|
Transaminase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins. Function and mechanism An amino acid contains an amino (NH2) group. A keto acid contains a ketone, keto (=O) group. In transamination, the NH2 group on one molecule is exchanged with the =O group on the other molecule. The amino acid becomes a keto acid, and the keto acid becomes an amino acid. Transaminases require the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate, which is converted into pyridoxamine in the first half-reaction, when an amino acid is converted into a keto acid. Enzyme-bound pyridoxamine in turn reacts with pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or alpha-ketoglutarate, giving alanine, aspartic acid, or glutamic acid, respectively. Many transamination reactions occur in tissues, catalysed by transaminases specific for a particular amino/keto acid pair. The reactions are readily reversible, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartate Transaminase
Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT, SGOT), is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme () that was first described by Arthur Karmen and colleagues in 1954. AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells and gall bladder. Serum AST level, serum ALT (alanine transaminase) level, and their ratio (AST/ALT ratio) are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood test, blood panels. The biological half-life, half-life of total AST in the circulation approximates 17 hours and, on average, 87 hours for ''mitochondrial'' AST. Aminotransferase is cleared by Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell, sinusoidal cells in the liver. Function Aspartate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alanine Cycle
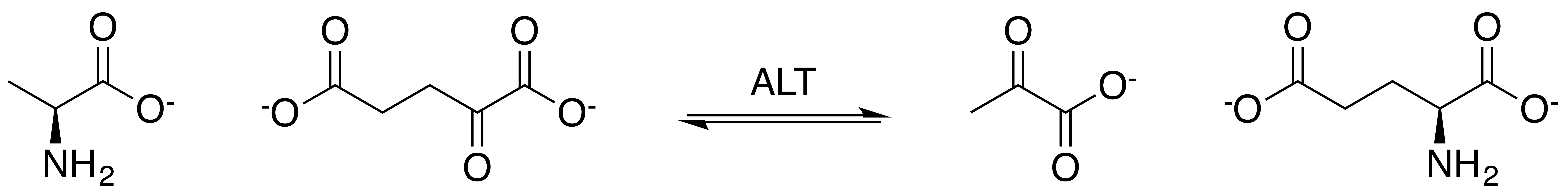
The Cahill cycle, also known as the alanine cycle or glucose-alanine cycle, is the series of reactions in which amino groups and carbons from muscle are transported to the liver. It is quite similar to the Cori cycle in the cycling of nutrients between skeletal muscle and the liver. When muscles degrade amino acids for energy needs, the resulting nitrogen is transaminated to pyruvate to form alanine. This is performed by the enzyme alanine transaminase (ALT), which converts L-Glutamic acid, glutamate and pyruvate into α-ketoglutarate and L-alanine. The resulting L-alanine is shuttled to the liver where the nitrogen enters the urea cycle and the pyruvate is used to make glucose. The Cahill cycle is less productive than the Cori cycle, which uses lactate, since a byproduct of energy production from alanine is production of urea. Removal of the urea is energy-dependent, requiring four "high-energy" phosphate bonds (3 Adenosine triphosphate, ATP hydrolyzed to 2 Adenosine diphosphate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevated Transaminases
In medicine, the presence of elevated transaminases, commonly the transaminases alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), may be an indicator of liver dysfunction. Other terms include transaminasemia, and elevated liver enzymes (though they are not the only enzymes in the liver). Normal ranges for both ALT and AST vary by gender, age, and geography and are roughly 8-40 U/L (0.14-0.67 μkal/L). Mild transaminesemia refers to levels up to 250 U/L. Drug-induced increases such as that found with the use of anti-tuberculosis agents such as isoniazid are limited typically to below 100 U/L for either ALT or AST. Muscle sources of the enzymes, such as intense exercise, are unrelated to liver function and can markedly increase AST and ALT. Cirrhosis of the liver or fulminant liver failure secondary to hepatitis commonly reach values for both ALT and AST in the >1000 U/L range; however, many people with liver disease have normal transaminases. Elevated transaminases t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alanine Transaminase
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT or ALAT), formerly alanine transaminase (ALT), and even earlier referred to as serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT) or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), is a transaminase enzyme () that was first characterized in the mid-1950s by Arthur Karmen and colleagues. ALT is found in plasma and in various body tissues but is most common in the liver. It catalyzes the two parts of the alanine cycle. Serum ALT level, serum AST ( aspartate transaminase) level, and their ratio ( AST/ALT ratio) are routinely measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The half-life of ALT in the circulation approximates 47 hours. Aminotransferase is cleared by sinusoidal cells in the liver. Function ALT catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from L-alanine to α-ketoglutarate, the products of this reversible transamination reaction being pyruvate and L-glutamate. :L-alanine + α-ketoglutarate ⇌ pyruvate + L-glutamate ALT (and all aminotran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transamination
Transamination is a chemical reaction that transfers an amino group to a ketoacid to form new amino acids.This pathway is responsible for the deamination of most amino acids. This is one of the major degradation pathways which convert essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids (amino acids that can be synthesized de novo by the organism). Transamination in biochemistry is accomplished by enzymes called transaminases or aminotransferases. α-ketoglutarate acts as the predominant amino-group acceptor and produces glutamate as the new amino acid. :Amino acid, Aminoacid + α-ketoglutarate ↔ α-keto acid + Glutamic acid, glutamate Glutamate's amino group, in turn, is transferred to oxaloacetate in a second transamination reaction yielding aspartate. :Glutamic acid, Glutamate + oxaloacetate ↔ α-ketoglutarate + aspartate Mechanism of action Transamination catalyzed by aminotransferase occurs in two stages. In the first step, the α amino group of an amino acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keto Acid
In organic chemistry, keto acids or ketoacids (also called oxo acids or oxoacids) are organic compounds that contain a carboxylic acid group () and a ketone group ().Franz Dietrich Klingler, Wolfgang Ebertz "Oxocarboxylic Acids" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. In several cases, the keto group is hydrated. The alpha-keto acids are especially important in biology as they are involved in the Krebs citric acid cycle and in glycolysis. Common types of keto acids include: *Alpha-keto acids, alpha-ketoacids, or 2-oxoacids have the keto group adjacent to the carboxylic acid. They often arise by oxidative deamination of amino acids, and reciprocally, they are precursors to the same. Alpha-keto acids possesses extensive chemistry as acylation agents. Furthermore, alpha-keto acids such as phenylpyruvic acid are endogenous sources for carbon monoxide (as a gasotransmitter) and pharmaceutical prodrug scaffold. Important representatives: ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergy, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, Abnormality (behavior), dysfunction, distress (medicine), distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injury in humans, injuries, disability, disabilities, Disorder (medicine) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', and '' volume concentration''. The concentration can refer to any kind of chemical mixture, but most frequently refers to solutes and solvents in solutions. The molar (amount) concentration has variants, such as normal concentration and osmotic concentration. Dilution is reduction of concentration, e.g. by adding solvent to a solution. The verb to concentrate means to increase concentration, the opposite of dilute. Etymology ''Concentration-'', ''concentratio'', action or an act of coming together at a single place, bringing to a common center, was used in post-classical Latin in 1550 or earlier, similar terms attested in Italian (1589), Spanish (1589), English (1606), French (1632). Qualitative description Often in informal, non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Metabolism
Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O2). Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain. In aerobic organisms undergoing respiration, electrons are shuttled to an electron transport chain, and the final electron acceptor is oxygen. Molecular oxygen is an excellent electron acceptor. Anaerobes instead use less-oxidizing substances such as nitrate (), fumarate (), sulfate (), or elemental sulfur (S). These terminal electron acceptors have smaller reduction potentials than O2. Less energy per oxidized molecule is released. Therefore, anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic. As compared with fermentation Anaerobic cellular respiration and fermentation generate ATP in very different ways, and the terms should not be treated as synonyms. Cellular respiration (both aerobic and anaerobic) uses highly reduced chemical compounds such as NADH and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cori Cycle
The Cori cycle (also known as the lactic acid cycle), named after its discoverers, Carl Ferdinand Cori and Gerty Cori, is a metabolic pathway in which lactic acid, lactate, produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles, is transported to the liver and converted to glucose, which then returns to the muscles and is cyclically metabolized back to lactate. Process Muscular activity requires Adenosine triphosphate, ATP, which is provided by the breakdown of glycogen in the skeletal muscles. The breakdown of glycogen, known as glycogenolysis, releases glucose in the form of glucose-1-phosphate, glucose 1-phosphate (G1P). The G1P is converted to G6P by phosphoglucomutase. G6P is readily fed into glycolysis, (or can go into the pentose phosphate pathway if G6P concentration is high) a process that provides ATP to the muscle cells as an energy source. During muscular activity, the store of ATP needs to be constantly replenished. When the supply of dioxygen, oxygen is sufficient, this energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
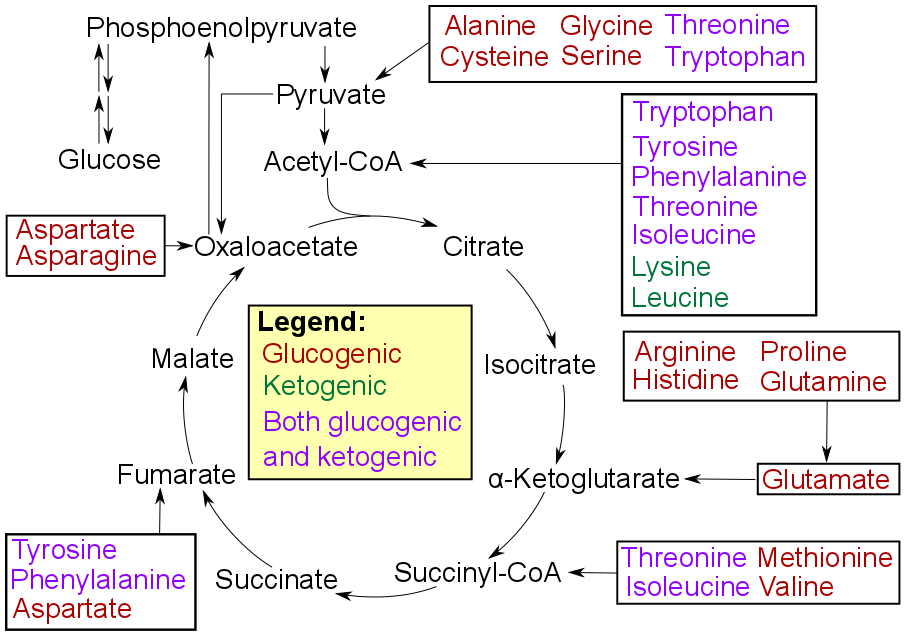
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen ( glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise. In humans, substrates for gluconeogenesis may come from any non-carbohydrate sources that can be converted to pyruvate or inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |