Shinkolobwe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shinkolobwe, or Kasolo, or Chinkolobew, or Shainkolobwe, was a
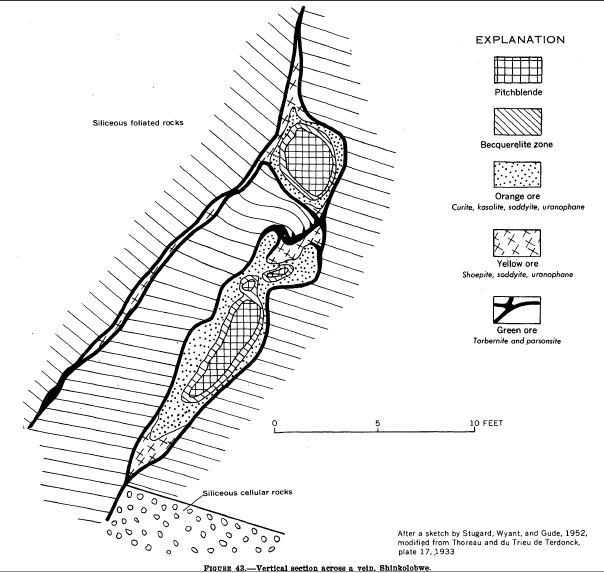 The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discovered in 1915 by the English geologist Robert Rich Sharp (1881–1960).
The formations of the Shinkolobwe ore deposit form a spur of the Mine Series wedged into a fold- fault.
The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discovered in 1915 by the English geologist Robert Rich Sharp (1881–1960).
The formations of the Shinkolobwe ore deposit form a spur of the Mine Series wedged into a fold- fault.
 The first mine was opened in the
The first mine was opened in the
 The United States used Shinkolobwe's
The United States used Shinkolobwe's
The DRC and Uranium for Iran
Retrieved August 19, 2006.
Amherst.edu: photograph of Shinkolobwe
Google Maps: Shinkolobwe
{{Democratic Republic of the Congo topics Uranium mines Uranium mining in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Former mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Haut-Katanga Province Underground mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Belgian Congo in World War II World War II sites in the Democratic Republic of the Congo 1921 establishments in the Belgian Congo 2004 disestablishments in Africa 2000s disestablishments in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Geological type localities
radium
Radium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in alkaline earth metal, group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, ...
and uranium mine in the Haut-Katanga Province
Haut-Katanga (French for "Upper Katanga") is one of the 21 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the Subdivisions of the DR Congo#New provinces, 2015 repartitioning. Haut-Katanga, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba Province, Lualaba, an ...
of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
(DRC), located west of Likasi
Likasi (formerly official names: Jadotville (French language, French) and Jadotstad (Dutch language, Dutch)) is a Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, city in Haut-Katanga Province, in the south-east of the Democratic Republic of Congo.
...
(formerly Jadotville), south of Kambove, and about northwest of Lubumbashi
Lubumbashi ( , ; former ; former ) is the second-largest Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, city in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, located in the country's southeasternmost part, along the border with Zambia. The capital ...
.
The mine produced the most economical uranium ore
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the most common Chemical element, elements in Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than ...
in the world and was used for the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
and subsequent nuclear weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either nuclear fission, fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and nuclear fusion, fusion reactions (thermonuclear weap ...
produced by the United States in the 1940s and 50s. Before World War II, uranium extracted here was originally taken to Belgium to be processed; this supply was captured by the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
in 1940 and subsequently used for the unsuccessful German nuclear program.
The Shinkolobwe mine was officially closed in 2004.
Toponym
The mine's name was taken from the long-gone nearby village of Shinkolobwe. It is also slang for "a man who is easygoing on the surface but who becomes angry when provoked".Geology
 The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discovered in 1915 by the English geologist Robert Rich Sharp (1881–1960).
The formations of the Shinkolobwe ore deposit form a spur of the Mine Series wedged into a fold- fault.
The mineral deposits at Shinkolobwe were discovered in 1915 by the English geologist Robert Rich Sharp (1881–1960).
The formations of the Shinkolobwe ore deposit form a spur of the Mine Series wedged into a fold- fault. Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
minerals, and associated cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element; it has symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs nat ...
and arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, occur as massive sulfide ore
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families of ...
in veinlets along fractures
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
, joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
, and minor faults within the Katanga synclinorium. Uraninite
Uraninite, also known as pitchblende, is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2 but because of oxidation typically contains variable proportions of U3O8. Radioactive decay of the uranium c ...
mineralization occurred 630 Ma ago, when uraniferous solutions percolated into the dolomitic shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of Clay mineral, clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g., Kaolinite, kaolin, aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4) and tiny f ...
s of the Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
Mine Series (Serie des Mines), under the Roche Argilotalqueuse (R.A.T.) nappe
In geology, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than or above a thrust fault from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision zones or on the ...
. The Mine Series is a Schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a l ...
- Dolomite System postulated to be in the Roan System. This schistose-dolomite appears structurally between two contacts of the Kundelungu System, the Middle Kundelungu and the Lower Kundelungu, of the Katanga Group. The Lower and Upper Kundelungu form a double syncline, the northern limb of which overlies the Shinkolobwe Fault. These structural complexities aside, the Katanga stratigraphic column
A stratigraphic column is a representation used in geology and its subfield of stratigraphy to describe the vertical location of rock units in a particular area. A typical stratigraphic column shows a sequence of sedimentary rocks, with the oldest ...
consists, top to bottom, of the Precambrian Kundelungu System (Upper, Middle and Lower), the Grand Conglomerate and Mwashya Systems, the Schist-Dolomite System (Roan System-Mine Series of R.G.S., C.M.N., S.D., R.S.C., R.S.F., D. Strat., R.A.T. Gr., and R.A.T.) and the Kibara Group.
Uraninite crystals from 1 to 4 centimeter cubes were common. New minerals identified here include ianthinite, becquerelite
Becquerelite is a uranium mineral with the chemical formula: Ca(UO2)6O4(OH)6·8(H2O). It is a secondary mineral which contains calcium and is a bright yellow colour. It has a Mohs hardness of about 2.
It was named after the French physicist Anto ...
, schoepite
Schoepite, empirical formula (UO2)8O2(OH)12·12(H2O) is a rare alteration product of uraninite in hydrothermal uranium deposits. It may also form directly from ianthinite. The mineral presents as a transparent to translucent yellow, lemon ye ...
, curite
}
Curite is a rare mineral with the chemical composition Pb3 UO2)4O4(OH)3sub>2·2 H2O. It is therefore a hydrated lead uranyl oxide, which forms red needles or orange, massive aggregates.
Etymology and history
Curite was first found at ...
, fourmarierite, masuyite, vandendriesscheite, richetite, billietite
Billietite is an uncommon mineral of uranium that contains barium. It has the chemical formula: Ba(UO2)6O4(OH)6•8H2O. It usually occurs as clear yellow orthorhombic crystals.M. Katherine Pagoaga, Daniel E, Appleman, & James M. Stewart "Crysta ...
, vandenbrandeite
Vandenbrandeite is a mineral named after a belgian geologist, Pierre Van den Brande, who discovered an ore deposit. It was named in 1932, and has been a valid mineral ever since then.
Properties
Vandenbrandeite grows in microcrystals, up to ha ...
, kasolite
Kasolite is an uncommon lead uranyl silicate monohydrate mineral. It is an IMA approved mineral, that had been a valid species before the foundation of the association, that had been first described and published in 1921 by Schoep. It is a grand ...
, soddyite
Soddyite is a mineral of uranium. It has yellow crystals and usually mixed with curite in oxidized uranium ores. It is named after the British radiochemist and physicist Frederick Soddy (1877–1956). Soddyite has been a valid species since 192 ...
, sklodowskite
Sklodowskite is a uranium mineral with the chemical formula: Mg(UO2)2(HSiO4)2·5H2O. It is a secondary mineral which contains magnesium and is a bright yellow colour, its crystal habit is acicular, but can form in other shapes. It has a Mohs h ...
, cuprosklodowskite
Cuprosklodowskite is a secondary uranium mineral formed by alteration of earlier uranium minerals. Its empirical formula is Cu(UO2)2(HSiO4)2·6(H2O). Cuprosklodowskite is a nesosilicate mineral, It is grass green to dark green in color, and its c ...
, dewindtite, dumontite, renardite, parsonsite
Parsonsite is a lead uranium phosphate mineral with chemical formula: Pb2(UO2)(PO4)2·2H2O. Parsonsite contains about 45% lead and 25% uranium. It forms elongated lathlike pseudo monoclinic crystals, radial spherulites, encrustations and powde ...
, saleite, sharpite, studtite
Studtite, chemical formula UO2)O2(H2O)2�2(H2O) or UO4·4(H2O), is a secondary uranium mineral containing peroxide formed by the alpha- radiolysis of water during formation. It occurs as pale yellow to white needle-like crystals often in acicula ...
, and diderichite. Similar uraninite deposits occur west at Swampo, and west at Kalongwe.
Surface ores consist of oxidized minerals from supergene alteration above the water table and the formation of uranyl
The uranyl ion with the chemical formula has a linear structure with short U–O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen, with uranium in the oxidation state +6. Four or more ligands may be bound to the u ...
minerals. Below the water table, hypogene
In ore deposit geology, hypogene processes occur deep below the Earth's surface, and tend to form deposits of primary minerals, as opposed to supergene processes that occur at or near the surface, and tend to form secondary minerals.
At great d ...
ores include uraninite (pitchblende), cobalt-nickel sulfides and selenide
A selenide is a chemical compound containing a selenium with oxidation number of −2. Similar to sulfide, selenides occur both as inorganic compounds and as organic derivatives, which are called organoselenium compound.
Inorganic selenides
Th ...
s.
History
 The first mine was opened in the
The first mine was opened in the Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (, ; ) was a Belgian colonial empire, Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960 and became the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville). The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Repu ...
in 1921. Uranium-bearing ore was initially exported to Olen, Belgium for the extraction of radium
Radium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in alkaline earth metal, group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, ...
, and uranium. Only the richest ore was sent to Olen, with the remainder held in reserve. Open-cut mining was suspended at level and at the level underground in 1936, though exploration had commenced at level , and water pumps installed at level .
Both Britain and France expressed interest in the Belgium inventory of uranium ore in 1939. Nothing further happened though after the Nazis occupied Belgium in 1940 and got control of the ore still "on the docks". However, of the 1200 tons confiscated, the Alsos Mission was able to recover most of this uranium in 1945.
Open-cut operations restarted in 1944, and underground in 1945, which required pumping the mine dry since the water table was at about 45 m. The 255 m level was reached in 1955.
Manhattan Project
 The United States used Shinkolobwe's
The United States used Shinkolobwe's uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
resources to supply the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
to construct the atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear expl ...
in World War II. Edgar Sengier
Edgar Edouard Bernard Sengier (9 October 1879 – 26 July 1963) was a Belgian mining engineer and director of the Union Minière du Haut Katanga mining company that operated in the Belgian Congo during World War II.
Sengier is credited ...
, then director of Union Minière du Haut Katanga
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Unio ...
, had stockpiled 1,200 tonnes of uranium ore in a warehouse on Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is the southernmost of the boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County and situated at the southernmost point of New York (state), New York. The borough is separated from the ad ...
, New York. This ore and an additional 3,000 tonnes of ore stored above-ground at the mine was purchased by Colonel Ken Nichols for use in the project. Nichols wrote:
In 1940, 1,200 tons of stockpiled uranium ore
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the most common Chemical element, elements in Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than ...
were shipped to the US by Sengier's African Metals Corp., a commercial arm of Union Minière. After the September 1942 agreement with Nichols, an average of 400 tons of uranium oxide
Uranium oxide is an oxide of the element uranium.
The metal uranium forms several oxides:
* Uranium dioxide or uranium(IV) oxide (UO2, the mineral uraninite or pitchblende)
* Diuranium pentoxide or uranium(V) oxide (U2O5)
* Uranium trioxide or ...
was then shipped to the US each month. Initially, the port of Lobito was used to ship the ore, but later Matadi was used to improve security. Only two shipments were lost at sea. The aerodromes in Elizabethville and Leopoldville were also expanded. Additionally, the mine was reopened with the help of the United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is the military engineering branch of the United States Army. A direct reporting unit (DRU), it has three primary mission areas: Engineer Regiment, military construction, and civil wo ...
, which involved draining the water and retooling the facility. Finally, the Office of Strategic Services
The Office of Strategic Services (OSS) was the first intelligence agency of the United States, formed during World War II. The OSS was formed as an agency of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) to coordinate espionage activities behind enemy lines ...
were enlisted to deal with the threat of smuggling to Germany.
American interest in the Shinkolobwe mine for the purpose of developing of nuclear weapons led to the implementation of extensive security measures. Shinkolobwe's location was removed from maps and journalists were denied access to the mine and official information.
Cold War era
Just as a lack of uranium ore impeded the German and Japanese attempts to make an atomic bomb, the Americans wanted to maintain their monopoly against the Soviets. Security measures were slightly more relaxed in the wake of World War II, but in the 1950s, most journalists were able to gather only scraps of information on the mine's operation, from unofficial sources. In 1950, a uranium processing plant was said to be under construction near the mine. At the time, Shinkolobwe was believed to contain roughly half of the world's known reserves of uranium. In 1947, the US received 1,440 tons of uranium concentrates from the Belgian Congo, 2,792 in 1951, and 1,600 in 1953. A processing plant was added nearby, and for increased security, a garrison was also established, with a supporting NATO military base in Kamina. Jadotville became a security checkpoint for foreigners. However, by the time of Congo independence, Union Minière had sealed the mine with concrete. Despite the American presence in the 1940s and 1950s, the increased opening of uranium mines in the US and Congolese independence made the United States in 1960 leave the mine, which caused the sealing of the mine by Union Minière.Israeli yellowcake
In what was termed Operation Plumbat, Israel, in 1968, obtained yellowcake (processeduranium ore
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the most common Chemical element, elements in Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than ...
) to support the Israeli nuclear weapons effort in a clandestine operation after France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
stopped supplying it with uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
fuel for the Dimona nuclear reactor in reaction to the 1967 Arab-Israeli War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
. Numerous sources believe that in 1968 Israel managed to obtain 200 tonnes of yellowcake from the Belgian mining company Union Minière. The company collaborated with Mossad
The Institute for Intelligence and Special Operations (), popularly known as Mossad ( , ), is the national intelligence agency of the Israel, State of Israel. It is one of the main entities in the Israeli Intelligence Community, along with M ...
in shipping out the ore from Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
to Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
for a European front company which then surreptitiously transferred the ore to another vessel at night on the Mediterranean Sea.
Closure
The mine was officially closed on January 28, 2004, by presidential decree. However, eight people died and a further thirteen people were injured in July 2004, when part of the old mine collapsed. Although industrial production has ceased with cement lids sealing off the mine shafts, there is evidence that someartisanal mining
Artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) is a blanket term for a type of subsistence mining involving a miner who may or may not be officially employed by a List of mining companies, mining company but works independently, mining minerals using the ...
still goes on here. A United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
inter-agency mission, led by the UN Office for Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) and the United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
(UNEP), and organised through their Joint Environment Unit, visited the mine. The UNEP/OCHA concluded:
Artisanal mining and smuggling
On July 18, 2006, the DRC Sanctions Committee (United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
Committee Established Pursuant to Resolution 1533 (2004), to give it its full name) released a report dated June 15, 2006, which stated that artisanal mining for various minerals continues at the Shinkolobwe mine:
On August 9, 2006, the British ''Sunday Times
''The Sunday Times'' is a British Sunday newspaper whose circulation makes it the largest in Britain's quality press market category. It was founded in 1821 as ''The New Observer''. It is published by Times Newspapers Ltd, a subsidiary of N ...
'' published a report claiming that Iran was seeking to import "bomb-making uranium" from the Shinkolobwe mine, providing no evidence but quoting the UN report of July 18, 2006. It gives "Tanzanian customs officials" as its sole source for the claim that the uranium was destined for processing in the former Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
via the Iranian port of Bandar Abbas. American journalist Douglas Farah has compared this to North Korean attempts to get uranium from the same mine.Retrieved August 19, 2006.
See also
* K-65 residues * Mining industry of the Democratic Republic of the Congo * Operation PlumbatReferences
External links
Amherst.edu: photograph of Shinkolobwe
Google Maps: Shinkolobwe
{{Democratic Republic of the Congo topics Uranium mines Uranium mining in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Former mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Haut-Katanga Province Underground mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Belgian Congo in World War II World War II sites in the Democratic Republic of the Congo 1921 establishments in the Belgian Congo 2004 disestablishments in Africa 2000s disestablishments in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Geological type localities