Cimbri on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
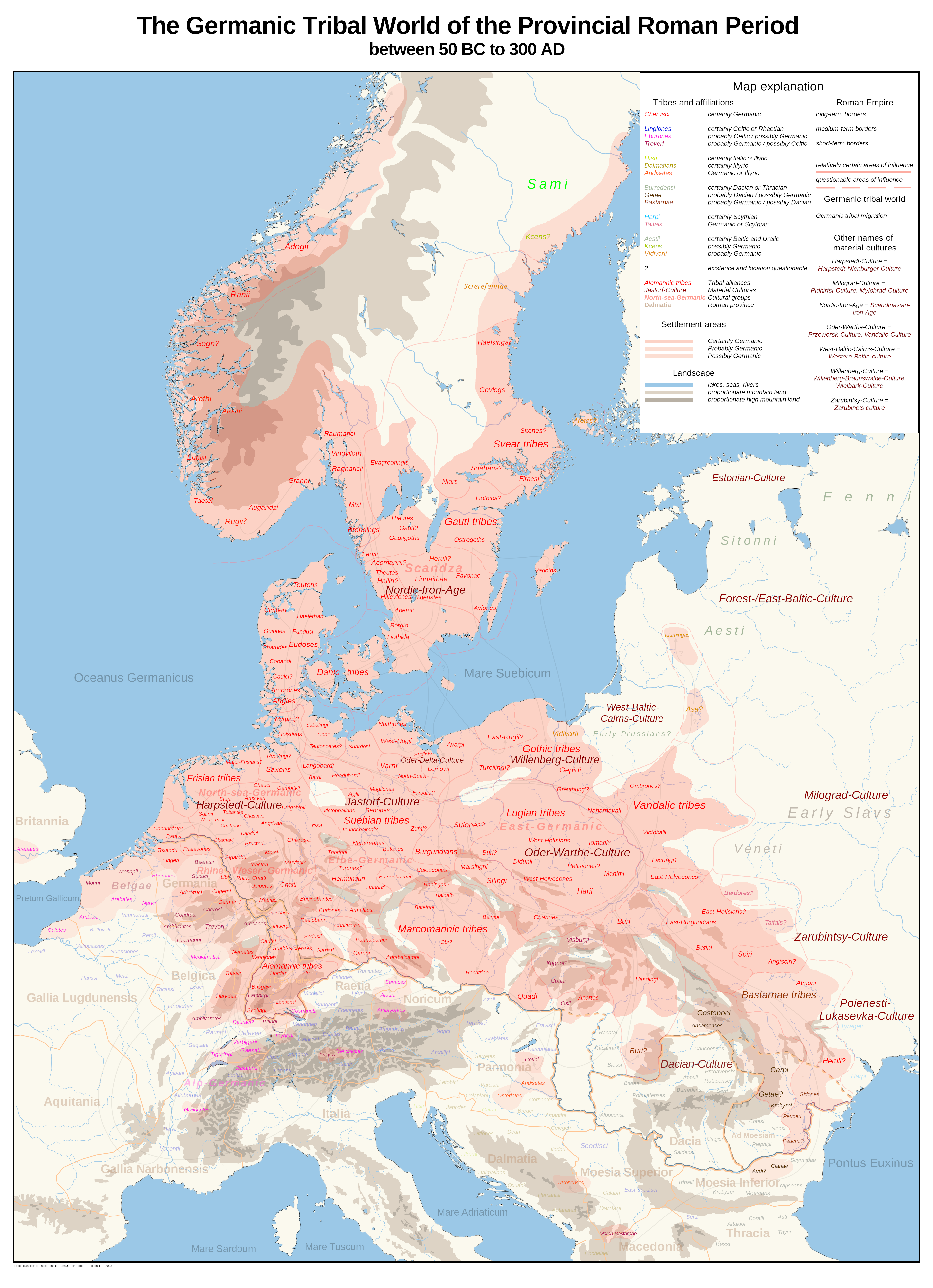 The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a
The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a
 In 104–103 BC, the Cimbri had turned to the Iberian Peninsula where they pillaged far and wide, until they were confronted by a coalition of
In 104–103 BC, the Cimbri had turned to the Iberian Peninsula where they pillaged far and wide, until they were confronted by a coalition of
 The Cimbri are depicted as ferocious warriors who did not fear death. The host was followed by women and children on carts. Aged women,
The Cimbri are depicted as ferocious warriors who did not fear death. The host was followed by women and children on carts. Aged women,
 The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a
The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
, Gaulish
Gaulish is an extinct Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, ...
, Germanic, or even Cimmerian
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
people. Several ancient sources indicate that they lived in Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It ...
, which in some classical texts was called the Cimbrian peninsula. There is no direct evidence for the language they spoke, though some scholars argue that it was a Germanic language, while others argue that it was Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
.
Together with the Teutones and the Ambrones, they fought the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
between 113 and 101 BC during the Cimbrian War
The Cimbrian or Cimbric War (113–101 BC) was fought between the Roman Republic and the Germanic peoples, Germanic and Celts, Celtic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutons, Ambrones and Tigurini, who migrated from the Jutland peninsula into Roma ...
. The Cimbri were initially successful, particularly at the Battle of Arausio, in which a large Roman army was routed. They then raided large areas in Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
and Hispania
Hispania was the Ancient Rome, Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two Roman province, provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divide ...
. In 101 BC, during an attempted invasion of the Italian peninsula, the Cimbri were decisively defeated at the Battle of Vercellae
The Battle of Vercellae or Battle of the Raudine Plain was fought on 30 July 101 BC on a plain near Vercellae in Gallia Cisalpina (modern-day Northern Italy). A Celto-Germanic confederation under the command of the Cimbric king Boiorix was de ...
by Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbrian War, Cimbric and Jugurthine War, Jugurthine wars, he held the office of Roman consul, consul an unprecedented seven times. Rising from a fami ...
, and their king, Boiorix, was killed. Some of the surviving captives are reported to have been among the rebellious gladiator
A gladiator ( , ) was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their ...
s in the Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directl ...
.
Name
The origin of the name ''Cimbri'' is unknown. One etymology is , from "home" (English ''home''), itself a derivation from "live" (, ); then, the Germanic finds an exact cognate in Slavic ''sębrъ'' "farmer" (Croatian, Serbian ''sebar'', Belarusian сябар ''sjábar''). The name has also been related to the word ''kimme'' meaning "rim", i.e., "the people of the coast". Finally, since Antiquity, the name has been related to that of theCimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
.
The name of the Danish region Himmerland (Old Danish ''Himbersysel'') has been proposed to be a derivative of their name. According to such proposals, the word ''Cimbri'' with a ''c'' would be an older form before Grimm's law
Grimm's law, also known as the First Germanic Consonant Shift or First Germanic Sound Shift, is a set of sound laws describing the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) stop consonants as they developed in Proto-Germanic in the first millennium BC, first d ...
( PIE ''k'' > Germanic ''h''). Alternatively, Latin ''c-'' represents an attempt to render the unfamiliar Proto-Germanic ''h'' = (Latin ''h'' was but was becoming silent in common speech at the time), perhaps due to Celtic-speaking interpreters (a Celtic intermediary could also explain why one proposed etymology for the Teutons, Germanic ''*Þeuðanōz'', became Latin ''Teutones'').
Because of the similarity of the names, the Cimbri have been at times associated with Cymry, the Welsh name for themselves. However, ''Cymry'' is derived from Brittonic ''*Kombrogi'' (cf. Allobroges
The Allobroges (Gaulish language, Gaulish: *''Allobrogis'', 'foreigner, exiled'; ) were a Gauls, Gallic people dwelling in a large territory between the Rhône river and the Alps during the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman period.
The Allob ...
), meaning "compatriots", and is linguistically unrelated to Cimbri.
History
Origins
Scholars generally see the Cimbri as originating inJutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It ...
, but archaeologists have found no clear indications of any mass migration from Jutland in the early Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
. The Gundestrup Cauldron, which was deposited in a bog in Himmerland in the 2nd or 1st century BC, shows that there was some sort of contact with southeastern Europe, but it is uncertain if this contact can be associated with the Cimbrian militia expeditions against Rome of the 1st Century BC. It is known that the peoples of Northern Europe and the British Isles participated in annual partial population seasonal Winter migrations southward to what is now central Iberia and southern France where goods and resources were traded and cross-culture marriages were arranged.
Advocates for a northern homeland point to Greek and Roman sources that associate the Cimbri with the Jutland peninsula. According to the '' Res gestae'' (ch. 26) of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
, the Cimbri were still found in the area around the turn of the 1st century AD:
The contemporary Greek geographer Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
testified that the Cimbri still existed as a Germanic tribe, presumably in the "Cimbric peninsula" (since they are said to live by the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
and to have paid tribute to Augustus):
On the map of Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
, the "Kimbroi" are placed on the northernmost part of the peninsula of Jutland, i.e., in the modern landscape of Himmerland south of Limfjorden (since Vendsyssel-Thy north of the fjord was at that time a group of islands).
Migration
Some time before 100 BC many of the Cimbri, as well as theTeutons
The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late seco ...
and Ambrones, migrated south-east. After several unsuccessful battles with the Boii
The Boii (Latin language, Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; ) were a Celts, Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (present-day Northern Italy), Pannonia (present-day Austria and Hungary), present-day Ba ...
and other Celtic tribes
This is a list of ancient Celts, Celtic peoples and tribes.
Continental Celts
Continental Celts were the Celtic peoples that inhabited mainland Europe and Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Celts inhabited a la ...
, they appeared 113 BC in Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, R ...
, where they invaded the lands of one of Rome's allies, the Taurisci
The Taurisci were a federation of Celtic tribes who dwelt in today's Carinthia and northern Slovenia (Carniola) before the coming of the Romans (c. 200 BC). According to Pliny the Elder, they are the same as the people known as the Norici.
Et ...
.
On the request of the Roman consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states thro ...
Gnaeus Papirius Carbo, sent to defend the Taurisci, they retreated, only to find themselves deceived and attacked at the Battle of Noreia, where they defeated the Romans. Only a storm, which separated the combatants, saved the Roman forces from complete annihilation.
Invading Gaul
Now the road to Italy was open, but they turned west towardsGaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
. They came into frequent conflict with the Romans, who usually came out the losers. In 109 BC, they defeated a Roman army under the consul Marcus Junius Silanus, who was the commander of Gallia Narbonensis
Gallia Narbonensis (Latin for "Gaul of Narbonne", from its chief settlement) was a Roman province located in Occitania and Provence, in Southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), because it was the first ...
. In 107 BC they defeated another Roman army under the consul Gaius Cassius Longinus
Gaius Cassius Longinus (; – 3 October 42 BC) was a Roman senator and general best known as a leading instigator of the plot to assassinate Julius Caesar on 15 March 44 BC. He was the brother-in-law of Brutus, another leader of the conspir ...
, who was killed at the Battle of Burdigala (modern day Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
) against the Tigurini, who were allies of the Cimbri.
Attacking the Roman Republic
It was not until 105 BC that they planned an attack on the Roman Republic itself. At theRhône
The Rhône ( , ; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Ròse''; Franco-Provençal, Arpitan: ''Rôno'') is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and Southeastern France before dischargi ...
, the Cimbri clashed with the Roman armies. Discord between the Roman commanders, the proconsul Quintus Servilius Caepio and the consul Gnaeus Mallius Maximus, hindered Roman coordination and so the Cimbri succeeded in first defeating the legate Marcus Aurelius Scaurus and later inflicted a devastating defeat on Caepio and Maximus at the Battle of Arausio. The Romans lost as many as 80,000 men, according to Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
; Mommsen (in his '' History of Rome'') thought that excluded auxiliary cavalry and non-combatants who brought the total loss closer to 112,000. Other estimates are much smaller, but by any account a large Roman army was routed.
Rome was in panic, and the ''terror cimbricus'' became proverbial. Everyone expected to soon see the ''new Gauls'' outside of the gates of Rome. Desperate measures were taken: contrary to the Roman constitution, Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbrian War, Cimbric and Jugurthine War, Jugurthine wars, he held the office of Roman consul, consul an unprecedented seven times. Rising from a fami ...
, who had defeated Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen (c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia, the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Micipsa's two sons, Hiempsal and Adherbal ...
, was elected consul and supreme commander for five years in a row (104–100 BC).
Defeat

 In 104–103 BC, the Cimbri had turned to the Iberian Peninsula where they pillaged far and wide, until they were confronted by a coalition of
In 104–103 BC, the Cimbri had turned to the Iberian Peninsula where they pillaged far and wide, until they were confronted by a coalition of Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BC. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strabo) ...
. Defeated, the Cimbri returned to Gaul, where they joined their allies, the Teutons
The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late seco ...
. During this time, C. Marius had the time to prepare and, in 102 BC, he was ready to meet the Teutons and the Ambrones at the Rhône. These two tribes intended to pass into Italy through the western passes, while the Cimbri and the Tigurines were to take the northern route across the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
and later across the Central Eastern Alps.
At the estuary of the Isère
Isère ( , ; ; , ) is a landlocked Departments of France, department in the southeastern French Regions of France, region of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. Named after the river Isère (river), Isère, it had a population of 1,271,166 in 2019.
, the Teutons and the Ambrones met Marius, whose well-defended camp they did not manage to overrun. Instead, they pursued their route, and Marius followed them. At Aquae Sextiae, the Romans won two battles and took the Teuton king Teutobod prisoner.
The Cimbri had penetrated through the Alps into northern Italy. The consul Quintus Lutatius Catulus
Quintus Lutatius Catulus (149–87 BC) was a Roman consul, consul of the Roman Republic in 102 BC. His consular colleague was Gaius Marius. During their consulship the Cimbri and Teutons, Teutones marched south again and Cimbrian War, threatened ...
had not dared to fortify the passes, but instead he had retreated behind the river Po, and so the land was open to the invaders. The Cimbri did not hurry, and the victors of Aquae Sextiae had the time to arrive with reinforcements. At the Battle of Vercellae
The Battle of Vercellae or Battle of the Raudine Plain was fought on 30 July 101 BC on a plain near Vercellae in Gallia Cisalpina (modern-day Northern Italy). A Celto-Germanic confederation under the command of the Cimbric king Boiorix was de ...
, at the confluence of the river Sesia with the Po, in 101 BC, the long voyage of the Cimbri also came to an end.
It was a devastating defeat. Two chieftains, Lugius and Boiorix, died on the field, while the other chieftains Caesorix and Claodicus were captured. The women killed both themselves and their children in order to avoid slavery. The Cimbri were annihilated, although some may have survived to return to the homeland where a population with this name was residing in northern Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It ...
in the 1st century AD, according to the sources quoted above. Some of the surviving captives may have had sons that joined Spartacus's cause, and been among the rebelling gladiator
A gladiator ( , ) was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their ...
s in the Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directl ...
.
Justin
Justin may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Justin (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Justin (historian), Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527) ...
's epitome of Trogus has Mithridates VI send emissaries to the Cimbri to request military aid during the Social War (91-88 BCE). Justin also states that the Cimbri were again in Italy at this time, i.e. over ten years later.
Supposed descendants
According toJulius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
, the Belgian tribe of the Atuatuci "was descended from the Cimbri and Teutoni, who, upon their march into our province and Italy, set down such of their stock and stuff as they could not drive or carry with them on the near (i.e. west) side of the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, and left six thousand men of their company there as guard and garrison" (''Gall.'' 2.29, trans. Edwards). They founded the city of Atuatuca in the land of the Belgic Eburones, whom they dominated. Thus Ambiorix king of the Eburones paid tribute and gave his son and nephew as hostages to the Atuatuci (''Gall.'' 6.27). In the first century AD, the Eburones were replaced or absorbed by the Germanic Tungri, and the city was known as Atuatuca Tungrorum, i.e. the modern city of Tongeren
Tongeren (; ; ; ) is a city and former municipality located in the Belgian province of Limburg, in the southeastern corner of the Flemish region of Belgium. Tongeren is the oldest town in Belgium, as the only Roman administrative capital wit ...
.
The population of modern-day Himmerland claims to be the heirs of the ancient Cimbri. The adventures of the Cimbri are described by the Danish Nobel Prize–winning author Johannes V. Jensen, himself born in Himmerland, in the novel ''Cimbrernes Tog'' (1922), included in the epic cycle ''Den lange Rejse'' (English '' The Long Journey'', 1923). The so-called Cimbrian bull (" Cimbrertyren"), a sculpture by Anders Bundgaard, was erected on 14 April 1937 in a central town square in Aalborg
Aalborg or Ålborg ( , , ) is Denmark's List of cities and towns in Denmark, fourth largest urban settlement (behind Copenhagen, Aarhus, and Odense) with a population of 119,862 (1 July 2022) in the town proper and an Urban area, urban populati ...
, the capital of the region of North Jutland.
A German ethnic minority speaking the Cimbrian language
Cimbrian (, ; ; ) is any of several local Upper German varieties spoken in parts of the Italian regions of Trentino and Veneto. The speakers of the language are known as in German.
Cimbrian is a Germanic language related to Bavarian most ...
, having settled in the mountains between Vicenza, Verona, and Trento in Italy (also known as Seven Communities), is also called the ''Cimbri''. For hundreds of years this isolated population and its present 4,400 inhabitants have claimed to be the direct descendants of the Cimbri retreating to this area after the Roman victory over their tribe. However, it is more likely that Bavarians settled here in the Middle Ages. Most linguists remain committed to the hypothesis of a medieval (11th to 12th century AD) immigration to explain the presence of small German-speaking communities in the north of Italy. Some genetic studies seem to prove a Celtic, not Germanic, descent for most inhabitants in the region that is reinforced by Gaulish toponyms such as those ending with the suffix ''-ago'' < Celtic ''-*ako(n)'' (e.g. Asiago
Asiago (; Venetian language, Venetian: ''Axiago'', Cimbrian: ''Slege'', German language, German: ''Schlägen'' ) is a minor township (population roughly 6,500) with the title of ciin the surrounding plateau region (the ''Altopiano di Asiago'' o ...
is clearly the same place name as the numerous variants – Azay, Aisy, Azé, Ezy – in France, all of which derive from ''*Asiacum'' < Gaulish ''*Asiāko(n)''). On the other hand, the original place names in the region, from the specifically localized language known as 'Cimbro' are still in use alongside the more modern names today. These indicate a different origin (e.g., Asiago is known also by its original Cimbro name of ''Sleghe''). The Cimbrian origin myth was popularized by humanists in the 14th century.
Despite these connections to southern Germany, belief in a Himmerland origin persisted well into modern times. On one occasion in 1709, for instance, Frederick IV of Denmark
Frederick IV (Danish language, Danish: ''Frederik''; 11 October 1671 – 12 October 1730) was List of Danish monarchs, King of Denmark and List of Norwegian monarchs, Norway from 1699 until his death. Frederick was the son of Christian V of Denma ...
paid the region's inhabitants a visit and was greeted as their king. The population, which kept its independence during the time of the Venice Republic, was later severely devastated by World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. As a result, many Cimbri have left this mountainous region of Italy, effectively forming a worldwide diaspora.
Culture
Religion
 The Cimbri are depicted as ferocious warriors who did not fear death. The host was followed by women and children on carts. Aged women,
The Cimbri are depicted as ferocious warriors who did not fear death. The host was followed by women and children on carts. Aged women, priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in parti ...
esses, dressed in white sacrificed the prisoners of war and sprinkled their blood, the nature of which allowed them to see what was to come.
Strabo gives this vivid description of the Cimbric folklore:
If the Cimbri did in fact come from Jutland, evidence that they practiced ritualistic sacrifice may be found in the Haraldskær Woman discovered in Jutland in the year 1835. Noosemarks and skin piercing were evident and she had been thrown into a bog rather than buried or cremated. Furthermore, the Gundestrup cauldron, found in Himmerland, may be a sacrificial vessel like the one described in Strabo's text. In style, the work looks like Thracian silver work, while many of the engravings are Celtic objects.
Language
A major problem in determining whether the Cimbri were speaking aCeltic language
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves ...
or a Germanic language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, ...
is that, at that time, the Greeks and Romans tended to refer to all groups to the north of their sphere of influence as Gauls, Celts, or Germani rather indiscriminately, and not based upon languages. Caesar seems to be one of the first authors to distinguish the ''Celtae'' and ''Germani'', and he had a political motive for doing so, because it was an argument in favour of his push to set the Rhine as a new Roman border. Yet, one cannot always trust Caesar and Tacitus when they ascribe individuals and tribes to one or the other category, although Caesar made clear distinctions between the two cultures. Some ancient sources categorize the Cimbri as a Germanic tribe, but some ancient authors include the Cimbri among the Celts.
There are few direct testimonies to the language of the Cimbri: referring to the Northern Ocean (the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
or the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
), Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
states: "Philemon says that it is called Morimarusa, i.e. the Dead Sea, by the Cimbri, until the promontory of Rubea, and after that Cronium." The contemporary Gaulish terms for "sea" and "dead" appear to have been ''mori'' and ''*maruo-''; compare their well-attested modern Insular Celtic
Insular Celtic languages are the group of Celtic languages spoken in Brittany, Great Britain, Ireland, and the Isle of Man. All surviving Celtic languages are in the Insular group, including Breton, which is spoken on continental Europe in Br ...
cognates ''muir'' and ''marbh'' ( Irish), ''môr'' and ''marw'' ( Welsh), and ''mor'' and ''marv'' ( Breton). The same word for "sea" is also known from Germanic, but with an ''a'' (*''mari-''), whereas a cognate of ''marbh'' is unknown in all dialects of Germanic. Yet, given that Pliny had not heard the word directly from a Cimbric speaker, it cannot be ruled out that the word he heard had been translated into Gaulish.
The known Cimbri chiefs have Celtic names, including Boiorix (which may mean "King of the Boii" or, more literally, "King of Strikers"), Gaesorix (which means "Spear King"), and Lugius (which may be named after the Celtic god Lugus
Lugus (sometimes Lugos or Lug) is a Celtic god whose worship is attested in the epigraphic record. No depictions of the god are known. Lugus perhaps also appears in Ancient Rome, Roman sources and medieval Insular Celts, Insular mythology.
Va ...
).Rives, J.B. (Trans.) (1999). ''Germania: Germania''. Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
Other evidence to the language of the Cimbri is circumstantial: thus, we are told that the Romans enlisted Gaulish Celts to act as spies in the Cimbri camp before the final showdown with the Roman army in 101 BC.
Jean Markale wrote that the Cimbri were associated with the Helvetii
The Helvetii (, , Gaulish: *''Heluētī''), anglicized as Helvetians, were a Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their contact with the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. According to Ju ...
, and more especially with the indisputably Celtic Tigurini. These associations may link to a common ancestry, recalled from two hundred years previous, but that is not certain. Henri Hubert states "All these names are Celtic, and they cannot be anything else". Some authors take a different perspective.
Countering the argument of a Celtic origin is the literary evidence that the Cimbri originally came from northern Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It ...
, an area with no Celtic placenames, instead only Germanic ones. This long-standing, well-known article on the languages can be found in almost any edition of ''Britannica''. This does not rule out Cimbric Gallicization during the period when they lived in Gaul. Boiorix, who may have had a Celtic if not a Celticized Germanic name, was king of the Cimbri after they moved away from their ancestral home of northern Jutland. Boiorix and his tribe lived around Celtic peoples during his era as J. B. Rives points out in his introduction to Tacitus' ''Germania
Germania ( ; ), also more specifically called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Superio ...
''; furthermore, the name "Boiorix" can be seen as having either Proto-Germanic or Celtic roots.
In fiction
Thescience fiction
Science fiction (often shortened to sci-fi or abbreviated SF) is a genre of speculative fiction that deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts. These concepts may include information technology and robotics, biological manipulations, space ...
story " Delenda Est" by Poul Anderson depicts an alternate history
Alternate history (also referred to as alternative history, allohistory, althist, or simply A.H.) is a subgenre of speculative fiction in which one or more historical events have occurred but are resolved differently than in actual history. As ...
in which Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
won the Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of Punic Wars, three wars fought between Ancient Carthage, Carthage and Roman Republic, Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For ...
and destroyed Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, but Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
proved unable to rule Italy – which fell into utter chaos. Thus, there was no one to stop the Cimbri two hundred years later. They filled the vacuum, conquered Italy, assimilated the local population to their own culture and by the equivalent of the 20th century had made of Italy a flourishing, technologically advanced kingdom speaking a Germanic language. He also wrote an unrelated historical novel "The Golden Slave", about a Cimbrian chieftain who is enslaved by the Romans after the Battle of Vercellae.
Cimbri is referenced in Italo Calvino
Italo Calvino (, ; ;. RAI (circa 1970), retrieved 25 October 2012. 15 October 1923 – 19 September 1985) was an Italian novelist and short story writer. His best-known works include the ''Our Ancestors'' trilogy (1952–1959), the '' Cosm ...
's novel '' If on a Winter's Night a Traveller'' as a fictional country that warred with a similarly fictionalised version of Cimmeria, thus imposing its own written language onto the Cimmerians.
Jeff Hein's historical fiction series The Cimbrian War tells the story of the Cimbri and their migration across Iron-Age Europe.
See also
*Cimbrian language
Cimbrian (, ; ; ) is any of several local Upper German varieties spoken in parts of the Italian regions of Trentino and Veneto. The speakers of the language are known as in German.
Cimbrian is a Germanic language related to Bavarian most ...
* Cymbrian flood
* Cimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
* Sugambri
* Zimmern Chronicle
References
External links
* * * {{Germanic peoples Early Germanic peoples Ingaevones Istvaeones North Sea Germanic Pre-Roman Iron Age