|
International Reference Ionosphere
International Reference Ionosphere (IRI) is a common permanent scientific project of the Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) and the International Union of Radio Science (URSI) started 1968/69. It is the international Standard (metrology), standard empirical model for the terrestrial ionosphere since 1999. For a specified geographic location, time, and date, IRI provides average monthly values for electron density, electron temperature and ion temperature, and the molecular composition of the ions in the range of altitudes from 50 km to 2000 km. The latest standard is IRI-2012. A new version, IRI-2016, has since been released. The IRI has been extended to plasmasphere in the IRI-Plas model. History Karl Rawer, the first chairman of the ''URSI/COSPAR Task group on the IRI'' (1968–84) specified as goal of the IRI to establish a (monthly) average Ionospheric model, model of the terrestrial ionosphere based on reliably-measured data obtained with ground- and space-ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IRI TotalElectronContent
IRI or I.R.I. refers to: Businesses and organizations * Iringa Airport, an airport in Tanzania serving Iringa and the surrounding Iringa Region by IATA airport code * India Rejuvenation Initiative, an Indian anti-corruption organization formed by top bureaucrats and other dignitaries * Industrial Research Institute, a nonprofit association for the sharing of best practices in research and development * Innovative Routines International, Inc., an American software company specializing in data sorting, transformation, reporting, and privacy protection * Institut de Recherche et d'Innovation, a French research institute, founded by Centre Pompidou and now operated independently * Institutet för rättsinformatik (Law and Informatics Research Institute), a Swedish research body examining relationships between law and IT * Intellectual Reserve, Inc., a legal entity of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints * International Registries, Inc., a company that arranges tax and ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ITU-R
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is responsible for radio communications. Its role is to manage the international radio-frequency spectrum and satellite orbit resources and to develop standards for radiocommunication systems with the objective of ensuring the effective use of the spectrum. ITU is required, according to its constitution, to allocate spectrum and register frequency allocation, orbital positions and other parameters of satellites, "in order to avoid harmful interference between radio stations of different countries". The international spectrum management system is therefore based on regulatory procedures for frequency coordination, notification and registration. ITU-R has a permanent secretariat, the Radiocommunication Bureau, based at the ITU HQ in Geneva, Switzerland. The elected Director of the Bureau is Mario Maniewicz; he was first elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Space Weather
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the varying conditions within the Solar System and its heliosphere. This includes the effects of the solar wind, especially on the Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Though physically distinct, space weather is analogous to the terrestrial weather of Earth's atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (troposphere and stratosphere). The term "space weather" was first used in the 1950s and popularized in the 1990s. Later, it prompted research into "space climate", the large-scale and long-term patterns of space weather. History For many centuries, the effects of space weather were noticed, but not understood. Displays of aurora (astronomy), auroral light have long been observed at high latitudes. Beginnings In 1724, George Graham (clockmaker), George Graham reported that the needle of a magnetic compass was regularly deflected from magnetic north over the course of each day. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be used: \rho = \frac, where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance, the density is equal to its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium is the densest known element at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different systems of units, it is sometimes replaced by the dimensionless quantity "relative den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Legendre Polynomials
In mathematics, Legendre polynomials, named after Adrien-Marie Legendre (1782), are a system of complete and orthogonal polynomials with a wide number of mathematical properties and numerous applications. They can be defined in many ways, and the various definitions highlight different aspects as well as suggest generalizations and connections to different mathematical structures and physical and numerical applications. Closely related to the Legendre polynomials are associated Legendre polynomials, Legendre functions, Legendre functions of the second kind, big q-Legendre polynomials, and associated Legendre functions. Definition and representation Definition by construction as an orthogonal system In this approach, the polynomials are defined as an orthogonal system with respect to the weight function w(x) = 1 over the interval [-1,1]. That is, P_n(x) is a polynomial of degree n, such that \int_^1 P_m(x) P_n(x) \,dx = 0 \quad \text n \ne m. With the additional standardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fourier Analysis
In mathematics, Fourier analysis () is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Joseph Fourier, who showed that representing a function as a sum of trigonometric functions greatly simplifies the study of heat transfer. The subject of Fourier analysis encompasses a vast spectrum of mathematics. In the sciences and engineering, the process of decomposing a function into oscillatory components is often called Fourier analysis, while the operation of rebuilding the function from these pieces is known as Fourier synthesis. For example, determining what component frequencies are present in a musical note would involve computing the Fourier transform of a sampled musical note. One could then re-synthesize the same sound by including the frequency components as revealed in the Fourier analysis. In mathematics, the term ''Fourier an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
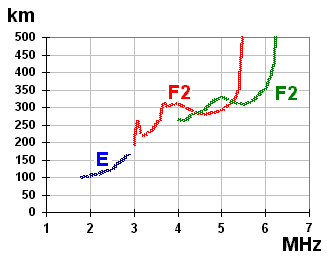
Ionospheric Sounding
In telecommunications and radio science, an ionospheric sounding is a technique that provides real-time data on high-frequency ionospheric-dependent radio propagation, using a basic system consisting of a synchronized transmitter and receiver. The time delay between transmission and reception is translated into effective ionospheric layer altitude. Vertical incident sounding uses a collocated transmitter and receiver and involves directing a range of frequencies vertically to the ionosphere and measuring the values of the reflected returned signals to determine the effective ionosphere layer altitude. This technique is also used to determine the critical frequency. Oblique sounders use a transmitter at one end of a given propagation path, and a synchronized receiver, usually with an oscilloscope-type display (ionogram), at the other end. The transmitter emits a stepped- or swept-frequency signal which is displayed or measured at the receiver. The measurement converts time delay t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ionogram
An ionosonde, or chirpsounder, is a special radar for the examination of the ionosphere. The basic ionosonde technology was invented in 1925 by Gregory Breit and Merle A. Tuve and further developed in the late 1920s by a number of prominent physicists, including Edward Victor Appleton. The term ''ionosphere'' and hence, the etymology of its derivatives, was proposed by Robert Watson-Watt. Components An ionosonde consists of: * A high frequency (HF) radio transmitter, automatically tunable over a wide range. Typically the frequency coverage is 0.5–23 MHz or 1–40 MHz, though normally sweeps are confined to approximately 1.6–12 MHz. * A tracking HF receiver which can automatically track the frequency of the transmitter. * An antenna with a suitable radiation pattern, which transmits well vertically upwards and is efficient over the whole frequency range used. * Digital control and data analysis circuits. The transmitter sweeps all or part of the HF frequency r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radio Propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are wave propagation, propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection (physics), reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, polarization (waves), polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave Broadcasting, broadcasters, to designing reliable Mobile phone, mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems. Several different types of propagation are used in practical radio transmission systems. ''Line-of-sight propagation'' means radio waves which travel in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the receiving ante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
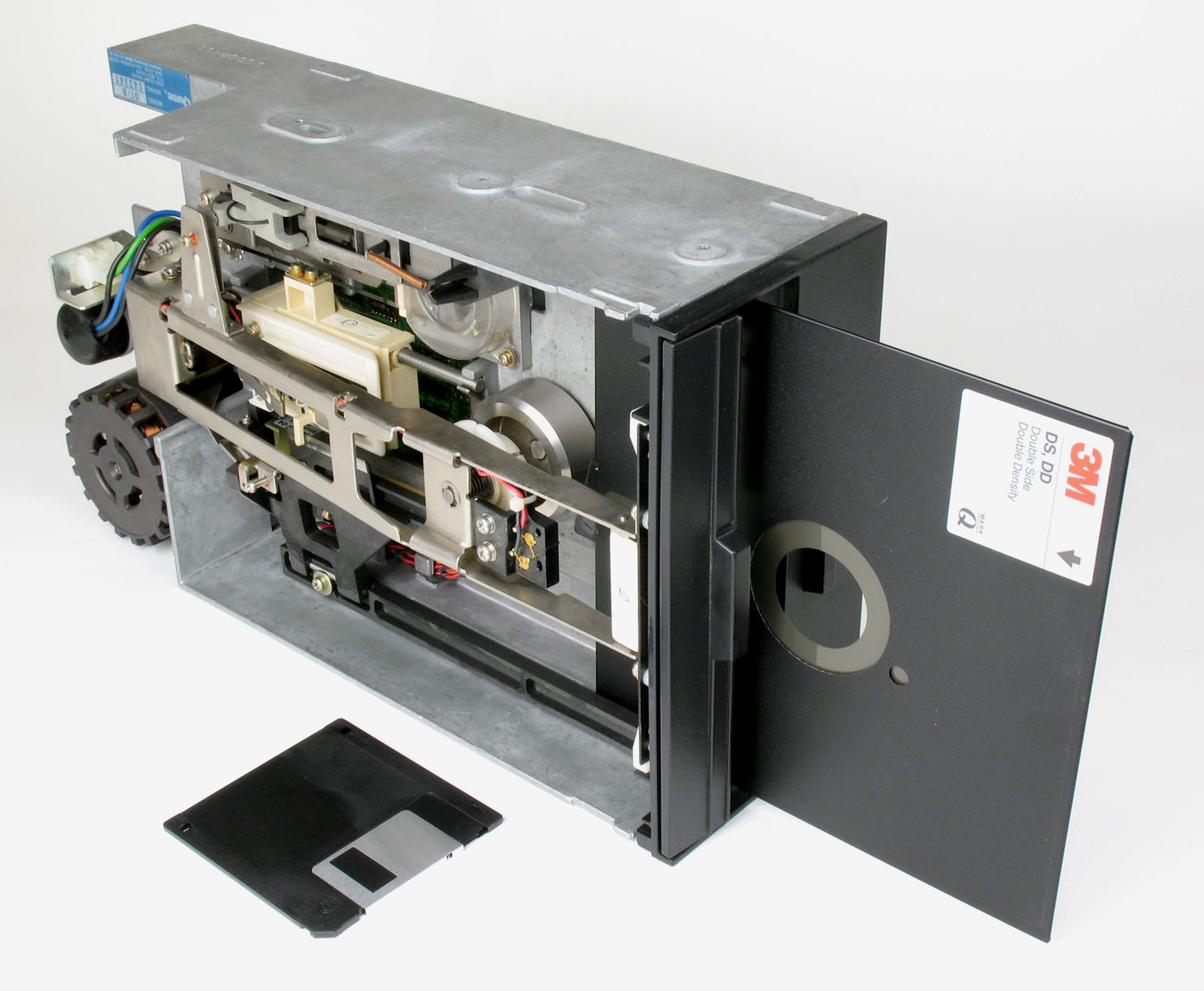
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. The three most popular (and commercially available) floppy disks are the 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch floppy disks. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM in 1971, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch (133.35 mm) and then the 3½-inch (88.9 mm) became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |