|
Sanskritisation (linguistics)
Sanskritisation is the process of introducing features from Sanskrit, such as vocabulary and grammar, into other languages. It is sometimes associated with the "Hinduisation" of a linguistic community, or less commonly, with introducing a more upper-Caste system in India, caste status into a community. Many languages throughout South Asia and Southeast Asia were greatly influenced by Sanskrit (or its descendant languages, the Prakrit, Prakrits and modern-day Indo-Aryan languages) historically. Sanskritisation often stands in opposition to the Persianisation or Englishization, Englishisation of a language within South Asia, as occurs with the Hindustani language, which in its Sanskritised, Persianised, and English-influenced registers becomes Hindi, Urdu, and Hinglish/Urdish respectively. Support for Sanskritisation in South Asia runs highest among Hindutva, Hindu nationalists. Sanskritization of the names of people and places is also commonplace in India. History Ancient era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindutva
Hindutva (; ) is a Far-right politics, far-right political ideology encompassing the cultural justification of Hindu nationalism and the belief in establishing Hindu hegemony within India. The political ideology was formulated by Vinayak Damodar Savarkar in 1922. It is used by the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), the Vishva Hindu Parishad (VHP), the current ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), and other organisations, collectively called the Sangh Parivar. Inspired by Fascism in Europe, European fascism, the Hindutva movement has been variously described as a variant of right-wing extremism, as "almost fascist in the classical sense", adhering to a concept of homogenised majority and cultural hegemony and as a Separatism, separatist ideology. Some analysts dispute the identification of Hindutva with fascism and suggest that Hindutva is an extreme form of conservatism or ethno-nationalism. Proponents of Hindutva, particularly its early ideologues, have used political rhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Nationalism
Hindu nationalism has been collectively referred to as the expression of political thought, based on the native social and cultural traditions of the Indian subcontinent. "Hindu nationalism" is a simplistic translation of . It is better described as "Hindu polity". The native thought streams became highly relevant in Indian history when they helped form a distinctive identity about the Indian polityChatterjee Partha (1986) and provided a basis for questioning colonialism.Peter van der Veer, Hartmut Lehmann, Nation and religion: perspectives on Europe and Asia, Princeton University Press, 1999 p. 90 These also inspired Indian nationalism, Indian nationalists during the Indian independence movement, independence movement based on armed struggle,Li Narangoa, R. B. Cribb ''Imperial Japan and National Identities in Asia'', 1895–1945, Published by Routledge, 2003 p. 78 coercive politics,Bhatt, Chetan, ''Hindu Nationalism: Origins, Ideologies and Modern Myths'', Berg Publishers (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
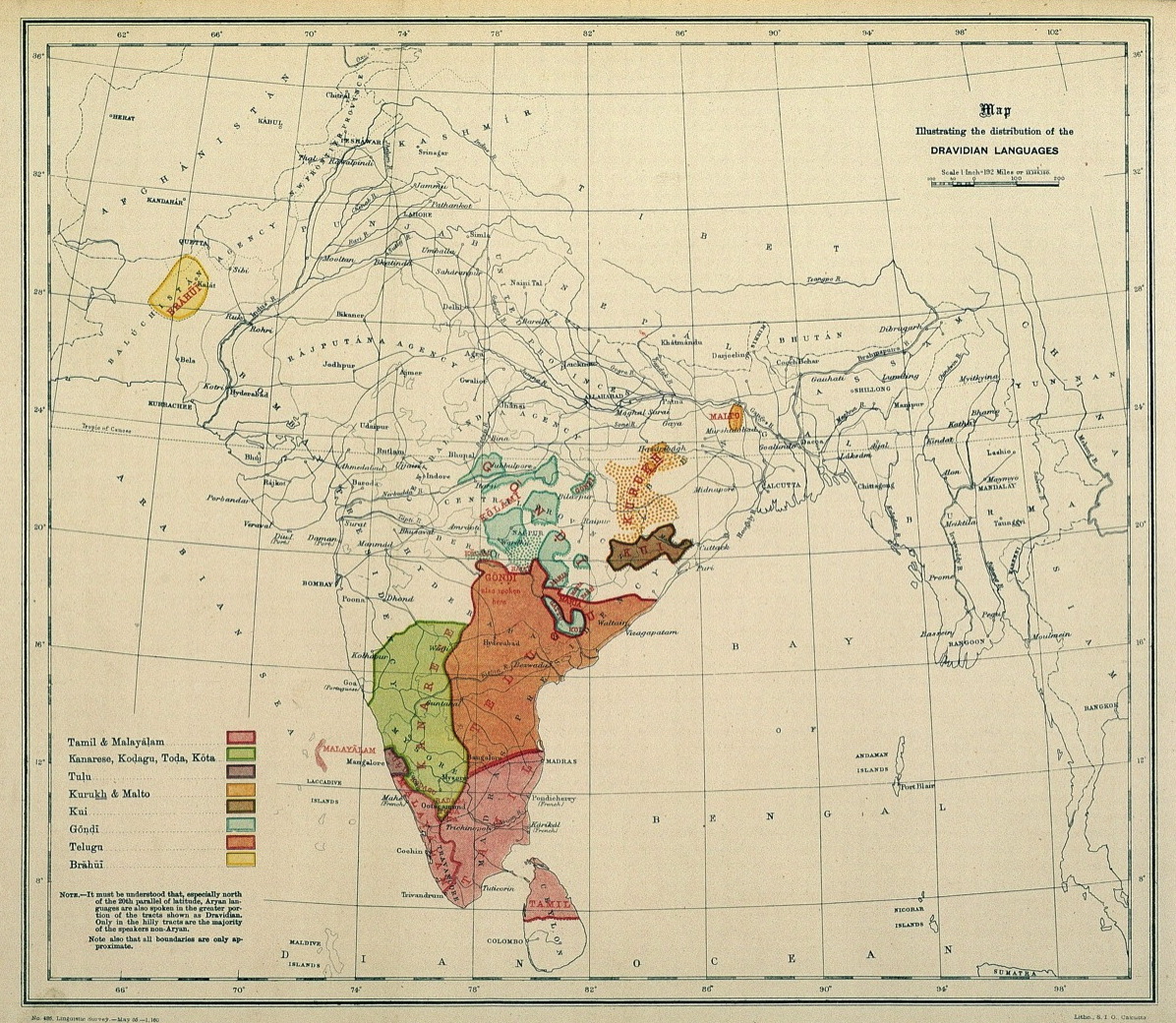
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language while translating its components, so as to create a new word or phrase ( lexeme) in the target language. For instance, the English word ''skyscraper'' has been calqued in dozens of other languages, combining words for "sky" and "scrape" in each language, as for example in German, in Portuguese, in Dutch, in Spanish, in Italian, in Turkish, and ''matenrō'' in Japanese. Calques, like direct borrowings, often function as linguistic gap-fillers, emerging when a language lacks existing vocabulary to express new ideas, technologies, or objects. This phenomenon is widespread and is often attributed to the shared conceptual frameworks across human languages. Speakers of different languages tend to perceive the world through common categori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskritism
Sanskritism is a term used to indicate words that are coined out of Sanskrit for modern usage in India, in Sri Lanka and elsewhere or for neologisms. They are often formed as calques of English words.Ganpat Teli, M.Phil"Revisiting the Making of Hindi as a ‘National’ Language" M.Phil. These terms are similar in nature to taxon terms coined from Latin and Greek. See also * Sanskritisation (language) Sanskritisation is the process of introducing features from Sanskrit, such as vocabulary and grammar, into other languages. It is sometimes associated with the " Hinduisation" of a linguistic community, or less commonly, with introducing a more up ... ReferencesInfluence of Sanskritisms in Sinhala Sanskrit Neologisms Word coinage {{IndoAryan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in India as well as the List of first-level administrative divisions by population, most populous country subdivision in the world – more populous than List of countries and dependencies by population, all but four other countries outside of India (China, United States, Indonesia, and Pakistan) – and accounting for 16.5 percent of the population of India or around 3 percent of the total world population. The state is bordered by Rajasthan to the west, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Delhi to the northwest, Uttarakhand and Nepal to the north, Bihar to the east, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand to the south. It is the List of states of India by area, fourth-largest Indian state by area covering , accounting for 7.3 percent of the total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of India
The partition of India in 1947 was the division of British India into two independent dominion states, the Dominion of India, Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan. The Union of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan is the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The Partition (politics), partition involved the division of two provinces, Bengal and the Punjab Province (British India), Punjab, based on district-wise Hindu or Muslim majorities. It also involved the division of the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Indian Civil Service, the History of rail transport in India, railways, and the central treasury, between the two new dominions. The partition was set forth in the Indian Independence Act 1947 and resulted in the dissolution of the British Raj, or Crown rule in India. The two self-governing countries of India and Pakistan legally came into existence at midnight on 14–15 August 1947. The partiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic (Arabic alphabet) and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world (after the Latin script), the second-most widely used List of writing systems by adoption, writing system in the world by number of countries using it, and the third-most by number of users (after the Latin and Chinese characters, Chinese scripts). The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Quran, the holy book of Islam. With Spread of Islam, the religion's spread, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols. Such languages still using it are Arabic language, Arabic, Persian language, Persian (Western Persian, Farsi and Dari), Urdu, Uyghur language, Uyghur, Kurdish languages, Kurdish, Pashto, Punjabi language, Punjabi (Shahmukhi), Sindhi language, Sindhi, South Azerbaijani, Azerb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nastaliq
''Nastaliq'' (; ; ), also Romanization of Persian, romanized as ''Nastaʿlīq'' or ''Nastaleeq'' (), is one of the main book hand, calligraphic hands used to write Arabic script and is used for some Indo-Iranian languages, predominantly Persian language#Classical Persian, Classical Persian, Kashmiri language, Kashmiri, Shahmukhi, Punjabi and Urdu. It is often used also for Ottoman Turkish poetry, but rarely for Arabic. ''Nastaliq'' developed in Iran from ''Naskh (script), naskh'' beginning in the 13th century and remains widely used in Iran, India, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and other countries for written poetry and as a form of art. History The name ''Nastaliq'' "is a contraction of the Persian (), meaning a hanging or suspended ''Naskh (script), naskh.''" Virtually all Safavid Iran, Safavid authors (like Dust Muhammad or Ahmad Monshi Ghomi, Qadi Ahmad) attributed the invention of to Mir Ali Tabrizi, who lived at the end of the 14th and the beginning of the 15th century. Tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perso-Arabic Literature
Persian literature comprises oral compositions and written texts in the Persian language and is one of the world's oldest literatures. It spans over two-and-a-half millennia. Its sources have been within Greater Iran including present-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, the Caucasus, and Turkey, regions of Central Asia (such as Tajikistan), South Asia and the Balkans where the Persian language has historically been either the native or official language. For example, Rumi, one of the best-loved Persian poets, born in Balkh (in modern-day Afghanistan) or Wakhsh (in modern-day Tajikistan), wrote in Persian and lived in Konya (in modern-day Turkey), at that time the capital of the Seljuks in Anatolia. The Ghaznavids conquered large territories in Central and South Asia and adopted Persian as their court language. There is thus Persian literature from Iran, Mesopotamia, Azerbaijan, the wider Caucasus, Turkey, Pakistan, Bangladesh, India, Tajikistan and other parts of Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brāhmī'' script. It is one of the official scripts of India, official scripts of India and Nepal. It was developed in, and was in regular use by, the 8th century CE. It had achieved its modern form by 1000 CE. The Devanāgarī script, composed of 48 primary characters, including 14 vowels and 34 consonants, is the fourth most widely List of writing systems by adoption, adopted writing system in the world, being used for over 120 languages, the most popular of which is Hindi (). The orthography of this script reflects the pronunciation of the language. Unlike the Latin alphabet, the script has no concept of letter case, meaning the script is a unicase, unicameral alphabet. It is written from left to right, has a strong preference for symmetri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |