|
Ikšudum
Ikšudum or Yakšudum was a Mesopotamian god worshiped in the kingdom of Mari, possibly a deified ancestor. He was closely associated with Lagamal. A possibly related deity is also listed among the hounds of Marduk in the god list ''An = Anum''. Texts from Mari mention a ritual procession of Ikšudum and Lagamal. The pair was also invoked in oath formulas. Name and character Ikšudum's name was spelled as '' dIk-šu-du-um'' in cuneiform. A variant spelling attested in a text from Terqa is Yakšudum. Wilfred G. Lambert suggested it can be translated as "he seized". However, Karel van der Toorn instead translates it as "he has arrived", to be implicitly understood as "the god has arrived". Dietz Otto Edzard suggested Ikšudum might be a shortened form of a theophoric name (''Ikšud'' + theonym), but according to Ichiro Nakata this is uncertain.( The name is also attested as an ordinary given name, not preceded by the "divine determinative", a cuneiform sign preceding theonyms, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagamal
Lagamal or Lagamar ( Akkadian: "no mercy") was a Mesopotamian deity associated chiefly with Dilbat (modern Tell al-Deylam). A female form of Lagamal was worshiped in Terqa on the Euphrates in Upper Mesopotamia. The male Lagamal was also at some point introduced to the pantheon of Susa in Elam. Lagamal was regarded as an underworld deity, and in that capacity could be associated with Mesopotamian Nergal or Elamite Inshushinak. In Mesopotamian sources, his father was Urash, the tutelary god of Dilbat. In Susa, Lagamal formed a pair with Ishmekarab, a deity associated with law and justice, while documents from Mari indicate that in Terqa she was connected with the local god Ikšudum. Character Lagamal's name means "no mercy" in Akkadian. According to Wilfred G. Lambert, grammatical analysis indicates it is a negated infinitive. Attested spellings include '' dLa-ga-ma-al'', ''dLa-ga-mal'', ''dLa-qa-ma-al'', ''dLa-qa-mar'', ''dLa-ga-mar'' and ''dLa-ga-ma-ru''. The spellings en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
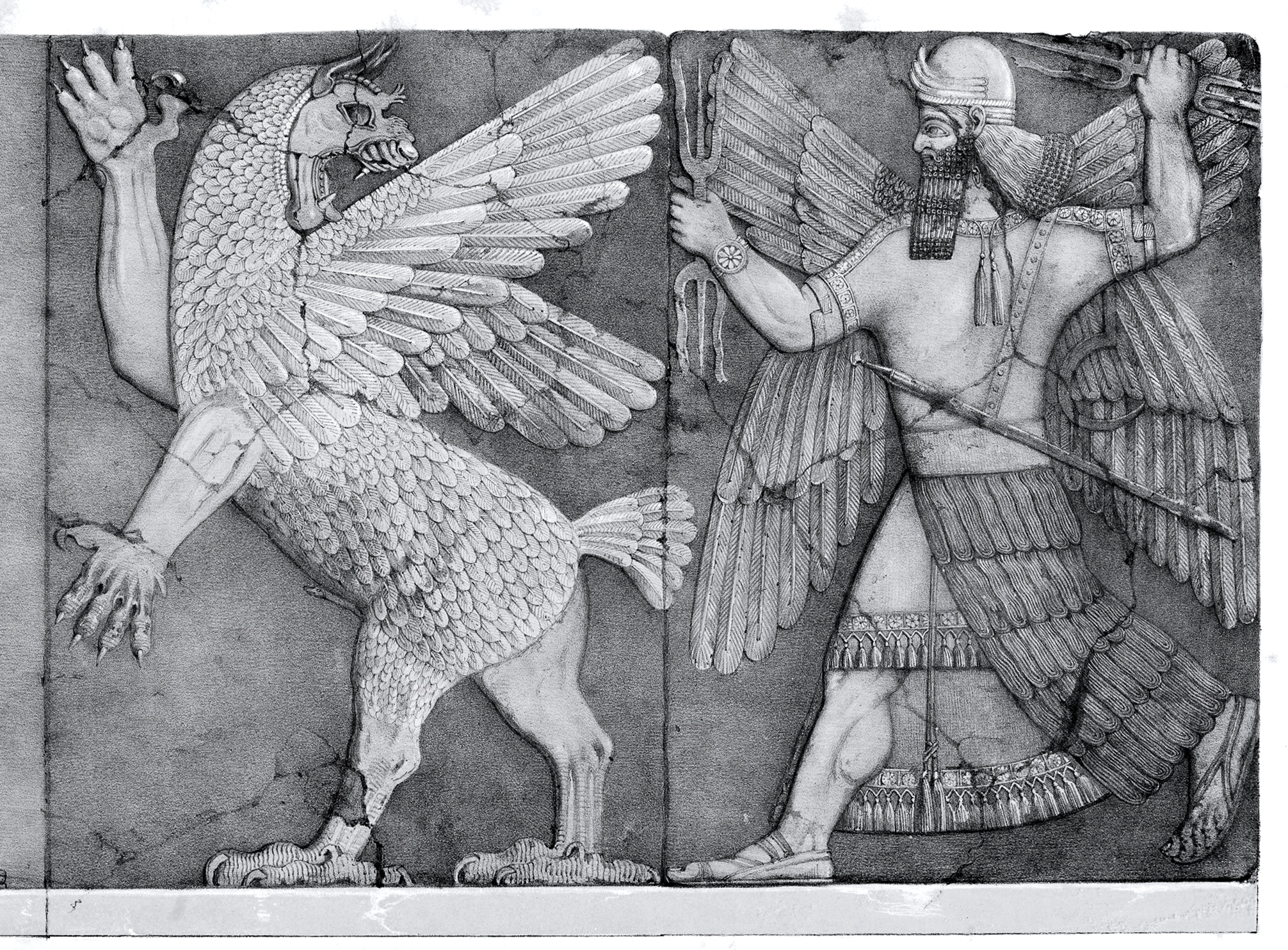
Mari, Syria
Mari (Cuneiform: , ''ma-riki'', modern Tell Hariri; ) was an ancient Semitic people, Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a Tell (archaeology), tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates, Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Ebla, Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west. Mari was first abandoned in the middle of the 26th century BC but was rebuilt and became the capital of a hegemonic East Semitic languages, East Semitic state before 2500 BC. This second Mari engaged in a long war with its rival Ebla and is known for its strong affinity with Sumerian culture. It was destroyed in the 23rd century BC by the Akkadians, who allowed the city to be rebuilt and appointed a military governor (''Shakkanakku''). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zimri-Lim
__NOTOC__ Zimri-Lim was in the Middle Bronze Age the king of Mari, Syria, Mari (c. 1767–1752 BCE; low chronology). Background Family Zimri-Lim (Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''Zi-im-ri Li-im'') was the son or grandson of king Yahdun-Lim of Mari. Exile The assassination of Yahdun-Lim by his own servants during a palace coup, forced Zimri-Lim to flee to the neighboring Great Kingdom of Yamhad (Halab, Aleppo). Mari was occupied by Shamshi-Adad I, the king of Ekallatum, who put his own son Yasmah-Adad on the throne. Ruler of Alalakh Zimri-Lim went into exile under Sumu-Epuh of Yamhad, and became the vassal ruler of Alalakh, unable to claim his rightful heritage to the throne of Mari. Reign Following the death of Shamshi-Adad I, Shamshi-Adad I of Assyria (c. 1776/1775 BC; middle chronology), Zimri-Lim was aided by Yarim-Lim I, the Great King of Yamhad, to oust Yasmah-Adad from the throne of Mari. There is an Akkadian literary text, written in the early years of his reign, entitl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enlil
Enlil, later known as Elil and Ellil, is an List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian god associated with wind, air, earth, and storms. He is first attested as the chief deity of the Sumerian pantheon, but he was later worshipped by the Akkadian Empire, Akkadians, Babylonian Empire, Babylonians, Assyrian Empire, Assyrians, and Hurrians. Enlil's primary center of worship was the Ekur temple in the city of Nippur, which was believed to have been built by Enlil himself and was regarded as the "mooring-rope" of heaven and earth. He is also sometimes referred to in Sumerian texts as Nunamnir. According to one Sumerian hymn, Enlil himself was so holy that not even the other gods could look upon him. Enlil rose to prominence during the twenty-fourth century BC with the rise of Nippur. His Cult (religious practice), cult fell into decline after Nippur was sacked by the Elamites in 1230 BC and he was eventually supplanted as the chief god of the Mesopotamian pantheon by the Baby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninurta
Ninurta (: , possible meaning "Lord [of] Barley"), also known as Ninĝirsu (: , meaning "Lord [of] Girsu"), is an List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian god associated with farming, healing, hunting, law, scribes, and war who was first worshipped in early Sumer. In the earliest records, he is a god of agriculture and healing, who cures humans of sicknesses and releases them from the power of Demons#Mesopotamia, demons. In later times, as Mesopotamia grew more militarized, he became a warrior deity, though he retained many of his earlier agricultural attributes. He was regarded as the son of the chief god Enlil and his main Cult (religious practice), cult center in Sumer was the Eshumesha temple in Nippur. Ninĝirsu was honored by Gudea, King Gudea of Lagash (ruled 2144–2124 BC), who rebuilt Ninĝirsu's temple in Lagash. Later, Ninurta became beloved by the Assyrians as a formidable warrior. The Assyrian king Ashurnasirpal II (ruled 883–859 BC) built a massive tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"I. E. S. Edwards, C. J. Gadd, N. G. L. Hammond, ''The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory'': Vol. 1, Part 1, Cambridge University Press, 1970 Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''Nibbur'') was an ancient Sumerian city. It was the special seat of the worship of the Sumerian god Enlil, the "Lord Wind", ruler of the Ancient Near Eastern cosmology , cosmos, subject to Anu, An alone. Nippur was located in modern Nuffar 5 miles north of modern Afak, Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq. It is roughly 200 kilometers south of modern Baghdad and about 100 km southeast of the ancient city of Babylon. Occupation at the site extended back to the Ubaid period (Ubaid 2 – Hajji Muhammed), the Uruk period, and the Jemdet Nasr period. The origin of the ancient name is unknown but different proposals have been made. History Nippur never enjoyed political hegemony in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagan (god)
Dagon or Dagan (; ) was a god worshipped in ancient Syria, across the middle of the Euphrates, with primary temples located in Tuttul and Terqa, though many attestations of his cult come from cities such as Mari and Emar as well. In settlements situated in the upper Euphrates area, he was regarded as the "father of gods" similar to Mesopotamian Enlil or Hurrian Kumarbi, as well as a lord of the land, a god of prosperity, and a source of royal legitimacy. A large number of theophoric names, both masculine and feminine, attests that he was a popular deity. He was also worshiped further east, in Mesopotamia, where many rulers regarded him as the god capable of granting them kingship over the western areas. Attestations of Dagan from coastal areas are much less frequent and come mostly from the northern city of Ugarit, where Dagan's cult had a limited scope. According to the Hebrew Bible, Dagan was also the national god of the Philistines, with temples at Ashdod and Gaza, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominique Charpin
Dominique Charpin (born 12 June 1954, in Neuilly-sur-Seine) is a French Assyriologist, professor at the Collège de France, and corresponding member of the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, specialized in the "Old-Babylonian" period. Biography Born on 12 June 1954 in Neuilly-sur-Seine, Charpin was in high school when a trip to Turkey and a stay in Syria and Lebanon in the following year determined his vocation. After graduating with a bachelor's degree in 1971, he pursued his studies in history, and more specifically chose to study epigraphy rather than archaeology, but learned these two subjects, and began to practice them during excavations in Iraq. He passed the agrégation of history in 1976, a doctoral dissertation in 1979 on the subject of ''Archives familiales et propriété privée en Babylonie ancienne'', and his doctorate thesis on ''Le Clergé d'Ur au siècle d'Hammu-rabi'' in 1984, under the direction of Paul Garelli... He participates in excavations a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gan De
Gan De (; fl. 4th century BC), also known as the Lord Gan (Gan Gong), was an ancient Chinese astronomer and astrologer born in the State of Qi. Along with Shi Shen, he is believed to be the first in history known by name to compile a star catalogue, preceded by the anonymous authors of the early Babylonian star catalogues and followed by the Greek Hipparchus who is the first known in the Western tradition of Hellenistic astronomy to have compiled a star catalogue. He also made observations of the planets, particularly Jupiter. His writings are lost, but some of his works' titles and fragments quoted from them are known from later texts. Gan De may have been the first to describe one of the Galilean moons of Jupiter, usually invisible without the aid of telescopes. In the 20th century, a fragment of Gan's work, in a later compilation of astronomical texts, was identified by Xi Zezong as describing a naked-eye observation of either of the two largest and brightest moons, Ganym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyriology
Assyriology (from Greek , ''Assyriā''; and , ''-logia''), also known as Cuneiform studies or Ancient Near East studies, is the archaeological, anthropological, historical, and linguistic study of the cultures that used cuneiform writing. The field covers Pre Dynastic Mesopotamia, Sumer, the early Sumero-Akkadian city-states, the Akkadian Empire, Ebla, the Akkadian and Imperial Aramaic speaking states of Assyria, Babylonia and the Sealand Dynasty, the migrant foreign dynasties of southern Mesopotamia, including the Gutians, Amorites, Kassites, Arameans, Suteans and Chaldeans. Assyriology can be included to cover Neolithic pre-Dynastic cultures dating to as far back as 8000 BC, to the Islamic Conquest of the 7th century AD, so the topic is significantly wider than that implied by the root "Assyria". The large number of cuneiform clay tablets preserved by these Sumero-Akkadian and Assyro-Babylonian cultures provide an extremely large resource for the study of the period. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth and a tenth that of the Sun. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of . It is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third-brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky, after the Moon and Venus, and has been observed since prehistoric times. Its name derives from that of Jupiter (god), Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter was the first of the Sun's planets to form, and its inward migration during the primordial phase of the Solar System affected much of the formation history of the other planets. Jupiter's atmosphere consists of 76% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with a denser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galilean Moons
The Galilean moons (), or Galilean satellites, are the four largest moons of Jupiter. They are, in descending-size order, Ganymede (moon), Ganymede, Callisto (moon), Callisto, Io (moon), Io, and Europa (moon), Europa. They are the most apparent magnitude, readily visible Solar System objects after Saturn, the dimmest of the classical planets; though their closeness to bright Jupiter makes naked-eye observation very difficult, they are readily seen with common binoculars, even under night sky Bortle scale, conditions of high light pollution. The invention of the telescope allowed astronomers to discover the moons in 1610. Through this, they became the first Timeline of discovery of Solar System planets and their moons, Solar System objects discovered since humans have started tracking the classical planets, and the first objects to be found to orbit any planet beyond Earth. They are planetary-mass moons and among the List of Solar System objects by size, largest objects in the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |