|
Long-lived Plasma Cell
Long-lived plasma cells (LLPCs) are a distinct subset of plasma cells that play a crucial role in maintaining humoral memory and long-term immunity. They continuously produce and secrete high-affinity antibodies into the bloodstream, conversely to memory B cells, which are quiescent and respond quickly to antigens upon recall. Initially, it was believed that memory B cells replenish LLPCs. However, allergen-specific IgE production through bone marrow transplantation in non-allergic individuals suggests LLPCs may be long-lived. Allergies developed without antigenic re-stimulation. That led to the understanding that LLPCs are long-lived cells, contributing to the sustained production of specific antibodies Niche of LLPCs The niche for long-lived plasma cells is a subject of ongoing research, and while some aspects are understood, many questions remain. LLPCs are not inherently long-lived, and their survival relies on accessing specific pro-survival niches in the bone marrow (BM), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B lymphocytes and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances called antigens. These antibodies are transported from the plasma cells by the blood plasma and the lymphatic system to the site of the target antigen (foreign substance), where they initiate its neutralization or destruction. B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibody molecules closely modeled after the receptors of the precursor B cell. Structure Plasma cells are large lymphocytes with abundant cytoplasm and a characteristic appearance on light microscopy. They have basophilic cytoplasm and an eccentric nucleus with heterochromatin in a characteristic cartwheel or clock face arrangement. Their cytoplasm also contains a pale zone that on electron microscopy contains an extensive Golgi apparatus and ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
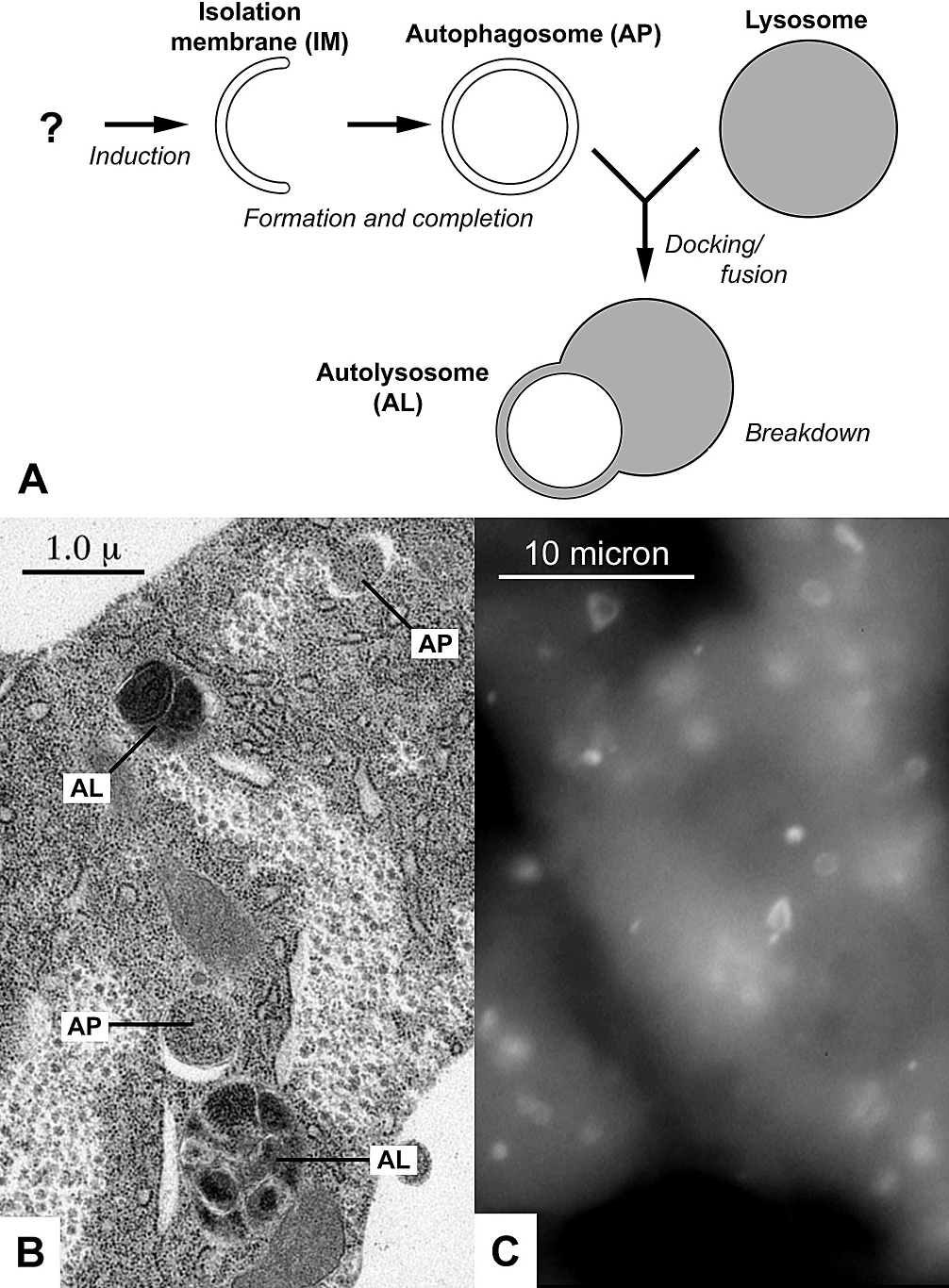
Autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD86
Cluster of Differentiation 86 (also known as CD86 and B7-2) is a protein constitutively expressed on dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, macrophages, B-cells (including memory B-cells), and on other antigen-presenting cells. Along with CD80, CD86 provides costimulatory signals necessary for T cell activation and survival. Depending on the ligand bound, CD86 can signal for self-regulation and cell-cell association, or for attenuation of regulation and cell-cell disassociation. The ''CD86'' gene encodes a type I membrane protein that is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Additional transcript variants have been described, but their full-length sequences have not been determined. Structure CD86 belongs to the B7 family of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is a 70 kDa glycoprotein made up of 329 amino acids. Both CD80 and CD86 share a conserved amino acid motif that forms their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular responses to stimuli such as stress, cytokines, free radicals, heavy metals, ultraviolet irradiation, oxidized LDL, and bacterial or viral antigens. NF-κB plays a key role in regulating the immune response to infection. Incorrect regulation of NF-κB has been linked to cancer, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, septic shock, viral infection, and improper immune development. NF-κB has also been implicated in processes of synaptic plasticity and memory. Discovery NF-κB was discovered by Ranjan Sen in the lab of Nobel laureate David Baltimore via its interaction with an 11-base pair sequence in the immunoglobulin light-chain enhancer in B cells. Later work by Alexander Poltorak and Bruno Lemaitre in mice and ''Drosophil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD28
CD28 (Cluster of Differentiation 28) is one of the proteins expressed on T cells that provide co-stimulatory signals required for T cell activation and survival. T cell stimulation through CD28 in addition to the T-cell receptor ( TCR) can provide a potent signal for the production of various interleukins ( IL-6 in particular). CD28 is the receptor for CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) proteins. When activated by Toll-like receptor ligands, the CD80 expression is upregulated in antigen-presenting cells (APCs). The CD86 expression on antigen-presenting cells is constitutive (expression is independent of environmental factors). CD28 is the only B7 receptor constitutively expressed on naive T cells. Association of the TCR of a naive T cell with MHC:antigen complex without CD28:B7 interaction results in a T cell that is anergic. Furthermore, CD28 was also identified on bone marrow stromal cells, plasma cells, neutrophils and eosinophils, but the functional importance of CD28 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PRDM1
PR domain zinc finger protein 1, or B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1 (BLIMP-1), is a protein in humans encoded by the gene ''PRDM1'' located on chromosome 6q21. BLIMP-1 is considered a 'master regulator' of hematopoietic stem cells, and plays a critical role in the development of plasma B cells, T cells, dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages, and osteoclasts. Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) can activate BLIMP-1, both as a direct target and through downstream activation. BLIMP-1 is a transcription factor that triggers expression of many downstream signaling cascades. As a fine-tuned and contextual rheostat of the immune system, BLIMP-1 up- or down-regulates immune responses depending on the precise scenarios. BLIMP-1 is highly expressed in exhausted T-cells – clones of dysfunctional T-cells with diminished functions due to chronic immune response against cancer, viral infections, or organ transplant. Function As a potent repressor of beta-interferon (IFN-β), B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD93
CD93 (Cluster of Differentiation 93) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CD93'' gene. CD93 is a C-type lectin transmembrane receptor which plays a role not only in cell–cell adhesion processes but also in host defense. Family CD93 belongs to the Group XIV C-Type lectin family, a group containing three other members, endosialin (CD248), CLEC14A and thrombomodulin, a well characterized anticoagulant. All of them contain a C-type lectin domain, a series of epidermal growth factor like domains, a highly glycosylated mucin-like domain, a unique transmembrane domain and a short cytoplasmic tail. Due to their strong homology and their close proximity on chromosome 20, CD93 has been suggested to have arisen from the thrombomodulin gene through a duplication event. Expression CD93 was originally identified in mice as an early B cell marker through the use of AA4.1 monoclonal antibody. Then this molecule was shown to be expressed on an early population of hematopoieti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene. In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth muscle cells in the tunica media of many blood vessels also produce IL-6 as a pro-inflammatory cytokine. IL-6's role as an anti-inflammatory myokine is mediated through its inhibitory effects on TNF-alpha and IL-1 and its activation of IL-1ra and IL-10. There is some early evidence that IL-6 can be used as an inflammatory marker for severe COVID-19 infection with poor prognosis, in the context of the wider coronavirus pandemic. Function Immune system IL-6 is secreted by macrophages in response to specific microbial molecules, referred to as pathogen-associated molecular patterns ( PAMPs). These PAMPs bind to an important group of detection molecules of the innate immune system, called pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT3
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT3'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. Function STAT3 is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT3 is phosphorylated by receptor-associated Janus kinases (JAK), forms homo- or heterodimers, and translocates to the cell nucleus where it acts as a transcription activator. Specifically, STAT3 becomes activated after phosphorylation of tyrosine 705 in response to such ligands as interferons, epidermal growth factor (EGF), Interleukin (IL-)5 and IL-6. Additionally, activation of STAT3 may occur via phosphorylation of serine 727 by Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and through c-src non-receptor tyrosine kinase. STAT3 mediates the expression of a variety of genes in response to cell stimuli, and thus plays a key role in many cellular processes such as cell growth and apoptosis. STAT3-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-cell Maturation Antigen
B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA or BCM), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 17 (TNFRSF17), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF17 gene. TNFRSF17 is a cell surface receptor of the TNF receptor superfamily which recognizes B-cell activating factor (BAFF). Serum B-cell maturation antigen (sBCMA) is the cleaved form of BCMA, found at low levels in the serum of normal patients and generally elevated in patients with multiple myeloma (MM). Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor is preferentially expressed in mature B lymphocytes, and may be important for B cell development and autoimmune response. This receptor has been shown to specifically bind to the tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b (TNFSF13B/TALL-1/BAFF), and to lead to NF-kappaB and MAPK8/JNK activation. This receptor also binds to various TRAF family members, and thus may transduce signals for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |