cardiac stress testing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A cardiac stress test is a cardiological examination that evaluates the cardiovascular system's response to external stress within a controlled clinical setting. This stress response can be induced through physical exercise (usually a treadmill) or intravenous pharmacological stimulation of heart rate.
As the heart works progressively harder (stressed) it is monitored using an electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor. This measures the heart's electrical rhythms and broader
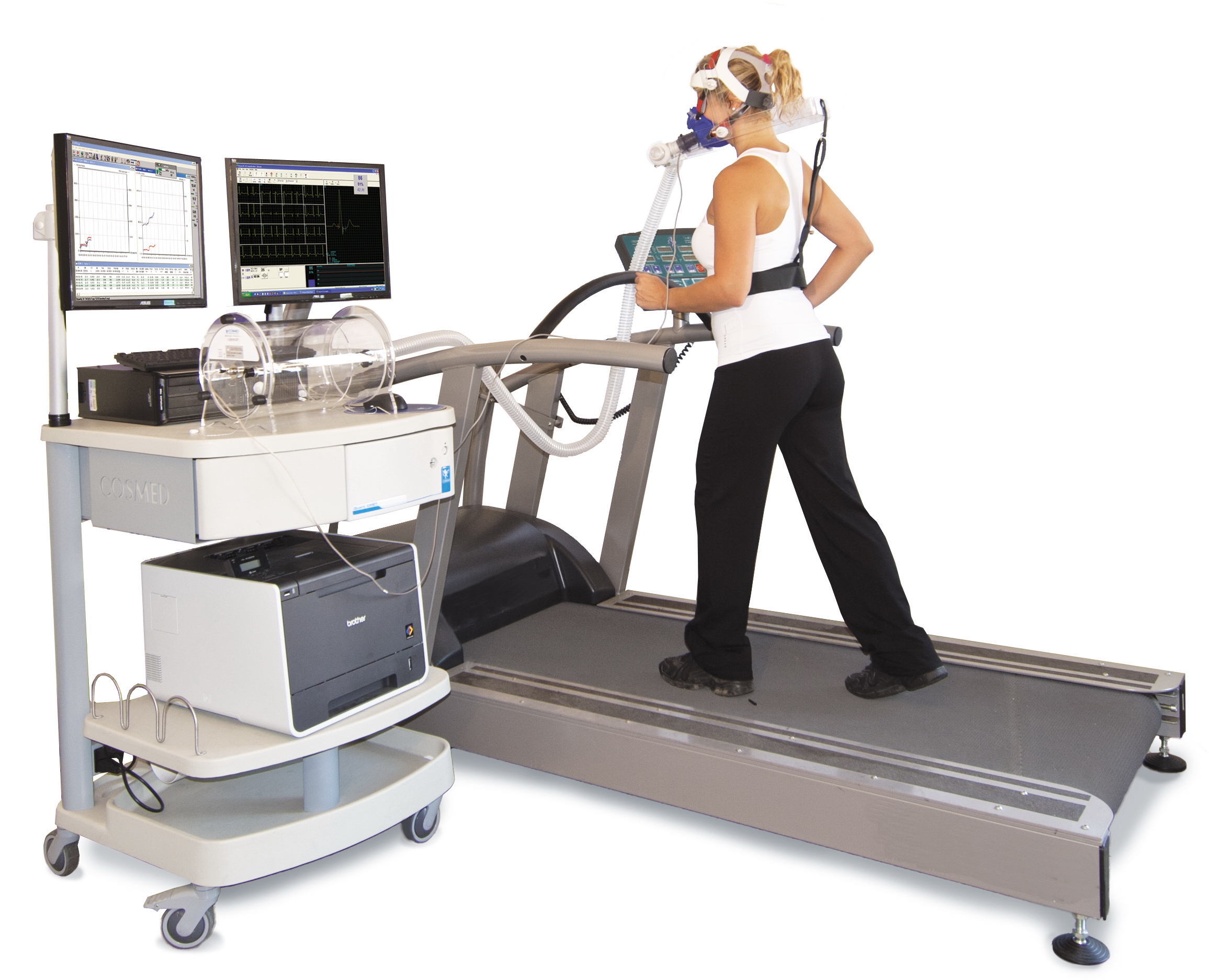 While also measuring breathing gases (e.g.,
While also measuring breathing gases (e.g.,
Preparing for the exercise stress test
"A Simple Exercise Tolerance Test for Circulatory Efficiency with Standard Tables for Normal Individuals," ''American Journal of the Medical Sciences''
"Optimal Medical Therapy with or without PCI for Stable Coronary Disease," ''New England Journal of Medicine''
Stress test information from the American Heart Association
at NIH MedLine {{DEFAULTSORT:Cardiac Stress Test Diagnostic cardiology Nuclear medicine
electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from ee the Electron#Etymology, etymology of "electron" ; and ) is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cell (biology), cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change ...
. Pulse rate, blood pressure and symptoms such as chest discomfort or fatigue are simultaneously monitored by attending clinical staff. Clinical staff will question the patient throughout the procedure asking questions that relate to pain and perceived discomfort. Abnormalities in blood pressure, heart rate, ECG or worsening physical symptoms could be indicative of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
.
Stress testing does not accurately diagnose all cases of coronary artery disease, and can often indicate that it exists in people who do not have the condition. The test can also detect heart abnormalities such as arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats ...
, and conditions affecting electrical conduction within the heart such as various types of fascicular blocks.
A "normal" stress test does not offer any substantial reassurance that a future unstable coronary plaque will not rupture and block an artery, inducing a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
. As with all medical diagnostic procedures, data is only from a moment in time. A primary reason stress testing is not perceived as a robust method of CAD detection is that stress testing generally only detects arteries that are severely narrowed (~70% or more).
Stress testing and echocardiography
A stress test may be accompanied byechocardiography
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ec ...
. The echocardiography is performed both before and after the exercise so that structural differences can be compared.
A resting echocardiogram is obtained prior to stress. The ultrasound images obtained are similar to the ones obtained during a full surface echocardiogram, commonly referred to as transthoracic echocardiogram
A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) is the most common type of Echocardiography, echocardiogram, which is a still or moving image of the internal parts of the heart using ultrasound. In this case, the probe (or ultrasonic transducer) is placed on ...
. The patient is subjected to stress in the form of exercise or chemically (often dobutamine
Dobutamine is a medication used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock (as a result of inadequate tissue perfusion) and severe heart failure. It may also be used in certain types of cardiac stress tests. It is given by IV only, as an injection ...
). After the target heart rate is achieved, 'stress' echocardiogram images are obtained. The two echocardiogram images are then compared to assess for any abnormalities in wall motion of the heart. This is used to detect obstructive coronary artery disease.
Cardiopulmonary exercise stress testing
 While also measuring breathing gases (e.g.,
While also measuring breathing gases (e.g., oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is Dissolution (chemistry), dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the g ...
, maximal oxygen consumption), the test is often referred to as a cardiopulmonary exercise test. Common indications for a cardiopulmonary exercise test include evaluation of shortness of breath, workup before heart transplantation
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart ...
, and prognosis and risk assessment of heart failure patients.
The test is also common in sport science for measuring athletes' maximal oxygen consumption, V̇O2 max. In 2016, the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate Heart, cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability ...
published an official scientific statement advocating that cardiorespiratory fitness, quantifiable as V̇O2 max and measured during a cardiopulmonary exercise test, be categorized as a clinical vital sign and should be routinely assessed as part of clinical practice.
The CPX test can be done on a treadmill
A treadmill is a device generally used for walking, running, or climbing while staying in the same place. Treadmills were introduced before the development of powered machines to harness the power of animals or humans to do work, often a type of ...
or cycle ergometer. In untrained subjects, V̇O2 max is 10% to 20% lower when using a cycle ergometer compared with a treadmill.
Stress testing using injected nuclear markers
A nuclear stress test uses agamma camera
A gamma camera (γ-camera), also called a scintillation camera or Anger camera, is a device used to image gamma radiation emitting radioisotopes, a technique known as scintigraphy. The applications of scintigraphy include early drug development ...
to image radioisotopes injected into the bloodstream. The best known example is myocardial perfusion imaging
Myocardial perfusion imaging or scanning (also referred to as MPI or MPS) is a nuclear medicine procedure that illustrates the function of the heart muscle (myocardium).
It evaluates many heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease (CAD), ...
. Typically, a radiotracer ( Tc-99 sestamibi, Myoview or thallous chloride 201) may be injected during the test. After a suitable waiting period to ensure proper distribution of the radiotracer, scans are acquired with a gamma camera to capture images of the blood flow. Scans acquired before and after exercise are examined to assess the state of the coronary arteries of the patient. By showing the relative amounts of radioisotope within the heart muscle, the nuclear stress tests more accurately identify regional areas of reduced blood flow.
Stress and potential cardiac damage from exercise during the test is a problem in patients with ECG abnormalities at rest or in patients with severe motor disability. Pharmacological stimulation from vasodilators such as dipyridamole or adenosine, or positive chronotropic agents such as dobutamine can be used. Testing personnel can include a cardiac radiologist, a nuclear medicine physician, a nuclear medicine technologist, a cardiology technologist, a cardiologist, and/or a nurse. The typical dose of radiation received during this procedure can range from 9.4 to 40.7 millisieverts.
Recommended utility of this procedure
The American Heart Association recommends ECG treadmill testing as the first choice for patients with medium risk of coronary heart disease according to risk factors of smoking, family history of coronary artery stenosis, hypertension, diabetes and high cholesterol. In 2013, in its "Exercise Standards for Testing and Training", the AHA indicated that high frequency QRS analysis during ECG treadmill test have useful test performance for detection of coronary heart disease.Gerald F., Philip A., Kligfield P., et al., Exercise Standards for Testing and Training A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013; 128: 873-934 *Perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ (anatomy), organ or a tissue (biology), tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer t ...
stress test (with 99mTc labelled sestamibi) is appropriate for select patients, especially those with an abnormal resting electrocardiogram.
* Intracoronary ultrasound or angiogram can provide more information but is invasive and carries the risk of complications associated with cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath) is the insertion of a catheter into a heart chamber, chamber or Blood vessel, vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
A common example of cardiac catheterization is c ...
procedures.
Diagnostic value
The common approach for stress testing recommended by the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association involves several methods to assess cardiac health. These methods provide information for diagnosing and managing heart-related conditions. Two primary stress tests utilized are a treadmill test usingECG
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles.
It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of ...
/electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from ee the Electron#Etymology, etymology of "electron" ; and ) is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cell (biology), cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change ...
metrics and nuclear testing, each have unique sensitivity and specificity values.
The treadmill test, employing the modified Bruce protocol, demonstrates a sensitivity range of around 73-90% and a specificity range of around 50-74%. Sensitivity refers to the percentage of individuals with the condition correctly identified by the test, while specificity denotes the percentage of individuals without the condition correctly identified as not having it. The nuclear stress test exhibits a sensitivity of 81% and a specificity ranging from 85 to 95%.
To arrive at the patient's post test likelihood of disease, the interpretation of the stress test result necessitates the integration of the patient's pretest likelihood with the test's sensitivity and specificity. This method, initially introduced by Diamond and Forrester in the 1970s, provides an estimate of the patient's post-test likelihood of disease. Stress tests have limitations in assessing the significance and nature of cardiac problems, they should be seen in context - as an initial assessment that can lead to a number of other diagnostic approaches in the broader management of cardiac diseases.
According to data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) common first systems of coronary artery disease is a heart attack. According to the American Heart Association, a significant percentage of individuals, approximately 65% of men and 47% of women, present with a heart attack or sudden cardiac arrest as their first symptom of cardiovascular disease. Consequently, stress tests performed shortly before these events may not be highly relevant for predicting infarction in the majority of individuals tested.
Contraindications and termination conditions
Stress cardiac imaging is not recommended for asymptomatic, low-risk patients as part of their routine care. Some estimates show that such screening accounts for 45% of cardiac stress imaging, and evidence does not show that this results in better outcomes for patients. Unless high-risk markers are present, such as diabetes in patients aged over 40,peripheral arterial disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a vascular disorder that causes abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.
When narr ...
, or a risk of coronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
greater than 2 percent yearly, most health societies do not recommend the test as a routine procedure.
Absolute contraindications to cardiac stress test include:
* Acute myocardial infarction within 48 hours
* Unstable angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of parti ...
not yet stabilized with medical therapy
* Uncontrolled cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the cardiac cycle, heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – ab ...
, which may have significant hemodynamic responses (e.g. ventricular tachycardia)
* Severe symptomatic aortic stenosis, aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
, and pericarditis
Pericarditis () is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe whe ...
* Multivessel coronary artery diseases that have a high risk of producing an acute myocardial infarction
* Decompensated or inadequately controlled congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically pr ...
* Uncontrolled hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
(blood pressure > 200/110 mmHg)
* Severe pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swell ...
* Acute aortic dissection
* Acutely ill for any reason
Indications for termination:
A cardiac stress test should be terminated before completion under the following circumstances:
Absolute indications for termination include:
* Systolic blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
decreases by more than 10 mmHg with increase in work rate, or drops below baseline in the same position, with other evidence of ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
.
* Increase in nervous system symptoms: Dizziness, ataxia
Ataxia (from Greek α- negative prefix+ -τάξις rder= "lack of order") is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in e ...
or near syncope
* Moderate to severe anginal pain (above 3 on standard 4-point scale)
* Signs of poor perfusion, e.g. cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
or pallor
* Request of the test subject
* Technical difficulties (e.g. difficulties in measuring blood pressure or EGC)
* ST Segment elevation of more than 1 mm in aVR, V1 or non-Q wave leads
* Sustained ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a cardiovascular disorder in which fast heart rate occurs in the ventricles of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple ...
Relative indications for termination include:
* Systolic blood pressure decreases by more than 10 mmHg with increase in work rate, or drops below baseline in the same position, without other evidence of ischemia.
* ST or QRS segment changes, e.g. more than 2 mm horizontal or downsloping ST segment depression in non-Q wave leads, or marked axis shift
* Arrhythmias other than sustained ventricular tachycardia e.g. Premature ventricular contraction
A premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is a common event where the heartbeat is initiated by Purkinje fibers in the ventricles rather than by the sinoatrial node. PVCs may cause no symptoms or may be perceived as a "skipped beat" or felt as ...
s, both multifocal or triplet; heart block; supraventricular tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower cham ...
or bradyarrhythmias
* Intraventricular conduction delay or bundle branch block
A bundle branch block is a partial or complete interruption in the flow of electrical impulses in either of the bundle branches of the heart's electrical system.
Anatomy and physiology
The heart's electrical activity begins in the sinoatri ...
or that cannot be distinguished from ventricular tachycardia
* Increasing chest pain
* Fatigue, shortness of breath, wheezing, claudication
Claudication is a medical term usually referring to impairment in walking, or pain, discomfort, numbness, or tiredness in the legs that occurs during walking or standing and is relieved by rest. The perceived level of pain from claudication can ...
or leg cramps
* Hypertensive response (systolic blood pressure > 250 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure > 115 mmHg)
Adverse effects
Side effects from cardiac stress testing may include * Palpitations, chest pain, myocardial infarction, shortness of breath, headache, nausea or fatigue. * Adenosine and dipyridamole can cause mild hypotension. * As the radioactive tracers used for this test are chemically carcinogenic, frequent use of these tests carries a small risk of cancer.Use of pharmacological agents to stress the heart
Pharmacologic stress testing relies on coronary steal. Vasodilators are used to dilate coronary vessels, which causes increased blood velocity and flow rate in normal vessels and less of a response in stenotic vessels. This difference in response leads to a steal of flow and perfusion defects appear in cardiac nuclear scans or as ST-segment changes. The choice of pharmacologic stress agents used in the test depends on factors such as potential drug interactions with other treatments and concomitant diseases. Pharmacologic agents such as adenosine, regadenoson (Lexiscan), or dipyridamole is generally used when a patient cannot achieve adequate work level with treadmill exercise, or has poorly controlledhypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
or left bundle branch block
A bundle branch block is a partial or complete interruption in the flow of electrical impulses in either of the bundle branches of the heart's electrical system.
Anatomy and physiology
The heart's electrical activity begins in the sinoatri ...
. However, an exercise stress test may provide more information about exercise tolerance than a pharmacologic stress test.
Commonly used agents include:
* Vasodilators
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wal ...
acting as adenosine receptor
The adenosine receptors (or P1 receptors) are a class of Purinergic receptor, purinergic G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as the endogenous ligand (biochemistry), ligand. There are four known types of adenosine receptors in humans: Aden ...
agonists, such as adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside build ...
itself, and dipyridamole (Persantine), which acts indirectly at the receptor.
* Regadenoson (Lexiscan), which acts specifically at the adenosine A2A receptor
The adenosine A2A receptor, also known as ADORA2A, is an adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.
Structure
This protein is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family which possess seven transmembrane al ...
, thus affecting the heart more than the lung.
* Dobutamine
Dobutamine is a medication used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock (as a result of inadequate tissue perfusion) and severe heart failure. It may also be used in certain types of cardiac stress tests. It is given by IV only, as an injection ...
The effects of beta-agonists such as dobutamine can be reversed by administering beta-blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention) ...
s such as propranolol
Propranolol is a medication of the beta blocker class. It is used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, some types of cardiac dysrhythmia, irregular heart rate, thyrotoxicosis, capillary hemangiomas, akathisia, performance anxiety, and ...
.
Regadenoson or dobutamine is often used in patients with severe reactive airway disease (asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
or COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
) as adenosine and dipyridamole can cause acute exacerbation of these conditions. If the patient's asthma is treated with an inhaler then it should be used as a pre-treatment prior to the injection of the pharmacologic stress agent. In addition, if the patient is actively wheezing then the physician should determine the benefits versus the risk to the patient of performing a stress test especially outside of a hospital setting. Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
is usually held 24 hours prior to an adenosine stress test, as it is a competitive antagonist of the A2A adenosine receptor and can attenuate the vasodilatory effects adenosine.
Aminophylline may be used to attenuate severe and/or persistent adverse reactions to adenosine and regadenoson.
History
Cardiac stress testing, used since the 1960s, has a history rooted in the diagnostic and prognostic assessment of patients with suspectedcoronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
. It has evolved to evaluate inducible myocardial ischemia
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of heart disease involving the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the a ...
as an indicator of adverse outcomes. The factors influencing mortality risk have changed over time due to decreasing angina symptoms, increasing prevalence of conditions like diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, and the rise in pharmacologic testing for patients unable to exercise during stress tests.
See also
* Cardiac steal syndrome * Duke Treadmill Score * Harvard step test * Metabolic equivalent * Robert A. Bruce * Wasserman 9-Panel PlotReferences
External links
Preparing for the exercise stress test
"A Simple Exercise Tolerance Test for Circulatory Efficiency with Standard Tables for Normal Individuals," ''American Journal of the Medical Sciences''
"Optimal Medical Therapy with or without PCI for Stable Coronary Disease," ''New England Journal of Medicine''
Stress test information from the American Heart Association
at NIH MedLine {{DEFAULTSORT:Cardiac Stress Test Diagnostic cardiology Nuclear medicine