
Amino acids are
organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbonâhydrogen or carbonâcarbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
s that contain both
amino and
carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
s. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the
22 Îą-amino acids incorporated into
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s. Only these 22 appear in the
genetic code
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cell (biology), cells to Translation (biology), translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished ...
of life.
Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups (
alpha- (Îą-), beta- (Îē-), gamma- (Îģ-) amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to
polarity,
ionization
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive Electric charge, charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged at ...
, and side-chain group type (
aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated (in which all ...
,
acyclic,
aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugati ...
,
polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid ''
residues'' form the second-largest component (
water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
being the largest) of human
muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s and other
tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as
neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
transport and
biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthe ...
. It is thought that they played a key role in
enabling life on Earth and its emergence.
Amino acids are formally named by the
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
-
IUBMB Joint Commission
The Joint Commission is a United States-based nonprofit tax-exempt 501(c) organization that accredits more than 22,000 US health care organizations and programs. The international branch accredits medical services from around the world.
A majori ...
on Biochemical Nomenclature in terms of the fictitious "neutral" structure shown in the illustration. For example, the systematic name of alanine is 2-aminopropanoic acid, based on the formula . The Commission justified this approach as follows:
The systematic names and formulas given refer to hypothetical forms in which amino groups are unprotonated and carboxyl groups are undissociated. This convention is useful to avoid various nomenclatural problems but should not be taken to imply that these structures represent an appreciable fraction of the amino-acid molecules.
History
The first few amino acids were discovered in the early 1800s. In 1806, French chemists
Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin and
Pierre Jean Robiquet isolated a compound from
asparagus
Asparagus (''Asparagus officinalis'') is a perennial flowering plant species in the genus ''Asparagus (genus), Asparagus'' native to Eurasia. Widely cultivated as a vegetable crop, its young shoots are used as a spring vegetable.
Description ...
that was subsequently named
asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated âNH form under biological conditions), an Îą-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
, the first amino acid to be discovered.
Cystine
Cystine is the oxidized derivative of the amino acid cysteine and has the formula (SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. As a residue in proteins, cystine serves two functions: a site of redox reactions and a mec ...
was discovered in 1810, although its monomer,
cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
, remained undiscovered until 1884.
[ ]Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
and leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an Îą-amino acid, meaning it contains an Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated âNH3+ form under biological conditions), an Îą-Car ...
were discovered in 1820. The last of the 20 common amino acids to be discovered was threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated âNH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated âCOOâ ...
in 1935 by William Cumming Rose, who also determined the essential amino acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms ...
s and established the minimum daily requirements of all amino acids for optimal growth.
The unity of the chemical category was recognized by Wurtz in 1865, but he gave no particular name to it. The first use of the term "amino acid" in the English language dates from 1898, while the German term, , was used earlier. Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s were found to yield amino acids after enzymatic digestion or acid hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
. In 1902, Emil Fischer
Hermann Emil Louis Fischer (; 9 October 1852 â 15 July 1919) was a German chemist and List of Nobel laureates in Chemistry, 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fisch ...
and Franz Hofmeister independently proposed that proteins are formed from many amino acids, whereby bonds are formed between the amino group of one amino acid with the carboxyl group of another, resulting in a linear structure that Fischer termed "peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
".
General structure
 2-, alpha-, or Îą-amino acids have the generic
2-, alpha-, or Îą-amino acids have the generic formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwe ...
in most cases, where R is an organic substituent
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.
The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond r ...
known as a "side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a substituent, chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone chain, backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a mo ...
".
Of the many hundreds of described amino acids, 22 are proteinogenic ("protein-building"). It is these 22 compounds that combine to give a vast array of peptides and proteins assembled by ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
s.post-translational modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biolog ...
or during nonribosomal peptide
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacterium, bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be ma ...
synthesis.
Chirality
The carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalentâmeaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atom next to the carboxyl group
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g. ...
is called the Îąâcarbon. In proteinogenic amino acids, it bears the amine and the R group or side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a substituent, chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone chain, backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a mo ...
specific to each amino acid, as well as a hydrogen atom. With the exception of glycine, for which the side chain is also a hydrogen atom, the Îąâcarbon is stereogenic
In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups cr ...
. All chiral
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is dist ...
proteogenic amino acids have the L configuration. They are "left-handed" enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer (Help:IPA/English, /ÉŠËnÃĶnti.ÉmÉr, É-, -oĘ-/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''ih-NAN-tee-É-mÉr''), also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities whi ...
s, which refers to the stereoisomers of the alpha carbon.
A few D-amino acids ("right-handed") have been found in nature, e.g., in bacterial envelopes, as a neuromodulator (D-serine
Serine
(symbol Ser or S) is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Îą- amino group (which is in the protonated â form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated â ...
), and in some antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s.post-translational modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biolog ...
.
Side chains
Polar charged side chains
Five amino acids possess a charge at neutral pH. Often these side chains appear at the surfaces on proteins to enable their solubility in water, and side chains with opposite charges form important electrostatic contacts called salt bridges that maintain structures within a single protein or between interfacing proteins.aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protein ...
, glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an Îą-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
and histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Amine, Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated âNH3+ form under Physiological condition, biological conditions), a carboxylic ...
. Under certain conditions, each ion-forming group can be charged, forming double salts.
The two negatively charged amino acids at neutral pH are aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protein ...
(Asp, D) and glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an Îą-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
(Glu, E). The anionic carboxylate groups behave as BrÃļnsted bases in most circumstances.pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. It is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pe ...
in mammalian stomachs, may have catalytic aspartate or glutamate residues that act as BrÃļnsted acids.
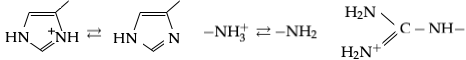 There are three amino acids with side chains that are cations at neutral pH:
There are three amino acids with side chains that are cations at neutral pH: arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (âCO2â) a ...
(Arg, R), lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an Îą-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an Îą-carboxylic acid group ( ...
(Lys, K) and histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Amine, Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated âNH3+ form under Physiological condition, biological conditions), a carboxylic ...
(His, H). Arginine has a charged guanidino group and lysine a charged alkyl amino group, and are fully protonated at pH 7. Histidine's imidazole group has a pKa of 6.0, and is only around 10% protonated at neutral pH. Because histidine is easily found in its basic and conjugate acid forms it often participates in catalytic proton transfers in enzyme reactions.
Polar uncharged side chains
The polar, uncharged amino acids serine
Serine
(symbol Ser or S) is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Îą- amino group (which is in the protonated â form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated â ...
(Ser, S), threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated âNH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated âCOOâ ...
(Thr, T), asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated âNH form under biological conditions), an Îą-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
(Asn, N) and glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
(Gln, Q) readily form hydrogen bonds with water and other amino acids.threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated âNH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated âCOOâ ...
.
Hydrophobic side chains
Nonpolar amino acid interactions are the primary driving force behind the processes that fold proteins into their functional three dimensional structures.tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
(Tyr, Y). The hydroxyl of tyrosine can deprotonate at high pH forming the negatively charged phenolate. Because of this one could place tyrosine into the polar, uncharged amino acid category, but its very low solubility in water matches the characteristics of hydrophobic amino acids well.
Special case side chains
Several side chains are not described well by the charged, polar and hydrophobic categories. Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
(Gly, G) could be considered a polar amino acid since its small size means that its solubility is largely determined by the amino and carboxylate groups. However, the lack of any side chain provides glycine with a unique flexibility among amino acids with large ramifications to protein folding.Cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
(Cys, C) can also form hydrogen bonds readily, which would place it in the polar amino acid category, though it can often be found in protein structures forming covalent bonds, called disulphide bonds, with other cysteines. These bonds influence the folding and stability of proteins, and are essential in the formation of antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
. Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
(Pro, P) has an alkyl side chain and could be considered hydrophobic, but because the side chain joins back onto the alpha amino group it becomes particularly inflexible when incorporated into proteins. Similar to glycine this influences protein structure in a way unique among amino acids. Selenocysteine
Selenocysteine (symbol Sec or U, in older publications also as Se-Cys) is the 21st proteinogenic amino acid. Selenoproteins contain selenocysteine residues. Selenocysteine is an analogue of the more common cysteine with selenium in place of the ...
(Sec, U) is a rare amino acid not directly encoded by DNA, but is incorporated into proteins via the ribosome. Selenocysteine has a lower redox potential compared to the similar cysteine, and participates in several unique enzymatic reactions. Pyrrolysine
Pyrrolysine (symbol Pyl or O), encoded by the 'amber' stop codon UAG, is a proteinogenic amino acid that is used in some methanogenic archaea and in bacteria. It consists of lysine with a 4-methylpyrroline-5-carboxylate in amide linkage with the ...
(Pyl, O) is another amino acid not encoded in DNA, but synthesized into protein by ribosomes. It is found in archaeal species where it participates in the catalytic activity of several methyltransferases.
Îē- and Îģ-amino acids
Amino acids with the structure , such as Îē-alanine, a component of carnosine and a few other peptides, are Îē-amino acids. Ones with the structure are Îģ-amino acids, and so on, where X and Y are two substituents (one of which is normally H).
Zwitterions
 The common natural forms of amino acids have a zwitterionic structure, with ( in the case of proline) and functional groups attached to the same C atom, and are thus Îą-amino acids, and are the only ones found in proteins during translation in the ribosome.
In aqueous solution at pH close to neutrality, amino acids exist as
The common natural forms of amino acids have a zwitterionic structure, with ( in the case of proline) and functional groups attached to the same C atom, and are thus Îą-amino acids, and are the only ones found in proteins during translation in the ribosome.
In aqueous solution at pH close to neutrality, amino acids exist as zwitterion
In chemistry, a zwitterion ( ; ), also called an inner salt or dipolar ion, is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively and negatively charged functional groups.
:
(1,2- dipolar compounds, such as ylides, are sometimes excluded from ...
s, i.e. as dipolar ions with both and in charged states, so the overall structure is . At physiological pH the so-called "neutral forms" are not present to any measurable degree. Although the two charges in the zwitterion structure add up to zero it is misleading to call a species with a net charge of zero "uncharged".
In strongly acidic conditions (pH below 3), the carboxylate group becomes protonated and the structure becomes an ammonio carboxylic acid, . This is relevant for enzymes like pepsin that are active in acidic environments such as the mammalian stomach and lysosomes, but does not significantly apply to intracellular enzymes. In highly basic conditions (pH greater than 10, not normally seen in physiological conditions), the ammonio group is deprotonated to give .
Although various definitions of acids and bases are used in chemistry, the only one that is useful for chemistry in aqueous solution is that of BrÃļnsted:
Isoelectric point
 For amino acids with uncharged side-chains the zwitterion predominates at pH values between the two p''K''a values, but coexists in equilibrium with small amounts of net negative and net positive ions. At the midpoint between the two p''K''a values, the trace amount of net negative and trace of net positive ions balance, so that average net charge of all forms present is zero. This pH is known as the
For amino acids with uncharged side-chains the zwitterion predominates at pH values between the two p''K''a values, but coexists in equilibrium with small amounts of net negative and net positive ions. At the midpoint between the two p''K''a values, the trace amount of net negative and trace of net positive ions balance, so that average net charge of all forms present is zero. This pH is known as the isoelectric point
The isoelectric point (pI, pH(I), IEP), is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electric charge, electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean. The standard nomenclature to represent the isoelectric point is pH(I). Howe ...
p''I'', so p''I'' = (p''K''a1 + p''K''a2).
For amino acids with charged side chains, the p''K''a of the side chain is involved. Thus for aspartate or glutamate with negative side chains, the terminal amino group is essentially entirely in the charged form , but this positive charge needs to be balanced by the state with just one C-terminal carboxylate group is negatively charged. This occurs halfway between the two carboxylate p''K''a values: p''I'' = (p''K''a1 + p''K''a(R)), where p''K''a(R) is the side chain p''K''a.electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is the motion of charged dispersed particles or dissolved charged molecules relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. As a rule, these are zwitterions with a positive or negative net ch ...
at their isoelectric point, although this behaviour is more usually exploited for peptides and proteins than single amino acids. Zwitterions have minimum solubility at their isoelectric point, and some amino acids (in particular, with nonpolar side chains) can be isolated by precipitation from water by adjusting the pH to the required isoelectric point.
Physicochemical properties
The 20 canonical amino acids can be classified according to their properties. Important factors are charge, hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly intermolecular force, repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to b ...
, size, and functional groups.protein structure
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid ...
and proteinâprotein interaction
Proteinâprotein interactions (PPIs) are physical contacts of high specificity established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical events steered by interactions that include electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding and t ...
s. The water-soluble proteins tend to have their hydrophobic residues ( Leu, Ile, Val, Phe, and Trp) buried in the middle of the protein, whereas hydrophilic side chains are exposed to the aqueous solvent. (In biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
, a residue refers to a specific monomer
A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Chemis ...
''within'' the polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
ic chain of a polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
, protein or nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
.) The integral membrane protein
An integral, or intrinsic, membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All transmembrane proteins can be classified as IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comp ...
s tend to have outer rings of exposed hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
amino acids that anchor them in the lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes form a continuous barrier around all cell (biology), cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses a ...
. Some peripheral membrane proteins have a patch of hydrophobic amino acids on their surface that sticks to the membrane. In a similar fashion, proteins that have to bind to positively charged molecules have surfaces rich in negatively charged amino acids such as glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an Îą-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
and aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protein ...
, while proteins binding to negatively charged molecules have surfaces rich in positively charged amino acids like lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an Îą-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an Îą-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an Îą-carboxylic acid group ( ...
and arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (âCO2â) a ...
. For example, lysine and arginine are present in large amounts in the low-complexity regions of nucleic-acid binding proteins.disulfide bond
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups.
In inor ...
s to other cysteine residues. Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
forms a cycle to the polypeptide backbone, and glycine is more flexible than other amino acids.
Glycine and proline are strongly present within low complexity regions of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins, whereas the opposite is the case with cysteine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, which are highly reactive, or complex, or hydrophobic.posttranslational modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translate mRNA ...
s, whereby additional chemical groups are attached to the amino acid residue side chains sometimes producing lipoproteins (that are hydrophobic), or glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
s (that are hydrophilic) allowing the protein to attach temporarily to a membrane. For example, a signaling protein can attach and then detach from a cell membrane, because it contains cysteine residues that can have the fatty acid palmitic acid
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature) is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms.Gunstone, F. D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra. The ...
added to them and subsequently removed.
Table of standard amino acid abbreviations and properties
Although one-letter symbols are included in the table, IUPACâIUBMB recommend[ that "Use of the one-letter symbols should be restricted to the comparison of long sequences".
The one-letter notation was chosen by IUPAC-IUB based on the following rules:]codons
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links pro ...
that are usually interpreted as stop codon
In molecular biology, a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in messenger RNA correspond to the additio ...
s:
In addition to the specific amino acid codes, placeholders are used in cases where chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
or crystallographic analysis of a peptide or protein cannot conclusively determine the identity of a residue. They are also used to summarize conserved protein sequence motifs. The use of single letters to indicate sets of similar residues is similar to the use of abbreviation codes for degenerate bases.
Unk is sometimes used instead of Xaa, but is less standard.
Ter or * (from termination) is used in notation for mutations in proteins when a stop codon occurs. It corresponds to no amino acid at all.protecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In man ...
s, which have specific codes. Bortezomib is PyzâPheâboroLeu, and MG132 is ZâLeuâLeuâLeuâal. To aid in the analysis of protein structure, photo-reactive amino acid analogs are available. These include photoleucine (pLeu) and photomethionine (pMet).
Occurrence and functions in biochemistry
Proteinogenic amino acids
Amino acids are the precursors to proteins.translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
'' and involves the step-by-step addition of amino acids to a growing protein chain by a ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to Catalysis, catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozy ...
that is called a ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
. The order in which the amino acids are added is read through the genetic code
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cell (biology), cells to Translation (biology), translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished ...
from an mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
template, which is an RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
derived from one of the organism's gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s.
Twenty-two amino acids are naturally incorporated into polypeptides and are called proteinogenic or natural amino acids.selenocysteine
Selenocysteine (symbol Sec or U, in older publications also as Se-Cys) is the 21st proteinogenic amino acid. Selenoproteins contain selenocysteine residues. Selenocysteine is an analogue of the more common cysteine with selenium in place of the ...
and pyrrolysine
Pyrrolysine (symbol Pyl or O), encoded by the 'amber' stop codon UAG, is a proteinogenic amino acid that is used in some methanogenic archaea and in bacteria. It consists of lysine with a 4-methylpyrroline-5-carboxylate in amide linkage with the ...
, are incorporated into proteins by unique synthetic mechanisms. Selenocysteine is incorporated when the mRNA being translated includes a SECIS element
In biology, the SECIS element (SECIS: ''selenocysteine insertion sequence'') is an RNA element around 60 nucleotides in length that adopts a stem-loop structure. This structural motif (pattern of nucleotides) directs the cell to translate ...
, which causes the UGA codon to encode selenocysteine instead of a stop codon. Pyrrolysine
Pyrrolysine (symbol Pyl or O), encoded by the 'amber' stop codon UAG, is a proteinogenic amino acid that is used in some methanogenic archaea and in bacteria. It consists of lysine with a 4-methylpyrroline-5-carboxylate in amide linkage with the ...
is used by some methanogen
Methanogens are anaerobic archaea that produce methane as a byproduct of their energy metabolism, i.e., catabolism. Methane production, or methanogenesis, is the only biochemical pathway for Adenosine triphosphate, ATP generation in methanogens. A ...
ic archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
in enzymes that they use to produce methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
. It is coded for with the codon UAG, which is normally a stop codon in other organisms.
Several independent evolutionary studies have suggested that Gly, Ala, Asp, Val, Ser, Pro, Glu, Leu, Thr may belong to a group of amino acids that constituted the early genetic code, whereas Cys, Met, Tyr, Trp, His, Phe may belong to a group of amino acids that constituted later additions of the genetic code.
Standard vs nonstandard amino acids
The 20 amino acids that are encoded directly by the codons of the universal genetic code are called ''standard'' or ''canonical'' amino acids. A modified form of methionine ( ''N''-formylmethionine) is often incorporated in place of methionine as the initial amino acid of proteins in bacteria, mitochondria and plastid
A plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Examples of plastids include chloroplasts ...
s (including chloroplasts). Other amino acids are called ''nonstandard'' or ''non-canonical''. Most of the nonstandard amino acids are also non-proteinogenic (i.e. they cannot be incorporated into proteins during translation), but two of them are proteinogenic, as they can be incorporated translationally into proteins by exploiting information not encoded in the universal genetic code.
The two nonstandard proteinogenic amino acids are selenocysteine (present in many non-eukaryotes as well as most eukaryotes, but not coded directly by DNA) and pyrrolysine
Pyrrolysine (symbol Pyl or O), encoded by the 'amber' stop codon UAG, is a proteinogenic amino acid that is used in some methanogenic archaea and in bacteria. It consists of lysine with a 4-methylpyrroline-5-carboxylate in amide linkage with the ...
(found only in some archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
and at least one bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the ...
). The incorporation of these nonstandard amino acids is rare. For example, 25 human proteins include selenocysteine in their primary structure, and the structurally characterized enzymes (selenoenzymes) employ selenocysteine as the catalytic moiety in their active sites. Pyrrolysine and selenocysteine are encoded via variant codons. For example, selenocysteine is encoded by stop codon and SECIS element
In biology, the SECIS element (SECIS: ''selenocysteine insertion sequence'') is an RNA element around 60 nucleotides in length that adopts a stem-loop structure. This structural motif (pattern of nucleotides) directs the cell to translate ...
.mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
, and chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s) is generally considered as a form of methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
rather than as a separate proteinogenic amino acid. CodonâtRNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the gene ...
combinations not found in nature can also be used to "expand" the genetic code and form novel proteins known as alloproteins incorporating non-proteinogenic amino acids.
Non-proteinogenic amino acids
Aside from the 22 proteinogenic amino acid
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation from RNA. The word "proteinogenic" means "protein creating". Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) ...
s, many ''non-proteinogenic'' amino acids are known. Those either are not found in proteins (for example carnitine
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids from the cytosol into mitochondria to be oxidized for f ...
, GABA
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, Îģ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
GA ...
, levothyroxine) or are not produced directly and in isolation by standard cellular machinery. For example, hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gela ...
, is synthesised from proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
. Another example is selenomethionine).
Non-proteinogenic amino acids that are found in proteins are formed by post-translational modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biolog ...
. Such modifications can also determine the localization of the protein, e.g., the addition of long hydrophobic groups can cause a protein to bind to a phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
membrane. Examples:
*the carboxylation of glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an Îą-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
allows for better binding of calcium cations,
*Hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gela ...
, generated by hydroxylation of proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
, is a major component of the connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
.
* Hypusine in the translation initiation factor EIF5A, contains a modification of lysine.
Some non-proteinogenic amino acids are not found in proteins. Examples include 2-aminoisobutyric acid and the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, Îģ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
GA ...
. Non-proteinogenic amino acids often occur as intermediates in the metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
s for standard amino acids â for example, ornithine
Ornithine is a non-proteinogenic Îą-amino acid that plays a role in the urea cycle. It is not incorporated into proteins during translation. Ornithine is abnormally accumulated in the body in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, a disorder of th ...
and citrulline
The organic compound citrulline is an Îą-amino acid. Its name is derived from '' citrullus'', the Latin word for watermelon. Although named and described by gastroenterologists since the late 19th century, it was first isolated from watermelon in ...
occur in the urea cycle, part of amino acid catabolism
Catabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that breaks down molecules into smaller units that are either oxidized to release energy or used in other anabolic reactions. Catabolism breaks down large molecules (such as polysaccharides, lipid ...
(see below). A rare exception to the dominance of Îą-amino acids in biology is the Îē-amino acid beta alanine (3-aminopropanoic acid), which is used in plants and microorganisms in the synthesis of pantothenic acid
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is a B vitamin and an essential nutrient. All animals need pantothenic acid in order to synthesize coenzyme A (CoA), which is essential for cellular energy production and for the synthesis and degradation of prote ...
(vitamin B5), a component of coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the Fatty acid metabolism#Synthesis, synthesis and Fatty acid metabolism#.CE.B2-Oxidation, oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvic acid, pyruvate in the citric ac ...
.
In mammalian nutrition
 Animals ingest amino acids in the form of protein. The protein is broken down into its constituent amino acids in the process of digestion. The amino acids are then used to synthesize new proteins and other
Animals ingest amino acids in the form of protein. The protein is broken down into its constituent amino acids in the process of digestion. The amino acids are then used to synthesize new proteins and other nitrogenous
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh ...
biomolecules, or they are further catabolized through oxidation
Redox ( , , reductionâoxidation or oxidationâreduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
to provide a source of energy. The oxidation pathway starts with the removal of the amino group by a transaminase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an Îą-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins.
Function and mechanism
An amino acid con ...
; the amino group is then fed into the urea cycle. The other product of transamidation is a keto acid that enters the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycleâalso known as the Krebs cycle, SzentâGyÃķrgyiâKrebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)âis a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
. Glucogenic amino acids can also be converted into glucose, through gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
.
Of the 20 standard amino acids, nine ( His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp and Val) are called essential amino acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms ...
s because the human body
The human body is the entire structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently Organ (biology), organs and then Organ system, org ...
cannot synthesize them from other compounds at the level needed for normal growth, so they must be obtained from food.
Semi-essential and conditionally essential amino acids, and juvenile requirements
In addition, cysteine, tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
, and arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (âCO2â) a ...
are considered semiessential amino acids, and taurine
Taurine (), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a naturally occurring amino sulfonic acid that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine. It is named after Latin (cogna ...
a semi-essential aminosulfonic acid in children. Some amino acids are conditionally essential for certain ages or medical conditions. Essential amino acids may also vary from species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
to species. The metabolic pathways that synthesize these monomers are not fully developed.
Non-protein functions
Many proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids have biological functions beyond being precursors to proteins and peptides. In humans, amino acids also have important roles in diverse biosynthetic pathways. Defenses against herbivores in plants sometimes employ amino acids.
Standard amino acids
* Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an Îą-amino group, an Îą-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
is a precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
.
* Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
(and its precursor phenylalanine) are precursors of the catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine.
Cate ...
neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
, epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
and various trace amine
Trace amines are an endogenous group of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonists â and hence, monoaminergic neuromodulators â that are structurally and metabolically related to classical monoamine neurotransmitters. Compared to ...
s.
* Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential Îą-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
is a precursor of phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace ami ...
and tyrosine in humans. In plants, it is a precursor of various phenylpropanoid
The phenylpropanoids are a diverse family of organic compounds that are biosynthesized by plants from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine in the shikimic acid pathway. Their name is derived from the six-carbon, aromatic phenyl group and ...
s, which are important in plant metabolism.
* Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
is a precursor of porphyrins such as heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prostheti ...
.
* Arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (âCO2â) a ...
is a precursor of nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
.
* Ornithine
Ornithine is a non-proteinogenic Îą-amino acid that plays a role in the urea cycle. It is not incorporated into proteins during translation. Ornithine is abnormally accumulated in the body in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, a disorder of th ...
and ''S''-adenosylmethionine are precursors of polyamines.
* Aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protein ...
, glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
, and glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an Îą-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
are precursors of nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers â deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s.
Roles for nonstandard amino acids
*Carnitine
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids from the cytosol into mitochondria to be oxidized for f ...
is used in lipid transport.
*gamma-aminobutyric acid
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, Îģ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
GA ...
is a neurotransmitter.
*5-HTP
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), used medically as oxitriptan, is a naturally occurring amino acid and chemical precursor as well as a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin.
5-HTP can be manufactured and us ...
(5-hydroxytryptophan) is used for experimental treatment of depression.
* L-DOPA (L-dihydroxyphenylalanine) for Parkinson's treatment,
* Eflornithine inhibits ornithine decarboxylase
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (, ODC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine (a product of the urea cycle) to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids ...
and used in the treatment of sleeping sickness
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals.
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species '' Trypanosoma b ...
.
*Canavanine
L-(+)-(''S'')-Canavanine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid found in certain leguminous plants. It is structurally related to the proteinogenic Îą-amino acid L-arginine, the sole difference being the replacement of a methylene bridge ( unit) in ...
, an analogue of arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (âCO2â) a ...
found in many legume
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
s is an antifeedant, protecting the plant from predators.
* Mimosine found in some legumes, is another possible antifeedant. This compound is an analogue of tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
and can poison animals that graze on these plants.
However, not all of the functions of other abundant nonstandard amino acids are known.
Uses in industry
Animal feed
Amino acids are sometimes added to animal feed
Animal feed is food given to domestic animals, especially livestock, in the course of animal husbandry. There are two basic types: fodder and forage. Used alone, the word ''feed'' more often refers to fodder. Animal feed is an important input ...
because some of the components of these feeds, such as soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source o ...
s, have low levels of some of the essential amino acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms ...
s, especially of lysine, methionine, threonine, and tryptophan.
Food
The food industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, ...
is a major consumer of amino acids, especially glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an Îą- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can ...
, which is used as a flavor enhancer,aspartame
Aspartame is an artificial non-saccharide sweetener commonly used as a sugar substitute in foods and beverages. 200 times sweeter than sucrose, it is a methyl ester of the aspartic acid/phenylalanine dipeptide with brand names NutraSwe ...
(aspartylphenylalanine 1-methyl ester), which is used as an artificial sweetener
A sugar substitute or artificial sweetener, is a food additive that provides a sweetness like that of sugar while containing significantly less food energy than sugar-based sweeteners, making it a zero-calorie () or low-calorie sweetener. Arti ...
. Amino acids are sometimes added to food by manufacturers to alleviate symptoms of mineral deficiencies, such as anemia, by improving mineral absorption and reducing negative side effects from inorganic mineral supplementation.[
]
Chemical building blocks
Amino acids are low-cost feedstock
A raw material, also known as a feedstock, unprocessed material, or primary commodity, is a basic material that is used to produce goods, finished goods, energy, or intermediate materials/Intermediate goods that are feedstock for future finishe ...
s used in chiral pool synthesis as enantiomerically pure building blocks.cosmetics
Cosmetics are substances that are intended for application to the body for cleansing, beautifying, promoting attractiveness, or altering appearance. They are mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either Natural product, natural source ...
.[
]
Aspirational uses
Fertilizer
The chelating ability of amino acids is sometimes used in fertilizers to facilitate the delivery of minerals to plants in order to correct mineral deficiencies, such as iron chlorosis. These fertilizers are also used to prevent deficiencies from occurring and to improve the overall health of the plants.
Biodegradable plastics
Amino acids have been considered as components of biodegradable polymers, which have applications as environmentally friendly
Environment friendly processes, or environmental-friendly processes (also referred to as eco-friendly, nature-friendly, and green), are sustainability and marketing terms referring to goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that c ...
packaging and in medicine in drug delivery
Drug delivery involves various methods and technologies designed to transport pharmaceutical compounds to their target sites helping therapeutic effect. It involves principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specif ...
and the construction of prosthetic implants.diaper
A diaper (, North American English) or a nappy (British English, Australian English, Hiberno-English) is a type of underwear that allows the wearer to urinate or defecate without using a toilet, by absorbing or containing waste products to p ...
s and agriculture.corrosion inhibitor
A corrosion inhibitor or anti-corrosive is a chemical compound added to a liquid or gas to decrease the corrosion rate of a metal that comes into contact with the fluid. The effectiveness of a corrosion inhibitor depends on fluid composition and ...
.
Synthesis
Chemical synthesis
The commercial production of amino acids usually relies on mutant bacteria that overproduce individual amino acids using glucose as a carbon source. Some amino acids are produced by enzymatic conversions of synthetic intermediates. 2-Aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid
2-Aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid (ACTA) is the organosulfur compound and a heterocycle with the formula HO2CCHCH2SCNH2N. This derivative of thiazoline is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of L-cysteine, an amino acid
Amino a ...
is an intermediate in one industrial synthesis of cysteine, L-cysteine for example. Aspartic acid is produced by the addition of ammonia to fumarate using a lyase.
Biosynthesis
In plants, nitrogen is first assimilated into organic compounds in the form of glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an Îą-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
, formed from alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia in the mitochondrion. For other amino acids, plants use transaminase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an Îą-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins.
Function and mechanism
An amino acid con ...
s to move the amino group from glutamate to another alpha-keto acid. For example, aspartate aminotransferase converts glutamate and oxaloacetate to alpha-ketoglutarate and aspartate. Other organisms use transaminases for amino acid synthesis, too.
Nonstandard amino acids are usually formed through modifications to standard amino acids. For example, homocysteine is formed through the transsulfuration pathway or by the demethylation of methionine via the intermediate metabolite S-adenosylmethionine, ''S''-adenosylmethionine,hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gela ...
is made by a post translational modification of proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
.
Microorganisms and plants synthesize many uncommon amino acids. For example, some microbes make 2-aminoisobutyric acid and lanthionine, which is a sulfide-bridged derivative of alanine. Both of these amino acids are found in peptidic lantibiotics such as alamethicin. However, in plants, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid is a small disubstituted cyclic amino acid that is an intermediate in the production of the plant hormone ethylene#Ethylene as a plant hormone, ethylene.
Primordial synthesis
The formation of amino acids and peptides is assumed to have preceded and perhaps induced the abiogenesis, emergence of life on earth. Amino acids can form from simple precursors under various conditions.peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
s, with peptides being considered key players in the origin of life. In the famous Urey-Miller experiment, the passage of an electric arc through a mixture of methane, hydrogen, and ammonia produces a large number of amino acids. Since then, scientists have discovered a range of ways and components by which the potentially prebiotic formation and chemical evolution of peptides may have occurred, such as condensing agents, the design of self-replicating peptides and a number of non-enzymatic mechanisms by which amino acids could have emerged and elaborated into peptides.
In the famous Urey-Miller experiment, the passage of an electric arc through a mixture of methane, hydrogen, and ammonia produces a large number of amino acids. Since then, scientists have discovered a range of ways and components by which the potentially prebiotic formation and chemical evolution of peptides may have occurred, such as condensing agents, the design of self-replicating peptides and a number of non-enzymatic mechanisms by which amino acids could have emerged and elaborated into peptides.nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers â deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s are far more difficult to synthesize chemically than amino acids." For a chronological order, it suggests that there must have been a 'protein world' or at least a 'polypeptide world', possibly later followed by the 'RNA world' and the 'DNA world'. Codonâamino acids mappings may be the biology, biological information system at the primordial origin of life on Earth. While amino acids and consequently simple peptides must have formed under different experimentally probed geochemical scenarios, the transition from an abiotic world to the first life forms is to a large extent still unresolved.
Reactions
Amino acids undergo the reactions expected of the constituent functional groups.
Peptide bond formation
 As both the amine and carboxylic acid groups of amino acids can react to form amide bonds, one amino acid molecule can react with another and become joined through an amide linkage. This polymerization of amino acids is what creates proteins. This condensation reaction yields the newly formed peptide bond and a molecule of water. In cells, this reaction does not occur directly; instead, the amino acid is first activated by attachment to a transfer RNA molecule through an ester bond. This aminoacyl-tRNA is produced in an Adenosine triphosphate, ATP-dependent reaction carried out by an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. This aminoacyl-tRNA is then a substrate for the ribosome, which catalyzes the attack of the amino group of the elongating protein chain on the ester bond. As a result of this mechanism, all proteins made by ribosomes are synthesized starting at their ''N''-terminus and moving toward their ''C''-terminus.
However, not all peptide bonds are formed in this way. In a few cases, peptides are synthesized by specific enzymes. For example, the tripeptide glutathione is an essential part of the defenses of cells against oxidative stress. This peptide is synthesized in two steps from free amino acids. In the first step, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase condenses cysteine and
As both the amine and carboxylic acid groups of amino acids can react to form amide bonds, one amino acid molecule can react with another and become joined through an amide linkage. This polymerization of amino acids is what creates proteins. This condensation reaction yields the newly formed peptide bond and a molecule of water. In cells, this reaction does not occur directly; instead, the amino acid is first activated by attachment to a transfer RNA molecule through an ester bond. This aminoacyl-tRNA is produced in an Adenosine triphosphate, ATP-dependent reaction carried out by an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. This aminoacyl-tRNA is then a substrate for the ribosome, which catalyzes the attack of the amino group of the elongating protein chain on the ester bond. As a result of this mechanism, all proteins made by ribosomes are synthesized starting at their ''N''-terminus and moving toward their ''C''-terminus.
However, not all peptide bonds are formed in this way. In a few cases, peptides are synthesized by specific enzymes. For example, the tripeptide glutathione is an essential part of the defenses of cells against oxidative stress. This peptide is synthesized in two steps from free amino acids. In the first step, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase condenses cysteine and glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an Îą-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
through a peptide bond formed between the side chain carboxyl of the glutamate (the gamma carbon of this side chain) and the amino group of the cysteine. This dipeptide is then condensed with glycine by glutathione synthetase to form glutathione.
In chemistry, peptides are synthesized by a variety of reactions. One of the most-used in peptide synthesis, solid-phase peptide synthesis uses the aromatic oxime derivatives of amino acids as activated units. These are added in sequence onto the growing peptide chain, which is attached to a solid resin support. Libraries of peptides are used in drug discovery through high-throughput screening.
The combination of functional groups allow amino acids to be effective polydentate ligands for metalâamino acid chelates.
The multiple side chains of amino acids can also undergo chemical reactions.
Catabolism
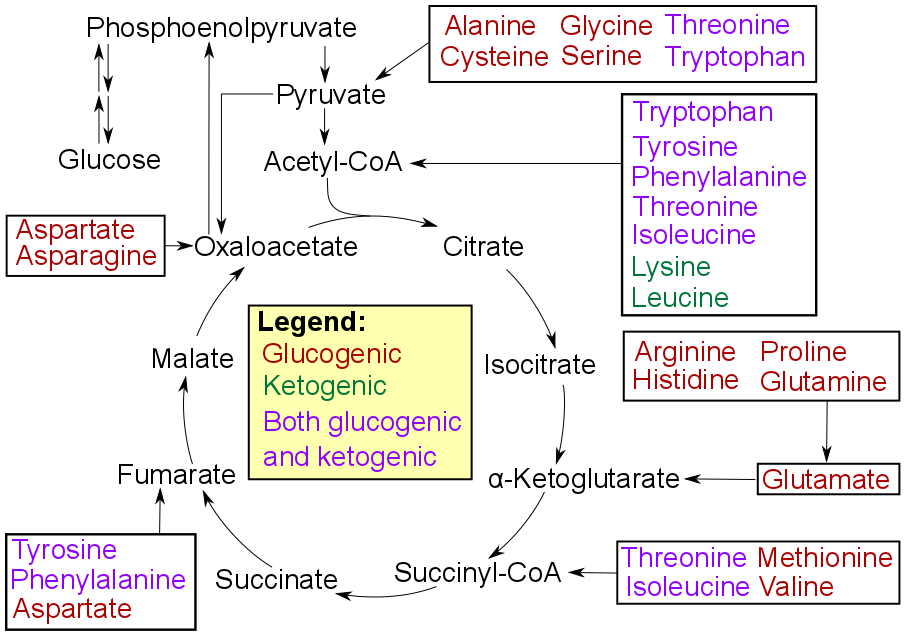 Degradation of an amino acid often involves deamination by moving its amino group to Îą-ketoglutarate, forming
Degradation of an amino acid often involves deamination by moving its amino group to Îą-ketoglutarate, forming glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an Îą-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
. This process involves transaminases, often the same as those used in amination during synthesis. In many vertebrates, the amino group is then removed through the urea cycle and is excreted in the form of urea. However, amino acid degradation can produce uric acid or ammonia instead. For example, serine dehydratase converts serine to pyruvate and ammonia.citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycleâalso known as the Krebs cycle, SzentâGyÃķrgyiâKrebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)âis a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
, as detailed in image at right.
Complexation
Amino acids are bidentate ligands, forming transition metal amino acid complexes.

Chemical analysis
The total nitrogen content of organic matter is mainly formed by the amino groups in proteins. The Kjeldahl method#Applications, total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) is a measure of nitrogen widely used in the analysis of (waste) water, soil, food, feed and organic matter in general. As the name suggests, the Kjeldahl method is applied. More sensitive methods are available.
See also
* Amino acid dating
* Beta-peptide
* Degron
* Erepsin
* Homochirality
* Hyperaminoacidemia
* Leucines
* MillerâUrey experiment
* Nucleic acid sequence
* RNA codon table
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
External links
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Amino Acid
Amino acids,
Nitrogen cycle
Zwitterions
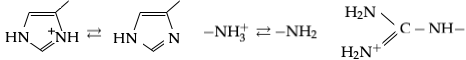 There are three amino acids with side chains that are cations at neutral pH:
There are three amino acids with side chains that are cations at neutral pH:  The common natural forms of amino acids have a zwitterionic structure, with ( in the case of proline) and functional groups attached to the same C atom, and are thus Îą-amino acids, and are the only ones found in proteins during translation in the ribosome.
In aqueous solution at pH close to neutrality, amino acids exist as
The common natural forms of amino acids have a zwitterionic structure, with ( in the case of proline) and functional groups attached to the same C atom, and are thus Îą-amino acids, and are the only ones found in proteins during translation in the ribosome.
In aqueous solution at pH close to neutrality, amino acids exist as  For amino acids with uncharged side-chains the zwitterion predominates at pH values between the two p''K''a values, but coexists in equilibrium with small amounts of net negative and net positive ions. At the midpoint between the two p''K''a values, the trace amount of net negative and trace of net positive ions balance, so that average net charge of all forms present is zero. This pH is known as the
For amino acids with uncharged side-chains the zwitterion predominates at pH values between the two p''K''a values, but coexists in equilibrium with small amounts of net negative and net positive ions. At the midpoint between the two p''K''a values, the trace amount of net negative and trace of net positive ions balance, so that average net charge of all forms present is zero. This pH is known as the  Animals ingest amino acids in the form of protein. The protein is broken down into its constituent amino acids in the process of digestion. The amino acids are then used to synthesize new proteins and other
Animals ingest amino acids in the form of protein. The protein is broken down into its constituent amino acids in the process of digestion. The amino acids are then used to synthesize new proteins and other  Degradation of an amino acid often involves deamination by moving its amino group to Îą-ketoglutarate, forming
Degradation of an amino acid often involves deamination by moving its amino group to Îą-ketoglutarate, forming 