|
Channel Capacity
Channel capacity, in electrical engineering, computer science, and information theory, is the theoretical maximum rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel. Following the terms of the noisy-channel coding theorem, the channel capacity of a given Channel (communications), channel is the highest information rate (in units of information entropy, information per unit time) that can be achieved with arbitrarily small error probability. Information theory, developed by Claude E. Shannon in 1948, defines the notion of channel capacity and provides a mathematical model by which it may be computed. The key result states that the capacity of the channel, as defined above, is given by the maximum of the mutual information between the input and output of the channel, where the maximization is with respect to the input distribution. The notion of channel capacity has been central to the development of modern wireline and wireless communication system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, Electromagnetism, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (information Theory)
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable quantifies the average level of uncertainty or information associated with the variable's potential states or possible outcomes. This measures the expected amount of information needed to describe the state of the variable, considering the distribution of probabilities across all potential states. Given a discrete random variable X, which may be any member x within the set \mathcal and is distributed according to p\colon \mathcal\to[0, 1], the entropy is \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or "shannon (unit), shannons"), while base Euler's number, ''e'' gives "natural units" nat (unit), nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or "Hartley (unit), hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power (physics)
Power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. Power is a Scalar (physics), scalar quantity. Specifying power in particular systems may require attention to other quantities; for example, the power involved in moving a ground vehicle is the product of the aerodynamic drag plus traction (engineering), traction force on the wheels, and the velocity of the vehicle. The output power of a Engine, motor is the product of the torque that the motor generates and the angular velocity of its output shaft. Likewise, the power dissipated in an electrical element of a electrical circuit, circuit is the product of the electric current, current flowing through the element and of the voltage across the element. Definition Power is the Rate (mathematics), rate with respect to time at which work is done or, more generally, the rate of change of total mechanical energy. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base units is 1/s or s−1, meaning that one hertz is one per second or the Inverse second, reciprocal of one second. It is used only in the case of periodic events. It is named after Heinrich Hertz, Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. For high frequencies, the unit is commonly expressed in metric prefix, multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Logarithm
The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of a logarithm, base of the e (mathematical constant), mathematical constant , which is an Irrational number, irrational and Transcendental number, transcendental number approximately equal to . The natural logarithm of is generally written as , , or sometimes, if the base is implicit, simply . Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity, giving , , or . This is done particularly when the argument to the logarithm is not a single symbol, so as to prevent ambiguity. The natural logarithm of is the exponentiation, power to which would have to be raised to equal . For example, is , because . The natural logarithm of itself, , is , because , while the natural logarithm of is , since . The natural logarithm can be defined for any positive real number as the Integral, area under the curve from to (with the area being negative when ). The simplicity of this definition, which is matched in many other formulas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nat (unit)
The natural unit of information (symbol: nat), sometimes also nit or nepit, is a unit of information or information entropy, based on natural logarithms and powers of e (mathematical constant), ''e'', rather than the powers of 2 and binary logarithm, base 2 logarithms, which define the shannon (unit), shannon. This unit is also known by its unit symbol, the nat. One nat is the information content of an event when the probability of that event occurring is 1/e (mathematical constant), ''e''. One nat is equal to shannon (unit), shannons ≈ 1.44 Sh or, equivalently, hartley (unit), hartleys ≈ 0.434 Hart. History Boulton and Chris Wallace (computer scientist), Wallace used the term ''nit'' in conjunction with minimum message length, which was subsequently changed by the minimum description length community to ''nat'' to avoid confusion with the nit (unit), nit used as a unit of luminance. Alan Turing used the ''natural ban (unit), ban''. Entropy Shan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , then is the logarithm of to base , written , so . As a single-variable function, the logarithm to base is the inverse of exponentiation with base . The logarithm base is called the ''decimal'' or ''common'' logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The ''natural'' logarithm has the number as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics because of its very simple derivative. The ''binary'' logarithm uses base and is widely used in computer science, information theory, music theory, and photography. When the base is unambiguous from the context or irrelevant it is often omitted, and the logarithm is written . Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bits Per Second
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time. The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction with an SI prefix such as kilo (1 kbit/s = 1,000 bit/s), mega (1 Mbit/s = 1,000 kbit/s), giga (1 Gbit/s = 1,000 Mbit/s) or tera (1 Tbit/s = 1,000 Gbit/s). The non-standard abbreviation bps is often used to replace the standard symbol bit/s, so that, for example, 1 Mbps is used to mean one million bits per second. In most computing and digital communication environments, one byte per second (symbol: B/s) corresponds roughly to 8 bit/s. However if stop bits, start bits, and parity bits need to be factored in, a higher number of bits per second will be required to achieve a throughput of the same number of bytes. Prefixes When quantifying large or small bit rates, SI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
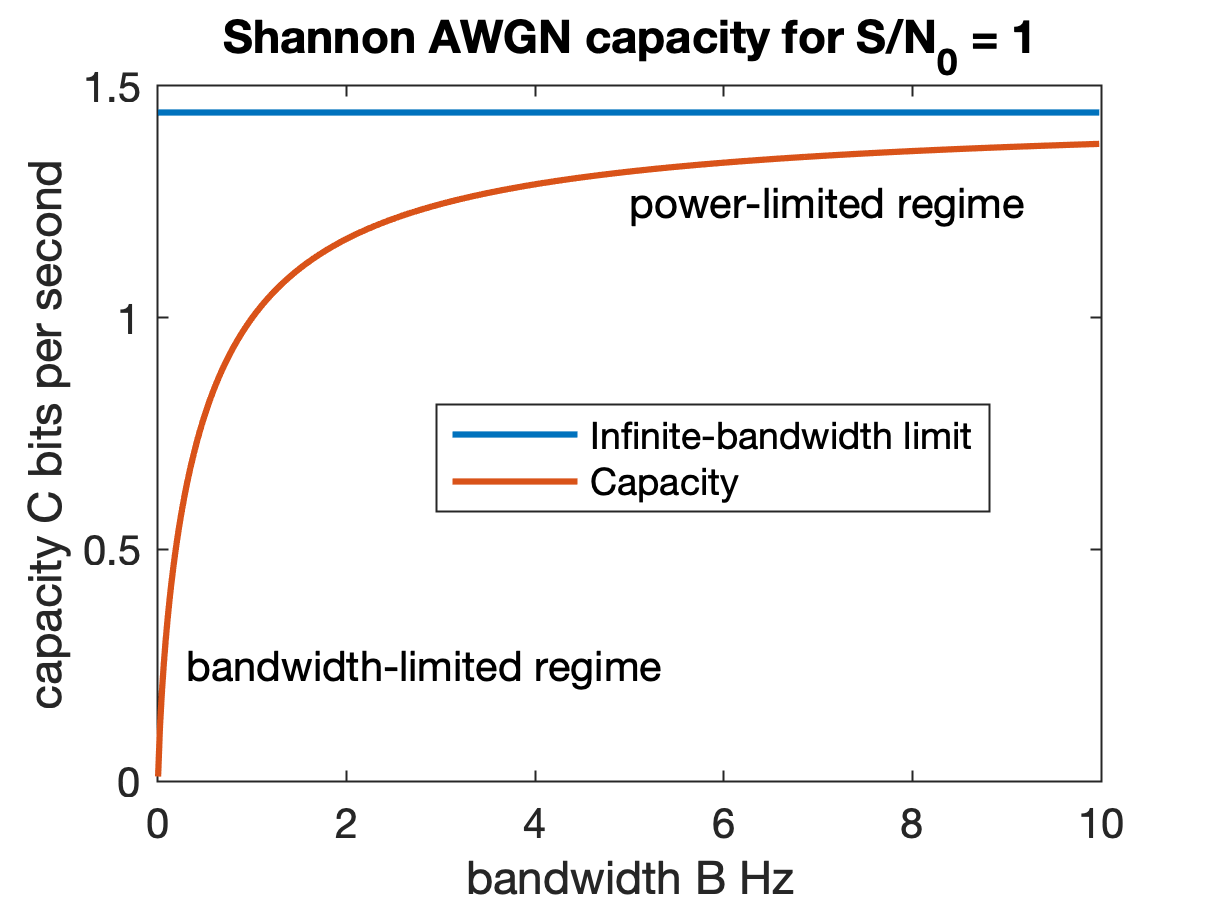
Shannon–Hartley Theorem
In information theory, the Shannon–Hartley theorem tells the maximum rate at which information can be transmitted over a communications channel of a specified bandwidth in the presence of noise. It is an application of the noisy-channel coding theorem to the archetypal case of a continuous-time analog communications channel subject to Gaussian noise. The theorem establishes Shannon's channel capacity for such a communication link, a bound on the maximum amount of error-free information per time unit that can be transmitted with a specified bandwidth in the presence of the noise interference, assuming that the signal power is bounded, and that the Gaussian noise process is characterized by a known power or power spectral density. The law is named after Claude Shannon and Ralph Hartley. Statement of the theorem The Shannon–Hartley theorem states the channel capacity C, meaning the theoretical tightest upper bound on the information rate of data that can be communicated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR is an important parameter that affects the performance and quality of systems that process or transmit signals, such as communication systems, audio systems, radar systems, imaging systems, and data acquisition systems. A high SNR means that the signal is clear and easy to detect or interpret, while a low SNR means that the signal is corrupted or obscured by noise and may be difficult to distinguish or recover. SNR can be improved by various methods, such as increasing the signal strength, reducing the noise level, filtering out unwanted noise, or using error correction techniques. SNR also determines the maximum possible amount of data that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower Frequency, frequencies in a continuous Frequency band, band of frequencies. It is typically measured in unit of measurement, unit of hertz (symbol Hz). It may refer more specifically to two subcategories: ''Passband bandwidth'' is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. ''Baseband bandwidth'' is equal to the upper cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter or baseband signal, which includes a zero frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive White Gaussian Noise
Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) is a basic noise model used in information theory to mimic the effect of many random processes that occur in nature. The modifiers denote specific characteristics: * ''Additive'' because it is added to any noise that might be intrinsic to the information system. * ''White'' refers to the idea that it has uniform power spectral density across the frequency band for the information system. It is an analogy to the color white which may be realized by uniform emissions at all frequencies in the visible spectrum. * ''Gaussian'' because it has a normal distribution in the time domain with an average time domain value of zero ( Gaussian process). Wideband noise comes from many natural noise sources, such as the thermal vibrations of atoms in conductors (referred to as thermal noise or Johnson–Nyquist noise), shot noise, black-body radiation from the earth and other warm objects, and from celestial sources such as the Sun. The central limit theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |