|
Ambrones
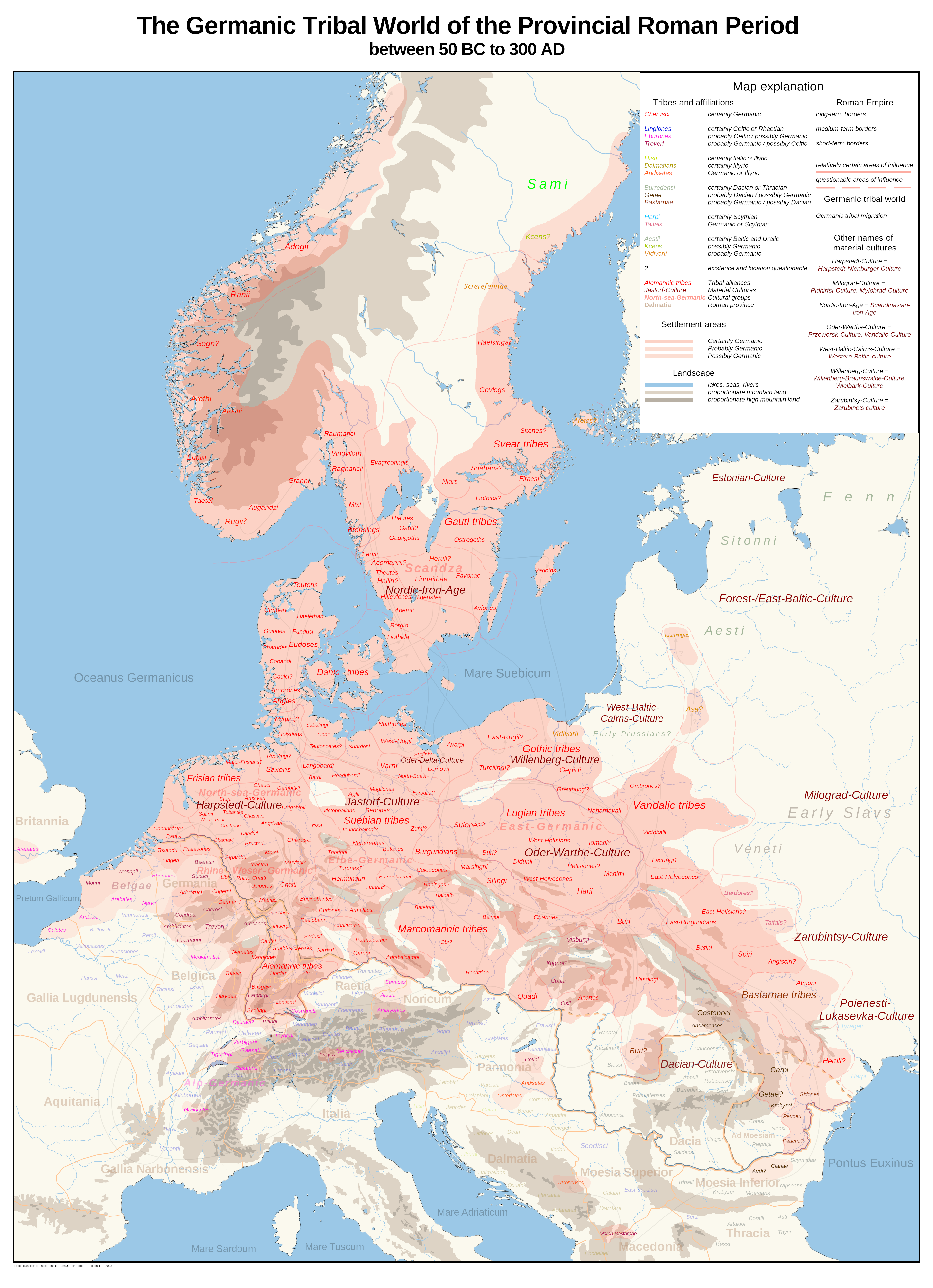
The Ambrones () were an ancient tribe mentioned by Roman authors. They are believed by some to have been a Germanic tribe from Jutland; the Romans were not clear about their exact origin. In the late 2nd century BC, along with the fellow Cimbri and Teutons, the Ambrones migrated from their original homes and invaded the Roman Republic, winning a spectacular victory at the Battle of Arausio in 105 BC. The Ambrones and the Teutons, led by Teutobod, were eventually defeated at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae in 102 BC. Name The origin of the name ''Ambrones'' poses a great difficulty in explanation, since the root ''Ambr''- and its variants are found in many areas of the European continent: the Ombrones of the upper Vistula; the *''Ymbre'' (dat. ''Ymbrum''), a tribe mentioned in the ''Widsith''; the islands of Amrum (older ''Ambrum'') and Imbria (modern Fehmarn); the river names Ammer, Amper, and Emmer; the region of Ammerland; the town of Emmerich; the Italic Umbri (or ''Ombrii' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Aquae Sextiae
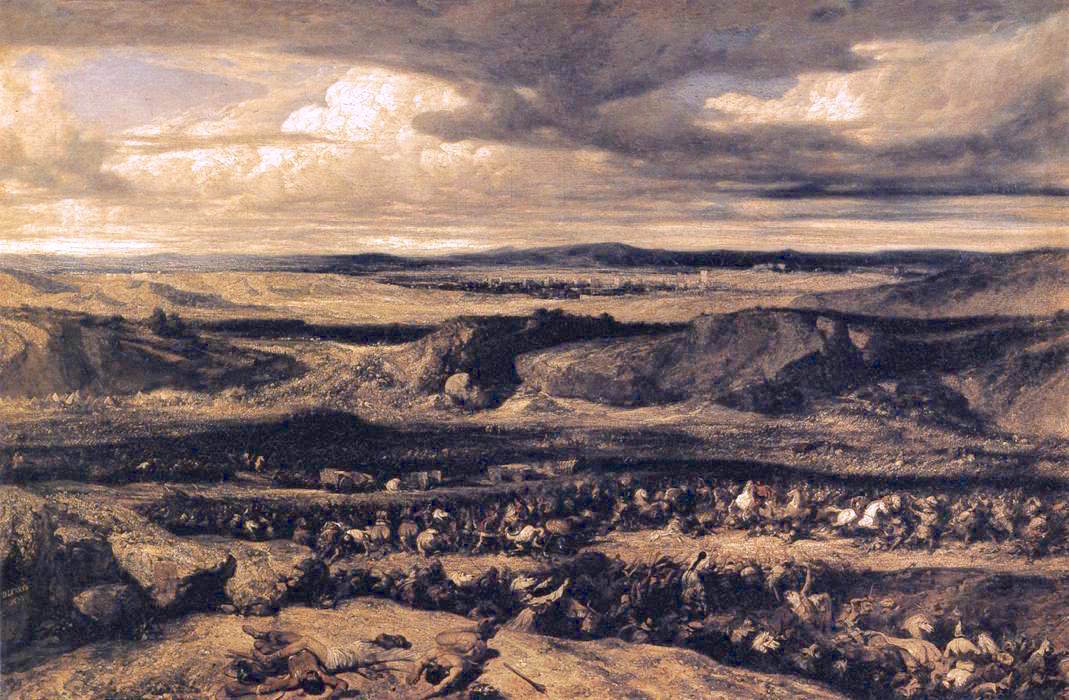
The Battle of Aquae Sextiae (Aix-en-Provence) took place in 102 BC. After a string of Roman defeats (see: the Battle of Noreia, the Battle of Burdigala, and the Battle of Arausio), the Romans under Gaius Marius finally defeated the Teutones and Ambrones as they attempted to advance through the Alps into Italy. Local lore associates the name of the mountain, Mont St. Victoire, with the Roman victory at the battle of Aquae Sextiae, but Frédéric Mistral and other scholars have debunked this theory. Background According to ancient sources, sometime around 120–115 BC, the Germanic tribe of the Cimbri left their homeland around the North Sea due to climate changes. They supposedly journeyed to the south-east and were soon joined by their neighbours the Teutones. On their way south they defeated several other Germanic tribes, but also Celtic and Germano-Celtic tribes. A number of these defeated tribes joined their migration. In 113 BC the Cimbri-Teutones confederation, led by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimbrian War
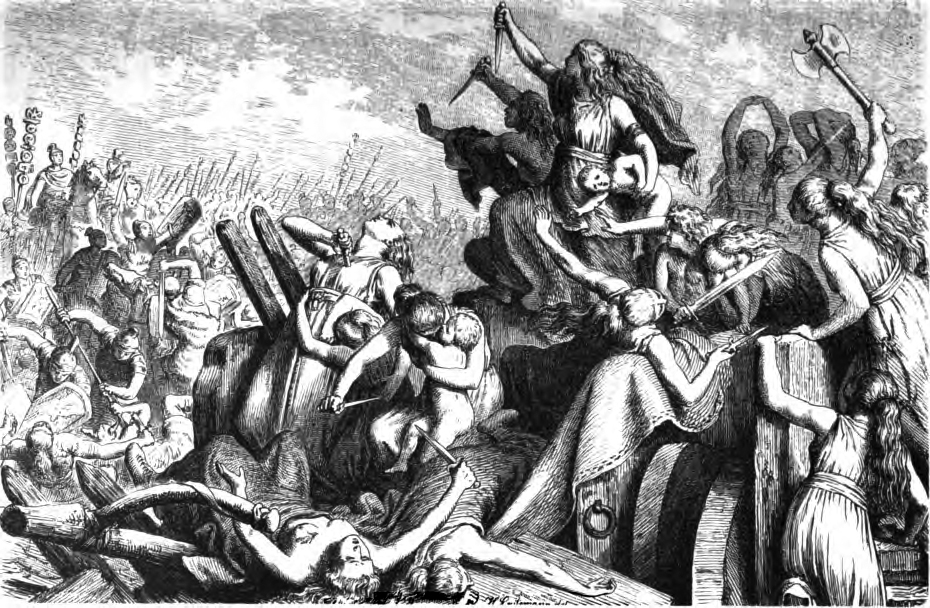
The Cimbrian or Cimbric War (113–101 BC) was fought between the Roman Republic and the Germanic peoples, Germanic and Celts, Celtic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutons, Ambrones and Tigurini, who migrated from the Jutland peninsula into Roman-controlled territory, and clashed with Rome and her allies. The Cimbrian War was the first time since the Second Punic War that Italia (Roman province), Italia and Rome itself had been seriously threatened. The timing of the war had a great effect on the internal politics of Rome, and the organization of its military. The war contributed greatly to the political career of Gaius Marius, whose consulships and political conflicts challenged many of the Roman Republic's political institutions and customs of the time. The Cimbrian threat, along with the Jugurthine War, allegedly inspired the putative Marian reforms of the Roman legions, a view now contested by modern historians. Rome was finally victorious, and its Germanic adversaries, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbri
The Umbri were an Italic peoples, Italic people of ancient Italy. A region called Umbria still exists and is now occupied by Italian speakers. It is somewhat smaller than the Regio VI Umbria, ancient Umbria. Most ancient Umbrian cities were settled in the 9th-4th centuries BC on easily defensible hilltops. Regio VI Umbria, Umbria was bordered by the Tiber and Nar rivers and included the Apennine slopes on the Adriatic. The ancient Umbrian language is a branch of a group called Osco-Umbrian languages, Oscan-Umbrian, which is related to the Latino-Faliscan languages. Origins They are also called ''Ombrii'' in some Roman Empire, Roman sources. Ancient Roman writers thought the Umbri to be of Gauls, Gaulish origin; Cornelius Bocchus wrote that they were descended from an ancient Gaulish tribe. Plutarch wrote that the name might be a different way of writing the name of a northern European tribe, the Ambrones, and that both ethnonyms were cognate with "King of the Boii". However, both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimbri
The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic, Gaulish, Germanic, or even Cimmerian people. Several ancient sources indicate that they lived in Jutland, which in some classical texts was called the Cimbrian peninsula. There is no direct evidence for the language they spoke, though some scholars argue that it was a Germanic language, while others argue that it was Celtic. Together with the Teutones and the Ambrones, they fought the Roman Republic between 113 and 101 BC during the Cimbrian War. The Cimbri were initially successful, particularly at the Battle of Arausio, in which a large Roman army was routed. They then raided large areas in Gaul and Hispania. In 101 BC, during an attempted invasion of the Italian peninsula, the Cimbri were decisively defeated at the Battle of Vercellae by Gaius Marius, and their king, Boiorix, was killed. Some of the surviving captives are reported to have been among the rebellious gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligures
The Ligures or Ligurians were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day Northern Italy, north-western Italy, is named. Because of the strong Celts, Celtic influences on their language and culture, they were also known in antiquity as Celto-Ligurians. In pre-Roman times, the Ligurians occupied the present-day Italian region of Liguria, Piedmont, northern Tuscany, western Lombardy, western Emilia-Romagna, and northern Sardinia, reaching also Elba and Sicily. They inhabited also the Regions of France, French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and Corsica;Strabo, ''Geography'', book 4, chapter 6Livy, ''History of Rome'', book XLVII however, it is generally believed that around 20th century BC, 2000 BC the Ligurians occupied a much larger area, extending as far as what is today Catalonia (in the north-eastern corner of the Iberian Peninsula). The origins of the ancient Ligurians are unclear, and an autochthonous origin is increasingly probable. What little is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutons
The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late second century BC. Some generations later, Julius Caesar compared them to the Germanic peoples of his own time, and used this term for all northern peoples located east of the Rhine. Later Roman authors followed his identification. However, there is no direct evidence about whether or not they spoke a Germanic language. Evidence such as the tribal name, and the names of their rulers, as they were written up by Roman historians, indicates a strong influence from Celtic languages. On the other hand, the indications that classical authors gave about the homeland of the Teutones is considered by many scholars to show that they lived in an area associated with early Germanic languages, and not in an area associated with Celtic languages. Name Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of the Roman Empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of ''Germani'' involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of ''Germania'' was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term ''Germani ''is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE. Different ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Arausio
The Battle of Arausio took place on 6 October 105 BC, at a site between the town of Arausio, now Orange, Vaucluse, and the Rhône river, where two Roman armies, commanded by proconsul Quintus Servilius Caepio and consul Gnaeus Mallius Maximus, were heavily defeated after clashing with the migratory tribes of the Cimbri under Boiorix and the Teutons under Teutobod. Differences between the Roman commanders prevented regular coordination between their armies, resulting in annihilation by the united Cimbrian-Teutonic force. Roman losses are thought to have been up to 80,000 legionaries in addition to 40,000 auxiliary troops. Total losses numbered up to 120,000 soldiers, the entirety of both armies. In terms of losses, this battle is regarded as the worst defeat in the history of ancient Rome, surpassing the Battle of Cannae. As a direct result of the catastrophe, the Roman military was restructured under Gaius Marius via putative reforms to the organisation and recruitment of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
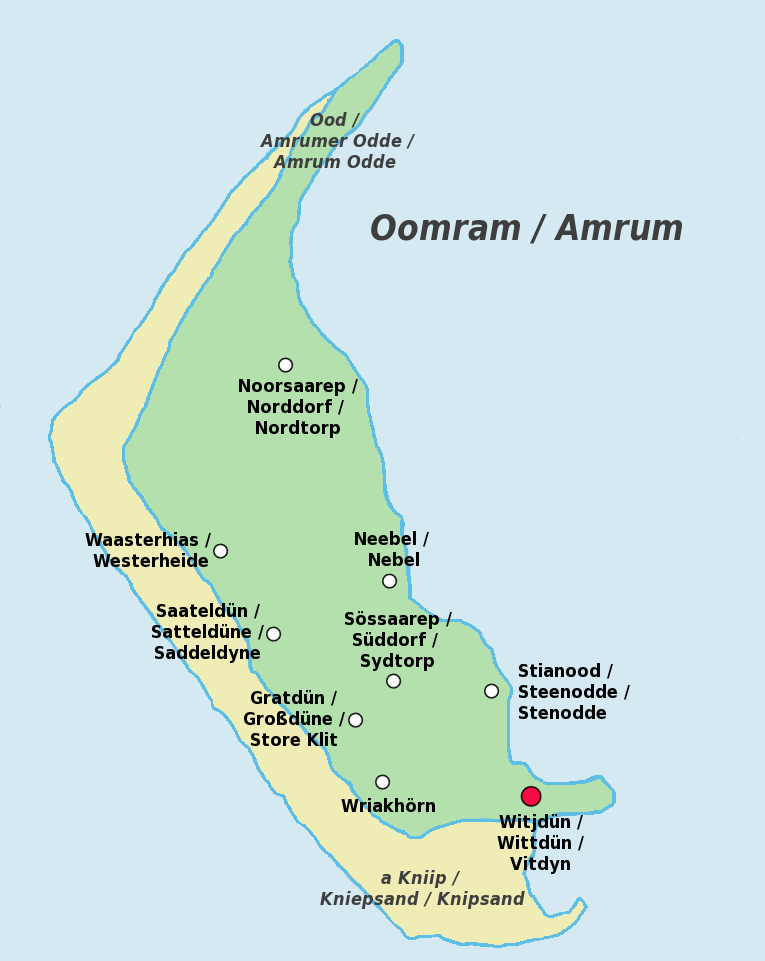
Amrum
Amrum (; Öömrang, ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the Germany, German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants. The island is made up of a sandy core of geestland and features an extended beach all along its west coast, facing the open North Sea. The east coast borders to mudflats of the Wadden Sea. Sand dunes are a characteristic part of Amrum's landscape, resulting in a vegetation that is largely made up of heath and shrubs. The island's only forest was planted in 1948. Amrum is a refuge for many species of birds and a number of marine mammals including the grey seal and harbour porpoise. Settlements on Amrum have been traced back to the Neolithic period when the area was still a part of the mainland of the Jutland peninsula. During the Middle Ages, Frisians, Frisian settlers arrived at Amrum and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambiani
The Ambiani (Gaulish: ''Ambiāni'', 'those around') were a Belgic coastal tribe dwelling in the modern Picardy region during the Iron Age and Roman periods. They settled in the region between the 4th century and the second part of the 2nd century BC. In 113–101 BC, they took part in the fights against the Cimbri and Teutoni invaders during the Cimbrian War. In 57 and 52 BC, they participated in Gallic coalitions against Caesar, before their eventual subjugation by Rome in 51 BC. The Ambiani are known for their gold coinage, found in both northern France and Britain, which attest of extensive trading relations across the Channel. Name They are mentioned as ''Ambianos'' and ''Ambianis'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''Ambianos'' in the summary of Livy's ''Ab Urbe Condita Libri'' (late 1st c. BC), ''Ambianoì'' (Ἀμβιανοὶ) and ''Ambianoĩs'' (Ἀμβιανοῖς) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), ''Ambiani'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), ''Ambianoí'' (Ἀμβιανοί) by Ptolemy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambigatus
Ambicatus or Ambigatus (Gaulish: 'He who fights in both directions') is a legendary Gallic king of the Bituriges, said to have lived ca. 600 BC. According to a legend recounted by Livy, he sent his sister's sons Bellovesus and Segovesus in search of new lands to settle because of overpopulation in their homeland. Segovesus headed towards the Hercynian Forest, while Bellovesus is said to have led the Gallic invasion of the Po Valley during the legendary reign of the fifth king of Rome, Tarquinius Priscus (616–579 BC), where he allegedly conquered the Etruscans and founded the city of Mediolanum (Milan). Name The Gaulish personal name ''Ambigatus'' is a variant form of an earlier ''Ambicatus'', meaning 'the one who fights in both directions'. It is a compound formed with the root ''ambi''- ('around, on both sides') attached to -''catu''- ('combat, battle'). Peter E. Busse and John T. Koch note that Gaulish names that entered Latin through the Etruscan language often show this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambiorix
Ambiorix (Gaulish "king of the surroundings", or "king-protector") ( 54–53 BC) was, together with Cativolcus, prince of the Eburones, leader of a Belgic tribe of north-eastern Gaul (Gallia Belgica), where modern Belgium is located. In the 19th century, Ambiorix became a Belgian national hero because of his resistance against Julius Caesar, as written in Caesar's ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. Name It is generally accepted that ''Ambiorix'' is a Gaulish personal name formed with the prefix ''ambio-'' attached to ''rix'' ('king'), but the meaning of the first element is debated. Some scholars translate ''Ambiorix'' as the 'king of the surroundings' or 'king of the enclosure', by interpreting ''ambio-'' as a thematized form of ''ambi-'' ('around, on both sides') meaning 'surroundings' or else 'enclosure' (cf. Old Irish ''imbe'' 'enclosure'). Alternatively, Fredrik Otto Lindeman renders ''Ambiorix'' as the 'protector-king', by deriving ''ambio-'' from the Proto-Indo-Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |