|
Additive White Gaussian Noise
Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) is a basic noise model used in information theory to mimic the effect of many random processes that occur in nature. The modifiers denote specific characteristics: * ''Additive'' because it is added to any noise that might be intrinsic to the information system. * ''White'' refers to the idea that it has uniform power spectral density across the frequency band for the information system. It is an analogy to the color white which may be realized by uniform emissions at all frequencies in the visible spectrum. * ''Gaussian'' because it has a normal distribution in the time domain with an average time domain value of zero ( Gaussian process). Wideband noise comes from many natural noise sources, such as the thermal vibrations of atoms in conductors (referred to as thermal noise or Johnson–Nyquist noise), shot noise, black-body radiation from the earth and other warm objects, and from celestial sources such as the Sun. The central limit theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, though early contributions were made in the 1920s through the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley. It is at the intersection of electronic engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer science, Neuroscience, neurobiology, physics, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a Fair coin, fair coin flip (which has two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy, less uncertainty) than identifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (which has six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
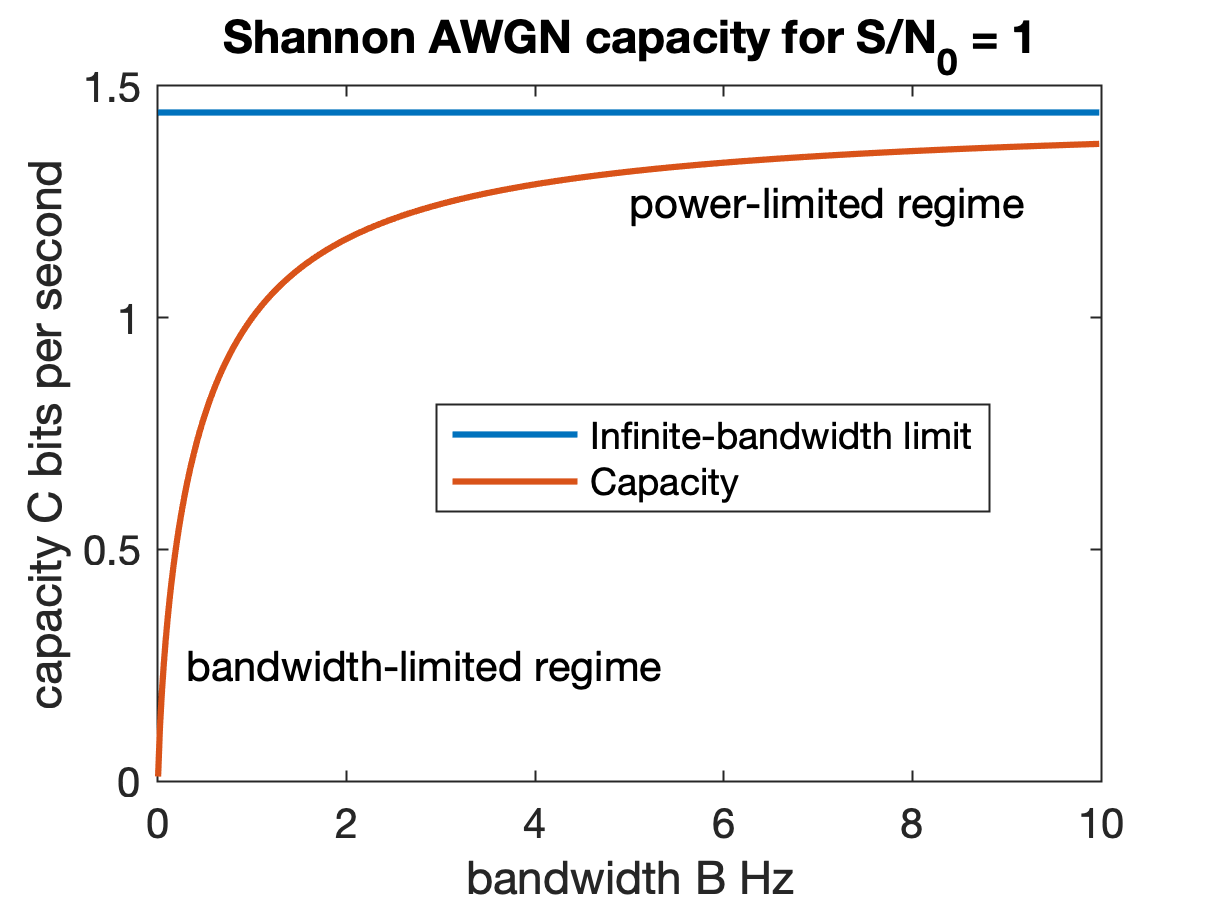
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower Frequency, frequencies in a continuous Frequency band, band of frequencies. It is typically measured in unit of measurement, unit of hertz (symbol Hz). It may refer more specifically to two subcategories: ''Passband bandwidth'' is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. ''Baseband bandwidth'' is equal to the upper cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter or baseband signal, which includes a zero frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Packing
In geometry, a sphere packing is an arrangement of non-overlapping spheres within a containing space. The spheres considered are usually all of identical size, and the space is usually three-dimensional Euclidean space. However, sphere packing problems can be generalised to consider unequal spheres, spaces of other dimensions (where the problem becomes circle packing in two dimensions, or hypersphere packing in higher dimensions) or to Non-Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean spaces such as hyperbolic space. A typical sphere packing problem is to find an arrangement in which the spheres fill as much of the space as possible. The proportion of space filled by the spheres is called the ''packing density'' of the arrangement. As the local density of a packing in an infinite space can vary depending on the volume over which it is measured, the problem is usually to maximise the average or asymptotic density, measured over a large enough volume. For equal spheres in three dimensions, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information (MI) of two random variables is a measure of the mutual Statistical dependence, dependence between the two variables. More specifically, it quantifies the "Information content, amount of information" (in Units of information, units such as shannon (unit), shannons (bits), Nat (unit), nats or Hartley (unit), hartleys) obtained about one random variable by observing the other random variable. The concept of mutual information is intimately linked to that of Entropy (information theory), entropy of a random variable, a fundamental notion in information theory that quantifies the expected "amount of information" held in a random variable. Not limited to real-valued random variables and linear dependence like the Pearson correlation coefficient, correlation coefficient, MI is more general and determines how different the joint distribution of the pair (X,Y) is from the product of the marginal distributions of X and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Entropy
Differential entropy (also referred to as continuous entropy) is a concept in information theory that began as an attempt by Claude Shannon to extend the idea of (Shannon) entropy (a measure of average surprisal) of a random variable, to continuous probability distributions. Unfortunately, Shannon did not derive this formula, and rather just assumed it was the correct continuous analogue of discrete entropy, but it is not. The actual continuous version of discrete entropy is the limiting density of discrete points (LDDP). Differential entropy (described here) is commonly encountered in the literature, but it is a limiting case of the LDDP, and one that loses its fundamental association with discrete entropy. In terms of measure theory, the differential entropy of a probability measure is the negative relative entropy from that measure to the Lebesgue measure, where the latter is treated as if it were a probability measure, despite being unnormalized. Definition Let X be a rand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Capacity
Channel capacity, in electrical engineering, computer science, and information theory, is the theoretical maximum rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel. Following the terms of the noisy-channel coding theorem, the channel capacity of a given Channel (communications), channel is the highest information rate (in units of information entropy, information per unit time) that can be achieved with arbitrarily small error probability. Information theory, developed by Claude E. Shannon in 1948, defines the notion of channel capacity and provides a mathematical model by which it may be computed. The key result states that the capacity of the channel, as defined above, is given by the maximum of the mutual information between the input and output of the channel, where the maximization is with respect to the input distribution. The notion of channel capacity has been central to the development of modern wireline and wireless communication system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. It is the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for example, the variance of a sum of uncorrelated random variables is equal to the sum of their variances. A disadvantage of the variance for practical applications is that, unlike the standard deviation, its units differ from the random variable, which is why the standard devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent And Identically Distributed Random Variables
Independent or Independents may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups * Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in Pennsylvania, United States * Independentes (English: Independents), a Portuguese artist group Music Groups, labels, and genres * Independent music, a number of genres associated with independent labels * Independent record label, a record label not associated with a major label * Independent Albums, American albums chart Albums * ''Independent'' (Ai album), 2012 * ''Independent'' (Faze album), 2006 * ''Independent'' (Sacred Reich album), 1993 Songs * "Independent" (song), a 2007 song by Webbie * "Independent", a 2002 song by Ayumi Hamasaki from '' H'' News media organizations * Independent Media Center (also known as Indymedia or IMC), an open publishing network of journalist collectives that report on political and social issues, e.g., in ''The Indypendent'' newspaper of NYC * ITV (TV network) (Independent Televi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersion (optics)
Dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency. Sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used to refer to optics specifically, as opposed to wave propagation in general. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium. Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the Pulse (signal processing), pulses of light in optical fiber. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of refraction of different colors of light, as seen in the spectrum produced by a dispersive Prism (optics), prism and in chromatic aberration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinearity
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists since most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference (communication)
In telecommunications, an interference is that which modifies a signal in a disruptive manner, as it travels along a communication channel between its source and receiver. The term is often used to refer to the addition of unwanted signals to a useful signal. Common examples include: * Electromagnetic interference (EMI) * Co-channel interference (CCI), also known as crosstalk * Adjacent-channel interference (ACI) * Intersymbol interference (ISI) * Inter-carrier interference (ICI), caused by doppler shift in OFDM modulation (multitone modulation). * Common-mode interference (CMI) * Conducted interference Noise is a form of interference but not all interference is noise. Radio resource management aims at reducing and controlling the co-channel and adjacent-channel interference. Interference alignment A solution to interference problems in wireless communication networks is interference alignment, which was crystallized by Syed Ali Jafar at the University of Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |