|
Nearchus
Nearchus or Nearchos (; – 300 BC) was one of the Greeks, Greek officers, a navarch, in the army of Alexander the Great. He is known for his celebrated expeditionary voyage starting from the Indus River, through the Persian Gulf and ending at the mouth of the Tigris, Tigris River following the Indian campaign of Alexander the Great, in 326–324 BC. Early life A native of Lato in Crete and son of Androtimus, his family settled at Amphipolis in Ancient Macedonia, Macedonia at some point during Philip II of Macedon, Philip II's reign (we must assume after Philip took the city in 357 BC), at which point Nearchus was probably a young boy. He was almost certainly older than Alexander, as were Ptolemy I, Ptolemy, Erigyius, and the others of the ‘boyhood friends’; so depending on when Androtimus came to Macedonia Nearchus was quite possibly born in Crete. Nearchus, along with Ptolemy I Soter, Ptolemy, Erigyius and Laomedon of Mytilene, Laomedon, and Harpalus, was one of Alexand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
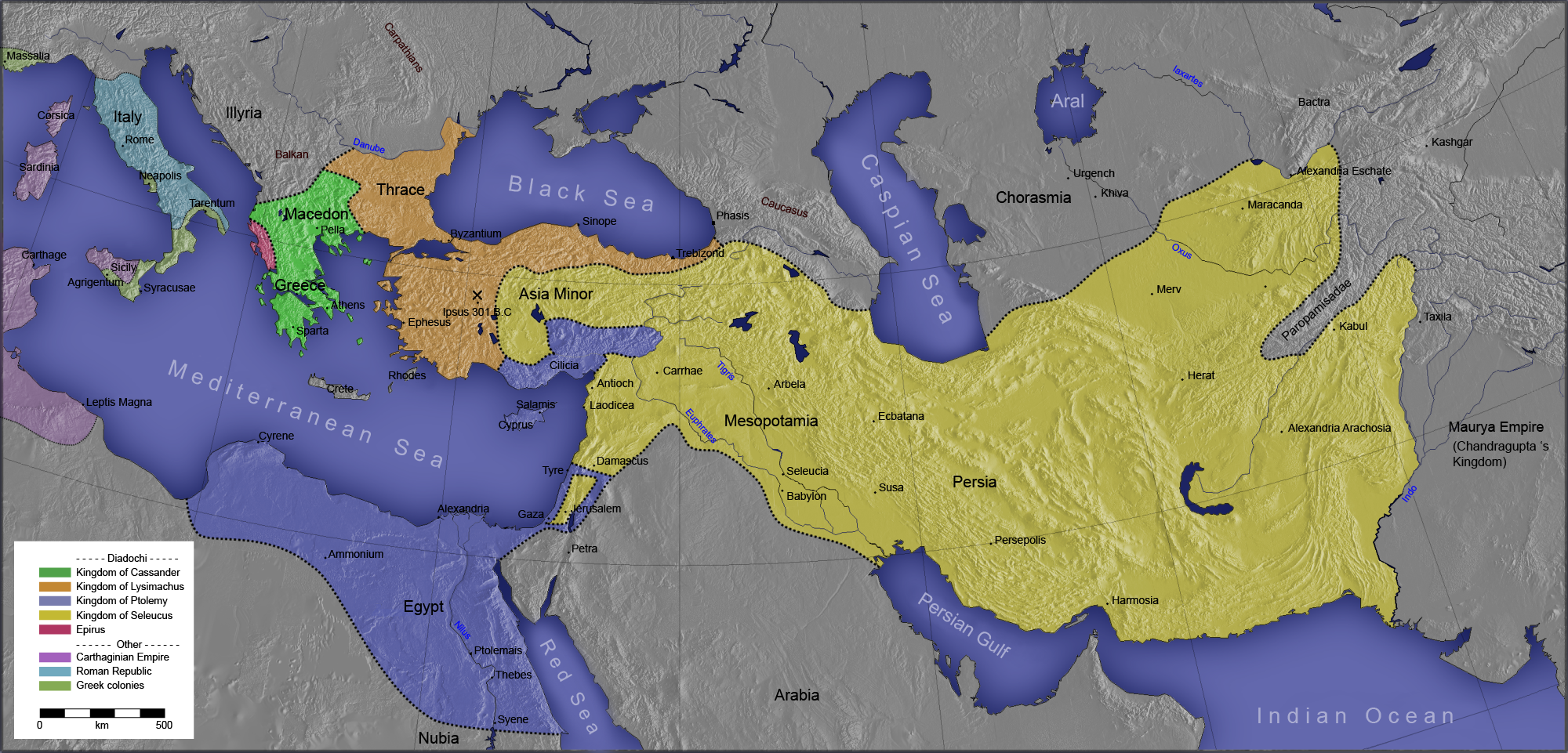
Indian Campaign Of Alexander The Great
The Indian campaign of Alexander the Great began in 327BC and lasted until 325BC. After conquering the Achaemenid Persian Empire, the Macedonian army undertook an expedition into the Indus Valley of Northwestern Indian subcontinent. Within two years, Alexander expanded the Macedonian Empire, a kingdom closely linked to the broader Greek world, to include Gandhara and the Indus Valley of Punjab and Sindh (now in India and Pakistan), surpassing the earlier frontiers established by the Persian Achaemenid conquest. Following Macedon's absorption of Gandhara (a former Persian satrapy), including the city of Taxila, Alexander and his troops advanced into Punjab, where they were confronted by Porus, the regional Indian king. In 326 BC, Alexander defeated Porus and the Pauravas during the Battle of the Hydaspes,Fuller, p. 198 but that engagement was possibly the Macedonians' most costly battle. Alexander's continued eastward march was leading his army into a confrontation wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indica (Arrian)
''Indica'' ( ''Indikḗ'') is the name of a short military history about interior Asia, particularly India, written by Arrian in the 2nd century CE. The subject of the book is the expedition of Alexander the Great that occurred between 336 and 323 BCE, about 450 years before Arrian. The book mainly tells the story of Alexander's officer Nearchus' voyage from India to the Persian Gulf after Alexander the Great's conquest of the Indus Valley. However, much of the importance of the work comes from Arrian's in-depth asides describing the history, geography, and culture of Ancient India. Arrian wrote his ''Indica'' in the Ionic dialect, taking Herodotus for his literary mode. Arrian was born in 86 CE, did not visit the Indian subcontinent, and the book is based on a variety of legends and texts known to Arrian, such as the '' Indica'' by Megasthenes. Arrian also wrote a companion text, ''Anabasis''. Of all ancient Greek records available about Alexander and interior Asia, Arrian's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting Wars of Alexander the Great, a lengthy military campaign throughout West Asia, Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from History of Greece, Greece to northwestern History of India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical NameWorking Paper No. 61, 23rd Session, Vienna, 28 March – 4 April 2006. accessed 9 October 2010 It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz. The river delta of the Shatt al-Arab forms the northwest shoreline. The Persian Gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive reefs (mostly rocky, but also Coral reef, coral), and abundant pearl oysters, however its ecology has been damaged by industrialization and oil spills. The Persian Gulf is in the Persian Gulf Basin, which is of Cenozoic origin and related to the subduction of the Arabian plate under the Zagros Mountains. The current flooding of the basin started 15,000 years ago due to sea level rise, rising sea levels of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipolis
Amphipolis (; ) was an important ancient Greek polis (city), and later a Roman city, whose large remains can still be seen. It gave its name to the modern municipality of Amphipoli, in the Serres regional unit of northern Greece. Amphipolis was originally a colony of ancient Athenians and was the site of the battle between the Spartans and Athenians in 422 BC. It was later the place where Alexander the Great prepared for campaigns leading to his invasion of Asia in 335 BC. Alexander's three finest admirals, Nearchus, Androsthenes and Laomedon, resided in Amphipolis. After Alexander's death, his wife Roxana and their son Alexander IV were imprisoned and murdered there in 311 BC. Excavations in and around the city have revealed important buildings, ancient walls and tombs. The finds are displayed at the archaeological museum of Amphipolis. At the nearby vast Kasta burial mound, an ancient Macedonian tomb has recently been revealed. The Lion of Amphipolis monument near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Macedonia
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula,. and bordered by Epirus to the southwest, Illyria to the northwest, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south. Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king PhilipII (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. With a reformed army containing phalanxes wielding the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laomedon Of Mytilene
Laomedon (Greek: Λαoμέδων ὁ Μυτιληναῖος; lived during the 4th century BC) was a Greek military commander, native of Mytilene and son of Larichus. He was one of Alexander the Great's generals, and appears to have enjoyed a high place in his confidence even before the death of Philip II, as he was one of those banished by that monarch (together with his brother Erigyius, Ptolemy, Nearchus, and others) for taking part in the intrigues of the young prince. After the death of Philip in 336 BC, Laomedon, in common with the others who had suffered on this occasion, was held by Alexander in the highest honour: he accompanied him to Asia, where, on account of his acquaintance with the Persian language, he was appointed in charge of the captives. Though his name is not afterwards mentioned during the wars of Alexander, the high consideration he enjoyed is sufficiently attested by his obtaining in the division of the provinces, after the king's death in 323 BC, the im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lato
Lato () was an ancient city of Crete, the ruins of which are located approximately 3 km from the village of Kritsa. History The Dorian city-state was built in a defensible position overlooking Mirabello Bay between two peaks, both of which became acropolises to the city. Although the city probably predates the arrival of the Dorians, the ruins date mainly from the Dorian period (5th and 4th centuries BCE). The city was destroyed c. 200 BCE, but its port (Lato Etera or Lato pros Kamara), located near Agios Nikolaos was in use during Roman rule. This has led to the confusion: Stephanus of Byzantium, for example, quoted Xenion, a 3rd-century Cretan historian, repeating the latter's error that Kamara and Lato were one and the same. Modern scholarship distinguishes the two. The city most likely was named after the goddess Leto (of which Lato is the usual Doric form) and may be mentioned in Linear B tablets as RA-TO. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disputed Kashmir region, first through the Indian-administered Ladakh, and then the Pakistani administered Gilgit Baltistan, Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and southeastern portions constitute the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. The Indian- and Pakistani-administered portions are divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy I
Ptolemy I Soter (; , ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'', "Ptolemy the Savior"; 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian, and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the Ptolemaic Kingdom centered on Egypt. Ptolemy was ''basileus'' and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 BC to his death in 282 BC, and his descendants continued to rule Egypt until 30 BC. During their rule, Egypt became a thriving bastion of Hellenistic civilization and Alexandria a great seat of Greek culture. Ptolemy I was the son of Arsinoe of Macedon by either her husband Lagus or Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander. However, the latter is unlikely and may be a myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic Dynasty. Ptolemy was one of Alexander's most trusted companions and military officers. After the death of Alexander in 323 BC, Ptolemy retrieved his body as it was en route to be buried in Macedon, placing it in Memphis instead, where it was later moved to A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; , ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'', "Ptolemy the Savior"; 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian, and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the Ptolemaic Kingdom centered on Egypt. Ptolemy was ''basileus'' and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 BC to his death in 282 BC, and his descendants continued to rule Egypt until 30 BC. During their rule, Egypt became a thriving bastion of Hellenistic civilization and Alexandria a great seat of Greek culture. Ptolemy I was the son of Arsinoe of Macedon by either her husband Lagus or Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander. However, the latter is unlikely and may be a myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic Dynasty. Ptolemy was one of Alexander's most trusted companions and military officers. After the death of Alexander in 323 BC, Ptolemy retrieved his body as it was en route to be buried in Macedon, placing it in Memphis instead, where it was later moved to Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea. They also form a significant Greek diaspora, diaspora (), with many Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean Sea, Aegean and Ionian Sea, Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |