|
Rinteln
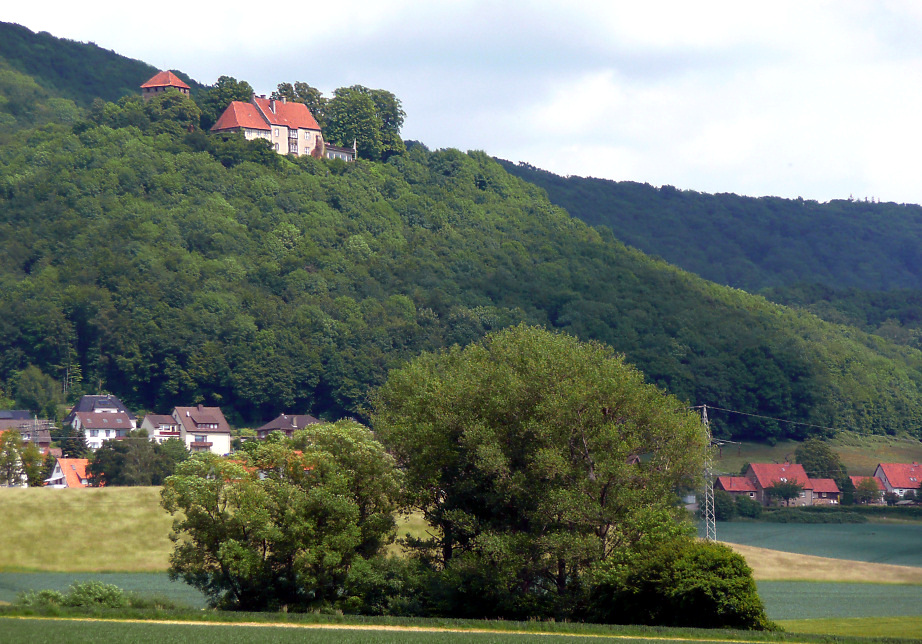
Rinteln () is a small town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located on the banks of the Weser river north of the Porta Westfalica. The town of Rinteln is in the broad valley between the hills of the Weserbergland and the North Lippe Bergland. In relation to some well known places, it is 60 kilometers west of Hanover, and just 20 kilometers from Hamelin of Pied Piper fame. Its population is about 28,500. It is accessed by the A2 autobahn (E30). History The settlement of Rinteln was founded about 1150 on the northern bank of the Weser. Later, in 1235, the village of Neu-Rinteln ("New Rinteln") was founded on the southern bank. It is the origin of the modern town, since the northern village was abandoned in 1350 due to the plague. The village grew to a fortified town, that served as a southern stronghold of the Counts of Schaumburg. From 1621 until its dissolution in 1810 during the Westphalian rule under Jérôme Bonaparte, Rinteln was the seat of Ernestina University. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rinteln Station
Rinteln station is located on the Elze–Löhne railway in the town of Rinteln in the district of Schaumburg in the German state of Lower Saxony. The town lies on the Weser and is important for tourism. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a German railway station categories, category 6 station. It also served by heritage railway operations on the Rinteln–Stadthagen railway. History The station was opened in 1875. Location and operations Rinteln station is located north of town centre on the Elze–Löhne railway, Weser Railway from Bünde station, Bünde and Löhne station, Löhne via Bad Oeynhausen Süd station, Bad Oeynhausen Süd and Rinteln to Hildesheim Hauptbahnhof, Hildesheim and Bodenburg. The line is operated by NordWestBahn. Trains run hourly on week days and every two hours on weekends. Conditions Since the carrying out of some restoration measures, the station has only two platform tracks next to an island platform, as well as a through track (next to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm Von Lossberg
Friedrich Wilhelm von Lossberg (20 April 1720 – 25 June 1800) was a Hessian Lieutenant General fighting with the British-allied German contingents in the American Revolutionary War. He was sent to America in 1776 as a colonel commanding the First Brigade of the Second Hessian Division under Lieutenant General Wilhelm von Knyphausen. Von Knyphausen in turn was second in command under General Leopold Philip de Heister. During the course of the war, in 1777, disagreements between General Sir William Howe and Heister led to the latter's recall, and Von Knyphausen replaced him. In May 1782, after the British surrender at the Battle of Yorktown in October 1781, Von Lossberg replaced Von Knyphausen as the last commander of the Hessian troops in North America. Early life Von Lossberg was born in Sylbach, County of Lippe on 20 April 1720 and married Dorothea Elisabeth Gmeling (1725-1821). His son Johann Karl Jeremias von Lossberg (1750-1804) served as a lieutenant during the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Schaumburg
The County of Schaumburg (), until ca. 1485 known as Schauenburg, was a state of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the present German state of Lower Saxony. Its territory was more or less congruent with the present district . History Schaumburg originated as a medieval county, which was founded at the beginning of the 12th century. It was named after Schauenburg Castle, near Rinteln on the Weser, where the owners started calling themselves Lords (from 1295 Counts) of Schauenburg. Adolf I probably became the first Lord of Schauenburg in 1106. In 1110, Adolf I, Lord of Schauenburg was appointed by Lothair, Duke of Saxony to hold Holstein and Stormarn, including Hamburg, as fiefs.Lemma Schauenburg/Schaumburg. In: Klaus-Joachim Lorenzen-Schmidt, Ortwin Pelc (Hrsg.): ''Schleswig-Holstein Lexikon''. 2. Aufl., Wachholtz, Neumünster, 2006. Subsequently, the House of Schaumburg were also counts of Holstein and its partitions Holstein-Itzehoe, Holstein-Kiel, Holstein-Pinneb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diederik Lodewijk Bennewitz
Diederik Lodewijk Bennewitz (20 July 1764 – 21 September 1826), also referred to as Dirk Lodewijk Bennewitz, was a Dutch goldsmith, silversmith and jeweller. Biography Bennewitz was born in Rinteln in 1764 (near Hanover), born as the son of the Master Armourer (sword maker) Johann Ludewich Bennewitz (1734–1789) and Maria Margaretha Wingendorff (1727–1812). Bennewitz left Germany to move to Amsterdam, where he started working for Cornelis Leonard Diemont. He completed his Master’s in silversmithing in 1785 after two years. He married Dorothea Korff (1765–1842) in Amsterdam during that same year. According to Van Benthem, Bennewitz had built up an excellent reputation as a silversmith. He had been asked to represent the Amsterdam Guild in The Hague on several occasions. He took over the company, together with Adrianus Bonebakker, in 1802, from the by then deceased brothers Jacob and Jan Hendrik Peirolet. Bennewitz & Bonebakker Bennewitz was tasked with managing the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip II, Count Of Schaumburg-Lippe
Philipp II Ernst, Count of Schaumburg-Lippe (5 July 1723– 13 February 1787) was a ruler of the counties of Lippe-Alverdissen and Schaumburg-Lippe. Early life He was born at Rinteln the son of Friedrich Ernst, Count of Lippe-Alverdissen (1687-1777) and his wife Elisabeth Philippine von Friesenhausen (1696-1764). His father was the son of Count Philipp Ernest I, the founder of the Lippe-Alverdissen line of the House of Lippe and his wife Duchess Dorothea Amalia of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Beck (1656-1739). Biography He succeeded his father as Count of Lippe-Alverdissen in 1749 and ruled until he inherited the Schaumburg-Lippe territories following the death of his cousin William on the 10 September 1777. He reigned as Count until his death on the 13 February 1787 when he was succeeded by his only surviving son Georg Wilhelm. Marriages and children He was married firstly on the 6 May 1756 at Weimar to Princess Ernestine Albertine of Saxe-Weimar (1722-1769), the daughter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westendorf (Rinteln)
Westendorf is a village in the town of Rinteln, in the Lower Saxon district of Schaumburg. Geography and Transportation The village is east of the main core of Rinteln. The Weser flows along the southern border. To the west, north, and east is the 452 hectare Wesergebirge Ridge ''Naturschutzgebiet A ''Naturschutzgebiet'' (abbreviated NSG) is a category of protected area (nature reserve) within Germany's Federal Nature Conservation Act (the ''Bundesnaturschutzgesetz'' or ''BNatSchG''). Although often translated as 'Nature Reserve' in Engli ...''. Along the southern edge of town runs the B 83, and along the northern edge is the A 2. {{authority control Schaumburg Villages in Lower Saxony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Kohlrausch (physicist)
Friedrich Wilhelm Georg Kohlrausch (14 October 1840 – 17 January 1910) was a German physicist who investigated the conductive properties of electrolytes and contributed to knowledge of their behaviour. He also investigated elasticity, thermoelasticity, and thermal conduction as well as magnetic and electrical precision measurements. Nowadays, Friedrich Kohlrausch is classed as one of the most important experimental physicists. His early work helped to extend the absolute system of Carl Friedrich Gauss and Wilhelm Weber to include electrical and magnetic measuring units. Biography Education Son of Rudolf Kohlrausch, Friedrich Wilhelm Georg Kohlrausch was born on October 14, 1840, in Rinteln, Germany. After studying physics at Erlangen and Göttingen, Friedrich Kohlrausch completed his doctorate in Göttingen. Teaching After a two-year work as a lecturer in Frankfurt, Kohlrausch was appointed a professor of physics at the University of Göttingen (1866–70). During 1870 Ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Schauenburg And Holstein
The Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein were titles of the Holy Roman Empire. The dynastic family came from the County of Schauenburg near Rinteln (district Schaumburg) on the Weser in Germany. Together with its ancestral possessions in Bückeburg and Stadthagen, the House of Schauenburg ruled the County of Schauenburg and the County of Holstein. The comital titles of Holstein were subject to the liege lord, the Dukes of Duchy of Saxony, undivided Saxony until 1296, and thereafter the Dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg. The counties of Schauenburg and Holstein The County of Schaumburg originated as a medieval county, which was founded at the beginning of the 12th century. It was named after Schaumburg Castle, Lower Saxony, Schauenburg Castle, near Rinteln on the Weser, where the owners started calling themselves Lords (from 1295 Counts) of Schauenburg. Adolf I, Count of Holstein, Adolf I probably became the first Lord of Schauenburg in 1106. In 1110, Adolf I, Count of Holstein, Adolf I, Lord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kendal
Kendal, once Kirkby in Kendal or Kirkby Kendal, is a market town and civil parish in the unitary authority of Westmorland and Furness, England. It lies within the River Kent's dale, from which its name is derived, just outside the boundary of the Lake District National Park. In the Domesday Book of 1086, the area was collected under Yorkshire. The area came under the Honour of Lancaster before the barony split. The town became the Barony of Kendal's seat, in 1226/7 this barony merged with the Barony of Westmorland to form the historic county of Westmorland with Appleby-in-Westmorland, Appleby as the historic county town.F.A. Youngs, ''Guide to the Local Administrative units of England, Vol.II, Northern England'', London, 1991 In 1889, Kendal became the county town. Under the 1974 reforms, it became the administrative centre of the South Lakeland district. The town became Westmorland and Furness district's administrative centre in a 2023 reform. It is south-east of Windermere, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sławno
Sławno ( Kashubian: ''Słôwno'', ) is a town on the Wieprza river in Middle Pomerania region, north-western Poland, with 12,511 inhabitants (2019). It is the administrative seat of Gmina Sławno, though not part of it. The town is also the capital of Sławno County in West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Sławno is a railway junction on the major Gdańsk–Szczecin line, with access to secondary importance connections to Darłowo and Korzybie. It is also a stop on the European route E28 running parallel to the south coast of the Baltic Sea between the cities of Koszalin and Słupsk. History The territory became part of the emerging Polish state under Mieszko I around 967. Since the mid-12th century the Land of Słupsk-Sławno was under the rule of Duke Ratibor I of Pomerania and his descendants, a cadet branch of the Griffin dynasty. From 1190 to 1238 it was the capital of a small eponymous duchy. When the line became extinct about 1227, their estates were the matter of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian language, Saterland Frisian are still spoken, though by declining numbers of people. Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the Bremen (state), state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-exclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single '. The state's largest cities are the state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weser Watershed 3
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports of Bremerhaven and Nordenham. The latter is on the Butjadingen Peninsula. It then merges into the North Sea via two highly saline, estuarine mouths. It connects to the canal network running east–west across the North German Plain. The river, when combined with the Werra (a dialectal form of ''Weser''), is long and thus, the longest river entirely situated within Germany (the Main, however, is the longest if the Weser-Werra are considered separate). The Weser itself is long. The Werra rises in Thuringia, the German state south of the main projection (tongue) of Lower Saxony. Etymology "Weser" and "Werra" are the same words in different dialects. The difference reflects the old linguistic border between Central and Low German, passing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |