|
Studtite
Studtite, chemical formula UO2)O2(H2O)2�2(H2O) or UO4·4(H2O), is a secondary uranium mineral containing peroxide formed by the alpha- radiolysis of water during formation. It occurs as pale yellow to white needle-like crystals often in acicular, white sprays. Studtite was originally described by Vaes in 1947Annales de la Société Géologique de Belgique - 1947 - pp B212 to B226- J.F. Vaes - Six nouveaux minéraux d'urane provenant de Shinkolobwe (Katanga) - from specimens from Shinkolobwe, Katanga Copper Crescent, Katanga (Shaba), Democratic Republic of Congo, and has since been reported from several other localities. The mineral was named for Franz Edward Studt, an English prospector and geologist who was working for the Belgians. When exposed to air studtite converts over a short time to the metastudtite UO4·2(H2O) form. Despite their apparent chemical simplicity, these two uranyl species are the only reported peroxide minerals. They may also be readily formed on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corium (nuclear Reactor)
The Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station, Three Mile Island reactor 2 after the partial meltdown. Corium, also called fuel-containing material (FCM) or lava-like fuel-containing material (LFCM), is a material that is created in a nuclear reactor core during a nuclear meltdown accident. Resembling lava in consistency, it consists of a mixture of nuclear fuel, fission products, control rods, structural materials from the affected parts of the reactor, products of their chemical reaction with air, water, steam, and in the event that the reactor vessel is breached, molten concrete from the floor of the reactor room. Composition and formation The heat causing the melting of a reactor may originate from the nuclear chain reaction, but more commonly decay heat of the fission products contained in the fuel rods is the primary heat source. The heat production from radioactive decay drops quickly, as the short half-life isotopes provide most of the heat and radioactive decay, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranyl Peroxide
Uranyl peroxide or uranium peroxide hydrate (UO4·nH2O) is a pale-yellow, soluble peroxide of uranium. It is found to be present at one stage of the enriched uranium fuel cycle and in yellowcake prepared via the ''in situ'' leaching and resin ion exchange system. This compound, also expressed as UO3·(H2O2)·(H2O), is very similar to uranium trioxide hydrate UO3·''n''H2O. The dissolution behaviour of both compounds are very sensitive to the hydration state (n can vary between 0 and 4). One main characteristic of uranium peroxide is that it consists of small needles with an average AMAD of about 1.1 μm. The uranyl minerals studtite, UO4·4H2O, and metastudtite, UO4·2H2O, are the only minerals discovered to date found to contain peroxide. The product is a light yellow powder. Synthesis In general, uranyl peroxide can be obtained from a solution of uranium(VI) by adding a peroxide, usually hydrogen peroxide solution. The dihydrate is obtained from a boiling solution of urany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide Mineral
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. Minerals with complex anion groups such as the silicates, sulfates, carbonates and phosphates are classed separately. Simple oxides *XO form **Periclase group *** Periclase *** Manganosite **Zincite group *** Zincite *** Bromellite *** Tenorite *** Litharge * form ** Cuprite **Ice * form **Hematite group ***Corundum ***Hematite *** Ilmenite * form **Rutile group ***Rutile *** Pyrolusite *** Cassiterite ** Baddeleyite ** Uraninite ** Thorianite * form **Spinel group ***Spinel ***Gahnite ***Magnetite *** Franklinite ***Chromite ** Chrysoberyl ** Columbite *Hydroxide subgroup: **Brucite ** Manganite ** Romanèchite **Goethite group: *** Diaspore ***Goethite Nickel–Strunz class 4: oxides IMA-CNMNC proposes a new hierarchical scheme (Mills et al., 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
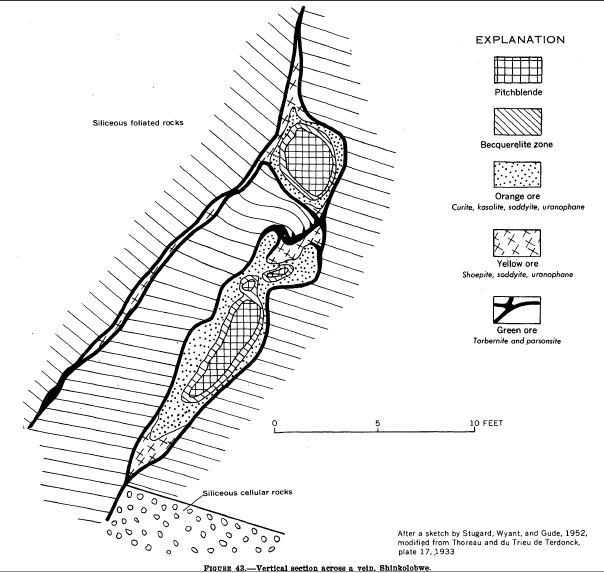
Shinkolobwe
Shinkolobwe, or Kasolo, or Chinkolobew, or Shainkolobwe, was a radium and uranium mine in the Haut-Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), located west of Likasi (formerly Jadotville), south of Kambove, and about northwest of Lubumbashi. The mine produced the most economical uranium ore in the world and was used for the Manhattan Project and subsequent Nuclear weapons of the United States, nuclear weapons produced by the United States in the 1940s and 50s. Before World War II, uranium extracted here was originally taken to Belgium to be processed; this supply was captured by the Wehrmacht in 1940 and subsequently used for the unsuccessful German nuclear program. The Shinkolobwe mine was officially closed in 2004. Toponym The mine's name was taken from the long-gone nearby village of Shinkolobwe. It is also slang for "a man who is easygoing on the surface but who becomes angry when provoked". Geology The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide Minerals
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. Minerals with complex anion groups such as the Silicate mineral, silicates, Sulfate mineral, sulfates, carbonate mineral, carbonates and Phosphate mineral, phosphates are classed separately. Simple oxides *XO form **Periclase group ***Periclase ***Manganosite **Zincite group ***Zincite ***Bromellite ***Tenorite ***Litharge * form **Cuprite **Ice * form **Hematite group ***Corundum ***Hematite ***Ilmenite * form **Rutile group ***Rutile ***Pyrolusite ***Cassiterite **Baddeleyite **Uraninite **Thorianite * form **Spinel group ***Spinel ***Gahnite ***Magnetite ***Franklinite ***Chromite **Chrysoberyl **Columbite *Hydroxide subgroup: **Brucite **Manganite **Romanèchite **Goethite group: ***Diaspore ***Goethite Nickel–Strunz class 4: oxides Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals (as well as wood and artificial materials) through contact with water, atmospheric gases, sunlight, and biological organisms. It occurs '' in situ'' (on-site, with little or no movement), and so is distinct from erosion, which involves the transport of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity. Weathering processes are either physical or chemical. The former involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through such mechanical effects as heat, water, ice and wind. The latter covers reactions to water, atmospheric gases and biologically produced chemicals with rocks and soils. Water is the principal agent behind both kinds, though atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and the activities of biological organisms are also important. Biological chemical weathering is also called biological weathering. The materials left after the rock breaks down combine with organic material to create so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fuel
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other atomic nucleus, nuclear devices to generate energy. Oxide fuel For fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is usually based on the metal oxide; the oxides are used rather than the metals themselves because the oxide melting point is much higher than that of the metal and because it cannot burn, being already in the oxidized state. Uranium dioxide Uranium dioxide is a black semiconductor, semiconducting solid. It can be made by heating uranyl nitrate to form . : This is then converted by heating with hydrogen to form UO2. It can be made from Enriched uranium, enriched uranium hexafluoride by reacting with ammonia to form a solid called ammonium diuranate, . This is then heated (Calcination, calcined) to form and U3O8 which is then converted by heating with hydrogen or ammonia to form UO2. The UO2 is mixed with an organic binder and pressed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium(VI) Minerals
Uranium is a chemical element; it has symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium radioactively decays, usually by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of this decay varies between 159,200 and 4.5 billion years for different isotopes, making them useful for dating the age of the Earth. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite. Many contemporar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranyl
The uranyl ion with the chemical formula has a linear structure with short U–O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen, with uranium in the oxidation state +6. Four or more ligands may be bound to the uranyl ion in an equatorial plane around the uranium atom. The uranyl ion forms many complex (chemistry), complexes, particularly with ligands that have oxygen donor atoms. Complexes of the uranyl ion are important in the extraction of uranium from its ores and in nuclear fuel reprocessing. Structure and bonding The uranyl ion is linear and symmetrical, specifically belonging to the D∞h point group, with both U–O bond lengths of about 180 pm. The bond lengths are indicative of the presence of multiple bonding between the uranium and oxygen atoms. Since uranium(VI) has the electronic configuration of the preceding noble gas, radon, the electrons used in forming the U–O bonds are supplied by the oxygen atoms. The electrons are donated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons reprocessing. The storage and disposal of radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment. Radioactive waste is broadly classified into 3 categories: low-level waste (LLW), such as paper, rags, tools, clothing, which contain small amounts of mostly short-lived radioactivity; intermediate-level waste (ILW), which contains higher amounts of radioactivity and requires some shielding; and high-level waste (HLW), which is highly radioactive and hot due to decay heat, thus requiring cooling and shielding. Spent nuclear fuel can be processed in nuclear reprocessing plants. One third of the total amount have already been reprocessed. With nuclear reprocessing 96% of the spent fue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucca Mountain Nuclear Waste Repository
The Yucca Mountain Nuclear Waste Repository, as designated by the Nuclear Waste Policy Act amendments of 1987, is a proposed deep geological repository storage facility within Yucca Mountain for spent nuclear fuel and other high-level radioactive waste in the United States. The site is on federal land adjacent to the Nevada Test Site in Nye County, Nevada, about northwest of the Las Vegas Valley. The project was approved in 2002 by the 107th United States Congress, but the 112th United States Congress, 112th Congress ended federal funding for the site via amendment to the continuing resolution, Department of Defense and Full-Year Continuing Appropriations Act, passed on April 14, 2011, during the Obama administration. The project has encountered many difficulties and was highly contested by the public, the Western Shoshone peoples, and many politicians. The project also faces strong state and regional opposition. The Government Accountability Office stated that the closure was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Geological Repository
A deep geological repository is a way of storing hazardous or radioactive waste within a stable geologic environment, typically 200–1,000 m below the surface of the earth. It entails a combination of waste form, waste package, engineered seals and geology that is suited to provide a high level of long-term isolation and containment without future maintenance. This is intended to prevent radioactive dangers. A number of mercury, cyanide and arsenic waste repositories are operating worldwide including Canada ( Giant Mine) and Germany (potash mines in Herfa-Neurode and Zielitz). Radioactive waste storage sites are under construction with the Onkalo in Finland being the most advanced. Principles and background Highly toxic waste that cannot be further recycled must be stored in isolation, to avoid contamination of air, ground and underground water. Deep geological repository is a type of long-term storage that isolates waste in geological structures that are expected to be st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |