Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a
viral hemorrhagic fever
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of animal and human illnesses in which fever and hemorrhage are caused by a viral infection. VHFs may be caused by five distinct families of RNA viruses: the families ''Filoviridae'', ''Flavi ...
in humans and other
primates, caused by
ebolaviruses.
[ Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and ]headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
s.[ These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function,][ at which point, some people begin to ]bleed
Bleeding usually means the leakage or loss of blood from the body.
Bleeding, bleed, or bleeder may also refer to:
*Bleed (printing), intentionally printing across the expected trim line or edge of the sheet
*Bleed, or spill (audio), when audio fro ...
both internally and externally.[ Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear.][ or from contact with items that have recently been contaminated with infected body fluids.][ There have been no documented cases, either in nature or under laboratory conditions, of the disease spreading through the air between humans or other primates.]breast milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by mammary glands located in the breast of a human female. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborns, containing fat, protein, carbohydrates ( lacto ...
may continue to carry the virus for anywhere between several weeks to several months.[ The symptoms of Ebola may resemble those of several other diseases, including malaria, ]cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
, typhoid fever, meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
and other viral hemorrhagic fevers.[ Diagnosis is confirmed by testing blood samples for the presence of viral ]RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
, viral antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
or the virus itself.[ including rapid detection, contact tracing of those exposed, quick access to laboratory services, care for those infected, and proper disposal of the dead through cremation or burial.][ Samples of body fluids and tissues from people with the disease should be handled with extreme caution.][ Prevention measures include wearing proper protective clothing and ]washing hands
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hand ...
when around a person with the disease,[ and limiting the spread of the disease from infected animals to humans – by wearing protective clothing while handling potentially infected ]bushmeat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are hunted for human consumption, most often referring to the meat of game in Africa. Bushmeat represents
a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity for inhabitants of humid tropi ...
, and by cooking bushmeat thoroughly before eating it.[ An Ebola vaccine was approved in the United States in December 2019.]ansuvimab
Ansuvimab, sold under the brand name Ebanga, is a monoclonal antibody medication for the treatment of ''Zaire ebolavirus'' (Ebolavirus) infection.
The most common symptoms include fever, tachycardia (fast heart rate), diarrhea, vomiting, hypote ...
) are associated with improved outcomes.[ These include oral rehydration therapy (drinking slightly sweetened and salty water) or giving ]intravenous fluids
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
, and treating symptoms.[ In October 2020, Atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab (Inmazeb) was approved for medical use in the United States to treat the disease caused by ''Zaire ebolavirus''.]
History and name
The disease was first identified in 1976, in two simultaneous outbreaks: one in Nzara
Nzara is a town in Western Equatoria State. It lies to the northwest of Yambio by road, and is 25 km (15m) from the border with the DR Congo.
Nzara was industrial center of the Azande Scheme also known as, Equatoria Project Scheme during ...
(a town in South Sudan) and the other in Yambuku ( the Democratic Republic of the Congo), a village near the Ebola River
The Ebola River ( or ), also commonly known by its indigenous name Legbala, is the headstream of the Mongala River, a tributary of the Congo River, in northern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is roughly in length.
The name ''Ebola'' is a F ...
, from which the disease takes its name.Ebola outbreaks
This list of Ebola outbreaks records the known occurrences of Ebola virus disease, a highly infectious and acutely lethal Virus, viral disease that has afflicted humans and animals primarily in equatorial Africa. The pathogens responsible for ...
occur intermittently in tropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
.[ Between 1976 and 2012, according to the World Health Organization, there were 24 outbreaks of Ebola resulting in a total of 2,387 cases, and 1,590 deaths.]
Signs and symptoms
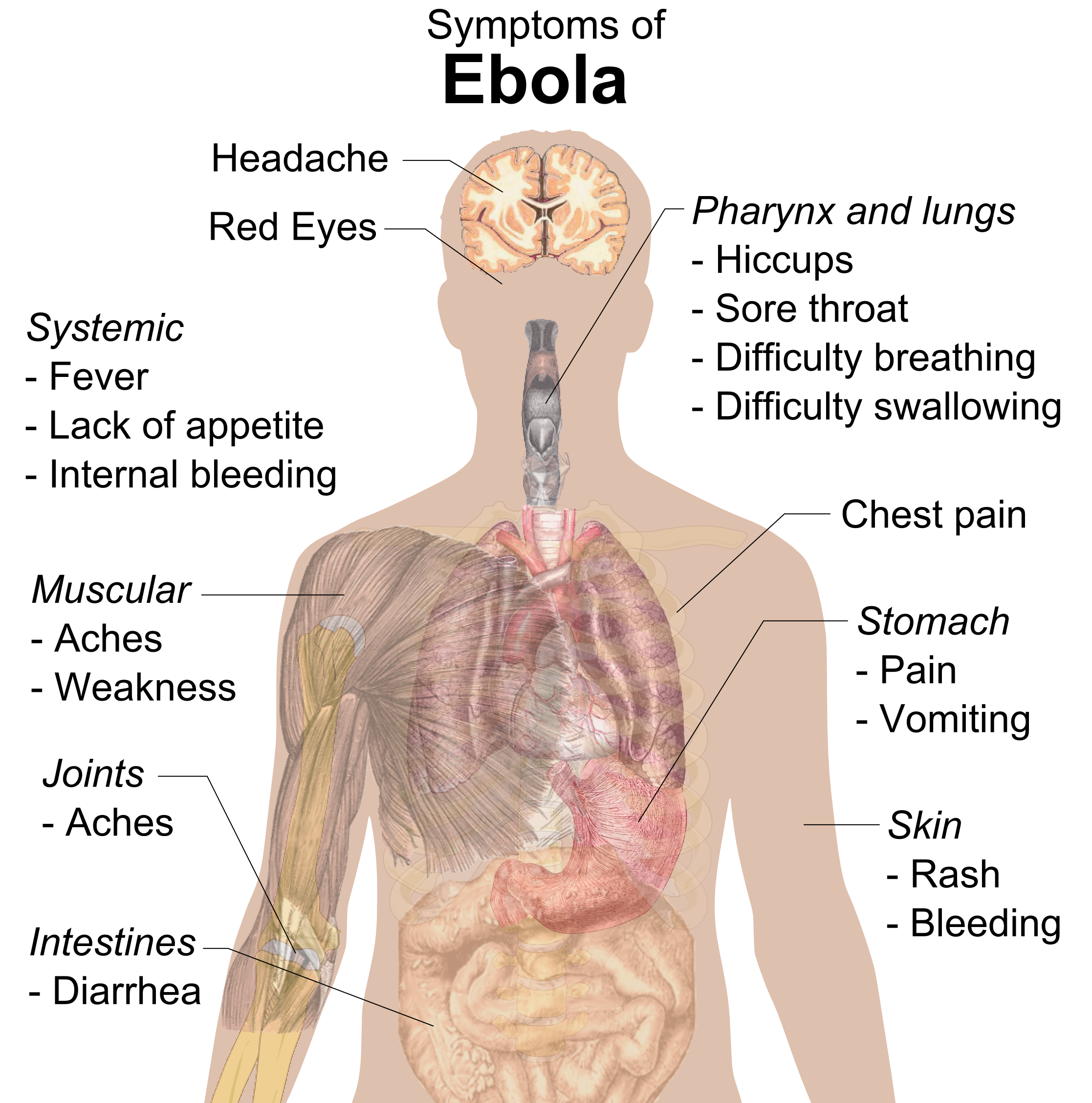
Onset
The length of time between exposure to the virus and the development of symptoms ( incubation period) is between 2 and 21 days,influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
-like stage characterised by fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
, fever, weakness, decreased appetite, muscular pain
Myalgia (also called muscle pain and muscle ache in layman's terms) is the medical term for muscle pain. Myalgia is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another lik ...
, joint pain, headache, and sore throat.chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
may occur, along with swelling, headaches, and confusion.[ In about half of the cases, the skin may develop a maculopapular rash, a flat red area covered with small bumps, five to seven days after symptoms begin.]
Bleeding
In some cases, internal and external bleeding may occur.blood in stool
Blood in stool looks different depending on how early it enters the digestive tract—and thus how much digestive action it has been exposed to—and how much there is. The term can refer either to melena, with a black appearance, typically orig ...
. Bleeding into the skin may create petechia
A petechia () is a small red or purple spot (≤4 mm in diameter) that can appear on the skin, conjunctiva, retina, and Mucous membrane, mucous membranes which is caused by haemorrhage of capillaries. The word is derived from Italian , 'freckle,' ...
e, purpura, ecchymoses or haematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is b ...
s (especially around needle injection sites).gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
.disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts o ...
.
Recovery or death
Recovery may begin between seven and 14 days after first symptoms.[ Death, if it occurs, follows typically six to sixteen days from first symptoms and is often due to shock from fluid loss.][ In general, bleeding often indicates a worse outcome, and blood loss may result in death.]coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
near the end of life.[
Those who survive often have ongoing muscular and joint pain, ]liver inflammation
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain ...
, and decreased hearing, and may have continued tiredness, continued weakness, decreased appetite, and difficulty returning to pre-illness weight.antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
against Ebola that last at least 10 years, but it is unclear whether they are immune to additional infections.
Cause
EVD in humans is caused by four of six viruses of the genus '' Ebolavirus''. The four are Bundibugyo virus
The species ''Bundibugyo ebolavirus'' ( ) is the taxonomic home of one virus, Bundibugyo virus (BDBV), that forms filamentous virions and is closely related to the infamous Ebola virus (EBOV). The virus causes severe disease in humans in the form ...
(BDBV), Sudan virus (SUDV), Taï Forest virus
Taï is a town in southwestern Ivory Coast. It is a sub-prefecture of and the seat of Taï Department in Cavally Region, Montagnes District. Taï is also a commune. The town is between Taï National Park and the Cavally River. The river—which ...
(TAFV) and one simply called Ebola virus (EBOV, formerly Zaire Ebola virus).marburgvirus
The genus ''Marburgvirus'' is the taxonomic home of ''Marburg marburgvirus'', whose members are the two known marburgviruses, Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV). Both viruses cause Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primate ...
es.
Virology
 Ebolaviruses contain single-stranded, non-infectious
Ebolaviruses contain single-stranded, non-infectious RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
genomes.3'-UTR
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally ...
-''NP''-''VP35''-''VP40''-''GP''-''VP30''-''VP24''-''L''- 5'-UTR.cell-surface receptors
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
such as C-type lectins, DC-SIGN, or integrins, which is followed by fusion of the viral envelope with cellular membranes.nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
.RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
, encoded by the ''L'' gene, partially uncoats the nucleocapsid and transcribes the genes into positive-strand mRNAs, which are then translated
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
into structural and nonstructural proteins. The most abundant protein produced is the nucleoprotein, whose concentration in the host cell determines when L switches from gene transcription to genome replication. Replication of the viral genome results in full-length, positive-strand antigenomes that are, in turn, transcribed into genome copies of negative-strand virus progeny.
Transmission
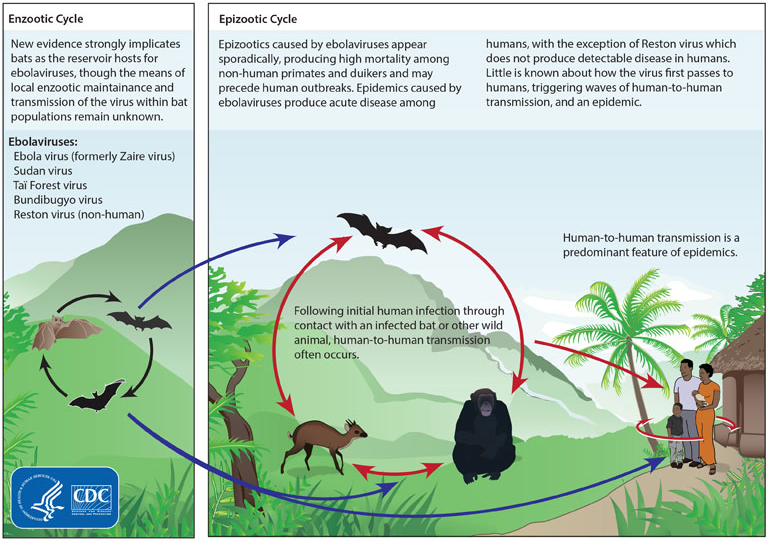
 It is believed that between people, Ebola disease spreads only by direct contact with the blood or other body fluids of a person who has developed symptoms of the disease.
It is believed that between people, Ebola disease spreads only by direct contact with the blood or other body fluids of a person who has developed symptoms of the disease.[ The WHO states that only people who are very sick are able to spread Ebola disease in ]saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
, and the virus has not been reported to be transmitted through sweat. Most people spread the virus through blood, feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
and vomit. Entry points for the virus include the nose, mouth, eyes, open wounds, cuts and abrasions.[ Contact with surfaces or objects contaminated by the virus, particularly needles and syringes, may also transmit the infection.][
The Ebola virus may be able to persist for more than three months in the semen after recovery, which could lead to infections via ]sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (or coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion and thrusting of the penis into the vagina for sexual pleasure or reproduction.Sexual intercourse most commonly means penile–vaginal penetrat ...
.[ Virus persistence in semen for over a year has been recorded in a national screening programme. Ebola may also occur in the breast milk of women after recovery, and it is not known when it is safe to breastfeed again.][ The virus was also found in the eye of one patient in 2014, two months after it was cleared from his blood. Otherwise, people who have recovered are not infectious.][
The potential for widespread infections in countries with medical systems capable of observing correct medical isolation procedures is considered low.][ Of the cases of Ebola infections in Guinea during the 2014 outbreak, 69% are believed to have been contracted via unprotected (or unsuitably protected) contact with infected corpses during certain Guinean burial rituals.][ This risk is particularly common in parts of Africa where the disease mostly occurs and health systems function poorly. There has been transmission in hospitals in some African countries that reuse hypodermic needles. Some health-care centres caring for people with the disease do not have running water.][ and airborne transmission has only been demonstrated in very strict laboratory conditions, and then only from pigs to ]primates
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
, but not from primates to primates.[ Other possible methods of transmission are being studied.]
Initial case
 Although it is not entirely clear how Ebola initially spreads from animals to humans, the spread is believed to involve direct contact with an infected wild animal or fruit bat.
Although it is not entirely clear how Ebola initially spreads from animals to humans, the spread is believed to involve direct contact with an infected wild animal or fruit bat.[ Besides bats, other wild animals that are sometimes infected with EBOV include several species of monkeys such as baboons, great apes (]chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative th ...
s and gorillas), and duikers (a species of antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mammals ...
).[ Fruit production, animal behavior and other factors may trigger outbreaks among animal populations.]
Reservoir
The natural reservoir for Ebola has yet to be confirmed; however, bats are considered to be the most likely candidate.Republic of the Congo
The Republic of the Congo (french: République du Congo, ln, Republíki ya Kongó), also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply either Congo or the Congo, is a country located in the western coast of Central Africa to the w ...
, immunoglobulin G (IgG) immune defense molecules indicative of Ebola infection were found in three bat species; at various periods of study, between 2.2 and 22.6% of bats were found to contain both RNA sequences and IgG molecules indicating Ebola infection. Antibodies against Zaire and Reston viruses have been found in fruit bats in Bangladesh, suggesting that these bats are also potential hosts of the virus and that the filoviruses are present in Asia.Mus setulosus
Peters's mouse (''Mus setulosus'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae.
It is found in Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon ...
'' and '' Praomys'') and one shrew (''Sylvisorex ollula
The greater forest shrew (''Sylvisorex ollula'') is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae found in Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Nigeria. Its natural habitat is subtropical ...
'') collected from the Central African Republic.
Pathophysiology
 Like other
Like other filoviruses
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known re ...
, EBOV replicates very efficiently in many cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
, producing large amounts of virus in monocytes, macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s, dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s and other cells including liver cells, fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound ...
s, and adrenal gland cells.lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
s where further reproduction of the virus takes place.lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
and spread throughout the body.white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
s, such as lymphocytes, also undergo programmed cell death leading to an abnormally low concentration of lymphocytes in the blood.glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
s. This damage occurs due to the synthesis of Ebola virus glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
(GP), which reduces the availability of specific integrins responsible for cell adhesion to the intercellular structure and causes liver damage, leading to improper clotting. The widespread bleeding that occurs in affected people causes swelling and shock due to loss of blood volume.coagulation cascade
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
due to excessive tissue factor
Tissue factor, also called platelet tissue factor, factor III, or CD142, is a protein encoded by the ''F3'' gene, present in subendothelial tissue and leukocytes. Its role in the clotting process is the initiation of thrombin formation from the ...
production by macrophages and monocytes.glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
, small soluble glycoprotein (sGP or GP) is synthesised. EBOV replication overwhelms protein synthesis of infected cells and the host immune defences. The GP forms a trimeric complex, which tethers the virus to the endothelial cells. The sGP forms a dimeric protein
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has ...
that interferes with the signalling of neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
, another type of white blood cell. This enables the virus to evade the immune system by inhibiting early steps of neutrophil activation.
Immune system evasion
Filoviral infection also interferes with proper functioning of the innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
.interferon-beta
The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p21.3 cyto ...
, and interferon gamma.TLR7
Toll-like receptor 7, also known as TLR7, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR7'' gene. Orthologs are found in mammals and birds. It is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family and detects single stranded RNA.
Function
T ...
, TLR8
Toll-like receptor 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR8'' gene. TLR8 has also been designated as CD288 (cluster of differentiation 288). It is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family.
Function
TLR8 seems to function d ...
and TLR9) recognise infectious molecules associated with the virus.interferon regulatory factor 3
Interferon regulatory factor 3, also known as IRF3, is an interferon regulatory factor.
Function
IRF3 is a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family. IRF3 was originally discovered as a homolog of IRF1 and IRF2. IR ...
and interferon regulatory factor 7 trigger a signalling cascade that leads to the expression of type 1 interferon
The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p21.3 cyto ...
s.IFNAR1
Interferon-alpha/beta receptor alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IFNAR1'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a type I membrane protein that forms one of the two chains of a receptor for type I interfer ...
and IFNAR2 receptors expressed on the surface of a neighbouring cell.STAT2
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STAT2'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. This protein is critical to the biological response of type I interferons (IFNs). STAT2 se ...
are activated and move to the cell's nucleus.
Diagnosis
When EVD is suspected, travel, work history, and exposure to wildlife are important factors with respect to further diagnostic efforts.
Laboratory testing
Possible non-specific laboratory indicators of EVD include a low platelet count
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and ...
; an initially decreased white blood cell count followed by an increased white blood cell count; elevated levels of the liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST); and abnormalities in blood clotting often consistent with disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts o ...
(DIC) such as a prolonged prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and bleeding time
Bleeding time is a medical test done on someone to assess their platelets function. It involves making a patient bleed, then timing how long it takes for them to stop bleeding using a stopwatch or other suitable devices.
The term template bleedin ...
.electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
.RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
or proteins, or detecting antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
against the virus in a person's blood.[ Isolating the virus by ]cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This te ...
, detecting the viral RNA by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)[ Detecting antibodies against the virus is most reliable in the later stages of the disease and in those who recover.]IgM antibodies
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is one of several isotypes of antibody (also known as immunoglobulin) that are produced by vertebrates. IgM is the largest antibody, and it is the first antibody to appear in the response to initial exposure to an antig ...
are detectable two days after symptom onset and IgG antibodies
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG ...
can be detected six to 18 days after symptom onset.[ It is able to confirm Ebola in 92% of those affected and rule it out in 85% of those not affected.]
Differential diagnosis
Early symptoms of EVD may be similar to those of other diseases common in Africa, including malaria and dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characterist ...
.differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
is extensive and requires consideration of many other infectious diseases such as typhoid fever, shigellosis
Shigellosis is an infection of the intestines caused by ''Shigella'' bacteria. Symptoms generally start one to two days after exposure and include diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, and feeling the need to pass stools even when the bowels are emp ...
, rickettsial diseases, cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
, sepsis, borreliosis
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migran ...
, EHEC enteritis, leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacteria ''Leptospira''. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild (headaches, muscle pains, and fevers) to severe ( bleeding in the lungs or meningitis). Weil's disease, the acute, severe ...
, scrub typhus, plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
, Q fever, candidiasis, histoplasmosis, trypanosomiasis, visceral
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a ...
leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the trypanosome genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' and ''Lutzomyia'', and occurs most freq ...
, measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, and viral hepatitis among others.
Non-infectious diseases that may result in symptoms similar to those of EVD include acute promyelocytic leukaemia
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML, APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a cancer of the white blood cells. In APL, there is an abnormal accumulation of immature granulocytes called promyelocytes. The disease is characterized by a ...
, haemolytic uraemic syndrome
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo o ...
, snake envenomation
A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occu ...
, clotting factor
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
deficiencies/platelet disorders, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia, Kawasaki disease, and warfarin poisoning.
Prevention
Vaccines
An Ebola vaccine, rVSV-ZEBOV
Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus–Zaire Ebola virus (rVSV-ZEBOV), also known as Ebola Zaire vaccine live and sold under the brand name Ervebo, is an Ebola vaccine for adults that prevents Ebola caused by the Zaire ebolavirus. When used ...
, was approved in the United States in December 2019.[ It was studied in Guinea between 2014 and 2016.][ More than 100,000 people have been vaccinated against Ebola .
]
Infection control
 Community awareness of the benefits on survival chances of admitting cases early is important for the infected and infection control
Community awareness of the benefits on survival chances of admitting cases early is important for the infected and infection control
Caregivers
 People who care for those infected with Ebola should wear protective clothing including masks, gloves, gowns and goggles.
People who care for those infected with Ebola should wear protective clothing including masks, gloves, gowns and goggles.[ The U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommend that the protective gear leaves no skin exposed.][ These measures are also recommended for those who may handle objects contaminated by an infected person's body fluids.][ In 2014, the CDC began recommending that medical personnel receive training on the proper suit-up and removal of personal protective equipment (PPE); in addition, a designated person, appropriately trained in biosafety, should be watching each step of these procedures to ensure they are done correctly.]
Patients and household members
The infected person should be in barrier-isolation from other people.[ All equipment, medical waste, patient waste and surfaces that may have come into contact with body fluids need to be ]disinfected
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than st ...
.chlorine powder
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is ...
and other cleaning supplies. Education of caregivers in these techniques, and providing such barrier-separation supplies has been a priority of Doctors Without Borders.
Disinfection
Ebolaviruses can be eliminated with heat (heating for 30 to 60 minutes at 60 °C or boiling for five minutes). To disinfect surfaces, some lipid solvents such as some alcohol-based products, detergents, sodium hypochlorite (bleach) or calcium hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with formula Ca(OCl)2. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent. Thi ...
(bleaching powder), and other suitable disinfectants may be used at appropriate concentrations.
General population
Education of the general public about the risk factors for Ebola infection and of the protective measures individuals may take to prevent infection is recommended by the World Health Organization.[ These measures include avoiding direct contact with infected people and regular hand washing using soap and water.
]
Bushmeat
Bushmeat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are hunted for human consumption, most often referring to the meat of game in Africa. Bushmeat represents
a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity for inhabitants of humid tropi ...
, an important source of protein in the diet of some Africans, should be handled and prepared with appropriate protective clothing and thoroughly cooked before consumption.[ Some research suggests that an outbreak of Ebola disease in the wild animals used for consumption may result in a corresponding human outbreak. Since 2003, such animal outbreaks have been monitored to predict and prevent Ebola outbreaks in humans.]
Corpses, burial
If a person with Ebola disease dies, direct contact with the body should be avoided.burial ritual
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
s, which may have included making various direct contacts with a dead body, require reformulation so that they consistently maintain a proper protective barrier between the dead body and the living.
Transport, travel, contact
Transportation crews are instructed to follow a certain isolation procedure, should anyone exhibit symptoms resembling EVD.[ In October 2014, the CDC defined four risk levels used to determine the level of 21-day monitoring for symptoms and restrictions on public activities.][
* having been in a country with widespread Ebola disease transmission and having no known exposure (low risk); or having been in that country more than 21 days ago (no risk)
* encounter with a person showing symptoms; but not within three feet of the person with Ebola without wearing PPE; and no direct contact with body fluids
* having had brief skin contact with a person showing symptoms of Ebola disease when the person was believed to be not very contagious (low risk)
* in countries without widespread Ebola disease transmission: direct contact with a person showing symptoms of the disease while wearing PPE (low risk)
* contact with a person with Ebola disease before the person was showing symptoms (no risk).
The CDC recommends monitoring for the symptoms of Ebola disease for those both at "low risk" and at higher risk.][
]
Laboratory
In laboratories where diagnostic testing is carried out, biosafety level 4-equivalent containment is required.[
]
Isolation
Isolation refers to separating those who are sick from those who are not. Quarantine refers to separating those who may have been exposed to a disease until they either show signs of the disease or are no longer at risk. Quarantine, also known as enforced isolation, is usually effective in decreasing spread.
Contact tracing
Contact tracing is considered important to contain an outbreak. It involves finding everyone who had close contact with infected individuals and monitoring them for signs of illness for 21 days. If any of these contacts comes down with the disease, they should be isolated, tested and treated. Then the process is repeated, tracing the contacts' contacts.
Management
two treatments ( atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab and ansuvimab
Ansuvimab, sold under the brand name Ebanga, is a monoclonal antibody medication for the treatment of ''Zaire ebolavirus'' (Ebolavirus) infection.
The most common symptoms include fever, tachycardia (fast heart rate), diarrhea, vomiting, hypote ...
) are associated with improved outcomes.[ The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advises people to be careful of advertisements making unverified or fraudulent claims of benefits supposedly gained from various anti-Ebola products.]indication
Indication may refer to:
* A synonym for sign
* Human interface, highlighting the single object pointed to as a cursor is moved, without any other user action such as clicking, is indication
* Indication (medicine). A valid reason to use a certain ...
for the treatment of infection caused by ''Zaire ebolavirus''.[ ]
Standard support
 Treatment is primarily supportive in nature.
Treatment is primarily supportive in nature.[ Rehydration may be via the oral or ]intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
route.[ These measures may include pain management, and treatment for nausea, fever, and anxiety.][ The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends avoiding aspirin or ]ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arte ...
for pain management, due to the risk of bleeding associated with these medications.
Blood products such as packed red blood cells, platelets, or fresh frozen plasma may also be used.[ Other regulators of coagulation have also been tried including ]heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
in an effort to prevent disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts o ...
and clotting factors to decrease bleeding.[ Antimalarial medications and antibiotics are often used before the diagnosis is confirmed,][ though there is no evidence to suggest such treatment helps. Several experimental treatments are being studied.]
Intensive care
Intensive care is often used in the developed world.Dialysis Dialysis may refer to:
*Dialysis (chemistry), a process of separating molecules in solution
**Electrodialysis, used to transport salt ions from one solution to another through an ion-exchange membrane under the influence of an applied electric pote ...
may be needed for kidney failure, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), also known as extracorporeal life support (ECLS), is an extracorporeal technique of providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequat ...
may be used for lung dysfunction.
Prognosis
EVD has a risk of death in those infected of between 25% and 90%.Republic of the Congo
The Republic of the Congo (french: République du Congo, ln, Republíki ya Kongó), also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply either Congo or the Congo, is a country located in the western coast of Central Africa to the w ...
outbreak.
Early admission significantly increases survival rates
Death, if it occurs, follows typically six to sixteen days after symptoms appear and is often due to low blood pressure from fluid loss.[ Early supportive care to prevent dehydration may reduce the risk of death.]joint pains
Arthralgia (from Greek ''arthro-'', joint + ''-algos'', pain) literally means ''joint pain''. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication.
According to MeSH, ...
, fatigue, hearing loss, mood and sleep disturbances, muscular pain
Myalgia (also called muscle pain and muscle ache in layman's terms) is the medical term for muscle pain. Myalgia is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another lik ...
, abdominal pain, menstrual abnormalities, miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical lo ...
s, skin peeling
Desquamation occurs when the outermost layer of a tissue, such as the skin, is shed. The term is . Physiologic desquamation
Keratinocytes are the predominant cells of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Living keratinocytes reside in ...
, or hair loss.meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
has been reported many months after recovery, .
A study of 44 survivors of the Ebola virus in Sierra Leone reported musculoskeletal pain in 70%, headache in 48%, and eye problems in 14%.
Epidemiology
The disease typically occurs in outbreaks in tropical regions of Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
.Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
, Sierra Leone, and Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
.
1976
Sudan
 The first known outbreak of EVD was identified only after the fact. It occurred between June and November 1976, in Nzara, South Sudan
The first known outbreak of EVD was identified only after the fact. It occurred between June and November 1976, in Nzara, South SudanSudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
), and was caused by Sudan virus (SUDV). The Sudan outbreak infected 284 people and killed 151. The first identifiable case in Sudan occurred on 27 June in a storekeeper in a cotton factory in Nzara
Nzara is a town in Western Equatoria State. It lies to the northwest of Yambio by road, and is 25 km (15m) from the border with the DR Congo.
Nzara was industrial center of the Azande Scheme also known as, Equatoria Project Scheme during ...
, who was hospitalised on 30 June and died on 6 July.
Zaire
 On 26 August 1976, the second outbreak of EVD began in Yambuku, a small rural village in Mongala District in northern Zaire (now known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo).
On 26 August 1976, the second outbreak of EVD began in Yambuku, a small rural village in Mongala District in northern Zaire (now known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo).Mabalo Lokela
Yambuku is a small village in Mongala Province in northern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was the center of the first documented outbreak of Ebola virus disease, in 1976, with the World Health Organization identifying a man from Yambuku as th ...
, who began displaying symptoms on 26 August 1976.Ebola River
The Ebola River ( or ), also commonly known by its indigenous name Legbala, is the headstream of the Mongala River, a tributary of the Congo River, in northern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is roughly in length.
The name ''Ebola'' is a F ...
between 12 and 22 August. He was originally believed to have malaria and was given quinine. However, his symptoms continued to worsen, and he was admitted to Yambuku Mission Hospital on 5 September. Lokela died on 8 September 14 days after he began displaying symptoms.Mobutu Sese Seko
Mobutu Sese Seko Kuku Ngbendu Wa Za Banga (; born Joseph-Désiré Mobutu; 14 October 1930 – 7 September 1997) was a Congolese politician and military officer who was the president of Zaire from 1965 to 1997 (known as the Democratic Republic o ...
declared the entire region, including Yambuku and the country's capital, Kinshasa
Kinshasa (; ; ln, Kinsásá), formerly Léopoldville ( nl, Leopoldstad), is the capital and largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Once a site of fishing and trading villages situated along the Congo River, Kinshasa is now one o ...
, a quarantine zone. No-one was permitted to enter or leave the area, and roads, waterways, and airfields were placed under martial law. Schools, businesses and social organisations were closed.Jean-Jacques Muyembe-Tamfum
Jean-Jacques Muyembe is a Congolese microbiologist. He is the general director of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Institut National pour la Recherche Biomedicale (''INRB''). He was part of team at the Yambuku Catholic Mission Hospital that ...
, one of the discoverers of Ebola. Muyembe took a blood sample from a Belgian nun; this sample would eventually be used by Peter Piot to identify the previously unknown Ebola virus. Muyembe was also the first scientist to come into direct contact with the disease and survive. Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), including Piot, co-discoverer of Ebola, later arrived to assess the effects of the outbreak, observing that "the whole region was in panic."[
During this outbreak, Ngoy Mushola recorded the first clinical description of EVD in Yambuku, where he wrote the following in his daily log: "The illness is characterised with a high temperature of about , ]haematemesis
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood. It is always an important sign. It can be confused with hemoptysis (coughing up blood) or epistaxis (nosebleed), which are more common. The source is generally the upper gastrointestinal tract, typically abo ...
, diarrhoea with blood, retrosternal abdominal pain, prostration with 'heavy' articulations, and rapid evolution death after a mean of three days."
The virus responsible for the initial outbreak, first thought to be the Marburg virus
Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the ''Filoviridae'' family of viruses and a member of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', genus ''Marburgvirus''. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic f ...
, was later identified as a new type of virus related to the genus ''Marburgvirus
The genus ''Marburgvirus'' is the taxonomic home of ''Marburg marburgvirus'', whose members are the two known marburgviruses, Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV). Both viruses cause Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primate ...
''. Virus strain samples isolated from both outbreaks were named "Ebola virus" after the Ebola River
The Ebola River ( or ), also commonly known by its indigenous name Legbala, is the headstream of the Mongala River, a tributary of the Congo River, in northern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is roughly in length.
The name ''Ebola'' is a F ...
, near the first-identified viral outbreak site in Zaire.[ Reports conflict about who initially coined the name: either Karl Johnson of the American CDC team][
]
1995–2014
 The second major outbreak occurred in Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo, DRC), in 1995, affecting 315 and killing 254.
The second major outbreak occurred in Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo, DRC), in 1995, affecting 315 and killing 254.bush meat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are hunted for human consumption, most often referring to the meat of game in Africa. Bushmeat represents
a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity for inhabitants of humid tro ...
hunted by local villagers around the towns of Isiro
Isiro (pronounced ) is the capital of Haut-Uele Province in the northeastern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It lies between the equatorial forest and the savannah and its main resource is coffee. Isiro's population is estimated a ...
and Viadana.
2013–2016 West Africa
 In March 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a major Ebola outbreak in
In March 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a major Ebola outbreak in Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
, a West African nation.[
] The disease rapidly spread to the neighbouring countries of Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and Sierra Leone. It was the largest Ebola outbreak ever documented, and the first recorded in the region. In September 2014, it was estimated that the countries' capacity for treating Ebola patients was insufficient by the equivalent of 2,122 beds; by December there were a sufficient number of beds to treat and isolate all reported Ebola cases, although the uneven distribution of cases was causing serious shortfalls in some areas.
In September 2014, it was estimated that the countries' capacity for treating Ebola patients was insufficient by the equivalent of 2,122 beds; by December there were a sufficient number of beds to treat and isolate all reported Ebola cases, although the uneven distribution of cases was causing serious shortfalls in some areas.
2014 spread outside West Africa
On 19 September, Eric Duncan flew from his native Liberia to Texas; five days later he began showing symptoms and visited a hospital but was sent home. His condition worsened and he returned to the hospital on 28 September, where he died on 8 October. Health officials confirmed a diagnosis of Ebola on 30 September – the first case in the United States.
In early October, Teresa Romero, a 44-year-old Spanish nurse, contracted Ebola after caring for a priest who had been repatriated from West Africa. This was the first transmission of the virus to occur outside Africa. Romero tested negative for the disease on 20 October, suggesting that she may have recovered from Ebola infection.
On 12 October, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed that a nurse in Texas, Nina Pham
Four laboratory-confirmed cases of Ebola virus disease (commonly known as "Ebola") occurred in the United States in 2014. Eleven cases were reported, including these four cases and seven cases medically evacuated from other countries. The first ...
, who had treated Duncan tested positive for the Ebola virus, the first known case of transmission in the United States.high-level isolation unit
In hospitals and other medical facilities, an isolation ward is a separate ward used to isolate patients with infectious diseases. Several wards for individual patients are usually placed together in an isolation unit.
Design
In an isolation un ...
at the Royal Free Hospital
The Royal Free Hospital (also known simply as the Royal Free) is a major teaching hospital in the Hampstead area of the London Borough of Camden. The hospital is part of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, which also runs services at Barn ...
in London for longer-term treatment.
2017 Democratic Republic of the Congo
On 11 May 2017, the DRC Ministry of Public Health notified the WHO about an outbreak of Ebola. Four people died, and four people survived; five of these eight cases were laboratory-confirmed. A total of 583 contacts were monitored. On 2 July 2017, the WHO declared the end of the outbreak.
2018 Équateur province
On 14 May 2018, the World Health Organization reported that "the Democratic Republic of Congo reported 39 suspected, probable or confirmed cases of Ebola between 4 April and 13 May, including 19 deaths."[
]
2018–2020 Kivu
On 1 August 2018, the world's 10th Ebola outbreak was declared in North Kivu province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was the first Ebola outbreak in a military conflict zone, with thousands of refugees in the area. By November 2018, nearly 200 Congolese had died of Ebola, about half of them from the city of Beni, where armed groups are fighting over the region's mineral wealth, impeding medical relief efforts.
By March 2019, this became the second largest Ebola outbreak ever recorded, with more than 1,000 cases and insecurity continuing to be the major resistance to providing an adequate response.
2020 Équateur province
On 1 June 2020, the Congolese health ministry announced a new DRC outbreak of Ebola in Mbandaka, Équateur Province, a region along the Congo River. Genome sequencing suggests that this outbreak, the 11th outbreak since the virus was first discovered in the country in 1976, is unrelated to the one in North Kivu Province or the previous outbreak in the same area in 2018. It was reported that six cases had been identified; four of the people had died. It is expected that more people will be identified as surveillance activities increase. By 15 June the case count had increased to 17 with 11 deaths, with more than 2,500 people having been vaccinated. The 11th EVD outbreak was officially declared over on 19 November 2020. By the time the Équateur outbreak ended, it had 130 confirmed cases with 75 recoveries and 55 deaths.
2021
North Kivu
On 7 February 2021, the Congolese health ministry announced a new case of Ebola near Butembo, North Kivu detected a day before. The case was a 42-year-old woman who had symptoms of Ebola in Biena on 1 February 2021. A few days after, she died in a hospital in Butembo. The WHO said that more than 70 people with contact with the woman had been tracked.
Guinea
In February 2021, Dr Sakoba Keita, head of Guinea's national health agency confirmed that three people had died of Ebola in the south-eastern region near the city of Nzérékoré. A further five people also tested positive. Keita also confirmed more testing was underway, and attempts to trace and isolate further cases had begun. On 14 February, the Guinean government declared an Ebola epidemic. The outbreak may have started following reactivation of a latent case in a survivor of an earlier outbreak.
Ivory Coast
On 14 August 2021, The Ministry of Health of Cote d’Ivoire
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
confirmed the country's first case of Ebola since 1994. This came after the Institut Pasteur in Cote d'Ivoire confirmed the Ebola Virus Disease in samples collected from a patient, who was hospitalized in the commercial capital of Abidjan, after arriving from Guinea.
However, on 31 August 2021, the WHO found that, after further tests in a laboratory in Lyon, the patient did not have Ebola. The cause of her disease is still being analyzed.
2022
On 23 April 2022, a case of Ebola was confirmed in the DRC in the Equateur province. The case was a 31-year-old man whose symptoms began on 5 April, but did not seek treatment for over a week. On 21 April, he was admitted to an Ebola treatment centre and died later that day. By 24 May 2022, there were 5 recorded deaths in the DRC. On 15 August, the fifth case was buried, and the outbreak was declared over, 42 days after, on 4 July 2022.
In September 2022, Uganda reported 7 cases infected with the Ebola Sudan strain, but by mid-October the count had increased to 63.
In November 2022 (present), the outbreak in Uganda continued - still without a vaccine.
Society and culture
Weaponisation
''Ebolavirus'' is classified as a biosafety level 4 agent, as well as a Category A bioterrorism agent by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.Biopreparat
The All-Union Science Production Association Biopreparat (russian: Биопрепарат, p=bʲɪəprʲɪpɐˈrat, lit: "biological preparation") was the Soviet agency created in April 1974, which spearheaded the largest and most sophisticated ...
for such use, but might be difficult to prepare as a weapon of mass destruction because the virus becomes ineffective quickly in open air.
Literature
Richard Preston's 1995 best-selling book, '' The Hot Zone'', dramatised the Ebola outbreak in Reston, Virginia.
William Close's 1995 ''Ebola: A Documentary Novel of Its First Explosion'' and 2002 ''Ebola: Through the Eyes of the People'' focused on individuals' reactions to the 1976 Ebola outbreak in Zaire.
Tom Clancy's 1996 novel, ''Executive Orders
''Executive Orders'' is a techno-thriller novel, written by Tom Clancy and released on July 1, 1996. It picks up immediately where the final events of ''Debt of Honor'' (1994) left off, and features now-U.S. President Jack Ryan as he tries to d ...
'', involves a Middle Eastern terrorist attack on the United States using an airborne form of a deadly Ebola virus strain named "Ebola Mayinga" (see Mayinga N'Seka).
As the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa developed in 2014, a number of popular self-published and well-reviewed books containing sensational and misleading information about the disease appeared in electronic and printed formats. The authors of some such books admitted that they lacked medical credentials and were not technically qualified to give medical advice. The World Health Organization and the United Nations stated that such misinformation had contributed to the spread of the disease.
Other animals
Wild animals
Ebola has a high mortality rate among primates.
Domestic animals
In 2012, it was demonstrated that the virus can travel without contact from pigs to nonhuman primates, although the same study failed to achieve transmission in that manner between primates.
Reston virus
In late 1989, Hazelton Research Products' Reston Quarantine Unit in Reston, Virginia
Reston is a census-designated place in Fairfax County, Virginia and a principal city of the Washington metropolitan area. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, Reston's population was 63,226.
Founded in 1964, Reston was influenced by the Garden City movem ...
, had an outbreak of fatal illness amongst certain lab monkeys. This lab outbreak was initially diagnosed as simian haemorrhagic fever virus
''Deltaarterivirus hemfev'', formerly ''Simian hemorrhagic fever virus'' or ''simian haemorrhagic fever virus'' (SHFV), is a highly pathogenic virus in monkeys. It is a positive-stranded RNA virus classified in the family ''Arteriviridae''. It i ...
(SHFV) and occurred amongst a shipment of crab-eating macaque
The crab-eating macaque (''Macaca fascicularis''), also known as the long-tailed macaque and referred to as the cynomolgus monkey in laboratories, is a cercopithecine primate native to Southeast Asia. A species of macaque, the crab-eating macaqu ...
monkeys imported from the Philippines. Hazelton's veterinary pathologist in Reston sent tissue samples from dead animals to the United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID) at Fort Detrick, Maryland
Fort Detrick () is a United States Army Futures Command installation located in Frederick, Maryland. Historically, Fort Detrick was the center of the U.S. biological weapons program from 1943 to 1969. Since the discontinuation of that program, i ...
, where an ELISA test indicated the antibodies present in the tissue were a response to Ebola virus and not SHFV.filoviruses
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known re ...
similar in appearance, in crystalloid aggregates and as single filaments with a shepherd's hook, to Ebola in the tissue samples sent from Hazelton Research Products' Reston Quarantine Unit.Reston ebolavirus
Reston virus (RESTV) is one of six known viruses within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Reston virus causes Ebola virus disease in non-human primates; unlike the other five ebolaviruses, it is not known to cause disease in humans, but has caused asymp ...
'' (RESTV) after the location of the incident.symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an disease, illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormali ...
of the disease.
Research
Treatments
 , no medication has been proven safe and effective for treating Ebola. By the time the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa began in 2013, there were at least nine different candidate treatments. Several trials were conducted in late 2014, and early 2015, but some were abandoned due to lack of efficacy or lack of people to study.
, two experimental treatments known as atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab and
, no medication has been proven safe and effective for treating Ebola. By the time the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa began in 2013, there were at least nine different candidate treatments. Several trials were conducted in late 2014, and early 2015, but some were abandoned due to lack of efficacy or lack of people to study.
, two experimental treatments known as atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab and ansuvimab
Ansuvimab, sold under the brand name Ebanga, is a monoclonal antibody medication for the treatment of ''Zaire ebolavirus'' (Ebolavirus) infection.
The most common symptoms include fever, tachycardia (fast heart rate), diarrhea, vomiting, hypote ...
were found to be 90% effective.
Diagnostic tests
The diagnostic tests currently available require specialised equipment and highly trained personnel. Since there are few suitable testing centres in West Africa, this leads to delay in diagnosis.
On 29 November 2014, a new 15-minute Ebola test was reported that if successful, "not only gives patients a better chance of survival, but it prevents transmission of the virus to other people." The new equipment, about the size of a laptop and solar-powered, allows testing to be done in remote areas.
On 29 December 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the LightMix Ebola Zaire rRT-PCR test for patients with symptoms of Ebola.
Disease models
Animal models and in particular non-human primates are being used to study different aspects of Ebola virus disease. Developments in organ-on-a-chip
An organ-on-a-chip (OOC) is a multi-channel 3-D microfluidic cell culture, integrated circuit (chip) that simulates the activities, mechanics and physiological response of an entire organ or an organ system, a type of artificial organ. It constitu ...
technology have led to a chip-based model for Ebola haemorrhagic syndrome.
See also
* Bibliography of Ebola
Notes
References
* ''The article uses public domain text from the CDC as cited.''
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Ebola (Ebola Virus Disease)
nbsp;– Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Viral Special Pathogens Branch.
Health topics: Ebola virus disease
nbsp;– World Health Organization.
Videos: Ebola outbreak response
nbsp;– World Health Organization.
*
Ebola: What You Need to Know
nbsp;– '' Scientific American'' articles related to Ebola; note these are general reading articles, they are not scientific peer-reviewed research articles.
{{Authority control
Animal viral diseases
Arthropod-borne viral fevers and viral haemorrhagic fevers
Articles containing video clips
Bat virome
Biological weapons
Health in Africa
Hemorrhagic fevers
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate
Sexually transmitted diseases and infections
Tropical diseases
Virus-related cutaneous conditions
West African Ebola virus epidemic
Wikipedia pages referenced by the press
Zoonoses
so:Ebola virus disease

 Ebolaviruses contain single-stranded, non-infectious
Ebolaviruses contain single-stranded, non-infectious 
 It is believed that between people, Ebola disease spreads only by direct contact with the blood or other body fluids of a person who has developed symptoms of the disease. Body fluids that may contain Ebola viruses include saliva, mucus, vomit, feces, sweat, tears, breast milk, urine and semen. The WHO states that only people who are very sick are able to spread Ebola disease in
It is believed that between people, Ebola disease spreads only by direct contact with the blood or other body fluids of a person who has developed symptoms of the disease. Body fluids that may contain Ebola viruses include saliva, mucus, vomit, feces, sweat, tears, breast milk, urine and semen. The WHO states that only people who are very sick are able to spread Ebola disease in  Community awareness of the benefits on survival chances of admitting cases early is important for the infected and infection control
Community awareness of the benefits on survival chances of admitting cases early is important for the infected and infection control
 People who care for those infected with Ebola should wear protective clothing including masks, gloves, gowns and goggles. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommend that the protective gear leaves no skin exposed. These measures are also recommended for those who may handle objects contaminated by an infected person's body fluids. In 2014, the CDC began recommending that medical personnel receive training on the proper suit-up and removal of personal protective equipment (PPE); in addition, a designated person, appropriately trained in biosafety, should be watching each step of these procedures to ensure they are done correctly. In Sierra Leone, the typical training period for the use of such safety equipment lasts approximately 12 days.
In 2022 in Uganda, lighter personal protection equipment has become available as well as possibilities to monitor and communicate with patients from windows in the treatment tents until it is necessary to enter if e.g. a patient's oxygen levels drop.
People who care for those infected with Ebola should wear protective clothing including masks, gloves, gowns and goggles. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommend that the protective gear leaves no skin exposed. These measures are also recommended for those who may handle objects contaminated by an infected person's body fluids. In 2014, the CDC began recommending that medical personnel receive training on the proper suit-up and removal of personal protective equipment (PPE); in addition, a designated person, appropriately trained in biosafety, should be watching each step of these procedures to ensure they are done correctly. In Sierra Leone, the typical training period for the use of such safety equipment lasts approximately 12 days.
In 2022 in Uganda, lighter personal protection equipment has become available as well as possibilities to monitor and communicate with patients from windows in the treatment tents until it is necessary to enter if e.g. a patient's oxygen levels drop.
 Treatment is primarily supportive in nature. Early supportive care with rehydration and symptomatic treatment improves survival. Rehydration may be via the oral or
Treatment is primarily supportive in nature. Early supportive care with rehydration and symptomatic treatment improves survival. Rehydration may be via the oral or  The first known outbreak of EVD was identified only after the fact. It occurred between June and November 1976, in Nzara, South Sudan (then part of
The first known outbreak of EVD was identified only after the fact. It occurred between June and November 1976, in Nzara, South Sudan (then part of  On 26 August 1976, the second outbreak of EVD began in Yambuku, a small rural village in Mongala District in northern Zaire (now known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo). This outbreak was caused by EBOV, formerly designated ''Zaire ebolavirus'', a different member of the genus ''Ebolavirus'' than in the first Sudan outbreak. The first person infected with the disease was the village school's headmaster
On 26 August 1976, the second outbreak of EVD began in Yambuku, a small rural village in Mongala District in northern Zaire (now known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo). This outbreak was caused by EBOV, formerly designated ''Zaire ebolavirus'', a different member of the genus ''Ebolavirus'' than in the first Sudan outbreak. The first person infected with the disease was the village school's headmaster  The second major outbreak occurred in Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo, DRC), in 1995, affecting 315 and killing 254.
In 2000, Uganda had an outbreak infecting 425 and killing 224; in this case, the Sudan virus was found to be the Ebola species responsible for the outbreak.
In 2003, an outbreak in the DRC infected 143 and killed 128, a 90% death rate, the highest of a genus ''Ebolavirus'' outbreak to date.
In 2004, a Russian scientist died from Ebola after sticking herself with an infected needle.
Between April and August 2007, a fever epidemic in a four-village region of the DRC was confirmed in September to have been cases of Ebola. Many people who attended the recent funeral of a local village chief died. The 2007 outbreak eventually infected 264 individuals and killed 187.
On 30 November 2007, the Uganda Ministry of Health confirmed an outbreak of Ebola in the Bundibugyo District in Western Uganda. After confirming samples tested by the United States National Reference Laboratories and the Centers for Disease Control, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed the presence of a new species of genus ''Ebolavirus'', which was tentatively named Bundibugyo. The WHO reported 149 cases of this new strain and 37 of those led to deaths.
The WHO confirmed two small outbreaks in Uganda in 2012, both caused by the Sudan variant. The first outbreak affected seven people, killing four, and the second affected 24, killing 17.
On 17 August 2012, the Ministry of Health of the DRC reported an outbreak of the Ebola-Bundibugyo variant in the eastern region. Other than its discovery in 2007, this was the only time that this variant has been identified as responsible for an outbreak. The WHO revealed that the virus had sickened 57 people and killed 29. The probable cause of the outbreak was tainted
The second major outbreak occurred in Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo, DRC), in 1995, affecting 315 and killing 254.
In 2000, Uganda had an outbreak infecting 425 and killing 224; in this case, the Sudan virus was found to be the Ebola species responsible for the outbreak.
In 2003, an outbreak in the DRC infected 143 and killed 128, a 90% death rate, the highest of a genus ''Ebolavirus'' outbreak to date.
In 2004, a Russian scientist died from Ebola after sticking herself with an infected needle.
Between April and August 2007, a fever epidemic in a four-village region of the DRC was confirmed in September to have been cases of Ebola. Many people who attended the recent funeral of a local village chief died. The 2007 outbreak eventually infected 264 individuals and killed 187.
On 30 November 2007, the Uganda Ministry of Health confirmed an outbreak of Ebola in the Bundibugyo District in Western Uganda. After confirming samples tested by the United States National Reference Laboratories and the Centers for Disease Control, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed the presence of a new species of genus ''Ebolavirus'', which was tentatively named Bundibugyo. The WHO reported 149 cases of this new strain and 37 of those led to deaths.
The WHO confirmed two small outbreaks in Uganda in 2012, both caused by the Sudan variant. The first outbreak affected seven people, killing four, and the second affected 24, killing 17.
On 17 August 2012, the Ministry of Health of the DRC reported an outbreak of the Ebola-Bundibugyo variant in the eastern region. Other than its discovery in 2007, this was the only time that this variant has been identified as responsible for an outbreak. The WHO revealed that the virus had sickened 57 people and killed 29. The probable cause of the outbreak was tainted  In March 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a major Ebola outbreak in
In March 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a major Ebola outbreak in  , no medication has been proven safe and effective for treating Ebola. By the time the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa began in 2013, there were at least nine different candidate treatments. Several trials were conducted in late 2014, and early 2015, but some were abandoned due to lack of efficacy or lack of people to study.
, two experimental treatments known as atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab and
, no medication has been proven safe and effective for treating Ebola. By the time the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa began in 2013, there were at least nine different candidate treatments. Several trials were conducted in late 2014, and early 2015, but some were abandoned due to lack of efficacy or lack of people to study.
, two experimental treatments known as atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab and