|
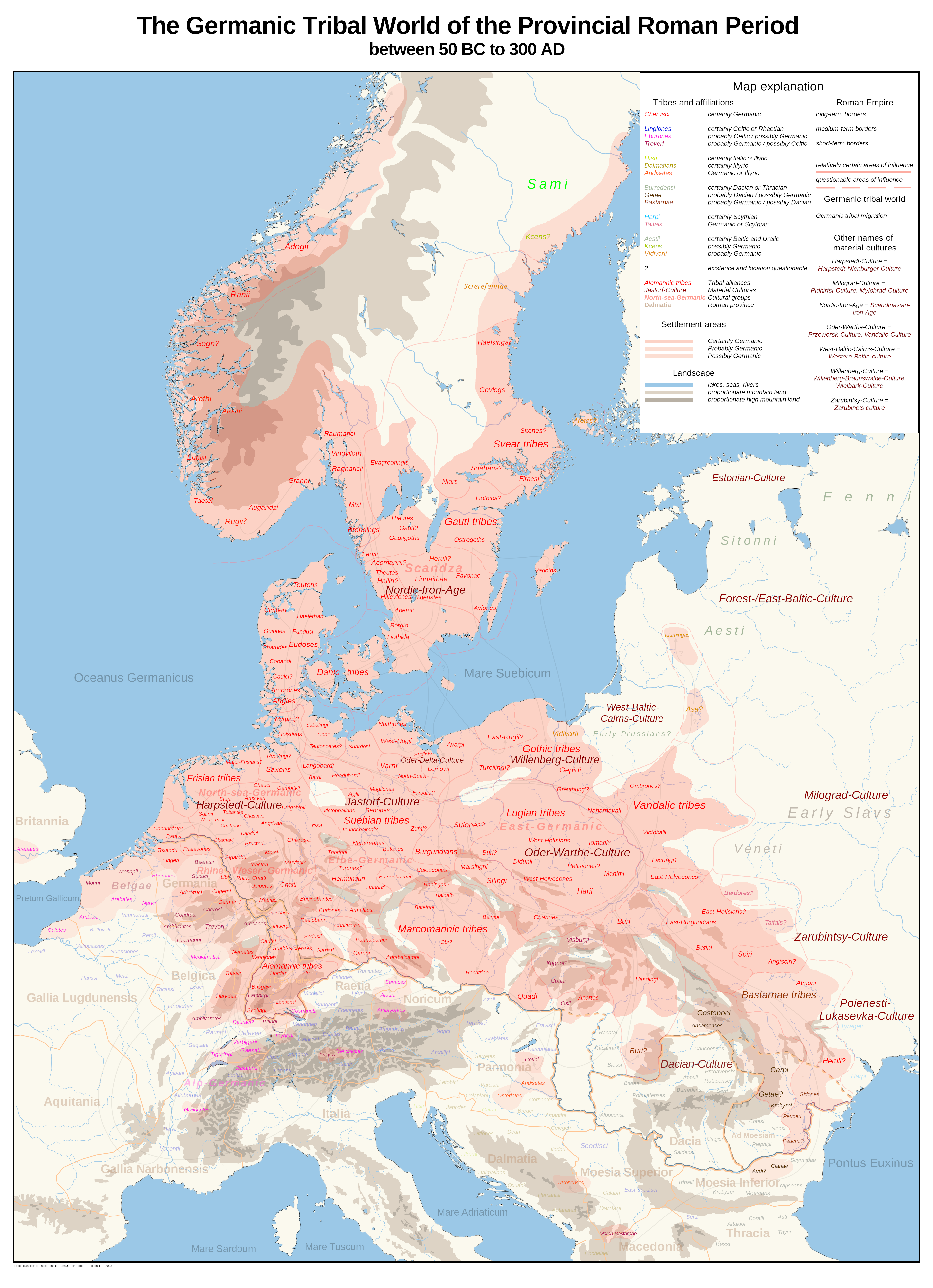
Cimbri
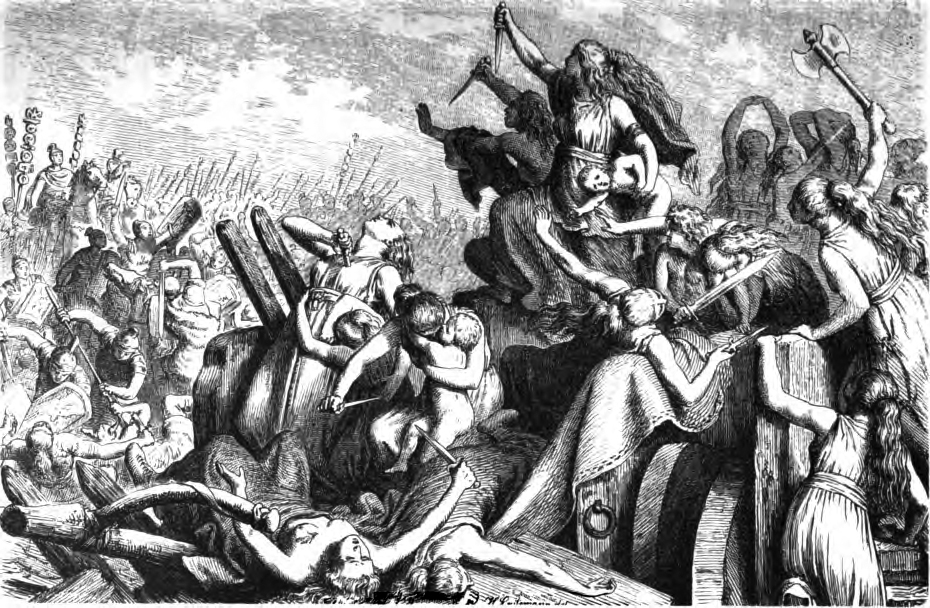
The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic, Gaulish, Germanic, or even Cimmerian people. Several ancient sources indicate that they lived in Jutland, which in some classical texts was called the Cimbrian peninsula. There is no direct evidence for the language they spoke, though some scholars argue that it was a Germanic language, while others argue that it was Celtic. Together with the Teutones and the Ambrones, they fought the Roman Republic between 113 and 101 BC during the Cimbrian War. The Cimbri were initially successful, particularly at the Battle of Arausio, in which a large Roman army was routed. They then raided large areas in Gaul and Hispania. In 101 BC, during an attempted invasion of the Italian peninsula, the Cimbri were decisively defeated at the Battle of Vercellae by Gaius Marius, and their king, Boiorix, was killed. Some of the surviving captives are reported to have been among the rebellious gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Vercellae
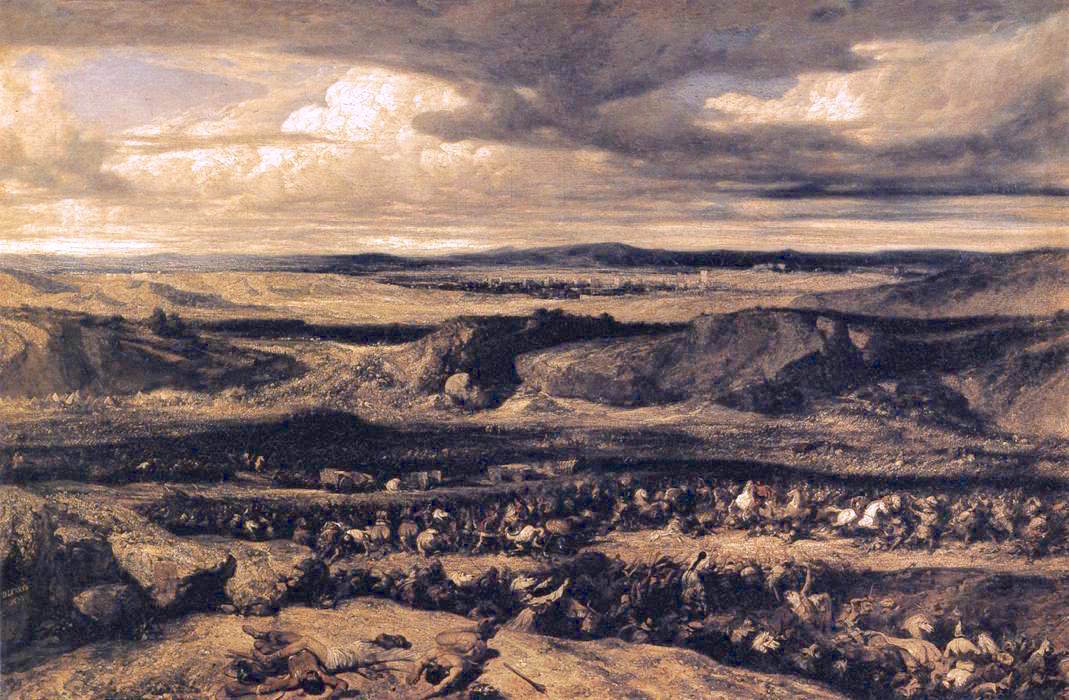
The Battle of Vercellae or Battle of the Raudine Plain was fought on 30 July 101 BC on a plain near Vercellae in Gallia Cisalpina (modern-day Northern Italy). A Celto-Germanic confederation under the command of the Cimbric king Boiorix was defeated by a Roman Republic, Roman army under the joint command of the Consul (Roman), consul Gaius Marius and the proconsul Quintus Lutatius Catulus. The battle marked the end of the Cimbrian War, Germanic threat to the Roman Republic. Background In 113 BC, a large migrating Germanic peoples, Germanic-Celts, Celtic alliance headed by the Cimbri and the Teutones entered the Roman sphere of influence. They invaded Noricum (located in present-day Austria and Slovenia) which was inhabited by the Taurisci people, friends and allies of Rome. The Senate commissioned Gnaeus Papirius Carbo (consul 113 BC), Gnaeus Papirius Carbo, one of the consuls, to lead a substantial Roman army to Noricum to force the barbarians out. An engagement, later calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
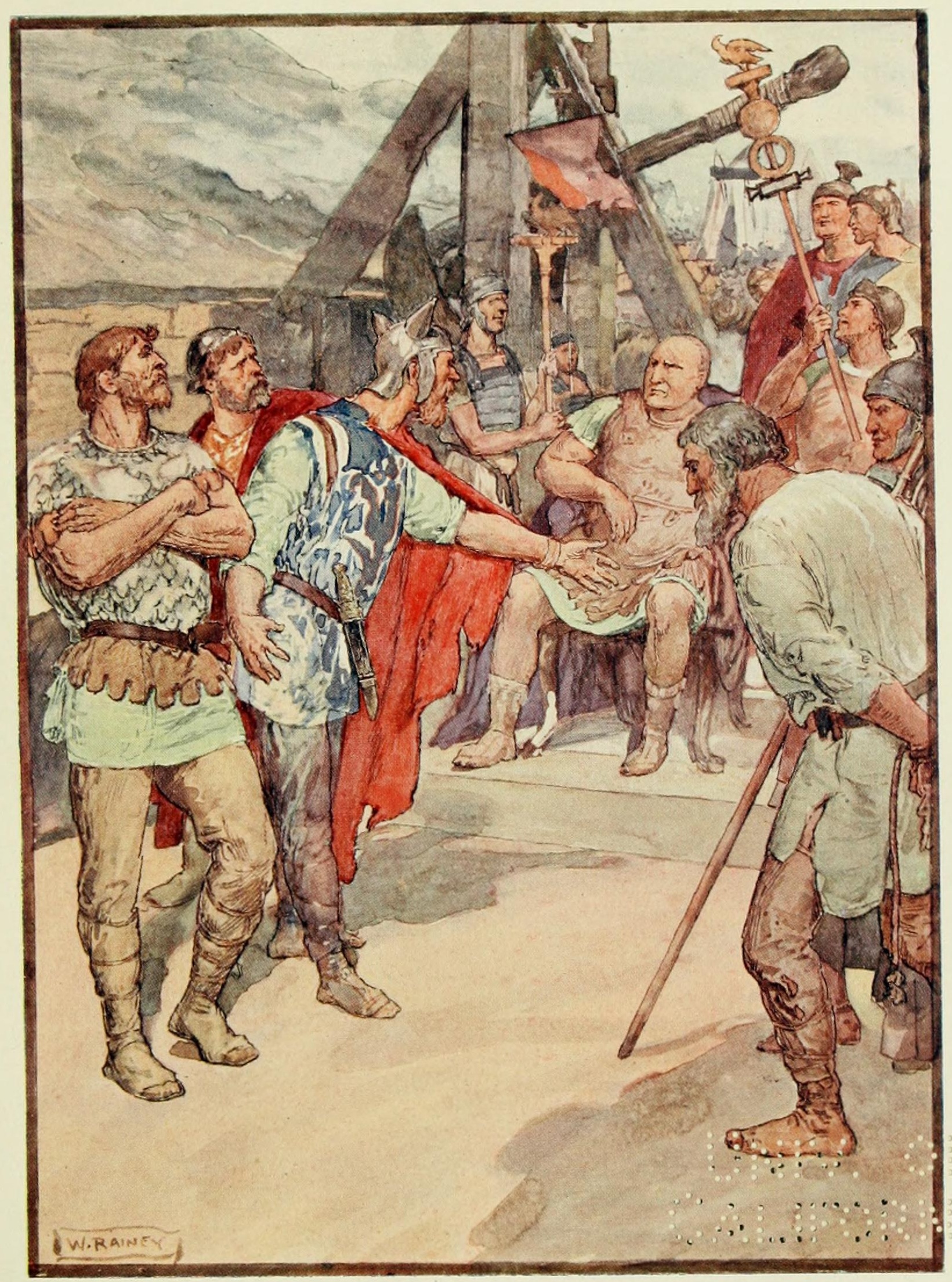
Boiorix
Boiorix or Boeorix was a king of the Cimbri tribe during the Cimbrian War. His most notable achievement was the spectacular victory against the Romans at the Battle of Arausio in 105 BC, seen as the worst Roman military disaster since the Battle of Cannae.Livy, ''Periochae,'' 67.2 He perished in a last stand with his noblemen at the Battle of Vercellae in 102 BC. Etymology Boiorix's name may be Celtic, meaning "King of the Boii" (suggesting he came to prominence among the Cimbri during their march south, and was not an original inhabitant of Jutland) or perhaps "King of Strikers." It can be seen as having either Proto-Germanic or Celtic roots. It is also possible Boiorix name was Celticized as a result of his tribe living among Celtic peoples in Jutland.Rives, J.B. (Trans.) (1999). ''Germania: Germania''. Oxford University Press Life and Cimbrian War How Boiorix became a king of the Cimbri is not known. His people, along with the Teutones, left their homelands around the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cimbrian War
The Cimbrian or Cimbric War (113–101 BC) was fought between the Roman Republic and the Germanic peoples, Germanic and Celts, Celtic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutons, Ambrones and Tigurini, who migrated from the Jutland peninsula into Roman-controlled territory, and clashed with Rome and her allies. The Cimbrian War was the first time since the Second Punic War that Italia (Roman province), Italia and Rome itself had been seriously threatened. The timing of the war had a great effect on the internal politics of Rome, and the organization of its military. The war contributed greatly to the political career of Gaius Marius, whose consulships and political conflicts challenged many of the Roman Republic's political institutions and customs of the time. The Cimbrian threat, along with the Jugurthine War, allegedly inspired the putative Marian reforms of the Roman legions, a view now contested by modern historians. Rome was finally victorious, and its Germanic adversaries, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbrian War, Cimbric and Jugurthine War, Jugurthine wars, he held the office of Roman consul, consul an unprecedented seven times. Rising from a family of smallholders in a village called Ceraetae in the district of Arpinum, Marius acquired his initial military experience serving with Scipio Aemilianus at the Siege of Numantia in 134 BC. He won election as tribune of the plebs in 119 BC and passed a law limiting aristocratic interference in elections. Barely elected praetor in 115 BC, he next became the governor of Further Spain where he campaigned against bandits. On his return from Spain he married Julia (wife of Marius), Julia, the aunt of Julius Caesar. Marius attained his first consulship in 107 BC and became the commander of Roman forces in Numidia, where he brought an end to the Jugurthine War. By 105 BC Rome faced an invasion by the Cimbri and Teutones, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Arausio
The Battle of Arausio took place on 6 October 105 BC, at a site between the town of Arausio, now Orange, Vaucluse, and the Rhône river, where two Roman armies, commanded by proconsul Quintus Servilius Caepio and consul Gnaeus Mallius Maximus, were heavily defeated after clashing with the migratory tribes of the Cimbri under Boiorix and the Teutons under Teutobod. Differences between the Roman commanders prevented regular coordination between their armies, resulting in annihilation by the united Cimbrian-Teutonic force. Roman losses are thought to have been up to 80,000 legionaries in addition to 40,000 auxiliary troops. Total losses numbered up to 120,000 soldiers, the entirety of both armies. In terms of losses, this battle is regarded as the worst defeat in the history of ancient Rome, surpassing the Battle of Cannae. As a direct result of the catastrophe, the Roman military was restructured under Gaius Marius via putative reforms to the organisation and recruitment of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Teutones
The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late second century BC. Some generations later, Julius Caesar compared them to the Germanic peoples of his own time, and used this term for all northern peoples located east of the Rhine. Later Roman authors followed his identification. However, there is no direct evidence about whether or not they spoke a Germanic language. Evidence such as the tribal name, and the names of their rulers, as they were written up by Roman historians, indicates a strong influence from Celtic languages. On the other hand, the indications that classical authors gave about the homeland of the Teutones is considered by many scholars to show that they lived in an area associated with early Germanic languages, and not in an area associated with Celtic languages. Name The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ambrones
The Ambrones () were an ancient tribe mentioned by Roman authors. They are believed by some to have been a Germanic tribe from Jutland; the Romans were not clear about their exact origin. In the late 2nd century BC, along with the fellow Cimbri and Teutons, the Ambrones migrated from their original homes and invaded the Roman Republic, winning a spectacular victory at the Battle of Arausio in 105 BC. The Ambrones and the Teutons, led by Teutobod, were eventually defeated at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae in 102 BC. Name The origin of the name ''Ambrones'' poses a great difficulty in explanation, since the root ''Ambr''- and its variants are found in many areas of the European continent: the Ombrones of the upper Vistula; the *''Ymbre'' (dat. ''Ymbrum''), a tribe mentioned in the ''Widsith''; the islands of Amrum (older ''Ambrum'') and Imbria (modern Fehmarn); the river names Ammer, Amper, and Emmer; the region of Ammerland; the town of Emmerich; the Italic Umbri (or ''Ombrii' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It stretches from the Grenen spit in the north to the confluence of the Elbe and the Sude (river), Sude in the southeast. The historic southern border river of Jutland as a cultural-geographical region, which historically also included Southern Schleswig, is the Eider (river), Eider. The peninsula, on the other hand, also comprises areas south of the Eider (river), Eider: Holstein, the Saxe-Lauenburg, former duchy of Lauenburg (district), Lauenburg, and most of Hamburg and Lübeck. Jutland's geography is flat, with comparatively steep hills in the east and a barely noticeable ridge running through the center. West Jutland is characterised by open lands, heaths, plains, and peat bogs, while East Jutland is more fertile with lakes and lush fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into West Asia. Although the Cimmerians were Scythian cultures, culturally Scythian, they formed an ethnic unit separate from the Scythians proper, to whom the Cimmerians were related and who displaced and replaced the Cimmerians.: "As the Cimmerians cannot be differentiated archeologically from the Scythians, it is possible to speculate about their Iranian origins. In the Neo-Babylonian texts (according to D’yakonov, including at least some of the Assyrian texts in Babylonian dialect) and similar forms designate the Scythians and Central Asian Saka, reflecting the perception among inhabitants of Mesopotamia that Cimmerians and Scythians represented a single cultural and economic group" The Cimmerians themselves left no written records, and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of the Roman Empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of ''Germani'' involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of ''Germania'' was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term ''Germani ''is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE. Different ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |