The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an
8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data bu ...
home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a s ...
introduced in January 1982 by
Commodore International
Commodore International Corporation was a home computer and electronics manufacturer with its head office in The Bahamas and its executive office in the United States founded in 1976 by Jack Tramiel and Irving Gould. It was the successor compan ...
(first shown at the
Consumer Electronics Show
CES (; formerly an initialism for Consumer Electronics Show) is an annual trade show organized by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). Held in January at the Las Vegas Convention Center in Winchester, Nevada, United States, the event typi ...
, January 7–10, 1982, in
Las Vegas
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
). It has been listed in the
Guinness World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a British reference book published annually, list ...
as the highest-selling single computer model of all time,
with independent estimates placing the number sold between 12.5 and 17 million units. Volume production started in early 1982, marketing in August for . Preceded by the
VIC-20
The VIC-20 (known as the VC-20 in Germany and the VIC-1001 in Japan) is an 8-bit entry level home computer that was sold by Commodore International, Commodore Business Machines. The VIC-20 was announced in 1980, roughly three years after Commod ...
and
Commodore PET, the C64 took its name from its of RAM. With support for multicolor
sprites and a custom chip for waveform generation, the C64 could create superior visuals and audio compared to systems without such custom hardware.
The C64 dominated the low-end computer market (except in the UK, France and Japan, lasting only about six months in Japan) for most of the later years of the 1980s. For a substantial period (1983–1986), the C64 had between 30% and 40% share of the US market and two million units sold per year,
outselling
IBM PC compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central p ...
s, the
Apple II
Apple II ("apple Roman numerals, two", stylized as Apple ][) is a series of microcomputers manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1977 to 1993. The Apple II (original), original Apple II model, which gave the series its name, was designed ...
, and
Atari 8-bit computers
The Atari 8-bit computers, formally launched as the Atari Home Computer System, are a series of home computers introduced by Atari, Inc., in 1979 with the Atari 400 and Atari 800. The architecture is designed around the 8-bit MOS Technology 650 ...
. Sam Tramiel, a later Atari president and the son of Commodore's founder, said in a 1989 interview, "When I was at Commodore we were building C64s a month for a couple of years."
In the UK market, the C64 faced competition from the
BBC Micro
The BBC Microcomputer System, or BBC Micro, is a family of microcomputers developed and manufactured by Acorn Computers in the early 1980s as part of the BBC's Computer Literacy Project. Launched in December 1981, it was showcased across severa ...
, the
ZX Spectrum
The ZX Spectrum () is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit home computer developed and marketed by Sinclair Research. One of the most influential computers ever made and one of the all-time bestselling British computers, over five million units were sold. ...
, and later the
Amstrad CPC 464, but the C64 was still the second-most-popular computer in the UK after the ZX Spectrum.
The Commodore 64 failed to make any impact in Japan, as their market was dominated by Japanese computers, such as the
NEC PC-8801,
Sharp X1
The , sometimes called the Sharp X1 or CZ-800C, is a series of home computers released by Sharp Corporation from 1982 to 1988. It is based on a Zilog Z80 CPU.
The RGB display monitor for the X1 had a television tuner, and a computer screen ...
,
Fujitsu FM-7 and
MSX
MSX is a standardized home computer architecture, announced by ASCII Corporation on June 16, 1983. It was initially conceived by Microsoft as a product for the Eastern sector, and jointly marketed by Kazuhiko Nishi, the director at ASCII Corpo ...
, and in France, where the ZX Spectrum,
Thomson MO5 and
TO7, and Amstrad CPC 464 dominated the market.
Part of the Commodore 64's success was its sale in regular retail stores instead of only
electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
or computer hobbyist specialty stores. Commodore produced many of its parts
in-house to control costs, including custom
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
chips from
MOS Technology
MOS Technology, Inc. ("MOS" being short for Metal Oxide Semiconductor), later known as CSG (Commodore Semiconductor Group) and GMT Microelectronics, was a semiconductor design and fabrication company based in Audubon, Pennsylvania. It is ...
. In the United States, it has been compared to the
Ford Model T
The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by the Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first mass-affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. Th ...
automobile for its role in bringing a new technology to middle-class households via creative and affordable mass-production.
Approximately 10,000 commercial
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
titles have been made for the Commodore 64, including development tools, office productivity applications, and
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
s.
allow anyone with a modern computer, or a compatible
video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
, to run these programs today. The C64 is also credited with popularizing the computer
demoscene
The demoscene () is an international computer art subculture focused on producing demos: self-contained, sometimes extremely small, computer programs that produce audiovisual presentations. The purpose of a demo is to show off computer programmi ...
and is still used today by some
computer hobbyists.
In 2011, 17 years after it was taken off the market, research showed that brand recognition for the model was still at 87%.
History

In January 1981, MOS Technology, Inc., Commodore's
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
design subsidiary, initiated a project to design the graphic and audio chips for a next-generation
video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
. Design work for the chips, named
MOS Technology VIC-II (Video Integrated Circuit for graphics) and
MOS Technology SID (Sound Interface Device for audio), was completed in November 1981.
Commodore then began a game console project that would use the new chips—called the ''Ultimax'' or the ''
MAX Machine'', engineered by Yash Terakura from Commodore Japan. This project was eventually cancelled after just a few machines were manufactured for the Japanese market. At the same time, Robert "Bob" Russell (system programmer and architect on the
VIC-20
The VIC-20 (known as the VC-20 in Germany and the VIC-1001 in Japan) is an 8-bit entry level home computer that was sold by Commodore International, Commodore Business Machines. The VIC-20 was announced in 1980, roughly three years after Commod ...
) and
Robert "Bob" Yannes (engineer of the SID) were critical of the current product line-up at Commodore, which was a continuation of the
Commodore PET line aimed at business users. With the support of Al Charpentier (engineer of the VIC-II) and Charles Winterble (manager of MOS Technology), they proposed to Commodore CEO
Jack Tramiel
Jack Tramiel (, ); born Idek Trzmiel (; December 13, 1928 – April 8, 2012) was a Polish- American businessman and Holocaust survivor, best known for founding Commodore International. The Commodore PET, VIC-20, and Commodore 64 are som ...
a low-cost sequel to the VIC-20. Tramiel dictated that the machine should have of
random-access memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of Computer memory, electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows ...
(RAM). Although 64-
Kbit dynamic random-access memory
Dynamics (from Greek language, Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' "power (disambiguation), power") or dynamic may refer to:
Physics and engineering
* Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and t ...
(DRAM) chips cost over at the time, he knew that 64K DRAM prices were falling and would drop to an acceptable level before full production was reached. The team was able to quickly design the computer because, unlike most other home-computer companies, Commodore had its own semiconductor
fab
Fab or FAB may refer to:
Commerce
* Fab (brand), a frozen confectionery
* Fab (website), an e-commerce design web site
* Fab, a digital asset marketplace by Epic Games
* The FAB Awards, a food and beverage award
* FAB Link, a European electricity ...
to produce test chips; because the fab was not running at full capacity, development costs were part of existing corporate overhead. The chips were complete by November, by which time Charpentier, Winterble, and Tramiel had decided to proceed with the new computer; the latter set a final deadline for the first weekend of January, to coincide with the 1982
Consumer Electronics Show
CES (; formerly an initialism for Consumer Electronics Show) is an annual trade show organized by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). Held in January at the Las Vegas Convention Center in Winchester, Nevada, United States, the event typi ...
(CES).
The product was
code name
A code name, codename, call sign, or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in ...
d the VIC-40 as the successor to the popular
VIC-20
The VIC-20 (known as the VC-20 in Germany and the VIC-1001 in Japan) is an 8-bit entry level home computer that was sold by Commodore International, Commodore Business Machines. The VIC-20 was announced in 1980, roughly three years after Commod ...
. The team that constructed it consisted of Yash Terakura,
Shiraz Shivji, Bob Russell, Bob Yannes, and David A. Ziembicki. The design, prototypes, and some sample software were finished in time for the show, after the team had worked tirelessly over both
Thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in October and November in the United States, Canada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Germany. It is also observed in the Australian territory ...
and
Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a Religion, religious and Culture, cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by coun ...
weekends. The machine used the same case, same-sized motherboard, and same
Commodore BASIC
Commodore BASIC, also known as PET BASIC or CBM-BASIC, is the Dialect (computing), dialect of the BASIC programming language used in Commodore International's 8-bit home computer line, stretching from the Commodore PET, PET (1977) to the Commodore ...
2.0 in
ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
as the VIC-20. BASIC also served as the
user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard outer layer of a marine ani ...
and was available immediately on startup at the
READY prompt. When the product was to be presented, the VIC-40 product was renamed C64. The C64 made an impressive debut at the January 1982
Consumer Electronics Show
CES (; formerly an initialism for Consumer Electronics Show) is an annual trade show organized by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). Held in January at the Las Vegas Convention Center in Winchester, Nevada, United States, the event typi ...
, as recalled by Production Engineer David A. Ziembicki: "All we saw at our booth were
Atari
Atari () is a brand name that has been owned by several entities since its inception in 1972. It is currently owned by French holding company Atari SA (formerly Infogrames) and its focus is on "video games, consumer hardware, licensing and bl ...
people with their mouths dropping open, saying, 'How can you do that for $595? The answer was
vertical integration
In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration, also referred to as vertical consolidation, is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each ...
; due to Commodore's ownership of MOS Technology's
semiconductor fabrication facilities, each C64 had an estimated production cost of (equivalent to $350 in 2022).
Reception
In July 1983, ''
BYTE
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
'' magazine stated that "the 64 retails for . At that price it promises to be one of the hottest contenders in the under- personal computer market." It described the SID as "a true music synthesizer ... the quality of the sound has to be heard to be believed", while criticizing the use of Commodore BASIC 2.0, the floppy disk performance which is "even slower than the
Atari 810 drive", and Commodore's quality control. ''BYTE'' gave more details, saying the C64 had "inadequate Commodore BASIC 2.0. An 8K-byte interpreted BASIC" which they assumed was because "Obviously, Commodore feels that most home users will be running prepackaged software - there is no provision for using graphics (or sound as mentioned above) from within a BASIC program except by means of POKE commands." This was one of very few warnings about C64 BASIC published in any computer magazines.
''Creative Computing'' said in December 1984 that the C64 was "the overwhelming winner" in the category of home computers under . Despite criticizing its "slow disk drive, only two cursor directional keys, zero manufacturer support, non-standard interfaces, etc.", the magazine said that at the C64's price of less than "you can't get another system with the same features: 64K, color, sprite graphics, and barrels of available software". The
Tandy Color Computer was the runner up. The
Apple II
Apple II ("apple Roman numerals, two", stylized as Apple ][) is a series of microcomputers manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1977 to 1993. The Apple II (original), original Apple II model, which gave the series its name, was designed ...
was the winner in the category of home computer over , which was the category the Commodore 64 was in when it was first released at the price of .
Market war: 1982–1983

Commodore had a reputation for Vaporware, announcing products that never appeared, so the company sought to ship the C64 quickly. Production began in the spring of 1982, and volume shipments began in August. The C64 faced a wide range of competing
home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a s ...
s,
but, with a lower price and more flexible hardware, it quickly outsold many of its competitors.
In the United States, the greatest competitors were the
Atari 8-bit computers
The Atari 8-bit computers, formally launched as the Atari Home Computer System, are a series of home computers introduced by Atari, Inc., in 1979 with the Atari 400 and Atari 800. The architecture is designed around the 8-bit MOS Technology 650 ...
, the Apple II, and the
TI-99/4A. The Atari 400 and 800 had been designed to accommodate previously stringent
FCC emissions requirements and so were expensive to manufacture. Though similar in specifications, the C64 and Apple II represented differing design philosophies; as an
open architecture system, upgrade capability for the Apple II was granted by internal expansion slots, whereas the C64's comparatively closed architecture had only a single external
ROM cartridge
A ROM cartridge, usually referred to in context simply as a cartridge, cart, cassette, or card, is a replaceable part designed to be connected to a consumer electronics device such as a home computer, video game console or, to a lesser extent, ...
port for bus expansion. However, the Apple II used its expansion slots for interfacing with common peripherals like disk drives, printers, and modems; the C64 had a variety of ports integrated into its motherboard, which were used for these purposes, usually leaving the cartridge port free. Commodore's was not a completely closed system, however; the company had published detailed specifications for most of their models since the Commodore PET and VIC-20 days, and the C64 was no exception. This was in contrast to the TI-99/4A, as
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
focused less on hobbyists and more towards unsophisticated users. C64 sales were relatively slow due to a lack of software, reliability issues with early production models, particularly high failure rates of the
PLA chip, which used a new production process, and a shortage of 1541 disk drives, which also suffered rather severe reliability issues. During 1983, however, a trickle of software turned into a flood and sales began rapidly climbing.
Commodore sold the C64 not only through its network of authorized dealers but also through department stores, discount stores, toy stores and college bookstores. The C64 had a built-in
RF modulator and thus could be plugged into any television set. This allowed it (like its predecessor, the VIC-20) to compete directly against video game consoles such as the
Atari 2600
The Atari 2600 is a home video game console developed and produced by Atari, Inc. Released in September 1977 as the Atari Video Computer System (Atari VCS), it popularized microprocessor-based hardware and games stored on swappable ROM cartridg ...
. Like the Apple IIe, the C64 could also output a
composite video
Composite video, also known as CVBS (composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync), is an analog video format that combines image information—such as brightness (luminance), color (chrominance), and synchronization, int ...
signal, avoiding the RF modulator altogether. This allowed the C64 to be plugged into a specialized monitor for a sharper picture. Unlike the IIe, the C64's NTSC output capability also included separate luminance/chroma signal output equivalent to (and electrically compatible with)
S-Video, for connection to the
Commodore 1702 monitor, providing even better video quality than a composite signal.
Aggressive pricing of the C64 is considered to have been a major catalyst in the
video game crash of 1983
The video game crash of 1983 (known in Japan as the Atari shock) was a large-scale recession in the video game industry that occurred from 1983 to 1985 in the United States. The crash was attributed to several factors, including market saturatio ...
. In January 1983, Commodore offered a $100
rebate in the United States on the purchase of a C64 to anyone that traded in another video game console or computer.
To take advantage of this rebate, some mail-order dealers and retailers offered a
Timex Sinclair 1000 (TS1000) for as little as with the purchase of a C64. This deal meant that the consumer could send the TS1000 to Commodore, collect the rebate, and pocket the difference;
Timex Corporation departed the computer market within a year. Commodore's tactics soon led to a
price war
A price war is a form of market competition in which companies within an industry engage in aggressive pricing activity "characterized by the repeated cutting of prices below those of competitors". This leads to a cycle, where each competitor att ...
with the major
home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a s ...
manufacturers. The success of the VIC-20 and C64 contributed significantly to Texas Instruments and other smaller competitors exiting the field.
The price war with Texas Instruments was seen as a personal battle for Commodore president Jack Tramiel.
Commodore dropped the C64's list price by within two months of its release. In June 1983 the company lowered the price to (equivalent to $ in ), and some stores sold the computer for . At one point, the company was selling as many C64s as all computers sold by the rest of the industry combined. Meanwhile, TI lost money by selling the TI-99/4A for .
TI's subsequent demise in the home computer industry in October 1983 was seen as revenge for TI's tactics in the
electronic calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable Electronics, electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.
The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. ...
market in the mid-1970s, when Commodore was almost bankrupted by TI.
All four machines had similar memory configurations which were standard in 1982–83: for the Apple II+
(upgraded within months of C64's release to with the Apple IIe) and for the Atari 800.
At upwards of , the Apple II was about twice as expensive, while the Atari 800 cost $899. One key to the C64's success was Commodore's aggressive marketing tactics, and they were quick to exploit the relative price/performance divisions between its competitors with a series of television commercials after the C64's launch in late 1982.
The company also published detailed documentation to help developers,
while Atari initially kept technical information secret.
Although many early C64 games were inferior Atari 8-bit
ports Ports collections (or ports trees, or just ports) are the sets of makefiles and Patch (Unix), patches provided by the BSD-based operating systems, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD, as a simple method of installing software or creating binary packages. T ...
, by late 1983, the growing installed base caused developers to create new software with better graphics and sound.
Rumors spread in late 1983 that Commodore would discontinue the C64,
but it was the only non-discontinued, widely available home computer in the US by then, with more than 500,000 sold during the Christmas season;
because of production problems in Atari's supply chain, by the start of 1984 "the Commodore 64 largely has
he low-endmarket to itself right now", ''
The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'', locally known as ''The'' ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'' or ''WP'', is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C., the national capital. It is the most widely circulated newspaper in the Washington m ...
'' reported.
1984–1987
With sales booming and the early reliability issues with the hardware addressed, software for the C64 began to grow in size and ambition during 1984. This growth shifted to the primary focus of most US game developers. The two holdouts were
Sierra, who largely skipped over the C64 in favor of Apple and PC-compatible machines, and
Broderbund
Broderbund Software, Inc. (stylized as Brøderbund) was an American maker of video games, educational software, and productivity tools. Broderbund is best known for the 8-bit video game hits '' Choplifter'', '' Lode Runner'', '' Karateka'', and ...
, who were heavily invested in educational software and developed primarily around the Apple II. In the North American market, the disk format had become nearly universal while cassette and cartridge-based software all but disappeared. Most US-developed games by this point grew large enough to require multi-loading from disk.
At a mid-1984 conference of game developers and experts at
Origins Game Fair
Origins Game Fair is an annual gaming convention that was first held in 1975. Since 1996, it has been held in Columbus, Ohio at the Greater Columbus Convention Center. Origins is run by the Game Manufacturers Association (GAMA). Origins was cha ...
,
Dan Bunten,
Sid Meier, and a representative of
Avalon Hill
Avalon Hill Games Inc. is a game company that publishes wargames and strategic board games. It has also published miniature wargaming rules, role-playing games and sports simulations. It is a subsidiary of Hasbro, and operates under the compan ...
said that they were developing games for the C64 first as the most promising market.
By 1985, games were an estimated 60 to 70% of Commodore 64 software.
''
Computer Gaming World
''Computer Gaming World'' (CGW) was an American Video game journalism, computer game magazine that was published between 1981 and 2006. One of the few magazines of the era to survive the video game crash of 1983, it was sold to Ziff Davis in 199 ...
'' stated in January 1985 that companies such as
Epyx
Epyx, Inc. was a video game developer and video game publisher active in the late 1970s and 1980s. The company was founded in 1978 as Automated Simulations by Jim Connelley and Jon Freeman, publishing a series of tactical combat games. The Epyx ...
that survived the video game crash did so because they "jumped on the Commodore bandwagon early".
Over 35% of
SSI's 1986 sales were for the C64, ten points higher than for the Apple II. The C64 was even more important for other companies,
which often found that more than half the sales for a title ported to six platforms came from the C64 version.
That year, ''Computer Gaming World'' published a survey of ten game publishers that found that they planned to release forty-three Commodore 64 games that year, compared to nineteen for Atari and forty-eight for Apple II,
and
Alan Miller stated that
Accolade
The accolade (also known as dubbing, adoubement, or knighting) () was the central act in the rite of passage Ceremony, ceremonies conferring knighthood in the Middle Ages.
Etymology
The term ''accolade'' entered English by 1591, when Thomas ...
developed first for the C64 because "it will sell the most on that system".
In Europe, the primary competitors to the C64 were British-built computers: the
Sinclair ZX Spectrum, the
BBC Micro
The BBC Microcomputer System, or BBC Micro, is a family of microcomputers developed and manufactured by Acorn Computers in the early 1980s as part of the BBC's Computer Literacy Project. Launched in December 1981, it was showcased across severa ...
, and the
Amstrad CPC 464. In the UK, the 48K Spectrum had not only been released a few months ahead of the C64's early 1983 debut, but it was also selling for £175, less than half the C64's £399 price. The Spectrum quickly became the market leader and Commodore had an uphill struggle against it in the marketplace. The C64 did however go on to rival the Spectrum in popularity in the latter half of the 1980s. Adjusted to the population size, the popularity of Commodore 64 was the highest in
Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
at roughly 3 units per 100 inhabitants, where it was subsequently marketed as "the Computer of the Republic".
By early 1985 the C64's price was ; with an estimated production cost of , its profitability was still within the industry-standard markup of two to three times. Commodore sold about one million C64s in 1985 and a total of 3.5 million by mid-1986. Although the company reportedly attempted to discontinue the C64 more than once in favor of more expensive computers such as the
Commodore 128, demand remained strong.
In 1986, Commodore introduced the 64C, a redesigned 64, which ''Compute!'' saw as evidence that—contrary to C64 owners' fears that the company would abandon them in favor of the
Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers produced by Commodore International, Commodore from 1985 until the company's bankruptcy in 1994, with production by others afterward. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16-b ...
and 128—"the 64 refuses to die".
Its introduction also meant that Commodore raised the price of the C64 for the first time, which the magazine cited as the end of the home-computer
price war
A price war is a form of market competition in which companies within an industry engage in aggressive pricing activity "characterized by the repeated cutting of prices below those of competitors". This leads to a cycle, where each competitor att ...
.
Software sales also remained strong;
MicroProse
MicroProse is an American video game publisher and video game developer, developer founded by Bill Stealey, Sid Meier, and Andy Hollis in 1982. It developed and published numerous games, including starting the ''Civilization (series), Civilizat ...
, for example, in 1987 cited the Commodore and IBM PC markets as its top priorities.
1988–1994
By 1988,
PC compatibles were the largest and fastest-growing home and entertainment software markets, displacing former leader Commodore.
Commodore 64 software sales were almost unchanged in the third quarter of 1988 year over year while the overall market grew 42%,
but the company was still selling 1 to 1.5 million units worldwide each year of what ''
Computer Chronicles'' that year called "the
Model T of personal computers". Epyx CEO
Dave Morse cautioned that "there are no new 64 buyers, or very few. It's a consistent group that's not growing... it's going to shrink as part of our business."
One computer gaming executive stated that the
Nintendo Entertainment System
The Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) is an 8-bit home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan on 15 July 1983 as the and was later released as the redesigned NES in several test markets in the ...
's enormous popularityseven million sold in 1988, almost as many as the number of C64s sold in its first five yearshad stopped the C64's growth.
Trip Hawkins reinforced that sentiment, stating that Nintendo was "the last hurrah of the 8-bit world".
exited the Commodore 64 market in 1991, after most competitors.
''
Ultima VI'', released in 1991, was the last major C64 game release from a North American developer, and
''The Simpsons'', published by
Ultra Games, was the last arcade conversion. The latter was a somewhat uncommon example of a US-developed arcade port as after the early years of the C64, most arcade conversions were produced by UK developers and converted to NTSC and disk format for the US market, American developers instead focusing on more computer-centered game genres such as RPGs and simulations. In the European market, disk software was rarer and cassettes were the most common distribution method; this led to a higher prevalence of arcade titles and smaller, lower-budget games that could fit entirely in the computer's memory without requiring multiloads. European programmers also tended to exploit advanced features of the C64's hardware more than their US counterparts.
The Commodore 64 Light Fantastic pack was released in time for the 1989 Christmas holiday season. The package included a C64C, a Cheetah Defender 64 Light gun and 3D-glasses. This pack included several games compatible with the light gun, including some developed purely for the packs release (Mindscape.)
In the United States, demand for 8-bit computers all but ceased as the 1990s began and PC compatibles completely dominated the computer market. However, the C64 continued to be popular in the UK and other European countries. The machine's eventual demise was not due to lack of demand or the cost of the C64 itself (still profitable at a retail price point between £44 and £50), but rather because of the cost of producing the disk drive. In March 1994, at
CeBIT
CeBIT was a computer expo which, at its peak, was the largest and most internationally representative. The trade fair was held each year on the Hanover fairground, the world's largest fairground, in Hanover, Germany. In its day, it was c ...
in
Hanover
Hanover ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Lower Saxony. Its population of 535,932 (2021) makes it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-l ...
,
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Commodore announced that the C64 would be finally discontinued in 1995, noting that the
Commodore 1541 cost more than the C64 itself.
However, only one month later in April 1994, the company filed for
bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the deb ...
. When Commodore went bankrupt, all production on their inventory, including the C64, was discontinued, thus ending the C64's -year production. Claims of sales of 17, 22 and 30 million of C64 units sold worldwide have been made. Company sales records, however, indicate that the total number was about 12.5 million. Based on that figure, the Commodore 64 was still the third most popular computing platform into the 21st century until 2017 when the
Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi ( ) is a series of small single-board computers (SBCs) developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in collaboration with Broadcom Inc., Broadcom. To commercialize the product and support its growing demand, the ...
family replaced it.
While 360,000 C64s were sold in 1982, about 1.3 million were sold in 1983, followed by a large spike in 1984 when 2.6 million were sold. After that, sales held steady at between 1.3 and 1.6 million a year for the remainder of the decade and then dropped off after 1989. North American sales peaked between 1983 and 1985 and gradually tapered off afterward, while European sales remained quite strong into the early 1990s. Commodore itself reported a robust sales figure of over 800,000 units during the 1991 fiscal year, but sales during the 1993 fiscal year had declined to fewer than 200,000 units. Throughout the early 1990s, European sales had accounted for more than 80% of Commodore's total sales revenue.
C64 family
Commodore MAX
In 1982, Commodore released the
MAX Machine in
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. It was called the Ultimax in the United States and VC-10 in Germany. The MAX was intended to be a game console with limited computing capability and was based on a cut-down version of the hardware family later used in the C64. The MAX was discontinued months after its introduction because of poor sales in Japan.
Commodore Educator 64
1983 saw Commodore attempt to compete with the
Apple II
Apple II ("apple Roman numerals, two", stylized as Apple ][) is a series of microcomputers manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1977 to 1993. The Apple II (original), original Apple II model, which gave the series its name, was designed ...
's hold on the US education market with the Commodore Educator 64, Educator 64,
essentially a C64 and "green" monochrome monitor in a PET case. Schools preferred the all-in-one metal construction of the PET over the standard C64's separate components, which could be easily damaged, vandalized, or stolen. Schools did not prefer the Educator 64 to the wide range of software and hardware options the
Apple IIe was able to offer, and it was produced in limited quantities.
SX-64
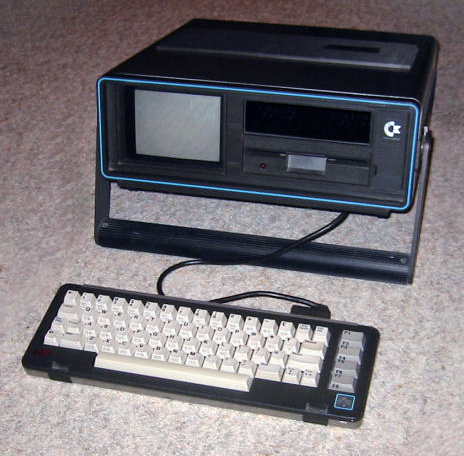

Also in 1983, Commodore released the
SX-64, a portable version of the C64. The SX-64 has the distinction of being the first commercial ''full-color''
portable computer
A portable computer is a computer designed to be easily moved from one place to another, as opposed to those designed to remain stationary at a single location such as desktops and workstations. These computers usually include a display a ...
. While earlier computers using this form factor only incorporate monochrome ("green screen") displays, the base SX-64 unit features a color
cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a ...
(CRT) and one integrated
1541 floppy disk drive. Even though Commodore claimed in advertisements that it would have dual 1541 drives, when the SX-64 was released there was only one and the other became a floppy disk storage slot. Also, unlike most other C64s, the SX-64 does not have a datasette connector so an external cassette was not an option.
Commodore 128
Two designers at Commodore, Fred Bowen and
Bil Herd, were determined to rectify the problems of the
Plus/4. They intended that the eventual successors to the C64—the
Commodore 128 and 128D computers (1985)—were to build upon the C64, avoiding the Plus/4's flaws.
The successors had many improvements such as a BASIC with graphics and sound commands (like almost all home computers not made by Commodore), 80-column display ability, and full
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/Intel 8085, 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Dig ...
compatibility. The decision to make the
Commodore 128 plug compatible
Plug compatible refers to " hardware that is designed to perform exactly like another vendor's product." The term PCM was originally applied to manufacturers who made replacements for IBM peripherals. Later this term was used to refer to IBM-com ...
with the C64 was made quietly by Bowen and Herd, software and hardware designers respectively, without the knowledge or approval by the management in the post
Jack Tramiel
Jack Tramiel (, ); born Idek Trzmiel (; December 13, 1928 – April 8, 2012) was a Polish- American businessman and Holocaust survivor, best known for founding Commodore International. The Commodore PET, VIC-20, and Commodore 64 are som ...
era. The designers were careful not to reveal their decision until the project was too far along to be challenged or changed and still make the impending Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas. Upon learning that the C128 was designed to be compatible with the C64, Commodore's marketing department independently announced that the C128 would be 100% compatible with the C64, thereby raising the bar for C64 support. In a case of
malicious compliance, the 128 design was altered to include a separate "64 mode" using a complete C64 environment to try to ensure total compatibility.
Commodore 64C

The C64's designers intended the computer to have a new, wedge-shaped case within a year of release, but the change did not occur. In 1986, Commodore released the 64C computer, which is functionally identical to the original. The exterior design was remodeled in the sleeker style of the
Commodore 128. The 64C uses new versions of the SID, VIC-II, and I/O chips being deployed. Models with the C64E board had the graphic symbols printed on the top of the keys, instead of the normal location on the front. The sound chip (SID) was changed to use the MOS 8580 chip, with the core voltage reduced from 12V to 9V. The most significant changes include different behavior in the filters and in the volume control, which result in some music/sound effects sounding differently than intended, and in digitally-sampled audio being almost inaudible, respectively (though both of these can mostly be corrected-for in software). The 64 KB RAM memory went from eight chips to two chips. BASIC and the
KERNAL went from two separate chips into one 16 KB ROM chip. The
PLA chip and some TTL chips were integrated into a
DIL 64-pin chip. The "252535-01" PLA integrated the color RAM as well into the same chip. The smaller physical space made it impossible to put in some internal expansions like a floppy-speeder. In the United States, the 64C was often bundled with the third-party
GEOS graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
(GUI)-based operating system, as well as the software needed to access
Quantum Link. The 1541 drive received a matching face-lift, resulting in the 1541C. Later, a smaller, sleeker 1541-II model was introduced, along with the 3.5-inch
microfloppy 1581.
Commodore 64 Games System
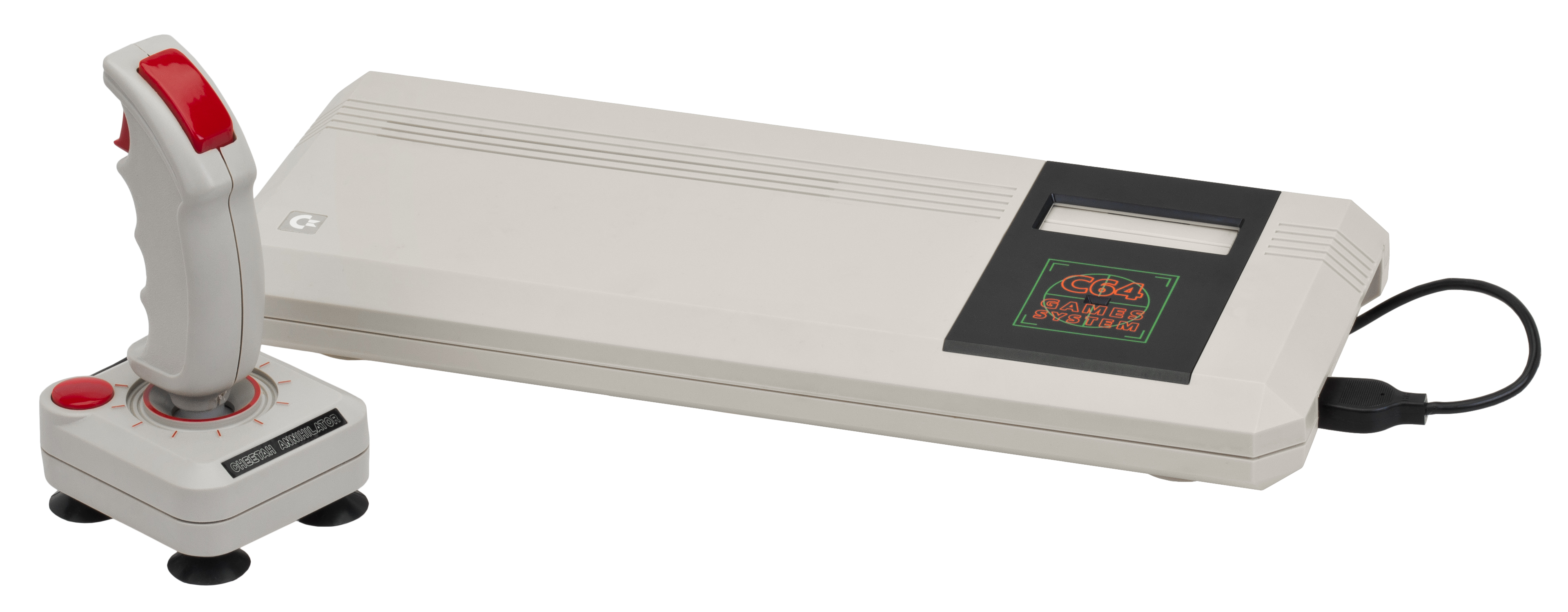

In 1990, the C64 was repackaged in the form of a game console, called the
C64 Games System (C64GS), with most external connectivity removed. A simple modification to the 64C's motherboard was made to allow cartridges to be inserted from above. A modified ROM replaced the BASIC interpreter with a boot screen to inform the user to insert a cartridge. Designed to compete with the
Nintendo Entertainment System
The Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) is an 8-bit home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan on 15 July 1983 as the and was later released as the redesigned NES in several test markets in the ...
and Sega's
Master System
The is an 8-bit Third generation of video game consoles, third-generation home video game console manufactured and developed by Sega. It was originally a remodeled export version of the Sega Mark III, the third iteration of the SG-1000 series ...
, it suffered from very low sales compared to its rivals. It was another commercial failure for Commodore, and it was never released outside Europe. The Commodore game system lacked a keyboard, so any software that required a keyboard could not be used.
Commodore 65
In 1990, an advanced successor to the C64, the
Commodore 65 (also known as the "C64DX"), was prototyped, but the project was canceled by Commodore's chairman
Irving Gould in 1991. The C65's specifications were impressive for an 8-bit computer, bringing specs comparable to the 16-bit
Apple IIGS. For example, it could display 256 colors on the screen, while
OCS based Amigas could only display 64 in
HalfBrite mode (32 colors and half-bright transformations). Although no specific reason was given for the C65's cancellation, it would have competed in the marketplace with Commodore's lower-end Amigas and the
Commodore CDTV.
Software
In 1982, the C64's graphics and sound capabilities were rivaled only by the
Atari 8-bit computers
The Atari 8-bit computers, formally launched as the Atari Home Computer System, are a series of home computers introduced by Atari, Inc., in 1979 with the Atari 400 and Atari 800. The architecture is designed around the 8-bit MOS Technology 650 ...
and appeared exceptional when compared with the popular
Apple II
Apple II ("apple Roman numerals, two", stylized as Apple ][) is a series of microcomputers manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1977 to 1993. The Apple II (original), original Apple II model, which gave the series its name, was designed ...
. The C64 is often credited with starting the
demoscene
The demoscene () is an international computer art subculture focused on producing demos: self-contained, sometimes extremely small, computer programs that produce audiovisual presentations. The purpose of a demo is to show off computer programmi ...
subculture (see Commodore 64 demos). It is still being actively used in the demoscene, especially for music (its SID sound chip even being used in special sound cards for PCs, and the Elektron SidStation synthesizer). Even though other computers quickly caught up with it, the C64 remained a strong competitor to the later
video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
s
Nintendo Entertainment System
The Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) is an 8-bit home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan on 15 July 1983 as the and was later released as the redesigned NES in several test markets in the ...
(NES) and
Master System
The is an 8-bit Third generation of video game consoles, third-generation home video game console manufactured and developed by Sega. It was originally a remodeled export version of the Sega Mark III, the third iteration of the SG-1000 series ...
, thanks in part to its by-then established software base, especially outside North America, where it comprehensively outsold the NES.
Because of lower incomes and the domination of the
ZX Spectrum
The ZX Spectrum () is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit home computer developed and marketed by Sinclair Research. One of the most influential computers ever made and one of the all-time bestselling British computers, over five million units were sold. ...
in the UK, almost all British C64 software used cassette tapes. Few cassette C64 programs were released in the US after 1983 and, in North America, the diskette was the principal method of software distribution. The cartridge slot on the C64 was also mainly a feature used in the computer's first two years on the US market and became rapidly obsolete once the price and reliability of 1541 drives improved. A handful of PAL region games used bank switched cartridges to get around the 16 KB memory limit.
BASIC

As is common for home computers of the early 1980s, the C64 comes with a BASIC interpreter, in ROM. KERNAL, I/O, and tape/disk drive operations are accessed via custom BASIC language commands. The disk drive has its own interfacing
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
and ROM (firmware) I/O routines, much like the earlier CBM/PET systems and the Atari 400 and Atari 800. This means that no memory space is dedicated to running a
disk operating system
A disk operating system (DOS) is a computer operating system that requires a disk or other direct-access storage device as secondary storage. A DOS provides a file system and a means for loading and running computer program, programs stored on th ...
, as was the case with earlier systems such as the Apple II and
TRS-80
The TRS-80 Micro Computer System (TRS-80, later renamed the Model I to distinguish it from successors) is a desktop microcomputer developed by American company Tandy Corporation and sold through their Radio Shack stores. Launched in 1977, it is ...
.
Commodore BASIC 2.0 is used instead of the more advanced BASIC 4.0 from the PET series, since C64 users were not expected to need the disk-oriented enhancements of BASIC 4.0. The company did not expect many to buy a disk drive, and using BASIC 2.0 simplified VIC-20 owners' transition to the 64.
"The choice of BASIC 2.0 instead of 4.0 was made with some soul-searching, not just at random. The typical user of a C64 is not expected to need the direct disk commands as much as other extensions, and the amount of memory to be committed to BASIC were to be limited. We chose to leave expansion space for color and sound extensions instead of the disk features. As a result, you will have to handle the disk in the more cumbersome manner of the 'old days'."
The version of
Microsoft BASIC
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first v ...
is not very comprehensive and does not include specific commands for sound or graphics manipulation, instead requiring users to use the "
PEEK and POKE" commands to access the graphics and sound chip registers directly. To provide extended commands, including graphics and sound, Commodore produced two different cartridge-based extensions to BASIC 2.0:
Simons' BASIC
Simons' BASIC is an BASIC extension, extension to Commodore BASIC, BASIC 2.0 for the Commodore 64 home computer. Written by British people, British programmer David Simons in 1983, who was 16 years old at the time, it was distributed by Commodore I ...
and
Super Expander 64. Other languages available for the C64 include
Pascal,
C,
Logo
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name that it represents, as in ...
,
Forth, and
FORTRAN. Compilers for BASIC 2.0 such as Petspeed 2 (from Commodore), Blitz (from Jason Ranheim), and Turbo Lightning (from
Ocean Software) were produced. Most commercial C64 software was written in assembly language, either cross-developed on a larger computer, or directly on the C64 using a machine code monitor or an assembler. This maximized speed and minimized memory use. Some games, particularly adventures, used high-level scripting languages and sometimes mixed BASIC and machine language.
Alternative operating systems
Many third-party operating systems have been developed for the C64. As well as the original
GEOS, two third-party GEOS-compatible systems have been written: Wheels and GEOS megapatch. Both of these require hardware upgrades to the original C64. Several other operating systems are or have been available, including WiNGS OS, the Unix-like LUnix, operated from a command-line, and the embedded systems OS
Contiki
Contiki is an operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Contiki is used for systems for street lighting, sound monitoring for smart cities, radiation monitori ...
, with full GUI. Other less well-known OSes include ACE, Asterix, DOS/65, and
GeckOS
Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates. They range from .
Geckos are unique among lizards f ...
. C64 OS is commercially available today and under active development. It features a full GUI in character mode, and many other modern features. A version of
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/Intel 8085, 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Dig ...
was released, but this requires the addition of an external
Z80 processor to the expansion bus. Furthermore, the Z80 processor is underclocked to be compatible with the C64's memory bus, so performance is poor compared to other CP/M implementations. C64 CP/M and C128 CP/M both suffer a lack of software; although most commercial CP/M software can run on these systems, software media is incompatible between platforms. The low usage of CP/M on Commodores means that software houses saw no need to invest in mastering versions for the Commodore disk format. The C64 CP/M cartridge is also not compatible with anything except the early 326298 motherboards.
Networking software
During the 1980s, the Commodore 64 was used to run
bulletin board system
A bulletin board system (BBS), also called a computer bulletin board service (CBBS), is a computer server running list of BBS software, software that allows users to connect to the system using a terminal program. Once logged in, the user perfor ...
s using software packages such as
Punter BBS, Bizarre 64,
Blue Board, C-Net,
Color 64, CMBBS, C-Base, DMBBS, Image BBS, EBBS, and The Deadlock Deluxe BBS Construction Kit, often with
sysop-made modifications. These boards sometimes were used to distribute
cracked software. As late as December 2013, there were 25 such Bulletin Board Systems in operation, reachable via the
Telnet
Telnet (sometimes stylized TELNET) is a client-server application protocol that provides access to virtual terminals of remote systems on local area networks or the Internet. It is a protocol for bidirectional 8-bit communications. Its main ...
protocol. There were major commercial
online services, such as
Compunet (UK),
CompuServe
CompuServe, Inc. (CompuServe Information Service, Inc., also known by its initialism CIS or later CSi) was an American Internet company that provided the first major commercial online service provider, online service. It opened in 1969 as a times ...
(US later bought by
America Online
AOL (formerly a company known as AOL Inc. and originally known as America Online) is an American web portal and online service provider based in New York City, and a brand marketed by Yahoo! Inc. (2017–present), Yahoo! Inc.
The service tra ...
),
The Source (US), and
Minitel (France) among many others. These services usually required custom software which was often bundled with a
modem
The Democratic Movement (, ; MoDem ) is a centre to centre-right political party in France, whose main ideological trends are liberalism and Christian democracy, and that is characterised by a strong pro-Europeanist stance. MoDem was establis ...
and included free online time as they were billed by the minute.
Quantum Link (or Q-Link) was a US and Canadian online service for Commodore 64 and 128 personal computers that operated from November 5, 1985, to November 1, 1994. It was operated by
Quantum Computer Services of
Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
, Virginia, which in October 1991 changed its name to
America Online
AOL (formerly a company known as AOL Inc. and originally known as America Online) is an American web portal and online service provider based in New York City, and a brand marketed by Yahoo! Inc. (2017–present), Yahoo! Inc.
The service tra ...
and continued to operate its
AOL service for the
IBM PC compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central p ...
and Apple
Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup inclu ...
. Q-Link was a modified version of the
PlayNET system, which
Control Video Corporation (CVC, later renamed Quantum Computer Services) licensed.
Online gaming
The first graphical character-based interactive environment is ''
Club Caribe''. First released as ''
Habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
'' in 1988, ''Club Caribe'' was introduced by
LucasArts
Lucasfilm Games (known as LucasArts between 1990 and 2021) is an American video game brand licensing, licensor, former video game developer and video game publisher, publisher, and a subsidiary of Lucasfilm. It was founded in May 1982 by George ...
for
Q-Link customers on their Commodore 64 computers. Users could interact with one another, chat and exchange items. Although the game's
open world was very basic, its use of online avatars and the combination of chat and graphics was revolutionary. Online graphics in the late 1980s were severely restricted by the need to support modem data transfer rates as low as 300
bits per second
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time.
The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction ...
. Habitat's graphics were stored locally on floppy disk, eliminating the need for network transfer.
Hardware
CPU and memory

The C64 uses an
8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data bu ...
MOS Technology 6510 microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
that is almost identical to the
6502 but has
three-state buses, a different
pinout, slightly different
clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and ...
s and other minor changes for this application. It also has six I/O lines on otherwise-unused legs on the 40-pin IC package. These are used for two purposes in the C64: to
bank-switch the machine's
read-only memory
Read-only memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be electronically modified after the manufacture of the memory device. Read-only memory is useful for storing sof ...
(ROM) in and out of the processor's address space, and to operate the
datasette tape recorder. The C64 has of 8-bit-wide dynamic
RAM, of 4-bit-wide static color RAM for text mode, and are available to built-in
Commodore BASIC
Commodore BASIC, also known as PET BASIC or CBM-BASIC, is the Dialect (computing), dialect of the BASIC programming language used in Commodore International's 8-bit home computer line, stretching from the Commodore PET, PET (1977) to the Commodore ...
2.0 on startup. There is of ROM, made up of the BASIC interpreter, the
KERNAL, and the character ROM. Because the processor can only address at a time, the ROM was mapped into memory and only of RAM (plus between the ROMs) were available at startup. Most "
breadbin" Commodore 64s used 4164 DRAM with eight chips totaling 64K of system RAM. Later models, featuring Assy 250466 and Assy 250469
motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It ho ...
s, used 41464 DRAM (64K×4) chips which stored per chip (so only two were required). Because 4164 DRAMs are 64K×1, eight chips are needed to make an entire byte; the computer will not function without all of them present. The first chip contains Bit 0 for the memory space, the second chip contains Bit 1, and so forth.
The C64 performs a RAM test on power-up and if a RAM error is detected, the amount of free BASIC memory will be lower than the normal 38,911. If the faulty chip is in lower memory, then an
?OUT OF MEMORY IN 0 error is displayed rather than the usual BASIC startup banner.
The C64 uses a complicated memory-banking scheme; the normal power-on default is the BASIC ROM mapped in at -, and the screen editor (KERNAL) ROM at –. RAM under the system ROMs can be written to, but not read back, without swapping out the ROMs. Memory location contains a register with control bits for enabling or disabling the system ROMs and the I/O area at . If the KERNAL ROM is swapped out, BASIC will be removed at the same time. BASIC is not active without the KERNAL; BASIC often calls KERNAL routines, and part of the ROM code for BASIC is in the KERNAL ROM.
The character ROM is normally invisible to the CPU. The character ROM may be mapped into –, where it is then visible to the CPU. Because doing so necessitates swapping out the I/O registers, interrupts must first be disabled. By removing I/O from the memory map, – becomes free RAM.
C64 cartridges map into assigned ranges in the CPU's address space. The most common cartridge auto-starting requires a
string
String or strings may refer to:
*String (structure), a long flexible structure made from threads twisted together, which is used to tie, bind, or hang other objects
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Strings'' (1991 film), a Canadian anim ...
at which contains "" followed by the address where program execution begins. A few C64 cartridges released in 1982 use Ultimax mode (or MAX mode), a leftover feature of the unsuccessful MAX Machine. These cartridges map into and displace the KERNAL ROM. If Ultimax mode is used, the programmer will have to provide code for handling system interrupts. The cartridge port has 16
address lines, which grants access to the computer's entire address space if needed. Disk and tape software normally load at the start of BASIC memory ($0801), and use a small BASIC stub (such as
10 SYS(2064)) to jump to the start of the program. Although no Commodore 8-bit machine except the C128 can automatically boot from a floppy disk, some software intentionally overwrites certain BASIC vectors in the process of loading so execution begins automatically (instead of requiring the user to type RUN at the BASIC prompt after loading).
About 300 cartridges were released for the C64, primarily during the machine's first years on the market, after which most software outgrew the cartridge limit. Larger software companies, such as
Ocean Software, began releasing games on bank-switched cartridges to overcome the cartridge limit during the C64's final years.
Commodore did not include a reset button on its computers until the CBM-II line, but third-party cartridges had a reset button. A
soft reset
In computing, rebooting is the process by which a running computer system is restarted, either intentionally or unintentionally. Reboots can be either a cold reboot (alternatively known as a hard reboot) in which the power to the system is physi ...
can be triggered by jumping to the CPU reset routine at (64738). A few programs use this as an
exit feature, although it does not clear memory.
The KERNAL ROM underwent three revisions, mainly designed to fix bugs. The initial version is only found on 326298 motherboards (used in the first production models), and cannot detect whether an NTSC or PAL VIC-II is present. The second revision is found on all C64s made from late 1982 through 1985. The final KERNAL ROM revision was introduced on the 250466 motherboard (late breadbin models with 41464 RAM), and is found in all C64Cs. The 6510 CPU is clocked at (NTSC) and (PAL), lower than some competing systems; the Atari 800, for example, is clocked at ). Performance can be boosted slightly by disabling the VIC-II's video output via a register write. This feature is often used by tape and disk
fast loaders and the KERNAL cassette routine to keep a standard CPU cycle timing not modified by the VIC-II's sharing of the bus.
The restore key is gated directly to the CPU's
NMI line, and will generate an NMI if pressed. The KERNAL handler for the NMI checks if run/stop is also pressed; if not, it ignores the NMI and exits. Run/stop-restore is normally a soft reset in BASIC which restores all I/O registers to their power-on default state, but does not clear memory or reset pointers; any BASIC programs in memory will be left untouched.
Machine-language software usually disables run/stop-restore by remapping the NMI vector to a dummy
RTI instruction. The NMI can also be used for an extra interrupt thread by programs, but risks a system lockup or other undesirable side effects if the restore key is accidentally pressed (which activates the NMI thread).
Joysticks, mice, and paddles
The C64 retained the VIC-20's
DE-9 Atari joystick port and added another; any Atari-specification game controller can be used on a C64. The joysticks are read from the registers at and , and most software is designed to use a joystick in port 2 for control rather than port 1; the upper bits of are used by the keyboard, and an I/O conflict can result. Although it is possible to use
Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
gamepads on a C64, it is not recommended; their slightly different signal can damage the
CIA chip. The
SID chip's register , used to control paddles, is an analog input. A handful of games, primarily released early in the computer's life cycle, can use paddles. In 1986, Commodore released two mice for the C64 and C128: the 1350 and
1351. The 1350 is a digital device read from the joystick registers, and can be used with any program supporting joystick input. The 1351 is an analog
potentiometer-based mouse, read with the SID's
analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a Digital signal (signal processing), digi ...
.
Graphics
The VIC-II
graphics chip features a new palette, eight hardware
sprites per
scanline (enabling up to 112 sprites per PAL screen),
scrolling
In computer displays, filmmaking, television production, video games and other kinetic displays, scrolling is sliding text, images or video across a monitor or display, vertically or horizontally. "Scrolling," as such, does not change the layout ...
capabilities, and two
bitmap graphics modes.
Text modes
The standard text mode features 40 columns, like most
Commodore PET models; the built-in character encoding is not standard
ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
but
PETSCII, an extended form of ASCII-1963. The KERNAL ROM sets the VIC-II to a dark-blue background on power-up, with a light-blue border and text. Unlike the PET and VIC-20, the C64 uses double-width text; some early VIC-IIs had poor video quality which resulted in a fuzzy picture. Most screenshots show borders around the screen, a feature of the VIC-II chip. By utilizing interrupts to reset hardware registers with precise timing, it was possible to place graphics within the borders and use the full screen.

The C64 has a resolution of 320×200 pixels, consisting of a 40×25 grid of 8×8 character blocks. It has 255 predefined character blocks, known as PETSCII. The character set can be copied into RAM and modified by a programmer.
There are two color modes: high resolution, with two colours available per character block (one foreground and one background), and multicolour (four colors per character blockthree foreground and one background). In multicolor mode, attributes are shared between pixel pairs so the effective visible resolution is 160×200 pixels; only 16 KB of memory is available for the VIC-II video processor.
Since the C64 has a bitmapped screen, it is possible (but slow) to draw each pixel individually. Most programmers used techniques developed for earlier, non-bitmapped systems like the Commodore PET and TRS-80. A programmer redraws the character set, and the video processor fills the screen block by block from the top left corner to the bottom right corner. Two types of animation are used: character block animation and hardware sprites.
Character block animation
The user draws a series of characters of a person walking, possibly two in the middle of the block and another two walking in and out of the block. Then the user sequences them so the character walks into the block and out again. Drawing a series of these gets a person walking across the screen. By timing the redraw to occur when the television screen blanks out to restart drawing the screen, there will be no flicker. For this to happen, a user programs the VIC-II that it generates a
raster interrupt when
video flyback occurs. This technique is used in the ''
Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' arcade game.
Horizontal and vertical pixel scrolling of up to one character block is supported by two hardware scroll registers. Depending on timing, hardware scrolling affects the entire screen or selected lines of character blocks. On a non-emulated C64, scrolling is glass-like and blur-free.
Hardware sprites
A sprite is a character which moves over an area of the screen, draws over the background, and redraws it after it moves. This differs from character block animation, where the user flips character blocks. On the C64, the VIC-II video controller handles most sprite emulation; the programmer defines the sprite and where it goes.
The C64 has two types of sprites, respecting their color-mode limitations. Hi-res sprites have one color (one background and one foreground), and multi-color sprites have three (one background and three foreground). Color modes can be split or windowed on a single screen. Sprites can be doubled in size vertically and horizontally up to four times their size, but the pixel attributes are the same – the pixels become "fatter". There are eight sprites, and all eight can be shown in each horizontal line concurrently. Sprites can move with glassy smoothness in front of, and behind, screen characters and other sprites.
The hardware sprites of a C64 can be displayed on a bitmapped (high-resolution) screen or a text-mode screen in conjunction with fast and smooth character block animation. Software-emulated sprites on systems without support for hardware sprites, such as the
Apple II
Apple II ("apple Roman numerals, two", stylized as Apple ][) is a series of microcomputers manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1977 to 1993. The Apple II (original), original Apple II model, which gave the series its name, was designed ...
and
ZX Spectrum
The ZX Spectrum () is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit home computer developed and marketed by Sinclair Research. One of the most influential computers ever made and one of the all-time bestselling British computers, over five million units were sold. ...
, required a bitmapped screen. Sprite-sprite and sprite-background collisions are detected in hardware, and the VIC-II can be programmed to trigger an interrupt accordingly.
Sound
The SID chip has three channels, each with its own
ADSR envelope
In sound and music, an envelope describes how a sound changes over time. For example, a piano key, when struck and held, creates a near-immediate initial sound which gradually decreases in volume to zero. An envelope may relate to elements such ...
generator and filter capabilities. Ring modulation makes use of channel three to work with the other two channels. Bob Yannes developed the SID chip and, later, co-founded the synthesizer company
Ensoniq. Composers and programmers of game music on the C64 include
Rob Hubbard,
Jeroen Tel,
Tim Follin,
David Whittaker,
Chris Hülsbeck,
Ben Daglish,
Martin Galway, Kjell Nordbø and David Dunn. Due to the chip's three channels, chords are often played as
arpeggio
An arpeggio () is a type of Chord (music), chord in which the Musical note, notes that compose a chord are individually sounded in a progressive rising or descending order. Arpeggios on keyboard instruments may be called rolled chords.
Arpe ...
s. It was also possible to continuously update the master volume with sampled data to enable the playback of 4-bit digitized audio. By 2008, it was possible to play four-channel 8-bit audio samples and two SID channels and still use filtering.
There are two versions of the SID chip: the 6581 and the 8580. The
MOS Technology 6581 was used in the original ("breadbin") C64s, the early versions of the 64C, and the
Commodore 128. The 6581 was replaced with the MOS Technology 8580 in 1987. Although the 6581 sound quality is a little crisper, it lacks the 8580's versatility; the 8580 can mix all available waveforms on each channel, but the 6581 can only mix waveforms in a channel in a limited fashion. The main difference between the 6581 and the 8580 is the supply voltage; the 6581 requires , and the 8580 . A modification can be made to use the 6581 in a newer 64C board (which uses the chip).
In 1986, the Sound Expander was released for the Commodore 64. It was a
sound module
A sound module is an electronic musical instrument without a human-playable interface such as a piano-style musical keyboard. Sound modules have to be operated using an externally connected device, which is often a MIDI controller, of which th ...
with a
Yamaha YM3526 chip capable of
FM synthesis
Frequency modulation synthesis (or FM synthesis) is a form of sound synthesis whereby the frequency of a waveform is changed by modulating its frequency with a modulator. The (instantaneous) frequency of an oscillator is altered in accordance wi ...
, primarily intended for professional
music production.
Revisions
Commodore made many changes to the C64's hardware, sometimes introducing compatibility issues.
The computer's rapid development and Commodore and
Jack Tramiel
Jack Tramiel (, ); born Idek Trzmiel (; December 13, 1928 – April 8, 2012) was a Polish- American businessman and Holocaust survivor, best known for founding Commodore International. The Commodore PET, VIC-20, and Commodore 64 are som ...
's focus on cost-cutting instead of product testing resulted in several defects which caused developers like Epyx to complain and required many revisions; Charpentier said that "not coming a little close to quality" was one of the company's mistakes.
Cost reduction was the reason for most of the revisions. Reducing
manufacturing cost
Manufacturing cost is the sum of costs of all resources consumed in the process of making a product. The manufacturing cost is classified into three categories: direct materials cost, direct labor cost and manufacturing overhead. It is a factor ...
s was vitally important to Commodore's survival during the
price war
A price war is a form of market competition in which companies within an industry engage in aggressive pricing activity "characterized by the repeated cutting of prices below those of competitors". This leads to a cycle, where each competitor att ...
and lean years of the 16-bit era. The C64's original (
NMOS-based) motherboard went through two major redesigns and a number of revisions, exchanging positions of the VIC-II, SID and
PLA chips. Much of the cost was initially eliminated by reducing the number of discrete components, such as
diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance ...
s and
resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
s, which enabled a smaller
printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
. There were 16 C64 motherboard revisions to simplify production and reduce manufacturing costs. Some board revisions were exclusive to
PAL regions. All C64 motherboards were manufactured in
Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
.
IC locations changed frequently with each motherboard revision, as did the presence (or lack) of the metal RF shield around the VIC-II; PAL boards often had aluminized cardboard instead of a metal shield. The SID and VIC-II are socketed on all boards, but the other ICs may be socketed or soldered. The first production C64s, made from 1982 to early 1983, are known as "silver label" models due to the case having a silver-colored "Commodore" logo. The power LED had a silver badge reading "64" around it. These machines have only a five-pin video cable, and cannot produce
S-Video. Commodore introduced the familiar "rainbow badge" case in late 1982, but many machines produced into early 1983 also used silver-label cases until the existing stock was used up. The original 326298 board was replaced in spring 1983 by the 250407 motherboard, which had an eight-pin video connector and added S-Video support. This case design was used until the C64C appeared in 1986. All ICs switched to plastic shells, but the silver-label C64s (notably the VIC-II) had some ceramic ICs. The case is made from
ABS plastic, which may become brown with time; this can be reversed with
retrobright.
ICs

The VIC-II was manufactured with 5-
micrometer NMOS technology, and was clocked at (PAL) or (NTSC). Internally, the clock was divided to generate the dot clock (about 8 MHz) and the
two-phase system clocks (about 1 MHz; the pixel and system clock speeds differ slightly on NTSC and PAL machines). At such high clock rates the chip generated considerable heat, forcing MOS Technology to use a ceramic
dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL) is an Semiconductor package, electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole technology, throu ...
known as a CERDIP. The ceramic package was more expensive, but dissipated heat more effectively than plastic.
After a redesign in 1983, the VIC-II was encased in a plastic dual in-line package; this reduced costs substantially, but did not eliminate the heat problem. Without a ceramic package, the VIC-II required a
heat sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is thermal management (electronics), ...
. To avoid extra cost, the metal
RF shielding doubled as the VIC's heat sink; not all units shipped with this type of shielding, however. Most C64s in
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
shipped with a cardboard
RF shield coated with a layer of metal foil. The effectiveness of the cardboard was questionable; it acted instead as an insulator, blocking airflow and trapping heat generated by the SID, VIC, and PLA chips. The SID was originally manufactured using NMOS at 7 micrometers and, in some areas, 6 micrometers. The prototype SID and some early production models had a ceramic dual in-line package, but (unlike the VIC-II) are very rare; the SID was encased in plastic when production began in early 1982.
Motherboard
In 1986, Commodore released the last revision of the classic C64
motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It ho ...
. It was otherwise identical to the 1984 design, except for two 64-
kilobit × 4-bit
DRAM
Dram, DRAM, or drams may refer to:
Technology and engineering
* Dram (unit), a unit of mass and volume, and an informal name for a small amount of liquor, especially whisky or whiskey
* Dynamic random-access memory, a type of electronic semicondu ...
chips which replaced the original eight 64-kilobit × 1-bit ICs. After the release of the Commodore 64C,
MOS Technology began to reconfigure the original C64's
chipset
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components on one or more integrated circuits that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. The chipset is usually found on the motherboard of computers. Chips ...
to use
HMOS technology. The main benefit of HMOS was that it required less voltage to drive the IC, generating less heat. This enhanced the reliability of the SID and VIC-II. The new chipset was renumbered 85xx to reflect the change to HMOS.
In 1987, Commodore released a 64C variant with a redesigned motherboard known as a "short board". The new board used the HMOS chipset, with a new 64-pin PLA chip. The "SuperPLA", as it was called, integrated discrete components and
transistor–transistor logic
Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function (the first "transistor") and the amplifying function (the second "transistor" ...
(TTL) chips. In the last revision of the 64C motherboard, the 2114 4-bit-wide color RAM was integrated into the SuperPLA.
Power supply
The C64 used an external
power supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, electric current, current, and frequency to power ...
, a linear transformer with multiple taps differing from
switch mode (presently used on PC power supplies). It was encased in
epoxy
Epoxy is the family of basic components or Curing (chemistry), cured end products of epoxy Resin, resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide fun ...
resin gel, which discouraged tampering but increased the heat level during use. The design saved space in the computer's case, and allowed international versions to be more easily manufactured. The
1541-II and
1581 disk drives and third-party clones also have external power-supply "bricks", like most peripherals.
Commodore power supplies often
failed sooner than expected. The computer reportedly had a 30-percent return rate in late 1983, compared to the 5–7 percent rate considered acceptable by the industry;
''
Creative Computing
''Creative Computing'' was one of the earliest magazines covering the microcomputer revolution. Published from October 1974 until December 1985, the magazine covered the spectrum of hobbyist/home/personal computing in a more accessible format t ...
'' reported four working C64s, out of seven.
Malfunctioning power bricks were notorious for damaging the RAM chips. Due to their higher density and single supply (+5V), they had less tolerance for over-voltage. The usually-failing
voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. It may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism or electronic components. Depending on the ...
could be replaced by piggybacking a new regulator on the board and fitting a heat sink on top.
The original
PSU on early-1982 and 1983 machines had a 5-pin connector which could accidentally be plugged into the computer's video output. Commodore later changed the design, omitting the resin gel to reduce costs. The following model, the Commodore 128, used a larger, improved power supply which included a fuse. The power supply for the
Commodore REU was similar to that of the Commodore 128, providing an upgrade for customers purchasing the accessory.
Specifications
Internal hardware
* Microprocessor CPU:
**
MOS Technology 6510/8500 (the 6510/8500 is a modified
6502 with an integrated 6-bit I/O port)
** Clock speed: or
* Video:
MOS Technology VIC-II 6567/8562 (NTSC), 6569/8565 (PAL)
** 16 colors
** Text mode: 40×25 characters; 256 user-defined chars (8×8
pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s, or 4×8 in multicolor mode); or extended background color; 64 user-defined chars with 4 background colors, 4-bit color RAM defines foreground color
** Bitmap modes: 320×200 (2 unique colors in each 8×8 pixel block),
160×200 (3 unique colors + 1 common color in each 4×8 block)
** 8 hardware
sprites of 24×21 pixels (12×21 in multicolor mode)
** Smooth scrolling,
raster interrupts
* Sound:
MOS Technology 6581/8580 SID
** 3-channel
synthesizer
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis a ...
with programmable
ADSR envelope
In sound and music, an envelope describes how a sound changes over time. For example, a piano key, when struck and held, creates a near-immediate initial sound which gradually decreases in volume to zero. An envelope may relate to elements such ...
** 8
octave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
s
** 4
waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its Graph of a function, graph as a function of time, independent of its time and Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude Scale (ratio), scales and of any dis ...
s per audio channel:
triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimension ...
,
sawtooth,
variable pulse,
noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
**
Oscillator synchronization,
ring modulation
** Programmable filter:
high pass,
low pass,
band pass,
notch filter
* Input/Output: Two
6526 Complex Interface Adapters
** 16 bit parallel I/O
** 8 bit serial I/O
** 24-hours (AM/PM) Time of Day clock (TOD), with programmable
alarm clock
An alarm clock or alarm is a clock that is designed to alert an individual or group of people at a specified time. The primary function of these clocks is to awaken people from their night's sleep or short naps; they can sometimes be used for o ...
** 16 bit interval timers
* RAM:
** 64 KB, of which 38 KB were available for BASIC programs
** 1024
nybbles color RAM (memory allocated for screen color data storage)
** Expandable to 320 KB with
Commodore 1764 256 KB
RAM Expansion Unit (REU); although only 64 KB directly accessible; REU used mostly for the
GEOS. REUs of 128 KB and 512 KB, originally designed for the C128, were also available, but required the user to buy a stronger power supply from some third party supplier; with the 1764 this was included.
Creative Micro Designs also produced a 2
MB REU for the C64 and C128, called the 1750 XL. The technology actually supported up to 16 MB, but 2 MB was the biggest one officially made. Expansions of up to 16 MB were also possible via the CMD
SuperCPU.
* ROM:
** (
Commodore BASIC
Commodore BASIC, also known as PET BASIC or CBM-BASIC, is the Dialect (computing), dialect of the BASIC programming language used in Commodore International's 8-bit home computer line, stretching from the Commodore PET, PET (1977) to the Commodore ...
2.0;
KERNAL; character generator, providing two character sets)
Input/output (I/O) ports and power supply

* I/O ports:
[ 090505 computermuseum.li]
**
ROM cartridge
A ROM cartridge, usually referred to in context simply as a cartridge, cart, cassette, or card, is a replaceable part designed to be connected to a consumer electronics device such as a home computer, video game console or, to a lesser extent, ...
expansion slot (44-pin slot for
edge connector with 6510 CPU address/data bus lines and control signals, as well as GND and voltage pins; used for program modules and memory expansions, among others)
** Integrated
RF modulator television antenna output via an
RCA connector. The used channel could be adjusted from number 36 with the
potentiometer to the left.
** 8-pin
DIN connector containing
composite video
Composite video, also known as CVBS (composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync), is an analog video format that combines image information—such as brightness (luminance), color (chrominance), and synchronization, int ...
output, separate
Y/C outputs and sound input/output. This is a 262° horseshoe version of the plug, rather than the 270° circular version. Early C64 units (with motherboard Assy 326298) use a 5-pin DIN connector that carries composite video and luminance signals, but lacks a chroma signal.
**
Serial bus (proprietary serial version of
IEEE-488, 6-pin DIN plug) for CBM printers and disk drives
**
PET-type
Commodore Datasette
file:Commodore-Datasette-C2N-Mk1-Front.jpg, The third, most common version of the 1530 C2N Datassette
The Commodore 1530 (C2N) Datasette, later also Datassette (a portmanteau of ''data'' and ''cassette''), is Commodore International, Commodore's d ...
300
baud tape interface (edge connector with digital cassette motor/read/write/key-sense signals), Ground and +5V DC lines. The cassette motor is controlled by a +5V DC signal from the 6510 CPU. The 9V AC input is transformed into unregulated 6.36V DC
[ 100610 zimmers.net] which is used to actually power the cassette motor.
[ 100610 zimmers.net]
** User port (edge connector with
TTL-level signals, for modems and so on; byte-parallel signals which can be used to drive third-party parallel printers, among other things, 17 logic signals, 7 Ground and voltage pins, including 9V AC)
** 2 × screwless
DE9M game controller
A game controller, gaming controller, or simply controller, is an input device or Input/Output Device, input/output device used with video games or entertainment systems to provide input to a video game. Input devices that have been classified as ...
ports (
compatible with Atari 2600 controllers), each supporting five digital inputs and two analog inputs. Available peripherals included digital
joystick
A joystick, sometimes called a flight stick, is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Also known as the control column, it is the principal control devic ...
s, analog
paddles, a
light pen
A light pen is a computer input device in the form of a light-sensitive wand used in conjunction with a computer's cathode-ray tube (CRT) display.
It allows the user to point to displayed objects or draw on the screen in a similar way to a to ...
, the Commodore
1351 mouse, and graphics tablets such as the
KoalaPad.
* Power supply:
** 5
V DC and 9V
AC from an external "power brick", attached to a 7-pin female DIN-connector on the computer.
[ 090505 allpinouts.org]
The is used to supply power via a
charge pump to the SID sound generator chip, provide via a rectifier to the cassette motor, a "0" pulse for every positive half wave to the time-of-day (TOD) input on the CIA chips, and directly to the user-port. Thus, as a minimum, a
square wave Square wave may refer to:
*Square wave (waveform)
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform, non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same ...
is required. But a
sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic function, periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric function, trigonometric sine, sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is ''simple ...
is preferred.
[ 090519 zimmers.net][ 090519 zimmers.net]
Memory map
Note that even if an I/O chip like the VIC-II only uses 64 positions in the memory address space, it will occupy 1,024 addresses because some address bits are left undecoded.
Peripherals
Commodore-64-1541-Floppy-Drive-01.jpg, Commodore 1541 floppy drive
Commodore 1541 white.jpg, Commodore 1541C floppy drive
C64-IMG 5372.jpg, Commodore 1541-II floppy drive
Commodore-Datasette-C2N-Mk1-Front.jpg, Commodore 1530 Datasette
Commodore Matrixdrucker MPS-802 (weißen hintergrund).jpg, Commodore MPS-802 dot matrix printer
CommodoreVICModem.jpg, Commodore VIC-Modem
Commodore blockomaus.jpg, Commodore 1351 mouse
Commodore 1702 (made by JVC) front.jpg, Commodore 1702 video monitor
Commodore 1581 Disk Drive Front.jpg, Commodore 1581 3.5" double-sided floppy drive
Manufacturing cost
Vertical integration
In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration, also referred to as vertical consolidation, is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each ...
was the key to keeping Commodore 64 production costs low. At the introduction in 1982, the production cost was US$135 and the retail price US$595. In 1985, the retail price went down to US$149 (US$ today) and the production costs were believed to be somewhere between US$35–50 ( Commodore would not confirm this cost figure. Dougherty of the
Berkeley Softworks estimated the costs of the Commodore 64 parts based on his experience at
Mattel
Mattel, Inc. ( ) is an American multinational corporation, multinational toy manufacturing and entertainment company headquartered in El Segundo, California. Founded in Los Angeles by Harold Matson and the husband-and-wife duo of Ruth Handler, ...
and
Imagic.
To lower costs, TTL chips were replaced with less expensive custom chips and ways to increase the
yields on the sound and graphics chips were found. The video chip
6567 had the ceramic package replaced with plastic but heat dissipation demanded a redesign of the chip and the development of a plastic package that can dissipate heat as well as ceramic.
Compatible hardware
C64 enthusiasts were developing new hardware in 2008, including
Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
cards,
specially-adapted
hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
s and
flash card interfaces (sd2iec).
A-SID, which gives the C-64 a
wah-wah effect, was introduced in 2022.
Clones and other reuse of the Commodore 64 name
Clones

Clones are computers which imitate C64 functions. In mid-2004, after an absence from the marketplace of more than 10 years, PC manufacturer
Tulip Computers (owners of the Commodore brand since 1997) announced the
C64 Direct-to-TV (C64DTV): a
joystick
A joystick, sometimes called a flight stick, is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Also known as the control column, it is the principal control devic ...
-based
TV game based on the C64, with 30 games in its ROM. Designed by
Jeri Ellsworth, a self-taught computer designer who had designed the
C-One C64 implementation, the C64DTV was similar to other mini-consoles based on the modestly-successful Atari 2600 and
Intellivision. The C64DTV was advertised on
QVC
QVC (short for "Quality Value Convenience") is an American free-to-air television network and a flagship shopping channel specializing in televised Shopping channel, home shopping, owned by QVC Group (formerly Qurate Retail Group). Founded in 19 ...
in the United States for the 2004 holiday season.
In 2015, a Commodore 64-compatible
motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It ho ...
was produced by
Individual Computers. Called the C64 Reloaded, it is a redesign of Commodore 64 motherboard revision 250466 with several new features. The motherboard is designed to be placed in an existing, empty C64 or C64C case. Produced in limited quantities, models of this Commodore 64 clone have machined or
ZIF sockets in which custom C64 chips are placed. The board contains
jumpers
Jumper or Jumpers may refer to:
Clothing
*Jumper (sweater), is a long-sleeve article of clothing; also called a top, pullover, or sweater
**A waist-length top garment of dense wool, part of the Royal Navy uniform and the Uniforms of the United St ...
to accept revisions of the VIC-II and SID chips and the ability to switch between the
PAL and
NTSC
NTSC (from National Television System Committee) is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170.
In 1953, a second ...
video systems. It has several innovations, including selection (via the restore key) of KERNAL and character ROMs, built-in reset toggle on the power switch, and an S-Video socket to replace the original
TV modulator. The motherboard is powered by a
DC-to-DC converter
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit or electromechanical device that converts a source of direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another. It is a type of Electric power conversion, electric power converter. Power levels range from ...
which uses from a mains adapter, rather than the original (and failure-prone) Commodore 64 power-supply brick.
Web.it Internet computer
The C64 brand was reused in 1998 for the Web.it Internet Computer,
a low-powered,
Internet-oriented, all-in-one
x86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. Th ...
PC running
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
and
Windows 3.1. It uses an
AMD Élan SC400
SoC with 16 MB of RAM, a 3.5-inch
floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a ...
drive, 56k
modem
The Democratic Movement (, ; MoDem ) is a centre to centre-right political party in France, whose main ideological trends are liberalism and Christian democracy, and that is characterised by a strong pro-Europeanist stance. MoDem was establis ...
and
PC Card. Despite its Commodore 64 nameplate, the C64 Web.it looks different and is only directly compatible with the original via included
emulation software. PC clones branded
C64x sold by
Commodore USA, a company licensing the Commodore
trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a form of intellectual property that consists of a word, phrase, symbol, design, or a combination that identifies a Good (economics and accounting), product or Service (economics), service f ...
, began shipping in June 2011. The C64x's case resembles the original C64 computer, but – like the Web.it – it is based on
x86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. Th ...
architecture and is not compatible with the Commodore 64.
Virtual Console
Several Commodore 64 games were released on the
Nintendo Wii's
Virtual Console
The Virtual Console was a line of downloadable retro video games for Nintendo's Wii and Wii U home video game consoles and the Nintendo 3DS family of handheld systems. The Virtual Console lineup consisted of titles originally released on pa ...
service in Europe and North America. They were delisted from the service in August 2013.
THEC64 and THEC64 Mini
THEC64 Mini, an unofficial
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
-based console emulating the Commodore 64, was released in 2018. It was designed and released by British company Retro Games, who licensed the name from Dutch based Commodore Corporation B.V. who own the Commodore marque. The console is a decorative, half-scale Commodore 64 with two
USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
and one
HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gam ...
port, and a
mini USB connection to power the system. The console's keyboard is non-functional; the system is controlled by an included THEC64 joystick or a separate USB keyboard. New software ROMs can be loaded into the console, which uses emulator x64 (as part of
VICE
A vice is a practice, behaviour, Habit (psychology), habit or item generally considered morally wrong in the associated society. In more minor usage, vice can refer to a fault, a negative character trait, a defect, an infirmity, or a bad or unhe ...
) to run software and has a built-in graphical operating system.
The full-size THEC64 was released in 2019 in Europe and Australia, and was scheduled for release in November 2020 in North America. The console and built-in keyboard are built to scale with the original Commodore 64, including a functional keyboard. Enhancements include VIC-20 emulation, four USB ports, and an upgraded joystick. Neither product has a Commodore trademark. The Commodore key on the original keyboard is replaced with a THEC64 key; Retro Games can call neither product a C64, although the system ROMs are licensed from Cloanto Corporation. The consoles can be switched between carousel mode (to access the built-in game library) and classic mode, in which they operate similarly to a traditional Commodore 64. USB storage can be used to hold disk, cartridge and tape images for use with the machine.
File:C64 + THEC64MINI.jpg, alt=A C64 and a much-smaller THEC64 Mini, THEC64 Mini ''(top)'' next to an original C64
File:THEC64 Maxi.jpg, alt=See caption, Full-size THEC64 in its original box
Emulators
Commodore 64
emulator
In computing, an emulator is Computer hardware, hardware or software that enables one computer system (called the ''host'') to behave like another computer system (called the ''guest''). An emulator typically enables the host system to run sof ...
s include the
open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
VICE
A vice is a practice, behaviour, Habit (psychology), habit or item generally considered morally wrong in the associated society. In more minor usage, vice can refer to a fault, a negative character trait, a defect, an infirmity, or a bad or unhe ...
, Hoxs64,
and
CCS64. An
iPhone app was also released with a compilation of C64 ports.
See also
*
History of personal computers
*
IDE64 – P-ATA interface cartridge for the C64
*
Keyboard computer
*
List of Commodore 64 games
*
SuperCPU – CPU upgrade for C64 and C128
Footnotes
References
Sources
*
* Bagnall, Brian (2005). ''On the Edge: the Spectacular Rise and Fall of Commodore''. Variant Press. . See especially pp. 224–260.
* Tomczyk, Michael (1984). ''The Home Computer Wars: An Insider's Account of Commodore and Jack Tramiel''.
COMPUTE! Publications, Inc. .
* Jeffries, Ron.
A best buy for '83: Commodore 64. ''
Creative Computing
''Creative Computing'' was one of the earliest magazines covering the microcomputer revolution. Published from October 1974 until December 1985, the magazine covered the spectrum of hobbyist/home/personal computing in a more accessible format t ...
'', January 1983.
* Amiga Format News Special. "Commodore at CeBIT '94". ''
Amiga Format'', Issue 59, May 1994.
*
Computer Chronicles;
Commodore 64 – Interview with Commodore president Max Toy, 1988.
* The C-64 Scene Database;
– Kjell Nordbø artist page (bio/release history) at CSDb.
*
**
External links
Commodore 64 history, manuals, and photos()
C64-Wiki (wiki-based encyclopaedia)C64.com (C64 game database)Lemon64 (C64 fanbase)Csdb.dk (Commodore Scene/Software Database)A History of Gaming Platforms: The Commodore 64from October 2007
*
Design Case History: The Commodore 64 ''IEEE Spectrum'', March 1985
Comparing different unit sales analyses
{{Authority control
6502-based home computers
American inventions
Products introduced in 1982
 In January 1981, MOS Technology, Inc., Commodore's
In January 1981, MOS Technology, Inc., Commodore's  Also in 1983, Commodore released the SX-64, a portable version of the C64. The SX-64 has the distinction of being the first commercial ''full-color''
Also in 1983, Commodore released the SX-64, a portable version of the C64. The SX-64 has the distinction of being the first commercial ''full-color''  The C64's designers intended the computer to have a new, wedge-shaped case within a year of release, but the change did not occur. In 1986, Commodore released the 64C computer, which is functionally identical to the original. The exterior design was remodeled in the sleeker style of the Commodore 128. The 64C uses new versions of the SID, VIC-II, and I/O chips being deployed. Models with the C64E board had the graphic symbols printed on the top of the keys, instead of the normal location on the front. The sound chip (SID) was changed to use the MOS 8580 chip, with the core voltage reduced from 12V to 9V. The most significant changes include different behavior in the filters and in the volume control, which result in some music/sound effects sounding differently than intended, and in digitally-sampled audio being almost inaudible, respectively (though both of these can mostly be corrected-for in software). The 64 KB RAM memory went from eight chips to two chips. BASIC and the KERNAL went from two separate chips into one 16 KB ROM chip. The PLA chip and some TTL chips were integrated into a DIL 64-pin chip. The "252535-01" PLA integrated the color RAM as well into the same chip. The smaller physical space made it impossible to put in some internal expansions like a floppy-speeder. In the United States, the 64C was often bundled with the third-party GEOS
The C64's designers intended the computer to have a new, wedge-shaped case within a year of release, but the change did not occur. In 1986, Commodore released the 64C computer, which is functionally identical to the original. The exterior design was remodeled in the sleeker style of the Commodore 128. The 64C uses new versions of the SID, VIC-II, and I/O chips being deployed. Models with the C64E board had the graphic symbols printed on the top of the keys, instead of the normal location on the front. The sound chip (SID) was changed to use the MOS 8580 chip, with the core voltage reduced from 12V to 9V. The most significant changes include different behavior in the filters and in the volume control, which result in some music/sound effects sounding differently than intended, and in digitally-sampled audio being almost inaudible, respectively (though both of these can mostly be corrected-for in software). The 64 KB RAM memory went from eight chips to two chips. BASIC and the KERNAL went from two separate chips into one 16 KB ROM chip. The PLA chip and some TTL chips were integrated into a DIL 64-pin chip. The "252535-01" PLA integrated the color RAM as well into the same chip. The smaller physical space made it impossible to put in some internal expansions like a floppy-speeder. In the United States, the 64C was often bundled with the third-party GEOS  In 1990, the C64 was repackaged in the form of a game console, called the C64 Games System (C64GS), with most external connectivity removed. A simple modification to the 64C's motherboard was made to allow cartridges to be inserted from above. A modified ROM replaced the BASIC interpreter with a boot screen to inform the user to insert a cartridge. Designed to compete with the
In 1990, the C64 was repackaged in the form of a game console, called the C64 Games System (C64GS), with most external connectivity removed. A simple modification to the 64C's motherboard was made to allow cartridges to be inserted from above. A modified ROM replaced the BASIC interpreter with a boot screen to inform the user to insert a cartridge. Designed to compete with the  As is common for home computers of the early 1980s, the C64 comes with a BASIC interpreter, in ROM. KERNAL, I/O, and tape/disk drive operations are accessed via custom BASIC language commands. The disk drive has its own interfacing
As is common for home computers of the early 1980s, the C64 comes with a BASIC interpreter, in ROM. KERNAL, I/O, and tape/disk drive operations are accessed via custom BASIC language commands. The disk drive has its own interfacing  The C64 has a resolution of 320×200 pixels, consisting of a 40×25 grid of 8×8 character blocks. It has 255 predefined character blocks, known as PETSCII. The character set can be copied into RAM and modified by a programmer.
There are two color modes: high resolution, with two colours available per character block (one foreground and one background), and multicolour (four colors per character blockthree foreground and one background). In multicolor mode, attributes are shared between pixel pairs so the effective visible resolution is 160×200 pixels; only 16 KB of memory is available for the VIC-II video processor.
Since the C64 has a bitmapped screen, it is possible (but slow) to draw each pixel individually. Most programmers used techniques developed for earlier, non-bitmapped systems like the Commodore PET and TRS-80. A programmer redraws the character set, and the video processor fills the screen block by block from the top left corner to the bottom right corner. Two types of animation are used: character block animation and hardware sprites.
The C64 has a resolution of 320×200 pixels, consisting of a 40×25 grid of 8×8 character blocks. It has 255 predefined character blocks, known as PETSCII. The character set can be copied into RAM and modified by a programmer.
There are two color modes: high resolution, with two colours available per character block (one foreground and one background), and multicolour (four colors per character blockthree foreground and one background). In multicolor mode, attributes are shared between pixel pairs so the effective visible resolution is 160×200 pixels; only 16 KB of memory is available for the VIC-II video processor.
Since the C64 has a bitmapped screen, it is possible (but slow) to draw each pixel individually. Most programmers used techniques developed for earlier, non-bitmapped systems like the Commodore PET and TRS-80. A programmer redraws the character set, and the video processor fills the screen block by block from the top left corner to the bottom right corner. Two types of animation are used: character block animation and hardware sprites.

 The VIC-II was manufactured with 5- micrometer NMOS technology, and was clocked at (PAL) or (NTSC). Internally, the clock was divided to generate the dot clock (about 8 MHz) and the two-phase system clocks (about 1 MHz; the pixel and system clock speeds differ slightly on NTSC and PAL machines). At such high clock rates the chip generated considerable heat, forcing MOS Technology to use a ceramic
The VIC-II was manufactured with 5- micrometer NMOS technology, and was clocked at (PAL) or (NTSC). Internally, the clock was divided to generate the dot clock (about 8 MHz) and the two-phase system clocks (about 1 MHz; the pixel and system clock speeds differ slightly on NTSC and PAL machines). At such high clock rates the chip generated considerable heat, forcing MOS Technology to use a ceramic  * I/O ports: 090505 computermuseum.li
**
* I/O ports: 090505 computermuseum.li
**  Clones are computers which imitate C64 functions. In mid-2004, after an absence from the marketplace of more than 10 years, PC manufacturer Tulip Computers (owners of the Commodore brand since 1997) announced the C64 Direct-to-TV (C64DTV): a
Clones are computers which imitate C64 functions. In mid-2004, after an absence from the marketplace of more than 10 years, PC manufacturer Tulip Computers (owners of the Commodore brand since 1997) announced the C64 Direct-to-TV (C64DTV): a