|
Shinkolobwe
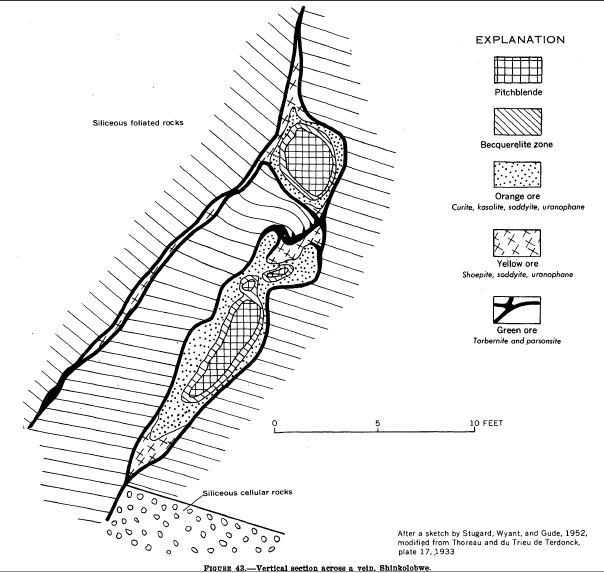
Shinkolobwe, or Kasolo, or Chinkolobew, or Shainkolobwe, was a radium and uranium mine in the Haut-Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), located west of Likasi (formerly Jadotville), south of Kambove, and about northwest of Lubumbashi. The mine produced the most economical uranium ore in the world and was used for the Manhattan Project and subsequent Nuclear weapons of the United States, nuclear weapons produced by the United States in the 1940s and 50s. Before World War II, uranium extracted here was originally taken to Belgium to be processed; this supply was captured by the Wehrmacht in 1940 and subsequently used for the unsuccessful German nuclear program. The Shinkolobwe mine was officially closed in 2004. Toponym The mine's name was taken from the long-gone nearby village of Shinkolobwe. It is also slang for "a man who is easygoing on the surface but who becomes angry when provoked". Geology The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katanga Province
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika Province, Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba Province, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997 (during the rule of Mobutu Sese Seko when Congo was known as Zaire), its official name was Shaba Province. Katanga's area encompassed . Farming and ranching are carried out on the Katanga Plateau. The eastern part of the province is a rich mining region which supplies cobalt, copper, tin, radium, uranium, and diamonds. The region's former capital, Lubumbashi, is the second-largest city in the Congo. History Copper mining in Katanga dates back over 1,000 years, and mines in the region were producing standard-sized ingots of copper for international transport by the end of the 10th century CE. In the 1890s, the province was beleaguered from the south by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likasi
Likasi (formerly official names: Jadotville (French language, French) and Jadotstad (Dutch language, Dutch)) is a Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, city in Haut-Katanga Province, in the south-east of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Demographics Likasi has a population of around 635,000 (2015). During the 1990s the United Nations set up feeding centres and refugee centres in and around Likasi to assist with the refugees fleeing ethnic violence in Shaba Province, Shaba, whose arrival had increased the population of the town some 41,000. History Shinkolobwe mine, 20 km west of Likasi (then called Jadotville), was described by a 1943 Manhattan Project intelligence report as the most important deposit of uranium yet discovered in the world. The uranium from this mine was used to build the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, atomic bombs used in Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945. In 1961, during the United Nations intervention in the State of Katanga, Katanga c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was directed by Major General Leslie Groves of the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the bombs. The Army program was designated the Manhattan District, as its first headquarters were in Manhattan; the name gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. The project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys, and subsumed the program from the American civilian Office of Scientific Research and Development. The Manhattan Project employed nearly 130,000 people at its peak and cost nearly US$2 billion (equivalent to about $ b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
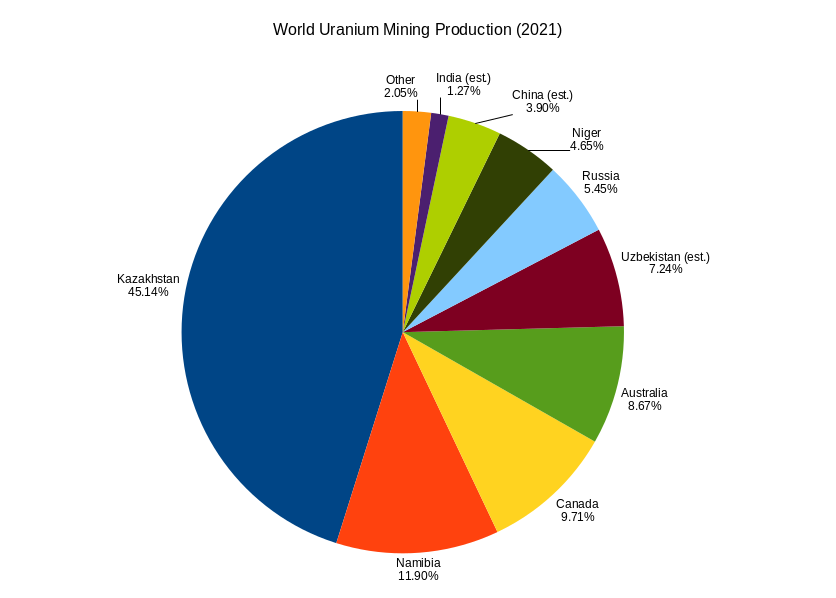
Uranium Mine
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the earth. Over 50,000 tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity and toxicity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived and than natural uranium. Uranium is mined by in-situ leaching (57% of world production) or by conventional underground or op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uraninite
Uraninite, also known as pitchblende, is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2 but because of oxidation typically contains variable proportions of U3O8. Radioactive decay of the uranium causes the mineral to contain oxides of lead and trace amounts of helium. It may also contain thorium and rare-earth elements. Overview Uraninite used to be known as pitchblende (from '' pitch'', because of its black color, and ''blende'', from ''blenden'' meaning "to deceive", a term used by German miners to denote minerals whose density suggested metal content, but whose exploitation, at the time they were named, was either unknown or not economically feasible). The mineral has been known since at least the 15th century, from silver mines in the Ore Mountains, on the German/Czech border. The type locality is the historic mining and spa town known as Joachimsthal, the modern-day Jáchymov, on the Czech side of the mountains, where F. E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Ore
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the most common Chemical element, elements in Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than gold. It can be found almost everywhere in rock, soil, rivers, and oceans. The challenge for commercial uranium extraction is to find those areas where the concentrations are adequate to form an economically viable deposit. The primary use for uranium obtained from mining is in fuel for nuclear reactors. Globally, the distribution of uranium ore deposits is widespread on all continents, with the largest deposits found in Australia, Kazakhstan, and Canada. To date, high-grade deposits are only found in the Athabasca Basin region of Canada. Uranium deposits are generally classified based on host rocks, structural setting, and mineralogy of the deposit. The most widely used classification scheme was developed by the International Atomic Ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncline
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure, whereas an anticline is the inverse of a syncline. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold (synform), termed a synformal syncline (i.e. a trough), but synclines that point upwards can be found when strata have been overturned and folded (an antiformal syncline). Characteristics On a geologic map, synclines are recognized as a sequence of rock layers, with the youngest at the fold's center or ''hinge'' and with a reverse sequence of the same rock layers on the opposite side of the hinge. If the fold pattern is circular or elongate, the structure is a basin. Folds typically form during crustal deformation as the result of compression that accompanies orogenic mountain building. Notable examples * Powder River Basin, Wyoming, US * Sideling Hill roadcut along Inters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
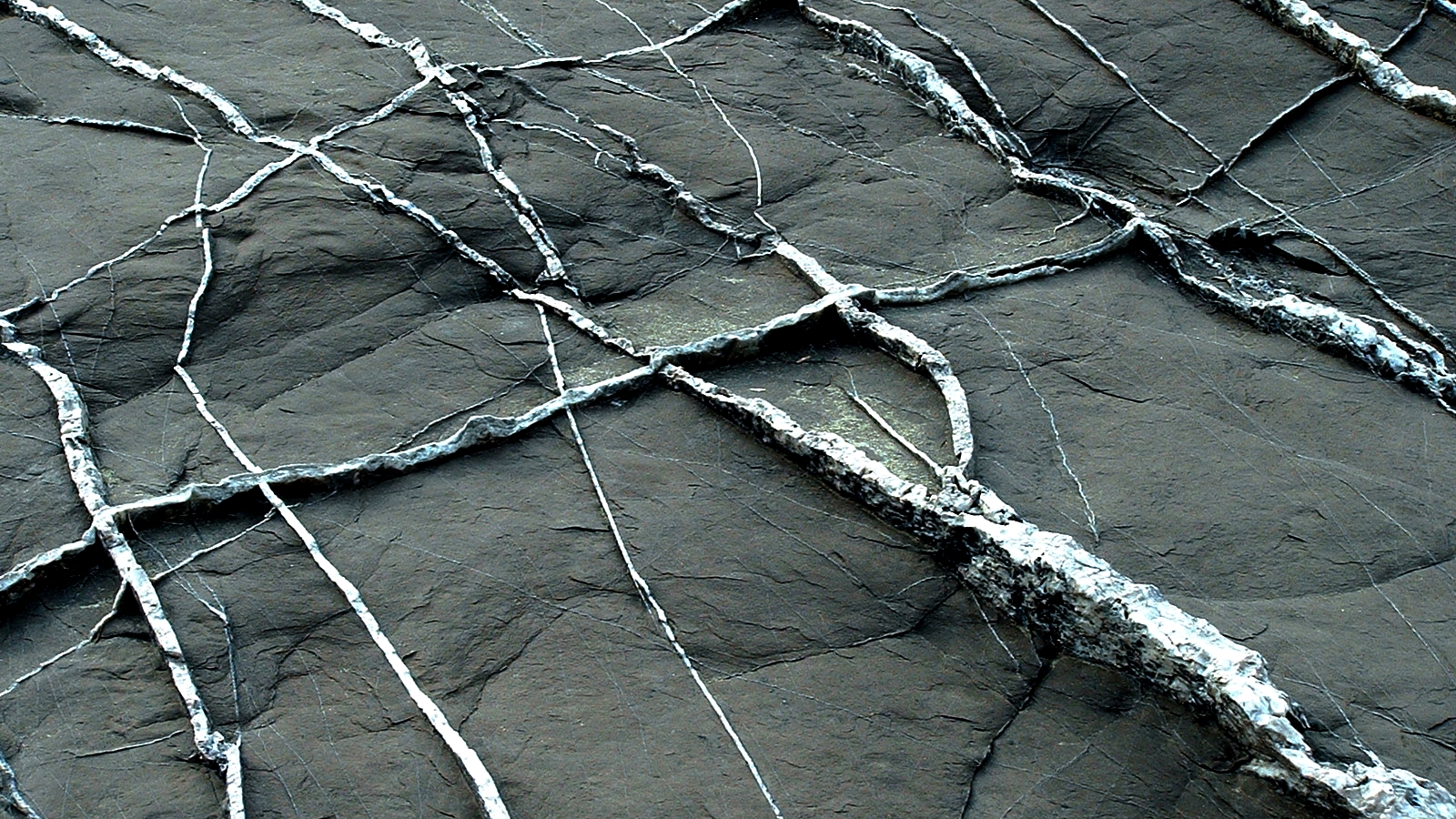
Joint (geology)
In geology, and more specifically in structural geology, a joint is a break (fracture (geology), fracture) of natural origin in a layer or body of Rock (geology), rock that lacks visible or measurable movement parallel to the surface (plane) of the fracture ("Mode 1" Fracture). Although joints can occur singly, they most frequently appear as joint sets and systems. A ''joint set'' is a family of parallel, evenly spaced joints that can be identified through mapping and analysis of their orientations, spacing, and physical properties. A ''joint system'' consists of two or more intersecting joint sets. The distinction between joints and Fault (geology), faults hinges on the terms ''visible'' or ''measurable,'' a difference that depends on the scale of observation. Faults differ from joints in that they exhibit visible or measurable lateral movement between the opposite surfaces of the fracture ("Mode 2" and "Mode 3" Fractures). Thus a joint may be created by either strict movement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, somewhat brittle, gray metal. Cobalt-based blue pigments (cobalt blue) have been used since antiquity for jewelry and paints, and to impart a distinctive blue tint to glass. The color was long thought to be due to the metal bismuth. Miners had long used the name ''kobold ore'' (German language, German for ''goblin ore'') for some of the blue pigment-producing minerals. They were so named because they were poor in known metals and gave off poisonous arsenic-containing fumes when smelted. In 1735, such ores were found to be reducible to a new metal (the first discovered since ancient times), which was ultimately named for the ''kobold''. Today, some cobalt is produced sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture (geology)
A fracture is any separation in a geologic formation, such as a Joint (geology), ''joint'' or a Fault (geology), ''fault'' that divides the Rock (geology), rock into two or more pieces. A fracture will sometimes form a deep fissure or crevice in the rock. Fractures are commonly caused by Stress (physics), stress exceeding the rock strength, causing the rock to lose cohesion along its weakest plane. Fractures can provide Permeability (fluid), permeability for fluid movement, such as water or hydrocarbons. Highly fractured rocks can make good aquifers or Oil reservoir, hydrocarbon reservoirs, since they may possess both significant Permeability (fluid), permeability and fracture porosity. Brittle deformation Fractures are forms of brittle deformation. There are two types of primary brittle deformation processes. Tensile fracturing results in ''joints''. ''Shear fractures'' are the first initial breaks resulting from shear forces exceeding the cohesive strength in that plane. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vein (geology)
In geology, a vein is a distinct sheetlike body of crystallized minerals within a rock. Veins form when mineral constituents carried by an aqueous solution within the rock mass are deposited through precipitation. The hydraulic flow involved is usually due to hydrothermal circulation. Veins are classically thought of as being planar fractures in rocks, with the crystal growth occurring normal to the walls of the cavity, and the crystal protruding into open space. This certainly is the method for the formation of some veins. However, it is rare in geology for significant open space to remain open in large volumes of rock, especially several kilometers below the surface. Thus, there are two main mechanisms considered likely for the formation of veins: ''open-space filling'' and ''crack-seal growth''. Open space filling Open space filling is the hallmark of epithermal vein systems, such as a stockwork, in greisens or in certain skarn environments. For open space fillin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |