|
Cilappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kaṇṇaki and her husband Kōvalaṉ. The ''Cilappatikāram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the '' Natṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-jain-monk Iḷaṅkō Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th century CE (although estimates range from 2nd to 6th century CE). The ''Cilappatikāram'' is an ancient literary masterpiece. It is to the Tamil culture what the ''Iliad'' is to the Greek culture, states R. Parthasarathy. It blends the themes, mythologies and theological v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilango Adigal
Ilango Adigal (a title, literally "prince ascetic", fl. c. 4th-6th century CE) was a Jain monk, belonging to the Chera royal family, from the city of Vanchi. He is traditionally credited as the author of the epic poem Cilappatikaram (the Song of the Anklet), one of the Five Great Epics of Tamil literature. In the patikam (the prologue) to the poem, Ilango Adigal identifies himself as the brother of the Chera king Cenkuttuvan (c. late 2nd century CE). However, it is generally assumed that the author was a member of the Chera royal family who lived much later than Cenkuttuvan and composed the poem based on a reliable version of the historical tradition concerning Cenkuttuvan and Kannaki. Biography No directly verifiable information about Ilango Adigal exists outside of Cilappatikaram ("The Lay of the Anklet") and its prologue. According to the text, Ilango Adigal was a Chera prince ("Kudakko Ceral Ilanko"). He was the younger son of the Chera king "Imayavarampan" Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manimekalai
''Maṇimēkalai'' (, ), also spelled ''Manimekhalai'' or ''Manimekalai'', is a Tamil Buddhist epic composed by Kulavāṇikaṉ Seethalai Sataṉar probably somewhere between the 2nd century to the 6th century. It is an "anti-love story", a sequel to the "love story" in the earliest Tamil epic '' Cilappatikaram'', with some characters from it and their next generation. The epic consists of 4,861 lines in ''akaval'' meter, arranged in 30 cantos. The title ''Manimekalai'' is also the name of the daughter of Kovalan and Madhavi, who follows in her mother's footsteps as a dancer and a Buddhist nun. The epic tells her story. Her physical beauty and artistic achievements seduces the Chola prince Udayakumara. He pursues her. She, a nun of Mahayana Buddhism persuasion, feels a commitment to free herself from human ties. She rejects his advances, yet finds herself drawn to him. She hides, prays and seeks the help of her mother, her Buddhist teacher Aravana Adikal and angels. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannagi (Tamil Mythology)
Kannagi (), sometimes spelled Kannaki, is a legendary Tamil people, Tamil woman who forms the central character of the Tamil epic poetry, epic ''Cilappatikāram''. Kannagi is described as a chaste woman who stays with her husband despite his adultery, their attempt to rebuild their marriage after her unrepentant husband had lost everything, how he is framed then punished without the due checks and processes of justice. Kannagi proves and protests the injustice, then curses the king and city of Madurai, leading to the death of the unjust Pandya dynasty, Pandyan king of Madurai, who had wrongfully put her husband Kovalan to death. The society that made her suffer then endures retribution as the city Madurai, in consequence, is burnt to the ground because of her curse. In Tamil folklore, Kannagi has been deified as the symbol – sometimes as a goddess – of chastity, with sculptures or reliefs in Hindu temples iconographically reminding the visitor of her breaking her anklet or te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannagi
Kannagi (), sometimes spelled Kannaki, is a legendary Tamil woman who forms the central character of the Tamil epic '' Cilappatikāram''. Kannagi is described as a chaste woman who stays with her husband despite his adultery, their attempt to rebuild their marriage after her unrepentant husband had lost everything, how he is framed then punished without the due checks and processes of justice. Kannagi proves and protests the injustice, then curses the king and city of Madurai, leading to the death of the unjust Pandyan king of Madurai, who had wrongfully put her husband Kovalan to death. The society that made her suffer then endures retribution as the city Madurai, in consequence, is burnt to the ground because of her curse. In Tamil folklore, Kannagi has been deified as the symbol – sometimes as a goddess – of chastity, with sculptures or reliefs in Hindu temples iconographically reminding the visitor of her breaking her anklet or tearing her bleeding breast and throwing it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indra
Indra (; ) is the Hindu god of weather, considered the king of the Deva (Hinduism), Devas and Svarga in Hinduism. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. [3 volumes] Indra is the most frequently mentioned deity in the ''Rigveda''. He is celebrated for his powers based on his status as a god of order, and as the one who killed the great evil, an Asura (Hinduism), asura named Vritra, who obstructed human prosperity and happiness. Indra destroys Vritra and his "deceiving forces", and thereby brings rain and sunshine as the saviour of mankind. Indra's significance diminishes in the post-Vedic Indian literature, but he still plays an important role in various mythological events. He is depicted as a powerful hero. According to the ''Vishnu Purana'', Indra is the title borne by the king of the gods, which changes every Manvantara – a cyclic period of time in Hindu cosmology. Each Manvantara has its own Indra and the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kovalan
Kovalan () is a central character in Ilango Adigal's '' Silappatikaram,'' one of the ancient Tamil epics. Family Father : Machattuvan Wife : Kannagi Lover : Madhavi Daughter : Manimekalai (Mother: Madhavi) Narrative Puharkkandam Kovalan, the son of a wealthy merchant, Machattuvan, married Kannagi, the daughter of another merchant, Manayakan. At the time of his marriage, he was sixteen years old. They lived together happily in the city of Kaveripattinam, until Kovalan met the courtesan Madhavi and fell in love with her. In his infatuation, he completely forgot his wife and spent his time and parental wealth with Madhavi. During the annual festival in the honour of Indra, there was a misunderstanding between Kovalan and Madhavi. As a result, the penniless Kovalan returned to Kannagi, who welcomed him whole-heartedly. Realising his mistake, he decided to start a new life by migrating to Madurai Madurai ( , , ), formerly known as Madura, is a major city in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Culture
Tamil culture refers to the culture of the Tamil people. The Tamils speak the Tamil language, one of the oldest languages in India with more than two thousand years of written history. Archaeological evidence from the Tamilakam region indicates a continuous history of human occupation for more than 3,800 years. Historically, the region was inhabited by Tamil-speaking Dravidian people. It was ruled by various kingdoms such as the Sangam period (3rd century BCE to 3rd century CE) triumvirate of the Cheras, Cholas and Pandyas, the Pallavas (3rd–9th century CE), and the later Vijayanagara Empire (14th–17th century CE). European colonization began in the 17th century CE, and continued for two centuries until the Indian Independence in 1947. Due to its long history, the culture has seen multiple influences over the years and have developed diversely. The Tamils had outside contact in the form of diplomatic and trade relations with other kingdoms to the north and with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
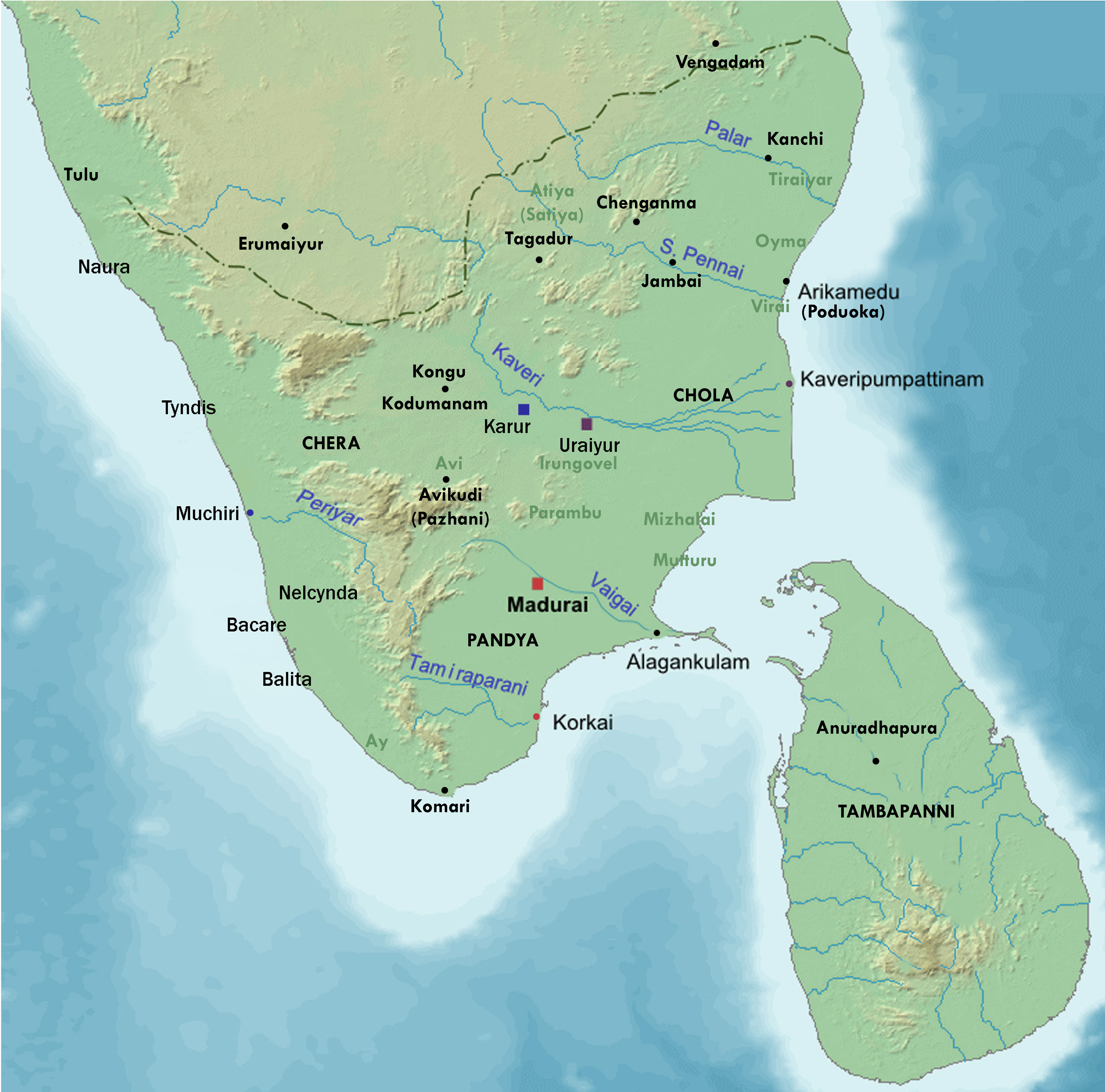
Chera Dynasty
The Chera dynasty ( or Cēra, ), also known as Keralaputra, from the early historic or the Sangam period in Tamil-speaking southern India, ruled over parts of present-day states Kerala and Tamil Nadu. The Cheras, known as one of the mu-ventar (the Three Crowned Kings) of Tamilakam (the Tamil Country) alongside the Cholas and Pandyas, have been documented as early as the third century BCE. The Chera country was geographically well placed at the tip of the Indian peninsula to profit from maritime trade via the extensive Indian Ocean networks. Exchange of spices, especially black pepper, with Middle Eastern or Graeco-Roman merchants is attested to in several sources. Chera influence extended over central Kerala and western Tamil Nadu until the end of the early historic period in southern India. The Cheras of the early historical period (c. second century BCE – c. third/fifth century CE) had their capital in interior Tamil country ( Vanchi-Karur, Kongu Nadu), and ports/capit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cholas
The Early Cholas were a Tamil kingdom of the Chola dynasty - pre and post Sangam period (600 BCE–300 CE). It was one of the three main kingdoms of Tamilakam. Their early capitals were Urayur or Tiruchirapalli and Kaveripattinam. Along with the Pandyas and the Cheras, the Chola history goes back to the period when written records were scarce. Sources Ancient Tamil Nadu contained three monarchical states, headed by kings called ''Vendhar'' and several chieftaincies, headed by the chiefs called by the general denomination ''Vel'' or '' Velir''. Still lower at the local level there were clan chiefs called ''kizhar'' or ''mannar''. The Tamil area had an independent existence outside the control of these northern empires. The Tamil kings and chiefs were always in conflict with each other mostly over property. The royal courts were mostly places of social gathering rather than places of dispensation of authority; they were centres for distribution of resources. The names of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation for the sounds of speech. The IPA is used by linguists, lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of lexical item, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, Intonation (linguistics), intonation and the separation of syllables. To represent additional qualities of speechsuch as tooth wikt:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made with a cleft lip and cleft palate, cleft palatean extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet, extended set of symbols may be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (1985), reported statements from present generation which "specifies that the message must be oral statements spoken, sung or called out on musical instruments only"; "There must be transmission by word of mouth over at least a generation". He points out, "Our definition is a working definition for the use of historians. Sociologists, linguists or scholars of the verbal arts propose their own, which in, e.g., sociology, stresses common knowledge. In linguistics, features that distinguish the language from common dialogue (linguists), and in the verbal arts features of form and content that define art (folklorists)."Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: "Methodology and African Pre-history", 1990, ''UNESCO International Scientific Committee for the Drafting of a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sattanar
Satthanar or Chithalai Satthanar (, ''cītalai cāttanār'') was the Tamil poet who composed the epic Manimekalai. A total of 11 verses of the Sangam literature have been attributed to Satthanar, including verse 10 of the Tiruvalluva Maalai. Etymology Pronounced ''Sa-tha-naar,'' the name is derived from (, ''sāttu'') meaning Buddhist monk. Applying this principle to the name Maturai Kulavāṇikan Cāttan, the author of Manimekalai, we see that the two appellations Maturai and Kulavanikan were prefixed to his name in order to distinguish him from another poet of Maturai with the same name and from a third who lived elsewhere. Several examples could be cited of this system of nomenclature which prevailed during the early days. Biography Satthanar hailed from a place known as Seerthandalai, later came to be known as Seethalai. He was a grain merchant at Madurai and hence came to be called "Koolavanigan". He was a contemporary of Cheran Senguttuvan and was believed to have pract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |