|
Spiracle (vertebrates)
Spiracles () are openings on the surface of some animals, which usually lead to respiratory systems. The spiracle is a small hole behind each eye that opens to the mouth in some fish. In the Agnatha, jawless fish, the first gill opening immediately behind the mouth is essentially similar to the other gill openings. With the evolution of the jaw in the early gnathostomes, jawed vertebrates, this gill slit was caught between the forward gill-rod (now functioning as the jaw) and the next rod, the Hyomandibula, hyomandibular bone, supporting the jaw hinge and anchoring the jaw to the skull proper. The gill opening was closed off from below, the remaining opening was small and hole-like, and is termed a spiracle. In many species of Shark, sharks and all Batoidea, rays the spiracle is responsible for the intake of water into the buccal space before being expelled from the gills. The spiracle is often located towards the top of the animal allowing breathing even while the animal is most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taeniura Lymma By Marek Jakubowski
''Taeniura'' is a genus of stingrays in the family (biology), family Dasyatidae. The species ''Taeniurops grabata'' and ''Taeniura meyeni, T. meyeni'' were formerly placed in this genus. However, phylogenetic research has shown that these two species are not closely related to ''T. lymma'', and they have been assigned to a separate genus, ''Taeniurops''. Species *''Taeniura lessoni'' Peter R. Last, Last, William Toby White, W. T. White, & Gavin J. P. Naylor, Naylor, 2016 (Oceania fantail ray) *''Bluespotted ribbontail ray, Taeniura lymma'' (Peter Forsskål, Forsskål, 1775) (Bluespotted ribbontail ray) References Taeniura, Dasyatidae Ray genera Taxa named by Johannes Peter Müller Taxa named by Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle {{Rajiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmobranchii
Elasmobranchii () is a subclass of Chondrichthyes or cartilaginous fish, including modern sharks ( division Selachii), and batomorphs (division Batomorphi, including rays, skates, and sawfish). Members of this subclass are characterised by having five to seven pairs of gill slits opening individually to the exterior, rigid dorsal fins and small placoid scales on the skin. The teeth are in several series; the upper jaw is not fused to the cranium, and the lower jaw is articulated with the upper. The details of this jaw anatomy vary between species, and help distinguish the different elasmobranch clades. The pelvic fins in males are modified to create claspers for the transfer of sperm. There is no swim bladder; instead, these fish maintain buoyancy with large livers rich in oil. The definition of the clade is unclear with respect to fossil chondrichthyans. Some authors consider it as equivalent to Neoselachii (the crown group clade including modern sharks, rays, and all o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otic Notch
Otic notches are invaginations in the posterior margin of the skull roof, one behind each orbit. Otic notches are one of the features lost in the evolution of amniotes from their tetrapod ancestors. The notches have been interpreted as part of an auditory structure and are often reconstructed as holding a tympanum similar to those seen in modern anurans. Analysis of the ''columella'' (the stapes in amphibians and reptiles) of labyrinthodonts however indicates that it did not function in transmitting low-energy vibrations, thus rendering these animals effectively deaf to airborne sound. The otic notch instead functioned as a spiracle, at least in the early forms.Laurin, M. (1996)Hearing in Stegocephalians from the Tree of Life Web Project The Tree of Life Web Project (ToL) is an Internet project providing information about the diversity and phylogeny of life on Earth. This collaborative peer reviewed project began in 1995, and is written by biologists from around the world. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleost
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all neontology, extant species of fish. The Teleostei, which is variously considered a Division (zoology), division or an infraclass in different taxonomic systems, include over 26,000 species that are arranged in about 40 order (biology), orders and 448 family (biology), families. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over , to the minute male anglerfish ''Photocorynus spiniceps'', just long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses. The difference between teleosts and other bony fish lies mainly in their jaw bones; teleosts have a movable premaxilla and corresponding modifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holostei
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by the single living genus, '' Amia'' with two species, the bowfins (''Amia calva'' and '' Amia ocellicauda''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars (Lepisosteidae), represented by seven living species in two genera ('' Atractosteus'', '' Lepisosteus''). The earliest members of the clade, which are putative " semionotiforms" such as '' Acentrophorus'' and '' Archaeolepidotus'', are known from the Middle to Late Permian and are among the earliest known neopterygians. Holostei was thought to be regarded as paraphyletic. However, a recent study provided evidence that the Holostei are the closest living relatives of the Teleostei, both within the Neopterygii. This was found from the morphology of the Holostei, for example presence of a paired vomer. Holosteans are closer to teleosts than are the chondrosteans, the other group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paddlefish
Paddlefish (family Polyodontidae) are a family of ray-finned fish belonging to order Acipenseriformes, and one of two living groups of the order alongside sturgeons (Acipenseridae). They are distinguished from other fish by their elongated rostra, which are thought to enhance electroreception to detect prey. Paddlefish have been referred to as " primitive fish" because the Acipenseriformes are among the earliest diverging lineages of ray-finned fish, having diverged from all other living groups over 300 million years ago. Both living and fossil paddlefish are found almost exclusively in North America and China. Eight species are known: Six of those species are extinct, and known only from fossils (five from North America, one from China), one of the extant species, the American paddlefish (''Polyodon spathula''), is native to the Mississippi River basin in the U.S. The other is the Chinese paddlefish (''Psephurus gladius''), which was declared extinct in 2022 following a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sturgeon
Sturgeon (from Old English ultimately from Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European *''str̥(Hx)yón''-) is the common name for the 27 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the Late Cretaceous, and are descended from other, earlier Acipenseriformes, acipenseriform fish, which date back to the Early Jurassic period, some 174 to 201 million years ago. They are one of two living families of the Acipenseriformes alongside paddlefish (Polyodontidae). The family is grouped into five genera: ''Acipenser'', ''Huso'', ''Scaphirhynchus,'' ''Sinosturio'', and ''Pseudoscaphirhynchus''. Two species (''Adriatic sturgeon, H. naccarii'' and ''Dabry's sturgeon, S. dabryanus'') may be extinct in the wild, and one (''Syr Darya sturgeon, P. fedtschenkoi'') may be entirely extinct. Sturgeons are native to subtropical, temperate and sub-Arctic rivers, lakes and coastlines of Eurasia and North America. A Maastrichtian-age fossil found i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acipenseriformes
Acipenseriformes is an order (biology), order of basal (phylogenetics), basal Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes that includes living and fossil sturgeons and paddlefishes (Acipenseroidei), as well as the extinct family (biology), families Chondrosteidae and Peipiaosteidae. They are the second earliest diverging group of living ray-finned fish after the bichirs. Despite being early diverging, they are highly Primitive (phylogenetics), derived, having only weakly Ossification, ossified skeletons that are mostly made of cartilage, and in modern representatives highly modified skulls. Description The axial skeleton of Acipenseriformes is only partially ossified, with the majority of the bones being replaced with cartilage. The notochord, usually only found in fish embryos, is unconstricted and retained throughout life. The premaxilla and maxilla bones of the skull present in other vertebrates have been lost. While larvae and early juvenile acipenseriforms have teeth, the adult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelacanth
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals) than to ray-finned fish. The name coelacanth originates from the Permian genus '' Coelacanthus'', which was the first scientifically named genus of coelacanths (in 1839), becoming the type genus of Coelacanthiformes as other species were discovered and named. Well-represented in freshwater and marine deposits from as early as the Devonian period (more than 410million years ago), they were thought to have become extinct in the Late Cretaceous, around 66million years ago. The first living species, ''Latimeria chalumnae'', the West Indian Ocean coelacanth, was described from specimens fished off the coast of South Africa from 1938 onward; they are now also known to inhabit the seas around the Comoro Islands off the eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant and Extinction, extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn Evolution, evolving into two major clades, the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct pelycosaur, "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including Homo sapiens, humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming Limbless vertebrate, limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, Bipedidae, some lizards, kiwi (bird), kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bichir
Bichirs and the reedfish comprise Polypteridae , a family (biology), family of archaic Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes and the only family in the order (biology), order Polypteriformes .Helfman GS, Collette BB, Facey DE, Bowen BW. 2009. The Diversity of Fishes. West Sussex, UK: Blackwell Publishing. 720 p. All the species occur in freshwater habitats in tropical Africa and the Nile River system, mainly swampy, shallow floodplains and estuary, estuaries. Cladistia, polypterids and their fossil relatives, are considered the sister group to all other extant ray-finned fishes (Actinopteri).Dai Suzuki, Matthew C. Brandley, Masayoshi Tokita: ''CORRECTION: The mitochondrial phylogeny of an ancient lineage of ray-finned fishes (Polypteridae) with implications for the evolution of body elongation, pelvic fin loss, and craniofacial morphology in Osteichthyes.'' BMC Evolutionary Biology. Bd. 10, Art.-Nr. 209, 2010, They likely diverged from Actinopteri at least 330 million ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
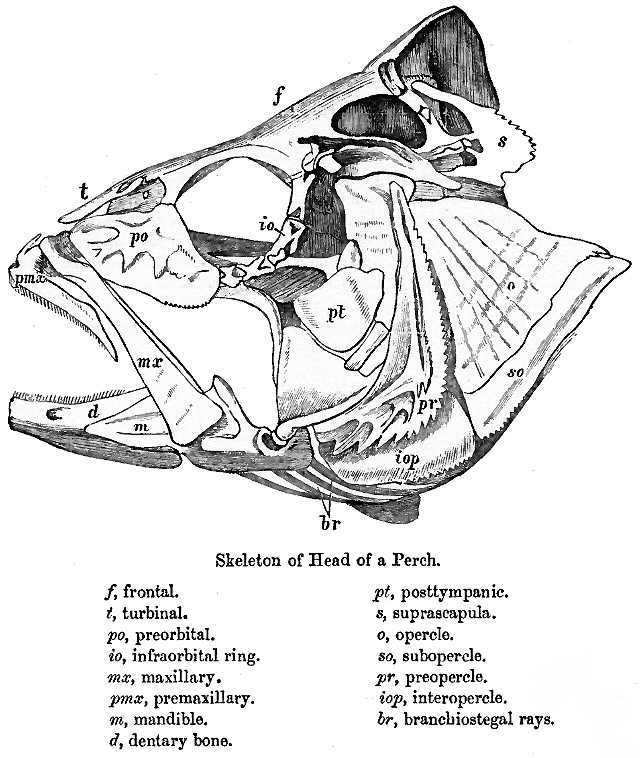
Operculum (fish)
The operculum is a series of bones found in bony fish and chimaeras that serves as a facial support structure and a protective covering for the gills; it is also used for respiration and feeding. Anatomy The opercular series contains four bone segments known as the preoperculum, suboperculum, interoperculum and operculum. The preoperculum is a crescent-shaped structure that has a series of ridges directed posterodorsally to the organism’s canal pores. The preoperculum can be located through an exposed condyle that is present immediately under its ventral margin; it also borders the operculum, suboperculum, and interoperculum posteriorly. The suboperculum is rectangular in shape in most bony fish and is located ventral to the preoperculum and operculum components. It is the thinnest bone segment out of the opercular series and is located directly above the gills. The interoperculum is triangular shaped and borders the suboperculum posterodorsally and the preoperculum anterodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |