|
Yambuku
Yambuku is a small village in Mongala Province in northern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was the center of the first documented outbreak of Ebola virus disease, in 1976, with the World Health Organization identifying a man from Yambuku as the index case. It is northeast of the capital city of Kinshasa. During the 1976 Zaire Ebola virus outbreak, the village had no running water or electricity. The village had a hospital but no radio, phone, or ambulances, and communication was by motorbike messenger. See also * Western African Ebola virus epidemic * Zaire ebolavirus ''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and ot ... References {{DRC-geo-stub Populated places in Mongala Ebola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1976 Zaire Ebola Virus Outbreak
In August–November 1976, an outbreak of Ebola virus disease occurred in Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo). The first recorded case was from Yambuku, a small village in Mongala District, northeast of the capital city of Kinshasa. The virus responsible for the initial outbreak, named after the nearby Ebola River, was first thought to be Marburg virus but was later identified as a new type of virus related to the genus ''Marburgvirus''. A total of 318 cases and 280 deaths (an 88% fatality rate) resulted from this outbreak, which, along with an outbreak in Sudan that had begun a few weeks previously, were the first outbreaks of Ebola ever recorded. History The people of north-central Zaire were most heavily affected by this specific epidemic. This area is located within the Bumba Zone in the Equator Region, which consists mostly of tropical rainforests in the biome. In 1976, there were approximately 275,000 people in the entire Bumba Zone, including 35,000 Zaire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
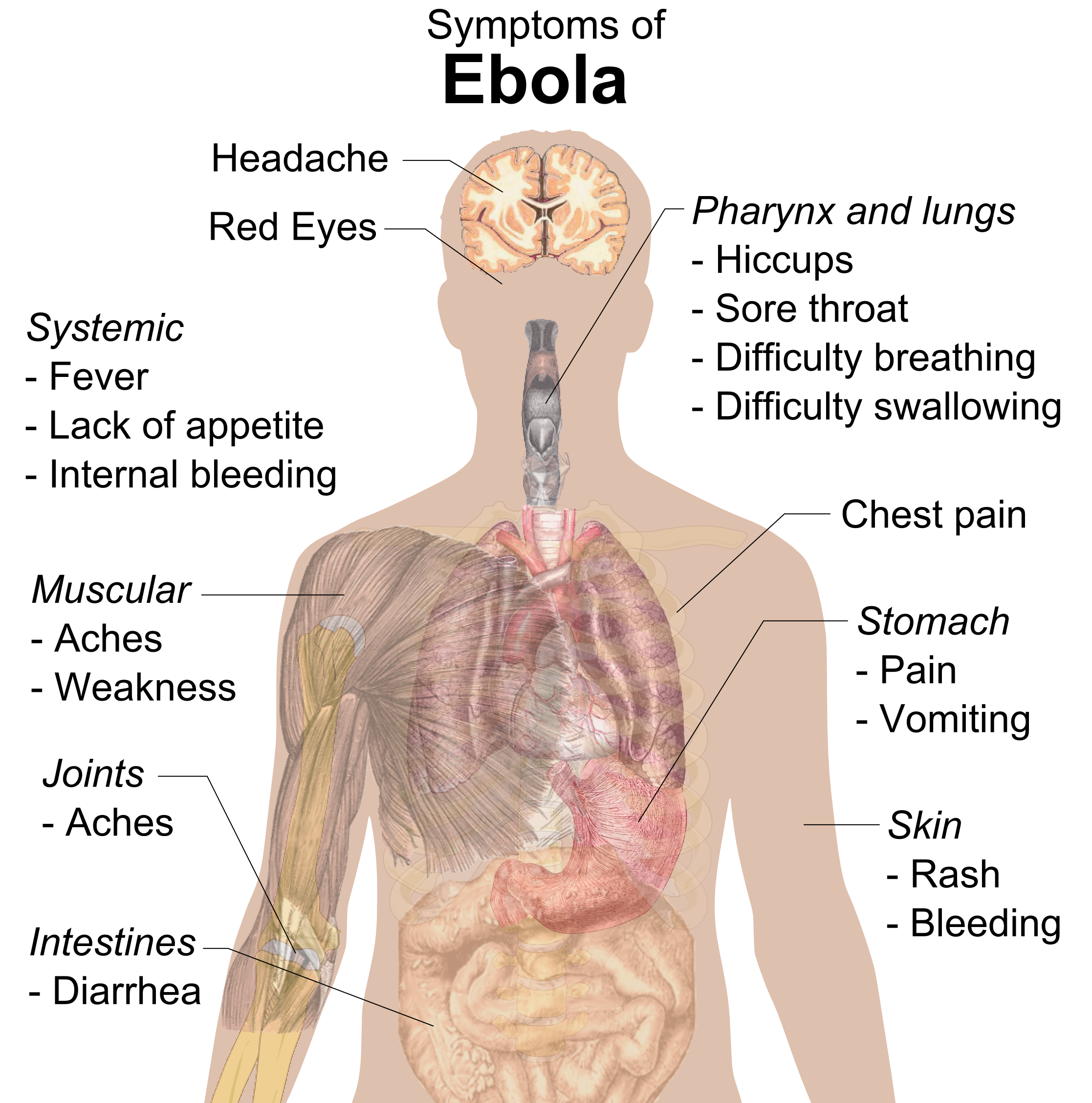
Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or from contact with items that have recently been conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaire Ebolavirus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned to the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of the species are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongala
Mongala is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Mongala, Équateur, Nord-Ubangi, Sud-Ubangi, and Tshuapa provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Équateur province. Mongala was formed from the Mongala District whose town of Lisala was elevated to capital city of the new province. Location Mongala is located at the northwest of the country on the Congo River, and borders the provinces of Tshopo, Bas-Uele, Nord-Ubangi, Sud-Ubangi, Équateur and Tshuapa. It is divided into three territories: * Bongandanga * Bumba, major town and site of a former secessionist state (1963) in the province. * Lisala The province includes the village of Yambuku. History From 1963–1966, Mongala Province was known as Moyen-Congo. However, under Mobutu, the province was reintegrated into the former Équateur province where it was administered as Mongala District, until 2015. Presidents (later governors) of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in Central Africa. It is bordered to the northwest by the Republic of the Congo, to the north by the Central African Republic, to the northeast by South Sudan, to the east by Uganda, Rwanda, and Burundi, and by Tanzania (across Lake Tanganyika), to the south and southeast by Zambia, to the southwest by Angola, and to the west by the South Atlantic Ocean and the Cabinda exclave of Angola. By area, it is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 108 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the nation's economic center. Centered on the Cong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of The Democratic Republic Of The Congo
Article 2 of the Constitution of the Democratic Republic of the Congo divides the country into the capital city of Kinshasa and 25 named provinces. It also gives the capital the status of a province. Therefore, in many contexts Kinshasa is regarded as the 26th province. List History When Belgium annexed the Belgian Congo as a colony in November 1908, it was initially organised into 22 districts. Ten western districts were administered directly by the main colonial government, while the eastern part of the colony was administered under two vice-governments: eight northeastern districts formed Orientale Province, and four southeastern districts formed Katanga. In 1919, the colony was organised into four provinces: * Congo-Kasaï (five southwestern districts), * Équateur (five northwestern districts), * Orientale Province and Katanga (previous vice-governments). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bumba, Democratic Republic Of The Congo
Bumba is a town and river port in Mongala Province, in the northern part of the Democratic Republic of Congo, lying on the River Congo. As of 2009 it had an estimated population of 107,626. The town has neither electricity nor running water. Transport The narrow gauge Vicicongo line from Bumba to Isiro as of 2007 is not operational (see Transport in DR Congo). The town is served by Bumba Airport. The Congo River serves as the main transportation artery. Notable People * Marcel Lihau See also * List of railway stations in the Democratic Republic of the Congo * Dr. Ngoy Mushola Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after bec ... * AS Lokole References Populated places in Mongala {{DRCongo-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care coverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Case
The index case or patient zero is the first documented patient in a disease epidemic within a population, or the first documented patient included in an epidemiological study. It can also refer to the first case of a condition or syndrome (not necessarily contagious) to be described in the medical literature, whether or not the patient is thought to be the first person affected. An index case can achieve the status of a "classic" case study in the literature, as did Phineas Gage, the first known person to exhibit a definitive personality change as a result of a brain injury. Term The index case may or may not indicate the source of the disease, the possible spread, or which reservoir holds the disease in between outbreaks, but may bring awareness of an emerging outbreak. Earlier cases may or may not be found and are labeled primary or coprimary, secondary, tertiary, etc. The term primary case can only apply to infectious diseases that spread from human to human, and refers to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinshasa
Kinshasa (; ; ln, Kinsásá), formerly Léopoldville ( nl, Leopoldstad), is the capital and largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Once a site of fishing and trading villages situated along the Congo River, Kinshasa is now one of the world's fastest growing megacities. The city of Kinshasa is also one of the DRC's 26 provinces. Because the administrative boundaries of the city-province cover a vast area, over 90 percent of the city-province's land is rural in nature, and the urban area occupies a small but expanding section on the western side. Kinshasa is Africa's third-largest metropolitan area after Cairo and Lagos. It is also the world's largest nominally Francophone urban area, with French being the language of government, education, media, public services and high-end commerce in the city, while Lingala is used as a ''lingua franca'' in the street. Kinshasa hosted the 14th Francophonie Summit in October 2012. Residents of Kinshasa are known as ''Kinoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western African Ebola Virus Epidemic
The 2013–2016 epidemic of Ebola virus disease, centered in Western Africa, was the most widespread outbreak of the disease in history. It caused major loss of life and socioeconomic disruption in the region, mainly in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone. The first cases were recorded in Guinea in December 2013; later, the disease spread to neighbouring Liberia and Sierra Leone, with minor outbreaks occurring in Ebola virus disease in Nigeria, Nigeria and Mali. Secondary infections of medical workers occurred in the United States and Spain. In addition, isolated cases were recorded in Senegal, the United Kingdom and Italy. The number of cases peaked in October 2014 and then began to decline gradually, following the commitment of substantial international resources. It caused significant mortality, with a considerable case fatality rate. By the end of the epidemic, 28,616 people had been infected; of these, 11,310 had died, for a case-fatality rate of 40%. , the World Health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |