|
Lycée Albert Sarraut
Lycée Albert Sarraut () was a French language, French lyceum in Hanoi, Vietnam, during the Tonkin (French protectorate), French colonial period and in the early post-colonial period, active from 1919 to 1965. It was one of 69 high schools founded by the French in their colonies worldwide, named for Albert Sarraut. The school offered high standard academic programs for students between the ages of 11 and 18. It is currently the . Former students Many Vietnamese scholars and leaders graduated from lycée Albert Sarraut. Among them were: *Bui Tuong Phong, a pioneer computer scientist *Hoàng Xuân Hãn *Nguyen Tien Lang *Hoàng Văn Chí *Nguyễn Phan Long *Phạm Văn Đồng *Trần Lệ Xuân (Madame Ngô Đình Nhu) *Nguyễn Mạnh Tường: Lawyer, participant in the Nhân Văn–Giai Phẩm affair *Đào Sĩ Chu, artist painter *Lê Thành Khôi, Vietnamese-French scientist in education and economics, author of history and UNESCO consultant *Nhất Linh (Nguyên Tuong Tam) - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycée Albert Sarraut-Trường THPT Trần Phú-Hoàn Kiếm-050520091067
In France, secondary education is in two stages: * ''Collèges'' () cater for the first four years of secondary education from the ages of 11 to 14. * ''Lycées'' () provide a three-year course of further secondary education for students between the ages of 15 and 19. Pupils are prepared for the ''baccalauréat'' (; baccalaureate, colloquially known as ''bac'', previously ''bachot''), which can lead to higher education studies or directly to professional life. There are three main types of ''baccalauréat'': the ''baccalauréat général'', ''baccalauréat technologique'' and ''baccalauréat professionnel''. School year The school year starts in early September and ends in early July. Metropolitan French school holidays are scheduled by the Ministry of Education (France), Ministry of Education by dividing the country into three zones (A, B, and C) to prevent overcrowding by family holidaymakers of tourist destinations, such as the Mediterranean coast and ski resorts. Lyon, for exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nhân Văn–Giai Phẩm Affair
The ''Nhân Văn-Giai Phẩm'' affair () was a cultural-political movement in North Vietnam in the late 1950s. Two periodicals were established during that time, Nhân Văn (, ''Humanities'') and Giai Phẩm (, ''Masterpieces''), many issues of which were published demanding freedom of speech, creativity and human rights. Following a loosening of political restrictions with some similarities to the Chinese Hundred Flowers Campaign, there was a hardening of attitudes. After those two major journals were closed down, their political associates were imprisoned or reeducated. Moreover, the agenda of ''Nhân Văn-Giai Phẩm'' was linked to "reactionary" political projects against the North Vietnamese government (the Ngo Dinh Diem regime reprinted Nhan Van-Giai Pham articles and distributed them as anti-communist propaganda materials. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Laos
The president of the Lao People's Democratic Republic is the head of state of Laos. The current president is Thongloun Sisoulith, since 22 March 2021. He was previously elected as the General Secretary of the Lao People's Revolutionary Party, Laos' most powerful position in January 2021, ranking him first in the Politburo of the Lao People's Revolutionary Party, Politburo. History Background The office of the President of the People's Democratic Republic traces its lineage back to Prince Souphanouvong, the first President of the People's Democratic Republic, a member of the deposed Lao royal family, royal family and one of the Three Princes of the Kingdom of Laos, Three Princes, who became President when the former Kingdom of Laos was overthrown by the Pathet Lao in 1975, at the end of the Laotian Civil War. Duties and rights Term limits The president is elected by the National Assembly of Laos, National Assembly for a term of five years, and may serve no more than two terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang (Lao language, Lao: wikt:ຫຼວງພະບາງ, ຫຼວງພະບາງ, pronounced ), historically known as Xieng Thong (ຊຽງທອງ) and alternatively spelled Luang Phabang or Louangphabang, is the capital of Luang Prabang province, Luang Prabang Province in north-central Laos. Its name, meaning “Royal Buddha Image,” derives from the Phra Bang, a statue symbolizing Lao sovereignty. Designated a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1995, the city is recognized for blending traditional Lao architecture, European colonial buildings, and over 30 Buddhist temples. The protected area encompasses 33 of its 58 villages, where daily rituals like the morning alms-giving ceremony persist. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Souphanouvong
Prince Souphanouvong (13 July 1909 – 9 January 1995; ), nicknamed the Red Prince, was along with his half-brother Prince Souvanna Phouma and Prince Boun Oum of Champasak (town), Champasak, one of the "Three Princes of the Kingdom of Laos, Three Princes" who represented respectively the communist (pro-Vietnam), neutralist and royalist political factions in Kingdom of Laos, Laos. He was the President of Laos from December 1975 to October 1986. Early life Souphanouvong was born in Xiengkeo Palace, Palace Sisouvanna, Luang Prabang, Xieng Dong, Luang Prabang Province, Luang-Prabang. He was one of the sons of Prince Bounkhong, the last Uparat, viceroy of Luang Prabang. Unlike his half-brothers, Souvanna Phouma and Phetsarath Ratanavongsa, whose mothers were of royal birth, his mother was a commoner, Mom Kham Ouane. He attended the Lycée Albert Sarraut in Hanoi and then studied civil engineering at the École des ponts ParisTech, École nationale des ponts et chaussées in Paris, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest. The country has a population of approximately eight million. Its Capital city, capital and most populous city is Vientiane. The country is characterized by mountainous terrain, Buddhist temples, including the UNESCO's World Heritage Site of Luang Prabang, and French colonial architecture. The country traces its historic and cultural identity to Lan Xang, a kingdom which existed from the 13th to 18th centuries. Through its location, the kingdom was a hub for overland trade. In 1707, Lan Xang split into three kingdoms: Kingdom of Luang Phrabang, Luang Prabang, Kingdom of Vientiane, Vientiane, and Kingdom of Champasak, Champasak. In 1893, these kingdoms were unified under French protection as part of French Indochina. Laos was und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trường Chinh
Trường Chinh (, meaning "Long March"), born Đặng Xuân Khu (9 February 1907 – 30 September 1988) was a Vietnamese communism, communist political leader, revolutionary and theoretician. He was one of the key figures of Vietnamese politics for over 40 years, and played a major role in the 1946-54 war against the French. Trường also played an important role in shaping the politics of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV) and creating the Socialism, socialist structure of the new Vietnam. Between November 9, 1940 and November 11, 1945, when the party dissolved, Trường was General Secretary of the Indochinese Communist Party Central Committee. Between 1946 and 1954, the First Indochina War led to the fall of French Indochina and the partitioning of Vietnam between North Vietnam, north and South Vietnam, south. On February 19, 1951, Trường became First Secretary of the Workers' Party of Vietnam Central Committee (although Ho Chi Minh, Hồ Chí Minh, in his capacity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Võ Nguyên Giáp
Võ Nguyên Giáp ( vi-hantu, , ; 25 August 1911 – 4 October 2013) was a Vietnamese general, communist revolutionary and politician. Highly regarded as a military strategist, Giáp led Vietnamese communist forces to victories in wars against Japan, France, South Vietnam, the United States, and China. Giáp was the military commander of the Việt Minh and the People's Army from 1941 to 1972, minister of defense of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North Vietnam) and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam in 1946–1947 and from 1948 to 1980, and deputy prime minister from 1955 to 1991. He was a member of the Politburo of the Communist Party of Vietnam. Born in Quảng Bình province to an affluent peasant family, Giáp participated in anti-colonial political activity in his youth, and in 1931 joined the Communist Party of Vietnam, led by Ho Chi Minh. Giáp rose to prominence during World War II as the military leader of the Việt Minh resistance against the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Việt Minh
The Việt Minh (, ) is the common and abbreviated name of the League for Independence of Vietnam ( or , ; ), which was a communist-led national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1941. Also known as the Việt Minh Front (), it was created by the Indochinese Communist Party (ICP) as a united front to achieve the independence of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. The was previously formed by Hồ Học Lãm in Nanjing, China, at some point between August 1935 and early 1936, when Vietnamese nationalist parties formed an anti-imperialist united front. This organization soon lapsed into inactivity, only to be taken over by Hồ Chí Minh and the ICP in 1941. They presented the organization as inclusive of political groups, with a founding charter more nationalist than communist. It exhorted "soldiers, workers, peasants, intellectuals, civil servants, merchants, young men and women" to overthrow "French jackals" and "Japanese fascists" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khái Hưng
Trần Khánh Giư, pen-name Khái Hưng (1896 in Cổ Am village, Vĩnh Bảo, Hải Phòng – 1947 in Nam Định) was a Vietnamese novelist, member of Self-Reliant Literary Group, and a nationalist intellectual. As a boy, he studied at the Lycée Albert Sarraut in Hanoi. From 1933 he was a member of the new ''Self-Reliant Literary Group'' with editor Nhất Linh; his novels were first serialized in the group's magazines before being published as books. Just as Nhất Linh was a pen name ("One-Zero" 壹零) Giu briefly adopted the pen name Nhị Linh ("Two-Zero" 貳零). In 1941, as a member of Nhat Linh's Đại Việt Dân chính Đảng he was arrested by the French, along with the artist Nguyễn Gia Trí. He was captured by the Việt Minh in the Lạc Quần, Trực Ninh area, then executed at Cựa Gà on 17 November 1947. Works His novels were written in a style influenced by social realism, and were critical of many aspects of traditional Vietnamese society.V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyên Tuong Tam
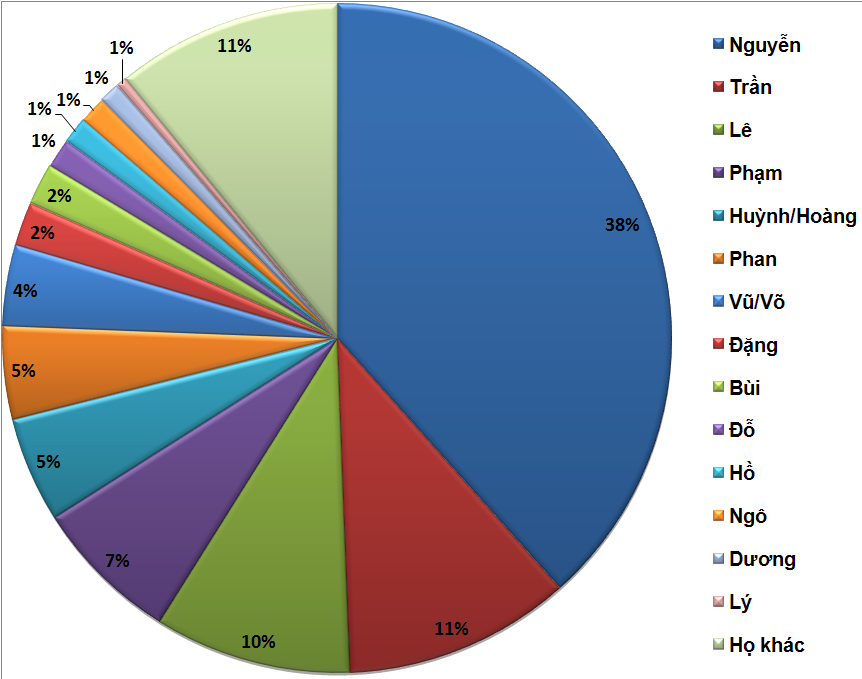
Nguyễn (阮) (sometimes abbreviated as Ng̃) is the most common surname of the Vietnamese people. Outside of Vietnam, the surname is commonly rendered without diacritics as ''Nguyen''. By some estimates 30 to 39 percent of Vietnamese people bear this surname.Lê Trung Hoa, ''Họ và tên người Việt Nam'', NXB Khoa học - Xã hội, 2005 Origin and usage is the transcription of the Sino-Vietnamese pronunciation of the character 阮, which originally was used to write a name of a state in Gansu or ruan, an ancient Chinese instrument. The same Chinese character is often romanized as in Mandarin and as in Cantonese. The first recorded mention of a person surnamed Nguyễn is a description dating AD 317, of a journey to Giao Châu undertaken by Eastern Jin dynasty officer Nguyễn Phu and his family. Many events in Vietnamese history have contributed to the name's prominence. In 1232, after usurping the Lý dynasty, Trần Thủ Độ forced the descendants of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nhất Linh
Nguyễn Tường Tam (; chữ Hán: 阮祥三 or 阮祥叄; Cẩm Giàng, Hải Dương 25 July 1906 – Saigon, 7 July 1963) better known by his pen-name Nhất Linh (, 一灵, "One Spirit") was a Vietnamese writer, editor and publisher in colonial Hanoi. He founded the literary group and publishing house Tự Lực Văn Đoàn ("Self-Strengthening Literary Group") in 1932 with the literary magazines ''Phong Hóa'' ("Customs", or "Mores") and ''Ngày Nay'' ("Today"), and serialized, then published, many of the influential realism-influenced novels of the 1930s. In 1935, Nguyễn published a satirical and fictional travelogue about his time in France, ''Going to the West'' (Đi Tây). His aim was to show that the French colonialists did not grant to the working classes in Vietnam the same rights they accorded to workers in France. In addition to Nhất Linh, scholars have noted that the many Vietnamese westernized elites returning from France had been embracing the French “id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |