Ancient Greece–Ancient India Relations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 For the
For the
/ref>
/ref> ''
/ref> terms derived from the

/ref>Arrian, Anabasis of Alexander, 5.2
/ref> In addition, Philostratus mentions that at
/ref> Furthermore, he reports that the Indians living in
 Megasthenes also wrote about the legendary arrival of
Megasthenes also wrote about the legendary arrival of
/ref> An Indian tribe called the Sourasenoi worshipped Heracles at the time of Alexander the Great.
/ref>
/ref> The
 During the
During the
/ref> and added
/ref> In addition, he gave
/ref>
/ref> Maliarpha (Μαλιάρφα,) was a place of considerable commerce in the territory of the Arvarni.
/ref> and the Rarassa (Ῥαράσσα or Ἠράρασα).Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), Rarassa
/ref>
/ref>
/ref> The Unani System of Medicine, a traditional system of medicine practiced in India, refers to Graeco-Arabic medicine, which is based on the teachings of Greek physicians
Tombs rich in artifacts discovered by Swedish expedition in Cyprus
/ref>
Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), William Smith, LLD, Ed., India
Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), William Smith, LLD, Ed., Taprobane
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ancient Greece-Ancient India relations
 For the
For the ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically re ...
, ''India'' () referred to the geographical region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
located east of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and south of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
, excluding Serica
Serica (, ) was one of the easternmost countries of Asia known to the Ancient Greek and Roman geographers. It is generally taken as referring to North China during its Zhou, Qin, and Han dynasties, as it was reached via the overland Silk Roa ...
. At different points in history, the term also came to refer either to the more extensive Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
or to the less extensive Indus Plain.Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854) William Smith, LLD, Ed. - India/ref>
Names
The Greeks referred to the ancient Indians as ''Indoi'' (. The Vedic Aryans referred to the Greeks as ''Yavanas'',The Influence of Greek Classics on Indian Culture in Ancient Era/ref> ''
Yona
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit, were used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" (), who were probably the first Gr ...
'' or ''Yonaka,''Lal, Shyam Bihari. “YAVANAS IN THE ANCIENT INDIAN INSCRIPTIONS.” Proceedings of the Indian History Congress, vol. 65, 2004, pp. 1115–20. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/44144820. Accessed 24 Feb. 2024./ref> terms derived from the
Ionians
The Ionians (; , ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the traditional four major tribes of Ancient Greece, alongside the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaeans. The Ionian dialect was one of the three major linguistic divisions of the ...
. ''Yawan'' is a Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
term that referred to the ancient Greeks. Inscriptions and Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
texts trace the Prakrit
Prakrit ( ) is a group of vernacular classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 5th century BCE to the 12th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Ind ...
equivalent of the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
word ''Yavana'' as ''Yona
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit, were used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" (), who were probably the first Gr ...
''. It has been suggested that the Indians adopted the term either from the Persians—who called the Greeks ''Yaunas''—or from a Semitic language.
Traditional Indian grammarians believed that the word ''Yavanas'' was derived from the Sanskrit root ''Yu'' ('to mix, to mingle'). The earliest written record of the term ''Yavana'' appears in the '' Astadhyayi'', a work on grammar by Pāṇini
(; , ) was a Sanskrit grammarian, logician, philologist, and revered scholar in ancient India during the mid-1st millennium BCE, dated variously by most scholars between the 6th–5th and 4th century BCE.
The historical facts of his life ar ...
. When demonstrating the use of the suffix -''anuk'', he cites ''Yavanani'' as one of his examples. In addition, Katyayana explains that when the suffix is added to the word ''Yavana'', it indicates handwriting. ''Yavanani'' and ''Yavanallipyam'' are examples of scripts used by the Yavana people.
Although originally the word ''Yavana'' meant 'Greek', in later centuries it was also applied to Romans, Arabs, and Westerners in general.
Mythology and legends
Dionysus

Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; , died 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, indologist, diplomat, ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has been partially reconstructe ...
wrote about the prehistoric arrival of the god Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ...
in India, as did Apollodorus
Apollodorus ( Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to:
:''Note: A ...
in '' Bibliotheca''. Polyaenus
Polyaenus or Polyenus ( ; see ae (æ) vs. e; , "much-praised") was a 2nd-century Roman Macedonian author and rhetorician, known best for his ''Stratagems in War'' (), which has been preserved. He was born in Bithynia, Asia Minor. The ''Suda'' c ...
wrote that, after fighting King Deriades
King Deriades is a prominent figure in Greek mythology, featured as the king of the Indians in Nonnus of Panopolis epic poem, Dionysiaca. He serves as the primary antagonist to Dionysus during the god's mythical campaign to conquer India.(The ter ...
, Dionysus subdued the Indians, allied with them and the Amazons
The Amazons (Ancient Greek: ', singular '; in Latin ', ') were a people in Greek mythology, portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercules, Labours of Heracles, the ''Argonautica'' and the ''Iliad''. ...
, and took them into his service. He later employed them in his campaign against Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
.
The epic poem ''Dionysiaca
The ''Dionysiaca'' (, ''Dionysiaká'') is an ancient Greek epic poem and the principal work of Nonnus. It is an epic in 48 books, the longest surviving poem from Greco-Roman antiquity at 20,426 lines, composed in Homeric dialect and dactylic hex ...
'' by Nonnus
Nonnus of Panopolis (, ''Nónnos ho Panopolítēs'', 5th century AD) was the most notable Greek epic poet of the Imperial Roman era. He was a native of Panopolis (Akhmim) in the Egyptian Thebaid and probably lived in the 5th century AD. He i ...
recounts Dionysus' expedition to India. Nonnus also wrote about Colletes (), a huge, formidable figure, whose ancestor was said to be the founder of the Indian race. In addition, in Book 14, Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; ; in Ionic Greek, Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Oly ...
assumes the likeness of an Indian in order to speak with and persuade the Indian chief to fight Dionysus' army.
A hymn to Dionysus in the ''Greek Anthology'' is titled ''Dionysus Indoletes'' ('Ἰνδολέτης'), which means 'slayer' or 'killer of Indians'. Other poems in the ''Greek Anthology'' also mention Dionysus' campaign against the Indians. Alphesiboea
Alphesiboea () was the name of several characters in Greek mythology:
*Alphesiboea, mother of Adonis with Phoenix.
* Alphesiboea, a Psophian princess as the daughter of King Phegeus in Arcadia. She was the sister of Axion and Temenus, and m ...
('Ἀλφεσιβοῖα') was an Indian nymph
A nymph (; ; sometimes spelled nymphe) is a minor female nature deity in ancient Greek folklore. Distinct from other Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature; they are typically tied to a specific place, land ...
who was loved by Dionysus.
Philostratus
Philostratus or Lucius Flavius Philostratus (; ; 170s – 240s AD), called "the Athenian", was a Greek sophist of the Roman imperial period. His father was a minor sophist of the same name. He flourished during the reign of Septimius Severus ...
reports that Dionysus was called Nysian or Nysean (Ancient Greek: 'Νύσιος') by the Indians. According to legend, he founded the city of Nysa, sometimes identified with Nagara. When Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
arrived in Nysa, representatives of the city met him and asked him not to capture the city or its land, explaining that Dionysus had founded it and named it after his nurse. He had also named the mountain near the city Meron (Ancient Greek: 'Μηρόν'), meaning 'thigh', because Dionysus grew in the thigh of Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
.Arrian, Anabasis of Alexander, 5.1/ref>Arrian, Anabasis of Alexander, 5.2
/ref> In addition, Philostratus mentions that at
Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
, a silver offering disc bore the inscription 'Dionysus the son of Semele
Semele (; ), or Thyone (; ) in Greek mythology, was the youngest daughter of Cadmus and Harmonia (Greek goddess), Harmonia, and the mother of Dionysus by Zeus in one of his many origin myths.
Certain elements of the cult of Dionysus and Semele ...
and Zeus, from the men of India to the Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
of Delphi' (Ancient Greek: 'ΔΙΟΝΥΣΟΣ Ο ΣΕΜΕΛΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΟΣ ΑΠΟ ΙΝΔΩΝ ΑΠΟΛΛΩΝΙ ΔΕΛΦΩΙ').Philostratus, Life of Apollonius of Tyana, 2.9/ref> Furthermore, he reports that the Indians living in
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
and along the river Cophen said that Dionysus was an Assyrian visitor who knew the religious rites of the city of Thebes in Greece (according to Ancient Greek legend, Dionysus was born there).
In ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' () is a Greek literature, Greek epic poem written by Apollonius of Rhodes, Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only entirely surviving Hellenistic civilization, Hellenistic epic (though Aetia (Callimachus), Callim ...
,'' Apollonius Rhodius
Apollonius of Rhodes ( ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; ; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and the Argonauts and their quest for the Golden Fleece. The poem is ...
wrote about the Nysean son of Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
, who left the tribes of the Indians and came to dwell at Thebes. Indians inhabiting the district between the Indus and the Hydraotes and the continental region extending up to the river Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
declared that Dionysus was the son of the river Indus and that Dionysus of Thebes was his disciple. Phylarchus
Phylarchus (, ''Phylarkhos''; fl. 3rd century BC) was a Greek historical writer whose works have been lost, but not before having been considerably used by other historians whose works have survived.
Life
Phylarchus was a contemporary of Aratus, ...
wrote that Dionysus was the first to bring two bulls, named Apis and Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wikt:wsjr, wsjr'') was the ancient Egyptian deities, god of fertility, agriculture, the Ancient Egyptian religion#Afterlife, afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was ...
, from India to Egypt; Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
found this theory absurd.
Heracles
 Megasthenes also wrote about the legendary arrival of
Megasthenes also wrote about the legendary arrival of Heracles
Heracles ( ; ), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a Divinity, divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of ZeusApollodorus1.9.16/ref> and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive descent through ...
in India. Pandaie () was a daughter of Heracles, whom he fathered in India. He gave her the southern part of India, where she reigned as queen. According to legend, the Indian tribe of Pandae was descended from her, and for this reason, they were the only tribe in India to have the custom of female sovereigns.Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), Pandae/ref> An Indian tribe called the Sourasenoi worshipped Heracles at the time of Alexander the Great.
Quintus Curtius Rufus
Quintus Curtius Rufus (; ) was a Ancient Rome, Roman historian, probably of the 1st century, author of his only known and only surviving work, ''Historiae Alexandri Magni'', "Histories of Alexander the Great", or more fully ''Historiarum Alex ...
mentions Indian soldiers carrying a banner with the name 'Herakles' during Alexander's push eastwards.
Contact, records, and influence between the two civilizations
Coinage
Between about 200 BC and the very beginning of the first millennium AD, theIndo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
covered an area encompassing modern-day Pakistan, parts of Afghanistan and of north-west India. The city of Kapisi
The Kingdom of Kapisa, appearing in contemporary Chinese sources as () and (), was a state located in what is now Afghanistan during the late 1st millennium. Its capital was the city of Kapisa. The kingdom stretched from the Hindu Kush in the n ...
appeared on Indo-Greek coins.
The Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
, which succeeded the Indo-Greek Kingdom and lasted nearly four hundred years, used the Greek alphabet and Greek legends on their coins. The Kushans also adopted other elements of Greek culture. Art themes derived from Greek mythology were common initially, but later Buddhist imagery dominated. In broadly the same era and south of the Kushan Empire, the Western Kshatrapas
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering moder ...
established coinage derived from Indo-Greek coinage. The obverse of the coins consists of the profile of the ruler with a legend in Greek, while the reverse represents a thunderbolt and an arrow, with Brahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or ...
and Kharoshthi
Kharosthi script (), also known as the Gandhari script (), was an ancient script originally developed in the Gandhara Region of modern-day Pakistan, between the 5th and 3rd century BCE. used primarily by the people of Gandhara alongside vari ...
legends. In the first century CE, Gondophares
Gondophares I ( Greek: Γονδοφαρης ''Gondopharēs'', Υνδοφερρης ''Hyndopherrēs''; Kharosthi: 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪𐨿𐨣 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨂𐨵𐨪 ', ') was the founder of the Indo-Parthian K ...
, king of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom, minted coins with the Greek title of autokrator
''Autokrator'' or Autocrator (, from + ) is a Greek epithet applied to an individual who is unrestrained by superiors. It has been applied to military commanders-in-chief as well as Roman and Byzantine emperors as the translation of the Latin ...
.
Inscriptions
Greeks are mentioned in theYavanarajya inscription
The Yavanarajya inscription, also called the Maghera Well Stone Inscription, was discovered in the village of Maghera, 17 kilometers north of Mathura, India in 1988. The Sanskrit inscription, carved on a block of red sandstone, is dated to the ...
in northern India, and on the Rukhuna reliquary. In a Kharoshthi inscription found in the Swat
A SWAT (''Special Weapons and Tactics'') team is a generic term for a police tactical unit within the United States, though the term has also been used by other nations.
SWAT units are generally trained, equipped, and deployed to res ...
area of Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
, which dates to the 1st century BC, there is a dedication from the Greek meridarch
A meridarch or ''meridarches'' (, from ''meris'', "division", and ''-arches'', "ruler") was the civil governor of a province in the Hellenistic world (4th–1st centuries BCE), and could be translated as "Divisional Commissioner". Only three mentio ...
Theodorus. The Rabatak inscription
The Rabatak Inscription is a stone inscribed with text written in the Bactrian language and Greek script, found in 1993 at Rabatak, near Surkh Kotal in Afghanistan. The inscription relates to the rule of the Kushan emperor Kanishka, and gives ...
uses Greek script
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as w ...
to write a language described as ''Arya''. The inscription relates to the rule of the Kushan ''Kushan'' or Kushana may refer to:
* Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan ...
emperor Kanishka
Kanishka I, also known as Kanishka the Great, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (–150 CE) the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadp ...
.
Art and literature
In the ''Greek Anthology'', India and Indians are mentioned on many occasions. InSophocles
Sophocles ( 497/496 – winter 406/405 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. was an ancient Greek tragedian known as one of three from whom at least two plays have survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or contemporary with, those ...
' play ''Antigone
ANTIGONE (Algorithms for coNTinuous / Integer Global Optimization of Nonlinear Equations), is a deterministic global optimization solver for general Mixed-Integer Nonlinear Programs (MINLP).
History
ANTIGONE is an evolution of GloMIQO, a global ...
'', Creon mentions the gold of India. The satirist Lucian
Lucian of Samosata (Λουκιανὸς ὁ Σαμοσατεύς, 125 – after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer who is best known for his characteristic tongue-in-cheek style, with which he frequently ridi ...
wrote that Indians get drunk with wine very easily and worse than any Greek or Roman would be.
Kalidasa
Kālidāsa (, "Servant of Kali"; 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on Hindu Puranas and philosophy. His surviv ...
mentions the ''Yayanis'' (Greek maidens) in his work and the ''Yavana Ganika'' (Greek Ganika) was a common sight in India (Gaṇikā
Gaṇikā or ganika (Sanskrit: गणिका) were female courtesans in early Ancient India, with their earliest reference in the Vedic period. Mentioned in the ''Kamasutra'', ''Gaṇikās'' were also dubbed as "courtesans de luxe," this was h ...
in India was similar to a Hetaira
A (; , ; . , ), Latinized as ( ), was a type of highly educated female companion in ancient Greece who served as an artist, entertainer, and conversationalist. Historians have often classed them as courtesans, but the extent to which they ...
in the Greek world). These girls were also trained in the theatrical arts. The Indian theater had adopted some elements of Greek comedy.
Hellenistic influence on Indian art
Hellenistic influence on Indian art and architecture reflects the artistic and architectural influence of the Greeks on Indian art following the conquests of Alexander the Great, from the end of the 4th century BCE to the first centuries of the com ...
is well documented. Gandhara art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
was heavily influenced by the Greek style. The Art of Mathura
The Art of Mathura refers to a particular school of Indian art, almost entirely surviving in the form of sculpture, starting in the 2nd century BCE, which centered on the city of Mathura, in central northern India, during a period in which Bu ...
is a blend of Indian and Greek art. The ''Pompeii Yakshii'', an Indian sculpture of a Yakshii, was found in the ruins of Roman Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and p ...
. Bharhut Yavana is a relief, discovered among the reliefs of the railings around the Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
Stupa, representing a Greek warrior.
At the Nasik Caves
The Trirashmi Caves, or Nashik Caves or Pandavleni is a holy Buddhist and Jain site and is located about 8 km south of the centre of Nashik (or Nasik), Maharashtra, India. Most of the caves are Viharas except for Cave 18 which is a Chai ...
, some of the caves were built by people with Greek heritage. The murals in the Ajanta Caves
The Ajanta Caves are 30 rock-cut architecture, rock-cut Buddhist caves in India, Buddhist cave monuments dating from the second century Common Era, BCE to about 480 CE in Aurangabad district, Maharashtra, Aurangabad district of Maharashtra sta ...
are painted in a way which suggests a Greek influence.
Philosophy and religion
Pyrrhonism
The philosopherPyrrho
Pyrrho of Elis (; ; ) was a Greek philosopher of Classical antiquity, credited as being the first Greek skeptic philosopher and founder of Pyrrhonism.
Life
Pyrrho of Elis is estimated to have lived from around 365/360 until 275/270 BCE. Py ...
accompanied Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
on his Indian campaign. According to Diogenes Laërtius
Diogenes Laërtius ( ; , ; ) was a biographer of the Greek philosophers. Little is definitively known about his life, but his surviving book ''Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers'' is a principal source for the history of ancient Greek ph ...
, Pyrrho developed his philosophy, now known as Pyrrhonism
Pyrrhonism is an Ancient Greek school of philosophical skepticism which rejects dogma and advocates the suspension of judgement over the truth of all beliefs. It was founded by Aenesidemus in the first century BCE, and said to have been inspired ...
, in India. Diogenes Laërtius wrote that Anaxarchus Anaxarchus (; ; c. 380 – c. 320 BC) was a Greek philosopher of the school of Democritus. Together with Pyrrho, he accompanied Alexander the Great into Asia. The reports of his philosophical views suggest that he was a forerunner of the Greek skep ...
, Pyrrho
Pyrrho of Elis (; ; ) was a Greek philosopher of Classical antiquity, credited as being the first Greek skeptic philosopher and founder of Pyrrhonism.
Life
Pyrrho of Elis is estimated to have lived from around 365/360 until 275/270 BCE. Py ...
's teacher, met and spoke with Indian gymnosophist
Gymnosophists (, ''gymnosophistaí'', i.e. "naked philosophers" or "naked wise men" (from Greek γυμνός ''gymnós'' "naked" and σοφία ''sophía'' "wisdom")) were ancient Indian philosophers who pursued asceticism to the point of regar ...
s and magi
Magi (), or magus (), is the term for priests in Zoroastrianism and earlier Iranian religions. The earliest known use of the word ''magi'' is in the trilingual inscription written by Darius the Great, known as the Behistun Inscription. Old Per ...
. In the view of Christopher I. Beckwith, Pyrrho's philosophy was strikingly similar to the Buddhist three marks of existence
In Buddhism, the three marks of existence are three characteristics (Pali: ''tilakkhaṇa''; Sanskrit: त्रिलक्षण ''trilakṣaṇa'') of all existence and beings, namely '' anicca'' (impermanence), '' dukkha'' (commonly translated ...
, suggesting that his teaching was influenced by contact with Buddhism.
Because of the high degree of similarity between Nāgārjuna
Nāgārjuna (Sanskrit: नागार्जुन, ''Nāgārjuna''; ) was an Indian monk and Mahāyāna Buddhist philosopher of the Madhyamaka (Centrism, Middle Way) school. He is widely considered one of the most important Buddhist philosoph ...
's philosophy and Pyrrhonism
Pyrrhonism is an Ancient Greek school of philosophical skepticism which rejects dogma and advocates the suspension of judgement over the truth of all beliefs. It was founded by Aenesidemus in the first century BCE, and said to have been inspired ...
, particularly the surviving works of Sextus Empiricus
Sextus Empiricus (, ; ) was a Greek Pyrrhonist philosopher and Empiric school physician with Roman citizenship. His philosophical works are the most complete surviving account of ancient Greek and Roman Pyrrhonism, and because of the argument ...
, Nāgārjuna was likely influenced by Greek Pyrrhonist texts imported to India.
Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
flourished under the Indo-Greeks, leading to the Greco-Buddhist
Greco-Buddhism or Graeco-Buddhism was a cultural syncretism between Hellenistic period, Hellenistic culture and Buddhism developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Gandhara, which was in present-day Pakistan and parts of ...
cultural syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the ...
. The iconography of Vajrapani
(Sanskrit; Pali: Vajirapāṇi, 'holder of the thunderbolt', lit. meaning, "Vajra in ishand") is one of the earliest-appearing bodhisattvas in Mahayana Buddhism. The personification of Indra, the King of the Devas in the Hindu order, he is t ...
is clearly that of the hero Heracles
Heracles ( ; ), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a Divinity, divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of ZeusApollodorus1.9.16/ref> and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive descent through ...
, with varying degrees of hybridization. Menander I
Menander I Soter (, ; ), sometimes called Menander the Great, was an Indo-Greek king (reigned /155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectively. The first date is estimated by Osmund Bopearachchi and R. C. Senior, the other Boperachchi –1 ...
was one of the patrons of Buddhism; he was also the subject of the Milinda Panha
The ''Milindapañha'' () is a Buddhist text which dates from sometime between 100 BC and 200 AD. It purports to record a dialogue between the Indian Buddhist sage Nāgasena, and the 2nd century BC Indo-Greek king Menander I (Pali: ''Milinda'') ...
and is mentioned on the Shinkot casket
The Shinkot casket, also Bajaur reliquary of the reign of Menander, is a Buddhism, Buddhist reliquary from the Bajaur District, Bajaur area in Gandhara, thought to mention the reign of the 2nd century BCE Indo-Greek king Menander I. The steatite ...
. It has been claimed (by G. R. Sharma) that Menander is mentioned in the Reh Inscription
The Reh Inscription was discovered in 1979 near the Reh archaeological site along Yamuna River about east of Mathura in India. It is a Prakrit inscription in Brahmi script near the bottom of a Shiva linga. The inscription is dated to between the ...
, but other scholars disagree. Many Greek rulers after Menander had the description "Maharajasa dhramikasa" (follower of the Dharma) next to their name on their coinage; this does not necessarily imply that they were Buddhists or that Buddhism was dominant in their kingdom, as symbols of the Greek religion were also on the same coins, but it does indicate that Buddhism played a significant role. Buddhist manuscripts in cursive Greek
Cursive (also known as joined-up writing) is any style of penmanship in which characters are written joined in a flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing faster, in contrast to block letters. It varies in functionality and m ...
, dated later than the 2nd century AD, have been found in Afghanistan. Some mention the "Lokesvararaja Buddha" (λωγοασφαροραζοβοδδο). The Greco Indian Kingdoms, Dr. Uday Dokras/ref>

Dharmaraksita
Dharmarakṣita (Sanskrit, 'Protected by the Dharma'; Pali: Dhammarakkhita), was one of the missionaries sent by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka to proselytize Buddhism. He is described as being a Greek (Pali: '' Yona'', lit. "Ionian") in the '' M ...
was a Greek who converted to Buddhism. He was one of the missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group who is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Miss ...
sent by the Mauryan
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
emperor Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
to proselytize Buddhism. Mahadharmaraksita
Mahadharmarakkhita (Sanskrit: ''Mahadharmaraksita'', literally "Great protector of the Dharma") was a Greek (in Pali:" Yona", Sanskrit: " Yavana", lit. "Ionian") Buddhist master, who lived during the 2nd century BCE during the reign of the Ind ...
was a Greek Buddhist master who, according to Mahāvaṃsa
''Mahāvaṃsa'' (Sinhala: මහාවංශ (Mahāvansha), Pali: ''මහාවංස (Mahāvaṃsa)'') is the meticulously kept historical chronicle of Sri Lanka until the period of Mahasena of Anuradhapura. It was written in the style of ...
traveled to Anuradhapura
Anuradhapura (, ; , ) is a major city located in the north central plain of Sri Lanka. It is the capital city of North Central Province, Sri Lanka, North Central Province and the capital of Anuradhapura District. The city lies north of the cur ...
in Sri Lanka together with 30,000 Greek Buddhist monks from Alexandria of the Caucasus
Alexandria in the Caucasus ( ''Alexándreia''; medieval Kapisa, modern Bagram) was a colony of Alexander the Great. It was one of many colonies designated with the name "Alexandria". He founded the colony at an important junction of communicat ...
. Mahāvaṃsa also mentions how early Buddhists from Sri Lanka went to Alexandria of the Caucasus to learn Buddhism.
The Kandahar Greek Edicts of Ashoka
The Kandahar Greek Edicts of Ashoka are among the Major Rock Edicts of the Indian Emperor Ashoka (reigned 269-233 BCE), which were written in the Greek language and Prakrit language. They were found in the ancient area of Old Kandahar (known as ...
, which are among Ashoka's Major Rock Edicts
The Major Rock Edicts of Indian emperor Ashoka refer to 14 separate major Edicts of Ashoka which are significantly detailed and represent some of the earliest dated rock inscriptions of any Indian monarch. These edicts are preceded chronologica ...
, were written in the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
and Prakrit
Prakrit ( ) is a group of vernacular classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 5th century BCE to the 12th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Ind ...
languages. In addition, the Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription
The Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription, also known as the Kandahar Edict of Ashoka and less commonly as the Chehel Zina Edict, is an inscription in the Ancient Greek, Greek and Aramaic languages that dates back to 260 BCE and was carved b ...
was written in Greek and Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
. The emperor Ashoka used the word "eusebeia
Eusebeia (Greek: from "pious" from ''eu'' meaning "well", and ''sebas'' meaning "reverence", itself formed from ''seb-'' meaning sacred awe and reverence especially in actions) is a Greek word abundantly used in Greek philosophy as well as in ...
" (piety) as a Greek translation for the central Buddhist and Hindu concept of "dharma
Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold ...
" in the Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription
The Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription, also known as the Kandahar Edict of Ashoka and less commonly as the Chehel Zina Edict, is an inscription in the Ancient Greek, Greek and Aramaic languages that dates back to 260 BCE and was carved b ...
.Hacker, Paul. ''Dharma in Hinduism'', Journal of Indian Philosophy, 2006, 34:479-496
Buddhist gravestones from Ptolemaic Egypt Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
*Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
have been found in Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
decorated with depictions of the dharma wheel
The dharmachakra (Sanskrit: धर्मचक्र, ) or wheel of dharma is a symbol used in the Dharmic religions. It has a widespread use in Buddhism.John C. Huntington, Dina Bangdel, ''The Circle of Bliss: Buddhist Meditational Art,'' p ...
, showing the presence of Buddhists in Hellenistic Egypt. Ptolemy II Philadelphus
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the G ...
is mentioned in the Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 268 BCE to 2 ...
as a recipient of the Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
proselytism of Ashoka:
Peripateticism
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
's knowledge of India came essentially from Scylax and Ctesias
Ctesias ( ; ; ), also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Historical events
Ctesias, who lived in the fifth century BC, was physician to the Acha ...
. He quoted Scylax to refer to Indian politics and mentions seven Indian animals, by clearly drawing on Ctesias.Strabo and India/ref> The
Peripatetic
Peripatetic may refer to:
*Peripatetic school, a school of philosophy in Ancient Greece
*Peripatetic axiom, in philosophy
*Peripatetic minority, a mobile population moving among settled populations offering a craft or trade.
*Peripatetic Jats
T ...
philosopher Clearchus of Soli
Clearchus of Soli (, ''Klearkhos ho Soleus'') was a Greek philosopher of the 4th–3rd century BCE, belonging to Aristotle's Peripatetic school. He was born in Soli in Cyprus.
He wrote extensively on eastern cultures, and is thought to have tra ...
traveled to the east to study Indian religions.
Another Peripatetic philosopher, Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; ; c. 371 – c. 287 BC) was an ancient Greek Philosophy, philosopher and Natural history, naturalist. A native of Eresos in Lesbos, he was Aristotle's close colleague and successor as head of the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum, the ...
, in his book on the history of plants, wrote an excursus
An excursus (from Latin ''excurrere'', 'to run out of') is a short episode or anecdote in a work of literature. Often excursuses have nothing to do with the matter being discussed by the work, and are used to lighten the atmosphere in a tragic stor ...
on Indian species. Also, in his work "On Stones," he describes rocks, stones and gems produced in India.
Peripatetic philosopher Aristocles of Messene
Aristocles of Messene (; ), in Sicily,Suda, ''Aristokles'' was a Peripatetic philosopher, who probably lived in the 1st century AD.
Life
Little is known about the life of Aristocles. He came from Messene in Sicily (Messana, now Messina), not fro ...
(cited by the Christian polemicist
Polemic ( , ) is contentious rhetoric intended to support a specific position by forthright claims and to undermine the opposing position. The practice of such argumentation is called polemics, which are seen in arguments on controversial to ...
Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
) said an Indian conversed with Socrates
Socrates (; ; – 399 BC) was a Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher from Classical Athens, Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and as among the first moral philosophers of the Ethics, ethical tradition ...
in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
.
AndAristoxenus Aristoxenus of Tarentum (; born 375, fl. 335 BC) was a Ancient Greece, Greek Peripatetic school, Peripatetic philosopher, and a pupil of Aristotle. Most of his writings, which dealt with philosophy, ethics and music, have been lost, but one musi ...the musician said that this argument comes from the Indians. For a man of that people met Socrates in Athens and asked him what his philosophy was about; and when he said that he was investigating human life, the Indian laughed at him, saying that no one could understand human affairs if he ignored the divine. Whether this is true, no one can say for sure.
Christian
Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria (; – ), was a Christian theology, Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen and Alexander of Jerusalem. A ...
wrote about India, Gymnosophists
Gymnosophists (, ''gymnosophistaí'', i.e. "naked philosophers" or "naked wise men" (from Greek γυμνός ''gymnós'' "naked" and σοφία ''sophía'' "wisdom")) were ancient Indian philosophers who pursued asceticism to the point of regar ...
, Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' (; IAST: ''Brahman'') connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality of the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part XII In the ...
s, Buddha, etc. in the ''Stromata
The ''Stromata'' (), a mistake for ''Stromateis'' (Στρωματεῖς, "Patchwork," i.e., ''Miscellanies''), attributed to Clement of Alexandria (c. 150 – c. 215), is the third of a trilogy of works regarding the Christian life. The oldest ...
.''
The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
theologian
Theology is the study of religious belief from a religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of ...
Pantaenus
Saint Pantaenus the Philosopher (; died c. 200) was a Sicilian theologian and a significant figure in the Catechetical School of Alexandria from around AD 180. This school was the earliest catechetical school, and became influential in the dev ...
was said to have traveled to India.
Sophism
The GreekSophist
A sophist () was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BCE. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics and mathematics. They taught ''arete'', "virtue" or "excellen ...
Philostratus
Philostratus or Lucius Flavius Philostratus (; ; 170s – 240s AD), called "the Athenian", was a Greek sophist of the Roman imperial period. His father was a minor sophist of the same name. He flourished during the reign of Septimius Severus ...
, in his work ''Life of Apollonius of Tyana
''Life of Apollonius of Tyana'' (), also known by its Latin title , is a text in eight books written in Ancient Greece by Philostratus (c. AD 170 – c. AD 245). It tells the story of Apollonius of Tyana (c. AD 15 – c. AD 100), a Pythagorean ph ...
'' () and the Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; ; ) is a large 10th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine encyclopedia of the History of the Mediterranean region, ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas () or Souidas (). It is an ...
, mentioned that the Greek philosopher Apollonius
Apollonius () is a masculine given name which may refer to:
People Ancient world Artists
* Apollonius of Athens (sculptor) (fl. 1st century BC)
* Apollonius of Tralles (fl. 2nd century BC), sculptor
* Apollonius (satyr sculptor)
* Apo ...
had traveled to India.
The Sophist Dio Chrysostom
Dio Chrysostom (; ''Dion Chrysostomos''), Dio of Prusa or Cocceianus Dio (c. 40 – c. 115 AD), was a Greek orator, writer, philosopher and historian of the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD. Eighty of his ''Discourses'' (or ''Orations''; ) are ...
mentioned India in his work ''Discourses'' and wrote that Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
's poetry is sung in India. He also mentioned that Bactrians
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area within the north of modern Afghani ...
and Indians were to be found in his audience in Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
(circa 100 CE).
Political and military
 During the
During the second Persian invasion of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasi ...
, the Persian army had Indian troops, both infantry and cavalry.
At the Battle of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela ( ; ), also called the Battle of Arbela (), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Ancient Macedonian army, Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Army, Persian Army under Darius III, ...
, Darius
Darius may refer to:
Persian royalty
;Kings of the Achaemenid Empire
* Darius I (the Great, 550 to 487 BC)
* Darius II (423 to 404 BC)
* Darius III (Codomannus, 380 to 330 BC)
;Crown princes
* Darius (son of Xerxes I), crown prince of Persia, ma ...
used Indian troops against Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
. Later, during the Indian campaign of Alexander the Great
The Indian campaign of Alexander the Great began in 327BC and lasted until 325BC. After conquering the Achaemenid Persian Empire, the Macedonian army undertook an expedition into the Indus Valley of Northwestern Indian subcontinent. Within ...
, Alexander's army fought many battles against Indian tribes and kingdoms, including against the army of Porus the Elder
Porus or Poros ( ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of what is now India and Pakistan. He is only mentioned in Gre ...
. Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
wrote about the battle in his work ''Parallel Lives
*
Culture of ancient Greece
Culture of ancient Rome
Ancient Greek biographical works
Ethics literature
History books about ancient Rome
Cultural depictions of Gaius Marius
Cultural depictions of Mark Antony
Cultural depictions of Cicero
...
'', "The Life of Alexander." The Indian King Ambhi
Taxiles or Taxilas ( lived 4th century BC) was the Greek chroniclers' name for the ruler who reigned over the tract between the Indus and the Jhelum (Hydaspes) Rivers in the Punjab region at the time of Alexander the Great's expedition. His real ...
(the Greeks called him ''Taxiles'') supported Alexander with his forces. Philostratus the Elder
Philostratus of Lemnos (; c. 190 – c. 230 AD), also known as Philostratus the Elder to distinguish him from Philostratus the Younger who was also from Lemnos, was a Greek sophist of the Roman imperial period. He was probably a nephew of the sop ...
in the ''Life of Apollonius of Tyana
''Life of Apollonius of Tyana'' (), also known by its Latin title , is a text in eight books written in Ancient Greece by Philostratus (c. AD 170 – c. AD 245). It tells the story of Apollonius of Tyana (c. AD 15 – c. AD 100), a Pythagorean ph ...
'' wrote that in the army of Porus there was an elephant who fought bravely against Alexander's army, and Alexander dedicated it to the Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; ; Homeric Greek: ) is the god who personification, personifies the Sun. His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyperion ("the one above") an ...
(Sun) and named it "Ajax" because he thought that such a so great animal deserved a great name. The elephant had gold rings around its tusks and an inscription was on them written in Greek: "Alexander the son of Zeus dedicates Ajax to the Helios" (ΑΛΕΞΑΝΔΡΟΣ Ο ΔΙΟΣ ΤΟΝ ΑΙΑΝΤΑ ΤΩΙ ΗΛΙΩΙ). Alexander also met and talked with Indian gymnosophist
Gymnosophists (, ''gymnosophistaí'', i.e. "naked philosophers" or "naked wise men" (from Greek γυμνός ''gymnós'' "naked" and σοφία ''sophía'' "wisdom")) were ancient Indian philosophers who pursued asceticism to the point of regar ...
s, including Dandamis
Dandamis (presumably Greek rendering of "Dandayan-Swami, Svami") was a philosopher, swami and gymnosophist whom Alexander the Great, Alexander encountered in the woods near Taxila, when he invaded India in 4th century B.C. He is also referred t ...
and Kalanos
Kalanos, also spelled Calanus () ( – 323 BCE), was an ancient Indian gymnosophist and philosopher from Taxila who accompanied Alexander the Great and was his teacher. He accompanied Alexander the Great to Persis and later self-immolated, aft ...
.
Alexander let Taxiles
Taxiles or Taxilas ( lived 4th century BC) was the Greek chroniclers' name for the ruler who reigned over the tract between the Indus and the Jhelum (Hydaspes) Rivers in the Punjab region at the time of Alexander the Great's expedition. His real ...
and Porus
Porus or Poros ( ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of what is now India and Pakistan. He is only mentioned in Gr ...
keep their kingdomsDiodorus Siculus, Library 18.3.1/ref> and added
Paropamisadae
Paropamisadae or Parapamisadae () was a satrapy of the Alexandrian Empire in modern Afghanistan and Pakistan, which largely coincided with the Achaemenid province of Parupraesanna. It consisted of the districts of Sattagydia (Bannu basin), Ga ...
to the kingdom of Oxyartes
Oxyartes (Old Persian: 𐎢𐎺𐎧𐏁𐎫𐎼, Greek: ''Ὀξυάρτης'', in ("Vaxš-ard"), from an unattested form in an Old Iranian language: ''*Huxšaθra-'') was a Sogdian or Bactrian nobleman of Bactria, father of Roxana, the wife ...
.Diodorus Siculus, Library 18.39.1/ref> In addition, he gave
Peithon
Peithon or Pithon (Greek: ''Πείθων'' or ''Πίθων'', 355 – 314 BC) was the son of Crateuas, a nobleman from Eordaia in western Macedonia. He was famous for being one of the bodyguards of Alexander the Great, becoming the later ...
and Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male name derived from the Macedonian Old Koine language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominen ...
Indian satrapies. The Indian king Abisares
Abisares (or Abhisara; in Greek Ἀβισάρης), called Embisarus (Ἐμβίσαρος,) by Diodorus, was a Kasmira king whose territory lay in the river Hydaspes beyond the mountains. On his death in 325 BC, Alexander the Great appointed A ...
who sent embassies of submission to Alexander was allowed to retain his kingdom with considerable additions.
Alexander also conquered the kingdom of the Indian king Phegeus. The inhabitants welcomed Alexander's army and the king met Alexander and gave him many gifts. He also conquered the city of Sagala
Sagala, Sakala (), or Sangala () was a city in ancient India, which is generally identified as the predecessor of the modern city of Sialkot that is located in what is now Pakistan's northern Punjab province. The city was the capital of the Ma ...
.
Alexander asked Phegeus and Porus what was after the Hyphasis River and after their response he decided to continue. He was preparing to march against the Indian King Xandrames
Dhana Nanda (died ), according to the Buddhist text '' Mahabodhivamsa'', was the last Nanda king of Magadha.
Chandragupta Maurya raised an army that eventually conquered the Nanda capital Pataliputra and defeated him. This defeat marked the fal ...
, before his army mutinied. After the mutiny of his army, he conducted the Mallian campaign
The Mallian campaign was conducted by Alexander the Great from November 326 to February 325 BC, against the
Mallian people, Mallians of the Punjab region, Punjab. Alexander was defining the eastern limit of his power by marching down-river alon ...
.
After he conquered the Oritians and Arabitians, Alexander made Apollophanes
Apollophanes Soter (Greek: ; epithet means "the Saviour"; reigned c. 35 – 25 BCE) was an Indo-Greek king in the area of eastern and central Punjab in modern India and Pakistan.
Rule
Little is known about him, except for some of his remaining ...
the Satrap in the area.
According to ancient writers, the Queen Cleophis
Cleophis (Sanskrit: ''Kripa'' ) was an Assacani Rani, queen and key figure in the war between the Assacani people and Alexander the Great. Cleophis was the mother of Assacanus, the Assacanis' war-leader at the time of Alexander's invasion in 326 ...
of Massaga had a son with Alexander the Great. Modern historians deny this.
After the Battle of Gabiene
Battle of Gabiene was the second great battle between Antigonus I Monophthalmus, Antigonus Monophthalmus and Eumenes, two of Alexander the Great's successors (the so-called Diadochi). The battle was fought near Gabiene in Persia in the winter o ...
, Antigonus I Monophthalmus
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( , "Antigonus the One-Eyed"; 382 – 301 BC) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Diadochi, successor of Alexander the Great. A prominent military leader in Alexander's army, he went on to control lar ...
sent the Argyraspides
The Argyraspides () were elite Macedonian soldiers who carried silver-plated shields, hence their name. The original unit were hypaspists serving in the army of Alexander the Great. During the Wars of the Diadochi, they initially served Eumenes, b ...
to Sibyrtius
Sibyrtius ( ''Sivyrtios''; lived 4th century BC) was a Greek officer from Crete in the service of Alexander the Great, who was the satrap of Arachosia and Gedrosia shortly after the death of Alexander until about 303 BC.
After serving in Alexan ...
at Arachosia
Arachosia (; ), or Harauvatis ( ), was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire. Mainly centred around the Arghandab River, a tributary of the Helmand River, it extended as far east as the Indus River. The satrapy's Persian-language name is the et ...
.
Indo-Greek kingdoms
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
and Greco-Bactrian Kingdoms were founded by the successors of Alexander the Great ( Greek conquests in India). Yavana era
The Yavana Era, or Yona (Prakrit: ''Yoṇaṇa vaṣaye'') was a computational era used in the Indian subcontinent from the 2nd century BCE for several centuries thereafter, probably starting in 174 BCE.Des Indo-Grecs aux Sassanides: données pour ...
describes the period with Greek presence in India.
According to Indian sources, Greek troops seem to have assisted Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (Sanskrit: elp:IPA/Sanskrit, t̪͡ɕɐn̪d̪ɾɐgupt̪ɐ mɐʊɾjɐ (reigned 320 BCE – c. 298 BCE) was the founder and the first emperor of the Maurya Empire, based in Magadha (present-day Bihar) in the Indian ...
in toppling the Nanda Dynasty
The Nanda Empire was a vast empire that governed in Magadha and Gangetic plains with an enormous geographical reach in 4th-century BCE northeastern India, with some accounts suggesting existence as far back as the 5th century BCE. The Nandas ...
and founding the Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
. Later, Seleucus I's army encountered Chandragupta's army. Chandragupta and Seleucus eventually concluded an alliance. Seleucus gave him his daughter in marriage, ceded the territories of Arachosia
Arachosia (; ), or Harauvatis ( ), was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire. Mainly centred around the Arghandab River, a tributary of the Helmand River, it extended as far east as the Indus River. The satrapy's Persian-language name is the et ...
, Herat
Herāt (; Dari/Pashto: هرات) is an oasis city and the third-largest city in Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Se ...
, Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
and Makran
Makran (), also mentioned in some sources as ''Mecran'' and ''Mokrān'', is the southern coastal region of Balochistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in the Balochistan province in Pakistan and in Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. I ...
, and received 500 war elephants.
Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; , died 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, indologist, diplomat, ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has been partially reconstructe ...
had traveled to India and had several interviews with Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (Sanskrit: elp:IPA/Sanskrit, t̪͡ɕɐn̪d̪ɾɐgupt̪ɐ mɐʊɾjɐ (reigned 320 BCE – c. 298 BCE) was the founder and the first emperor of the Maurya Empire, based in Magadha (present-day Bihar) in the Indian ...
, known as Sandracottus to the Greeks.
Bindusara
Bindusara (320 BCE – 273 BCE) () was the second Mauryan emperor of Magadha in Ancient India. The ancient Greco-Roman writers called him Amitrochates, a name likely derived from his Sanskrit title ''Amitraghāta'' ("slayer of enemies").
...
, the second Mauryan emperor of India, had diplomatic relations with and very friendly feelings towards the Greeks. He even asked Antiochus I Soter
Antiochus I Soter (, ''Antíochos Sōtér''; "Antiochus Soter, the Savior"; 2 June 261 BC) was a Ancient Greece, Greek king of the Seleucid Empire. Antiochus succeeded his father Seleucus I Nicator in 281 BC and reigned during a period of instabi ...
to send him a Greek sophist
A sophist () was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BCE. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics and mathematics. They taught ''arete'', "virtue" or "excellen ...
for his court.
Ptolemy II Philadelphus
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the G ...
is recorded by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
as having sent an ambassador named Dionysius
The name Dionysius (; ''Dionysios'', "of Dionysus"; ) was common in classical and post-classical times. Etymologically it is a nominalized adjective formed with a -ios suffix from the stem Dionys- of the name of the Greek god, Dionysus, parallel ...
to the Mauryan
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
court at Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, probably to Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
:
:"But ndia Ndia or NDIA may refer to:
*Ndia Constituency, Kirinyaga District, Central Province, Kenya
*Alternative name for the Southern Kirinyaga dialect of the Kikuyu language
*National Defense Industrial Association, an American trade association
*Nationa ...
has been treated of by several other Greek writers who resided at the courts of Indian kings, such, for instance, as Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; , died 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, indologist, diplomat, ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has been partially reconstructe ...
, and by Dionysius
The name Dionysius (; ''Dionysios'', "of Dionysus"; ) was common in classical and post-classical times. Etymologically it is a nominalized adjective formed with a -ios suffix from the stem Dionys- of the name of the Greek god, Dionysus, parallel ...
, who was sent thither by Philadelphus expressly for the purpose: all of whom have enlarged upon the power and vast resources of these nations." Pliny the Elder, "The Natural History", Chap. 21
Asoka also appointed some Greeks to high offices of state (Yavanaraja, meaning Greek King or Governor), for example, the Tushaspha. In addition, his edicts mention a Yona (Greek) province on the north-west border of India, most probably Arachosia.
Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 ...
wrote about the use of Indian elephants in battles and about the alliance between the Indian king Sophagasenus
Sophagasenos, also spelt Sophagasenus or Sophagasenas (Sanskrit: Subhagasena), was a local Indian king ruling in Kabul and Kapisa valley ( Paropamisadae of the classical writings) during the last decades of 3rd century BCE. Sophagasenus finds re ...
and Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; , ; 3 July 187 BC) was the sixth ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of West Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to th ...
.
Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, b ...
, quoting Iambulus __NOTOC__
Iambulus or Jambulus (, ''Iamboulos'') was an ancient Greek merchant and the likely author of a utopian novel about the strange forms and figures of the inhabitants of the " Islands of the Sun". His name seems not to be Greek and reveals a ...
, mentioned that the king of Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
had a "great love for the Greeks".
The Greek historian Apollodorus
Apollodorus ( Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to:
:''Note: A ...
and the Roman historian Justin
Justin may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Justin (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Justin (historian), Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527) ...
affirmed that the Bactrian Greeks
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid satrap Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, and continued to dominate Central Asia until its fall ar ...
conquered India. Justin also described Demetrius I as "King of the Indians". Greek and Indian sources indicate the Greeks campaigned as far as Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
until they were forced to retreat following a coup in Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
in 170 BC.
The Heliodorus pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (Vidisha), Madhya Pradesh. The pillar is commonly named after Heliodorus (identified by him as a Garuda-standard), who was an ambassador of the In ...
is a stone column erected around 110 BCE in present-day central India in Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar and Bhaddilpur in ancient times) is a city in Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of Vidisha district. It is located 62.5 km north ...
, by Heliodorus
Heliodorus is a Greek name meaning "Gift of the Sun". Several persons named Heliodorus are known to us from ancient times, the best known of which are:
* Heliodorus (minister) a minister of Seleucus IV Philopator c. 175 BC
* Heliodorus of Athen ...
(), a Greek ambassador of the Indo-Greek king Antialcidas
Antialcidas Nikephoros (; epithet means "the Bearer of Victory" or "the Victorious", Brahmi: 𑀅𑀁𑀢𑀮𑀺𑀓𑀺𑀢𑀲 ''Aṃtalikitasa'', in the Heliodorus Pillar) was a king of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, who reigned from his capital at ...
to the court of the Shunga
is a type of Japanese erotic art typically executed as a kind of ukiyo-e, often in Woodcut, woodblock print format. While rare, there are also extant erotic painted handscrolls which predate ukiyo-e. Translated literally, the Japanese word '' ...
king Bhagabhadra
Bhagabhadra ( Brāhmī: 𑀪𑀸𑀕𑀪𑀤𑁆𑀭 , ) was a Shunga Emperor who reigned in northern and central India from around 114 BCE to 83 BCE. Although the capital of the Shungas was at Pataliputra, he was also known to have held court a ...
. The site is located about 5 miles from the Buddhist stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
of Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
.
The King Phraotes Phraotes was an Indo-Parthian king of Taxila, in northern Ancient India, met by the Greek philosopher Apollonius of Tyana around 46 CE according to the '' Life of Apollonius Tyana'' written by Philostratus
Philostratus or Lucius Flavius Philostr ...
received a Greek education at the court of his father and spoke Greek fluently.
Stephanus of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephen of Byzantium (; , ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD) was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethnica'' (). Only meagre fragments of the dictionary survive, but the epit ...
called the city Daedala in India an Indo-Cretan city, most probably because it was a settlement of Cretan
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
mercenaries.Stephanus of Byzantium, Ethnica, D216.8/ref>
Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
People, culture and language
* Tamils, an ethno-linguistic group native to India, Sri Lanka, and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka
** Myanmar or Burmese Tamils, Tamil people of Ind ...
poems describe the Greek soldiers who served as mercenaries for Indian kings as "the valiant-eyed Yavanas, whose bodies were strong and of terrible aspect".
Alfred Charles Auguste Foucher Alfred Charles Auguste Foucher (1865–1952), was a French scholar, who argued that the Buddha image has Greek origins. He has been called the "father of Gandhara studies", and is a much-cited scholar on ancient Buddhism in northwest Indian subconti ...
has posited that some of the troops of Mara in the Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
sculptures may represent Greek mercenaries.
The Cilappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciri ...
mentions Yavana soldiers, which, according to scholars, including Professor Dikshitar, is a reference to the Greek mercenaries employed by the Tamil kings.
Patanjali
Patanjali (, , ; also called Gonardiya or Gonikaputra) was the name of one or more author(s), mystic(s) and philosopher(s) in ancient India. His name is recorded as an author and compiler of a number of Sanskrit works. The greatest of these a ...
, the commentator of Pāṇini
(; , ) was a Sanskrit grammarian, logician, philologist, and revered scholar in ancient India during the mid-1st millennium BCE, dated variously by most scholars between the 6th–5th and 4th century BCE.
The historical facts of his life ar ...
, describes two sieges the Greeks made: the siege of Saketa and the siege of Madhyamika.
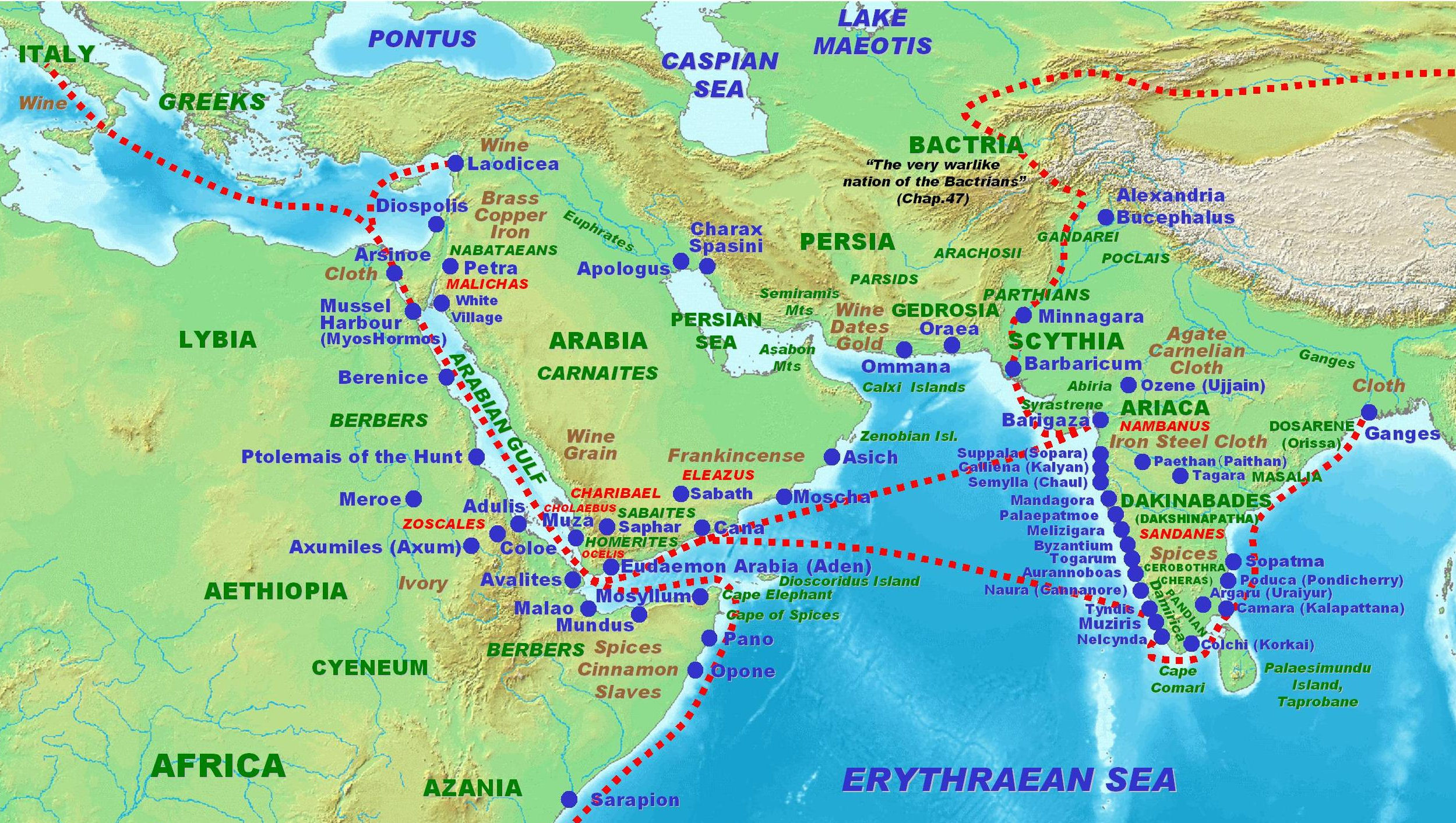
Trade

Ptolemy II Philadelphus
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the G ...
founded the Myos Hormos and selected it as the principal harbour of the trade with India, in preference to Arsinoe Arsinoe (), meaning "elevated mind", may refer to:
People
* Arsinoe of Macedon, mother of Ptolemy I Soter
* Apama II or Arsinoe (c. 292 BC–after 249 BC), wife of Magas of Cyrene and mother of Berenice II
* Arsinoe, probable mother of Lysimachu ...
, since Arsinoe was at the head of the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
and navigation down the Heroopolite Gulf was tedious and difficult. Vessels from Myos Hormos traded with Africa, Arabia, and India.
During the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
and Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
period there were trade relations between India and the Roman Empire.
Isidore of Charax
Isidore of Charax (; , ''Isídōros o Charakēnós''; ) was a Greek geographer of the 1st century BC and 1st century AD, a citizen of the Parthian Empire, about whom nothing is known but his name and that he wrote at least one work.
Name
Isidore ...
in his work ''The Parthian Stations'' () described the trade route between the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and India in the 1st century BC.
The so-called Muziris
''Muciṟi'' (, ), commonly anglicized as Muziris (, Malayalam, Old Malayalam: ''Muciṟi'' or ''Muciṟipaṭṭaṇam'', possibly identical with the medieval ''Muyiṟikkōṭŭ'') was an ancient harbour and urban centre on India's Malabar C ...
papyrus, written in Greek, contains crucial information regarding the cargo of a ship named the Hermapollon that sailed back to Egypt from Muziris in India. Muziris is also mentioned in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and Roman commerce, trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports lik ...
as one of the Indian ports Greek ships were sailing to. Other Indian ports Greek merchants visited were Barygaza, Barbarikon
Barbarikon () was the name of a sea port near the modern-day city of Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan, important in the ancient era of the Indian subcontinent in Indian Ocean trade. The port is considered one of the premiere ports regarding the interacti ...
, Minnagara
Minnagara () was a city of the Indo-Scythian kingdom, located on the Indus river in Pakistan, north of the coastal city of Barbaricum, North and West of Barygaza.
Minnagara is mentioned in the 1st century CE Periplus of the Erythraean Sea:
:"B ...
, Ujjain
Ujjain (, , old name Avantika, ) or Ujjayinī is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative as well as religious centre of Ujjain ...
and Ariaca
Ariaca () was a region of Western India beyond Barigaza, mentioned in ancient geographical sources, usually associated with the Western Satraps.
According to the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Ariaca was part of the kingdom of ''Nambanus'', tho ...
.
Tacola (Τάκωλα) was a place on the west coast of the Aurea Chersonesus, in India extra Gangem, which Ptolemy calls an emporium.
The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and Roman commerce, trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports lik ...
was a manual written in Greek for navigators who carried trade between the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
and other regions, including ancient India. It gives detailed information about the ports, routes and commodities.
Ancient Greek and Roman writers also describe the ports of the Arabia Felix
Arabia Felix (literally: Fertile/Happy Arabia; also Ancient Greek: Εὐδαίμων Ἀραβία, ''Eudaemon Arabia'') was the Latin name previously used by geographers to describe South Arabia, or what is now Yemen.
Etymology
The Latin term ...
, which were used for the Indian trade.
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea (; ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; ; – 565) was a prominent Late antiquity, late antique Byzantine Greeks, Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Justinian I, Empe ...
writes that, when the Byzantines didn't want to purchase their silk from the Persians any longer due to their conflicts, some monks coming from India, who had also spent a long time in a country called Serinda () which was beyond India, talked with the Emperor Justinian
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
and promised to settle the silk question. Thus, the Byzantines would not need to buy silk from the Persians.
Chanakya
Chanakya (ISO 15919, ISO: ', चाणक्य, ), according to legendary narratives preserved in various traditions dating from the 4th to 11th century CE, was a Brahmin who assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta Maurya, Chandragup ...
mentioned Greeks and their polities in his ''Arthashastra
''Kautilya's Arthashastra'' (, ; ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, politics, economic policy and military strategy. The text is likely the work of several authors over centuries, starting as a compilation of ''Arthashas ...
''.
Athenaeus
Athenaeus of Naucratis (, or Nαυκράτιος, ''Athēnaios Naukratitēs'' or ''Naukratios''; ) was an ancient Greek rhetorician and Grammarian (Greco-Roman), grammarian, flourishing about the end of the 2nd and beginning of the 3rd century ...
in the Deipnosophistae
The ''Deipnosophistae'' (, ''Deipnosophistaí'', lit. , where ''sophists'' may be translated more loosely as ) is a work written in Ancient Greek by Athenaeus of Naucratis. It is a long work of Greek literature, literary, Ancient history, h ...
wrote that ''Euthydemus the Athenian'' in his book ''on Vegetables'' calls a species of gourd
Gourds include the fruits of some flowering plant species in the family Cucurbitaceae, particularly '' Cucurbita'' and '' Lagenaria''. The term refers to a number of species and subspecies, many with hard shells, and some without. Many gourds ha ...
the Indian gourd (σικύαν Ἰνδικὴν) because the seed of that gourd was originally introduced from India.
After Alexander's time, there were trade relations between the Greek world and Sri Lanka. Ancient writers describe in details what was traded. Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes (; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a merchant and later hermit from Alexandria in Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who made several voyages to India during the reign of emperor Justinian. His work '' Christian Topogr ...
wrote about a specific Greek merchant named ‘Sopatrus’ who had a trade relationship with Sri Lanka. At the Jaffna Peninsula
The Jaffna Peninsula (, or ) is a region in the Northern Province of Sri Lanka. It is home to the capital city of the province, Jaffna, and comprises much of the former land mass of the medieval Jaffna Kingdom.
The peninsula was historically ...
, archaeologists discovered gold coins with Greek inscriptions, most probably belonging to the Byzantine period.
Travelers and explorers
The Greek historianHerodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
in the fifth century BCE was aware of dark-skinned people who lived far to the east, whom the Greeks named Aethiopes, although Greek beliefs seem to have been confused by conflating African and Indian characteristics and peoples. Ancient Greek knowledge of and interest in India hugely increased following the conquests of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
and his campaign in northern India between 327–25 BCE.
Classical period
Fragments of the writings ofHecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; ; c. 550 – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Persian rule in the satrapy of Lydia ...
(549–486 BCE) convey a knowledge of nations living on the banks of the river Indus, using names for them including Indi, Indus, Argante and the people of Opia. Herodotus records that the Greek explorer Scylax, in about 515 BCE, was sent by King Darius I of Persia
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
to follow the course of the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
and discover where it led. Writings attributed to Scylax, however, have been shown to have been written much later, in the fourth century BCE. No mention of India can be found in any of the works of Homer, Pinder or the Athenian playwrights.
Hellenistic period
Things changed dramatically near the end of the fourth century BCE, after the conquests of Alexander the Great.Nearchus
Nearchus or Nearchos (; – 300 BC) was one of the Greeks, Greek officers, a navarch, in the army of Alexander the Great. He is known for his celebrated expeditionary voyage starting from the Indus River, through the Persian Gulf and ending at t ...
, an officer in the army of Alexander who probably wrote his memoirs near the very end of the fourth century BCE, described India and the people living there. Onecicritus of Astypaleia, who was a captain of Alexander's navy, wrote about Sri Lanka.
The Greek ethnographer
Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining ...
and explorer of the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
, Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; , died 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, indologist, diplomat, ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has been partially reconstructe ...
was a Macedonian ambassador sent by Seleucus I
Seleucus I Nicator (; Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the eponymous Seleucid Empire, ...
to the courts of Sandrocottus (Chandragupta) who ruled an area in northern India that lay north of the river Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
. In his work, ''Indika'' (), he wrote about the history of Indians
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
and their culture. Megasthenes also mentioned the prehistoric arrival of the god Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ...
and Herakles
Heracles ( ; ), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of ZeusApollodorus1.9.16/ref> and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive descent through Amphitr ...
(Megasthenes' Herakles
Porus or Poros ( ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of what is now India and Pakistan. He is only mentioned in Gre ...
) in India. Some years later, Deimachus
Deimachus or Daimachus (; ) was a Greek from Plataeae, who lived during the third-century BCE. He became an ambassador to the court of the Mauryan ruler Bindusara "Amitragatha" (son of Chandragupta Maurya) in Pataliputra in India.
Deimachus wa ...
, who was an ambassador to the court of Bindusara, also wrote about India.
Patrocles was an admiral of Seleucus who sailed into the Indian Ocean and left an account of his travels, confirming Megasthenes' estimate of the breadth of India. His knowledge of the eastern seaboard of India was in error, however, believing that sea encircled the Indian subcontinent, linking the Indian Ocean with the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
. We know all this from the surviving works of the Greek historian Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, who was active in the first century BCE. He did not trust previous writings about India because he believed they included a lot of fables in their writings, especially the recountings of Deimachus and Megasthenes, while Onesicritus and Nearchus together with some others wrote "a few words of truth," in his view. On the other hand, he trusted the works of Patrocles and Eratosthenes.
Eudoxus of Cyzicus
Eudoxus of Cyzicus ( ; ; ) was a Greek navigator and diplomat who explored the Arabian Sea for Ptolemy VIII, king of the Hellenistic Ptolemaic dynasty in Egypt.
Voyages to India
According to Poseidonius, later reported in Strabo's ''Geography ...
, near the end of the second century BCE, and Hippalus
Hippalus (Ancient Greek: Ἵππαλος) was a Greek navigator and merchant who probably lived in the 1st century BCE. He is sometimes conjectured to have been the captain of the Greek explorer Eudoxus of Cyzicus' ship.
Use of monsoon
The writ ...
, who was possibly associated with Eudoxus, traveled to India with their ships. Hippalus is credited by the writer of the 1st-century CE ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' with establishing currents, winds and a route to use for trade with stopping points along the coast of India between the Red Sea and the very south of India.
Roman period
In the first century BCE, the naked Indian philosopher and monkZarmanochegas
Zarmanochegas (; according to Strabo) or Zarmarus (according to Dio Cassius) was a gymnosophist (naked philosopher), a monk of the Sramana tradition (possibly, but not necessarily a Buddhist) who, according to ancient historians such as Strabo a ...
(possibly, but not necessarily, a Buddhist) met Nicholas of Damascus
Nicolaus of Damascus (Greek: , ''Nikolāos Damaskēnos''; Latin: ''Nicolaus Damascenus''; – after 4 AD) was a Greek historian, diplomat and philosopher who lived during the Augustan age of the Roman Empire. His name is derived from that of his ...
in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
and later he also traveled to Athens, where he burned himself to death in 19 BCE. According to Plutarch, writing near the end of the first century CE or the beginning of the second, his tomb could still be seen in Athens.
Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine, Islamic, and ...
, in the second century CE, mentions in his work a Greek captain named Diogenes, who was returning from his trip to India when the winds blew him off course and he had to stop below the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
. Since the winds were not favorable to travel north, he traveled south and explored the east coast of Africa where he found the city of Rhapta
Rhapta () was an emporion said to be on the coast of Southeast Africa, first described in the 1st century CE. Its location has not been firmly identified, although there are a number of plausible candidate sites. The ancient ''Periplus of the Er ...
. According to Ptolemy, this happened during the second trip of Diogenes to India.
Christian period
The ''Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; ; ) is a large 10th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine encyclopedia of the History of the Mediterranean region, ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas () or Souidas (). It is an ...
'', a 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia, mentioned that when Theophilos the Indian
Theophilos the Indian, also known as Theophilus Indus () (died 364), also called "the Ethiopian", was an Aetian or Heteroousian bishop who fell alternately in and out of favor with the court of the Roman emperor Constantius II. He is mentioned in ...
returned from India, he spent time in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
and the Emperor Constantius II
Constantius II (; ; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic peoples, while internally the Roman Empire went through repeated civ ...
treated him with all honor and respect.
Sozomen
Salamanes Hermias Sozomenos (; ; c. 400 – c. 450 AD), also known as Sozomen, was a Roman lawyer and historian of the Christian Church.
Family and home
Sozoman was born around 400 in Bethelia, a small town near Gaza, into a wealthy Christia ...
wrote that Meropius (Μερόπιός), a philosopher of Tyre, traveled together with two of his relatives, Frumentius
Saint Frumentius (; died c. 383) was a Phoenician Christian missionary and the first bishop of Axum who brought Christianity to the Kingdom of Aksum. He is sometimes known by other names, such as Abuna ("Our Father") and Aba Salama ("Father ...
(Φρουμέντιός) and Edesius (Ἐδέσιος) to India.
The Christian Topography
The ''Christian Topography'' (, ) is a 6th-century work, one of the earliest essays in scientific geography written by a Christian author. It originally consisted of five books written by Cosmas Indicopleustes and expanded to ten and eventually t ...
by Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes (; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a merchant and later hermit from Alexandria in Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who made several voyages to India during the reign of emperor Justinian. His work '' Christian Topogr ...
was an essay in scientific geography written in Greek with illustrations and maps. The work mentioned India, and the writer Cosmas Indicopleustes had actually made the journey, and he described and sketched some of what he saw in his topography. Cosmas Indicopleustes means "Cosmas who sailed to India".
Cities and places
Around 510 BCE, Persians, under the rule ofDarius the Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
moved the inhabitants of the Greek colony of Barca in Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
into Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
. Later, Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was ...
also settled there with the "Branchidae," who were the descendants of Greek priests who had once lived at Didyma
Didyma (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek sanctuary on the coast of Ionia in the domain of the famous city of Miletus. Apollo was the main deity of the sanctuary of Didyma, also called ''Didymaion''. But it was home to both of the Ancient ...
. Herodotus also records Persian generals threatening to enslave daughters of the revolting Ionians and send them to Bactria if they didn't stop fighting.
According to legend the god Dionysus founded the city of Nysa and named it Nysa and the land Nysaea (Νυσαία) after his nurse and he named the mountain near the city, Meron (Μηρὸν) (i.e. thigh), because he grew in the thigh of Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
. When Alexander arrived at the city, he and his Companion cavalry
The Companions (, , ''hetairoi'') were the elite heavy cavalry of the Macedonian army from the time of King Philip II of Macedon, achieving their greatest prestige under Alexander the Great, and regarded as the first or among the first shock ca ...
went to the mountain, where they made ivy garlands and crowned themselves with them, singing hymns in honor of Dionysus. Alexander also offered sacrifices to Dionysus, and feasted in company with his companions.
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
founded the cities of Nicaea
Nicaea (also spelled Nicæa or Nicea, ; ), also known as Nikaia (, Attic: , Koine: ), was an ancient Greek city in the north-western Anatolian region of Bithynia. It was the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and seve ...
and Alexandria Bucephalous
Boukephala () and Nikaia () were two cities founded by Alexander the Great on either side of the Hydaspes (modern-day Jhelum River, Pakistan) during his invasion of the Indian subcontinent. The cities, two of many founded by Alexander, were bui ...
. He also founded a city and named it after his dog, Peritas
Peritas () was Alexander the Great's favorite dog, who accompanied him during his military exploits.
History The eponymous city
Not much is known of the historical Peritas aside from a city named in his honor. Like Alexander's horse Bucephalus, ...
. In addition, he ordered Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male name derived from the Macedonian Old Koine language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominen ...
to build Alexandria on the Indus
Alexandria on the Indus (, likely modern Uch, Pakistan) was a city founded by Alexander the Great at the junction of the Indus and the Acesines river. Arrian tells that colonists, mainly Thracian veterans and natives, were settled there.
Th ...
. He also founded other cities in India. Quintus Curtius Rufus
Quintus Curtius Rufus (; ) was a Ancient Rome, Roman historian, probably of the 1st century, author of his only known and only surviving work, ''Historiae Alexandri Magni'', "Histories of Alexander the Great", or more fully ''Historiarum Alex ...
wrote that Alexander founded a number of cities in the Indus Delta, but most probably he meant some garrisons. Claudius Aelianus
Claudius Aelianus (; ), commonly Aelian (), born at Praeneste, was a Roman author and teacher of rhetoric who flourished under Septimius Severus and probably outlived Elagabalus, who died in 222. He spoke Greek so fluently that he was called "h ...
wrote that there were Macedonians who settled in India in the cities founded by Alexander.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
wrote that Nearchus
Nearchus or Nearchos (; – 300 BC) was one of the Greeks, Greek officers, a navarch, in the army of Alexander the Great. He is known for his celebrated expeditionary voyage starting from the Indus River, through the Persian Gulf and ending at t ...
founded the town of Arbis during his voyage to India.
The ancient Greeks called the modern Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
''Gangeticus Sinus'' (), meaning "Gulf of the Ganges".
According to Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
, many Greek cities were founded by the Greco-Bactrians in northern India.
The cities of Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. Demetr ...
and Demetriapolis were founded by Demetrius I of Bactria
Demetrius I Anicetus (, "Demetrius the Unconquered"), also called Dimetriya in Indian sources, was a Greco-Bactrian king and the founder of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, Indo-Greek kingdom, who ruled areas from Bactria to ancient northwestern of Subcon ...
.
Eucratideia was founded by Eucratides I
Eucratides I (, ''Eukratídēs''; Pali: ''Evukratida''; reigned 172/171–145 BC), also known as Eucratides the Great, was one of the most important Greco-Bactrian kings. He conquered large parts of northern India, and minted a vast and pre ...
.
Panchaia was an island paradise located in the Indian Ocean mentioned by Greek writers.
Contacossyla (Κοντακόσσυλα) and Allosygna were emporia in the district of Maesolia (Μαισωλία or Μασαλία) (modern Masulipatam
Machilipatnam (), also known as Masulipatnam and Bandar (), is a city in Krishna district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is a municipal corporation and the administrative headquarters of Krishna district. It is also the mandal headqua ...
).Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), Maesolia/ref> Maliarpha (Μαλιάρφα,) was a place of considerable commerce in the territory of the Arvarni.
Stephanus of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephen of Byzantium (; , ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD) was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethnica'' (). Only meagre fragments of the dictionary survive, but the epit ...
wrote about a city called Daedala or Daidala () in India, which he called an Indo-Cretan city, most probably because it was a settlement of Cretan
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
mercenaries.Stephanus also described many other Indian cities and places.
The Greeks called the Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
region ''Pentapotamía'' (), meaning five rivers.
Caspeiria (Κασπειρία) was a district of India intra Gangem with Ptolemy naming 18 cities there, including the Caspeira (Κάσπειρα)Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), caspeiria/ref> and the Rarassa (Ῥαράσσα or Ἠράρασα).Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), Rarassa
/ref>
Caspatyrus
Scylax of Caryanda (; ) was a Greek explorer and writer during the late 6th and early 5th centuries BCE of the Achaemenid Empire. His own writings are lost, though occasionally cited or quoted by later Greek and Roman authors. The periplus sometim ...
(Κασπάτυρος) or Caspapyrus (Κασπάπυρος) was a city in the district of Pactyice.
Calinipaxa was a city in India made known to the Greeks by the expedition of Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to fo ...
.
Gange (Γάγγη), according to Ptolemy, was the capital of the Gangaridae, at the mouth of the Ganges river. While Strabo speaks of a town with a similar name but places it far up the river, in the vicinity of Palibothra or Patna
Patna (; , ISO 15919, ISO: ''Paṭanā''), historically known as Pataliputra, Pāṭaliputra, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, ...
.
Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and Roman commerce, trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports lik ...
mention a city called Ganges (Γάγγης).
The Greeks called the Eastern Himalayas
]
The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. I ...
in the district of India intra Gangem Damassi Montes/Mountains (τὰ Δάμασσα ὄρη).
The Saurashtra (region)
Kathiawar (), also known as Saurashtra, is a peninsula in the south-western Gujarat state in India, bordering the Arabian Sea and covering about . It is bounded by the Kutch district in the north, the Gulf of Kutch in the northwest, and by t ...
was called by the Greeks Syrastrene (Συραστρηνή). Ptolemy mentions Syrastra, which may have once been its capital. Larica (Λαρική) was a rich commercial district between Syrastrene and Ariaca
Ariaca () was a region of Western India beyond Barigaza, mentioned in ancient geographical sources, usually associated with the Western Satraps.
According to the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Ariaca was part of the kingdom of ''Nambanus'', tho ...
.
Dyrta (τὰ Δύρτα) was a small town in the country of the Assacani.
Peperine (Πεπερίνη) was an island off the south-west coast of India, undoubtedly derived its name from producing pepper.
Pactyice (Πακτϋική) was a district of North-Western India.
Triglyphon was the metropolis and royal residence of Cirrhadia (the modern Tipperah).
Palimbothra (Παλιμβόθρα) was one of the most important cities in India.
Chryse and Argyre
Chryse and Argyre ( and ) were a pair of legendary islands, located in the Indian Ocean and said to be made of gold and silver. They took their name from the Greek words for gold (''chrysos'') and silver (''argyros'').
Pomponius Mela in his wor ...
were a pair of legendary islands, located in the Indian Ocean mentioned by ancient writers.
Bessyga (Βήσσυγα) was, according to Stephanus of Byzantium, an emporium in India.
Taprobana/Taprobane-Palaesimundu-Salice
At the Anuradhapura Kingdom inSri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, there was a Greek settlement. Professor Merlin Peris, former professor of classics at the University of Peradeniya
The University of Peradeniya (, ) is a Public research university, public university in Sri Lanka, funded by the University Grants Commission of Sri Lanka, University Grants Commission. It is the largest university in Sri Lanka, which was origin ...
, wrote that “the Greeks whom King Pandukabhaya
Pandukabhaya was a king of Upatissa Nuwara and the first monarch of the Anuradhapura Kingdom and 6th over all of the island of Sri Lanka since the arrival of the Vijaya; he reigned from 437 BC to 367 BC. According to many historians and philo ...
settled in the West Gate of Anuradhapura were not the second or third generation of Greeks who arrived in northwest India but were men who, just two decades ago at the most, left Greek homelands as Alexander's camp followers and came to Sri Lanka with or in the wake of Alexander's troops. When their fellow Greeks showed reluctance to push further south, these Greeks apparently had done so.” The Greeks called Sri Lanka Taprobana
Taprobana (; ), Trapobana, and Taprobane (, ) was the name by which the Indian Ocean island of Sri Lanka was known to the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks.
Tabrobane is suggested to be derived from Sanskrit "Tamraparni". This name could be a ref ...
, some Greek authors also used ''Palaisimoundou'', ''Salike'' and ''Sieladiba''.
Palaesimundum (Παλαισιμούνδου) was a town in Taprobane, but in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea the writer inform us that at his time the whole island was called like this (Ptolemy and Stephanus state that the island was called Simundum (Σιμούνδου), but it is very probable that they made a mistake and the correct name was Palaesimundum). Later the island was also called Salice (Σαλική).
Stephanus of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephen of Byzantium (; , ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD) was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethnica'' (). Only meagre fragments of the dictionary survive, but the epit ...
writes that a metropolis of the Taprobana was called Argyra () and that there was also a river called Phasis (). Ptolemy called one of a group of islands which surrounded Sri Lanka Nagadiba () (see Jaffna Peninsula
The Jaffna Peninsula (, or ) is a region in the Northern Province of Sri Lanka. It is home to the capital city of the province, Jaffna, and comprises much of the former land mass of the medieval Jaffna Kingdom.
The peninsula was historically ...
). Talacory (Ταλάκωρυ) or Aacote (Ἀακότη) was a port emporium on the north-western side of Taprobana.
Tarachi (Τάραχοι) was a tribe in Taprobane who had a port called Ἡλίου λίμην.
Galiba (Γάλιβα ἄκρα) was a promontory on the northern coast of Taprobane, close to the Cory island. Certain mountains in the immediate neighbourhood of it had the same name Γάλιβα ὄρη and the inhabitants of which were called Galibi (Γάλιβοι). Cape of Zeus (Δίος ἄκρα) was a promontory on the south of Taprobane. Its exact position cannot be identified, but it must have been close to present Galle
Galle (, ; , ) (formerly ) is a major city on the southwestern tip of Sri Lanka, south of Colombo. Galle is the provincial capital and largest city of Southern Province, Sri Lanka and is the capital of Galle District.
Galle was known as ''Gi ...
, if not the same.
Tribes
Greek writers mention many tribes. For example, the: * Abastanes or Abastani or Sambastae (Σαμβασταί) or Sabarcae, probably theAmbashtha
Ambashtha or Ambastha is a caste or sub-caste or a community of Hindus in India. According to Hindu scriptures, the term Ambastha refers to the offspring of a Brahmin father and a Vaishya mother, whose traditional occupation was the practice of m ...
.
* Arvarni (Ἀρούαρνοι), a tribe of India intra Gangem.
* Assakenoi or Assacani (Ἀσσακηνοί) or Astakenoi (Ἀστακηνοί).
* Calingae, people of India, live Gangem, close to the sea.
* Caspeiraei (Κασπειραῖοι), a tribe of India intra Gangem.
* Gangaridae
Gangaridai (, ) is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE–2nd century AD) to describe people or a geographical region of the ancient Indian subcontinent. Some of these writers state that Alexander the Great withdrew fr ...
(Γαγγαρίδαι), people near the mouths of the Ganges. Ptolemy assigns them a capital, called Ganga Regia, on the western side of the Ganges.
* Guraeans (Γουραίοι).
* Harmatotrophi, a small tribe mentioned by Pliny as living at the foot of the Hindu Kush.
* Hippasii (Ἱππάσιοι), most probably the same tribe as the Aspasii (Ἀσπάσιοι) or Aspii (Ἄσπιοι).
* Kirradae (Κιρρᾶδαι).
* Maesoli (Μαισώλοι), people of the Maesolia.
* Mallian people
Mallian people () were a tribe from modern day southern Punjab, with capital at today's Multan city, south of the confluence of the Jhelum (Hydaspes) and Ravi, ( Hydraotes) rivers. They confronted Alexander the Great during his Mallian campaign in ...
.
* Mandalae (Μανδάλαι).
* Padaei
The Padaei () or the Padaeans are an Indian tribe described by the Greek historian Herodotus in ''The Histories''. Herodotus describes them (III.101) as being darker than other Indians and living in a place which is very distant from Persia toward ...
(Παδαῖοι), an Indian tribe.
* Pandae, an Indian tribe with the habit of having female sovereigns.
* Parapiotae (Παραπιῶται), an Indian tribe along the banks of the Namadus river.
* Pargyetae (Παργυῆται), a tribe who occupied part of the Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central Asia, Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and eastern Afghanistan into northwestern Pakistan and far southeastern Tajikistan. The range forms the wester ...
.
* Passalae (Πασσάλαι) a tribe in India extra Gangem.
* Zamirae or Zamirai (Ζαμῖραι) and Gamerae or Gamerai (Γαμῆραι) was a tribe in India extra Gangem roughly in modern Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
.
* Oritae (Ὠρεῖται), a tribe of the sea-coast of Gedrosia
Gedrosia (; , ) is the Hellenization, Hellenized name of the part of coastal Balochistan that roughly corresponds to today's Makran. In books about Alexander the Great and his Diadochi, successors, the area referred to as Gedrosia runs from the I ...
.
* Xathri (Ξάθροι), a tribe Indians dwelling along the banks of the Hydraotes. They may have derived their name from the caste of the Kshatriyas
Kshatriya () (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority"; also called Rajanya) is one of the four varnas (social orders) of Hindu society and is associated with the warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
.
* Tacaraei (Τακαραῖοι), a mountain tribe of India extra Gangem. They must have occupied part of modern Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
.
* Taluctae, a tribe of India extra Gangem, mentioned by Pliny.
* Tabassi (Τάβασσοι), a tribe of Indians who occupied the interior of the southern part of Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( English: /ˈhɪndustæn/ or /ˈhɪndustɑn/, ; ) was a historical region, polity, and a name for India, historically used simultaneously for northern Indian subcontinent and the entire subcontinent, used in the modern day ...
, in the neighbourhood of the present province of Mysore
Mysore ( ), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. As the traditional seat of the Wadiyar dynasty, the city functioned as the capital of the ...
. It seems that they derived their name from the Sanskrit Tapasja, “woods.”
Other
Pāṇini
(; , ) was a Sanskrit grammarian, logician, philologist, and revered scholar in ancient India during the mid-1st millennium BCE, dated variously by most scholars between the 6th–5th and 4th century BCE.
The historical facts of his life ar ...
, an ancient Sanskrit grammarian, was acquainted with the word yavana (Greek) in his composition.
Kātyāyana
Kātyāyana (कात्यायन) also spelled as Katyayana ( century BCE) was a Sanskrit grammarian, mathematician and Vedic priest who lived in ancient India.
Origins
According to some legends, he was born in the Katya lineage origina ...
was a Sanskrit grammarian, mathematician and Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
priest who lived in ancient India. He explained the term yavanānī as the script of the Yavanas. He took the same line as Pāṇini that the Old Persian
Old Persian is one of two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of the Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native speakers as (I ...
term yauna became Sanskritised to name all Greeks.
Theodectes
Theodectes (; c. 380c. 340 BC) was a Greek rhetorician and tragic poet, of Phaselis in Lycia.
Life
He lived in the period which followed the Peloponnesian War. Along with the continual decay of political and religious life, tragedy sank more and ...
thought the dark color of some Indians was because of the sun.GREEK IMAGE OF THE INDIAN SOCIETY/ref>
Athenaeus
Athenaeus of Naucratis (, or Nαυκράτιος, ''Athēnaios Naukratitēs'' or ''Naukratios''; ) was an ancient Greek rhetorician and Grammarian (Greco-Roman), grammarian, flourishing about the end of the 2nd and beginning of the 3rd century ...
in his Deipnosophistae
The ''Deipnosophistae'' (, ''Deipnosophistaí'', lit. , where ''sophists'' may be translated more loosely as ) is a work written in Ancient Greek by Athenaeus of Naucratis. It is a long work of Greek literature, literary, Ancient history, h ...
mentions a Basilis (Βάσιλις) who wrote a series of books about the History of India.
Claudius Aelianus
Claudius Aelianus (; ), commonly Aelian (), born at Praeneste, was a Roman author and teacher of rhetoric who flourished under Septimius Severus and probably outlived Elagabalus, who died in 222. He spoke Greek so fluently that he was called "h ...
wrote about the animals in India. He also mentioned that there were Macedonians who settled in India in the cities founded by Alexander.Aelian, Characteristics of Animals, § 16.3/ref> The Unani System of Medicine, a traditional system of medicine practiced in India, refers to Graeco-Arabic medicine, which is based on the teachings of Greek physicians
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
and Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one o ...
. The ancient Greek medical system was enriched with local elements and received positively by the Indian people and physicians.
India and Indians are mentioned in some of Martial's Epigrams.
A lot of entries in the Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; ; ) is a large 10th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine encyclopedia of the History of the Mediterranean region, ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas () or Souidas (). It is an ...
, the Byzantine encyclopedia, are about India.
Modern archaeological evidence from Bronze Age
A wall-painting from the Minoan town of Akrotiri has been identified as depicting a grey langur, a species of monkey native to theIndus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disp ...
. Bronze-age contact between the Minoan world and the Indian subcontinent was likely mediated by the civilisations of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
.
The historian Peter Frankopan
Peter Frankopan (born 22 March 1971) is a British historian, writer, and hotelier. He is a professor of global history at Worcester College, Oxford, and the Director of the Oxford Centre for Byzantine Research. He is a fellow of the Royal Asiati ...
said that “long-distance trade, and connections between the Mediterranean, Asia and the Indian Ocean are well attested, even in this period he Bronze Age for high value, expensive objects.” (See Indo-Mediterranean
The Indo-Mediterranean is the region comprising the Mediterranean world, the Indian Ocean world, and their connecting regions in the vicinity of the Suez Canal.
History
Prehistory
From around 3000 BCE to 1000 CE, connectivity within Afro-Eu ...
).
The area of modern Hala Sultan Tekke
Hala Sultan Tekke ( ''Tekés Chalá Soultánas''; ) is a mosque and takya (or ''tekke'' in Turkish) on the west bank of Larnaca Salt Lake, in Larnaca, Cyprus. Umm Haram, known as Hala Sultan in Turkish tradition, was the wife of Ubada bin al-S ...
in Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
was an important trade hub during the Late Bronze Age, with large quantities of imported goods from neighbouring regions but also faraway regions like Afghanistan and India./ref>
See also
*India (Herodotus)
In ancient Greek geography, the Indus Basin, basin of the Indus River, was on the extreme eastern fringe of the ecumene, known world.
The Greek geographer Herodotus (5th century BC) describes the land as India, calling it (Roman transliteration ...
*Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
*Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Ancient Greece, Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central Asia, Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid satrap Diodotus I, Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, ...
*Indo-Scythians
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranic Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwestern Indian subcontinent: p ...
* Greek campaigns in India
*Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley
Around 535 BCE, the Persian king Cyrus the Great initiated a protracted campaign to absorb parts of India into his nascent Achaemenid Empire. In this initial incursion, the Persian army annexed a large region to the west of the Indus River, con ...
*''The Shape of Ancient Thought
''The Shape of Ancient Thought: Comparative Studies in Greek and Indian Philosophies'' is a book by the American writer Thomas McEvilley, published in 2001 by Allworth Press.
Summary
Thomas McEvilley traces exchanges between ancient Greek philos ...
''
Greco-Buddhism
*Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism or Graeco-Buddhism was a cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Gandhara, which was in present-day Pakistan and parts of north-east Afghanis ...
*Greco-Buddhist monasticism
The role of Greek Buddhist monks in the development of the Buddhist faith under the patronage of Emperor Ashoka around 260 BCE and subsequently during the reign of the Indo-Greek king Menander (r. 165/155–130 BCE) is described in the '' Maha ...
*Greco-Buddhist art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
*Gandharan Buddhism
Gandhāran Buddhism was the Buddhist culture of ancient Gandhāra, which was a major center of Buddhism in the northwestern Indian subcontinent from the 3rd century BCE to approximately 1200 CE.Kurt Behrendt, Pia Brancaccio, Gandharan Buddhism ...
*Buddhism and the Roman world
Several instances of interaction between Buddhism and the Roman world are documented by Classical and early Christian writers.
Textual sources in the Tamil language, moreover, suggest the presence of Buddhism among some Roman citizens in the ...
* Indo-Greek religions
*Buddhas of Bamiyan
The Buddhas of Bamiyan (, ) were two monumental Buddhist statues in the Bamiyan Valley of Afghanistan, built possibly around the 6th-century. Located to the northwest of Kabul, at an elevation of , carbon dating of the structural components o ...
*Third Buddhist council
Since the Mahaparinirvana of the historical Buddha, Siddhartha Gautama, Buddhist monastic communities, the "''sangha''", have periodically convened for doctrinal and disciplinary reasons and to revise and correct the contents of the Buddhist c ...
Trade and relations
*Buddhism and the Roman world
Several instances of interaction between Buddhism and the Roman world are documented by Classical and early Christian writers.
Textual sources in the Tamil language, moreover, suggest the presence of Buddhism among some Roman citizens in the ...
* Economic history of India
Around 500 BC, the Mahajanapadas minted punch-marked silver coins. The period was marked by intensive trade activity and urban development. By 300 BC, the Maurya Empire had united most of the Indian subcontinent except Tamilakam, allowing fo ...
* Historic GDP of India (1-1947 CE)
* Indus–Mesopotamia relations
Indus–Mesopotamia relations are thought to have developed during the second half of 3rd millennium BCE, until they came to a halt with the extinction of the Indus valley civilization after around 1900 BCE. Mesopotamia had already been an interme ...
* Indo-Mediterranean
The Indo-Mediterranean is the region comprising the Mediterranean world, the Indian Ocean world, and their connecting regions in the vicinity of the Suez Canal.
History
Prehistory
From around 3000 BCE to 1000 CE, connectivity within Afro-Eu ...
* Indo-Roman relations
* Indian Ocean trade
Indian Ocean trade has been a key factor in East–West exchanges throughout history. Long-distance maritime trade by Austronesian trade ships and South Asian and Middle Eastern dhows, made it a dynamic zone of interaction between peoples, cu ...
* Sino-Roman relations
Between the Roman Empire and the Han dynasty, as well as between the later Eastern Roman Empire and various successive Chinese dynasties, there were (primarily indirect) contacts and flows of trade goods, information, and occasional travelers ...
* Indian maritime history
Indian maritime history begins during the 3rd millennium BCE when inhabitants of the Indus Valley initiated maritime trading contact with Mesopotamia. India's long coastline, which occurred due to the protrusion of India's Deccan Plateau, hel ...
* Meluhha trade with Sumer
Other
*Romani people in Greece
The Romani people in Greece, or Romá (Greek: Ρομάνι/Ρομά), are called Tsinganoi (Greek: Τσιγγάνοι), Athinganoi (Αθίγγανοι), or the more derogatory term Gyftoi (Greek: Γύφτοι) (Romani people).
On 8 April 2019 ...
References
Bibliography
* *Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), William Smith, LLD, Ed., India
Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), William Smith, LLD, Ed., Taprobane
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ancient Greece-Ancient India relations
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
Greece–India relations
Greece-India
Greece–Pakistan relations
Indian Ocean trade
Indo-Greek religions and philosophy
Indo-Greeks
Buddhism in the ancient Mediterranean