census indicated that 5.9% of commuters in Dublin cycled. A 2013 report by Dublin City Council on traffic flows crossing the canals in and out of the city found that just under 10% of all traffic was made up of cyclists, representing an increase of 14.1% over 2012 and an 87.2% increase over 2006 levels. The increase was attributed to measures such as the Dublinbikes bike rental scheme, the provision of cycle lanes, public awareness campaigns to promote cycling and the introduction of the 30 km/h city centre speed limit.
Dublin City Council began installing cycle lanes and tracks throughout the city in the 1990s, and the city had over of specific on- and off-road tracks for cyclists. In 2011, the city was ranked 9th of major world cities on the ''Copenhagenize Index of Bicycle-Friendly Cities''. The same index showed a fall to 15th in 2015, and Dublin was outside the top 20 in 2017.
 Heuston and Connolly stations are the two main railway termini in Dublin. Operated by
Heuston and Connolly stations are the two main railway termini in Dublin. Operated by
 The
The
 The City of Dublin is the area administered by
The City of Dublin is the area administered by


 In addition public
In addition public
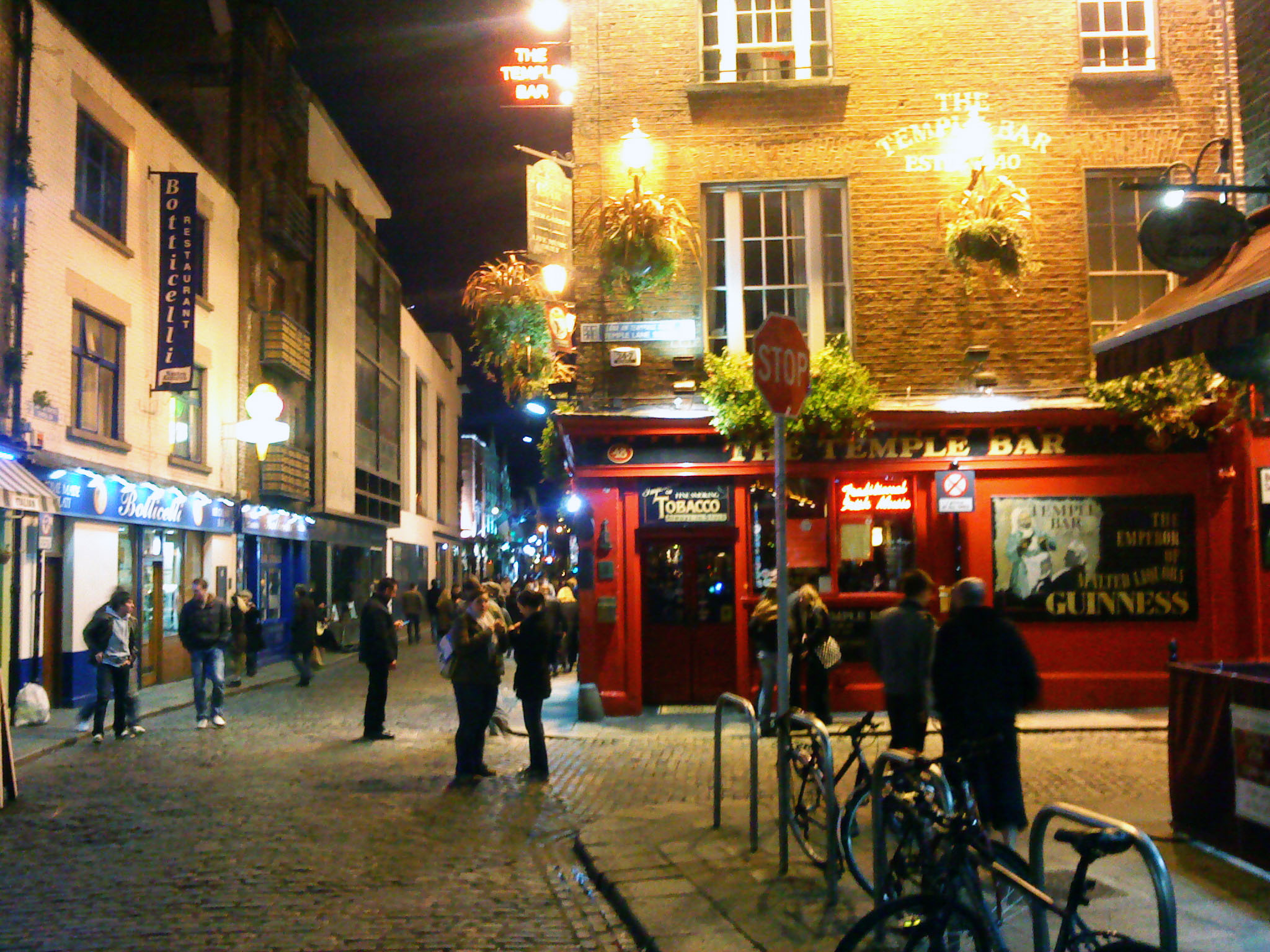 The best known area for nightlife is Temple Bar, south of the River Liffey. The area has become popular among tourists, including
The best known area for nightlife is Temple Bar, south of the River Liffey. The area has become popular among tourists, including
 Live music is played on streets and at venues throughout Dublin, and the city has produced several musicians and groups of international success, including
Live music is played on streets and at venues throughout Dublin, and the city has produced several musicians and groups of international success, including
 Croke Park is the largest sport stadium in Ireland. The headquarters of the Gaelic Athletic Association, it has a capacity of 82,300. It is the third-largest stadium in Europe after Nou Camp in Barcelona and Wembley Stadium in London. It hosts the premier Gaelic football and hurling games, international rules football and irregularly other sporting and non-sporting events including concerts. Muhammad Ali fought there in 1972 and it played host to the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2003 Special Olympics. It also has conference and banqueting facilities. There is a GAA Museum there and tours of the stadium are offered, including a rooftop walk of the stadium. During the redevelopment of Lansdowne Road, Croke Park played host to the Ireland national rugby union team, Irish Rugby Union Team and Republic of Ireland national football team as well as hosting the Heineken Cup rugby 2008–09 Heineken Cup#Semi-finals, 2008–09 semi-final between Munster and Leinster, which set a world record attendance for a club rugby match. The Dublin GAA team plays most of their home league hurling games at Parnell Park.
Croke Park is the largest sport stadium in Ireland. The headquarters of the Gaelic Athletic Association, it has a capacity of 82,300. It is the third-largest stadium in Europe after Nou Camp in Barcelona and Wembley Stadium in London. It hosts the premier Gaelic football and hurling games, international rules football and irregularly other sporting and non-sporting events including concerts. Muhammad Ali fought there in 1972 and it played host to the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2003 Special Olympics. It also has conference and banqueting facilities. There is a GAA Museum there and tours of the stadium are offered, including a rooftop walk of the stadium. During the redevelopment of Lansdowne Road, Croke Park played host to the Ireland national rugby union team, Irish Rugby Union Team and Republic of Ireland national football team as well as hosting the Heineken Cup rugby 2008–09 Heineken Cup#Semi-finals, 2008–09 semi-final between Munster and Leinster, which set a world record attendance for a club rugby match. The Dublin GAA team plays most of their home league hurling games at Parnell Park.
 Lansdowne Road, IRFU Stadium Lansdowne Road was laid out in 1874. This was the venue for home games of both the Irish Rugby Union Team and the Republic of Ireland national football team. A joint venture between the Irish Rugby Football Union, the Football Association of Ireland, FAI and the Government, saw it redeveloped into a new state-of-the-art 50,000 seat Aviva Stadium, which opened in May 2010. Lansdowne Road/Aviva Stadium hosted the European Rugby Champions Cup, Heineken Cup final in 1999, 2003, 2013, and 2023. Rugby union team Leinster Rugby play their competitive home games in the RDS Arena and the Aviva Stadium, while Donnybrook Stadium hosts their friendlies and A games, Ireland A and Women, Leinster Schools and Youths and the home club games of AIB League, All Ireland League clubs Old Wesley and Bective Rangers.
Lansdowne Road, IRFU Stadium Lansdowne Road was laid out in 1874. This was the venue for home games of both the Irish Rugby Union Team and the Republic of Ireland national football team. A joint venture between the Irish Rugby Football Union, the Football Association of Ireland, FAI and the Government, saw it redeveloped into a new state-of-the-art 50,000 seat Aviva Stadium, which opened in May 2010. Lansdowne Road/Aviva Stadium hosted the European Rugby Champions Cup, Heineken Cup final in 1999, 2003, 2013, and 2023. Rugby union team Leinster Rugby play their competitive home games in the RDS Arena and the Aviva Stadium, while Donnybrook Stadium hosts their friendlies and A games, Ireland A and Women, Leinster Schools and Youths and the home club games of AIB League, All Ireland League clubs Old Wesley and Bective Rangers.
Dublin City Council
nbsp;– Official website of the local authority for Dublin
Dublin Tourist Board
nbsp;– Official tourism site
Dublin UNESCO City of Literature official site
Dublin Historic Maps, Boundaries & an OSM Miscellany
{{Authority control Dublin (city), 841 establishments 9th-century establishments in Ireland Capitals in Europe Cities in the Republic of Ireland County towns in the Republic of Ireland Former boroughs in the Republic of Ireland Leinster Local government areas of the Republic of Ireland Populated coastal places in the Republic of Ireland Populated places established in the 9th century Port cities and towns of the Irish Sea Staple ports Tourism regions of the island of Ireland Viking Age populated places
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
. Situated on Dublin Bay
Dublin Bay () is a C-shaped inlet of the Irish Sea on the east coast of Ireland. The bay is about 10 kilometres wide along its north–south base, and 7 km in length to its apex at the centre of the city of Dublin; stretching from Howth He ...
at the mouth of the River Liffey
The River Liffey (Irish language, Irish: ''An Life'', historically ''An Ruirthe(a)ch'') is a river in eastern Ireland that ultimately flows through the centre of Dublin to its mouth within Dublin Bay. Its major Tributary, tributaries include t ...
, it is in the province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland.
The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century ...
, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, part of the Wicklow Mountains
The Wicklow Mountains (, archaic: '' Cualu'') form the largest continuous upland area in Ireland. They occupy the whole centre of County Wicklow and stretch outside its borders into the counties of Dublin, Wexford and Carlow. Where the mountai ...
range. Dublin is the largest city by population on the island of Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
; at the 2022 census, the city council area had a population of 592,713, while the city including suburbs had a population of 1,263,219, County Dublin
County Dublin ( or ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and holds its capital city, Dublin. It is located on the island's east coast, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Until 1994, County Dubli ...
had a population of 1,501,500. Various definitions of a metropolitan Greater Dublin Area
The Greater Dublin Area (GDA; Irish: ''Mórcheantar Bhaile Átha Cliath''), or simply Greater Dublin, is an informal term that is taken to include the city of Dublin and its hinterland, with varying definitions as to its extent. At the expansive ...
exist.
A settlement was established in the area by the Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ; ; ) are an Insular Celts, Insular Celtic ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. They are associated with the Goidelic languages, Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising ...
during or before the 7th century, followed by the Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
s. As the Kingdom of Dublin
The Kingdom of Dublin (Old Norse: ''Dyflin'') was a Norse kingdom in Ireland that lasted from roughly 853 AD to 1170 AD. It was the first and longest-lasting Norse kingdom in Ireland, founded by Vikings who invaded the territory around Dublin ...
grew, it became Ireland's principal settlement by the 12th century Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land in Ireland over which the List of English monarchs, monarchs of England then claimed sovere ...
. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest in the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
and sixth largest in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
after the Acts of Union in 1800. Following independence in 1922, Dublin became the capital of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
, renamed Ireland in 1937. , the city was listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network
The Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) is a British think tank that studies the relationships between world cities in the context of globalization. It is based in the geography department of Loughborough University in Leic ...
(GaWC) as a global city
A global city (also known as a power city, world city, alpha city, or world center) is a city that serves as a primary node in the global economic network. The concept originates from geography and urban studies, based on the thesis that glo ...
, with a ranking of "Alpha minus", which placed it among the top thirty cities in the world.
Etymology
The name ''Dublin'' comes from theMiddle Irish
Middle Irish, also called Middle Gaelic (, , ), is the Goidelic language which was spoken in Ireland, most of Scotland and the Isle of Man from AD; it is therefore a contemporary of Late Old English and Early Middle English. The modern Goideli ...
(literally "Blackpool"), from "black, dark" and "pool". This evolved into the Early Modern Irish
Early Modern Irish () represented a transition between Middle Irish and Modern Irish. Its literary form, Classical Gaelic, was used in Ireland and Scotland from the 13th to the 18th century.
Classical Gaelic
Classical Gaelic or Classical Irish ( ...
form , which was pronounced "Duílinn" in the local dialect
Local may refer to:
Geography and transportation
* Local (train), a train serving local traffic demand
* Local, Missouri, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Local'' (comics), a limited series comic book by Bria ...
. The name refers to a dark tidal pool on the site of the castle gardens at the rear of Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle () is a major Government of Ireland, Irish government complex, conference centre, and tourist attraction. It is located off Dame Street in central Dublin.
It is a former motte-and-bailey castle and was chosen for its position at ...
, where the River Poddle
The River Poddle () is a river in Dublin, Ireland, a pool of which (', "black pool" or "dark pool" in Irish) gave the city its English language name. Boosted by a channel made by the Abbey of St. Thomas à Becket, taking water from the far lar ...
entered the Liffey.
The Middle Irish pronunciation is preserved in the names for the city in other languages such as Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
, Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
, modern Icelandic and modern Manx as well as Welsh and Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
**Breton people
**Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Gale ...
. Other localities in Ireland also bear the name ''Duibhlinn'', variously anglicised as Devlin, Divlin and Difflin. Variations on the name are also found in traditionally Gaelic-speaking areas of Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
, such as ("the black pool"), which is part of Loch Linnhe
Loch Linnhe ( ) is a sea loch in the Highland Council area, in the west of Scotland. The part upstream of Corran is known in Gaelic as (the black pool, originally known as Loch Abar), and downstream as (the salty pool). The name ''Linnhe ...
.
It is now thought that the Viking settlement was preceded by a Christian ecclesiastical settlement known as ''Duibhlinn'', from which ''Dyflin'' took its name. Beginning in the 9th and 10th centuries, there were two settlements where the modern city stands. The Viking settlement of about 841, ''Dyflin'', and a Gaelic settlement, Áth Cliath ("ford of hurdles") further up the river, at the present-day Father Mathew Bridge (also known as Dublin Bridge), at the bottom of Church Street.
, meaning "town of the hurdled ford", is the common name for the city in Modern Irish, which is often contracted to or when spoken. is a place name referring to a fording point of the River Liffey near Father Mathew Bridge. ' was an early Christian monastery, believed to have been in the area of Aungier Street, currently occupied by Whitefriar Street Carmelite Church
Whitefriar Street Carmelite Church is a Roman Catholic church in Dublin, Ireland maintained by the Carmelite order. The church is noted for having the relics of Saint Valentine, which were donated to the church in the 19th century by Pope Grego ...
.
History
The area ofDublin Bay
Dublin Bay () is a C-shaped inlet of the Irish Sea on the east coast of Ireland. The bay is about 10 kilometres wide along its north–south base, and 7 km in length to its apex at the centre of the city of Dublin; stretching from Howth He ...
has been inhabited by humans since prehistoric times; fish traps discovered from excavations during the construction of the Convention Centre Dublin
The Convention Centre Dublin () is a convention centre in the Dublin Docklands, Ireland. The Convention centre overlooks the River Liffey at Spencer Dock. It was designed by the Irish-born American architect Kevin Roche.
Construction started i ...
indicate human habitation as far back as 6,000 years ago. Further traps were discovered closer to the old settlement of the city of Dublin on the south quays near St. James's Gate
St. James's Gate, located off the south quays of Dublin, on James's Street, Dublin, James's Street, was the western entrance to the city during the Middle Ages. During this time the gate was the traditional starting point for the Camino pilgrima ...
which also indicate mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
human activity.
Ptolemy's map of Ireland
Ptolemy's map of Ireland is a part of his "first European map" (depicting the British Isles) in the series of maps included in his ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which he compiled in the second century AD in Roman Egypt and which is the oldes ...
, of about 140 AD, provides possibly the earliest reference to a settlement near Dublin. Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
, the Greco-Roman astronomer and cartographer
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
, called it '' Eblana polis'' ().

 Dublin celebrated its 'official' millennium in 1988, meaning the Irish government recognised 988 as the year in which the city was settled and that this first settlement would later become the city of Dublin.
It is now thought the Viking settlement of about 841 was preceded by a Christian ecclesiastical settlement known as ''Duibhlinn'', from which ''Dyflin'' took its name. Evidence indicating that Anglo-Saxons occupied Dublin before the Vikings arrived in 841 has been found in an archaeological dig in Temple Bar.
Beginning in the 9th and 10th centuries, there were two settlements which later became modern Dublin. The subsequent Scandinavian settlement centred on the
Dublin celebrated its 'official' millennium in 1988, meaning the Irish government recognised 988 as the year in which the city was settled and that this first settlement would later become the city of Dublin.
It is now thought the Viking settlement of about 841 was preceded by a Christian ecclesiastical settlement known as ''Duibhlinn'', from which ''Dyflin'' took its name. Evidence indicating that Anglo-Saxons occupied Dublin before the Vikings arrived in 841 has been found in an archaeological dig in Temple Bar.
Beginning in the 9th and 10th centuries, there were two settlements which later became modern Dublin. The subsequent Scandinavian settlement centred on the River Poddle
The River Poddle () is a river in Dublin, Ireland, a pool of which (', "black pool" or "dark pool" in Irish) gave the city its English language name. Boosted by a channel made by the Abbey of St. Thomas à Becket, taking water from the far lar ...
, a tributary of the Liffey in an area now known as Wood Quay
Wood Quay () is a riverside area of Dublin that was a site of Viking settlement. It is now the location of the Dublin City Council offices.
Location
The site is bounded on the north side by Wood Quay on the River Liffey, on the west by W ...
. The Dubhlinn was a pool on the lowest stretch of the Poddle, where ships used to moor. This pool was finally fully infilled during the early 18th century, as the city grew. The Dubhlinn lay where the Castle Garden is now located, opposite the Chester Beatty Library
The Chester Beatty Library, now known as the Chester Beatty, is a museum and library in Dublin. It was established in Ireland in 1953, to house the collections of mining magnate, Sir Alfred Chester Beatty. The present museum, on the grounds of ...
within Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle () is a major Government of Ireland, Irish government complex, conference centre, and tourist attraction. It is located off Dame Street in central Dublin.
It is a former motte-and-bailey castle and was chosen for its position at ...
. '' Táin Bó Cuailgne'' ("The Cattle Raid of Cooley") refers to ''Dublind rissa ratter Áth Cliath'', meaning "Dublin, which is called Ath Cliath".
Middle Ages
In 841, theVikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
established a fortified base in Dublin. The town grew into a substantial commercial center under Olaf Guthfrithson
Olaf Guthfrithson or Anlaf Guthfrithson ( ; ; ; died 941) was a Hiberno-Scandinavian (Irish-Viking) leader who ruled Dublin and Viking Northumbria in the 10th century. He was the son of Gofraid ua Ímair and great-grandson of Ímar, making ...
in the mid-to-late 10th century and, despite a number of attacks by the native Irish, it remained largely under Viking control until the Norman invasion of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land in Ireland over which the monarchs of England then claimed sovereignty. The Anglo-Normans ...
was launched from Wales in 1169. The hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning the 'land behind' a city, a port, or similar. Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated wi ...
of Dublin in the Norse period was named in . It was upon the death of Muirchertach Mac Lochlainn
Muircheartach Mac Lochlainn (; ) was king of Tír Eoghain, and High King of Ireland from around 1156 until his death in 1166. He succeeded Toirdhealbhach Ua Conchobhair who died in 1156.
Mac Lochlainn survived an attempt by Ruaidrí Ua Con ...
in early 1166 that Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair
Ruaidrí mac Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (Modern Irish: Ruairí Ó Conchúir; anglicised as Rory O'Conor) ( – 2 December 1198) was King of Connacht from 1156 to 1186, and High King of Ireland from 1166 to 1198. He was the last High King of Ire ...
, King of Connacht
The Kings of Connacht were rulers of the ''cóiced'' (variously translated as portion, fifth, province) of Connacht, which lies west of the River Shannon, Ireland. However, the name only became applied to it in the early medieval era, being named ...
, proceeded to Dublin and was inaugurated ''King of Ireland'' without opposition.
According to some historians, part of the city's early economic growth is attributed to a trade in slaves. Slavery in Ireland and Dublin reached its pinnacle in the 9th and 10th centuries. Prisoners from slave raids and kidnappings, which captured men, women and children, brought revenue to the Gaelic Irish Sea raiders, as well as to the Vikings who had initiated the practice. The victims came from Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
, England, Normandy and beyond.
The King of Leinster, Diarmait Mac Murchada
Diarmait Mac Murchada (Modern Irish: ''Diarmaid Mac Murchadha''; anglicised as Dermot MacMurrough or Dermot MacMurphy; – c. 1 May 1171), was King of Leinster in Ireland from 1127 to 1171. In 1167, he was deposed by the High King of Ireland ...
, after his exile by Ruaidhrí, enlisted the help of Strongbow, the Earl of Pembroke, to conquer Dublin. Following Mac Murchada's death, Strongbow declared himself King of Leinster after gaining control of the city. In response to Strongbow's successful invasion, Henry II of England
Henry II () was King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with the ...
affirmed his ultimate sovereignty by mounting a larger invasion in 1171 and pronounced himself Lord of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland (), sometimes referred to retrospectively as Anglo-Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of Kingdom of England, England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Normans in Ireland, Anglo ...
. Around this time, the ''county of the City of Dublin'' was established along with certain liberties adjacent to the city proper. This continued down to 1840 when the barony Barony may refer to:
* Barony, the peerage, office of, or territory held by a baron
* Barony, the title and land held in fealty by a feudal baron
* Barony (county division), a type of administrative or geographical division in parts of the British ...
of Dublin City was separated from the barony of Dublin
Dublin (
Placenames Database of Ireland.) is one of the Barony (Ireland), baronies in Irel ...
. Since 2001, both baronies have been redesignated as the ''City of Dublin''.
Placenames Database of Ireland.) is one of the Barony (Ireland), baronies in Irel ...
Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle () is a major Government of Ireland, Irish government complex, conference centre, and tourist attraction. It is located off Dame Street in central Dublin.
It is a former motte-and-bailey castle and was chosen for its position at ...
, which became the centre of Anglo-Norman power in Ireland, was founded in 1204 as a major defensive work on the orders of King John of England
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empi ...
. Following the appointment of the first Lord Mayor of Dublin
The Lord Mayor of Dublin () is the honorary title of the chairperson ( ) of Dublin City Council which is the local government body for the city of Dublin, the capital of Ireland. The incumbent, since December 2024, is Fine Gael councillor Emma ...
in 1229, the city expanded and had a population of 8,000 by the end of the 13th century. Dublin prospered as a trade centre, despite an attempt by King Robert the Bruce
Robert I (11 July 1274 – 7 June 1329), popularly known as Robert the Bruce (), was King of Scots from 1306 until his death in 1329. Robert led Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the First War of Scottish Independence against Kingdom of Eng ...
of Scotland to capture the city in 1317. It remained a relatively small walled medieval town during the 14th century and was under constant threat from the surrounding native clans. In 1348, the Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
, a lethal plague which had ravaged Europe, took hold in Dublin and killed thousands over the following decade.
 Dublin was the heart of the area known as
Dublin was the heart of the area known as the Pale
The Pale ( Irish: ''An Pháil'') or the English Pale (' or ') was the part of Ireland directly under the control of the English government in the Late Middle Ages. It had been reduced by the late 15th century to an area along the east coast s ...
, a narrow strip of English settlement along the eastern coast, under the control of the English Crown
This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself king of the Anglo-Sax ...
. The Tudor conquest of Ireland
Ireland was conquered by the Tudor monarchs of England in the 16th century. The Anglo-Normans had Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, conquered swathes of Ireland in the late 12th century, bringing it under Lordship of Ireland, English rule. In t ...
in the 16th century spelt a new era for Dublin, with the city enjoying a renewed prominence as the centre of administrative rule in Ireland where English control and settlement had become much more extensive. Determined to make Dublin a Protestant city, Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
established Trinity College Trinity College may refer to:
Australia
* Trinity Anglican College, an Anglican coeducational primary and secondary school in , New South Wales
* Trinity Catholic College, Auburn, a coeducational school in the inner-western suburbs of Sydney, New ...
in 1592 as a solely Protestant university and ordered that the Catholic St. Patrick's and Christ Church cathedrals be converted to the Protestant church. The earliest map of the city of Dublin is John Speed's Map of Dublin (1610).
The city had a population of 21,000 in 1640 before a plague from 1649 to 1651 wiped out almost half of the inhabitants. However, the city prospered again soon after as a result of the wool and linen trade with England and reached a population of over 50,000 in 1700. By 1698 the manufacture of wool employed 12,000 people.
Early modern
As the city continued to prosper during the 18th century,Georgian Dublin
''Georgian Dublin'' is a phrase used in terms of the history of Dublin that has two interwoven meanings:
# to describe a historic period in the development of the city of Dublin, Ireland, from 1714 (the beginning of the reign of King George I ...
became, for a short period, the second-largest city of the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
and the fifth largest city in Europe, with the population exceeding 130,000. While some medieval streets and layouts (including the areas around Temple Bar, Aungier Street, Capel Street and Thomas Street) were less affected by the wave of Georgian reconstruction, much of Dublin's architecture and layout dates from this period.
Dublin grew even more dramatically during the 18th century, with the construction of many new districts and buildings, such as Merrion Square
Merrion Square () is a Georgian architecture, Georgian garden square on the Southside Dublin, southside of Dublin city centre.
History
The square was laid out in 1762 to a plan by John Smyth and Jonathan Barker for the estate of Richard Fitz ...
, Parliament House
Parliament House may refer to:
Meeting places of parliament
Australia
* Parliament House, Canberra, Parliament of Australia
* Parliament House, Adelaide, Parliament of South Australia
* Parliament House, Brisbane, Parliament of Queensland
* P ...
and the Royal Exchange. The Wide Streets Commission
The Wide Streets Commission (officially the Commissioners for making Wide and Convenient Ways, Streets and Passages) was established by an Act of Parliament in 1758, at the request of Dublin Corporation, as a body to govern standards on the lay ...
was established in 1757 at the request of Dublin Corporation
Dublin Corporation (), known by generations of Dubliners simply as ''The Corpo'', is the former name of the city government and its administrative organisation in Dublin since the 1100s. Significantly re-structured in 1660–1661, even more si ...
to govern architectural standards on the layout of streets, bridges and buildings. In 1759, the Guinness brewery
St. James's Gate Brewery is a brewery founded in 1759 in Dublin, Ireland, by Arthur Guinness. The company is now a part of Diageo, a company formed from the merger of Guinness and Grand Metropolitan in 1997. The main product of the brewery is ...
was founded, and would eventually grow to become the largest brewery in the world and the largest employer in Dublin. During the 1700s, linen was not subject to the same trade restrictions with England as wool, and became the most important Irish export. Over 1.5 million yards of linen was exported from Ireland in 1710, rising to almost 19 million yards by 1779.
Late modern and contemporary
 Dublin suffered a period of political and economic decline during the 19th century following the
Dublin suffered a period of political and economic decline during the 19th century following the Acts of Union 1800
The Acts of Union 1800 were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland (previously in personal union) to create the United Kingdom of G ...
, under which the seat of government was transferred to the Westminster Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of ...
in London. The city played no major role in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, but remained the centre of administration and a transport hub for most of the island. Ireland had no significant sources of coal, the fuel of the time, and Dublin was not a centre of ship manufacturing, the other main driver of industrial development in Britain and Ireland. Belfast
Belfast (, , , ; from ) is the capital city and principal port of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan and connected to the open sea through Belfast Lough and the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel ...
developed faster than Dublin during this period on a mixture of international trade, factory-based linen cloth production and shipbuilding. By 1814, the population of Dublin was 175,319 as counted under the Population Act, making the population of Dublin higher than any town in England except London.
The Easter Rising
The Easter Rising (), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an ind ...
of 1916, the Irish War of Independence
The Irish War of Independence (), also known as the Anglo-Irish War, was a guerrilla war fought in Ireland from 1919 to 1921 between the Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), Irish Republican Army (IRA, the army of the Irish Republic) and Unite ...
, and the subsequent Irish Civil War
The Irish Civil War (; 28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United Kingdom but within the British Emp ...
resulted in a significant amount of physical destruction in central Dublin. The Government of the Irish Free State
The Executive Council () was the cabinet and executive branch of government of the 1922–1937 Irish Free State. Formally, executive power was vested in the Governor-General on behalf of Monarchy in the Irish Free State, the King. In practice, ...
rebuilt the city centre and located the new parliament, the Oireachtas
The Oireachtas ( ; ), sometimes referred to as Oireachtas Éireann, is the Bicameralism, bicameral parliament of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The Oireachtas consists of the president of Ireland and the two houses of the Oireachtas (): a house ...
, in Leinster House
Leinster House () is the seat of the Oireachtas, the parliament of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Originally, it was the ducal palace of the Duke of Leinster, Dukes of Leinster.
Since 1922, it has been a complex of buildings which houses Oirea ...
. Since the beginning of Norman rule in the 12th century, the city has functioned as the capital in varying geopolitical entities: Lordship of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland (), sometimes referred to retrospectively as Anglo-Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman Lords between 1177 and 1542. T ...
(1171–1541), Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland (; , ) was a dependent territory of Kingdom of England, England and then of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1542 to the end of 1800. It was ruled by the monarchs of England and then List of British monarchs ...
(1541–1800), as part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the union of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into one sovereign state, established by the Acts of Union 1800, Acts of Union in 1801. It continued in this form until ...
(1801–1922), and the Irish Republic
The Irish Republic ( or ) was a Revolutionary republic, revolutionary state that Irish Declaration of Independence, declared its independence from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in January 1919. The Republic claimed jurisdict ...
(1919–1922). Following the partition of Ireland
The Partition of Ireland () was the process by which the Government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (UK) divided Ireland into two self-governing polities: Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland (the area today known as the R ...
in 1922, it became the capital of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
(1922–1937) and now is the capital of Ireland. One of the memorials to commemorate that time is the Garden of Remembrance.
Dublin was also a victim of the Northern Irish Troubles
The Troubles () were an ethno-nationalist conflict in Northern Ireland that lasted for about 30 years from the late 1960s to 1998. Also known internationally as the Northern Ireland conflict, it began in the late 1960s and is usually deemed ...
, although during this 30-year conflict, violence mainly occurred within Northern Ireland. A Loyalist paramilitary group, the Ulster Volunteer Force
The Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) is an Ulster loyalism, Ulster loyalist paramilitary group based in Northern Ireland. Formed in 1965, it first emerged in 1966. Its first leader was Gusty Spence, a former Royal Ulster Rifles soldier from North ...
, bombed the city during this time – notably in an atrocity known as the Dublin and Monaghan bombings
The Dublin and Monaghan bombings of 17 May 1974 were a series of co-ordinated bombings in Dublin and Monaghan, Ireland, carried out by the Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF). Three car bombs exploded in Dublin during the evening rush hour and a ...
in which 34 people died, mainly in central Dublin.
Large parts of Georgian Dublin were demolished or substantially redeveloped in the mid-20th century during a boom in office building. After this boom, the recessions of the 1970s and 1980s slowed down the pace of building. Cumulatively, this led to a large decline in the number of people living in the centre of the city, and by 1985 the city had approximately 150 acres of derelict land which had been earmarked for development and of office space.
Since 1997, the landscape of Dublin has changed. The city was at the forefront of Ireland's economic expansion during the Celtic Tiger
The "Celtic Tiger" () is a term referring to the economy of the Republic of Ireland, economy of Ireland from the mid-1990s to the late 2000s, a period of rapid real economic growth fuelled by foreign direct investment. The boom was dampened by ...
period, with private sector and state development of housing, transport and business. Following an economic decline during the Great Recession, Dublin has rebounded and has close to full employment, but has a significant problem with housing supply in both the city and surrounds.
Government
Local
Dublin City Council
Dublin City Council () is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority of the city of Dublin in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. As a city council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. Until 2001, the authority was k ...
is a unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature consisting of one house or assembly that legislates and votes as one. Unicameralism has become an increasingly common type of legislature, making up nearly ...
assembly of 63 members elected every five years from local electoral area
A local electoral area (LEA; ) is an electoral area for elections to Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authorities in Ireland. All elections in the Republic of Ireland, elections use the single transferable vote. Republic of Ir ...
s. It is presided over by the Lord Mayor
Lord mayor is a title of a mayor of what is usually a major city in a Commonwealth realm, with special recognition bestowed by the sovereign. However, the title or an equivalent is present in other countries, including forms such as "high mayor". A ...
, who is elected for a yearly term and resides in Dublin's Mansion House. Council meetings occur at Dublin City Hall, while most of its administrative activities are based in the Civic Offices on Wood Quay
Wood Quay () is a riverside area of Dublin that was a site of Viking settlement. It is now the location of the Dublin City Council offices.
Location
The site is bounded on the north side by Wood Quay on the River Liffey, on the west by W ...
. The party or coalition of parties with the majority of seats assigns committee members, introduces policies, and proposes the Lord Mayor. The Council passes an annual budget for spending on areas such as housing, traffic management, refuse, drainage, and planning. The Dublin City Manager is responsible for implementing City Council decisions but also has considerable executive power. Neighbouring local authorities in the traditional County Dublin are South Dublin County Council
South Dublin County Council () is the local authority of the county of South Dublin, Ireland. It is one of three local authorities created by the Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993 to succeed the former Dublin County Council before its abolitio ...
, Fingal County Council
Fingal County Council () is the local authority of the county of Fingal, Ireland. It is one of three local authorities that succeeded the former Dublin County Council on abolition on 1 January 1994 and is one of four local authorities in County ...
and Dun Laoghaire-Rathdown County Council, and parts of the wider city lie in the functional areas of all three.
National
Oireachtas
The Oireachtas ( ; ), sometimes referred to as Oireachtas Éireann, is the Bicameralism, bicameral parliament of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The Oireachtas consists of the president of Ireland and the two houses of the Oireachtas (): a house ...
. It is composed of the President of Ireland
The president of Ireland () is the head of state of Republic of Ireland, Ireland and the supreme commander of the Defence Forces (Ireland), Irish Defence Forces. The presidency is a predominantly figurehead, ceremonial institution, serving as ...
, Dáil Éireann
Dáil Éireann ( ; , ) is the lower house and principal chamber of the Oireachtas, which also includes the president of Ireland and a senate called Seanad Éireann.Article 15.1.2° of the Constitution of Ireland reads: "The Oireachtas shall co ...
as the house of representatives, and Seanad Éireann
Seanad Éireann ( ; ; "Senate of Ireland") is the senate of the Oireachtas (the Irish legislature), which also comprises the President of Ireland and Dáil Éireann (defined as the house of representatives).
It is commonly called the Seanad or ...
as the upper house. The President resides in Áras an Uachtaráin
(; "Residence of the President"), formerly the Viceregal Lodge, is the List of official residences, official residence and principal workplace of the President of Ireland.
It is located off Chesterfield Avenue in the Phoenix Park in Dublin, ...
in Phoenix Park
The Phoenix Park () is a large urban park in Dublin, Ireland, lying west of the city centre, north of the River Liffey. Its perimeter wall encloses of recreational space. It includes large areas of grassland and tree-lined avenues, and since ...
, while both houses of the Oireachtas meet in Leinster House
Leinster House () is the seat of the Oireachtas, the parliament of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Originally, it was the ducal palace of the Duke of Leinster, Dukes of Leinster.
Since 1922, it has been a complex of buildings which houses Oirea ...
, a former ducal residence on Kildare Street
Kildare Street () is a street in Dublin, Ireland.
Location
Kildare Street is close to the principal shopping area of Grafton Street and Dawson Street, to which it is joined by Molesworth Street. Trinity College lies at the north end of t ...
. It has been the home of the Irish parliament since the foundation of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
in 1922. The old Irish Houses of Parliament
Parliament House () in Dublin, Ireland, was home to the Parliament of Ireland, and since 1803 has housed the Bank of Ireland. It was the world's first purpose-built bicameral parliament house. It is located at College Green, Dublin, College G ...
of the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland (; , ) was a dependent territory of Kingdom of England, England and then of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1542 to the end of 1800. It was ruled by the monarchs of England and then List of British monarchs ...
, which dissolved in 1801, are located in College Green.
Government Buildings
Government Buildings () is a large Edwardian building enclosing a quadrangle on Merrion Street in Dublin, Ireland, in which several key offices of the Government of Ireland are located. Among the offices of State located in the building are:
...
house the Department of the Taoiseach
The Department of the Taoiseach () is the government department of the Taoiseach, the title in Ireland for the head of government.Article 13.1.1° and Article 28.5.1° of the Constitution of Ireland. The latter provision reads: "The head of the ...
, the Council Chamber, the Department of Finance and the Office of the Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general (: attorneys general) or attorney-general (AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have executive responsibility for law enf ...
. It consists of a main building (completed 1911) with two wings (completed 1921). It was designed by Thomas Manley Dean and Sir Aston Webb
Sir Aston Webb, (22 May 1849 – 21 August 1930) was a British architect who designed the principal facade of Buckingham Palace and the main building of the Victoria and Albert Museum, among other major works around England, many of them in par ...
as the Royal College of Science
The Royal College of Science was a higher education institution located in South Kensington; it was a constituent college of Imperial College London from 1907 until it was wholly absorbed by Imperial in 2002. Still to this day, graduates from t ...
. The First Dáil
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
originally met in the Mansion House in 1919. The Irish Free State government took over the two wings of the building to serve as a temporary home for some ministries, while the central building became the College of Technology until 1989. Although both it and Leinster House were intended to be temporary locations, they became the permanent homes of parliament from then on.
For elections to Dáil Éireann
Dáil Éireann ( ; , ) is the lower house and principal chamber of the Oireachtas, which also includes the president of Ireland and a senate called Seanad Éireann.Article 15.1.2° of the Constitution of Ireland reads: "The Oireachtas shall co ...
, there are five constituencies that are wholly or predominantly in the Dublin City area: Dublin Central (4 seats), Dublin Bay North
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
(5 seats), Dublin North-West (3 seats), Dublin South-Central (4 seats) and Dublin Bay South (4 seats). Twenty TDs are elected in total. The constituency of Dublin West (4 seats) is partially in Dublin City, but predominantly in Fingal
Fingal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which ...
.
At the 2024 general election
This is a list of elections that were held in 2024. The National Democratic Institute also maintains a calendar of elections around the world.
* 2024 United Nations Security Council election
* 2024 national electoral calendar
* 2024 local electo ...
, the Dublin city area elected 5 Sinn Féin
Sinn Féin ( ; ; ) is an Irish republican and democratic socialist political party active in both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The History of Sinn Féin, original Sinn Féin organisation was founded in 1905 by Arthur Griffit ...
, 4 Fianna Fáil
Fianna Fáil ( ; ; meaning "Soldiers of Destiny" or "Warriors of Fál"), officially Fianna Fáil – The Republican Party (), is a centre to centre-right political party in Ireland.
Founded as a republican party in 1926 by Éamon de ...
, 4 Social Democrats
Social democracy is a social, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, s ...
, 3 Fine Gael
Fine Gael ( ; ; ) is a centre-right, liberal-conservative, Christian democratic political party in Ireland. Fine Gael is currently the third-largest party in the Republic of Ireland in terms of members of Dáil Éireann. The party had a member ...
, 2 Labour and 2 Independents.
Geography
Landscape
 Dublin is situated at the mouth of the
Dublin is situated at the mouth of the River Liffey
The River Liffey (Irish language, Irish: ''An Life'', historically ''An Ruirthe(a)ch'') is a river in eastern Ireland that ultimately flows through the centre of Dublin to its mouth within Dublin Bay. Its major Tributary, tributaries include t ...
and its urban area encompasses approximately in east-central Ireland. It is bordered by the Dublin Mountains, a low mountain range and sub range of the Wicklow Mountains
The Wicklow Mountains (, archaic: '' Cualu'') form the largest continuous upland area in Ireland. They occupy the whole centre of County Wicklow and stretch outside its borders into the counties of Dublin, Wexford and Carlow. Where the mountai ...
, to the south and surrounded by flat farmland to the north and west.
Watercourses
The River Liffey divides the city in two, between the Northside and the Southside. The Liffey bends atLeixlip
Leixlip ( or ; , ) is a town in north-east County Kildare, Ireland. Its location on the confluence of the River Liffey and the Rye Water has marked it as a frontier town historically: on the border between the ancient kingdoms of Leinster and ...
from a northeasterly route to a predominantly eastward direction, and this point also marks the transition to urban development from more agricultural land usage. The city itself was founded where the River Poddle
The River Poddle () is a river in Dublin, Ireland, a pool of which (', "black pool" or "dark pool" in Irish) gave the city its English language name. Boosted by a channel made by the Abbey of St. Thomas à Becket, taking water from the far lar ...
met the Liffey, and the early Viking settlement was also facilitated by the small Steine or Steyne River, the larger Camac and the Bradogue, in particular.
Two secondary rivers further divide the city: the River Tolka
The River Tolka (; , "the flood"), also once spelled ''Tolga'', is one of Dublin's three main rivers, flowing from County Meath to Fingal within the old County Dublin, and through the north of Dublin city, Ireland (the other main rivers are t ...
, running southeast into Dublin Bay, and the River Dodder
The River Dodder () is one of the three main rivers in Dublin, Ireland, the others being the River Liffey, Liffey, of which the Dodder is the largest tributary, and the River Tolka, Tolka.
Course and system
The Dodder rises on the northern s ...
running northeast to near the mouth of the Liffey, and these and the Liffey have multiple tributaries. A number of lesser rivers and streams also flow to the sea within the suburban parts of the city.
Two canals – the Grand Canal on the southside and the Royal Canal
The Royal Canal () is a canal originally built for freight and passenger transportation from Dublin to Longford in Ireland. It is one of two canals from Dublin to the River Shannon and was built in direct competition to the Grand Canal. Th ...
on the northside – ring the inner city on their way from the west, both connecting with the River Shannon
The River Shannon ( or archaic ') is the major river on the island of Ireland, and at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of I ...
.
Climate
Similar to much of the rest of northwestern Europe, Dublin experiences amaritime climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring ...
( ''Cfb'') with mild-warm summers, cool winters, and a lack of temperature extremes. At Merrion Square
Merrion Square () is a Georgian architecture, Georgian garden square on the Southside Dublin, southside of Dublin city centre.
History
The square was laid out in 1762 to a plan by John Smyth and Jonathan Barker for the estate of Richard Fitz ...
, the coldest month is February, with an average minimum temperature of , and the warmest month is July, with an average maximum temperature of . Due to the urban heat island
Urban areas usually experience the urban heat island (UHI) effect; that is, they are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent when winds ar ...
effect, Dublin city has the warmest summertime nights in Ireland. The average minimum temperature at Merrion Square in July is , and the lowest July temperature ever recorded at the station was on 3 July 1974.
The highest temperature officially recorded in Dublin is on 18 July 2022, at the Phoenix Park
The Phoenix Park () is a large urban park in Dublin, Ireland, lying west of the city centre, north of the River Liffey. Its perimeter wall encloses of recreational space. It includes large areas of grassland and tree-lined avenues, and since ...
. A non-official record of was also recorded at Phoenix Park in July 1876.
Dublin's sheltered location on the east coast makes it the driest place in Ireland, receiving only about half the rainfall of the west coast. Ringsend
Ringsend () is a Southside (Dublin), southside inner suburb of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is located on the south bank of the River Liffey and east of the River Dodder, about two kilometres east of the city centre. It is the sou ...
in the south of the city records the lowest rainfall in the country, with an average annual precipitation of , with the average annual precipitation in the city centre being . At Merrion Square, the wettest year and driest year on record occurred within 5 years of each other, with 1953 receiving just of rainfall, while 1958 recorded . The main precipitation in winter is rain; however snow showers do occur between November and March. Hail is more common than snow. Strong Atlantic winds are most common in autumn. These winds can affect Dublin, but due to its easterly location, it is least affected compared to other parts of the country. However, in winter, easterly winds render the city colder and more prone to snow showers.
The city experiences long summer days and short winter days. Based on satellite observations, Met Éireann
Met Éireann (; meaning "Meteorology, Met of Ireland") is the state meteorology, meteorological service of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, part of the Department of Housing, Local Government and Heritage.
History
The history of modern meteorolog ...
estimates that Dublin's coastal areas typically receive over 1,600 hours of sunshine per year, with the climate getting progressively duller inland. Dublin airport, located north of city and about from the coast, records an average of 1,485 hours of sunshine per year. The station at Dublin airport has been maintaining climate records since November 1941. The sunniest year on record was 1,740 hours in 1959, and the dullest year was 1987 with 1,240 hours of sunshine. The lowest amount of monthly sunshine on record was 16.4 hours in January 1996, while the highest was 305.9 hours in July 1955.
In the 20th century, smog and air-pollution were an issue in the city, precipitating a ban on bituminous fuels across Dublin. The ban was implemented in 1990 to address black smoke concentrations, that had been linked to cardiovascular and respiratory deaths in residents. Since the ban, non-trauma death rates, respiratory death rates and cardiovascular death rates have declined – by an estimated 350 deaths annually.
Cityscape
Areas
City centre
The historic city centre of Dublin is encircled by theRoyal Canal
The Royal Canal () is a canal originally built for freight and passenger transportation from Dublin to Longford in Ireland. It is one of two canals from Dublin to the River Shannon and was built in direct competition to the Grand Canal. Th ...
and Grand Canal, bounded to the west by Heuston railway station
Heuston Station, ( ; ; formerly Kingsbridge Station) also known as Dublin Heuston, is one of Dublin's largest railway stations and links the capital with the south, southwest and west of Ireland. It is operated by Iarnród Éireann (IÉ), ...
and Phoenix Park
The Phoenix Park () is a large urban park in Dublin, Ireland, lying west of the city centre, north of the River Liffey. Its perimeter wall encloses of recreational space. It includes large areas of grassland and tree-lined avenues, and since ...
, and to the east by the IFSC and the Docklands. O'Connell Street
O'Connell Street () is a street in the centre of Dublin, Ireland, running north from the River Liffey. It connects the O'Connell Bridge to the south with Parnell Street to the north and is roughly split into two sections bisected by Henry ...
is the main thoroughfare of the inner city and many Dublin Bus routes, as well as the Green line of the Luas
Luas (, Irish language, Irish: ; meaning 'speed') is a tram system in Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. There are two main lines: the Green Line (Luas), Green Line, which began operating on 30 June 2004, and the Red Line (Luas), Red Line ...
, have a stop at O'Connell Street. The main shopping streets of the inner city include Henry Street on the Northside, and Grafton Street
Grafton Street () is one of the two principal shopping streets in Dublin city centre — the other being Henry Street. It runs from St Stephen's Green in the south (at the highest point of the street) to College Green in the north (the low ...
on the Southside.
In some tourism and real-estate marketing contexts, inner Dublin is sometimes divided into a number of quarters. These include the Medieval Quarter (in the area of Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle () is a major Government of Ireland, Irish government complex, conference centre, and tourist attraction. It is located off Dame Street in central Dublin.
It is a former motte-and-bailey castle and was chosen for its position at ...
, Christ Church and St Patrick's Cathedral and the old city walls), the Georgian Quarter (including the area around St Stephen's Green, Trinity College, and Merrion Square
Merrion Square () is a Georgian architecture, Georgian garden square on the Southside Dublin, southside of Dublin city centre.
History
The square was laid out in 1762 to a plan by John Smyth and Jonathan Barker for the estate of Richard Fitz ...
), the Docklands Quarter (around the Dublin Docklands
Dublin Docklands () is an area of the city of Dublin, Ireland, on both sides of the River Liffey, roughly from Talbot Memorial Bridge eastwards to the 3Arena (Dublin), 3Arena. It mainly falls within the city's List of Dublin postal districts ...
and Silicon Docks
Silicon Docks is a nickname for the area in Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland around Grand Canal Dock, stretching to the International Financial Services Centre, Dublin, IFSC, city centre east, and city centre south near the Grand Canal (Irela ...
), the Cultural Quarter (around Temple Bar), and Creative Quarter (between South William Street and George's Street).
Suburbs
 Dublin has dozens of suburbs; northside suburbs include
Dublin has dozens of suburbs; northside suburbs include Blanchardstown
Blanchardstown () is a large outer suburb of Dublin in the modern Counties of Ireland, county of Fingal, Ireland. Located northwest of Dublin city centre, it has developed since the 1960s from a small village to a point where Greater Blanchards ...
, Finglas
Finglas (; ) is a northwestern outer suburb of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It lies close to Junction 5 of the M50 motorway (Ireland), M50 motorway, and the N2 road (Ireland), N2 road. Nearby suburbs include Glasnevin and Ballymun; Du ...
, Ballymun
Ballymun () is a suburb of Dublin, Ireland, at the northern edge of the city's Northside.
Ballymun has several sub-districts, such as Sillogue, Coultry, Shangan and Poppintree, and is close to Dublin Airport. A metro stop on a city-to-airpo ...
, Clontarf, Raheny
Raheny () is a northern suburb of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, halfway from the city centre to Howth. It is centred on a historic settlement, first documented in 570 AD (Mervyn Archdall (Irish antiquary), Mervyn Archdall). The district ...
, Malahide
Malahide ( ; ) is an affluent coastal settlement in Fingal, County Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, situated north of Dublin city. It has a village centre surrounded by suburban housing estates, with a population of 18,608 as per the 2022 ...
and Howth
Howth ( ; ; ) is a peninsular village and outer suburb of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The district as a whole occupies the greater part of the peninsula of Howth Head, which forms the northern boundary of Dublin Bay, and includes the ...
, while southside suburbs include Tallaght
Tallaght ( ; , ) is a southwestern outer suburb of Dublin, Ireland. The central village area was the site of a monastic settlement from at least the 8th century, which became one of medieval Ireland's more important monastic centres.
Up to th ...
, Sandyford
Sandyford () is a suburb of Dublin, located in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Ireland.
Sandyford Business District makes up much of the suburb and encompasses 4 business parks: Sandyford Business Park, Stillorgan Business Park, Central Park and S ...
, Templeogue
Templeogue is a southwestern suburb of Dublin in Ireland. It lies between the River Poddle and River Dodder, and is about halfway from Dublin's centre to the mountains to the south.
Geography Location
Templeogue is from Dublin city centre t ...
, Drimnagh
Drimnagh () is a suburb in Dublin, Ireland. It lies to the south of the city between Walkinstown, Crumlin and Inchicore, bordered by the Grand Canal to the north and east. Drimnagh is in postal district Dublin 12. Drimnagh is in a townland ...
, Rathmines
Rathmines (; ) is an inner suburb on the Southside (Dublin), Southside of Dublin in Ireland. It begins at the southern side of the Grand Canal of Ireland, Grand Canal and stretches along the Rathmines Road as far as Rathgar to the south, Ranela ...
, Dún Laoghaire
Dún Laoghaire ( , ) is a suburban coastal town in County Dublin in Ireland. It is the administrative centre of the county of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown. The town was built up alongside a small existing settlement following 1816 legislation th ...
and Dalkey
Dalkey ( ; ) is a village in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown county southeast of Dublin, Ireland. It was founded as a Viking settlement and became a port in the Middle Ages. According to chronicler John Clyn (c.1286–c.1349), it was one of the port ...
.
Starting in the late 2010s, there was a significant amount of high density residential developments in the suburbs of Dublin, with mid to high-rise apartments being built in Sandyford, Ashtown, and Tallaght.

Cultural divide
A north–south division once, to some extent, traditionally existed, with the River Liffey as the divider. The southside was, in recent times, generally seen as being more affluent and genteel than the northside. There have also been some social divisions evident between the coastal suburbs in the east of the city, and the newer developments further to the west.Landmarks
Dublin has many landmarks and monuments dating back hundreds of years. One of the oldest isDublin Castle
Dublin Castle () is a major Government of Ireland, Irish government complex, conference centre, and tourist attraction. It is located off Dame Street in central Dublin.
It is a former motte-and-bailey castle and was chosen for its position at ...
, which was first founded as a major defensive work on the orders of England's King John in 1204, shortly after the Norman invasion of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land in Ireland over which the monarchs of England then claimed sovereignty. The Anglo-Normans ...
in 1169, when it was commanded that a castle be built with strong walls and good ditches for the defence of the city, the administration of justice, and the protection of the King's treasure. Largely complete by 1230, the castle was of typical Norman courtyard design, with a central square without a keep
A keep is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in castles that were fortified residen ...
, bounded on all sides by tall defensive walls and protected at each corner by a circular tower. Sited to the south-east of Norman Dublin, the castle formed one corner of the outer perimeter of the city, using the River Poddle
The River Poddle () is a river in Dublin, Ireland, a pool of which (', "black pool" or "dark pool" in Irish) gave the city its English language name. Boosted by a channel made by the Abbey of St. Thomas à Becket, taking water from the far lar ...
as a natural means of defence.
One of Dublin's most prominent landmarks is the Spire of Dublin
The Spire of Dublin, alternatively titled the Millennium Spire or the ''Monument of Light'' (), is a large, stainless steel, pin-like monument in height, located on the site of the former Nelson's Pillar (and prior to that a statue of William B ...
, officially entitled the "Monument of Light". It is a conical spire made of stainless steel, completed in 2003 and located on O'Connell Street
O'Connell Street () is a street in the centre of Dublin, Ireland, running north from the River Liffey. It connects the O'Connell Bridge to the south with Parnell Street to the north and is roughly split into two sections bisected by Henry ...
, where it meets Henry Street and North Earl Street. It replaced Nelson's Pillar
Nelson's Pillar (also known as the Nelson Pillar or simply the Pillar) was a large granite column capped by a statue of Horatio Nelson, built in the centre of what was then Sackville Street (later renamed O'Connell Street) in Dublin, Ireland. ...
and is intended to mark Dublin's place in the 21st century. The spire was designed by Ian Ritchie Architects, who sought an "Elegant and dynamic simplicity bridging art and technology". The base of the monument is lit and the top is illuminated to provide a beacon in the night sky across the city.
The Old Library of Trinity College Dublin
Trinity College Dublin (), officially titled The College of the Holy and Undivided Trinity of Queen Elizabeth near Dublin, and legally incorporated as Trinity College, the University of Dublin (TCD), is the sole constituent college of the Unive ...
, holding the Book of Kells
The Book of Kells (; ; Dublin, Trinity College Library, MS A. I. 8 sometimes known as the Book of Columba) is an illustrated manuscript and Celts, Celtic Gospel book in Latin, containing the Gospel, four Gospels of the New Testament togeth ...
, is one of the city's most visited sites. The Book of Kells is an illustrated manuscript created by Irish monks circa 800 AD. The Ha'penny Bridge
The Ha'penny Bridge ( ; , or ''Droichead na Life''), known later for a time as the ''Penny Ha'penny Bridge'', and officially the Liffey Bridge, is a pedestrian bridge built in May 1816 over the River Liffey in Dublin, Ireland. Made of cast i ...
, an iron footbridge over the River Liffey, is one of the most photographed sights in Dublin and is considered to be one of Dublin's most iconic landmarks.
Other landmarks and monuments include Christ Church Cathedral and St Patrick's Cathedral, the Mansion House, the Molly Malone
"Molly Malone" ( Roud 16932, also known as "Cockles and Mussels" or "In Dublin's Fair City") is a song set in Dublin, Ireland, which has become the city's unofficial anthem.
A statue representing Molly Malone, designed by Dublin artist Jeanne ...
statue, the complex of buildings around Leinster House, including part of the National Museum of Ireland
The National Museum of Ireland () is Ireland's leading museum institution, with a strong emphasis on national and some international archaeology, Irish history, Irish art, culture, and natural history. It has three branches in Dublin, the arch ...
and the National Library of Ireland
The National Library of Ireland (NLI; ) is Ireland's national library located in Dublin, in a building designed by Thomas Newenham Deane. The mission of the National Library of Ireland is "To collect, preserve, promote and make accessible the ...
, The Custom House and Áras an Uachtaráin
(; "Residence of the President"), formerly the Viceregal Lodge, is the List of official residences, official residence and principal workplace of the President of Ireland.
It is located off Chesterfield Avenue in the Phoenix Park in Dublin, ...
. Other sights include the Anna Livia monument. The Poolbeg Towers are also landmark features of Dublin, and visible from various spots around the city.
Parks
There are 302 parks and 66 green spaces within theDublin City Council
Dublin City Council () is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority of the city of Dublin in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. As a city council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. Until 2001, the authority was k ...
area as of 2018, with the council managing over of parks. Public parks include the Phoenix Park
The Phoenix Park () is a large urban park in Dublin, Ireland, lying west of the city centre, north of the River Liffey. Its perimeter wall encloses of recreational space. It includes large areas of grassland and tree-lined avenues, and since ...
, Herbert Park, St Stephen's Green
St Stephen's Green () is a garden square and public park located in the city centre of Dublin, Ireland. The current landscape of the park was designed by William Sheppard. It was officially re-opened to the public on Tuesday, 27 July 1880 by ...
, Saint Anne's Park
Saint Anne's Park () is a public park situated between Raheny and Clontarf, suburbs on the northside of Dublin, Ireland. It is owned and managed by Dublin City Council.
The park, the second largest municipal park in Dublin, is formed from pa ...
and Bull Island
Bull Island (), more properly North Bull Island (), is an island located in Dublin Bay in Ireland, about 5 km long and 800 m wide, lying roughly parallel to the shore off Clontarf, Dublin, Clontarf (including Dollymount), Raheny, Kilbarra ...
. The Phoenix Park is about west of the city centre, north of the River Liffey
The River Liffey (Irish language, Irish: ''An Life'', historically ''An Ruirthe(a)ch'') is a river in eastern Ireland that ultimately flows through the centre of Dublin to its mouth within Dublin Bay. Its major Tributary, tributaries include t ...
. Its perimeter wall encloses , making it one of the largest walled city parks in Europe. It includes large areas of grassland and tree-lined avenues, and since the 17th century has been home to a herd of wild fallow deer
Fallow deer is the common name for species of deer in the genus ''Dama'' of subfamily Cervinae. There are two living species, the European fallow deer (''Dama dama''), native to Europe and Anatolia, and the Persian fallow deer (''Dama mesopotamic ...
. The residence of the President of Ireland
The president of Ireland () is the head of state of Republic of Ireland, Ireland and the supreme commander of the Defence Forces (Ireland), Irish Defence Forces. The presidency is a predominantly figurehead, ceremonial institution, serving as ...
(Áras an Uachtaráin), which was built in 1751, is located in the park. The park is also home to Dublin Zoo
Dublin Zoo (), in Phoenix Park, is a zoo in Dublin, Ireland, and one of Dublin's most popular attractions. Established and designed in 1830 by Decimus Burton, it opened the following year. Today, it focuses on conservation projects, breeding p ...
, Ashtown Castle
Ashtown Castle ( Irish: ''Caisleán Bhaile an Ásaigh'') is a tower house in the Phoenix Park in Dublin, Ireland.
It was found hidden within the walls of a much larger and more recent Georgian building, the Under Secretary's Lodge also known ...
, and the official residence of the United States Ambassador
Ambassadors of the United States are persons nominated by the president to serve as the United States' diplomatic representatives to foreign nations, international organizations, and as ambassadors-at-large. Under Article II, Section 2 of th ...
. Music concerts are also sometimes held in the park.
St Stephen's Green is adjacent to one of Dublin's main shopping streets, Grafton Street
Grafton Street () is one of the two principal shopping streets in Dublin city centre — the other being Henry Street. It runs from St Stephen's Green in the south (at the highest point of the street) to College Green in the north (the low ...
, and to a shopping centre named after it, while on its surrounding streets are the offices of a number of public bodies.
Saint Anne's Park
Saint Anne's Park () is a public park situated between Raheny and Clontarf, suburbs on the northside of Dublin, Ireland. It is owned and managed by Dublin City Council.
The park, the second largest municipal park in Dublin, is formed from pa ...
is a public park and recreational facility, shared between Raheny
Raheny () is a northern suburb of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, halfway from the city centre to Howth. It is centred on a historic settlement, first documented in 570 AD (Mervyn Archdall (Irish antiquary), Mervyn Archdall). The district ...
and Clontarf, both suburbs on the Northside. The park, the second largest municipal park in Dublin, is part of a former estate assembled by members of the Guinness family
The Guinness family is an extensive Irish family known for its achievements in brewing, banking, politics, and religious ministry. The brewing branch is particularly well known among the general public for producing the dry stout beer Guinnes ...
, beginning with Benjamin Lee Guinness
Sir Benjamin Lee Guinness, 1st Baronet, JP, DL (1 November 1798 – 19 May 1868) was an Anglo-Irish brewer and philanthropist.
Brewer
Born in Dublin, he was the third son of the second Arthur Guinness, and his wife Anne Lee, and a grandson ...
in 1835. The largest municipal park is adjacent (North) Bull Island
Bull Island (), more properly North Bull Island (), is an island located in Dublin Bay in Ireland, about 5 km long and 800 m wide, lying roughly parallel to the shore off Clontarf, Dublin, Clontarf (including Dollymount), Raheny, Kilbarra ...
, also shared between Clontarf and Raheny, featuring a 5 km beach, Dollymount Strand.
City boundaries
From 1842, the boundaries of the city were comprehended by thebaronies Barony may refer to:
* Barony, the peerage, office of, or territory held by a baron
* Barony, the title and land held in fealty by a feudal baron
* Barony (county division), a type of administrative or geographical division in parts of the British ...
of Dublin City and the barony of Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
. Over time, the city has absorbed area previously administered as part of County Dublin (now the three counties of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Fingal and South Dublin), with a change in 1985 also returning areas to the county.
Economy
The Dublin region is the economic centre of Ireland, and was at the forefront of the country's economic expansion during theCeltic Tiger
The "Celtic Tiger" () is a term referring to the economy of the Republic of Ireland, economy of Ireland from the mid-1990s to the late 2000s, a period of rapid real economic growth fuelled by foreign direct investment. The boom was dampened by ...
period. In 2009, Dublin was listed as the fourth richest city in the world by purchasing power
Purchasing power refers to the amount of products and services available for purchase with a certain currency unit. For example, if you took one unit of cash to a store in the 1950s, you could buy more products than you could now, showing that th ...
and 10th richest by personal income. According to ''Mercer's 2011 Worldwide Cost of Living Survey'', Dublin was the 13th most expensive city in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(down from 10th in 2010) and the 58th most expensive place to live in the world (down from 42nd in 2010). , approximately 874,400 people were employed in the Greater Dublin Area
The Greater Dublin Area (GDA; Irish: ''Mórcheantar Bhaile Átha Cliath''), or simply Greater Dublin, is an informal term that is taken to include the city of Dublin and its hinterland, with varying definitions as to its extent. At the expansive ...
. Around 60% of people who are employed in Ireland's financial, ICT, and professional sectors are located in this area.
A number of Dublin's traditional industries, such as food processing, textile manufacturing, brewing, and distilling have gradually declined, although Guinness
Guinness () is a stout that originated in the brewery of Arthur Guinness at Guinness Brewery, St. James's Gate, Dublin, Ireland, in the 18th century. It is now owned by the British-based Multinational corporation, multinational alcoholic bever ...
has been brewed at the St. James's Gate Brewery since 1759. Economic improvements in the 1990s attracted a number of global pharmaceutical, information and communications technology companies to the city and Greater Dublin Area. Companies such as Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
, Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
, Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
, eBay
eBay Inc. ( , often stylized as ebay) is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that allows users to buy or view items via retail sales through online marketplaces and websites in 190 markets worldwide. ...
, PayPal
PayPal Holdings, Inc. is an American multinational financial technology company operating an online payments system in the majority of countries that support E-commerce payment system, online money transfers; it serves as an electronic alter ...
, Yahoo!
Yahoo (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web portal that provides the search engine Yahoo Search and related services including My Yahoo, Yahoo Mail, Yahoo News, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Sports, y!entertainment, yahoo!life, and its a ...
, Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
, X, Accenture
Accenture plc is a global multinational professional services company originating in the United States and headquartered in Dublin, Ireland, that specializes in information technology (IT) services and management consulting. It was founded in 1 ...
, TikTok
TikTok, known in mainland China and Hong Kong as Douyin (), is a social media and Short-form content, short-form online video platform owned by Chinese Internet company ByteDance. It hosts user-submitted videos, which may range in duration f ...
and Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
now have European headquarters or operational bases in the city with several located in enterprise clusters like the Digital Hub
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Businesses
*Digital bank, a form of financial institution
*Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) or Digital, a computer company
*Digital Research (DR or DRI), a software ...
and Silicon Docks
Silicon Docks is a nickname for the area in Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland around Grand Canal Dock, stretching to the International Financial Services Centre, Dublin, IFSC, city centre east, and city centre south near the Grand Canal (Irela ...
. The presence of these companies has driven economic expansion in the city and led to Dublin sometimes being referred to as the "Tech Capital of Europe".
Financial services have also become important to the city since the establishment of Dublin's International Financial Services Centre International Financial Services Centre may refer to any of the following places:
* International Financial Services Centre, Dublin
The International Financial Services Centre (IFSC; ) is an area of central Dublin and part of the Central busi ...
in 1987. More than 500 operations are approved to trade under the IFSC programme. The centre is host to half of the world's top 50 banks and to half of the top 20 insurance companies. Many international firms have established major headquarters in the city, such as Citibank
Citibank, N.A. ("N. A." stands for "National bank (United States), National Association"; stylized as citibank) is the primary U.S. banking subsidiary of Citigroup, a financial services multinational corporation, multinational corporation. Ci ...
. The Irish Stock Exchange
Euronext Dublin (formerly the Irish Stock Exchange, ISE; ) is Ireland's main stock exchange, and has been in existence since 1793.
The Euronext Dublin lists debt and fund securities and is used as a European gateway exchange for companies seek ...
(ISEQ), Internet Neutral Exchange (INEX) and Irish Enterprise Exchange (IEX) are also located in Dublin. Dublin has been positioned as one of the main cities vying to host Financial Services companies hoping to retain access to the Eurozone after Brexit
Brexit (, a portmanteau of "Britain" and "Exit") was the Withdrawal from the European Union, withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU).
Brexit officially took place at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February ...
. The Celtic Tiger also led to a temporary boom in construction, with large redevelopment projects in the Dublin Docklands
Dublin Docklands () is an area of the city of Dublin, Ireland, on both sides of the River Liffey, roughly from Talbot Memorial Bridge eastwards to the 3Arena (Dublin), 3Arena. It mainly falls within the city's List of Dublin postal districts ...
and Spencer Dock
Spencer Dock () is a former wharf area, close to where the Royal Canal meets the River Liffey, in the North Wall (Dublin), North Wall area of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. As of the 21st century, the area has been redeveloped with oc ...
. Completed projects include the Convention Centre
A convention center (American and British English spelling differences, American English; or conference centre in British English) is a large building that is designed to hold a Convention (meeting), convention, where individuals and groups ...
, the 3Arena 3Arena may refer to the following:
* 3Arena (Dublin)
The 3Arena (originally The O2) is an indoor amphitheatre located at North Wall Quay in the Dublin Docklands in Dublin, Ireland. The venue opened as The O2 on 16 December 2008 and was re-bran ...
, and the Bord Gáis Energy Theatre
The Bord Gáis Energy Theatre (originally the Grand Canal Theatre) is a performing arts venue, located in the Dublin Docklands, Docklands of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is Ireland's largest fixed-seat theatre. It was designed by Da ...
.
In the second quarter of 2018, Dublin touched its lowest unemployment rate in a decade, when it fell down to 5.7% as reported by the Dublin Economic Monitor. In November 2022, Dublin was ranked as one of the worst cities in the world for travel, health and cost of living. On 24 September 2022, thousands took to the streets in protest against the cost of living crisis.
As of 2024, the Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
of Dublin is €253.6 billion, meaning it has one of the biggest city economies in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
.
Transport
Road
 The road network in Ireland is primarily focused on Dublin. The M50 motorway, a semi-
The road network in Ireland is primarily focused on Dublin. The M50 motorway, a semi-ring road
A ring road (also known as circular road, beltline, beltway, circumferential (high)way, loop or orbital) is a road or a series of connected roads encircling a town, city or country. The most common purpose of a ring road is to assist in reducin ...
which runs around the south, west and north of the city, connects important national primary routes to the rest of the country. In 2008, the West-Link
The West-Link () is a set of twin bridges over the River Liffey in Dublin. A toll bridge, the West Link forms the central section of the Western Parkway route of the M50 ring road motorway.
History
Plans were announced for the construction o ...
toll bridge was replaced by the eFlow barrier-free tolling system, with a three-tiered charge system based on electronic tags and car pre-registration.
The first phase of a proposed eastern bypass for the city is the Dublin Port Tunnel
The Dublin Tunnel ( Irish: ''Tollán Bhaile Átha Cliath''), originally and still commonly known as the Port Tunnel, is a road traffic tunnel in Dublin, Ireland, that forms part of the M50 motorway.
The twin tunnels form a two-lane dual car ...
, which officially opened in 2006 to mainly cater for heavy vehicles. The tunnel connects Dublin Port
Dublin Port () is the seaport of Dublin, Ireland, of both historical and contemporary economic importance. Approximately two-thirds of Ireland's port traffic travels via the port, which is by far the busiest on the island of Ireland.
Locatio ...
and the M1 motorway
The M1 motorway connects London to Leeds, where it joins the A1(M) motorway, A1(M) near Aberford, to connect to Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle. It was the first inter-urban motorway to be completed in the UK; the first motorway in the count ...
close to Dublin Airport. The city is also surrounded by an inner and outer orbital route. The inner orbital route runs approximately around the heart of the Georgian city and the outer orbital route runs primarily along the natural circle formed by Dublin's two canals, the Grand Canal and the Royal Canal
The Royal Canal () is a canal originally built for freight and passenger transportation from Dublin to Longford in Ireland. It is one of two canals from Dublin to the River Shannon and was built in direct competition to the Grand Canal. Th ...
, as well as the North and South Circular Roads.
The 2016 TomTom Traffic Index ranked Dublin the 15th most congested city in the world and the 7th most congested in Europe.
Bus
Dublin is served by a network of nearly 200 bus routes which cover the city and suburbs. The majority of these are provided byDublin Bus
Dublin Bus () is an Irish State-owned enterprise, state-owned bus operator providing services in Dublin. By far the largest bus operator in the city, it carried 145 million passengers in 2023. It is a subsidiary of CIÉ, Córas Iompair Éireann ...
, with a modest number having been transferred to Go Ahead Ireland since 2018. A number of smaller companies also operate. Fares are generally calculated on a stage system based on distance travelled. There are several different levels of fares, which apply on most services. A "Real Time Passenger Information" system was introduced at Dublin Bus bus stops in 2012 in which signs relay display the projected time of the next buses' arrival based on its GPS position. The National Transport Authority is responsible for integration of bus and rail services in Dublin and has been involved in introducing a pre-paid smart card, called a TFI Leap Card
The TFI Leap Card is a contactless smart card for automated fare collection overseen by Transport for Ireland (TFI). It was introduced in the Greater Dublin area in 2011 for Luas, DART, Iarnród Éireann and Dublin Bus, but acceptance has si ...
, which can be used on all of Dublin's public transport services.
The BusConnects programme includes a number of proposed improvements to Dublin's bus network, including new spine and orbital routes. The spine routes are intended to increase the frequency of buses along major corridors, and the orbital routes aim to "provide connections between suburbs and town centres, without having to travel into the City Centre". In 2022, Dublin Bus began the process of electrifying its fleet with new battery-powered buses, with plans for 85% of Dublin buses to be zero-emission by 2032.
Cycling
 The 2011 census indicated that 5.9% of commuters in Dublin cycled. A 2013 report by Dublin City Council on traffic flows crossing the canals in and out of the city found that just under 10% of all traffic was made up of cyclists, representing an increase of 14.1% over 2012 and an 87.2% increase over 2006 levels. The increase was attributed to measures such as the Dublinbikes bike rental scheme, the provision of cycle lanes, public awareness campaigns to promote cycling and the introduction of the 30 km/h city centre speed limit.
Dublin City Council began installing cycle lanes and tracks throughout the city in the 1990s, and the city had over of specific on- and off-road tracks for cyclists. In 2011, the city was ranked 9th of major world cities on the ''Copenhagenize Index of Bicycle-Friendly Cities''. The same index showed a fall to 15th in 2015, and Dublin was outside the top 20 in 2017.
The 2011 census indicated that 5.9% of commuters in Dublin cycled. A 2013 report by Dublin City Council on traffic flows crossing the canals in and out of the city found that just under 10% of all traffic was made up of cyclists, representing an increase of 14.1% over 2012 and an 87.2% increase over 2006 levels. The increase was attributed to measures such as the Dublinbikes bike rental scheme, the provision of cycle lanes, public awareness campaigns to promote cycling and the introduction of the 30 km/h city centre speed limit.
Dublin City Council began installing cycle lanes and tracks throughout the city in the 1990s, and the city had over of specific on- and off-road tracks for cyclists. In 2011, the city was ranked 9th of major world cities on the ''Copenhagenize Index of Bicycle-Friendly Cities''. The same index showed a fall to 15th in 2015, and Dublin was outside the top 20 in 2017.
Dublinbikes
Dublinbikes (styled "dublinbikes") is a public bicycle rental scheme which has operated in the city of Dublin since 2009. At its launch, the scheme, which is sponsored by JCDecaux, used 450 French-made unisex bicycles with 40 stations. By 201 ...
is a self-service bicycle rental scheme which has been in operation in Dublin since 2009. Sponsored by JCDecaux and Just Eat
Just Eat is an online food order and delivery platform. It was founded in 2001 in Kolding, Denmark, as a food delivery company, and later headquartered in London, United Kingdom, from 2006 (as Just Eat plc) until it was purchased by Netherla ...
, the scheme consists of hundreds of unisex bicycles stationed at 44 terminals throughout the city centre. Users must make a subscription for either an annual Long Term Hire Card or purchase a three-day ticket. , Dublinbikes had over 66,000 long-term subscribers making over 2 million journeys per year.
Rail
 Heuston and Connolly stations are the two main railway termini in Dublin. Operated by
Heuston and Connolly stations are the two main railway termini in Dublin. Operated by Iarnród Éireann
Iarnród Éireann, () or Irish Rail, is the operator of the national Rail transport in Ireland, railway network of Ireland. Established on 2 February 1987, it is a subsidiary of CIÉ, Córas Iompair Éireann (CIÉ). It operates all internal I ...
, the Dublin Suburban Rail
The Dublin Suburban Rail () network, branded as Commuter (Iarnród Éireann), Commuter, is a railway network that serves the city of Dublin, Ireland, most of the Greater Dublin Area and outlying towns. The system is made up of five lines:
* '' ...
network consists of five railway lines serving the Greater Dublin Area and commuter towns such as Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth ...
and Dundalk
Dundalk ( ; ) is the county town of County Louth, Ireland. The town is situated on the Castletown River, which flows into Dundalk Bay on the north-east coast of Ireland, and is halfway between Dublin and Belfast, close to and south of the bor ...
in County Louth, Gorey
Gorey () is a market town in north County Wexford, Ireland. It is bypassed by the main N11 road (Ireland), M11 Dublin to Wexford road. The town is also connected to the Gorey railway station, railway network along the same route. Local newspape ...
in County Wexford
County Wexford () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was ba ...
, and extending as far as Portlaoise
Portlaoise ( ), or Port Laoise (), is the county town of County Laois, Republic of Ireland, Ireland.
It is in the Midland Region, Ireland, South Midlands in the province of Leinster.
Portlaoise was the fastest growing of the top 20 largest town ...
in County Laois, and once a day to Newry
Newry (; ) is a City status in Ireland, city in Northern Ireland, standing on the Newry River, Clanrye river in counties County Down, Down and County Armagh, Armagh. It is near Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, the border with the ...
. One of the five lines is the electrified Dublin Area Rapid Transit
The Dublin Area Rapid Transit system (stylised as DART) is an electrified commuter rail railway network serving the coastline and city of Dublin, Ireland. The service makes up the core of Dublin's suburban railway network, stretching from Gre ...
(DART) line, which runs primarily along the coast of Dublin, comprising 31 stations, from Malahide
Malahide ( ; ) is an affluent coastal settlement in Fingal, County Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, situated north of Dublin city. It has a village centre surrounded by suburban housing estates, with a population of 18,608 as per the 2022 ...
and Howth
Howth ( ; ; ) is a peninsular village and outer suburb of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The district as a whole occupies the greater part of the peninsula of Howth Head, which forms the northern boundary of Dublin Bay, and includes the ...
southwards as far as Bray
Bray may refer to:
Places France
* Bray, Eure, in the Eure ''département''
* Bray, Saône-et-Loire, in the Saône-et-Loire ''département''
* Bray-Dunes, in the Nord ''département''
* Bray-en-Val, in the Loiret ''département''
* Bray-et-Lû ...
and Greystones
Greystones () is a coastal town and seaside resort in County Wicklow, Ireland. It lies on Ireland's east coast, south of Bray and south of Dublin city centre and has a population of 22,009, according to the 2022 census. The town is border ...
in County Wicklow. Commuter rail
Commuter rail or suburban rail is a Passenger train, passenger rail service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting Commuting, commuters to a Central business district, central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter town ...
operates on the other four lines using Irish Rail diesel multiple units. In 2013, passengers for DART and Dublin Suburban lines were 16 million and 11.7 million, respectively (around 75% of all Irish Rail passengers).
Dublin once had an extensive system of trams
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which Rolling stock, vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some ...
but this was largely phased out by 1949. A new light rail
Light rail (or light rail transit, abbreviated to LRT) is a form of passenger urban rail transit that uses rolling stock derived from tram technology National Conference of the Transportation Research Board while also having some features from ...
system, often described as a tram system, the Luas
Luas (, Irish language, Irish: ; meaning 'speed') is a tram system in Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. There are two main lines: the Green Line (Luas), Green Line, which began operating on 30 June 2004, and the Red Line (Luas), Red Line ...
, was launched in 2004, and is run by Transdev
Transdev, formerly Veolia Transdev, is a France-based international private-sector company which operates public transport. It has operations in 17 countries and territories as of November 2020.
Transdev was formed on 3 April 2011 via the merg ...
Ireland (under contract from Transport Infrastructure Ireland
Transport Infrastructure Ireland () is a state agency in Ireland, dealing with road and public transport
Public transport (also known as public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) are forms of transport available to the general ...
), carrying over 34 million passengers annually. The network consists of two interconnecting lines; the Red Line links the Docklands and city centre with the south-western suburbs of Tallaght
Tallaght ( ; , ) is a southwestern outer suburb of Dublin, Ireland. The central village area was the site of a monastic settlement from at least the 8th century, which became one of medieval Ireland's more important monastic centres.
Up to th ...
and Saggart
Saggart () is a village in County Dublin, Ireland, south west of Dublin, Dublin city, in the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government area of South Dublin. It lies between the N7 road (Ireland), N7 (Naas Road), Rathcoole, ...
, while the Green Line connects northern inner city suburbs and the main city centre with suburbs to the south of the city including Sandyford
Sandyford () is a suburb of Dublin, located in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Ireland.
Sandyford Business District makes up much of the suburb and encompasses 4 business parks: Sandyford Business Park, Stillorgan Business Park, Central Park and S ...
and Brides Glen, mostly along the former route of the Harcourt Street railway line
The Harcourt Street Railway Line () was a railway line that ran from '' Harcourt Street'' in Dublin through the southern suburbs to Bray. It was one of the Dublin and South Eastern Railway's two northern main lines, the other being the coastal ...
. Together these lines comprise a total 67 stops and of track. Construction of a 6 km extension to the Green Line, bringing it into the north of the city, commenced in June 2013 and was opened for passenger travel on 9 December 2017.
A metro service is proposed under the name of Metrolink, and planned to run from Dublin's northside
Northside or North Side may refer to:
Music
* Northside (band), a musical group from Manchester, EngIand
* NorthSide, an American record label
* NorthSide Festival (Denmark), a music festival in Aarhus, Denmark
* "Norf Norf", a 2015 song by Vince ...
to Charlemont via Dublin Airport
Dublin Airport () is an international airport serving Dublin, Ireland. It is operated by DAA (formerly Dublin Airport Authority). The airport is located in Collinstown, north of Dublin, and south of the town of Swords.
In 2024, over 34 ...
and St. Stephen's Green
St Stephen's Green () is a garden square and public park located in the city centre of Dublin, Ireland. The current landscape of the park was designed by William Sheppard. It was officially re-opened to the public on Tuesday, 27 July 1880 by Ar ...
.
Rail and ferry
Dublin Connolly
Connolly station () or Dublin Connolly is the busiest railway station in Dublin and Ireland, and is a focal point in the Irish route network. On the North side of the River Liffey, it provides InterCity, Enterprise and commuter services to ...
is connected by bus to Dublin Port
Dublin Port () is the seaport of Dublin, Ireland, of both historical and contemporary economic importance. Approximately two-thirds of Ireland's port traffic travels via the port, which is by far the busiest on the island of Ireland.
Locatio ...
and ferries run by Irish Ferries
Irish Ferries is an Irish ferry and transport company that operates passenger and freight services on routes between Ireland, Britain and Continental Europe, including Dublin Port–Holyhead; Rosslare Europort to Pembroke, Pembrokeshire, Pembr ...
and Stena Line
Stena Line is a Swedish Shipping line, shipping line company and one of the world's largest ferry operators. It services Denmark, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Latvia, the Netherlands, Poland, Finland and Sweden. Stena Line is a ...
to Holyhead
Holyhead (; , "Cybi's fort") is a historic port town, and is the list of Anglesey towns by population, largest town and a Community (Wales), community in the county of Isle of Anglesey, Wales. Holyhead is on Holy Island, Anglesey, Holy Island ...
for connecting trains on the North Wales Coast Line
The North Wales Main Line ( or ; ), also known as the North Wales Coast Line (), is a major railway line in the north of Wales and Cheshire, England, running from Crewe on the West Coast Main Line to Holyhead on the Isle of Anglesey. The lin ...
to Chester
Chester is a cathedral city in Cheshire, England, on the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, close to the England–Wales border. With a built-up area population of 92,760 in 2021, it is the most populous settlement in the borough of Cheshire West an ...
, Crewe
Crewe () is a railway town and civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire East in Cheshire, England. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the parish had a population of 55,318 and the built-up area had a population of 74,120. ...
and London Euston
Euston railway station ( ; or London Euston) is a major central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station managed by Network Rail in the London Borough of Camden. It is the southern terminus of the West Coast Main Line ...
. Dublin Connolly
Connolly station () or Dublin Connolly is the busiest railway station in Dublin and Ireland, and is a focal point in the Irish route network. On the North side of the River Liffey, it provides InterCity, Enterprise and commuter services to ...
to Dublin Port can be reached via Amiens Street, Dublin
Amiens Street () is a road in Dublin, Ireland, that runs from Memorial Road to North Strand.
History
The road was known as The Strand in the early 18th century. It was renamed after John Stratford, 1st Earl of Aldborough (Viscount Amiens) i ...
into Store Street or by Luas via Busáras where Dublin Bus
Dublin Bus () is an Irish State-owned enterprise, state-owned bus operator providing services in Dublin. By far the largest bus operator in the city, it carried 145 million passengers in 2023. It is a subsidiary of CIÉ, Córas Iompair Éireann ...
operates route 53 to the Irish Ferries
Irish Ferries is an Irish ferry and transport company that operates passenger and freight services on routes between Ireland, Britain and Continental Europe, including Dublin Port–Holyhead; Rosslare Europort to Pembroke, Pembrokeshire, Pembr ...
Terminal.
Air
Dublin Airport

Dublin Airport
Dublin Airport () is an international airport serving Dublin, Ireland. It is operated by DAA (formerly Dublin Airport Authority). The airport is located in Collinstown, north of Dublin, and south of the town of Swords.
In 2024, over 34 ...
(owned and operated by DAA) is located north of Dublin city, near Swords
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
in the administrative county of Fingal
Fingal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which ...
. The headquarters of Ireland's flag carrier Aer Lingus
Aer Lingus ( ; an anglicisation of the Irish language, Irish , meaning "air fleet") is an Irish airline company which is the flag carrier of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Founded by the Irish Government, it was privatised between 2006 and 201 ...
and regional airline CityJet
CityJet is an Irish regional airline with headquarters at Dublin Airport. It was founded in 1992 and has gone through a series of corporate structures. In 2023, it merged with Air Nostrum, forming Strategic Alliance of Regional Airlines (SAR ...
are located there, and those of low-cost carrier Ryanair
Ryanair is an Irish Low-cost carrier#Ultra low-cost carrier, ultra low-cost airline group headquartered in Swords, County Dublin, Ireland. The parent company, Ryanair Holdings plc, includes subsidiaries Ryanair , Malta Air, Buzz (Ryanair), Buzz ...
nearby. The airport offers a short and medium-haul network, domestic services to regional airports in Ireland, and long-haul services to the United States, Canada, and the Middle East. Dublin Airport is the 11th busiest in the European Union, and by far the busiest airport on the island of Ireland.
In 2015 and 2016, transatlantic traffic grew, with 158 summer flights a week to North America, making it the sixth largest European hub for that route over the year. Transatlantic traffic was also the fastest-growing segment of the market for the airport in 2016, in which a 16% increase from 2015 brought the yearly number of passengers travelling between Dublin and North America to 2.9 million.
From 2010 to 2016, Dublin Airport saw an increase of nearly 9.5 million passengers in its annual traffic, as the number of commercial aircraft movements has similarly followed a growth trend from 163,703 in 2013 to 191,233 in 2015.
In 2019, Dublin Airport was the 12th busiest airport in Europe, with almost 33 million passengers passing through the airport.
Other air transport
Dublin is also served by Weston Airport and other small facilities, by a range of helicopter operators, and the military and some State services useCasement Aerodrome
Casement Aerodrome () or Baldonnel Aerodrome is a military airbase to the southwest of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland situated off the N7 road (Ireland), N7 main roads in Ireland, road route to the south and south west. It is the headquar ...
nearby.
Education
Dublin is the largest centre of education in Ireland, and is home to four universities and a number of other higher education institutions. It was the European Capital of Science in 2012. The
The University of Dublin
The University of Dublin (), corporately named as The Chancellor, Doctors and Masters of the University of Dublin, is a research university located in Dublin, Republic of Ireland. It is the degree-awarding body for Trinity College Dublin, whi ...
is the oldest university in Ireland, dating from the 16th century, and is located in the city centre. Its sole constituent college, Trinity College Trinity College may refer to:
Australia
* Trinity Anglican College, an Anglican coeducational primary and secondary school in , New South Wales
* Trinity Catholic College, Auburn, a coeducational school in the inner-western suburbs of Sydney, New ...
(TCD), was established by Royal Charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
in 1592 under Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
. It was closed to Roman Catholics until 1793, and the Catholic hierarchy then banned Roman Catholics from attending until 1970. It is situated in the city centre, on College Green, and has over 18,000 students.
The National University of Ireland
The National University of Ireland (NUI) () is a federal university system of ''constituent universities'' (previously called '' constituent colleges'') and ''recognised colleges'' set up under the Irish Universities Act 1908, and signifi ...
(NUI) has its seat in Dublin, which is also the location of the associated ''constituent university'' of University College Dublin
University College Dublin (), commonly referred to as UCD, is a public research university in Dublin, Ireland, and a collegiate university, member institution of the National University of Ireland. With 38,417 students, it is Ireland's largest ...
(UCD), which has over 30,000 students. Founded in 1854, it is now the largest university in Ireland. UCD's main campus is at Belfield, about from the city centre, in the southeastern suburbs.
As of 2019, Dublin's principal, and Ireland's largest, institution for technological education and research, Dublin Institute of Technology
Dublin Institute of Technology (DIT, ) was a major third-level institution in Dublin, Ireland. On 1 January 2019 DIT was dissolved and its functions were transferred to the Technological University Dublin, as TU Dublin City Campus. The insti ...
(DIT), with origins in 1887, has merged with two major suburban third level institutions, Institute of Technology, Tallaght
The Institute of Technology Tallaght (also known as ITT or IT Tallaght) ( Irish: ''Institiúid Teicneolaíochta, Tamhlacht)'' was a third-level institution in Tallaght, the largest suburb of Dublin, Ireland. Established in 1992, IT Tallaght ...
and Institute of Technology, Blanchardstown
Institute of Technology, Blanchardstown (ITB) () established in 1999, was a third-level institution outside Dublin. In 2019, it merged with the Dublin Institute of Technology (DIT) and the Institute of Technology Tallaght (ITT) to form the n ...
, to form Technological University Dublin
Technological University Dublin () or TU Dublin is Ireland's first technological university. It was established on 1 January 2019, with a history going back to 1887 through the amalgamated Dublin Institute of Technology which progressed from t ...
, Ireland's second largest university by student population. The new university offers a wide range of courses in areas include engineering, architecture, the sciences, health, journalism, digital media, hospitality, business, art and design, music and the humanities programmes, and has three long-term campuses, at Grangegorman
Grangegorman () is an inner suburb on the Northside, Dublin, northside of Dublin city, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The area is administered by Dublin City Council. It was best known for decades as the location of St. Brendan's Hospital (Gra ...
, Tallaght and Blanchardstown.
Dublin City University
Dublin City University (abbreviated as DCU) () is a Third-level education in the Republic of Ireland, university based on the Northside, Dublin, Northside of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Created as the ''National Institute for Highe ...
(DCU), formerly the National Institute for Higher Education
A National Institute for Higher Education (NIHE) () was a category of higher education institution established in Ireland to provide higher level technical education above the standard of the then established Regional Technical College system, a ...
(NIHE) Dublin, offers courses in business, engineering, science, communication courses, languages and primary education. It has around 16,000 students, and its main campus is located about from the city centre, in the northern suburbs. Aside from the main Glasnevin Campus, the Drumcondra campuses includes the former St. Patrick's College of Education, Drumcondra now also hosting students from the nearby Mater Dei Institute of Education
Mater Dei Institute of Education () was a linked college of Dublin City University from 1999 until its closure in 2016, located in Drumcondra, Dublin City, Ireland, near Croke Park, on the site of what was formerly Clonliffe College, the Rom ...
and students from the Church of Ireland College of Education
The Church of Ireland College of Education (), or C.I.C.E. as it was more commonly known, was one of the Republic of Ireland's five Colleges of Education which provided a Bachelor of Education (B.Ed.) degree, the qualification generally requir ...
at the DCU Campus at All Hallows College
All Hallows College was a college of higher education in Dublin. It was founded in 1842 and was run by the Vincentians from 1892 until 2016. On 23 May 2014, it was announced that it was closing because of declining student enrollment. The sale ...
.
The Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland
The Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland (RCSI) is a not-for-profit medical professional and educational institution, which is also known as RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences. It was established in 1784 as the national body ...
(RCSI) conducts a medical school which is both a university (since 2019) and a recognised college of the NUI, and is situated at St. Stephen's Green
St Stephen's Green () is a garden square and public park located in the city centre of Dublin, Ireland. The current landscape of the park was designed by William Sheppard. It was officially re-opened to the public on Tuesday, 27 July 1880 by Ar ...
in the city centre; there are also large medical schools within UCD and Trinity College. The National College of Art and Design
The National College of Art and Design (NCAD) is Ireland's oldest art institution, offering the largest range of art and design degrees at undergraduate and postgraduate level in the country. Originating as a drawing school in 1746, many of t ...
(NCAD) provides education and research in art, design and media. The National College of Ireland
National College of Ireland (NCI) (''Coláiste Náisiúnta na hÉireann'' (''CNÉ'') in Irish) is a not-for-profit, state-aided third-level education institution in Dublin. It was founded in 1951 as a joint venture between the Jesuits in Ir ...
(NCI) is also based in Dublin, as well as the Economic and Social Research Institute
The Economic and Social Research Institute (Institiúid Taighde Eacnamaíochta agus Sóisialta in Irish) is an Irish research institute founded in 1960 to provide evidence-based research used to inform public policy debate and decision-making. ...
, a social science research institute, on Sir John Rogerson's Quay
Sir John Rogerson's Quay () is a street and quay in Dublin on the south bank of the River Liffey between City Quay in the west and Britain Quay. Named for politician and property developer Sir John Rogerson (1648–1724), the quay was form ...
, and the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies
The Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies (DIAS) () is a statutory independent research institute in Dublin, Ireland. It was established, under the Institute For Advanced Studies Act 1940, by the government of the then Taoiseach, Éamon de Vale ...
.
The Institute of International and European Affairs
The Institute of International and European Affairs (IIEA; ) is an Irish policy think tank focusing on European and international policy trends based in Dublin, Ireland. It is known for its seminars and speaking events which attract notable int ...
is also in Dublin. Dublin Business School
Dublin Business School (DBS), incorporating Portobello College, is a private college
Private universities and private colleges are higher education institutions not operated, owned, or institutionally funded by governments. However, they of ...
(DBS) is Ireland's largest private third level institution with over 9,000 students located on Aungier Street, and Griffith College Dublin
Griffith College Dublin (GCD) () is one of the longest-established private third level (higher education) colleges in Dublin, Ireland. Established in 1974, with four campuses in Dublin, Cork and Limerick.
Overview
Griffith College is the ...
has its main facility in Portobello. There are also smaller specialised colleges, including The Gaiety School of Acting
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The ...
. The Irish public administration and management training centre has its base in Dublin, the Institute of Public Administration provides a range of undergraduate and post graduate awards via the National University of Ireland and in some instances, Queen's University Belfast.
Dublin is also home to the Royal Irish Academy
The Royal Irish Academy (RIA; ), based in Dublin, is an academic body that promotes study in the natural sciences, arts, literature, and social sciences. It is Ireland's premier List of Irish learned societies, learned society and one of its le ...
, membership of which is considered Ireland's highest academic honour.
The suburban town of Dún Laoghaire is home to the Dún Laoghaire Institute of Art, Design and Technology
Dún Laoghaire Institute of Art, Design and Technology (), more commonly known as IADT Dún Laoghaire or simply IADT is an institute of technology with a focus on art and design located in Deansgrange near Dún Laoghaire, Ireland. It was esta ...
(IADT), which supports training and research in art, design, business, psychology and media technology. Dublin joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2019.
Demographics
Dublin City Council
Dublin City Council () is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority of the city of Dublin in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. As a city council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. Until 2001, the authority was k ...
. The traditional County Dublin
County Dublin ( or ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and holds its capital city, Dublin. It is located on the island's east coast, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Until 1994, County Dubli ...
includes the city and the administrative counties of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown
Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown () is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which was disestablished in 1994. It is named after the former ...
, Fingal
Fingal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which ...
and South Dublin
South Dublin () is a county in Ireland, within the province of Leinster and the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which was disestablished for administrative purposes in 1994. South Dublin Cou ...
. The Greater Dublin Area
The Greater Dublin Area (GDA; Irish: ''Mórcheantar Bhaile Átha Cliath''), or simply Greater Dublin, is an informal term that is taken to include the city of Dublin and its hinterland, with varying definitions as to its extent. At the expansive ...
includes County Dublin and the adjoining counties, County Kildare
County Kildare () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is named after the town of Kildare. Kildare County Council is the Local gove ...
, County Meath
County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, County ...
and County Wicklow
County Wicklow ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The last of the traditional 32 counties, having been formed as late as 1606 in Ireland, 1606, it is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the Provinces ...
.
In the 2022 census, the population of the City of Dublin was 592,713, while the population of Dublin city and suburbs was 1,263,219. County Dublin had a population of 1,458,154, and the population of the Greater Dublin Area was 2,082,605.
Of the population of Dublin city and its suburbs, 62.9% (794,925) were born in Dublin, 26.6% (336,021) were born outside of Ireland, while the remaining 10.5% (132,273) were born in a county other than Dublin.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Italians were by far the largest immigrant group in both Dublin and Ireland and became synonymous with the catering and restaurant landscape. Since the late 1990s, Dublin has experienced a significant level of net immigration, with the greatest numbers coming from the European Union, especially the United Kingdom, Poland and Lithuania. There is also immigration from outside Europe, including from Pakistan, Brazil, the Philippines, China, India and Nigeria. Dublin is home to a greater proportion of newer arrivals than any other part of the country. Sixty percent of Ireland's Asian population lives in Dublin.
The capital attracts the largest proportion of non-Catholic migrants from other countries. Increased secularisation in Ireland has prompted a drop in regular Catholic church attendance in Dublin from over 90 percent in the mid-1970s down to 14 percent according to a 2011 survey and less than 2% in some areas As of the 2016 census, 68.2% of Dublin's population identified as Catholic, 12.7% as other stated religions, with 19.1% having no religion or no religion stated.
According to the 2022 census, the population of County Dublin
County Dublin ( or ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and holds its capital city, Dublin. It is located on the island's east coast, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Until 1994, County Dubli ...
self-identified as 80.4% white (68.0% white Irish, 12.0% other white and 0.4% Irish traveller), 5.8% Asian, 3.0% mixed backgrounds, 2.2% Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
and 8.5% not stated. In the same census, the ethnic makeup of Dublin city was 76.81% white (including 64.23% white Irish and 12.19% other white people), 12.98% not stated, 5.11% Asian, 3.50% other and 1.58% black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
.
As of December 2024, there were 1,467 families living in emergency accommodation in the Dublin region. This is a decrease of 57 on the November 2024 number, and an increase of 67 when compared with December 2023 when there were 1,400 families in emergency accommodation.
Culture

The arts
Dublin has a significant literary history, and produced many literary figures, includingNobel laureates
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in th ...
William Butler Yeats
William Butler Yeats (, 13 June 186528 January 1939), popularly known as W. B. Yeats, was an Irish poet, dramatist, writer, and literary critic who was one of the foremost figures of 20th century in literature, 20th-century literature. He was ...
, George Bernard Shaw
George Bernard Shaw (26 July 1856 – 2 November 1950), known at his insistence as Bernard Shaw, was an Irish playwright, critic, polemicist and political activist. His influence on Western theatre, culture and politics extended from the 188 ...
and Samuel Beckett
Samuel Barclay Beckett (; 13 April 1906 – 22 December 1989) was an Irish writer of novels, plays, short stories, and poems. Writing in both English and French, his literary and theatrical work features bleak, impersonal, and Tragicomedy, tra ...
. Other influential writers and playwrights include Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Fflahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish author, poet, and playwright. After writing in different literary styles throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular and influential playwright ...
, Jonathan Swift
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish writer, essayist, satirist, and Anglican cleric. In 1713, he became the Dean (Christianity), dean of St Patrick's Cathedral, Dublin, and was given the sobriquet "Dean Swi ...
and the creator of Dracula
''Dracula'' is an 1897 Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novel by Irish author Bram Stoker. The narrative is Epistolary novel, related through letters, diary entries, and newspaper articles. It has no single protagonist and opens ...
, Bram Stoker
Abraham Stoker (8 November 1847 – 20 April 1912), better known by his pen name Bram Stoker, was an Irish novelist who wrote the 1897 Gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. The book is widely considered a milestone in Vampire fiction, and one of t ...
. It is also the location of key and notable works of James Joyce
James Augustine Aloysius Joyce (born James Augusta Joyce; 2 February 1882 – 13 January 1941) was an Irish novelist, poet, and literary critic. He contributed to the modernist avant-garde movement and is regarded as one of the most influentia ...
, including '' Ulysses'', which is set in Dublin and includes much topical detail. ''Dubliners
''Dubliners'' is a collection of fifteen short stories by James Joyce, first published in 1914. It presents a naturalistic depiction of Irish middle class life in and around Dublin in the early years of the 20th century.
The stories were writ ...
'' is a collection of short stories by Joyce about incidents and typical characters of the city during the early 20th century. Other renowned writers include J. M. Synge
Edmund John Millington Synge (; 16 April 1871 – 24 March 1909), popularly known as J. M. Synge, was an Irish playwright, poet, writer, essayist, and collector of folklores. As an important driving force behind the Irish Literary Renaissanc ...
, Seán O'Casey
Seán O'Casey ( ; born John Casey; 30 March 1880 – 18 September 1964) was an Irish dramatist and memoirist. A committed socialist, he was the first Irish playwright of note to write about the Dublin working classes.
Early life
O'Casey was ...
, Brendan Behan
Brendan Francis Aidan Behan (christened Francis Behan) ( ; ; 9 February 1923 – 20 March 1964) was an Irish poet, short story writer, novelist, playwright, and Irish Republican, an activist who wrote in both English and Irish. His widely ackno ...
, Maeve Binchy
Anne Maeve Binchy Snell (28 May 1939Born 1939 as per biography, ''Maeve Binchy'' by Piers Dudgeon, Thomas Dunne Books 2013; (hardcover), pp. 4, 280, 302; (ebook) – 30 July 2012) was an Irish novelist, playwright, short story writer, column ...
, John Banville
William John Banville (born 8 December 1945) is an Irish novelist, short story writer, Literary adaptation, adapter of dramas and screenwriter. Though he has been described as "the heir to Marcel Proust, Proust, via Vladimir Nabokov, Nabokov", ...
and Roddy Doyle
Roderick Doyle (born 8 May 1958) is an Irish novelist, dramatist and screenwriter. He is the author of eleven novels for adults, eight books for children, seven plays and screenplays, and dozens of short stories. Several of his books have been ...
. Ireland's biggest libraries and literary museums are found in Dublin, including the National Print Museum of Ireland and National Library of Ireland
The National Library of Ireland (NLI; ) is Ireland's national library located in Dublin, in a building designed by Thomas Newenham Deane. The mission of the National Library of Ireland is "To collect, preserve, promote and make accessible the ...
. In July 2010, Dublin was named as a UNESCO City of Literature
UNESCO's City of Literature programme is part of the wider Creative Cities Network.
The ''Network'' was launched in 2004, and now has member cities in seven creative fields. The other creative fields are: Crafts and Folk Arts, Design, Film ...
, joining Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
, Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
and Iowa City
Iowa City is the largest city in Johnson County, Iowa, United States, and its county seat. At the time of the 2020 census the population was 74,828, making it the state's fifth-most populous city. The Iowa City metropolitan area, which enc ...
with the permanent title.

Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti.
Born in Halle, Germany, H ...
's oratorio Messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
was first performed at Neal's Music Hall, in Fishamble Street
Fishamble Street (; ) is a street in Dublin, Ireland within the old city walls.
Location
The street joins Wood Quay at the Fish Slip near Fyan's Castle. It originally ran from Castle Street to Essex Quay until the creation of Lord Edward S ...
, on 13 April 1742
Events
January–March
* January 9 – Robert Walpole is made Earl of Orford, and resigns as First Lord of the Treasury and Chancellor of the Exchequer, effectively ending his period as Prime Minister of Great Britain. On his f ...
.
There are several theatres within the city centre, and various well-known actors have emerged from the Dublin theatrical scene, including Noel Purcell, Michael Gambon
Sir Michael John Gambon (; 19 October 1940 – 27 September 2023) was an Irish-English actor. Gambon started his acting career with Laurence Olivier as one of the original members of the Royal National Theatre. Over his six-decade-long career ...
, Brendan Gleeson
Brendan Gleeson (born 29 March 1955) is an Irish actor. He has received various accolades, including a Primetime Emmy Award, two British Independent Film Awards and three IFTA Awards, along with nominations for an Academy Award, three BAFTA Aw ...
, Stephen Rea
Stephen Rea ( ; born October 31, 1946) is an Irish actor. Born in Belfast, Northern Ireland, he began his career as a member of Dublin's Focus Theatre, and played many roles on the stage and on Irish television. He came to the attention of inte ...
, Colin Farrell
Colin James Farrell (; born 31 May 1976) is an Irish actor. A Leading actor, leading man in blockbuster (entertainment), blockbusters and independent films since the 2000s, he has received various List of awards and nominations received by Col ...
, Colm Meaney
Colm J. Meaney (; ; born 30 May 1953) is an Irish actor. Known for his performances across screen and stage, he has received seven nominations from the Irish Film & Television Academy, winning twice for 2001's '' How Harry Became a Tree'', and ...
and Gabriel Byrne
Gabriel James Byrne (born 12 May 1950) is an Irish actor. He has received a Golden Globe Award as well as nominations for a Grammy Award, two Primetime Emmy Awards and two Tony Awards. Byrne was awarded the Irish Film and Television Academy L ...
. The best known theatres include the Gaiety, Abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christians, Christian monks and nun ...
, Olympia, Gate
A gate or gateway is a point of entry to or from a space enclosed by walls. The word is derived from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*gatan'', meaning an opening or passageway. Synonyms include yett (which comes from the same root w ...
, and Grand Canal. The Gaiety specialises in musical and operatic productions, and also opens its doors after the evening theatre production to host a variety of live music, dancing, and films. The Abbey was founded in 1904 by a group that included Yeats
William Butler Yeats (, 13 June 186528 January 1939), popularly known as W. B. Yeats, was an Irish poet, dramatist, writer, and literary critic who was one of the foremost figures of 20th-century literature. He was a driving force behind the ...
with the aim of promoting indigenous literary talent. It went on to provide a breakthrough for some of the city's most famous writers, such as Synge, Yeats himself and George Bernard Shaw. The Gate was founded in 1928 to promote European and American Avant Garde works. The Grand Canal Theatre is a newer 2,111 capacity theatre which opened in 2010 in the Grand Canal Dock
Grand Canal Dock () is a Southside (Dublin), Southside area near the city centre of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is located on the border of eastern Dublin 2 and the westernmost part of Ringsend in Dublin 4, surrounding the Grand Cana ...
area.
Apart from being the focus of the country's literature and theatre, Dublin is also the focal point for much of Irish art
Irish art is art produced in the island of Ireland, and by artists from Ireland. The term normally includes Irish-born artists as well as expatriates settled in Ireland. Its history starts around 3200 BC with Neolithic stone carvings at the Newg ...
and the Irish artistic scene. The Book of Kells
The Book of Kells (; ; Dublin, Trinity College Library, MS A. I. 8 sometimes known as the Book of Columba) is an illustrated manuscript and Celts, Celtic Gospel book in Latin, containing the Gospel, four Gospels of the New Testament togeth ...
, a world-famous manuscript produced by Celtic monks in AD 800 and an example of Insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, was produced in the sub-Roman Britain, post-Roman era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term derives from ''insula'', the Latin language, Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland ...
, is on display in Trinity College Trinity College may refer to:
Australia
* Trinity Anglican College, an Anglican coeducational primary and secondary school in , New South Wales
* Trinity Catholic College, Auburn, a coeducational school in the inner-western suburbs of Sydney, New ...
. The Chester Beatty Library
The Chester Beatty Library, now known as the Chester Beatty, is a museum and library in Dublin. It was established in Ireland in 1953, to house the collections of mining magnate, Sir Alfred Chester Beatty. The present museum, on the grounds of ...
houses a collection of manuscripts, miniature paintings, prints, drawings, rare books and decorative art
]
The decorative arts are arts or crafts whose aim is the design and manufacture of objects that are both Beauty, beautiful and functional. This includes most of the objects for the interiors of buildings, as well as interior design, but typical ...
s assembled by American mining millionaire (and honorary Irish citizen) Sir Alfred Chester Beatty (1875–1968). The collections date from 2700 BCE onwards and are drawn from Asia, the Middle East, North Africa and Europe.
 In addition public
In addition public art galleries
An art gallery is a room or a building in which visual art is displayed. In Western cultures from the mid-15th century, a gallery was any long, narrow covered passage along a wall, first used in the sense of a place for art in the 1590s. The long ...
are found across the city and are free to visit, including the Irish Museum of Modern Art
The Irish Museum of Modern Art (), also known as IMMA, is Ireland's leading national institution for the collection and presentation of modern and contemporary art. It is located in Kilmainham, Dublin.
History
Irish art collector Gordon Lam ...
, the National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of more than 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current di ...
, the Hugh Lane Municipal Gallery, the Douglas Hyde Gallery, the Project Arts Centre
Project Arts Centre is a multidisciplinary arts centre based in Temple Bar, Dublin, which hosts visual arts, theatre, dance, music, and performance.
History
Project Arts Centre was founded by Jim FitzGerald and Colm O'Briain in 1967 after a th ...
and the exhibition space of the Royal Hibernian Academy
The Royal Hibernian Academy of Arts (RHA) is an artist-based and artist-oriented institution in Ireland, founded in Dublin in 1823. Like many other Irish institutions, such as the Royal Irish Academy, the academy retained the word "Royal" after mo ...
. Private galleries in Dublin include Green on Red Gallery, Kerlin Gallery, Kevin Kavanagh Gallery and Mother's Tankstation.
Three branches of the National Museum of Ireland
The National Museum of Ireland () is Ireland's leading museum institution, with a strong emphasis on national and some international archaeology, Irish history, Irish art, culture, and natural history. It has three branches in Dublin, the arch ...
are located in Dublin: Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
in Kildare Street
Kildare Street () is a street in Dublin, Ireland.
Location
Kildare Street is close to the principal shopping area of Grafton Street and Dawson Street, to which it is joined by Molesworth Street. Trinity College lies at the north end of t ...
, Decorative Arts and History in Collins Barracks
Collins Barracks () is a former military barracks in the Arbour Hill area of Dublin, Ireland. The buildings now house the National Museum of Ireland – Decorative Arts and History.
Previously housing first British Armed Forces and later Iri ...
and Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
in Merrion Street
Merrion Street (; ) is a major Georgian street on the southside of Dublin, Ireland, which runs along one side of Merrion Square. It is divided into Merrion Street Lower (north end), Merrion Square West and Merrion Street Upper (south end). It ...
. Dublin is home to the National College of Art and Design
The National College of Art and Design (NCAD) is Ireland's oldest art institution, offering the largest range of art and design degrees at undergraduate and postgraduate level in the country. Originating as a drawing school in 1746, many of t ...
, which dates from 1746, and Dublin Institute of Design, founded in 1991. Dublinia is a living history
Living history is an activity that incorporates historical tools, activities and dress into an interactive presentation that seeks to give observers and participants a sense of stepping back in time. Although it does not necessarily seek to ree ...
attraction showcasing the Viking and Medieval history of the city.
Dublin has long had an 'underground' arts scene, with Temple Bar hosting artists in the 1980s, and spaces such as the Project Arts Centre acting as a hub for collectives and new exhibitions. ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
'' noted that Dublin's independent and underground arts flourished during the economic recession of . Dublin also has many dramatic, musical and operatic companies, including Festival Productions, Lyric Opera Productions, the Pioneers' Musical & Dramatic Society, Rathmines and Rathgar Musical Society, the Glasnevin Musical Society, Third Day Chorale, Second Age Theatre Company, Irish National Opera.
Dublin was shortlisted to be World Design Capital 2014. Taoiseach
The Taoiseach (, ) is the head of government or prime minister of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The office is appointed by the President of Ireland upon nomination by Dáil Éireann (the lower house of the Oireachtas, Ireland's national legisl ...
Enda Kenny
Enda Kenny (born 24 April 1951) is an Irish former Fine Gael politician who served as Taoiseach from 2011 to 2017, Leader of Fine Gael from 2002 to 2017, Minister for Defence (Ireland), Minister for Defence from May to July 2014 and 2016 to 201 ...
was quoted to say that Dublin "would be an ideal candidate to host the World Design Capital in 2014".
In October 2021, Dublin was shortlisted for the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
's 2022 European Capital of Smart Tourism award along with Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
, Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
, Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
, Ljubljana
{{Infobox settlement
, name = Ljubljana
, official_name =
, settlement_type = Capital city
, image_skyline = {{multiple image
, border = infobox
, perrow = 1/2/2/1
, total_widt ...
, Palma de Mallorca
Palma (, ; ), also known as Palma de Mallorca (officially between 1983 and 1988, 2006–2008, and 2012–2016), is the capital and largest city of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of the Balearic Islands in Spain. It is ...
and Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
.
Entertainment
Dublin has a vibrant nightlife and is reputedly one of Europe's most youthful cities; in 2009 it was estimated that 50% of its citizens were younger than 25. There are many pubs across the city centre, with the area aroundSt. Stephen's Green
St Stephen's Green () is a garden square and public park located in the city centre of Dublin, Ireland. The current landscape of the park was designed by William Sheppard. It was officially re-opened to the public on Tuesday, 27 July 1880 by Ar ...
and Grafton Street
Grafton Street () is one of the two principal shopping streets in Dublin city centre — the other being Henry Street. It runs from St Stephen's Green in the south (at the highest point of the street) to College Green in the north (the low ...
, especially Harcourt Street
Harcourt Street (Irish: Sráid Fhearchair) is a street located in Dublin City, Ireland.
Location
It is a little over in length with its northerly start at the south-east corner of St Stephen's Green and terminates in the south at the poi ...
, Camden Street
Camden Street () is a street in Dublin 2. It links Ranelagh/Rathmines ( Dublin 6) to the southern city centre of Dublin. It is divided into Camden Street Upper (southern end) and Camden Street Lower (northern end).
History
The name is likely d ...
, Wexford Street
Wexford Street () is a street in southern Dublin, Ireland that connects Aungier Street to Camden Street.
History
As early as 1326, St Kevin's Gate is recorded as being one of the gates into the city of Dublin.
Later the street was known as ...
and Leeson Street
__NOTOC__
Leeson Street (; ) is a thoroughfare near central Dublin, Ireland.
Location
The street is divided into two parts by the Grand Canal: Lower Leeson Street, in Dublin 2 is to the north of the canal, linking to St Stephen's Green, wi ...
, the location of many nightclubs and pubs.
 The best known area for nightlife is Temple Bar, south of the River Liffey. The area has become popular among tourists, including
The best known area for nightlife is Temple Bar, south of the River Liffey. The area has become popular among tourists, including stag
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) a ...
and hen
Hen commonly refers to a female animal: a female chicken, other gallinaceous bird, any type of bird in general, or a lobster. It is also a slang term for a woman.
Hen, HEN or Hens may also refer to:
Places Norway
*Hen, Buskerud, a village in R ...
parties from the UK. It was developed as Dublin's cultural quarter and does retain this spirit as a centre for small arts productions, photographic and artists' studios, and in the form of street performers and small music venues; however, it has been criticised as overpriced, false and dirty by Lonely Planet. The areas around Leeson Street, Harcourt Street, South William Street and Camden/George's Street are popular nightlife spots for locals.
Music
 Live music is played on streets and at venues throughout Dublin, and the city has produced several musicians and groups of international success, including
Live music is played on streets and at venues throughout Dublin, and the city has produced several musicians and groups of international success, including the Dubliners
The Dubliners () were an Folk music of Ireland, Irish folk band founded in Dublin in 1962 as The Ronnie Drew Ballad Group, named after its founding member; they subsequently renamed themselves The Dubliners. The line-up saw many changes in pers ...
, Thin Lizzy
Thin Lizzy are an Irish rock band formed in Dublin in 1969. The band initially consisted of bass guitarist, lead vocalist and principal songwriter Phil Lynott, drummer Brian Downey, guitarist Eric Bell and organist Eric Wrixon although Wr ...
, the Boomtown Rats
The Boomtown Rats are an Irish rock/ new wave band originally formed in Dublin in 1975. Between 1977 and 1985, they had a series of Irish and UK hits including " Like Clockwork", " Rat Trap", " I Don't Like Mondays" and " Banana Republic". T ...
, U2, the Script
The Script are an Irish Soft rock, soft-rock band formed in 2001 in Dublin. The band currently consists of Danny O'Donoghue (lead vocals, guitar, piano, keyboards), Glen Power (drums, percussion, backing vocals), Benjamin Seargent (bass, backin ...
, Sinéad O'Connor, Boyzone, Kodaline, Fontaines D.C. and Westlife. Dublin has several mid-range venues that host live music throughout the week, including Whelan's (music venue), Whelans and Vicar Street. The 3Arena 3Arena may refer to the following:
* 3Arena (Dublin)
The 3Arena (originally The O2) is an indoor amphitheatre located at North Wall Quay in the Dublin Docklands in Dublin, Ireland. The venue opened as The O2 on 16 December 2008 and was re-bran ...
venue in the Dublin Docklands
Dublin Docklands () is an area of the city of Dublin, Ireland, on both sides of the River Liffey, roughly from Talbot Memorial Bridge eastwards to the 3Arena (Dublin), 3Arena. It mainly falls within the city's List of Dublin postal districts ...
plays host to visiting global performers.
Shopping
Dublin city centre is a popular shopping destination for both locals and tourists. The city has numerous shopping districts, particularly around Grafton Street (Dublin), Grafton Street and Henry Street (Dublin), Henry Street. The city centre is also the location of large department stores, including Arnotts (Ireland), Arnotts, Brown Thomas and (prior to its 2015 closure) Clerys. While the city has seen the loss of some traditional market sites, Moore Street remains one of the city's oldest trading districts. There has also been some growth in local farmers' markets and other markets. In 2007, Dublin Food Co-op relocated to a warehouse in The Liberties area, where it is home to market and community events. Suburban Dublin has several modern retail centres, including Dundrum Town Centre, Blanchardstown Centre, The Square Shopping Centre, the Square in Tallaght, Liffey Valley Shopping Centre in Clondalkin, Omni Shopping Centre in Santry, Nutgrove Shopping Centre in Rathfarnham, Northside Shopping Centre in Coolock and Swords Pavilions inSwords
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
.
Media
Dublin is the centre of both media and communications in Ireland, with many newspapers, radio stations, television stations and telephone companies based there. RTÉ is Ireland's national state broadcaster, and is based in Donnybrook, Dublin, Donnybrook. Fair City is RTÉ's soap opera, located in the fictional Dublin suburb of ''Carraigstown''. Virgin Media Television (Ireland), Virgin Media Television, eir Sport, MTV Ireland and Sky News are also based in the city. The headquarters of An Post and telecommunications companies such as Eir (telecommunications), Eir, as well as mobile operators Vodafone Ireland, Vodafone and Three Ireland, 3 are all located there. Dublin is also the headquarters of national newspapers such as ''The Irish Times'' and ''Irish Independent'', as well as local newspapers such as ''Evening Herald, The Evening Herald''. As well as being home to RTÉ Radio, Dublin also hosts the national radio networks Today FM and Newstalk, and local stations. Commercial radio stations based in the city include Classic Hits 4FM, 4fm (94.9 Hertz, MHz), Dublin's 98FM (98.1 MHz), Radio Nova 100FM (Ireland), Radio Nova 100FM (100.3 MHz), Dublin's Q102, Q102 (102.2 MHz), SPIN 1038 (103.8 MHz), FM104 (104.4 MHz), Sunshine 106.8 (106.8 MHz). There are also numerous community and special interest stations, including Dublin City FM (103.2 MHz), Dublin South FM (93.9 MHz), Liffey Sound FM (96.4 MHz), Near fm 90.3, Near FM (90.3 MHz), and Raidió Na Life (106.4 MHz).Sport
GAA
 Croke Park is the largest sport stadium in Ireland. The headquarters of the Gaelic Athletic Association, it has a capacity of 82,300. It is the third-largest stadium in Europe after Nou Camp in Barcelona and Wembley Stadium in London. It hosts the premier Gaelic football and hurling games, international rules football and irregularly other sporting and non-sporting events including concerts. Muhammad Ali fought there in 1972 and it played host to the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2003 Special Olympics. It also has conference and banqueting facilities. There is a GAA Museum there and tours of the stadium are offered, including a rooftop walk of the stadium. During the redevelopment of Lansdowne Road, Croke Park played host to the Ireland national rugby union team, Irish Rugby Union Team and Republic of Ireland national football team as well as hosting the Heineken Cup rugby 2008–09 Heineken Cup#Semi-finals, 2008–09 semi-final between Munster and Leinster, which set a world record attendance for a club rugby match. The Dublin GAA team plays most of their home league hurling games at Parnell Park.
Croke Park is the largest sport stadium in Ireland. The headquarters of the Gaelic Athletic Association, it has a capacity of 82,300. It is the third-largest stadium in Europe after Nou Camp in Barcelona and Wembley Stadium in London. It hosts the premier Gaelic football and hurling games, international rules football and irregularly other sporting and non-sporting events including concerts. Muhammad Ali fought there in 1972 and it played host to the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2003 Special Olympics. It also has conference and banqueting facilities. There is a GAA Museum there and tours of the stadium are offered, including a rooftop walk of the stadium. During the redevelopment of Lansdowne Road, Croke Park played host to the Ireland national rugby union team, Irish Rugby Union Team and Republic of Ireland national football team as well as hosting the Heineken Cup rugby 2008–09 Heineken Cup#Semi-finals, 2008–09 semi-final between Munster and Leinster, which set a world record attendance for a club rugby match. The Dublin GAA team plays most of their home league hurling games at Parnell Park.
Rugby Union
 Lansdowne Road, IRFU Stadium Lansdowne Road was laid out in 1874. This was the venue for home games of both the Irish Rugby Union Team and the Republic of Ireland national football team. A joint venture between the Irish Rugby Football Union, the Football Association of Ireland, FAI and the Government, saw it redeveloped into a new state-of-the-art 50,000 seat Aviva Stadium, which opened in May 2010. Lansdowne Road/Aviva Stadium hosted the European Rugby Champions Cup, Heineken Cup final in 1999, 2003, 2013, and 2023. Rugby union team Leinster Rugby play their competitive home games in the RDS Arena and the Aviva Stadium, while Donnybrook Stadium hosts their friendlies and A games, Ireland A and Women, Leinster Schools and Youths and the home club games of AIB League, All Ireland League clubs Old Wesley and Bective Rangers.
Lansdowne Road, IRFU Stadium Lansdowne Road was laid out in 1874. This was the venue for home games of both the Irish Rugby Union Team and the Republic of Ireland national football team. A joint venture between the Irish Rugby Football Union, the Football Association of Ireland, FAI and the Government, saw it redeveloped into a new state-of-the-art 50,000 seat Aviva Stadium, which opened in May 2010. Lansdowne Road/Aviva Stadium hosted the European Rugby Champions Cup, Heineken Cup final in 1999, 2003, 2013, and 2023. Rugby union team Leinster Rugby play their competitive home games in the RDS Arena and the Aviva Stadium, while Donnybrook Stadium hosts their friendlies and A games, Ireland A and Women, Leinster Schools and Youths and the home club games of AIB League, All Ireland League clubs Old Wesley and Bective Rangers. County Dublin
County Dublin ( or ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and holds its capital city, Dublin. It is located on the island's east coast, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Until 1994, County Dubli ...
is home for 13 of the senior rugby union clubs in Ireland including 5 of the 10 sides in the top division 1A.
Association football
Dublin is home to five League of Ireland association football clubs: Bohemian F.C., Bohemian, Shamrock Rovers F.C., Shamrock Rovers, Shelbourne F.C., Shelbourne, St Patrick's Athletic F.C., St Patrick's Athletic and University College Dublin A.F.C., University College Dublin. The first Irish side to reach the group stages of a European competition (2011–12 UEFA Europa League group stage) are Shamrock Rovers F.C., Shamrock Rovers, who play at Tallaght Stadium inSouth Dublin
South Dublin () is a county in Ireland, within the province of Leinster and the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which was disestablished for administrative purposes in 1994. South Dublin Cou ...
. Bohemian F.C., Bohemian F.C play at Dalymount Park, the oldest football stadium in the country, and home ground for the Republic of Ireland national football team, Ireland football team from 1904 to the 1970s. St Patrick's Athletic F.C., St Patrick's Athletic play at Richmond Park (football ground), Richmond Park; University College Dublin A.F.C., University College Dublin at the UCD Bowl in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown
Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown () is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which was disestablished in 1994. It is named after the former ...
; and Shelbourne F.C., Shelbourne at Tolka Park. Tolka Park, Dalymount Park, UCD Bowl and Tallaght Stadium, along with the Carlisle Grounds in Bray
Bray may refer to:
Places France
* Bray, Eure, in the Eure ''département''
* Bray, Saône-et-Loire, in the Saône-et-Loire ''département''
* Bray-Dunes, in the Nord ''département''
* Bray-en-Val, in the Loiret ''département''
* Bray-et-Lû ...
, hosted all Group 3 games in the intermediary round of the 2011 UEFA Regions' Cup. The Aviva Stadium hosted the 2011 UEFA Europa League final and the 2024 UEFA Europa League final.
Cricket
Dublin has two List of One Day International cricket grounds, ODI cricket grounds in Castle Avenue, Dublin, Castle Avenue (Clontarf Cricket Club) and Malahide Cricket Club Ground. College Park, Dublin, College Park has Test status and played host to Ireland's first Test cricket match, a women's match against Pakistan in 2000. The men's Irish cricket team also played their first Test cricket, Test match against Pakistan national cricket team, Pakistan at Malahide Cricket Club Ground during 2018. Leinster Lightning play their home Cricket in Ireland#Inter-Provincial Series, inter-provincial matches in Dublin at College Park.Other
The Dublin Marathon has been run since 1980 at the end of October. The Dublin Women's Mini Marathon, Women's Mini Marathon has been run since 1983 on the first Monday in June, which is also a bank holiday in Ireland. It is said to be the largest all female event of its kind in the world. The Great Ireland Run takes place in Dublin's Phoenix Park in mid-April. Two Dublin baseball clubs compete in the Irish Baseball League. The Dublin Spartans and the Dublin Bay Hurricanes are both based at The O'Malley Fields at Corkagh Park. The Portmarnock Red Rox, from outside the city, competes in the Baseball Ireland B League. The Dublin area hosts greyhound racing at Shelbourne Park and horse racing at Leopardstown Racecourse, Leopardstown. The Dublin Horse Show takes place at the Royal Dublin Society, RDS, which hosted the Show Jumping World Championships in 1982. The national boxing arena is located in National Stadium (Ireland), The National Stadium on the South Circular Road (Dublin), South Circular Road. The National Basketball Arena is located in Tallaght, is the home of the Ireland national basketball team, Irish basketball team, the venue for the basketball league finals, and has also hosted boxing and wrestling events. The National Aquatic Centre inBlanchardstown
Blanchardstown () is a large outer suburb of Dublin in the modern Counties of Ireland, county of Fingal, Ireland. Located northwest of Dublin city centre, it has developed since the 1960s from a small village to a point where Greater Blanchards ...
is Ireland's largest indoor water leisure facility. There are also Gaelic Handball, hockey and athletics stadia, most notably Morton Stadium in Santry, which held the athletics events of the 2003 Special Olympics World Summer Games, 2003 Special Olympics.
Cuisine
As of the 2024 Michelin Guide, seven Dublin restaurants shared ten Michelin stars – including Restaurant Patrick Guilbaud, Liath (restaurant), Liath and Chapter One (restaurant), Chapter One with two. Irish-born Kevin Thornton (chef), Kevin Thornton was awarded two Michelin stars in 2001 – though his restaurant, Thornton's Restaurant, Thornton's, closed in 2016. TheDublin Institute of Technology
Dublin Institute of Technology (DIT, ) was a major third-level institution in Dublin, Ireland. On 1 January 2019 DIT was dissolved and its functions were transferred to the Technological University Dublin, as TU Dublin City Campus. The insti ...
commenced a bachelor's degree in culinary skills in 1999.
Historically, Irish coffee houses and cafes were associated with those working in media. Since the beginning of the 21st century, with the growth of apartment living in the city, Dublin's cafés attracted younger patrons looking for an informal gathering place and an ad hoc office. Cafés became more popular in the city, and Irish-owned coffee chains like Java Republic, Insomnia, and O'Brien's Sandwich Bars now compete internationally. In 2008, Irish barista Stephen Morrissey won the title of World Barista Champion.
Immigrant groups, such as Overseas Chinese, Chinese, Japanese diaspora, Japanese and Italian diaspora, Italian émigrés, have also opened restaurants around Dublin. A number of South-East Asians immigrated from places such as Hong Kong, Malaysia and Mainland China to Dublin during the 1960s and opened restaurants featuring their cuisines. Modern Irish adaptions of Chinese cuisine include the Spice bag, a Takeaway food, takeaway dish consisting of mainly chicken, chips and vegetables. In 2020, it was voted 'Ireland's Favourite Takeaway Dish' in the Just Eat
Just Eat is an online food order and delivery platform. It was founded in 2001 in Kolding, Denmark, as a food delivery company, and later headquartered in London, United Kingdom, from 2006 (as Just Eat plc) until it was purchased by Netherla ...
National Takeaway Awards.
English and Irish languages
Dublin was traditionally a city of two languages, English and Irish language, Irish, a situation found also in the area around it,the Pale
The Pale ( Irish: ''An Pháil'') or the English Pale (' or ') was the part of Ireland directly under the control of the English government in the Late Middle Ages. It had been reduced by the late 15th century to an area along the east coast s ...
. The Irish of County Dublin represented the easternmost extension of a broad central dialect area which stretched between Leinster and Connacht, but had its own local characteristics. It may also have been influenced by the east Ulster dialect of County Meath
County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, County ...
and County Louth to the north.
In the words of a 16th-century English administrator, William Gerard (1518–1581): "All Englishe, and the most part with delight, even in Dublin, speak Irishe". The Normans in Ireland, Old English historian Richard Stanihurst (1547–1618) wrote as follows: "When their posteritie became not altogither so warie in keeping, as their ancestors were valiant in conquering, the Irish language was free dennized in the English Pale: this canker tooke such deep root, as the bodie that before was whole and sound, was by little and little festered, and in manner wholly putrified".
English authorities of the Cromwellian period accepted the fact that Irish was widely spoken in the city and its surrounds. In 1655 several local dignitaries were ordered to oversee a lecture in Irish to be given in Dublin. In March 1656 a converted Catholic priest, Séamas Corcy, was appointed to preach in Irish at Bride's parish every Sunday, and was also ordered to preach at Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth ...
and Athy. In 1657 the English colonists in Dublin presented a petition to the Municipal Council complaining that in Dublin itself "there is Irish commonly and usually spoken".
In early 18th century Dublin, Irish was the language of a group of poets and scribes led by Seán and Tadhg Ó Neachtain. Scribal activity in Irish persisted in Dublin right through the 18th century. There were still native Irish speakers in County Dublin at the time of the 1851 census.
Though the number of Irish speakers declined throughout Ireland in the 19th century, the end of the century saw a Gaelic revival, centred in Dublin and accompanied by renewed literary activity. This was the harbinger of a steady renewal of urban Irish, though with new characteristics of its own.
Current era
The native language of most Dubliners today is English, and several local dialects are subsumed under the label Dublin English. Dublin also has many thousands of habitual Irish speakers, with the 2016 census showing that daily speakers (outside the education system) numbered 14,903. They form part of an urban Irish-speaking cohort which is generally better-educated than monoglot English speakers. The Dublin Irish-speaking cohort is supported by a number of Irish-medium schools. There are 12,950 students in the Dublin region attending 34 gaelscoileanna (Irish-language primary schools) and 10 Gaelcholáiste, gaelcholáistí (Irish-language secondary schools). Two Irish language radio stations, Raidió Na Life and RTÉ Raidió na Gaeltachta, have studios in the city, and the online station Raidió Rí-Rá broadcasts from studios in the city. A number of Irish language agencies are also located in the capital. offers language classes and is used as a meeting place for different groups. The closest Gaeltacht to Dublin is theCounty Meath
County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, County ...
Gaeltacht of Ráth Cairn and Baile Ghib which is away.
International relations
Dublin city council has an International Relations Unit, established in 2007. It works on hosting of international delegations, staff exchanges, international promotion of the city, twinning and partnerships, work with multi-city organisations such as Eurocities, economic partnerships and advice to other Council units.Twin and partner cities
Dublin is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with five places: The city also has "friendship" or "co-operation agreements" with a number of other cities: Moscow (since 2009) and St Petersburg (since 2010) in Russia and Guadalajara in Mexico (since 2013), and has previously proposed an agreement with Rio de Janeiro also. Previous agreements have included those with Mexico City (2014−2018), Tbilisi in Georgia (2014−2017) and Wuhan in China (2016−2019).Notable people
See also
* Dublin English * List of people from Dublin * List of subdivisions of County DublinNotes
References
Sources *Further reading
* John Flynn and Jerry Kelleher, ''Dublin Journeys in America'' (High Table Publishing, 2003), * Pat Liddy, ''Dublin A Celebration: From the 1st to the 21st century'' (Dublin City Council, 2000), * Maurice Craig (historian), Maurice Craig, ''The Architecture of Ireland from the Earliest Times to 1880'' (Batsford, Paperback edition 1989), * Frank McDonald (journalist), Frank McDonald, ''Saving the City: How to Halt the Destruction of Dublin'' (Tomar Publishing, 1989), * Edward McParland, ''Public Architecture in Ireland 1680–1760'' (Yale University Press, 2001),External links
Dublin City Council
nbsp;– Official website of the local authority for Dublin
Dublin Tourist Board
nbsp;– Official tourism site
Dublin UNESCO City of Literature official site
Dublin Historic Maps, Boundaries & an OSM Miscellany
{{Authority control Dublin (city), 841 establishments 9th-century establishments in Ireland Capitals in Europe Cities in the Republic of Ireland County towns in the Republic of Ireland Former boroughs in the Republic of Ireland Leinster Local government areas of the Republic of Ireland Populated coastal places in the Republic of Ireland Populated places established in the 9th century Port cities and towns of the Irish Sea Staple ports Tourism regions of the island of Ireland Viking Age populated places