|
Günter Hessler
Günter Hessler (14 June 1909 – 4 April 1968) was a German naval officer during World War II. He commanded the Type IXB U-boat , sinking twenty-one ships on three patrols, totalling of Allied shipping. Hessler was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross and was commissioned after the war to write an account of the U-boat war by the British Ministry of Defence. Military career Günter Hessler joined the '' Reichsmarine'' of the Weimar Republic on 5 April 1927 as a member of "Crew 1927" (the incoming class of 1927). He underwent basic military training in the 8th company, 2nd department of the standing ship division of the Baltic Sea in Stralsund (5 April 1927 – 3 July 1927). Hessler was then transferred to the training ship SSS ''Niobe'' (4 July 1927 – 31 October 1927), attaining the rank of ''Seekadett'' (midshipman) on 1 October 1927. After more than 16 months aboard the light cruiser (1 November 1927 – 17 March 1929) he underwent officer cad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steinhöfel
Steinhöfel is a municipality in the Oder-Spree district, in Brandenburg, Germany. Since the beginning of 2019 it belongs to the collective municipality " Amt Odervorland" The contemporary municipality of Steinhöfel comprises a total of twelve physical villages, namely Steinhöfel, Arensdorf, Beerfelde, Buchholz, Demnitz, Gölsdorf, Hasenfelde, Heinersdorf, Jänickendorf, Neuendorf im Sande, Schönfelde and Tempelberg. History In 1774, the Prussian Minister of War and Treasurymore precisely, President of the General War and Finance Directory of Prussia - hence effectively Minister of War and Finance Joachim von Blumenthal purchased the estate of Steinhöfel, including a manor that was later expanded into a castle. When von Blumenthal died, the estate was inherited by his daughter Charlotte von Massow, whose husband the Court Marshal Valentin von Massow commissioned a rebuilding of the manor by the architect David Gilly. The property was inherited in turn by the couple's son Val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
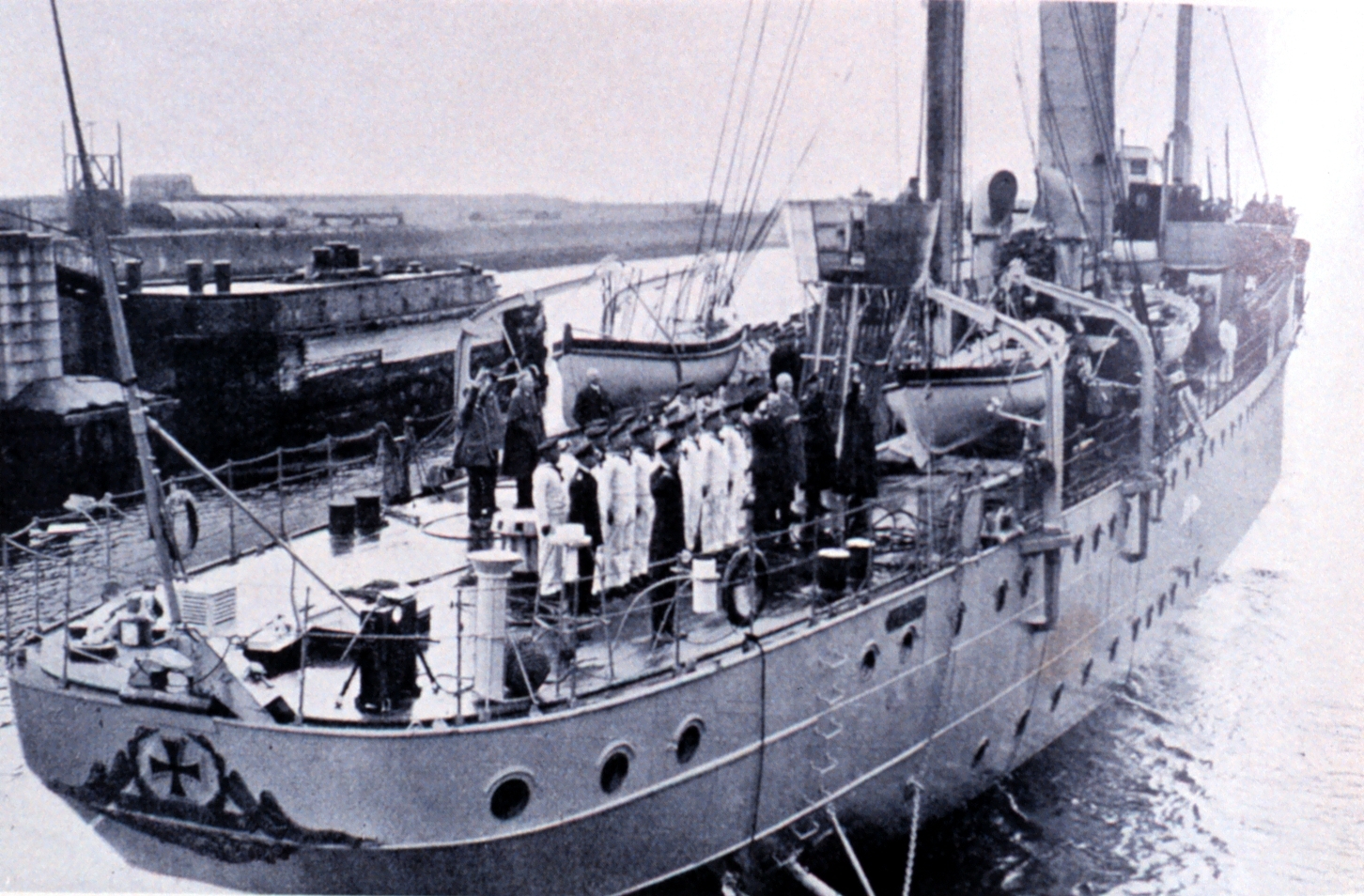
Niobe (schooner)
Segelschulschiff ''Niobe'' was a tall ship used by the ''Reichsmarine'' to train cadets and aspiring NCOs. She sank during a white squall on 26 July 1932, with the loss of 69 lives. A memorial monument to ''Niobe'' was erected at Gammendorfer Strand on Fehmarn island, within view of the site of the sinking. History Design The ship had a steel hull (watercraft), hull and displaced 645 tonnes. After her conversion into a training ship she measured in length overall, without the bowsprit, and in width. The height of the main mast was , and she carried 15 sails with of total sail area. She had an auxiliary diesel engine with . Her regular crew comprised seven officers and 27 men. Usually 65 cadets would be trained. Early service She was built as a four-masted schooner in 1913 by the Danish shipyard Frederikshavns Værft og Flydedok under her original name ''Morten Jensen'' and initially sailed as a freighter for F. L. Knakkergaard in Nykøbing Mors. In 1916 she was sold to Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind energy, wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Viking Age, Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Golden Age, Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive weapon placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Similar to anti-personnel mine, anti-personnel and other land mines, and unlike purpose launched naval depth charges, they are deposited and left to wait until, depending on their fuzing, they are triggered by the approach of or contact with any vessel. Naval mines can be used offensively, to hamper enemy shipping movements or lock vessels into a harbour; or defensively, to create "safe" zones protecting friendly sea lanes, harbours, and naval assets. Mines allow the minelaying force commander to concentrate warships or defensive assets in mine-free areas giving the adversary three choices: undertake a resource-intensive and time-consuming minesweeping effort, accept the casualties of challenging the minefield, or use the unmined waters where the greatest concentration of enemy firepower will be encountered. Although international law requires signatory nations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the insignia of the medieval Teutonic Order and borne by its knights from the 13th century. As well as being a military medal, it has also been used as an emblem by the Prussian Army, the Imperial German Army, and the of the Weimar Republic, while the ''Balkenkreuz'' (bar cross) variant was used by the ''Wehrmacht''. The Iron Cross is now the emblem of the , the modern German armed forces. King Frederick William III of Prussia established the Iron Cross award on 17 March 1813 during the Napoleonic Wars (EK 1813). The award was backdated to the birthday (10 March) of his late wife, Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Queen Louise, who was the first person to receive it (posthumously). The Iron Cross was also awarded during the Franco-Prussian War ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
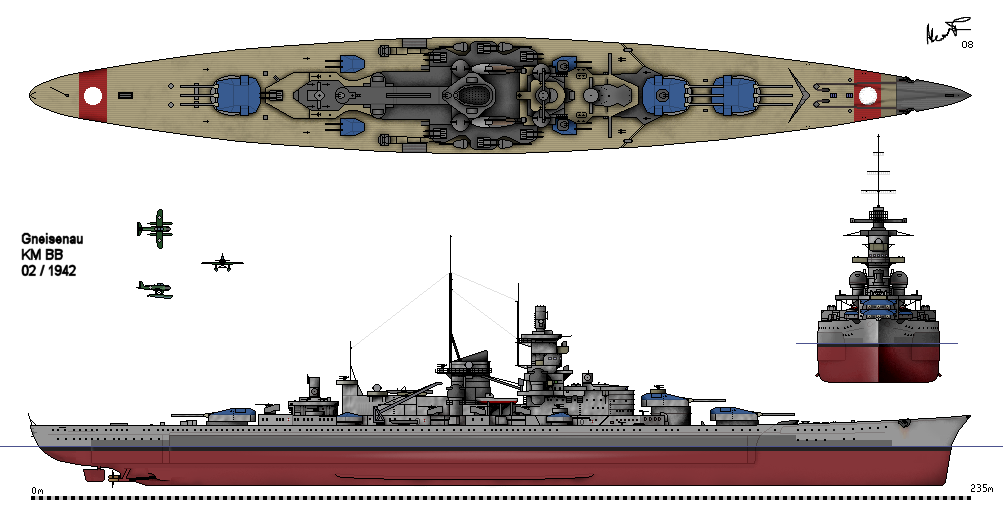
German Battleship Gneisenau
''Gneisenau'' () was a German capital ship, alternatively described as a battleship and battlecruiser, in Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine''. She was the second vessel of Scharnhorst-class battleship, her class, which included her sister ship, . The ship was built at the ''Deutsche Werke'' dockyard in Kiel; she was laid down on 6 May 1935 and launched on 8 December 1936. Her outfitting was completed in May 1938: she was armed with a main battery of nine 28 cm SK C/34 naval gun, 28 cm (11 in) C/34 guns in three triple turrets. At one point after construction had started, a plan had been approved to replace these weapons with six 38 cm SK C/34 naval gun, 38 cm (15 in) SK C/34 guns in twin turrets, but when it was realized that this would involve a lot of redesign, that plan was abandoned, and construction continued with the originally planned lower-calibre guns. The upgrade had been intended to be completed in the winter of 1940–41, but instead, due to the outbre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming Chancellor of Germany#Nazi Germany (1933–1945), the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. His invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 marked the start of the Second World War. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of Holocaust victims, about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and moved to German Empire, Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his service in the German Army in the First World War, receiving the Iron Cross. In 1919 he joined the German Workers' Party (DAP), the precursor of the Nazi Party, and in 1921 was app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Aviso Grille (1935)
was an aviso built in Nazi Germany for the (War Navy) in the mid-1930s for use as a state yacht by Adolf Hitler and other leading individuals in the Nazi regime. The ship received a light armament of three guns and was fitted to be capable of serving as an auxiliary minelayer. Completed in 1935, her experimental high-pressure steam turbines, which were installed to test them before they were used in destroyers, required significant modifications and the ship finally entered service in 1937. Over the next two years, she was used in a variety of roles, including as a training vessel and a target ship, in addition to her duties as a yacht. After the start of World War II in September 1939, was used as a minelayer and as a patrol vessel in the Baltic Sea, tasked with searching for enemy merchant vessels. She collided with a German transport ship in January 1940 and after repairs, resumed minelaying duties in the North Sea, thereafter being used as a gunnery training ship. She w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviso
An ''aviso'' was originally a kind of dispatch boat or "advice boat", carrying orders before the development of effective remote communication. The term, derived from the Portuguese and Spanish word for "advice", "notice" or "warning", an ''aviso'', was later adopted by the French and Portuguese navies to classify their medium-sized warships designed for colonial service. The term continued to be used in the French Navy to classify the patrol frigates until 2012, when the remaining ships of the class were reclassified as offshore patrol ships. It is equivalent to the modern use of " sloop" in other countries. Description The ''Dictionnaire de la Marine Française 1788–1792'' (by Nicolas-Charles Romme) describes ''avisos'' as "small boats designed to carry orders or dispatches". By the late 19th century, an aviso could be of several hundred tons displacement. Usually very lightly armed and often not significantly faster than battleships or cruisers, the aviso was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Bild 101II-MW-3956-05A, Frankreich, Lorient, U-107
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (, lit. "Federal Archive") are the national archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952. They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture and the Media (Claudia Roth since 2021) under the German Chancellery, and before 1998, to the Federal Ministry of the Interior. On 6 December 2008, the Archives donated 100,000 photos to the public, by making them accessible via Wikimedia Commons. History The federal archive for institutions and authorities in Germany, the first precursor to the present-day Federal Archives, was established in Potsdam, Brandenburg in 1919, a later date than in other European countries. This national archive documented German government dating from the founding of the North German Confederation in 1867. It also included material from the older German Confederation and the Imperial Chamber Court. The oldest documents in this collection dated back to the y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fähnrich Zur See
''Fähnrich zur See'' (Fähnr zS or FRZS) designates in the German Navy of the Bundeswehr a military person or member of the armed forces with the second highest Officer Aspirant (OA – ) rank. According to the salary class it is equivalent to the Portepeeunteroffizier ranks Bootsmann (Marine) and Feldwebel of Heer or Luftwaffe. It is also grouped as OR-6 in NATO, equivalent to Technical Sergeant, Staff Sergeant, or Petty Officer First Class in the US Armed forces, and to Petty officer in the British Army and Royal Navy. In navy context NCOs of this rank were formally addressed as ''Herr/ Frau Fähnrich zur See'' also informally / short ''Fähnrich''. The sequence of ranks (top-down approach) in that particular group is as follows: Portepeeunteroffiziere *OR-9: Oberstabsbootsmann / Oberstabsfeldwebel *OR-8: Stabsbootsmann / Stabsfeldwebel *OR-7: Oberfähnrich zur See and Hauptbootsmann / Oberfähnrich and Hauptfeldwebel *OR-6a: Oberbootsmann / Oberfeldwebel *OR-6b: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteor (1915)
''Meteor'' was a German survey vessel, noted for her survey work in the Atlantic Ocean between 1925 and 1927. Handed over to the Soviet Union following World War II, the ship was renamed ''Ekvator''. Her ultimate fate is not known. Design and construction Her keel was laid at the Kaiserliche Werft Danzig, Kaiserliche Werft at Gdańsk, Danzig in February 1914 and ''Meteor'' was launched in January 1915. Originally intended to become a gunboat for the Imperial German Navy's colonial service she was not finished during the First World War due to limited need for lightly armed vessels. After the war the uncompleted hull was tugged to Wilhelmshaven for outfitting work at the Kriegsmarinewerft Wilhelmshaven, Reichsmarinewerft. She was outfitted as a survey vessel and early sonar equipment was fitted. The ship had a steel hull with two propellers each driven by a triple-expansion steam engine. Additionally she had a brigantine rig to boost range. Career ''Meteor'' was commissioned a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |