Bruxelles Bourse on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region,
[ (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.)] is a
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
of
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
comprising
19 municipalities, including the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
, which is the capital of Belgium.
The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country. It is a part of both the
French Community of Belgium
In Belgium, the French Community (, , CFB) refers to one of the three constituent constitutional linguistic communities. Since 2011, the French Community has used the name Wallonia-Brussels Federation (, , FWB), which is controversial because ...
and the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community (, ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the ...
, and is separate from the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region (, ), usually simply referred to as Flanders ( ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—alongside the Wallonia, Walloon Region and the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region. ...
(Flanders), within which it forms an
enclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is so ...
, and the
Walloon Region
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three regions of Belgium—along with Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the country, Wallonia is primarily French-speaking. It accounts for 55% o ...
(Wallonia), located less than to the south.
Brussels grew from a small rural settlement on the river
Senne to become an important city-region in Europe. Since the end of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, it has been a major centre for
international politics
International relations (IR, and also referred to as international studies, international politics, or international affairs) is an academic discipline. In a broader sense, the study of IR, in addition to multilateral relations, concerns al ...
and home to numerous international organisations, politicians,
diplomat
A diplomat (from ; romanization, romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state (polity), state, International organization, intergovernmental, or Non-governmental organization, nongovernmental institution to conduct diplomacy with one ...
s and
civil servant
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil service personnel hired rather than elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leadership. A civil service offic ...
s.
Brussels is the ''
de facto'' capital of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, as it hosts a number of principal
EU institutions
The institutions of the European Union are the seven principal decision-making bodies of the European Union and Euratom governed under the Treaties of the European Union and European Union law. They are, as listed in Article 13 of the Treaty ...
, including its
administrative-legislative,
executive-political, and
legislative
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers ...
branches (though the judicial branch is located in
Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
, and the European Parliament meets for a minority of the year in
Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
).
Because of this, its name is sometimes used
metonymically
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something associated with that thing or concept. For example, the word "suit" may refer to a person from groups commonly wearing business attire, such as salespe ...
to describe the EU and its institutions. The secretariat of the
Benelux
The Benelux Union (; ; ; ) or Benelux is a politico-economic union, alliance and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighbouring states in Western Europe: Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. The name is a portma ...
and the
headquarters
Headquarters (often referred to as HQ) notes the location where most or all of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. The term is used in a wide variety of situations, including private sector corporations, non-profits, mil ...
of
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
are also located in Brussels.
Brussels is the most densely populated region in Belgium, and although it has the highest
GDP per capita
This is a list of countries by nominal GDP per capita. GDP per capita is the total value of a country's finished goods and services (gross domestic product) divided by its total population (per capita).
Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita is ...
,
it has the lowest available income per household.
The Brussels Region covers and has a population of over 1.2 million.
Its five times larger
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories which share Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport network ...
comprises over 2.5 million people, which makes it the
largest in Belgium.
[ Population of all municipalities in Belgium on 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 18 October 2008.][ Definitions of metropolitan areas in Belgium. The metropolitan area of Brussels is divided into three levels. First, the central agglomeration (''geoperationaliseerde agglomeratie'') with 1,451,047 inhabitants (2008-01-01, adjusted to municipal borders). Adding the closest surroundings (suburbs, ''banlieue'' or ''buitenwijken'') gives a total of 1,831,496. And, including the outer commuter zone (''forensenwoonzone'') the population is 2,676,701.] It is also part of a large
conurbation
A conurbation is a region consisting of a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which, through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ...
extending towards the cities of
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
,
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
, and
Leuven
Leuven (, , ), also called Louvain (, , ), is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipalit ...
, known as the
Flemish Diamond, as well as the province of
Walloon Brabant
Walloon Brabant ( ; ; ) is a province located in Belgium's French-speaking region of Wallonia. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the province of Flemish Brabant (Flemish Region) and the provinces of Liège, Namur and Hainaut. Walloon Br ...
, in total home to over 5 million people. As Belgium's economic capital and a top financial centre in Western Europe with
Euronext Brussels
The Brussels Stock Exchange ( ; ), abbreviated to BSE, was founded in Brussels, Belgium, by decree of Napoleon in 1801. In 2002, the BSE merged with the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, Amsterdam, Lisbon Stock Exchange, Lisbon and Paris Bourse, Paris ...
, Brussels is classified as an ''Alpha''
global city
A global city (also known as a power city, world city, alpha city, or world center) is a city that serves as a primary node in the global economic network. The concept originates from geography and urban studies, based on the thesis that glo ...
. It is also a national and international hub for rail, road and air traffic, and is sometimes considered, together with Belgium, as Europe's geographic, economic and cultural crossroads. The
Brussels Metro
The Brussels Metro ( ; ) is a rapid transit system serving a large part of the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It consists of four conventional metro lines and three '' premetro'' lines. The metro-grade lines are M1, M2, M5, and M6 wi ...
is the only
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT) or heavy rail, commonly referred to as metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport that is generally built in urban areas. A grade separation, grade separated rapid transit line below ground su ...
system in Belgium. In addition, both its
airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial Aviation, air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surf ...
and
railway stations
A train station, railroad station, or railway station is a railway facility where trains stop to load or unload passengers, freight, or both. It generally consists of at least one platform, one track, and a station building providing such a ...
are the largest and busiest in the country.
Historically Dutch-speaking, Brussels saw a
language shift to French from the late 19th century. Since its creation in 1989, the Brussels-Capital Region has been officially bilingual in French and Dutch, although French is the majority language and ''
lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
''.
Brussels is also increasingly becoming multilingual. English is spoken widely and many migrants and
expatriate
An expatriate (often shortened to expat) is a person who resides outside their native country.
The term often refers to a professional, skilled worker, or student from an affluent country. However, it may also refer to retirees, artists and ...
s speak other languages as well.
[O'Donnell, Paul; Toebosch, AnneMarie. ''Multilingualism in Brussels: "I'd Rather Speak English"''. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, 2008, v. 29 n. 2 p. 154-169.]
Brussels is known for its cuisine and gastronomic offer (including its local
waffle
A waffle is a dish made from leavened Batter (cooking), batter or dough that is cooked between two plates that are patterned to give a characteristic size, shape, and surface impression. There are many variations based on the type of waffle iron ...
, its
chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
, its
French fries
French fries, or simply fries, also known as chips, and finger chips (Indian English), are '' batonnet'' or '' julienne''-cut deep-fried potatoes of disputed origin. They are prepared by cutting potatoes into even strips, drying them, and f ...
and its numerous types of
beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the ...
s), as well as its historical and architectural landmarks; some of them are registered as
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
s. Principal attractions include its historic
Grand-Place/Grote Markt (main square), ''
Manneken Pis
(; ) is a landmark bronze fountain sculpture in central Brussels, Belgium, depicting a puer mingens; a Nudity, naked little boy urinating into the fountain's basin. Though its existence is attested as early as the mid-15th century, ''Manneke ...
'', the
Atomium
The Atomium ( , , ) is a landmark modernist building in Brussels, Belgium, originally constructed as the centrepiece of the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (Expo 58). Designed by the engineer André Waterkeyn and the architects André and Jean Pol ...
, and cultural institutions such as
La Monnaie/De Munt and the
Museums of Art and History. Due to its long tradition of
Belgian comics
Belgian comics are a distinct subgroup in the comics history, and played a major role in the development of European comics, alongside France with whom they share a long common history. While the comics in the two major language groups and r ...
, Brussels is also hailed as a capital of the
comic strip
A comic strip is a Comics, sequence of cartoons, arranged in interrelated panels to display brief humor or form a narrative, often Serial (literature), serialized, with text in Speech balloon, balloons and Glossary of comics terminology#Captio ...
.
Toponymy
Etymology
The most common theory of the origin of the name ''Brussels'' is that it derives from the
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch ( Modern Dutch: ') or Old Low Franconian (Modern Dutch: ') is the set of dialects that evolved from Frankish spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from around the 6th Page 55: "''Uit de zesde eeu ...
, or , meaning ( / ) and ( / / ) or .
[Zo ontstond Brussel]
Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie – Commission of the Flemish Community in Brussels Saint Vindicianus, the Bishop of
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; ; ), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river.
A sub-pref ...
, made the first recorded reference to the place in 695, when it was still a
hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a Shakespearean tragedy, tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play. Set in Denmark, the play (the ...
. The names of all the municipalities in the Brussels-Capital Region are also of Dutch origin, except for
Evere
Evere (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium). , the municipality had a population of 43,608 inhabitants. The total area is , which gives a population density of . In common with all of Brussels' municipal ...
, which is possibly
Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
or
Old Frankish
Frankish ( reconstructed endonym: *), also known as Old Franconian or Old Frankish, was the West Germanic language spoken by the Franks from the 5th to 10th centuries.
Franks under king Chlodio settled in Roman Gaul in the 5th century. O ...
.
Pronunciation
In French, is pronounced (the ''x'' is pronounced , as in English, and the final ''s'' is silent) and in Dutch, is pronounced . Inhabitants of Brussels are known in French as (pronounced ) and in Dutch as (pronounced ). In the
Brabantian dialect
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic or Brabantine (, , ), is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant, which corresponded mainly to the Netherlands, Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgi ...
of Brussels (known as
Brusselian, and also sometimes referred to as Marols or Marollien), they are called ''Brusseleers'' or ''Brusseleirs''.
Originally, the written ''x'' noted the group . In the
Belgian French
Belgian French () is the variety of French spoken mainly among the French Community of Belgium, alongside related Oïl languages of the region such as Walloon, Picard, Champenois, and Lorrain (Gaumais). The French language spoken in Belgi ...
pronunciation as well as in Dutch, the ''k'' eventually disappeared and ''z'' became ''s'', as reflected in the current
Dutch spelling, whereas in the more conservative
French form, the spelling remained. The pronunciation in French only dates from the 18th century, but this modification did not affect the traditional Brussels usage. In France, the pronunciations and (for ) are often heard, but are rather rare in Belgium.
[Alain Lerond, ''Dictionnaire de la prononciation'' (1980), Larousse, pp. 477.]
History
Early history
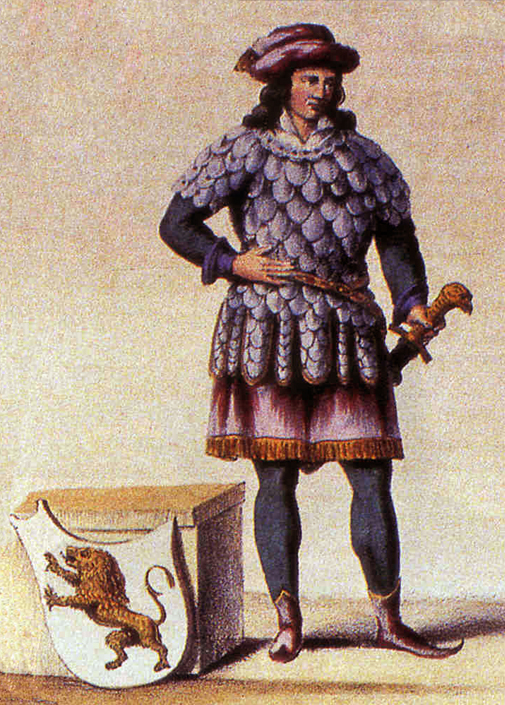

The history of Brussels is closely linked to that of
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
. Traces of human settlement go back to the
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
, with vestiges and place-names related to the civilisation of
megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging geographically f ...
s,
dolmen
A dolmen, () or portal tomb, is a type of single-chamber Megalith#Tombs, megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the Late Neolithic period (4000 ...
s and
standing stones
A menhir (; from Brittonic languages: ''maen'' or ''men'', "stone" and ''hir'' or ''hîr'', "long"), standing stone, orthostat, or lith is a large upright stone, emplaced in the ground by humans, typically dating from the European middle Br ...
(Plattesteen near the
Grand-Place/Grote Markt and
Tomberg in
Woluwe-Saint-Lambert
Woluwe-Saint-Lambert ( French, ) or Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe ( Dutch, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch). In French, ...
, for example). During
late antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
, the region was home to
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
occupation, as attested by archaeological evidence discovered on the current site of
Tour & Taxis, north-west of the
Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon () is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple polygon, simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simple or list of self-intersecting polygons, self-intersecting. A self-intersecting ...
(Brussels' city centre). Following the decline of the
Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
, it was incorporated into the
Frankish Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lomba ...
.
According to local legend, the origin of the settlement which was to become Brussels lies in Saint
Gaugericus
Saint Gaugericus, in French Saint Géry (also known as Gorik, Gau; in Walloon, Djèri) ( 550 – August 11, 619) was a bishop of Cambrai, France.
Biography
He was born to Roman parents, Gaudentius and Austadiola, at ''Eposium'' (present ...
' construction of a chapel on
an island in the river
Senne around 580. The official founding of Brussels is usually said to be around 979, when
Charles, Duke of Lower Lorraine
Charles (c. 953 – 22 June 992/995?) was the duke of Lower Lorraine from 977 until his death.
Life
Born at Reims in the summer of 953, Charles was the son of Louis IV of France and Gerberga of Saxony and the younger brother of King Lothair ...
, transferred the
relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains or personal effects of a saint or other person preserved for the purpose of veneration as a tangible memorial. Reli ...
s of the
martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', 'witness' Word stem, stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an external party. In ...
Saint
Gudula
Gudula of Brabant, also known as Saint Gudula (ca. 646–712), was a Christian saint who is venerated in Catholic and Orthodox churches. In Brabant, she is usually called ''Goedele'' or ''Goule''; (, later '; ; ). Her name is connected to s ...
from
Moorsel
Moorsel is a village in the Denderstreek in the province East Flanders in Belgium, a ''deelgemeente'' of the city of Aalst. The village belongs to a league of neighbouring villages, which call themselves the ''Faluintjesgemeenten''. Moorsel is t ...
(located in today's province of
East Flanders
East Flanders ( ; ; ; ) is a Provinces of Belgium, province of Belgium. It borders (clockwise from the North) the Netherlands, Dutch province of Zeeland and the Belgian provinces of Antwerp (province), Antwerp, Flemish Brabant, Hainaut (provinc ...
) to Saint Gaugericus' chapel. When
Otto II, Holy Roman Emperor
Otto II (955 – 7 December 983), called the Red (), was Holy Roman Emperor from 973 until his death in 983. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto II was the youngest and sole surviving son of Otto the Great and Adelaide of Italy.
Otto II was ...
, appointed the same Charles to become Duke of
Lower Lotharingia
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier'' in 977, Charles ordered the construction of the city's first permanent fortification, doing so on that same island.
Middle Ages
Lambert I, Count of Louvain, gained the County of Brussels around 1000 by marrying Charles' daughter. Because of its location on the banks of the Senne, on an
important trade route between the
Flemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
cities of
Bruges
Bruges ( , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders, in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is in the northwest of the country, and is the sixth most populous city in the country.
The area of the whole city amoun ...
and
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
, and
Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
in the
Kingdom of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( 'kingdom of the Germans', 'German kingdom', "kingdom of Germany", ) was the mostly Germanic language-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843. The king was elec ...
, Brussels became a commercial centre specialised in the textile trade. The town grew quite rapidly and extended towards the upper town (Treurenberg,
Coudenberg
The Palace of Coudenberg (; ) was a royal residence situated on the Coudenberg or Koudenberg (; Dutch for "Cold Hill"), a hill in what is today the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. For nearly 700 years, the Castle and then Palace of Couden ...
and
Sablon/Zavel areas), where there was a reduced risk of floods. As the town grew to a population of around 30,000, the surrounding marshes were drained to allow for further expansion. In 1183, the Counts of Leuven became
Dukes of Brabant
The Duke of Brabant (, ) was the ruler of the Duchy of Brabant since 1183/1184. The title was created by the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in favor of Henry I of the House of Reginar, son of Godfrey III of Leuven (who was duke of L ...
. Brabant, unlike the county of Flanders, was not fief of the king of France but was incorporated into the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
.
In the early 13th century, the
first walls of Brussels
The Fortifications of Brussels (; ) refers to the medieval city walls that surrounded Brussels, Belgium, built primarily to defend the city but also for administrative reasons. There were two stages of fortifications of Brussels: the first wall ...
were built and after this, the city grew significantly. Around this time, work began on what is now the
Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula (1225), replacing an older
Romanesque church. To let the city expand,
a second set of walls was erected between 1356 and 1383. Traces of these walls can still be seen; the
Small Ring, a series of boulevards bounding the historical city centre, follows their former course.
Early modern

In the 14th century, the marriage between heiress
Margaret III, Countess of Flanders
Margaret III (13 April 1350 – 16/21 March 1405) was a ruling Countess of Flanders, Countess of Artois, and Countess of Auvergne and Boulogne between 1384 and 1405. She was the last ruler of Flanders of the House of Dampierre.
She was al ...
, and
Philip the Bold
Philip II the Bold (; ; 17 January 1342 – 27 April 1404) was Duke of Burgundy and ''jure uxoris'' Count of Flanders, Artois and Burgundy. He was the fourth and youngest son of King John II of France and Bonne of Luxembourg.
Philip was th ...
,
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy () was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by the Crown lands of France, French crown in 1477, and later by members of the House of Habsburg, including Holy Roman E ...
, produced a new Duke of Brabant of the
House of Valois
The Capetian House of Valois ( , also , ) was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. They succeeded the House of Capet (or "Direct Capetians") to the List of French monarchs, French throne, and were the royal house of France from 1328 to 1589. ...
, namely
Anthony
Anthony, also spelled Antony, is a masculine given name derived from the '' Antonii'', a '' gens'' ( Roman family name) to which Mark Antony (''Marcus Antonius'') belonged. According to Plutarch, the Antonii gens were Heracleidae, being descenda ...
, their son. In 1477, the Burgundian duke
Charles the Bold
Charles Martin (10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), called the Bold, was the last duke of Burgundy from the House of Valois-Burgundy, ruling from 1467 to 1477. He was the only surviving legitimate son of Philip the Good and his third wife, ...
perished in the
Battle of Nancy
The Battle of Nancy was the final and decisive battle of the Burgundian Wars, fought outside the walls of Nancy on 5 January 1477 by Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, against René II, Duke of Lorraine, and the Swiss Confederacy.
René's ...
. Through the marriage of his daughter
Mary of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy (; ; 13 February 1457 – 27 March 1482), nicknamed the Rich, was a member of the House of Valois-Burgundy who ruled the Burgundian lands, comprising the Duchy of Burgundy, Duchy and Free County of Burgundy, County of Burgundy a ...
(who was born in Brussels) to Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I, the
Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
fell under
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
sovereignty. Brabant was integrated into this composite state, and Brussels flourished as the Princely Capital of the prosperous
Burgundian Netherlands
The Burgundian Netherlands were those parts of the Low Countries ruled by the Dukes of Burgundy during the Burgundian Age between 1384 and 1482. Within their Burgundian State, which itself belonged partly to the Holy Roman Empire and partly t ...
, also known as the
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the France, French Departments of Franc ...
. After the death of Mary in 1482, her son
Philip the Handsome
Philip the Handsome (22 June/July 1478 – 25 September 1506), also called the Fair, was ruler of the Burgundian Netherlands and titular Duke of Burgundy from 1482 to 1506, as well as the first Habsburg King of Castile (as Philip I) for a brief ...
succeeded as Duke of Burgundy and Brabant.
Philip died in 1506, and he was succeeded by his son
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
Kings and Emperors
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
Others
* Charles V, Duke ...
who then also became
King of Spain
The monarchy of Spain or Spanish monarchy () is the constitutional form of government of Spain. It consists of a Hereditary monarchy, hereditary monarch who reigns as the head of state, being the highest office of the country.
The Spanish ...
(crowned in the
Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula) and even Holy Roman Emperor at the death of his grandfather Maximilian I in 1519. Charles was now the ruler of a
Habsburg Empire
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
"on which the sun never sets" with Brussels serving as one of his main capitals.
It was in the
Coudenberg Palace
The Palace of Coudenberg (; ) was a royal residence situated on the Coudenberg or Koudenberg (; Dutch for "Cold Hill"), a hill in what is today the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. For nearly 700 years, the Castle and then Palace of Coudenb ...
that Charles V was declared of age in 1515, and it was there in 1555 that he abdicated all of his possessions and passed the
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands were the parts of the Low Countries that were ruled by sovereigns of the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. This rule began in 1482 and ended for the Northern Netherlands in 1581 and for the Southern Netherlands in 1797. ...
to King
Philip II of Spain
Philip II (21 May 152713 September 1598), sometimes known in Spain as Philip the Prudent (), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and List of Sicilian monarchs, Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He ...
. This palace, famous all over Europe, had greatly expanded since it had first become the seat of the Dukes of Brabant, but it was destroyed by fire in 1731.

In the 16th and 17th centuries, Brussels was a centre for the
lace
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is split into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted o ...
industry. In addition,
Brussels tapestry hung on the walls of castles throughout Europe. In 1695, during the
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
, King
Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
of France sent troops to
bombard Brussels with artillery. Together with the resulting fire, it was the most destructive event in the entire history of Brussels. The Grand-Place was destroyed, along with 4,000 buildings—a third of all the buildings in the city. The reconstruction of
the city centre, effected during subsequent years, profoundly changed its appearance and left numerous traces still visible today.
During the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
in 1708, Brussels again sustained a
French attack, which it repelled. Following the
Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
in 1713, Spanish sovereignty over the Southern Netherlands was transferred to the Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg. This event started the era of the
Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The period began with the acquisition by the Austrian Habsburg monarchy of the former Spanish Netherlands under the Treaty of Ras ...
. Brussels
was captured by France in 1746, during the
War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
, but was handed back to Austria three years later. It remained with Austria until 1795, when the Southern Netherlands were captured and annexed by France, and the city became the
chef-lieu
An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune, is located.
In countries with French as the administrative language, such as Belgiu ...
of the
department of the Dyle. The French rule ended in 1815, with the defeat of
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
on the
battlefield of Waterloo, located south of today's Brussels-Capital Region. With the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
, the Southern Netherlands joined the
United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed from 1815 to 1839. The United Netherlands was created in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars through the fusion of territories t ...
, under King
William I of Orange
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburgs that set off the Eighty Years' War (156 ...
. The former Dyle department became the province of
South Brabant, with Brussels as its capital.
Late modern
In 1830, the
Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was a conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
The ...
began in Brussels, after a performance of
Auber's opera ''
La Muette de Portici
''La muette de Portici'' (''The Mute Girl of Portici'', or ''The Dumb Girl of Portici''), also called ''Masaniello'' () in some versions, is an opera in five acts by Daniel Auber, with a libretto by Germain Delavigne, revised by Eugène Scri ...
'' at the
Royal Theatre of La Monnaie. The city became the capital and seat of government of the new nation. South Brabant was renamed simply
Brabant, with Brussels as its administrative centre. On 21 July 1831,
Leopold I, the first
King of the Belgians
The monarchy of Belgium is the Constitutional monarchy, constitutional and Inheritance, hereditary institution of the monarchical head of state of the Kingdom of Belgium. As a popular monarchy, the Belgian monarch uses the title king/quee ...
, ascended the throne, undertaking the destruction of the city walls and the construction of many buildings.
Following independence, Brussels underwent many more changes. It became a financial centre, thanks to the dozens of companies launched by the ''
Société Générale de Belgique
The ' (, ; often referred to in Belgium simply as "Société Générale" or SGB) was an investment bank and, subsequently, an industrial and financial conglomerate in Belgium between 1822 and 2003. It has been described as the world's first u ...
''. The
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
and the opening of the
Brussels–Charleroi Canal
The Brussels–Charleroi Canal (; ), also known as the Charleroi Canal amongst other similar names, is an important canal in Belgium. The canal is quite large, with a Class IV Freycinet gauge, and its Walloon portion is long. It runs from Ch ...
in 1832 brought prosperity to the city through commerce and manufacturing. The
Free University of Brussels was established in 1834 and
Saint-Louis University in 1858. In 1835, the
first passenger railway built outside England linked the municipality of
Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western p ...
with
Mechelen
Mechelen (; ; historically known as ''Mechlin'' in EnglishMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical context. T ...
.
During the 19th century, the population of Brussels grew considerably; from about 80,000 to more than 625,000 people for the city and its surroundings. The Senne had become a serious
health hazard
A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would potentially allow them to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probability of that ...
, and from 1867 to 1871, under the tenure of the
city's then-mayor,
Jules Anspach, its entire course through the urban area was
completely covered over. This allowed
urban renewal
Urban renewal (sometimes called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address real or perceived urban decay. Urban renewal involves the clearing ...
and the construction of modern buildings of ''
Haussmann-esque'' style along grand
central boulevards, characteristic of downtown Brussels today. Buildings such as the
Brussels Stock Exchange
The Brussels Stock Exchange ( ; ), abbreviated to BSE, was founded in Brussels, Belgium, by decree of Napoleon in 1801. In 2002, the BSE merged with the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, Amsterdam, Lisbon Stock Exchange, Lisbon and Paris Bourse, Paris ...
(1873), the
Palace of Justice (1883) and
Saint Mary's Royal Church
Saint Mary's Royal Church (; ) is a Catholic parish church located on the / in Schaerbeek, a municipality of Brussels, Belgium. Officially dedicated to Our Lady of the Assumption, it is popularly associated with Queen Louise-Marie, first Que ...
(1885) date from this period. This development continued throughout the reign of King
Leopold II. The
International Exposition of 1897 contributed to the promotion of the infrastructure. Among other things, the
Palace of the Colonies, today's
Royal Museum for Central Africa
The Royal Museum for Central Africa (RMCA) (; ; ), communicating under the name AfricaMuseum since 2018, is an ethnography and natural history museum situated in Tervuren in Flemish Brabant, Belgium, just outside Brussels. It was originally b ...
, in the suburb of
Tervuren
Tervuren (; ) is a municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant, in the Flemish region of Belgium. The municipality comprises the villages of Duisburg, Tervuren proper, Vossem and Moorsel. On 1 January 2006, Tervuren had a total population o ...
, was connected to the capital by the construction of an
grand alley.
Brussels became one of the major European cities for the development of the
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
style in the 1890s and early 1900s. The architects
Victor Horta
Victor Pierre Horta (; Victor, Baron Horta after 1932; 6 January 1861 – 8 September 1947) was a Belgian architect and designer, and one of the founders of the Art Nouveau movement. He was a fervent admirer of the French architectural theoris ...
,
Paul Hankar
Paul Hankar (; 11 December 1859 – 17 January 1901) was a Belgian architect and furniture designer, and an innovator in the Art Nouveau style.
Career
Hankar was born at Frameries, in Hainaut, Belgium, the son of a stonemason. He studied at ...
, and
Henry van de Velde
Henry Clemens van de Velde (; 3 April 1863 – 15 October 1957) was a Belgian painter, architect, interior designer, and art theorist. Together with Victor Horta and Paul Hankar, he is considered one of the founders of Art Nouveau in Belgium ...
, among others, were known for their designs, many of which survive today.
20th century
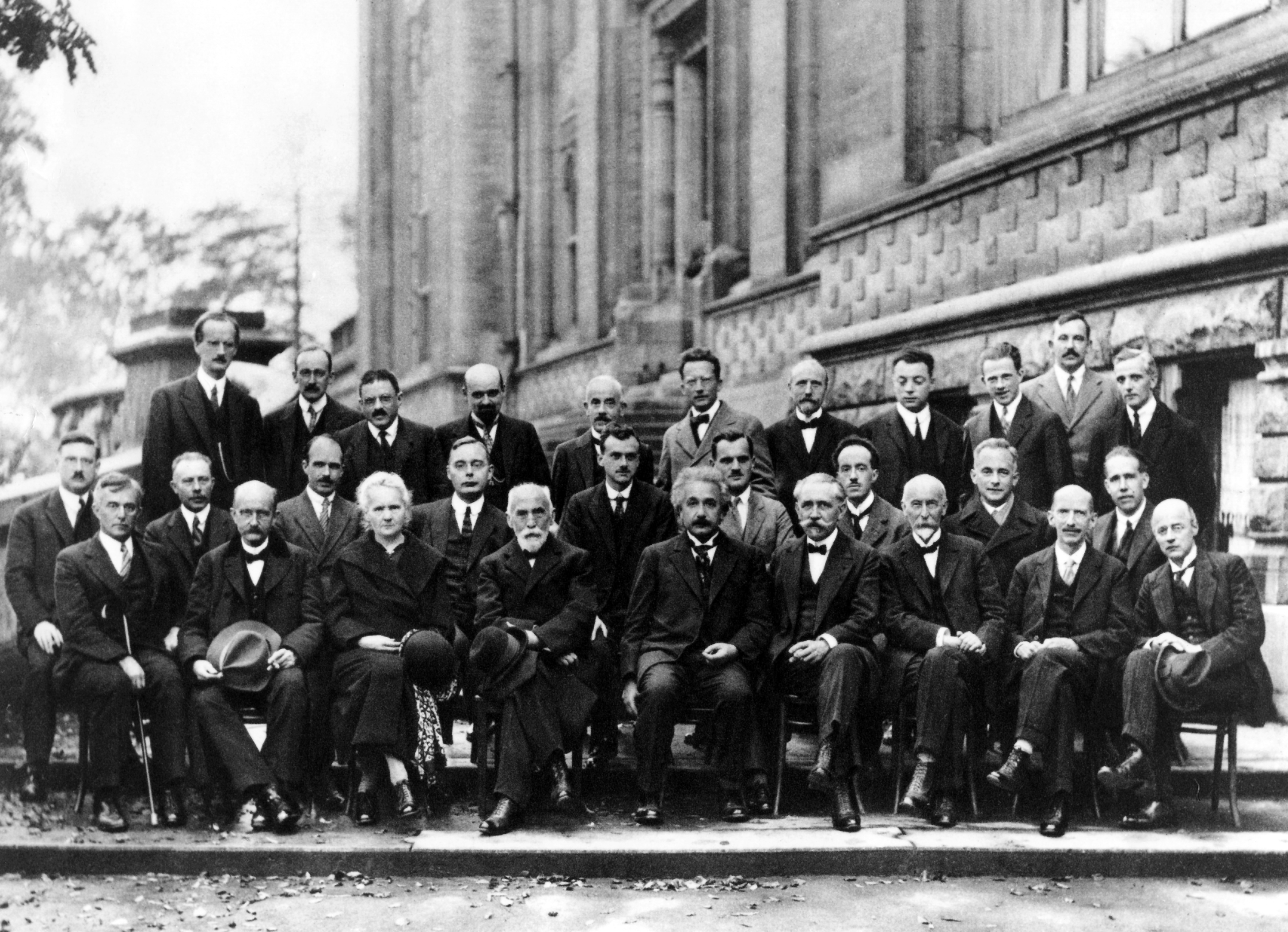

During the 20th century, the city hosted various fairs and conferences, including the
Solvay Conference
The Solvay Conferences () have been devoted to preeminent unsolved problems in both physics and chemistry. They began with the historic invitation-only 1911 Solvay Conference on Physics, considered a turning point in the world of physics, and ar ...
on Physics and on Chemistry, and three
world's fair
A world's fair, also known as a universal exhibition, is a large global exhibition designed to showcase the achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specific site for a perio ...
s: the
Brussels International Exposition of 1910, the
Brussels International Exposition of 1935 and the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (
Expo 58
Expo 58, also known as the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (; ), was a world's fair held on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Brussels, Belgium, from 17 April to 19 October 1958. It was the first major world's fair registered under the Bureau Internati ...
). During
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, Brussels was an
occupied city, but German troops did not cause much damage. During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, it was again
occupied by German forces, and spared major damage, before it was liberated by the British
Guards Armoured Division
The Guards Armoured Division was an armoured division of the British Army during the Second World War. The division was created in the United Kingdom on 17 June 1941 during the Second World War from elements of the Guards units, the Grenadie ...
on 3 September 1944.
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport is the main international airport of Belgium. It is located in the municipality of Zaventem in Flemish Brabant, northeast of Brussels. Also informally known as Brussels-National Airport or Brussels-Zaventem Airport, Brussels ...
, in the suburb of
Zaventem
Zaventem () is a municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant, in the Flemish region of Belgium. It is located in the Dijleland area, one of the three large recreational areas which together form the '' Groene Gordel'' ("Green Belt") around th ...
, dates from the occupation.
After World War II, Brussels underwent extensive modernisation. The construction of the
North–South connection
The North–South connection (; ) is a railway link of national and international importance through central Brussels, Belgium, that connects the major railway stations in the city. It is line 0 (zero) of the Belgian rail network. With 1200 t ...
, linking the main railway stations in the city, was completed in 1952, while the first ''
premetro'' (underground tram) service was launched in 1969,
and the first
Metro line was opened in 1976.
Starting from the early 1960s, Brussels became the ''de facto'' capital of what would become the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU), and many modern offices were built. Development was allowed to proceed with little regard to the aesthetics of newer buildings, and numerous architectural landmarks were demolished to make way for newer buildings that often clashed with their surroundings, giving name to the process of
Brusselisation.
Contemporary
The Brussels-Capital Region was formed on 18 June 1989, after a constitutional reform in 1988. It is one of the three
federal regions of Belgium, along with
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
and
Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the c ...
, and has bilingual status.
The
yellow iris is the emblem of the region (referring to the presence of these flowers on the city's original site) and a stylised version is featured on its official flag.
In recent years, Brussels has become an important venue for international events. In 2000, it was named
European Capital of Culture
A European Capital of Culture is a city designated by the European Union (EU) for a period of one calendar year during which it organises a series of cultural events with a strong pan-European dimension. Being a European Capital of Culture can ...
alongside eight other European cities. In 2013, the city was the site of the
Brussels Agreement. In 2014, it hosted the
40th G7 summit,
and in 2017, 2018 and 2021 respectively the
28th,
29th and
31st NATO Summits.
, three coordinated
nail bomb
A nail bomb is an anti-personnel explosive device containing nails to increase its effectiveness at harming victims. The nails act as shrapnel, leading almost certainly to more injury in inhabited areas than the explosives alone would. A nail ...
ings were detonated by
ISIL
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Daesh, is a transnational Salafi jihadist organization and unrecognized quasi-state. IS occupied signif ...
in Brussels—two at
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport is the main international airport of Belgium. It is located in the municipality of Zaventem in Flemish Brabant, northeast of Brussels. Also informally known as Brussels-National Airport or Brussels-Zaventem Airport, Brussels ...
in
Zaventem
Zaventem () is a municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant, in the Flemish region of Belgium. It is located in the Dijleland area, one of the three large recreational areas which together form the '' Groene Gordel'' ("Green Belt") around th ...
and one at
Maalbeek/Maelbeek metro station—resulting in 32 victims and three
suicide bombers
A suicide attack (also known by a wide variety of other names, see below) is a deliberate attack in which the perpetrators knowingly sacrifice their own lives as part of the attack. These attacks are a form of murder–suicide that is ofte ...
killed, and 330 people were injured. It was the deadliest act of
terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of violence against non-combatants to achieve political or ideological aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war aga ...
in Belgium.
Geography
Location and topography
Brussels lies in the north-central part of Belgium, about from the Belgian coast and about from Belgium's southern tip. It is located in the heartland of the Brabantian Plateau, about south of
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
(
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
), and north of
Charleroi
Charleroi (, , ; ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It is the largest city in both Hainaut and Wallonia. The city is situated in the valley of the Sambre, in the south-west of Belgium, not ...
(
Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the c ...
). Its average
elevation
The elevation of a geographic location (geography), ''location'' is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational equipotenti ...
is above
sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
, varying from a low point in the valley of the almost completely covered
Senne, which cuts the Brussels-Capital Region from east to west, up to high points in the
Sonian Forest
The Sonian Forest or Sonian Wood (, ; , ) is a forest at the south-eastern edge of Brussels, Belgium. It is connected to the Bois de la Cambre, Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamerenbos, an urban public park which enters the city up to from the Pentag ...
, on its southeastern side. In addition to the Senne, tributary streams such as the
Maelbeek and the
Woluwe
The Woluwe (; ) is a stream that flows through several municipalities in the south-east and east of Brussels, Belgium, and is a right tributary of the Senne in Vilvoorde. The Kleine (little) Maalbeek is a tributary of the Woluwe in Kraainem. M ...
, to the east of the region, account for significant elevation differences.
Brussels' central boulevards are above sea level. Contrary to popular belief, the highest point (at ) is not near the / in
Forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
, but at the / in the Sonian Forest.
Climate
Brussels experiences an
oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
(
Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
: ''Cfb'') with warm summers and cool winters.
Proximity to coastal areas influences the area's climate by sending marine air masses from the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
. Nearby wetlands also ensure a maritime temperate climate. On average (based on measurements in the period 1981–2010), there are approximately 135 days of rain per year in the Brussels-Capital Region. Snowfall is infrequent, averaging 24 days per year. The city also often experiences violent thunderstorms in summer months.
Brussels as a capital
Despite its name, the Brussels-Capital Region is not the capital of
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
. Article 194 of the
Belgian Constitution
The Constitution of Belgium (; ; ) dates back to 1831. Since then Belgium has been a parliamentary monarchy that applies the principles of ministerial responsibility for the government policy and the separation of powers.
The most recent majo ...
establishes that the capital of Belgium is the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
, the municipality in the region that is the city's core.
The City of Brussels is the location of many national institutions. The
Royal Palace of Brussels
The Royal Palace of Brussels ( ; ; ) is the official palace of the Monarchy of Belgium, King and Queen of the Belgians in the centre of the nation's capital, Brussels. However, it is not used as a royal residence, as the king and his family l ...
, where the
King of the Belgians
The monarchy of Belgium is the Constitutional monarchy, constitutional and Inheritance, hereditary institution of the monarchical head of state of the Kingdom of Belgium. As a popular monarchy, the Belgian monarch uses the title king/quee ...
exercises his prerogatives as head of state, is situated alongside
Brussels Park
Brussels Park ( ; or ) is the largest urban public park in central Brussels, Belgium. The park was formerly known and is still sometimes colloquially referred to as the Royal Park ( ; ). It was the city's first public park, being originally ...
(not to be confused with the
Royal Palace of Laeken, the official home of the
Belgian royal family
The monarchy of Belgium is the constitutional and hereditary institution of the monarchical head of state of the Kingdom of Belgium. As a popular monarchy, the Belgian monarch uses the title king/queen of the Belgians and serves as the ...
). The
Palace of the Nation
The Palace of the Nation (; ; ) is a neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium, housing the Belgian Federal Parliament. The Parliament consists of both the Chamber of Representatives (lower house) and the Senate (upper house), which convene in ...
is located on the opposite side of this park, and is the seat of the
Belgian Federal Parliament
The Federal Parliament (; ; ) is the bicameral parliament of Belgium. It consists of the Chamber of Representatives (lower house) and the Senate (upper house). It sits in the Palace of the Nation in the centre of the nation's capital, Brussels ...
. The office of the
Prime Minister of Belgium
The prime minister of Belgium (; ; ) or the premier of Belgium is the head of the federal government of Belgium, and the most powerful person in Belgian politics.
The first head of government in Belgian history was Henri van der Noot in 179 ...
, colloquially called ''Law Street 16'' (, ), is located adjacent to this building. It is also where the
Council of Ministers
Council of Ministers is a traditional name given to the supreme Executive (government), executive organ in some governments. It is usually equivalent to the term Cabinet (government), cabinet. The term Council of State is a similar name that also m ...
holds its meetings. The
Court of Cassation
A court of cassation is a high-instance court that exists in some judicial systems. Courts of cassation do not re-examine the facts of a case; they only interpret the relevant law. In this, they are appellate courts of the highest instance. In ...
, Belgium's main court, has its seat in the
Palace of Justice. Other important institutions in the City of Brussels are the
Constitutional Court
A constitutional court is a high court that deals primarily with constitutional law. Its main authority is to rule on whether laws that are challenged are in fact unconstitutional, i.e. whether they conflict with constitutionally established ru ...
, the
Council of State
A council of state is a governmental body in a country, or a subdivision of a country, with a function that varies by jurisdiction. It may be the formal name for the cabinet or it may refer to a non-executive advisory body associated with a head ...
, the
Court of Audit
A Court of Audit or Court of Accounts is a supreme audit institution, i.e. a government institution performing financial and/or legal audit (i.e. statutory audit or external audit) on the executive branch of power.
See also
*Most of those ...
, the
Royal Belgian Mint and the
National Bank of Belgium
The National Bank of Belgium (NBB; , NBB; , BNB; , BNB) is the National central bank (Eurosystem), national central bank for Belgium within the Eurosystem. It was the Belgian central bank from 1850 until 1998, established by law of and issuin ...
.
The City of Brussels is also the capital of both the
French Community of Belgium
In Belgium, the French Community (, , CFB) refers to one of the three constituent constitutional linguistic communities. Since 2011, the French Community has used the name Wallonia-Brussels Federation (, , FWB), which is controversial because ...
and the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community (, ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the ...
.
The
Flemish Parliament
The Flemish Parliament (Dutch language, Dutch: , formerly called Flemish Council or ''Vlaamse Raad'') constitutes the legislature, legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic reg ...
and
Flemish Government
The Flemish Government ( ) is the executive branch of the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region of Belgium. It consists of a government cabinet, headed by the Minister-President of Flanders, Minister-President and accountable to the Flemish Par ...
have their seats in Brussels, and so do the
Parliament of the French Community
The Parliament of the French Community ( ; PCF) is the legislative assembly of the French Community of Belgium, based in the Royal Quarter of Brussels. It consists of all 75 members of the Walloon Parliament except German-speaking members (curren ...
and the
Government of the French Community
The Cabinet of the French Community of Belgium (, ) is the executive branch of the French Community of Belgium, and it sits in Brussels. It consists of a number of ministers chosen by the Parliament of the French Community and is headed by a Minist ...
.

Municipalities
The 19
municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
(, ) of the Brussels-Capital
Region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
are political subdivisions with individual responsibilities for the handling of local level duties, such as law enforcement and the upkeep of schools and roads within its borders.
Municipal administration is also conducted by a mayor, a council, and an executive.
In 1831, Belgium was divided into 2,739 municipalities, including the 19 currently located in the Brussels-Capital Region.
Unlike most of the municipalities in Belgium, the ones now located in the Brussels-Capital Region were not merged with others during mergers occurring in 1964, 1970, and 1975.
However, a few neighbouring municipalities have been merged into the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
, including
Laeken
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is a residential suburb in the north-western part of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It belongs to the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality of the ...
,
Haren and
Neder-Over-Heembeek
Neder-Over-Heembeek (; ) is a former municipality of Brussels, Belgium, that was merged into the City of Brussels in 1921. Nowadays, it is a northern section of that municipality, and a predominantly industrial zone, especially known for the Qu ...
in 1921.
These comprise the northern bulge in the municipality. To the south-east is a strip of land along the
Avenue Louise/Louizalaan that, in addition to the
Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamerenbos, was annexed from
Ixelles
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Pentagon (Brussels), Brusse ...
in 1864. Part of the (ULB)'s Solbosch campus is also part of the City of Brussels, partially accounting for the bulge in the south-eastern end.
The largest municipality in area and population is the City of Brussels, covering and with 145,917 inhabitants; the least populous is
Koekelberg
Koekelberg (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren, Jette, and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean. In common with al ...
with 18,541 inhabitants. The smallest in area is
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode ( French, ) or Sint-Joost-ten-Node ( Dutch, ), often simply called Saint-Josse in French or Sint-Joost in Dutch, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part o ...
, which is only , but still has the highest population density in the region, with .
Watermael-Boitsfort
Watermael-Boitsfort (French language, French, ) or Watermaal-Bosvoorde (Dutch language, Dutch, ; ), often simply called Boitsfort in French or Bosvoorde in Dutch, is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipal ...
has the lowest population density in the region, with .
There is much controversy on the division of 19 municipalities for a highly urbanised region, which is considered as (half of) one city by most people. Some politicians mock the "19 baronies" and want to merge the municipalities under one city council and one mayor. That would lower the number of politicians needed to govern Brussels, and centralise the power over the city to make decisions easier, thus reduce the overall running costs. The current municipalities could be transformed into districts with limited responsibilities, similar to the current structure of
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
or to structures of other capitals like the
boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
in
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
or ''
arrondissements'' in
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, to keep politics close enough to the citizen.
In the 2010s,
Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western p ...
gained international attention as the
base for
Islamist terrorists who carried out attacks in both
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
and
Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
.
File:Town hall of Anderlecht (DSC 2233).jpg, Anderlecht
Anderlecht (; ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the south-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Forest, B ...
File:Château Sainte-Anne (DSCF7140).jpg, Auderghem
Auderghem ( French, ; former Dutch spelling) or Oudergem ( Dutch, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the south-eastern part of the region, along the Woluwe valley and at the entrance to the ...
(Oudergem)
File:SintAgathaBerchemMC7229.jpg, Berchem-Sainte-Agathe
Berchem-Sainte-Agathe ( French, ) or Sint-Agatha-Berchem ( Dutch, ), often simply called Berchem, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Gansh ...
(Sint-Agatha-Berchem)
File:Brussels, townhall oeg2043-00090 foto3 2015-06-07 08.38.jpg, City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
File:Town hall of Etterbeek (DSC 2183).jpg, Etterbeek
Etterbeek (; ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the municipalities of Auderghem, the Cit ...
File:EvereTownHall.jpg, Evere
Evere (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium). , the municipality had a population of 43,608 inhabitants. The total area is , which gives a population density of . In common with all of Brussels' municipal ...
File:MaisonCommunaleForest.jpg, Forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
(Vorst)
File:Ganshoren town hall.jpg, Ganshoren
Ganshoren (; ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Jette, and ...
File:MAISON-40.jpg, Ixelles
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Pentagon (Brussels), Brusse ...
(Elsene)
File:Jette voormalig gemeentehuis 27-04-2013.jpg, Jette
Jette (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Ganshoren, Koekelberg, and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean, as well as the Fl ...
File:Maison communale Koekelberg.jpg, Koekelberg
Koekelberg (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren, Jette, and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean. In common with al ...
File:Gemeentehuis St Jans Molenbeek.jpg, Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western p ...
(Sint-Jans-Molenbeek)
File:StGillesTownHall.jpg, Saint-Gilles (Sint-Gillis)
File:Town hall of Saint-Josse-ten-Noode.01.jpg, Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode ( French, ) or Sint-Joost-ten-Node ( Dutch, ), often simply called Saint-Josse in French or Sint-Joost in Dutch, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part o ...
(Sint-Joost-ten-Node)
File:Hôtel communal de Schaerbeek (2) - 2264-0007-0.jpg, Schaerbeek
(French language, French, ; former History of Dutch orthography, Dutch spelling) or (modern Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Reg ...
(Schaarbeek)
File:3557uccleTownHall.jpg, Uccle
Uccle (French language, French, ) or Ukkel (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the southern part of the region, it ...
(Ukkel)
File:WatermaelBoitsfortTownHall.jpg, Watermael-Boitsfort
Watermael-Boitsfort (French language, French, ) or Watermaal-Bosvoorde (Dutch language, Dutch, ; ), often simply called Boitsfort in French or Bosvoorde in Dutch, is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipal ...
(Watermaal-Bosvoorde)
File:Town hall of Woluwe-Saint-Lambert during golden hour (DSC 2171).jpg, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert
Woluwe-Saint-Lambert ( French, ) or Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe ( Dutch, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch). In French, ...
(Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe)
File:Mais.Comm.W-S-P.01.JPG, Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
Woluwe-Saint-Pierre ( French, ) or Sint-Pieters-Woluwe ( Dutch, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by Etterbeek, Auderghem and Woluwe-Saint-Lambe ...
(Sint-Pieters-Woluwe)
Brussels-Capital Region

Political status and administration
The Brussels-Capital Region is one of the three federated regions of Belgium, alongside the
Walloon Region
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three regions of Belgium—along with Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the country, Wallonia is primarily French-speaking. It accounts for 55% o ...
and the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region (, ), usually simply referred to as Flanders ( ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—alongside the Wallonia, Walloon Region and the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region. ...
. Geographically and linguistically, it is a bilingual
enclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is so ...
in the monolingual Flemish Region. Regions are one component of Belgium's institutions; the three communities being the other component. Brussels' inhabitants deal with either the
French Community
The French Community () was the constitutional organization set up in October 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which had reorganized the colonial em ...
or the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community (, ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the ...
for matters such as culture and education, as well as a
Common Community for competencies which do not belong exclusively to either Community, such as healthcare and social
welfare
Welfare may refer to:
Philosophy
*Well-being (happiness, prosperity, or flourishing) of a person or group
* Utility in utilitarianism
* Value in value theory
Economics
* Utility, a general term for individual well-being in economics and decision ...
.
Upon the reorganisation and split of the
Province of Brabant
The Province of Brabant (, ; ) was a province in Belgium from 1830 to 1995. It was created in 1815 as South Brabant, part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. In 1995, it was split into the Dutch-speaking Flemish Brabant, the French-speaki ...
in 1995, the Brussels Region ceased to belong to any of the
provinces of Belgium
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three Communities, regions, and language areas of Belgium, regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any p ...
, nor was it subdivided into provinces itself. However, the
Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital
The Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital (; ) is the only administrative arrondissement in the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. Because it is the only administrative arrondissement in the Brussels Region, its territory coincides with that of the ...
, whose borders coincide with the Brussels Region, continued to exist, and the areas of provincial jurisdiction were assumed by the newly created
Governor of the Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital and the Brussels regional institutions and community commissions. In 2014, the office of the Governor was formally abolished and replaced in September 2015 by the office of the "High official of the Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital", who retained responsibility for
crisis management
Crisis management is the process by which an organization deals with a disruptive and unexpected event that threatens to harm the organization or its stakeholders. The study of crisis management originated with large-scale industrial and envi ...
and
emergency planning, while responsibility for
crime prevention
Crime prevention refers to strategies and measures that seek to reduce the risk of crime occurring by intervening before a crime has been committed. It encompasses many approaches, including developmental, situational, community-based and crimin ...
was transferred to the
Minister-President of the Brussels-Capital Region
The minister-president of the Brussels-Capital Region (; ) leads the government of the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) The post is appointed for five years a ...
.
Institutions
The Brussels-Capital Region is governed by a
parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
of 89 members (72 French-speaking, 17 Dutch-speaking—parties are organised on a linguistic basis) and an eight-member regional cabinet consisting of a
minister-president, four ministers and three
state secretaries. By law, the cabinet must comprise two French-speaking and two Dutch-speaking ministers, one Dutch-speaking secretary of state and two French-speaking secretaries of state. The minister-president does not count against the language quota, but in practice every minister-president has been a bilingual francophone. The regional parliament can enact
ordinances (, ), which have equal status as a national legislative act.
Nineteen of the 72 French-speaking members of the Brussels Parliament are also members of the
Parliament of the French Community of Belgium
The Parliament of the French Community ( ; PCF) is the legislative assembly of the French Community of Belgium, based in the Royal Quarter of Brussels. It consists of all 75 members of the Walloon Parliament except German-speaking members (curren ...
, and, until 2004, this was also the case for six Dutch-speaking members, who were at the same time members of the
Flemish Parliament
The Flemish Parliament (Dutch language, Dutch: , formerly called Flemish Council or ''Vlaamse Raad'') constitutes the legislature, legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic reg ...
. Now, people voting for a Flemish party have to vote separately for 6 directly elected members of the Flemish Parliament.
Agglomeration of Brussels
Before the creation of the Brussels-Capital Region, regional competences in the 19 municipalities were performed by the Brussels Agglomeration. The Brussels Agglomeration was an administrative division established in 1971. This decentralised administrative public body also assumed jurisdiction over areas which, elsewhere in Belgium, were exercised by municipalities or provinces.
The Brussels Agglomeration had a separate legislative council, but the by-laws enacted by it did not have the status of a legislative act. The only election of the council took place on 21 November 1971. The working of the council was subject to many difficulties caused by the linguistic and socio-economic tensions between the two communities.
After the creation of the Brussels-Capital Region, the Brussels Agglomeration was never formally abolished, although it no longer has a purpose.
French and Flemish communities

The
French Community
The French Community () was the constitutional organization set up in October 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which had reorganized the colonial em ...
and the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community (, ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the ...
exercise their powers in Brussels through two community-specific public authorities: the
French Community Commission ( or COCOF) and the
Flemish Community Commission
The Flemish Community Commission () is the local representative of the Flemish authorities in the Brussels-Capital Region, one of the three regions of Belgium. The VGC depends on the Flemish Parliament, and its council is made up by the members of ...
( or VGC). These two bodies each have an assembly composed of the members of each linguistic group of the
Parliament of the Brussels-Capital Region
The Parliament of the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (; ) is the governing body of the Brussels-Capital Region, one of the three federated Communities and regions of Be ...
. They also have a board composed of the ministers and secretaries of state of each linguistic group in the Government of the Brussels-Capital Region.
The French Community Commission also has another capacity: some legislative powers of the French Community have been devolved to the Walloon Region (for the French language area of Belgium) and to the French Community Commission (for the bilingual language area). The Flemish Community, however, did the opposite; it merged the Flemish Region into the Flemish Community. This is related to different conceptions in the two communities, one focusing more on the Communities and the other more on the Regions, causing an asymmetrical
federalism
Federalism is a mode of government that combines a general level of government (a central or federal government) with a regional level of sub-unit governments (e.g., provinces, State (sub-national), states, Canton (administrative division), ca ...
. Because of this devolution, the French Community Commission can enact
decree
A decree is a law, legal proclamation, usually issued by a head of state, judge, monarch, royal figure, or other relevant Authority, authorities, according to certain procedures. These procedures are usually defined by the constitution, Legislativ ...
s, which are legislative acts.
Common Community Commission
A bi-communitarian public authority, the
Common Community Commission
The Common Community Commission (; ) is responsible for Brussels community matters that are common to both the French Community and the Flemish Community and for institutions that fall within the competencies of the Communities but do not belong ex ...
(, COCOM, , GGC) also exists. Its assembly is composed of the members of the regional parliament, and its board are the ministers—not the secretaries of state—of the region, with the minister-president not having the right to vote. This commission has two capacities: it is a decentralised administrative public body, responsible for implementing cultural policies of common interest. It can give subsidies and enact
by-law
A by-law (bye-law, by(e)law, by(e) law), is a set of rules or law established by an organization or community so as to regulate itself, as allowed or provided for by some higher authority. The higher authority, generally a legislature or some othe ...
s. In another capacity, it can also enact ordinances, which have equal status as a national legislative act, in the field of the welfare powers of the communities: in the Brussels-Capital Region, both the French Community and the Flemish Community can exercise powers in the field of welfare, but only in regard to institutions that are unilingual (for example, a private French-speaking retirement home or the Dutch-speaking hospital of the
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (Dutch language, Dutch, ; lit. Free University of Brussels; abbreviated VUB) is a Dutch- and English-speaking research university in Brussels, Belgium. It has four campuses: Brussels Humanities, Science and Engine ...
). The Common Community Commission is responsible for policies aiming directly at private persons or at bilingual institutions (for example, the centres for social welfare of the 19 municipalities). Its ordinances have to be enacted with a majority in both linguistic groups. Failing such a majority, a new vote can be held, where a majority of at least one third in each linguistic group is sufficient.
Brussels and the European Union
Brussels serves as ''
de facto'' capital of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU), hosting the major political
institutions of the Union. The EU has not declared a capital formally, though the
Treaty of Amsterdam
The Treaty of Amsterdam, officially the Treaty of Amsterdam amending the Treaty on European Union, the Treaties establishing the European Communities and certain related acts, was signed on 2 October 1997, and entered into force on 1 May 1999; i ...
formally gives Brussels the seat of the
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
(the executive branch of government) and the
Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union, often referred to in the treaties and other official documents simply as the Council, and less formally known as the Council of Ministers, is the third of the seven institutions of the European Union (EU) a ...
(a legislative institution made up from executives of member states).
[European Commission publication: ''Europe in Brussels'' 2007] It locates the formal seat of
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
in
Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
, where votes take place, with the council, on the proposals made by the commission. However, meetings of political groups and committee groups are formally given to Brussels, along with a set number of plenary sessions. Three quarters of Parliament sessions now take place at its
Brussels hemicycle. Between 2002 and 2004, the
European Council
The European Council (informally EUCO) is a collegiate body (directorial system) and a symbolic collective head of state, that defines the overall political direction and general priorities of the European Union (EU). It is composed of the he ...
also fixed its seat in the city.
In 2014, the Union hosted a
G7 summit in the city.

Brussels, along with
Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
and Strasbourg, began to host European institutions in 1957, soon becoming the centre of activities, as the Commission and Council based their activities in what has become the
European Quarter, in the east of the city.
Early building in Brussels was sporadic and uncontrolled, with little planning. The current major buildings are the
Berlaymont building
The Berlaymont building () is an office building in Brussels, Belgium, which houses the headquarters of the European Commission, the executive branch of the European Union (EU). The structure is located on the Robert Schuman Roundabout at 200, ...
of the commission, symbolic of the quarter as a whole, the
Europa building
The Europa building is the seat of the European Council and Council of the European Union, located on the Rue de la Loi, Rue de la Loi/Wetstraat in the Brussels and the European Union#European Quarter, European Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. It ...
of the Council and the
Espace Léopold
The Espace Léopold (French; commonly used in English) or Leopoldruimte (Dutch; ) is the complex of parliament buildings in Brussels, Belgium, housing the European Parliament, a legislative chamber of the European Union (EU). It consists of a ...
of the Parliament.
In recent years, the presence has increased considerably, with the Commission alone occupying within the European Quarter (a quarter of the total office space in Brussels). The concentration and density has caused concern that the presence of the institutions has created a ''
ghetto
A ghetto is a part of a city in which members of a minority group are concentrated, especially as a result of political, social, legal, religious, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished than other ...
effect'' in that part of the city.
However, the European presence has contributed significantly to the importance of Brussels as an international centre.
International institutions
Brussels has, since
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, become the administrative centre of many international organisations. The city is the political and administrative centre of the
North Atlantic Treaty Organization
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental transnational military alliance of 32 member states—30 European and 2 North American. Established in the aftermat ...
(NATO).
NATO's Brussels headquarters houses
29 embassies and brings together over 4,500 staff from allied nations, their militaries, and civil service personnel. Many other international organisations such as the
World Customs Organization
The World Customs Organization (WCO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. Notable projects include its collaboration with the WTO on trade facilitation and the implementation of the SAFE Framework of Standar ...
and
Eurocontrol
The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol (stylised ''EUROCONTROL''), is an international organisation working to achieve safe and seamless air traffic management across Europe. Founded in 1963, Eur ...
, as well as international corporations, have their main institutions in the city. In addition, the main international
trade union
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
confederations have their headquarters there: the
European Trade Union Confederation
The European Trade Union Confederation (ETUC) is the major trade union organisation representing workers at the European level. In its role as a European social partner, the ETUC works both in a consulting role with the European Commission and ...
(ETUC), the
International Confederation of Free Trade Unions
The International Confederation of Free Trade Unions (ICFTU) was an international trade union. It came into being on 7 December 1949 following a split within the World Federation of Trade Unions (WFTU), and was dissolved on 31 October 2006 whe ...
(ICFTU) and the
World Confederation of Labour
The World Confederation of Labour (WCL) was an international labour organization founded in 1920 and based in Europe. Fascist governments of the 1930s repressed the federation and imprisoned many of its leaders, limiting operations until the end o ...
(WCL).
Brussels is third in the number of international conferences it hosts,
also becoming one of the largest convention centres in the world.
The presence of the EU and the other international bodies has, for example, led to there being more ambassadors and journalists in Brussels than in
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
The city hosts 120 international institutions, 181
embassies
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually denotes a ...
() and more than 2,500
diplomat
A diplomat (from ; romanization, romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state (polity), state, International organization, intergovernmental, or Non-governmental organization, nongovernmental institution to conduct diplomacy with one ...
s, making it the second centre of diplomatic relations in the world (after
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
).
International school
International schools are private schools that promote education in an international environment or framework. Although there is no uniform definition or criteria, international schools are usually characterised by a multinational student body an ...
s have also been established to serve this presence.
The "international community" in Brussels numbers at least 70,000 people. In 2009, there were an estimated 286
lobbying
Lobbying is a form of advocacy, which lawfully attempts to directly influence legislators or government officials, such as regulatory agency, regulatory agencies or judiciary. Lobbying involves direct, face-to-face contact and is carried out by va ...
consultancies known to work in Brussels. Finally, Brussels has more than 1,400
NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
s.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization
The
Treaty of Brussels
The Treaty of Brussels, also referred to as the Brussels Pact, was the founding treaty of the Western Union (WU) between 1948 and 1954, when it was amended as the Modified Brussels Treaty (MTB) and served as the founding treaty of the Western Eu ...
, which was signed on 17 March 1948 between Belgium,
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
,
Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
, the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
and the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, was a prelude to the establishment of the
intergovernmental military alliance
A military alliance is a formal Alliance, agreement between nations that specifies mutual obligations regarding national security. In the event a nation is attacked, members of the alliance are often obligated to come to their defense regardless ...
which later became the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). , the alliance consists of 32 independent member countries across
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
and Europe. Several countries also have diplomatic missions to NATO
through embassies in Belgium. Since 1949, a number of
NATO Summits
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental transnational military alliance of 32 member states—30 European and 2 North American. Established in the aftermath ...
have been held in Brussels, the most recent taking place in June 2021.
The organisation's political and administrative
headquarters
Headquarters (often referred to as HQ) notes the location where most or all of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. The term is used in a wide variety of situations, including private sector corporations, non-profits, mil ...
are located on the / in
Haren, on the north-eastern perimeter of the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
. A new €750 million headquarters building begun in 2010 and was completed in 2017.
Eurocontrol
The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol, is an
international organisation
''International Organization'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that covers the entire field of international relations, international affairs. It was established in 1947 and is published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of th ...
which coordinates and plans
air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled air ...
across European
airspace
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as outer space which is t ...
. The corporation was founded in 1960 and has 41 member states.
Its headquarters are located in Haren, Brussels.
Demographics
Population

Brussels is located in one of the most
urbanised regions of Europe, between
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
,
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, the
Rhine-Ruhr
The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region () is the Metropolitan regions in Germany, largest metropolitan region in Germany, with over ten million inhabitants. A wikt:polycentric, polycentric conurbation with several major urban concentrations, the reg ...
(Germany), and the
Randstad
The Randstad (; "Rim City" or "Edge City") is a roughly crescent- or Circular arc, arc-shaped conurbation in the Netherlands, that includes almost half the country's population. With a central-western location, it connects and comprises the Net ...
(Netherlands). The Brussels-Capital Region has a population of around 1.2 million and has witnessed, in recent years, a remarkable increase in its population. In general, the population of Brussels is younger than the national average, and the gap between rich and poor is wider.
Brussels is the core of a built-up area that extends well beyond the region's limits. Sometimes referred to as the urban area of Brussels (, ) or Greater Brussels (, ), this area extends over a large part of the two Brabant provinces, including much of the surrounding
arrondissement of Halle-Vilvoorde
The Halle-Vilvoorde Arrondissement () is one of the two administrative arrondissements in the Belgian province of Flemish Brabant. It almost completely surrounds the Brussels-Capital Region and lies to the west of the other arrondissement in the ...
and some small parts of the
arrondissement of Leuven
The Leuven Arrondissement (; ) is one of two arrondissements in the Belgian province of Flemish Brabant. It lies east of the Brussels-Capital Region. The arrondissement has an area of and has (as of January 1, 2017) 502,602 inhabitants.
Munic ...
in
Flemish Brabant
Flemish Brabant ( ; ) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Hainaut and East Flanders. Flemish Brabant also ...
, as well as the northern part of
Walloon Brabant
Walloon Brabant ( ; ; ) is a province located in Belgium's French-speaking region of Wallonia. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the province of Flemish Brabant (Flemish Region) and the provinces of Liège, Namur and Hainaut. Walloon Br ...
.
The metropolitan area of Brussels is divided into three levels. Firstly, the central agglomeration (within the regional borders), with a population of 1,218,255 inhabitants.
Adding the closest suburbs (, ) gives a total population of 1,831,496. Including the outer
commuter
Commuting is periodically recurring travel between a place of residence and place of work or study, where the traveler, referred to as a commuter, leaves the boundary of their home community. By extension, it can sometimes be any regular o ...
zone (
Brussels Regional Express Network
The Brussels S Train, also known as the Brussels Regional Express Network ( or RER; or GEN) is a suburban rail system in and around the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It will offer fast connections and increased frequency within a radius ...
(RER/GEN) area), the population is 2,676,701.
Brussels is also part of a wider
diamond-shaped conurbation
A conurbation is a region consisting of a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which, through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ...
, with
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
,
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
and
Leuven
Leuven (, , ), also called Louvain (, , ), is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipalit ...
, which has about 4.4 million inhabitants (a little more than 40% of the Belgium's total population).
Nationalities
There have been numerous migrations towards Brussels since the end of the 18th century, when the city acted as a common destination for
political refugees from neighbouring or more distant countries, particularly France. From 1871, many of the
Paris Communards fled to Brussels, where they received political asylum. Other notable international exiles living in Brussels at the time included
Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo, vicomte Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romanticism, Romantic author, poet, essayist, playwright, journalist, human rights activist and politician.
His most famous works are the novels ''The Hunchbac ...
,
Karl Marx
Karl Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' (written with Friedrich Engels) ...
,
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (, ; ; 1809 – 19 January 1865) was a French anarchist, socialist, philosopher, and economist who founded mutualist philosophy and is considered by many to be the "father of anarchism". He was the first person to ca ...
,
Georges Boulanger
Georges Ernest Jean-Marie Boulanger (29 April 1837 – 30 September 1891), nicknamed Général Revanche ("General Revenge"), was a French general and politician. An enormously popular public figure during the second decade of the Third Repub ...
,
Paul Verlaine
Paul-Marie Verlaine ( ; ; 30 March 1844 – 8 January 1896) was a French poet associated with the Symbolism (movement), Symbolist movement and the Decadent movement. He is considered one of the greatest representatives of the ''fin de siècle'' ...
,
Arthur Rimbaud
Jean Nicolas Arthur Rimbaud (, ; ; 20 October 1854 – 10 November 1891) was a French poet known for his transgressive and surreal themes and for his influence on modern literature and arts, prefiguring surrealism.
Born in Charleville, he s ...
, and
Léon Daudet
Léon Daudet (; 16 November 1867 – 2 July 1942) was a French journalist, writer, an active monarchist, and a member of the Académie Goncourt.
Move to the right
Daudet was born in Paris. His father was the novelist Alphonse Daudet, his m ...
, to name a few. Attracted by the industrial opportunities, many workers moved in, first from the other
Belgian provinces
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province, nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead ...
(mainly rural residents from
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
) and France, then from
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, C ...
an, and more recently from
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
an and
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
n countries.
Since the second half of the 20th century, Brussels has been home to a large number of immigrants and
émigré
An ''émigré'' () is a person who has emigrated, often with a connotation of political or social exile or self-exile. The word is the past participle of the French verb ''émigrer'' meaning "to emigrate".
French Huguenots
Many French Hugueno ...
communities, as well as labour migrants, former foreign students or
expatriate
An expatriate (often shortened to expat) is a person who resides outside their native country.
The term often refers to a professional, skilled worker, or student from an affluent country. However, it may also refer to retirees, artists and ...
s, and many Belgian families in Brussels can claim at least one foreign grandparent. At the last Belgian census in 1991, 63.7% of inhabitants in Brussels-Capital Region answered that they were Belgian citizens, born as such in Belgium, indicating that more than a third of residents had not been born in the country.
[ – The linguistic situation in Belgium (and in particular various estimations of the population speaking French and Dutch in Brussels) is discussed in detail.] According to
Statbel (the Belgian Statistical Office), in 2020, taking into account the nationality of birth of the parents, 74.3% of the population of the Brussels-Capital Region was of foreign origin and 41.8% was of non-European origin (including 28.7% of African origin). Among those aged under 18, 88% were of foreign origin and 57% of non-European origin (including 42.4% of African origin).
This large concentration of immigrants and their descendants includes many of
Moroccan (mainly
Riffian and other
Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
) and
Turkish ancestry, together with French-speaking black Africans from former
Belgian colonies, such as the
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
,
Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
and
Burundi
Burundi, officially the Republic of Burundi, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is located in the Great Rift Valley at the junction between the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa, with a population of over 14 million peop ...
. Many immigrants were
naturalised
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-national of a country acquires the nationality of that country after birth. The definition of naturalization by the International Organization for Migration of the ...
following the great 1991 reform of the naturalisation process. In 2012, about 32% of city residents were of non-Belgian
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an origin (mainly expatriates from France, Romania, Italy, Spain, Poland, and Portugal) and 36% were of another background, mostly from Morocco, Turkey and
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
. Among all major migrant groups from outside the EU, a majority of the permanent residents have acquired Belgian nationality.
Languages
Brussels was historically
Dutch-speaking, using the
Brabantian dialect
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic or Brabantine (, , ), is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant, which corresponded mainly to the Netherlands, Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgi ...
,
but since the 19th century
has become the predominant language of the city.
The main cause of this transition was the rapid
assimilation of the local
Flemish population,
amplified by immigration from
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and
Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the c ...
.
The
rise of French in public life gradually began by the end of the 18th century,
quickly accelerating after
Belgian independence.
Dutch — of which
standardisation
Standardization (American English) or standardisation (British English) is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organiza ...
in Belgium was still very weak
— could not compete with French, which was the exclusive language of the judiciary, the administration, the army, education, cultural life and the media, and thus necessary for
social mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given socie ...
.
The value and prestige of the French language was universally acknowledged
to such an extent that after 1880,
and more particularly after the turn of the 20th century,
proficiency in French among Dutch-speakers in Brussels increased spectacularly.
Although a majority of the population remained bilingual until the second half of the 20th century,
family transmission of the historic Brabantian dialect
declined, leading to an increase of monolingual French-speakers from 1910 onwards.
From the mid-20th century, the number of monolingual French-speakers surpassed the number of mostly bilingual Flemish inhabitants.
This process of assimilation weakened after the 1960s,
as the
language border
A language border or language boundary is the line separating two language areas. The term is generally meant to imply a lack of mutual intelligibility between the two languages. If two adjacent languages or dialects are mutually intelligible, n ...
was fixed, the status of Dutch as an official language of Belgium was reinforced,
and the economic centre of gravity shifted northward to
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
.
However, with the continuing arrival of immigrants and the post-war emergence of Brussels as a
centre of international politics, the relative position of Dutch continued to decline.
Furthermore, as Brussels' urban area expanded,
a further number of Dutch-speaking municipalities in the
Brussels periphery
The Brussels Periphery (, i.e. the "Brussels Rim", or ''Vlaamse Rand'', i.e. the "Flemish Rim", or just ''De Rand'', "the Rim"; ) refers to 19 Flemish municipalities that encircle the Brussels-Capital Region. The Brussels Region is an enclave of ...
also became predominantly French-speaking.
This phenomenon of expanding Francisation — dubbed "oil slick" by its opponents
— is, together with the future of Brussels,
one of the most controversial topics in
Belgian politics.

Since its creation in 1989, the Brussels-Capital Region has been legally bilingual, with both French and Dutch having official status,
as is the administration of the 19 municipalities.
The creation of this bilingual, full-fledged region, with its own competencies and jurisdiction, had long been hampered by different visions of Belgian federalism. Nevertheless, some communitarian issues remain.
Flemish political parties demanded, for decades, that the Flemish part of
Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde
Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde (; ) is a judicial arrondissement encompassing the bilingual— French and Dutch—Brussels-Capital Region, which coincides with the administrative arrondissement of Brussels-Capital and the surrounding Dutch-speaking ...
(BHV) ''arrondissement'' be separated from the Brussels Region (which made Halle-Vilvoorde a monolingual Flemish electoral and judicial district). BHV was divided mid-2012. The French-speaking population regards the language border as artificial and demands the extension of the bilingual region to at least all six
municipalities with language facilities
In Belgium, there are 27 municipalities with language facilities (; ; ), which must offer linguistic services to residents in Dutch, French, or German in addition to their single official languages. All other municipalities – with the except ...
in the surroundings of Brussels. Flemish politicians have strongly rejected these proposals.
Owing to migration and to its international role, Brussels is home to a large number of native speakers of languages other than French or Dutch. Currently, about half of the population speaks a home language other than these two.
In 2013, academic research showed that approximately 17% of families spoke none of the official languages in the home, while in a further 23% a foreign language was used alongside French. The share of unilingual French-speaking families had fallen to 38% and that of Dutch-speaking families to 5%, while the percentage of bilingual Dutch-French families reached 17%. At the same time, French remains widely spoken: in 2013, French was spoken "well to perfectly" by 88% of the population, while for Dutch this percentage was only 23% (down from 33% in 2000);
the other most commonly known languages were English (30%), Arabic (18%), Spanish (9%), German (7%) and Italian and Turkish (5% each).
Meanwhile, surveys from 2023 to 2024 suggest that 29% of the population speaks only languages other than French and Dutch in the home, while residents speak a total of 104 languages, up from 72 in 2001.
Despite the rise of English as a second language in Brussels, including as an unofficial compromise language between French and Dutch, as well as the working language for some of its international businesses and institutions, French remains the ''lingua franca'' and all public services are conducted exclusively in French or Dutch.
The original dialect of Brussels (known as
Brusselian, and also sometimes referred to as Marols or Marollien), a form of
Brabantic (the variant of Dutch spoken in the ancient
Duchy of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant, a Imperial State, state of the Holy Roman Empire, was established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant of 1085–1183, and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries. The Duchy comprised part of the Bu ...
) with a significant number of loanwords from French, still survives among a small minority of inhabitants called ''Brusseleers''
[Mary Anne Evans, ''Frommer's Brussels and Bruges Day by Day. First Edition'' (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2008), 71.] (or ''Brusseleirs''), many of them quite bi- and multilingual, or educated in French and not writing in Dutch.
The ethnic and national self-identification of Brussels' inhabitants is nonetheless sometimes quite distinct from the French and Dutch-speaking communities. For the French-speakers, it can vary from Francophone Belgian,
(French
demonym
A demonym (; ) or 'gentilic' () is a word that identifies a group of people ( inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place ( hamlet, village, town, city, region, ...
for an inhabitant of Brussels),
Walloon (for people who migrated from the Walloon Region at an adult age); for Flemings living in Brussels, it is mainly either Dutch-speaking Belgian, Flemish or (Dutch demonym for an inhabitant), and often both. For the ''Brusseleers'', many simply consider themselves as belonging to Brussels.
Religions
Historically, Brussels has been predominantly
Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, especially since the expulsion of
Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
in the 16th century. This is clear from the large number of historical churches in the region, particularly in the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
. The pre-eminent Catholic
cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
in Brussels is the
Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula, serving as the
co-cathedral
A co-cathedral is a cathedral church which shares the function of being a bishop's seat, or ''cathedra'', with another cathedral, often in another city (usually a former see, anchor city of the metropolitan area or the civil capital). Instances o ...
of the
Archdiocese of Mechelen–Brussels. On the north-western side of the region, the
National Basilica of the Sacred Heart is a
Minor Basilica
Basilicas are Catholic church buildings that have a designation, conferring special privileges, given by the Pope. Basilicas are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building need not be a basilica in the architectura ...
and
parish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the Church (building), church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in com ...
, as well as one of the
largest churches by area in the world. The
Church of Our Lady of Laeken
The Church of Our Lady of Laeken (; ) is a Catholic parish church in the Brussels district of Laeken, Belgium. Built in neo-Gothic style, it was originally erected in memoriam of Queen Louise-Marie, wife of King Leopold I, to the design of th ...
holds the tombs of many members of the
Belgian royal family
The monarchy of Belgium is the constitutional and hereditary institution of the monarchical head of state of the Kingdom of Belgium. As a popular monarchy, the Belgian monarch uses the title king/queen of the Belgians and serves as the ...
, including all the former
Belgian monarchs, within the
Royal Crypt.
In reflection of its multicultural makeup, Brussels hosts a variety of religious communities, as well as large numbers of
atheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
and
agnostics
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, the divine, or the supernatural is either unknowable in principle or unknown in fact. (page 56 in 1967 edition) It can also mean an apathy towards such religious belief and refer to ...
. Minority faiths include Islam,
Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
,
Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
,
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, and Buddhism. According to a 2016 survey, approximately 40% of residents of Brussels declared themselves Catholics (12% were practising Catholics and 28% were non-practising Catholics), 30% were
non-religious
Irreligion is the absence or rejection of religious beliefs or practices. It encompasses a wide range of viewpoints drawn from various philosophical and intellectual perspectives, including atheism, agnosticism, religious skepticism, ration ...
, 23% were
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
(19% practising, 4% non-practising), 3% were Protestants and 4% were of another religion.
As guaranteed by Belgian law, recognised religions and non-religious philosophical organisations (, )
enjoy public funding and school courses. It was once the case that every pupil in an official school from 6 to 18 years old had to choose two hours per week of compulsory religious—or non-religious-inspired morals—courses. However, in 2015, the
Belgian Constitutional Court
The Constitutional Court ( Dutch: ; ; ) plays a central role within the federal Belgian state. This is a judicial court founded in 1980. Its jurisdiction was augmented in 1988 and 2003.
History
Founded as the Court of Arbitration, the court owe ...
ruled religious studies could no longer be required in the
primary
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Work ...
and
secondary educational systems.
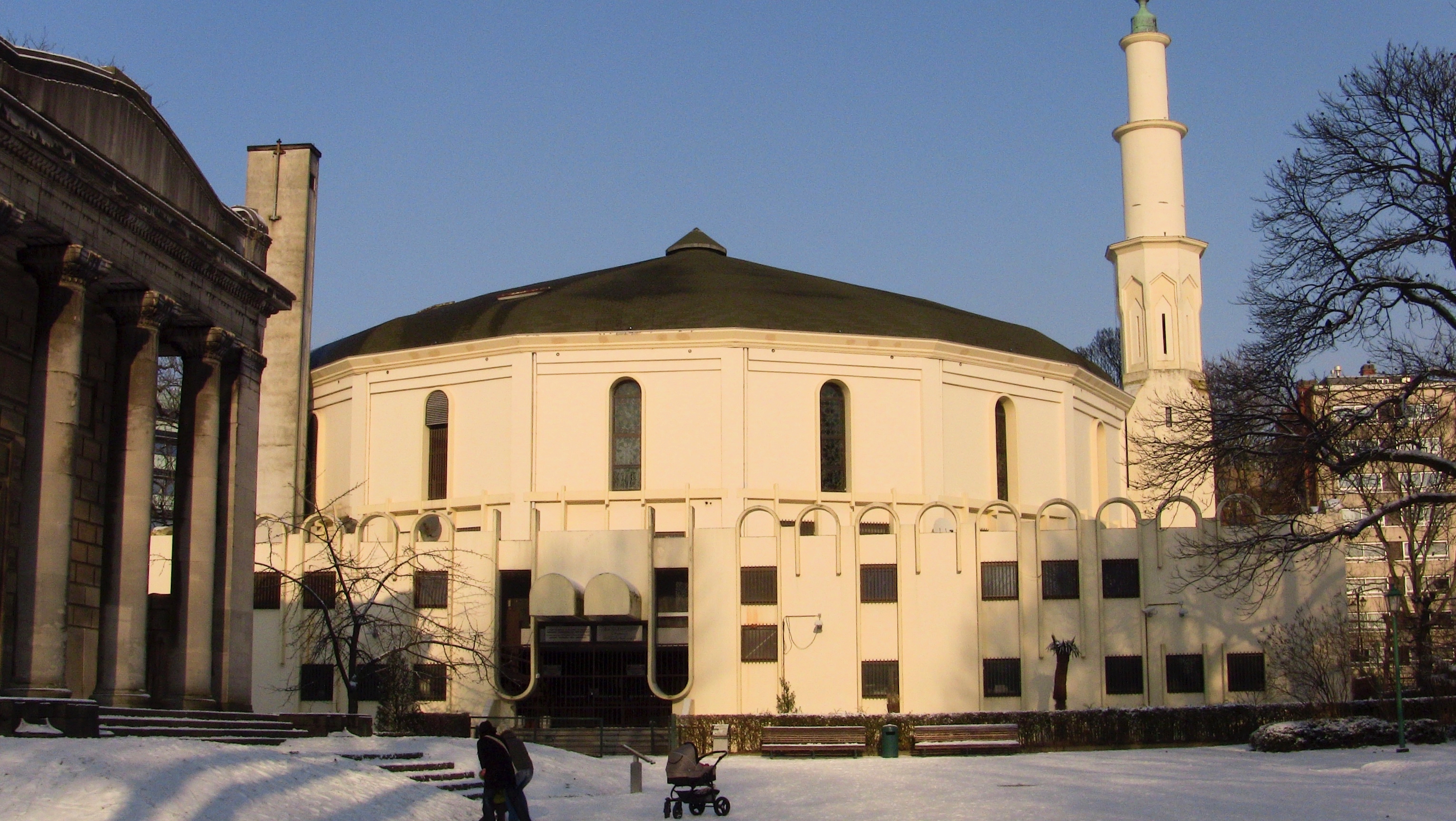

Brussels has a large concentration of
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, mostly of Moroccan, Turkish, Syrian and Guinean ancestry. The
Great Mosque of Brussels
The Great Mosque of Brussels (; ) is located in the Cinquantenaire, Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark. Originally built in 1897 as an exhibition attraction, it was transformed into a Muslim place of worship in 1978 by Saudi Arabia, which managed ...
, located in the
Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark, is the oldest
mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard.
Originally, mosques were si ...
in Brussels and the former seat of the Islamic and Cultural Centre of Belgium. Belgium does not collect statistics by ethnic background or religious beliefs, so exact figures are unknown. It was estimated that, in 2005, people of Muslim background living in the Brussels Region numbered 256,220 and accounted for 25.5% of the city's population, a much higher concentration than those of the other regions of Belgium.
Architecture
The architecture in Brussels is diverse, and spans from the clashing combination of
Gothic,
Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
, and
Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
styles on the
Grand-Place
The (French language, French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central Town square, square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque architecture, Baroque guildhalls of ...
to the
postmodern
Postmodernism encompasses a variety of artistic, cultural, and philosophical movements that claim to mark a break from modernism. They have in common the conviction that it is no longer possible to rely upon previous ways of depicting the wo ...
buildings of the
EU institutions
The institutions of the European Union are the seven principal decision-making bodies of the European Union and Euratom governed under the Treaties of the European Union and European Union law. They are, as listed in Article 13 of the Treaty ...
.

Very little
medieval architecture
Medieval architecture was the architecture, art and science of designing and constructing buildings in the Middle Ages. The major styles of the period included pre-Romanesque, Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, and Gothic architecture, Gothic. In ...
is preserved in Brussels. Buildings from that period are mostly found in the historical centre (called the ),
Saint Géry/Sint-Goriks and / neighbourhoods. The
Brabantine Gothic
Brabantine Gothic, occasionally called Brabantian Gothic, is a significant variant of Gothic architecture that is typical for the Low Countries. It surfaced in the first half of the 14th century at St. Rumbold's Cathedral in the city of Mechele ...
Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula remains a prominent feature in the skyline of downtown Brussels. Isolated portions of the
first city walls were saved from destruction and can be seen to this day. One of the only remains of the
second walls is the
Halle Gate. The Grand-Place is the main attraction in the city centre and has been a
UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
since 1998. The square is dominated by the 15th century
Flamboyant
Flamboyant () is a lavishly-decorated style of Gothic architecture that appeared in France and Spain in the 15th century, and lasted until the mid-sixteenth century and the beginning of the Renaissance.Encyclopedia Britannica, "Flamboyant style ...
Town Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or municipal hall (in the Philippines) is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses the city o ...
, the
neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half of the 19th century ...
''
Breadhouse'' and the Baroque
guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a guild hall or guild house, is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Europe, with many surviving today in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commo ...
s of the former
Guilds of Brussels
The Guilds of Brussels (; ), grouped in the Nine Nations of Brussels (; ), were associations of craft guilds that dominated the economic life of Brussels in the late medieval and early modern periods. From 1421 onwards, they were represented in ...
. ''
Manneken Pis
(; ) is a landmark bronze fountain sculpture in central Brussels, Belgium, depicting a puer mingens; a Nudity, naked little boy urinating into the fountain's basin. Though its existence is attested as early as the mid-15th century, ''Manneke ...
'', a fountain containing a small
bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
sculpture of a urinating youth, is a tourist attraction and
symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
of the city.

The
neoclassical style of the 18th and 19th centuries is represented in the
Royal Quarter
The Royal Quarter ( or ; or ) is a quarter in the historic upper town of Brussels, Belgium. It is situated between Brussels Park, the Royal Palace, the Mont des Arts/Kunstberg and the Sablon/Zavel. It is an excellent example of 18th-ce ...
/
Coudenberg
The Palace of Coudenberg (; ) was a royal residence situated on the Coudenberg or Koudenberg (; Dutch for "Cold Hill"), a hill in what is today the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. For nearly 700 years, the Castle and then Palace of Couden ...
area, around
Brussels Park
Brussels Park ( ; or ) is the largest urban public park in central Brussels, Belgium. The park was formerly known and is still sometimes colloquially referred to as the Royal Park ( ; ). It was the city's first public park, being originally ...
and the
Place Royale/Koningsplein. Examples include the
Royal Palace
This is a list of royal palaces, sorted by continent.
Africa
Americas
Asia
Europe
Oceania
{, class="wikitable" width="95%"
, - bgcolor="white"
!align=center, Residence
!align=center, Photo
!align=center, City
!align=cen ...
, the
Church of St. James on Coudenberg, the
Palace of the Nation
The Palace of the Nation (; ; ) is a neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium, housing the Belgian Federal Parliament. The Parliament consists of both the Chamber of Representatives (lower house) and the Senate (upper house), which convene in ...
(Parliament building), the
Academy Palace
The Academy Palace or Palace of the Academies ( ; or ) is a Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally built between 1823 and 1828 for William II of the Netherlands, Prince William II of Orange. No ...
, the
Palace of Charles of Lorraine
The Palace of Charles of Lorraine (; ) is a neoclassical palace in the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. Its construction started in 1757 to serve as the residence of the Governor of the Habsburg Netherlands, Prince Charles Alexander of L ...
, the
Palace of the Count of Flanders
The Palace of the Count of Flanders (; ) is a neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally built between 1776 and 1781 for Countess Brigitte of Tirimont-Templeuve, though it was heavily expanded in the 19th century. Nowadays, it ...
and the
Egmont Palace
The Egmont Palace (, ; ), also sometimes known as the Arenberg Palace (; ), is a neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally built between 1548 and 1560 for Countess Françoise of Luxembourg and Count Lamoral of Egmont, though ...
. Other uniform neoclassical ensembles can be found around the
Place des Martyrs/Martelaarsplein and the /. Some additional landmarks in the centre are the
Royal Saint-Hubert Galleries (1847), one of the oldest covered shopping arcades in Europe, the
Congress Column
The Congress Column ( ; ) is a monumental column in Brussels, Belgium, commemorating the creation of the Belgian Constitution by the National Congress of 1830–31. Inspired by Trajan's Column in Rome, it was erected between 1850 and 1859, ...
(1859), the former
Brussels Stock Exchange
The Brussels Stock Exchange ( ; ), abbreviated to BSE, was founded in Brussels, Belgium, by decree of Napoleon in 1801. In 2002, the BSE merged with the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, Amsterdam, Lisbon Stock Exchange, Lisbon and Paris Bourse, Paris ...
building (1873) and the
Palace of Justice (1883). The latter, designed by
Joseph Poelaert
Joseph Poelaert (21 March 1817 – 3 November 1879) was a Belgium, Belgian architect. He was entrusted with important projects in Brussels, such as Saint Catherine's Church, Brussels, Saint Catherine's Church, the Church of Our Lady of Laeken, t ...
, in
eclectic style, is reputed to be the largest building constructed in the 19th century.
Located outside the historical centre, in a greener environment bordering the
European Quarter, are the
Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark with its
memorial arcade and nearby museums, and in
Laeken
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is a residential suburb in the north-western part of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It belongs to the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality of the ...
, the
Royal Palace of Laeken and the
Royal Domain
Crown land, also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. Today, in Commonwealth realm ...
with its large
greenhouses
A greenhouse is a structure that is designed to regulate the temperature and humidity of the environment inside. There are different types of greenhouses, but they all have large areas covered with transparent materials that let sunlight pass an ...
, as well as the
Museums of the Far East
The Museums of the Far East (; ) is a complex of three museums in Laeken, in the north-west of the City of Brussels, Belgium. Consisting of the Chinese Pavilion, the Japanese Tower and the Museum of Japanese Art, it is dedicated to Asian art, O ...
.
Also particularly striking are the buildings in the
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
style, most famously by the Belgian architects
Victor Horta
Victor Pierre Horta (; Victor, Baron Horta after 1932; 6 January 1861 – 8 September 1947) was a Belgian architect and designer, and one of the founders of the Art Nouveau movement. He was a fervent admirer of the French architectural theoris ...
,
Paul Hankar
Paul Hankar (; 11 December 1859 – 17 January 1901) was a Belgian architect and furniture designer, and an innovator in the Art Nouveau style.
Career
Hankar was born at Frameries, in Hainaut, Belgium, the son of a stonemason. He studied at ...
and
Henry Van de Velde
Henry Clemens van de Velde (; 3 April 1863 – 15 October 1957) was a Belgian painter, architect, interior designer, and art theorist. Together with Victor Horta and Paul Hankar, he is considered one of the founders of Art Nouveau in Belgium ...
. Some of Brussels' municipalities, such as
Schaerbeek
(French language, French, ; former History of Dutch orthography, Dutch spelling) or (modern Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Reg ...
,
Etterbeek
Etterbeek (; ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the municipalities of Auderghem, the Cit ...
,
Ixelles
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Pentagon (Brussels), Brusse ...
, and
Saint-Gilles, were developed during the heyday of Art Nouveau and have many buildings in that style. The
Major Town Houses of the Architect Victor Horta—
Hôtel Tassel
The Hôtel Tassel (; ) is a historic town house in Brussels, Belgium. It was designed by Victor Horta for the scientist and professor Emile Tassel, and built between 1892 and 1893, in Art Nouveau style. It is considered one of the first buil ...
(1893),
Hôtel van Eetvelde (1898),
Hôtel Solvay (1900) and the
Horta Museum (1901)—have been listed as a
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
since 2000.
Another example of Brussels' Art Nouveau is the
Stoclet Palace
The Stoclet Palace ( ; ) is a mansion in Brussels, Belgium. It was designed by the Austrian architect Josef Hoffmann for the Belgian financier Adolphe Stoclet. Built between 1905 and 1911 in the Vienna Secession style, it is located at 279� ...
(1911), by the Viennese architect
Josef Hoffmann
Josef Hoffmann (15 December 1870 – 7 May 1956) was an Austrians, Austrian-Sudeten Germans, Moravian architect and designer. He was among the founders of Vienna Secession and co-establisher of the Wiener Werkstätte. His most famous architect ...
, designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in June 2009.
Art Nouveau in Brussels
The Art Nouveau movement of architecture and design first appeared in Brussels, Belgium, in the early 1890s, and quickly spread to France and to the rest of Europe. It began as a reaction against the formal vocabulary of European academic art, ...
">
File:Victor Horta Hotel Tassel.JPG,
Hôtel Tassel
The Hôtel Tassel (; ) is a historic town house in Brussels, Belgium. It was designed by Victor Horta for the scientist and professor Emile Tassel, and built between 1892 and 1893, in Art Nouveau style. It is considered one of the first buil ...
by
Victor Horta
Victor Pierre Horta (; Victor, Baron Horta after 1932; 6 January 1861 – 8 September 1947) was a Belgian architect and designer, and one of the founders of the Art Nouveau movement. He was a fervent admirer of the French architectural theoris ...
(1893)
File:Tassel House stairway-00.JPG, Stairway in the Hôtel Tassel
File:Hôtel Ciamberlani (DSCF7523).jpg,
Hôtel Albert Ciamberlani
The Hôtel Albert Ciamberlani (; ), occasionally also referred to as the Hôtel Veuve Ciamberlani (meaning ''House of Widow Ciamberlani''), is a historic Townhouse, town house in Brussels, Belgium. It was built in 1897 as the private residence ...
by
Paul Hankar
Paul Hankar (; 11 December 1859 – 17 January 1901) was a Belgian architect and furniture designer, and an innovator in the Art Nouveau style.
Career
Hankar was born at Frameries, in Hainaut, Belgium, the son of a stonemason. He studied at ...
(1897)
File:Old England facade, Brussels (DSCF7544).jpg, Former
Old England department store by
Paul Saintenoy (1899)
File:Maison Saint-Cyr (DSCF7558).jpg,
Saint-Cyr House by
Gustave Strauven (1903)
File:Maison Cauchie-445.jpg,
Cauchie House
The Cauchie House (; ) is a historic town house in Brussels, Belgium. It was designed by the architect, painter, and designer , and built in 1905, in Art Nouveau style. Its façade is remarkable for its allegorical sgraffito decoration.
The ho ...
by
Paul Cauchie (1905)
File:Maison Cauchie sgraffitopaneel.jpg, ''
Sgraffito
(; ) is an artistic or decorative technique of scratching through a coating on a hard surface to reveal parts of another underlying coating which is in a contrasting colour. It is produced on walls by applying layers of plaster tinted in con ...
'' panel in the Cauchie House
File:20120923 Brussels PalaisStoclet Hoffmann DSC06725 PtrQs.jpg,
Stoclet Palace
The Stoclet Palace ( ; ) is a mansion in Brussels, Belgium. It was designed by the Austrian architect Josef Hoffmann for the Belgian financier Adolphe Stoclet. Built between 1905 and 1911 in the Vienna Secession style, it is located at 279� ...
by
Josef Hoffmann
Josef Hoffmann (15 December 1870 – 7 May 1956) was an Austrians, Austrian-Sudeten Germans, Moravian architect and designer. He was among the founders of Vienna Secession and co-establisher of the Wiener Werkstätte. His most famous architect ...
(1911)
Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
structures in Brussels include the Résidence Palace (1927) (now part of the
Europa building
The Europa building is the seat of the European Council and Council of the European Union, located on the Rue de la Loi, Rue de la Loi/Wetstraat in the Brussels and the European Union#European Quarter, European Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. It ...
), the
Centre for Fine Arts
The Centre for Fine Arts (, ; , ) is a multi-purpose cultural venue in the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. It is often referred to as BOZAR (a homophone of ''Beaux-arts'') in French or by its initials PSK in Dutch. This multidisciplinary s ...
(1928), the
Villa Empain
The Villa Empain is a former private residence in Brussels, Belgium, which currently serves as a cultural centre and exhibition space. Built in 1930–1934 in Art Deco style by the Swiss-Belgian architect Michel Polak, the villa was commission ...
(1934), the
Town Hall of Forest (1938), and the
Flagey Building
The Flagey Building (; ), also known as the Radio House (; ), is a building located in Ixelles, a municipality of Brussels, Belgium, housing the Flagey cultural centre. It is located on the south-western corner of the Place Eugène Flagey/Eug ...
(also known as the ''Radio House'') on the
Place Eugène Flagey/Eugène Flageyplein (1938) in Ixelles. Some religious buildings from the
interwar era
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ...
were also constructed in that style, such as the
Church of St. John the Baptist (1932) in Molenbeek and the
Church of St. Augustine (1935) in Forest. Completed only in 1969, and combining Art Deco with
neo-Byzantine
Neo-Byzantine architecture (also referred to as Byzantine Revival) was a Revivalism (architecture), revival movement, most frequently seen in religious, institutional and public buildings. It incorporates elements of the Byzantine architecture, ...
elements, the
Basilica of the Sacred Heart in
Koekelberg
Koekelberg (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren, Jette, and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean. In common with al ...
is one of the
largest churches by area in the world, and its
cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, usually dome-like structure on top of a building often crowning a larger roof or dome. Cupolas often serve as a roof lantern to admit light and air or as a lookout.
The word derives, via Ital ...
provides a panoramic view of Brussels and its outskirts. Another example are the exhibition halls of the Centenary Palace, built for the
1935 World's Fair on the
Heysel/Heizel Plateau in northern Brussels, home to the Brussels Exhibition Centre (
Brussels Expo).

The
Atomium
The Atomium ( , , ) is a landmark modernist building in Brussels, Belgium, originally constructed as the centrepiece of the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (Expo 58). Designed by the engineer André Waterkeyn and the architects André and Jean Pol ...
is a symbolic
modernist
Modernism was an early 20th-century movement in literature, visual arts, and music that emphasized experimentation, abstraction, and Subjectivity and objectivity (philosophy), subjective experience. Philosophy, politics, architecture, and soc ...
structure, located on the Heysel Plateau, which was originally built for the 1958 World's Fair (
Expo 58
Expo 58, also known as the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (; ), was a world's fair held on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Brussels, Belgium, from 17 April to 19 October 1958. It was the first major world's fair registered under the Bureau Internati ...
). It consists of nine steel spheres connected by tubes, and forms a model of an
iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
(specifically, a
unit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector
In mathematics, a unit vector i ...
), magnified 165 billion times. The architect
André Waterkeyn devoted the building to science. It is now considered a
landmark
A landmark is a recognizable natural or artificial feature used for navigation, a feature that stands out from its near environment and is often visible from long distances.
In modern-day use, the term can also be applied to smaller structures ...
of Brussels. Next to the Atomium, is
Mini-Europe
Mini-Europe is a miniature park located in the Bruparck entertainment park, at the foot of the Atomium, in Brussels, Belgium. Mini-Europe has reproductions of monuments in the European Union and other countries within the continent of Europe on ...
miniature park
A miniature park is a display of miniature buildings and models, usually as a recreational and tourist attraction open to the public. A miniature park may contain a model of a single city or town, often called a miniature city or model village, o ...
, with 1:25 scale
maquette
A ''maquette'' is a scale model or rough draft of an unfinished sculpture or work of architecture. The term is a loanword from French. An equivalent term is ''bozzetto'', a diminutive of the Italian word for a sketch.
Sculpture
A maquette ...
s of famous buildings from across Europe.
Since the second half of the 20th century, modern office towers have been built in Brussels (
Madou Tower,
Rogier Tower
The Rogier Tower (; ) is a skyscraper located in the Northern Quarter central business district of Brussels, Belgium. It owes its name to the Place Charles Rogier/Karel Rogierplein on which it is situated. It is the fifth tallest building in ...
,
Proximus Towers
The Proximus Towers (; ) are twin skyscrapers on the / in the Northern Quarter central business district of Brussels, Belgium. The buildings take their name from the telecommunications company Proximus. They were formerly known as the Belgacom ...
,
Finance Tower
The Finance Tower (; ) is a skyscraper in the Northern Quarter central business district of Brussels, Belgium. It was designed by the architects Hugo Van Kuyck, Marcel Lambrichs and Léon Stynen and built between 1968 and 1982. The height of ...
, the
World Trade Center
World Trade Centers are the hundreds of sites recognized by the World Trade Centers Association.
World Trade Center may also refer to:
Buildings
* World Trade Center (1973–2001), a building complex that was destroyed during the September 11 at ...
, among others). There are some thirty towers, mostly concentrated in the city's
main business district: the
Northern Quarter (also called ''Little Manhattan''), near
Brussels-North railway station
Brussels-North railway station (; ) is one of the three major railway stations in Brussels, Belgium; the other two are Brussels Central Station, Brussels-Central and Brussels-South railway station, Brussels-South. Every regular domestic and i ...
. The
South Tower, standing adjacent to
Brussels-South railway station
Brussels-South railway station, also known as Brussels-Midi railway station (; ), is a major railway station in Brussels, Belgium. Geographically, it is located in Saint-Gilles, Belgium, Saint-Gilles/Sint-Gillis on the border with the adjacent ...
, is the
tallest building in Belgium, at . Along the
North–South connection
The North–South connection (; ) is a railway link of national and international importance through central Brussels, Belgium, that connects the major railway stations in the city. It is line 0 (zero) of the Belgian rail network. With 1200 t ...
, is the State Administrative Centre, an administrative complex in the
International Style
The International Style is a major architectural style and movement that began in western Europe in the 1920s and dominated modern architecture until the 1970s. It is defined by strict adherence to Functionalism (architecture), functional and Fo ...
. The postmodern buildings of the
Espace Léopold
The Espace Léopold (French; commonly used in English) or Leopoldruimte (Dutch; ) is the complex of parliament buildings in Brussels, Belgium, housing the European Parliament, a legislative chamber of the European Union (EU). It consists of a ...
complete the picture.
The city's embrace of modern architecture translated into an ambivalent approach towards historic preservation, leading to the destruction of notable architectural landmarks, most famously the
Maison du Peuple/Volkshuis by Victor Horta, a process known as
Brusselisation.
Culture
Visual arts and museums

Brussels
contains over 80 museums. The
Royal Museums of Fine Arts has an extensive collection of various painters, such as
Flemish old masters like
Bruegel,
Rogier van der Weyden
Rogier van der Weyden (; 1399 or 140018 June 1464), initially known as Roger de le Pasture (), was an Early Netherlandish painting, early Netherlandish painter whose surviving works consist mainly of religious triptychs, altarpieces, and commis ...
,
Robert Campin
Robert Campin (Valenciennes (France) c. 1375 - Tournai (Belgium) 26 April 1444) now usually identified with the Master of Flémalle (earlier the Master of the Merode Triptych, before the discovery of three other similar panels), was a master pai ...
,
Anthony van Dyck
Sir Anthony van Dyck (; ; 22 March 1599 – 9 December 1641) was a Flemish Baroque painting, Flemish Baroque artist who became the leading court painter in England after success in the Spanish Netherlands and Italy.
The seventh child of ...
,
, and
Peter Paul Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens ( ; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish painting, Flemish artist and diplomat. He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque painting, Flemish Baroque tradition. Rubens' highly charged comp ...
. The
Magritte Museum
The Magritte Museum (; ) is an art museum in the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium, dedicated to the work of the Belgian Surrealism, surrealist artist René Magritte. It is one of the constituent museums of the Royal Museums of Fine Arts of B ...
houses the world's largest collection of works by the
surrealist
Surrealism is an art movement, art and cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists aimed to allow the unconscious mind to express itself, often resulting in the depiction of illogical or dreamlike s ...
artist
René Magritte
René François Ghislain Magritte (; 21 November 1898 – 15 August 1967) was a Belgium, Belgian surrealist artist known for his depictions of familiar objects in unfamiliar, unexpected contexts, which often provoked questions about the nature ...
. Museums dedicated to the national history of Belgium include the
BELvue Museum, the
Royal Museums of Art and History
The Royal Museums of Art and History (RMAH) (; ) are a group of museums in Brussels, Belgium. They are part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office (BELSPO) and consist of five museums: the Art & History Museum, the ...
, and the
Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History
The Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History (; ), also known as the Royal Military Museum (; ), is a military museum that occupies the two northernmost halls of the historic complex in the Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark in Br ...
. The
Musical Instruments Museum (MIM), housed in the
Old England building, is part of the Royal Museums of Art and History, and is internationally renowned for its collection of over 8,000 instruments.
The Brussels Museums Council is an independent body for all the museums in the Brussels-Capital Region, covering around 100 federal, private, municipal, and community museums. It promotes member museums through the Brussels Card (giving access to public transport and 30 of the 100 museums), the Brussels Museums Nocturnes (every Thursday from 5 p.m. to 10 p.m. from mid-September to mid-December) and the Museum Night Fever (an event for and by young people on a Saturday night in late February or early March).
Brussels has had a distinguished artist scene for many years. The famous Belgian surrealists René Magritte and
Paul Delvaux
Paul Delvaux (; 23 September 1897 – 20 July 1994) was a Belgian painter noted for his dream-like scenes of women, classical architecture, trains and train stations, and skeletons, often in combination. He is often considered a surrealist, alt ...
, for instance, studied and lived there, as did the
avant-garde
In the arts and literature, the term ''avant-garde'' ( meaning or ) identifies an experimental genre or work of art, and the artist who created it, which usually is aesthetically innovative, whilst initially being ideologically unacceptable ...
dramatist
Michel de Ghelderode
Michel de Ghelderode (born Adémar Adolphe Louis Martens; 3 April 1898 – 1 April 1962) was an avant-garde Demographics of Belgium, Belgian dramatist, from Flanders, who spoke and wrote in French. His works often dealt with the extremes of huma ...
. The city was also home of the
impressionist
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by visible brush strokes, open Composition (visual arts), composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passage ...
painter
Anna Boch
Anna-Rosalie Boch (10 February 1848 – 25 February 1936), known as Anna, was a Belgium, Belgian Painting, painter, art collector, and the only female member of the artistic group, Les XX. Born in La Louvière, Saint-Vaast, Hainaut Province, Hai ...
from the artists' group ''
Les XX
''Les XX'' ( French; "''Les Vingt''"; ; ) was a group of twenty Belgian painters, designers and sculptors, formed in 1883 by the Brussels lawyer, publisher, and entrepreneur Octave Maus. For ten years, they held an annual exhibition of their a ...
'', and includes other famous Belgian painters such as
Léon Spilliaert
Léon Spilliaert (also Leon Spilliaert; 28 July 1881 – 23 November 1946) was a Belgian draughtsman, illustrator, lithographer and painter. In his early career, he contributed to the development of symbolism in the visual arts in Belgium ...
. Brussels is also a capital of the
comic strip
A comic strip is a Comics, sequence of cartoons, arranged in interrelated panels to display brief humor or form a narrative, often Serial (literature), serialized, with text in Speech balloon, balloons and Glossary of comics terminology#Captio ...
;
some treasured Belgian characters are
Tintin
Tintin usually refers to:
* ''The Adventures of Tintin'', the comics series by Belgian cartoonist Hergé
** Tintin (character), the protagonist and titular character of the series
Tintin or Tin Tin may also refer to:
Material related to ''The A ...
,
Lucky Luke
''Lucky Luke'' is a Western (genre), Western bande dessinée, comic album series created by Belgian cartoonist Morris (cartoonist), Morris in 1946. Morris wrote and drew the series single-handedly until 1955, after which he started collaborati ...
,
The Smurfs
''The Smurfs'' (; ) is a Belgian comic franchise centered on a fictional colony of small, blue, humanoid creatures who live in mushroom-shaped houses in the forest. ''The Smurfs'' was created and introduced as a series of comic characters by ...
,
Spirou,
Gaston
Gaston is a masculine given name of French origin and a surname. The name "Gaston" may refer to:
People
First name
*Gaston I, Count of Foix (1287–1315)
* Gaston II, Count of Foix (1308–1343)
*Gaston III, Count of Foix (1331–1391)
*Gaston ...
,
Marsupilami
''Marsupilami'' is a comic book character and fictional animal species created by André Franquin. Its first appearance was in the 31 January 1952 issue of the Franco-Belgian comics magazine '' Spirou''. Since then it appeared regularly in th ...
,
Blake and Mortimer,
Boule et Bill
''Boule et Bill'' (known in English as ''Billy & Buddy'') is a popular comics, comic, created in 1959 by Franco-Belgian comics, Belgian Comic book creator, writer-artist Jean Roba in collaboration with Maurice Rosy. In 2003, the artistic responsib ...
and
Cubitus
''Cubitus'' is a Franco-Belgian comics series, and the basis for the ''Wowser'' cartoon series appearing in the United States. ''Cubitus'' was created by the Belgian cartoonist Dupa, and features Cubitus, a large anthropomorphic dog, who liv ...
(see
Belgian comics
Belgian comics are a distinct subgroup in the comics history, and played a major role in the development of European comics, alongside France with whom they share a long common history. While the comics in the two major language groups and r ...
). Throughout the city, walls are painted with large motifs of comic book characters; these
mural
A mural is any piece of Graphic arts, graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.
Word mural in art
The word ''mural'' ...
s taken together are known as
Brussels' Comic Book Route.
Also, the interiors of some
Metro stations are designed by artists. The
Belgian Comic Strip Center combines two artistic leitmotifs of Brussels, being a museum devoted to Belgian comic strips, housed in the former ''Magasins Waucquez'' textile department store, designed by
Victor Horta
Victor Pierre Horta (; Victor, Baron Horta after 1932; 6 January 1861 – 8 September 1947) was a Belgian architect and designer, and one of the founders of the Art Nouveau movement. He was a fervent admirer of the French architectural theoris ...
in the
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
style. In addition,
street art
Street art is visual art created in public locations for public visibility. It has been associated with the terms "independent art", "post-graffiti", "neo-graffiti" and guerrilla art.
Street art has evolved from the early forms of defiant gr ...
is changing the landscape of this multicultural city.
Performing arts venues and festivals
Brussels is well known for its
performing arts
The performing arts are arts such as music, dance, and drama which are performed for an audience. They are different from the visual arts, which involve the use of paint, canvas or various materials to create physical or static art objects. P ...
scene, with the
Royal Theatre of La Monnaie, the
Royal Park Theatre
The Royal Park Theatre (; ) is a theatre in central Brussels, Belgium. It is located at 3, Rue de la Loi, rue de la Loi/Wetstraat, on the edge of Brussels Park, facing the Belgian Federal Parliament, Belgian House of Parliament (Palace of the N ...
, the
Théâtre Royal des Galeries, and the
Kaaitheater among the most notable institutions.
The
Kunstenfestivaldesarts, an international performing arts festival, is organised every year in May. Its main hub is the Kaaitheater, but performances and artworks are also hosted in around 30 venues throughout the city.
The
King Baudouin Stadium
The King Baudouin Stadium ( ; ) is a sports ground in Brussels, Belgium. Located in the north-western district of the City of Brussels, it was built to embellish the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in view of the 1935 Brussels International Exposition ...
is a concert and competition facility with a 50,000 seat capacity, the largest in Belgium. The site was formerly occupied by the
Heysel Stadium. The
Centre for Fine Arts
The Centre for Fine Arts (, ; , ) is a multi-purpose cultural venue in the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. It is often referred to as BOZAR (a homophone of ''Beaux-arts'') in French or by its initials PSK in Dutch. This multidisciplinary s ...
(often referred to as BOZAR in French or PSK in Dutch), a multi-purpose centre for theatre, cinema, music, literature, and art exhibitions, is home to the
National Orchestra of Belgium
The Belgian National Orchestra (, ) is a Belgian orchestra, based in Brussels. Its principal concert venue is the Brussels Centre for Fine Arts (BOZAR). The orchestra also gives concerts outside Brussels in such cities as Sankt-Vith and Hasselt. ...
and to the annual
Queen Elisabeth Competition
The Queen Elisabeth Competition (, ) is an international competition for career-starting musicians held in City of Brussels, Brussels. The competition is named after Elisabeth of Bavaria, Queen of Belgium, Queen Elisabeth of Belgium (1876–1 ...
for
classical singers and instrumentalists, one of the most challenging and prestigious competitions of the kind. Studio 4 in
Le Flagey cultural centre hosts the
Brussels Philharmonic
The Brussels Philharmonic is a Belgian orchestra located in Brussels. Formerly known as the Groot Symfonie-Orkest, BRT Philharmonic Orchestra, and later as the Flemish Radio Orchestra, the orchestra has been linked to the Flemish public broadc ...
.
Other concert venues include
Forest National/Vorst Nationaal, the
Ancienne Belgique
The (''AB'') is a concert hall for contemporary music in Brussels, Belgium. Located in the historic heart of Brussels, it is one of the leading concert venues in Belgium, hosting a wide variety of international and local acts. Some 300,000 pe ...
, the
Cirque Royal/Koninklijk Circus, the
Botanique and
Palais 12/Paleis 12. Furthermore, the
Jazz Station in
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode ( French, ) or Sint-Joost-ten-Node ( Dutch, ), often simply called Saint-Josse in French or Sint-Joost in Dutch, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part o ...
is a museum and archive on
jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
, and a venue for jazz concerts.
Other cultural events and festivals
Many events are organised or hosted in Brussels throughout the year. In addition, many festivals animate the Brussels scene.
The
Iris Festival is the official festival of the Brussels-Capital Region and is held annually in spring. The International Fantastic Film Festival of Brussels (BIFFF) is organised during the Easter holidays and the
Magritte Award
A Magritte Award (, ) is an accolade presented by the Académie André Delvaux of Belgium to recognize cinematic achievement in the film industry. Modelled after the French César Award, the formal ceremony at which the awards are presented is on ...
s in February. The
Festival of Europe, an open day and activities in and around the institutions of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, is held on 9 May. On
Belgian National Day
Belgian National Day (; ; ) is the national holiday of Belgium commemorated annually on 21 July. It is one of the country's ten public holidays and marks the anniversary of the investiture of Leopold I as the first King of the Belgians in 1 ...
, on 21 July, a military parade and celebrations take place on the / and in
Brussels Park
Brussels Park ( ; or ) is the largest urban public park in central Brussels, Belgium. The park was formerly known and is still sometimes colloquially referred to as the Royal Park ( ; ). It was the city's first public park, being originally ...
, ending with a fireworks display in the evening.
Some summer festivities include
Couleur Café Festival, a festival of
world
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that Existence, exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk ...
and
urban music
Urban contemporary music, also known as urban music, urban pop, or just simply urban, is a music radio format. The term was coined by New York radio DJ Frankie Crocker in the early to mid-1970s as a synonym for Black music. Urban contemporary r ...
, around the end of June or early July, the
Brussels Summer Festival (BSF), a music festival in August, the
Midi Fair, the most important yearly fair in Brussels, lasting more than a month, in July and August, and Brussels Beach, when the banks of the
canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
are turned into a temporary urban beach. Other biennial events are the
Zinneke Parade
The Zinneke Parade is a biennial parade held in the City of Brussels, Belgium, since 2000. It is a cultural event organised by the Zinneke Association that brings together at each edition about 2,500 participants and attracts between 50,000 an ...
, a colourful, multicultural parade through the city, which has been held since 2000 in May, as well as the popular
Flower Carpet at the
Grand-Place
The (French language, French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central Town square, square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque architecture, Baroque guildhalls of ...
in August.
Heritage Days are organised on the third weekend of September (sometimes coinciding with the car-free day) and are a good opportunity to discover the wealth of buildings, institutions and real estate in Brussels. The "Winter Wonders" animate the heart of Brussels in December; these winter activities were launched in Brussels in 2001.
Folklore

Brussels' identity owes much to its rich folklore and traditions, among the liveliest in the country.
The
Ommegang
Ommegang or Ommeganck (Dutch language, Dutch: "walk around" (the church, village or city), ) is the generic name for various medieval medieval pageant, pageants celebrated in the Low Countries (areas that are now within Belgium, the Netherlands, ...
, a folkloric costumed procession, commemorating the
Joyous Entry
A Joyous Entry (; ) is a ceremonial event marking the entry into a city by a monarch, prince, duke, or governor in parts of modern-day Belgium. Originating in the Middle Ages, it generally coincided with the affirmation or extension of the city' ...
of
Emperor Charles V
Charles V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain (as Charles I) from 1516 to 1556, and Lord of the Netherlands as titular Duke of Burgundy (as Charles II) fr ...
and his son Philip II of Spain, Philip II in the city in 1549, takes place every year in July. The colourful parade includes floats, traditional processional giants, such as Saint Michael and Saint Gudula, and scores of folkloric groups, either on foot or on horseback, dressed in medieval garb. The parade ends in a Medieval pageant, pageant on the
Grand-Place
The (French language, French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central Town square, square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque architecture, Baroque guildhalls of ...
. Since 2019, it has been recognised as a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity by
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
.
The Meyboom, an even-older folk tradition of Brussels (1308), celebrating the "Maypole, May tree"—in fact, a corruption of the Dutch word, meaning ''tree of joy''—takes place paradoxically on 9 August. After parading a young beech in the city, it is planted in a joyful spirit with lots of music, ''Brusseleir'' songs, and processional giants. It has also been recognised as an expression of intangible cultural heritage by UNESCO, as part of the bi-national inscription "Processional giants and dragons in Belgium and France". The celebration is reminiscent of the town's long-standing (folkloric) feud with
Leuven
Leuven (, , ), also called Louvain (, , ), is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipalit ...
, which dates back to the Middle Ages.
Saint Verhaegen (often shortened to ''St V''), a folkloric student procession, celebrating the anniversary of the founding of the (ULB) and the (VUB), is held on 20 November. Since 2019, it has also been listed as intangible cultural heritage of the Brussels-Capital Region.
Another good introduction to the ''Brusseleir'' Brusselian dialect, local dialect and way of life can be obtained at the Royal Theatre Toone, a folkloric theatre of marionettes, located a stone's throw away from the Grand-Place. Finally, two famous folkloric plays, ''Le Mariage de Mademoiselle Beulemans'' by Frantz Fonson and Fernand Wicheler, and ''Bossemans et Coppenolle'' by Joris d'Hanswyck and Paul Van Stalle, are still the subject of regular revivals.
Cuisine

Brussels is well known for its local
waffle
A waffle is a dish made from leavened Batter (cooking), batter or dough that is cooked between two plates that are patterned to give a characteristic size, shape, and surface impression. There are many variations based on the type of waffle iron ...
, its
chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
, its
French fries
French fries, or simply fries, also known as chips, and finger chips (Indian English), are '' batonnet'' or '' julienne''-cut deep-fried potatoes of disputed origin. They are prepared by cutting potatoes into even strips, drying them, and f ...
and its numerous types of
beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the ...
s. The Brussels sprout, which has long been popular in Brussels, and may have originated there, is also named after the city.
Owing to Brussels' cosmopolitan population, almost every national cuisine in the world can be found there. The gastronomic offer includes approximately 1,800 restaurants (including three 2-starred and ten 1-starred Michelin Guide, Michelin restaurants), and a number of bars. In addition to the traditional restaurants, there are many cafés, bistros and the usual range of international Fast food restaurant, fast food chains. The cafés are similar to bars, and offer beer and light dishes; coffee houses are called (literally "tea salons"). Also widespread are brasseries, which usually offer a variety of beers and typical national dishes.
Belgian cuisine is known among connoisseurs as one of the best in Europe. It is characterised by the combination of French cuisine with the more hearty Flemish fare. Notable specialities include Brussels waffles (gaufres) and mussels (usually as moules frites, ''moules-frites'', served with fries). The city is a stronghold of
chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
and praline (Belgian chocolate), praline manufacturers with renowned companies like Côte d'Or (chocolate), Côte d'Or, Chocolatier Neuhaus, Neuhaus, Leonidas (chocolate maker), Leonidas and Godiva Chocolatier, Godiva. Pralines were first introduced in 1912 by Jean Neuhaus II, a Belgian chocolatier of Swiss origin, in the
Royal Saint-Hubert Galleries. Numerous friteries are spread throughout the city, and in tourist areas, fresh hot waffles are also sold on the street.
As well as other Beer in Belgium, Belgian beers, the spontaneously fermented lambic style, brewed in and around Brussels, is widely available there and in the nearby
Senne valley where the wild yeasts that ferment it have their origin.
Kriek, a cherry lambic, is available in almost every bar or restaurant in Brussels.
Brussels is known as the birthplace of the Belgian endive. The technique for growing Blanching (horticulture), blanched endives was accidentally discovered in the 1850s at the Botanical Garden of Brussels in
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode ( French, ) or Sint-Joost-ten-Node ( Dutch, ), often simply called Saint-Josse in French or Sint-Joost in Dutch, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part o ...
.
Shopping
Famous shopping areas in Brussels include the pedestrian-only Rue Neuve (Brussels), Rue Neuve/Nieuwstraat, the second busiest shopping street in Belgium (after the Meir, Antwerp, Meir, in
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
) with a weekly average of 230,000 visitors, home to popular international chains (H&M, C&A, Zara (retailer), Zara, Primark), as well as the City 2 and Anspach galleries.
The
Royal Saint-Hubert Galleries hold a variety of luxury shops and some six million people stroll through them each year. The neighbourhood around the / has become, in recent years, a focal point for fashion and design; this main street and its side streets also feature Belgium's young and most happening artistic talent.
In Ixelles, the / and the Namur Gate area offer a blend of luxury shops, fast food restaurants and entertainment venues, and the /, in the mainly-Congolese ''Ixelles#Matongé, Matongé'' district, offers a taste of African fashion and lifestyle. The nearby
Avenue Louise/Louizalaan is lined with high-end fashion stores and boutiques, making it one of the most expensive streets in Belgium.
There are shopping centres outside the inner ring: Basilix, Woluwe Shopping Center, Westland Shopping Center, and Docks Bruxsel, which opened in October 2017.
In addition, Brussels ranks as one of Europe's best capital cities for flea market shopping. The ''Old Market'', on the Place du Jeu de Balle, Place du Jeu de Balle/Vossenplein, in the Marollen, Marolles/Marollen neighbourhood, is particularly renowned. The nearby Sablon (Brussels), Sablon/Zavel area is home to many of Brussels' antique dealers. The ''Midi Market'' around Brussels-South station and the / is reputed to be one of the largest markets in Europe.
Sports

Sport in Brussels is under the responsibility of the Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, Communities. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
The
King Baudouin Stadium
The King Baudouin Stadium ( ; ) is a sports ground in Brussels, Belgium. Located in the north-western district of the City of Brussels, it was built to embellish the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in view of the 1935 Brussels International Exposition ...
(formerly the Heysel Stadium) is the largest in the country and home to the national teams in Belgium national football team, football and Belgium national rugby union team, rugby union. It hosted the final of the 1972 UEFA European Football Championship, and the opening game of Euro 2000, the 2000 edition. Several European club finals have been held at the ground, including the 1985 European Cup Final which saw 39 deaths due to hooliganism and structural collapse. The King Baudouin Stadium is also home of the annual Memorial Van Damme athletics event, Belgium's foremost track and field competition, which is part of the Diamond League. Other important athletics events are the Brussels Marathon and the 20 km of Brussels, an annual run with 30,000 participants.
Football

R.S.C. Anderlecht, based in the Constant Vanden Stock Stadium in
Anderlecht
Anderlecht (; ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the south-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Forest, B ...
, is the most successful Belgian football club in the Belgian Pro League, with 34 titles. It has also won the most major European tournaments for a Belgian side, with 6 European titles. Brussels is also home to Union Saint-Gilloise, the most successful Belgian club before World War II, with 11 titles. The club was founded in
Saint-Gilles but is based in nearby
Forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
, and plays in the Belgian Pro League. RWDM47, Racing White Daring Molenbeek, based in
Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western p ...
, and often referred to as RWDM, is a very popular football club that, since 2023, is back playing in the Belgian Pro League.
Other Brussels clubs that played in the national series over the years were Royal White Star Bruxelles, Ixelles SC, Crossing Club de Schaerbeek (born from a merger between RCS de Schaerbeek and Crossing Club Molenbeek), Scup Jette, RUS de Laeken, Racing Jet de Bruxelles, AS Auderghem, KV Wosjot Woluwe and FC Ganshoren.
Cycling
Brussels is home to notable cycling races. The city is the arrival location of the Brussels Cycling Classic, formerly known as Paris–Brussels, which is one of the oldest classic cycle races, semi classic Road bicycle racing, bicycle races on the international calendar. From World War I until the early 1970s, the Six Days of Brussels was organised regularly. In the last decades of the 20th century, the Grand Prix Eddy Merckx was also held in Brussels.
Economy

Serving as the centre of administration for Belgium and Europe, Brussels' economy is largely Tertiary sector of the economy, service-oriented. It is dominated by regional and world headquarters of Multinational corporation, multinationals, by European institutions, by various local and federal administrations, and by related services companies, though it does have a number of notable craft industries, such as the Cantillon Brewery, a lambic brewery founded in 1900.

Brussels has a robust economy. The region contributes to one fifth of Belgium's GDP, and its 550,000 jobs account for 17.7% of Belgium's employment. Its
GDP per capita
This is a list of countries by nominal GDP per capita. GDP per capita is the total value of a country's finished goods and services (gross domestic product) divided by its total population (per capita).
Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita is ...
is nearly double that of Belgium as a whole,
and it has the highest GDP per capita of any Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics, NUTS 1 region in the EU, at ~$80,000 in 2016. That being said, the GDP is boosted by a massive inflow of commuters from neighbouring regions; over half of those who work in Brussels live in Flanders or Wallonia, with 230,000 and 130,000 commuters per day respectively. Conversely, only 16.0% of people from Brussels work outside Brussels (68,827 (68.5%) of them in Flanders and 21,035 (31.5%) in Wallonia). Not all of the wealth generated in Brussels remains in Brussels itself, and , the unemployment among residents of Brussels is 20.4%.
There are approximately 50,000 businesses in Brussels, of which around 2,200 are foreign. This number is constantly increasing and can well explain the role of Brussels in Europe. The city's infrastructure is very favourable in terms of starting up a new business. House prices have also increased in recent years, especially with the increase of young professionals settling down in Brussels, making it the most expensive city to live in Belgium. In addition, Brussels holds more than 1,000 business conferences annually, making it the ninth most popular conference city in Europe.
Brussels is rated as the 34th most important financial centre in the world as of 2020, according to the Global Financial Centres Index. The Brussels Stock Exchange, abbreviated to BSE, now called
Euronext Brussels
The Brussels Stock Exchange ( ; ), abbreviated to BSE, was founded in Brussels, Belgium, by decree of Napoleon in 1801. In 2002, the BSE merged with the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, Amsterdam, Lisbon Stock Exchange, Lisbon and Paris Bourse, Paris ...
, is part of the European stock exchange Euronext, along with Paris Bourse, Lisbon Stock Exchange and Amsterdam Stock Exchange. Its benchmark stock market index is the BEL20.
Media
Brussels is a centre of both media and communications in Belgium, with many Belgian television stations, radio stations, newspapers and telephone companies having their headquarters in the region. The French-language public broadcaster RTBF, the Dutch-language public broadcaster Vlaamse Radio- en Televisieomroeporganisatie, VRT, the two regional channels BX1 (formerly Télé Bruxelles) and Bruzz (formerly TV Brussel), the encrypted BeTV (Belgium), BeTV channel and private channels RTL-TVI and VTM (TV channel), VTM are headquartered in Brussels. Some national newspapers such as Le Soir, La Libre, De Morgen and the news agency Belga (news agency), Belga are based in or around Brussels. The Belgian Mail, postal company bpost, as well as the telecommunication companies and mobile operators Proximus, Orange Belgium and Telenet (Belgium), Telenet are all located there.
As English is spoken widely,
several English media organisations operate in Brussels. The most popular of these are the English-language daily news media platform and bi-monthly magazine ''The Brussels Times'' and the website ''The Bulletin (Brussels weekly), The Bulletin''. Dutch-language public broadcaster VRT has als
English versionof its online news. The multilingual Pan-European identity, pan-European news channel Euronews also maintains an office in Brussels.
Education
Tertiary education

There are several universities in Brussels. Except for the Royal Military Academy (Belgium), Royal Military Academy, a federal military college established in 1834, all universities in Brussels are private and autonomous. The Royal Military Academy also the only Belgian university organised on the boarding school model.
The Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), a French-speaking university, with about 20,000 students, has three campuses in the city, and the
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (Dutch language, Dutch, ; lit. Free University of Brussels; abbreviated VUB) is a Dutch- and English-speaking research university in Brussels, Belgium. It has four campuses: Brussels Humanities, Science and Engine ...
(VUB), its
Dutch-speaking sister university, has about 10,000 students. Both universities originate from a single ancestor university, founded in 1834, namely the
Free University of Brussels, which was split in 1970, at about the same time the Flemish and French Communities gained legislative power over the organisation of higher education.
Saint-Louis University, Brussels (also known as UCLouvain Saint-Louis – Bruxelles) was founded in 1858 and is specialised in social and human sciences, with 4,000 students, and located on two campuses in the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
and
Ixelles
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Pentagon (Brussels), Brusse ...
. From September 2018 on, the university uses the name ''UCLouvain'', together with the Université catholique de Louvain, Catholic University of Louvain, in the context of a merger between both universities.
Still other universities have campuses in Brussels, such as the French-speaking Catholic University of Louvain (UCLouvain), which has 10,000 students in the city with its medical faculties at UCLouvain Bruxelles Woluwe since 1973, in addition to its Faculty of Architecture, Architectural Engineering and Urban Planning and UCLouvain's Dutch-speaking sister Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (KU Leuven) (offering bachelor's and master's degrees in economics & business, law, arts, and architecture; 4,400 students). In addition, the University of Kent's Brussels School of International Studies is a specialised postgraduate school offering advanced international studies.
Also a dozen of university colleges are located in Brussels, including two drama schools, founded in 1832: the French-speaking Conservatoire royal de Bruxelles, Conservatoire Royal and its
Dutch-speaking equivalent, the Koninklijk Conservatorium (Brussel), Koninklijk Conservatorium.
Primary and secondary education
Most of Brussels pupils between the ages of 3 and 18 go to schools organised by the French-speaking Community or the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community (, ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the ...
, with close to 80% going to French-speaking schools, and roughly 20% to Dutch-speaking schools. Due to the post-war international presence in the city, there are also a number of international schools, including the International School of Brussels, with 1,450 pupils, between the ages of and 18, the British School of Brussels, and the four European Schools, which provide free education for the children of those working in the
EU institutions
The institutions of the European Union are the seven principal decision-making bodies of the European Union and Euratom governed under the Treaties of the European Union and European Union law. They are, as listed in Article 13 of the Treaty ...
. The combined student population of the four European Schools in Brussels is around 10,000.
Libraries

Brussels has a number of public or private-owned libraries on its territory. Most public libraries in Brussels fall under the competence of the Communities and are usually separated between French-speaking and Dutch-speaking institutions, although some are mixed.
The Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) is the national library of Belgium and one of the most prestigious libraries in the world. It owns several collections of historical importance, like the famous Fétis archives, and is the depository for all books ever published in Belgium or abroad by Belgian authors. It is located on the Mont des Arts, Mont des Arts/Kunstberg in central Brussels, near the Brussels Central Station, Central Station.
There are several academic libraries and archives in Brussels. The libraries of the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) and the
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (Dutch language, Dutch, ; lit. Free University of Brussels; abbreviated VUB) is a Dutch- and English-speaking research university in Brussels, Belgium. It has four campuses: Brussels Humanities, Science and Engine ...
(VUB) constitute the largest ensemble of university libraries in the city. In addition to the ''Solbosch'' location, there are branches in ''La Plaine'' and ''Erasme''/''Erasmus''. Other academic libraries include those of Saint-Louis University, Brussels and the Université catholique de Louvain, Catholic University of Louvain (UCLouvain).
Science and technology

Science and technology in Brussels is well-developed with the presence of several List of universities in Belgium, universities and research institutes. The Brussels-Capital Region is home to several national science and technology institutes including the National Fund for Scientific Research (NFSR), the Institute for the Encouragement of Scientific Research and Innovation of Brussels (ISRIB), the Royal Academies for Science and the Arts of Belgium (RASAB) and the Belgian Academy Council of Applied Sciences (BACAS). Several science parks associated with the universities are also spread over the region.
The Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, located in Leopold Park, houses the world's largest hall completely dedicated to dinosaurs, with its collection of 30 fossilised ''Iguanodon'' skeletons. In addition, the Planetarium (Belgium), Planetarium of the Royal Observatory of Belgium (part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office), on the Heysel Plateau in
Laeken
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is a residential suburb in the north-western part of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It belongs to the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality of the ...
, is one of the largest in Europe.
Healthcare
Brussels is home to a thriving Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and health care industry which includes pioneering biotechnology research. The health sector employs 70,000 employees in 30,000 companies. There are 3,000 life sciences researchers in the city and two large science parks: Da Vinci Research Park and Erasmus Research Park. There are five university hospitals, a military hospital and more than 40 general hospitals and specialist clinics.
Due to Languages of Belgium, its bilingual nature, hospitals in the Brussels-Capital Region can be either monolingual French, monolingual Dutch, or bilingual, depending on their nature. University hospitals belong to one of the two Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, linguistic communities and are thus monolingual French or Dutch by law. Other hospitals managed by a public authority must be legally bilingual. Private hospitals are legally not bound to either language, but most cater to both. However, all hospital emergency services in the Capital Region (whether part of a public or private hospital) are required to be bilingual, since patients transported by emergency ambulance cannot choose the hospital they will be brought to.
Transport
Brussels has an extensive network of both private or public transportation means. Public transportation includes Brussels buses, Brussels trams, trams, and Brussels Metro, metro (all three operated by the Brussels Intercommunal Transport Company (STIB/MIVB)), as well as a set of railway lines (operated by Infrabel) and railway stations served by public trains (operated by the National Railway Company of Belgium (NMBS/SNCB)). Air transport is available via one of the city's two airports (
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport is the main international airport of Belgium. It is located in the municipality of Zaventem in Flemish Brabant, northeast of Brussels. Also informally known as Brussels-National Airport or Brussels-Zaventem Airport, Brussels ...
and Brussels South Charleroi Airport), and boat transport is available via the Port of Brussels. Bicycle-sharing and car-sharing public systems are also available.
The complexity of the Belgian political landscape makes some transportation issues difficult to solve. The Brussels-Capital Region is surrounded by the Flemish Region, Flemish and Wallonia, Walloon regions, which means that the airports, as well as many roads serving Brussels (most notably the Brussels Ring) are located in the other two Belgian regions. The city is relatively car-dependent by northern European standards and is considered to be the most congested city in the world according to the INRIX traffic survey.
Air
The Brussels-Capital Region is served by two airports, both located outside of the administrative territory of the region. The most notable is
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport is the main international airport of Belgium. It is located in the municipality of Zaventem in Flemish Brabant, northeast of Brussels. Also informally known as Brussels-National Airport or Brussels-Zaventem Airport, Brussels ...
, located in the nearby Flemish municipality of
Zaventem
Zaventem () is a municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant, in the Flemish region of Belgium. It is located in the Dijleland area, one of the three large recreational areas which together form the '' Groene Gordel'' ("Green Belt") around th ...
, east of the capital, which can be accessed by highway (A201), train, taxi and bus. Brussels National Airport has its own railway station. This station is located in the underground (level -1) of the airport terminal building itself. The secondary airport is Brussels South Charleroi Airport, located in Gosselies, a part of the city of
Charleroi
Charleroi (, , ; ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It is the largest city in both Hainaut and Wallonia. The city is situated in the valley of the Sambre, in the south-west of Belgium, not ...
(
Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the c ...
), some south-west of Brussels, which can be accessed by highway (E19 then E420) or a private bus. There is also Melsbroek Air Base, located in Steenokkerzeel, a military airport which shares its infrastructure with Brussels Airport. The aforementioned airports are also the main airports of Belgium.
Water
Since the 16th century, Brussels has had its own harbour, the Port of Brussels. It has been enlarged throughout the centuries to become the second Belgian inland port. Historically situated near the Place Sainte-Catherine, Place Sainte-Catherine/Sint-Katelijneplein, it lies today to the north-west of the region, on the Brussels–Scheldt Maritime Canal (commonly called Willebroek Canal), which connects Brussels to
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
via the Scheldt. Ships and large barges up to can penetrate deep into the country, avoiding break-ups and load transfers between Antwerp and the centre of Brussels, hence reducing the cost for companies using the canal, and thus offering a competitive advantage.
Moreover, the connection of the Willebroek Canal with the
Brussels–Charleroi Canal
The Brussels–Charleroi Canal (; ), also known as the Charleroi Canal amongst other similar names, is an important canal in Belgium. The canal is quite large, with a Class IV Freycinet gauge, and its Walloon portion is long. It runs from Ch ...
, in the very heart of the capital, creates a north–south link, by means of waterways, between the Netherlands, Flanders and the industrial zone of Hainaut (province), Hainaut (
Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the c ...
). There, navigation can access the network of French canals, thanks to the important Canal inclined plane, inclined plane of Ronquières inclined plane, Ronquières and the lifts of Strépy-Bracquegnies.
The importance of river traffic in Brussels makes it possible to avoid the road equivalent of 740,000 trucks per year—almost 2,000 per day—which, in addition to easing traffic problems, represents an estimated carbon dioxide saving of per year.
Train

The Brussels-Capital Region has three main train stations: Brussels-South railway station, Brussels-South, Brussels-Central and Brussels-North railway station, Brussels-North, which are also the busiest of the country.
Brussels-South is also served by direct high-speed rail links: to London by Eurostar trains via the Channel Tunnel; to Amsterdam by Thalys and ''InterCity'' connections; to Amsterdam, Paris, and
Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
by Thalys; and to Cologne and Frankfurt by the German Intercity Express, ICE.
The train rails in Brussels go underground, near the centre, through the
North–South connection
The North–South connection (; ) is a railway link of national and international importance through central Brussels, Belgium, that connects the major railway stations in the city. It is line 0 (zero) of the Belgian rail network. With 1200 t ...
, with Brussels Central Station also being largely underground. The tunnel itself is only six tracks wide at its narrowest point, which often causes congestion and delays due to heavy use of the route.
The
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
has minor railway stations at Bockstael railway station, Bockstael, Brussels-Chapel railway station, Brussels-Chapel, Brussels-Congress railway station, Brussels-Congress, Brussels-Luxembourg railway station, Brussels-Luxembourg, Schuman station, Brussels-Schuman, Brussels-West station, Brussels-West, Haren railway station (Brussels), Haren, Haren-South railway station, Haren-South and Simonis metro station, Simonis. In the Brussels Region, there are also railways stations at Berchem-Sainte-Agathe railway station, Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Boitsfort railway station, Boitsfort, Boondael railway station, Boondael, Bordet railway station, Bordet (Evere), Etterbeek railway station, Etterbeek, Evere railway station, Evere, Forest-East railway station, Forest-East, Forest-South railway station, Forest-South, Jette railway station, Jette, Meiser railway station, Meiser (Schaerbeek), Moensberg railway station, Moensberg (Uccle), Saint-Job railway station, Saint-Job (Uccle), Schaerbeek railway station, Schaarbeek, Uccle-Calevoet railway station, Uccle-Calevoet, Uccle-Stalle railway station, Uccle-Stalle, Vivier d'Oie-Diesdelle (Uccle), Merode station, Merode and Watermael railway station, Watermael.
Public transport
The Brussels Intercommunal Transport Company (STIB/MIVB) is the local public transport operator in Brussels. It covers the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region and some surface routes extend to the near suburbs in the other two regions, linking with the De Lijn network in
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
and the TEC (transport), TEC network in
Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the c ...
.
Metro, trams and buses
The
Brussels Metro
The Brussels Metro ( ; ) is a rapid transit system serving a large part of the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It consists of four conventional metro lines and three '' premetro'' lines. The metro-grade lines are M1, M2, M5, and M6 wi ...
dates back to 1976, but underground lines known as the ''
premetro'' have been serviced by tramways since 1968. It is the only
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT) or heavy rail, commonly referred to as metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport that is generally built in urban areas. A grade separation, grade separated rapid transit line below ground su ...
system in Belgium (Antwerp Pre-metro, Antwerp and Métro Léger de Charleroi, Charleroi both having light rail systems). The network consists of four conventional metro lines and three ''premetro'' lines. The metro-grade lines are Brussels Metro line 1, M1, Brussels Metro line 2, M2, Brussels Metro line 5, M5, and Brussels Metro line 6, M6, with some shared sections, covering a total of .
, the Metro network within the region has a total of List of Brussels Metro stations, 69 metro and ''premetro'' stations. The Metro is an important Transport in Brussels, means of transport, connecting with six railway stations of the National Railway Company of Belgium (NMBS/SNCB), and many tram and bus stops operated by STIB/MIVB, as well as with Flanders, Flemish De Lijn and Wallonia, Walloon TEC (transport), TEC bus stops.
A comprehensive Brussels buses, bus and Brussels trams, tram network covers the region. , the Brussels tram system consists of 17 tram lines (three of which – lines Brussels tram route 4, T4, Brussels tram route 7, T7 and T10 – qualify as ''premetro'' lines that partly travel over underground sections that were intended to be eventually converted into metro lines).
The total route length is ,
making it one of the largest tram networks in Europe. The Brussels bus network is complementary to the rail network. It consists of 50 bus routes and 11 night routes, spanning .
Since April 2007, STIB/MIVB has also been operating a night bus network called Noctis on Friday and Saturday nights from midnight until 3 a.m.
[ The service consists of 11 routes (N04, N05, N06, N08, N09, N10, N11, N12, N13, N16 and N18). The fare on these night buses is the same as during the day. All the lines leave from the Place de la Bourse, Brussels, Place de la Bourse/Beursplein in the city centre at 30 minutes intervals and cover all the main streets in the capital, as they radiate outwards to the suburbs. Noctis services returned from 2 July 2021 after over a year of disruption due to the COVID-19 pandemic in Belgium.]
Ticketing
MoBIB is the STIB/MIVB electronic smart card, introduced in 2007, replacing the discontinued paper tickets. The hourly travel fare includes all means of transport (metro, tram and bus) operated by STIB/MIVB. Each trip has a different cost depending on the type of support purchased. Passengers can purchase monthly passes, yearly passes, 1 and 10-trip tickets and daily and 3-day passes. These can be bought over the Internet, but require customers to have a smart card reader. GO vending machines accept coins, local and international chip and PIN credit and debit cards.
Moreover, a complimentary interticketing system means that a combined STIB/MIVB ticket holder can, depending on the option, also use the train network operated by NMBS/SNCB and/or long-distance buses and commuter services operated by De Lijn or TEC. With this ticket, a single journey can include multiple stages across the different modes of transport and networks.
Other public transport
 Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with STIB/MIVB and the local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a Community bicycle program, public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas, though it ceased operating in the city in 2020.
Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with STIB/MIVB and the local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a Community bicycle program, public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas, though it ceased operating in the city in 2020.
Road network
 In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north–south (the modern /) and east–west (/–/–/). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the
In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north–south (the modern /) and east–west (/–/–/). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the Grand-Place
The (French language, French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central Town square, square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque architecture, Baroque guildhalls of ...
, in large part remains, but has been overlaid by boulevards built covering of the Senne, over the river Senne, Fortifications of Brussels#Construction of the Small Ring, over the city walls and over the railway connection between the North and South Stations. In 2012, Brussels had the most congested traffic in Europe and North America, according to US traffic information platform INRIX.
Brussels is the hub of a range of national roads, the main ones being clockwise: the N1 road (Belgium), N1 (N to Breda), N2 road (Belgium), N2 (E to Maastricht), N3 road (Belgium), N3 (E to Aachen), N4 road (Belgium), N4 (SE to Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
), N5 road (Belgium), N5 (S to Reims), N6 (S to Maubeuge), N7 (SW to Lille), N8 road (Belgium), N8 (W to Koksijde) and N9 (NW to Ostend). Usually named /, these highways normally run in a straight line, but sometimes lose themselves in a maze of narrow shopping streets. The region is skirted by the European route E19 (N-S) and the European route E40, E40 (E-W), while the E411 leads away to the SE. Brussels has an orbital motorway, numbered R0 (R-zero) and commonly referred to as the Brussels Ring, Ring. It is pear-shaped, as the southern side was never built as originally conceived, owing to residents' objections.
The city centre, sometimes known as the Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon () is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple polygon, simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simple or list of self-intersecting polygons, self-intersecting. A self-intersecting ...
, is surrounded by an inner ring road, the Small Ring (, ), a sequence of boulevards formally numbered R20 or N0. These were built upon the site of the Second walls of Brussels, second set of city walls following their demolition. The Brussels Metro line 2, Metro line 2 runs under much of these. Since June 2015, a number of central boulevards inside the Pentagon have become car-free, limiting transit traffic through the old city.
On the eastern side of the region, the R21 or Greater ring (Brussels), Greater Ring (, ) is formed by a string of boulevards that curves round from Laeken
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is a residential suburb in the north-western part of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It belongs to the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality of the ...
to Uccle
Uccle (French language, French, ) or Ukkel (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the southern part of the region, it ...
. Some ''premetro'' stations (see Brussels Metro
The Brussels Metro ( ; ) is a rapid transit system serving a large part of the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It consists of four conventional metro lines and three '' premetro'' lines. The metro-grade lines are M1, M2, M5, and M6 wi ...
) were built on that route. A little further out, a stretch numbered R22 leads from Zaventem to Uccle, Saint-Job.
Security and emergency services
Police
The Brussels local police, supported by the federal police, is responsible for law enforcement in Brussels. The 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region are divided into six police zones, all bilingual (French and Dutch):
* 5339 Brussels Capital Ixelles: the City of Brussels
The City of Brussels is the largest List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the French Community of Belgium, the ...
and Ixelles
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Pentagon (Brussels), Brusse ...
* 5340 Brussels West: Berchem-Sainte-Agathe
Berchem-Sainte-Agathe ( French, ) or Sint-Agatha-Berchem ( Dutch, ), often simply called Berchem, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Gansh ...
, Ganshoren
Ganshoren (; ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Jette, and ...
, Jette
Jette (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Ganshoren, Koekelberg, and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean, as well as the Fl ...
, Koekelberg
Koekelberg (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren, Jette, and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean. In common with al ...
and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
(French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western p ...
* 5341 South: Anderlecht
Anderlecht (; ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the south-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Forest, B ...
, Forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
and Saint-Gilles
* 5342 Uccle/Watermael-Boitsfort/Auderghem: Auderghem
Auderghem ( French, ; former Dutch spelling) or Oudergem ( Dutch, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the south-eastern part of the region, along the Woluwe valley and at the entrance to the ...
, Uccle
Uccle (French language, French, ) or Ukkel (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the southern part of the region, it ...
and Watermael-Boitsfort
Watermael-Boitsfort (French language, French, ) or Watermaal-Bosvoorde (Dutch language, Dutch, ; ), often simply called Boitsfort in French or Bosvoorde in Dutch, is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipal ...
* 5343 Montgomery: Etterbeek
Etterbeek (; ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the municipalities of Auderghem, the Cit ...
, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert
Woluwe-Saint-Lambert ( French, ) or Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe ( Dutch, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch). In French, ...
and Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
Woluwe-Saint-Pierre ( French, ) or Sint-Pieters-Woluwe ( Dutch, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by Etterbeek, Auderghem and Woluwe-Saint-Lambe ...
* 5344 Polbruno: Evere
Evere (; ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium). , the municipality had a population of 43,608 inhabitants. The total area is , which gives a population density of . In common with all of Brussels' municipal ...
, Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode ( French, ) or Sint-Joost-ten-Node ( Dutch, ), often simply called Saint-Josse in French or Sint-Joost in Dutch, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part o ...
and Schaerbeek
(French language, French, ; former History of Dutch orthography, Dutch spelling) or (modern Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Reg ...
Fire department
The Brussels Fire and Emergency Medical Care Service, commonly known by its acronym SIAMU (DBDMH), operates in the 19 municipalities of Brussels. It is a class X fire department and the largest fire service in Belgium in terms of annual operations, equipment, and personnel. It has 9 fire stations, spread over the entire Brussels-Capital Region, and employs about 1,000 professional firefighters. As well as preventing and fighting fires, SIAMU also provides emergency medical care services in Brussels via its centralised 100 number (and the single 112 emergency number for the 27 countries of the European Union). It is bilingual (French–Dutch).
Parks and green spaces
Brussels is one of the greenest capitals in Europe, with over 8,000 hectares of green spaces. Vegetation cover and natural areas are higher in the outskirts, where they have limited the peri-urbanisation of the capital, but they decrease sharply towards the centre of Brussels; 10% in the central Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon () is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple polygon, simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simple or list of self-intersecting polygons, self-intersecting. A self-intersecting ...
, 30% of the municipalities in the first ring, and 71% of the municipalities in the second ring are occupied by green spaces.
Many parks and gardens, both public and privately owned, are scattered throughout the city. In addition to this, the Sonian Forest
The Sonian Forest or Sonian Wood (, ; , ) is a forest at the south-eastern edge of Brussels, Belgium. It is connected to the Bois de la Cambre, Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamerenbos, an urban public park which enters the city up to from the Pentag ...
is located in its southern part and stretches out over the three Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, Belgian regions. , it has been inscribed as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
, the only Belgian component to the multinational inscription 'Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians and Other Regions of Europe'.
File:Brussels Park in summer 2007 1.JPG, Brussels Park
Brussels Park ( ; or ) is the largest urban public park in central Brussels, Belgium. The park was formerly known and is still sometimes colloquially referred to as the Royal Park ( ; ). It was the city's first public park, being originally ...
File:Brussels, Jardin du Mont des Arts foto5 2015-06-07 14.01.jpg, Mont des Arts, Mont des Arts/Kunstberg
File:Brussels Cinquantenaire R04.jpg, Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark
File:Brusel, Bois de la Cambre, jezero.jpg, Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamerenbos
File:Ixelles Ponds.JPG, Ixelles Ponds
File:Parc de Forest - 20080325.JPG, Forest park, Brussels, Forest Park
File:Autumn light in the Sonian Forest.jpg, Sonian Forest
The Sonian Forest or Sonian Wood (, ; , ) is a forest at the south-eastern edge of Brussels, Belgium. It is connected to the Bois de la Cambre, Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamerenbos, an urban public park which enters the city up to from the Pentag ...
Notable people
Twin towns – sister cities
Brussels is sister city, twinned with the following cities:Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, United States
See also
* Bourgeois of Brussels
* Nazi ghost train
* Seven Noble Houses of Brussels
* Sculpture in Brussels
* Brussels Regional Investment Company
* European Network of Information Centres for the Performing Arts
* List of urban areas in the European Union
References
Footnotes
Citations
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Brussels-Capital Region
Official tourism website
{{Authority control
Brussels,
Brabant
Regions of Belgium
Regions of Europe with multiple official languages
Enclaves and exclaves
French-speaking countries and territories
Autonomous regions
NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union
Populated places established in the 1st millennium
 The history of Brussels is closely linked to that of
The history of Brussels is closely linked to that of  In the 14th century, the marriage between heiress
In the 14th century, the marriage between heiress  In the 16th and 17th centuries, Brussels was a centre for the
In the 16th and 17th centuries, Brussels was a centre for the  During the 20th century, the city hosted various fairs and conferences, including the
During the 20th century, the city hosted various fairs and conferences, including the 
 Brussels, along with
Brussels, along with  Since its creation in 1989, the Brussels-Capital Region has been legally bilingual, with both French and Dutch having official status, as is the administration of the 19 municipalities. The creation of this bilingual, full-fledged region, with its own competencies and jurisdiction, had long been hampered by different visions of Belgian federalism. Nevertheless, some communitarian issues remain. Flemish political parties demanded, for decades, that the Flemish part of
Since its creation in 1989, the Brussels-Capital Region has been legally bilingual, with both French and Dutch having official status, as is the administration of the 19 municipalities. The creation of this bilingual, full-fledged region, with its own competencies and jurisdiction, had long been hampered by different visions of Belgian federalism. Nevertheless, some communitarian issues remain. Flemish political parties demanded, for decades, that the Flemish part of  Brussels has a large concentration of
Brussels has a large concentration of  Very little
Very little  The neoclassical style of the 18th and 19th centuries is represented in the
The neoclassical style of the 18th and 19th centuries is represented in the  The
The  Brussels contains over 80 museums. The Royal Museums of Fine Arts has an extensive collection of various painters, such as Flemish old masters like Bruegel,
Brussels contains over 80 museums. The Royal Museums of Fine Arts has an extensive collection of various painters, such as Flemish old masters like Bruegel,  Brussels' identity owes much to its rich folklore and traditions, among the liveliest in the country.
The
Brussels' identity owes much to its rich folklore and traditions, among the liveliest in the country.
The  Brussels is well known for its local
Brussels is well known for its local  Sport in Brussels is under the responsibility of the Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, Communities. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
The
Sport in Brussels is under the responsibility of the Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, Communities. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
The  R.S.C. Anderlecht, based in the Constant Vanden Stock Stadium in
R.S.C. Anderlecht, based in the Constant Vanden Stock Stadium in  Serving as the centre of administration for Belgium and Europe, Brussels' economy is largely Tertiary sector of the economy, service-oriented. It is dominated by regional and world headquarters of Multinational corporation, multinationals, by European institutions, by various local and federal administrations, and by related services companies, though it does have a number of notable craft industries, such as the Cantillon Brewery, a lambic brewery founded in 1900.
Serving as the centre of administration for Belgium and Europe, Brussels' economy is largely Tertiary sector of the economy, service-oriented. It is dominated by regional and world headquarters of Multinational corporation, multinationals, by European institutions, by various local and federal administrations, and by related services companies, though it does have a number of notable craft industries, such as the Cantillon Brewery, a lambic brewery founded in 1900.
 There are several universities in Brussels. Except for the Royal Military Academy (Belgium), Royal Military Academy, a federal military college established in 1834, all universities in Brussels are private and autonomous. The Royal Military Academy also the only Belgian university organised on the boarding school model.
The Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), a French-speaking university, with about 20,000 students, has three campuses in the city, and the
There are several universities in Brussels. Except for the Royal Military Academy (Belgium), Royal Military Academy, a federal military college established in 1834, all universities in Brussels are private and autonomous. The Royal Military Academy also the only Belgian university organised on the boarding school model.
The Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), a French-speaking university, with about 20,000 students, has three campuses in the city, and the  Brussels has a number of public or private-owned libraries on its territory. Most public libraries in Brussels fall under the competence of the Communities and are usually separated between French-speaking and Dutch-speaking institutions, although some are mixed.
The Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) is the national library of Belgium and one of the most prestigious libraries in the world. It owns several collections of historical importance, like the famous Fétis archives, and is the depository for all books ever published in Belgium or abroad by Belgian authors. It is located on the Mont des Arts, Mont des Arts/Kunstberg in central Brussels, near the Brussels Central Station, Central Station.
There are several academic libraries and archives in Brussels. The libraries of the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) and the
Brussels has a number of public or private-owned libraries on its territory. Most public libraries in Brussels fall under the competence of the Communities and are usually separated between French-speaking and Dutch-speaking institutions, although some are mixed.
The Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) is the national library of Belgium and one of the most prestigious libraries in the world. It owns several collections of historical importance, like the famous Fétis archives, and is the depository for all books ever published in Belgium or abroad by Belgian authors. It is located on the Mont des Arts, Mont des Arts/Kunstberg in central Brussels, near the Brussels Central Station, Central Station.
There are several academic libraries and archives in Brussels. The libraries of the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) and the  Science and technology in Brussels is well-developed with the presence of several List of universities in Belgium, universities and research institutes. The Brussels-Capital Region is home to several national science and technology institutes including the National Fund for Scientific Research (NFSR), the Institute for the Encouragement of Scientific Research and Innovation of Brussels (ISRIB), the Royal Academies for Science and the Arts of Belgium (RASAB) and the Belgian Academy Council of Applied Sciences (BACAS). Several science parks associated with the universities are also spread over the region.
The Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, located in Leopold Park, houses the world's largest hall completely dedicated to dinosaurs, with its collection of 30 fossilised ''Iguanodon'' skeletons. In addition, the Planetarium (Belgium), Planetarium of the Royal Observatory of Belgium (part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office), on the Heysel Plateau in
Science and technology in Brussels is well-developed with the presence of several List of universities in Belgium, universities and research institutes. The Brussels-Capital Region is home to several national science and technology institutes including the National Fund for Scientific Research (NFSR), the Institute for the Encouragement of Scientific Research and Innovation of Brussels (ISRIB), the Royal Academies for Science and the Arts of Belgium (RASAB) and the Belgian Academy Council of Applied Sciences (BACAS). Several science parks associated with the universities are also spread over the region.
The Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, located in Leopold Park, houses the world's largest hall completely dedicated to dinosaurs, with its collection of 30 fossilised ''Iguanodon'' skeletons. In addition, the Planetarium (Belgium), Planetarium of the Royal Observatory of Belgium (part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office), on the Heysel Plateau in  The Brussels-Capital Region has three main train stations: Brussels-South railway station, Brussels-South, Brussels-Central and Brussels-North railway station, Brussels-North, which are also the busiest of the country. Brussels-South is also served by direct high-speed rail links: to London by Eurostar trains via the Channel Tunnel; to Amsterdam by Thalys and ''InterCity'' connections; to Amsterdam, Paris, and
The Brussels-Capital Region has three main train stations: Brussels-South railway station, Brussels-South, Brussels-Central and Brussels-North railway station, Brussels-North, which are also the busiest of the country. Brussels-South is also served by direct high-speed rail links: to London by Eurostar trains via the Channel Tunnel; to Amsterdam by Thalys and ''InterCity'' connections; to Amsterdam, Paris, and  Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with STIB/MIVB and the local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a Community bicycle program, public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas, though it ceased operating in the city in 2020.
Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with STIB/MIVB and the local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a Community bicycle program, public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas, though it ceased operating in the city in 2020.
 In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north–south (the modern /) and east–west (/–/–/). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the
In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north–south (the modern /) and east–west (/–/–/). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the