Prior Park on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Prior Park is a
 Allen acquired the stone quarries at Combe Down and Bathampton Down. The unique honey-coloured
Allen acquired the stone quarries at Combe Down and Bathampton Down. The unique honey-coloured 
 The house described by Pevsner as "the most ambitious and most complete re-creation of Palladio's villas on English soil" was designed by John Wood the Elder, however, Wood and his patron, Allen, quarrelled and completion of the project was overseen by Richard Jones, the clerk-of-works.
The plan consists of a
The house described by Pevsner as "the most ambitious and most complete re-creation of Palladio's villas on English soil" was designed by John Wood the Elder, however, Wood and his patron, Allen, quarrelled and completion of the project was overseen by Richard Jones, the clerk-of-works.
The plan consists of a
 The first park on the site was set out by
The first park on the site was set out by  The features in the gardens include a
The features in the gardens include a
Neo-Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
house that was designed by John Wood, the Elder
John Wood, the Elder (1704 – 23 May 1754) was an English architect, working mainly in Bath.
In 1740 he surveyed Stonehenge and the Stanton Drew stone circles. He later wrote extensively about Bladud and Neo-Druidism. Because of some ...
, and built in the 1730s and 1740s for Ralph Allen
Ralph Allen (1693 – 29 June 1764) was an entrepreneur and philanthropist, who was notable for his reforms to the British postal system.
Allen was born in Cornwall but moved to Bath to work in the post office, becoming the postmaster a ...
on a hill overlooking Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
, England. It has been designated as a Grade I listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
.
The house was built in part to demonstrate the properties of Bath stone
Bath Stone is an oolitic limestone comprising granular fragments of calcium carbonate. Originally obtained from the Combe Down and Bathampton Down Mines under Combe Down, Somerset, England. Its honey colouring gives the World Heritage City of ...
as a building material. The design followed work by Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio ( ; ; 30 November 1508 – 19 August 1580) was an Italian Renaissance architect active in the Venetian Republic. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily Vitruvius, is widely considered to be one of th ...
and was influenced by drawings originally made by Colen Campbell
Colen Campbell (15 June 1676 – 13 September 1729) was a pioneering Scottish architect and architectural writer, credited as a founder of the Georgian style. For most of his career, he resided in Italy and England. As well as his architectural ...
for Wanstead House
Wanstead House was a mansion built to replace the earlier Wanstead Hall. It was commissioned in 1715, completed in 1722 and demolished in 1825. Its gardens now form the municipal Wanstead Park in the London Borough of Redbridge.
History Construct ...
in Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G ...
as well as the twelve sided plan form of the Roman theatre (of which the house's natural setting reminded Wood). The main block had 15 bays and each of the wings 17 bays
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narr ...
each. The surrounding parkland had been laid out in 1100 but following the purchase of the land by Allen were established as a landscape garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a sty ...
. Features in the garden include a bridge covered by Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
arches, which is also Grade I listed.
Following Allen's death the estate passed down through his family. In 1828, Bishop Baines bought it for use as a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
College. The house was then extended and a chapel and gymnasium built by Henry Goodridge
Henry Edmund Goodridge (1797, Bath – 26 October 1864) was an English architect based in Bath. He worked from the early 1820s until the 1850s, using Classical, Italianate and Gothic styles.
Life
He was born in Bath in 1797 the son of James Goo ...
. The house is now used by Prior Park College
Prior Park College is a Mixed-sex education, mixed Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Public school (United Kingdom), public school for both day and boarding students. Situated on a hill overlooking the city of Bath, Somerset, Bath, Somerset, in s ...
and the surrounding parkland owned by the National Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
.
History
Construction
Ralph Allen
Ralph Allen (1693 – 29 June 1764) was an entrepreneur and philanthropist, who was notable for his reforms to the British postal system.
Allen was born in Cornwall but moved to Bath to work in the post office, becoming the postmaster a ...
, an entrepreneur and philanthropist, was notable for his reforms to the British postal system
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letters, and parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal syst ...
. He moved in 1710 to Bath, where he became a post office clerk, and at the age of 19, in 1712, became the Postmaster
A postmaster is the head of an individual post office, responsible for all postal activities in a specific post office. When a postmaster is responsible for an entire mail distribution organization (usually sponsored by a national government), ...
. In 1742 he was elected Mayor of Bath, and was the Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
for Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
between 1757 and 1764. The building in Lilliput Alley, Bath (now North Parade Passage), which he used as a post office, became his town house
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type of city residence ...
.
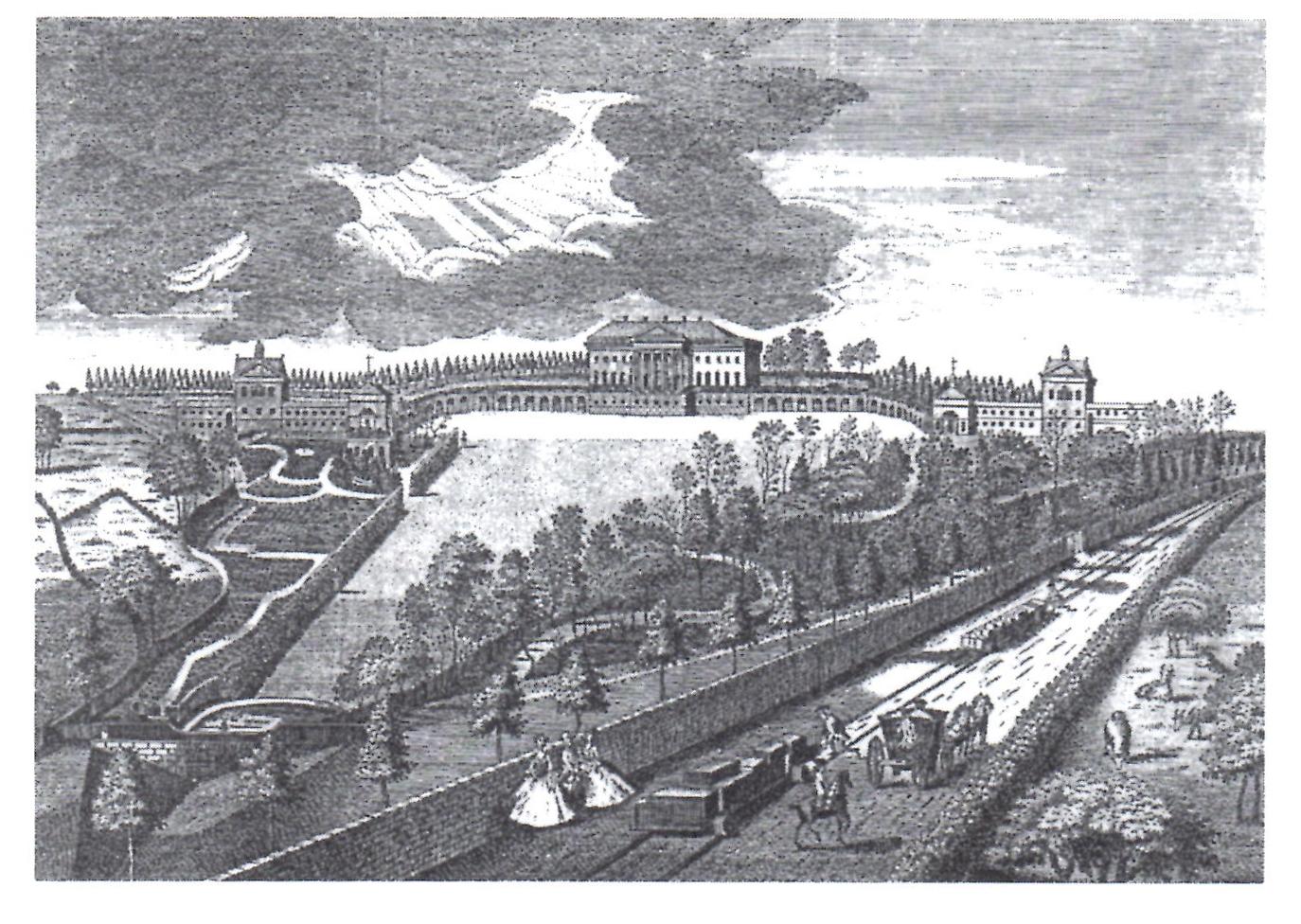
 Allen acquired the stone quarries at Combe Down and Bathampton Down. The unique honey-coloured
Allen acquired the stone quarries at Combe Down and Bathampton Down. The unique honey-coloured Bath stone
Bath Stone is an oolitic limestone comprising granular fragments of calcium carbonate. Originally obtained from the Combe Down and Bathampton Down Mines under Combe Down, Somerset, England. Its honey colouring gives the World Heritage City of ...
was used to build the Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
city, and as a result he made a second fortune. Allen instructed John Padmire to build a wooden wagon-way from his mine on Combe Down
Combe Down is a village on the outskirts of Bath, England in the Bath and North East Somerset unitary authority within the ceremonial county of Somerset.
Combe Down village consists predominantly of 18th and 19th century Bath stone-built villas ...
which carried the stone down the hill, now known as Ralph Allen Drive, which runs beside Prior Park, to a wharf he constructed at Bath Locks
Bath Locks () are a series of locks, now six locks, situated at the start of the Kennet and Avon Canal, at Bath, England.
Bath Bottom Lock, which is numbered as No 7 on the canal, is the meeting with the River Avon just south of Pulteney Bridge ...
on the Kennet and Avon Canal
The Kennet and Avon Canal is a waterway in southern England with an overall length of , made up of two lengths of navigable river linked by a canal. The name is used to refer to the entire length of the navigation rather than solely to the cent ...
for onward transport to London. An engraving of Prior Park, made in 1752 from a drawing by Anthony Walker and showing the railway passing the house, is the first known railway print. Following a failed bid to supply stone to buildings in London, Allen wanted a building which would show off the properties of Bath stone as a building material.
Hitherto, the quarry masons had always hewn stone roughly, providing blocks of varying size. Wood required stone blocks to be cut with crisp clean edges for his distinctive classical façades. The stone was extracted by the "room and pillar" method, by which chambers were dug out, leaving pillars of stone to support the roof. Bath stone is an Oolitic limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
comprising granular fragments of calcium carbonate laid down during the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
period (195 to 135 million years ago). An important feature of Bath stone is that it is a freestone, that is one that can be sawn or 'squared up' in any direction, unlike other rocks such as slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
, which has distinct layers. It was extensively used in the Roman and Medieval periods on domestic, ecclesiastical and civil engineering projects such as bridges.
John Wood, the Elder
John Wood, the Elder (1704 – 23 May 1754) was an English architect, working mainly in Bath.
In 1740 he surveyed Stonehenge and the Stanton Drew stone circles. He later wrote extensively about Bladud and Neo-Druidism. Because of some ...
was commissioned by Ralph Allen to build on the hill overlooking Bath: "To see all Bath, and for all Bath to see". Wood was born in Bath and is known for designing many of the streets and buildings of the city, such as The Circus (1754–68), St John's Hospital, (1727–28), Queen Square (1728–36), the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
(1740) and South Parades (1743–48), the Mineral Water Hospital
The Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases is a small, specialist NHS hospital on the Royal United Hospital (RUH) site in the northwestern outskirts of Bath, England.
The hospital was founded in 1738 as a general hospital for the poor ...
(1738–42) and other notable houses, many of which are Grade I listed buildings
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
. Queen Square was his first speculative development. Wood lived in a house on the square, which was described by Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (1 ...
as "one of the finest Palladian compositions in England before 1730".
The plan for Prior Park was to construct five buildings along three sides of a dodecagon
In geometry, a dodecagon or 12-gon is any twelve-sided polygon.
Regular dodecagon
A regular dodecagon is a figure with sides of the same length and internal angles of the same size. It has twelve lines of reflective symmetry and rotational sym ...
matching the sweep of the head of the valley, with the main building flanked by elongated wings based on designs by Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio ( ; ; 30 November 1508 – 19 August 1580) was an Italian Renaissance architect active in the Venetian Republic. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily Vitruvius, is widely considered to be one of th ...
. The plans were influenced by drawings in ''Vitruvius Britannicus'' originally made by Colen Campbell
Colen Campbell (15 June 1676 – 13 September 1729) was a pioneering Scottish architect and architectural writer, credited as a founder of the Georgian style. For most of his career, he resided in Italy and England. As well as his architectural ...
for Wanstead House
Wanstead House was a mansion built to replace the earlier Wanstead Hall. It was commissioned in 1715, completed in 1722 and demolished in 1825. Its gardens now form the municipal Wanstead Park in the London Borough of Redbridge.
History Construct ...
in Essex, which was yet to be built. The main block had 15 bays
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narr ...
and each of the wings 17 bays. Between each wing and the main block was a Porte-cochère
A porte-cochère (; , late 17th century, literally 'coach gateway'; plural: porte-cochères, portes-cochères) is a doorway to a building or courtyard, "often very grand," through which vehicles can enter from the street or a covered porch-like ...
for coaches to stop under. In addition to the stone from the local quarries, material, including the grand staircase and plasterwork, from the demolished Hunstrete House
Hunstrete () is a small village on the River Chew in the Chew Valley, Bath and North East Somerset, England. It falls within the civil parish of Marksbury and is from Bristol, and Bath, and from Keynsham.
History
The origin of the name ...
were used in the construction.
Construction work began in 1734 to Wood's plan but disagreements between Wood and Allen led to his dismissal and Wood's Clerk of Works, Richard Jones, replaced him and made some changes to the plans, particularly for the east wing. Jones also added the Palladian Bridge. The building was finished in 1743 and was occupied by Allen as his primary residence until his death in 1764.

Later use
After Allen's death in 1764,William Warburton
William Warburton (24 December 16987 June 1779) was an English writer, literary critic and churchman, Bishop of Gloucester from 1759 until his death. He edited editions of the works of his friend Alexander Pope, and of William Shakespeare.
Li ...
, Allen's relative, lived in the house for some time and it was passed down to other family members and then purchased, in 1809, by John Thomas, a Bristol Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
. After William Beckford sold Fonthill Abbey
Fonthill Abbey—also known as Beckford's Folly—was a large Gothic Revival country house built between 1796 and 1813 at Fonthill Gifford in Wiltshire, England, at the direction of William Thomas Beckford and architect James Wyatt. It was b ...
, in 1822, he was looking about for a suitable new seat, Prior Park was his first choice: ""They wanted too much for it," he recalled later; "I should have liked it very much; it possesses such great capability of being made a very beautiful spot." Prior Park was offered for sale after Thomas's death in 1827 but the asking price of £25,000 was not obtained and the offer of sale withdrawn.
Augustine Baines
Peter Augustine Baines (1786/87–1843) was an English Benedictine, Titular Bishop of Siga and Vicar Apostolic of the Western District of England.
Life
For his early education he was sent to Lamspringe Abbey, near Hildesheim, in the Kingdom of ...
, a Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
, Titular Bishop
A titular bishop in various churches is a bishop who is not in charge of a diocese.
By definition, a bishop is an "overseer" of a community of the faithful, so when a priest is ordained a bishop, the tradition of the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox an ...
of Siga and Vicar Apostolic of the Western District of England, was appointed to Bath in 1817. He purchased the mansion in 1828 for £22,000 and set to work to establish two colleges in either wing of the house, which he dedicated to St. Peter
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64–68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupation ...
and St. Paul
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
respectively, the former being intended as a lay college, the latter as a seminary. The new college never became prosperous, however. Renovations were made according to designs by Henry Goodridge
Henry Edmund Goodridge (1797, Bath – 26 October 1864) was an English architect based in Bath. He worked from the early 1820s until the 1850s, using Classical, Italianate and Gothic styles.
Life
He was born in Bath in 1797 the son of James Goo ...
in 1834 including the addition of the staircase in front of the main building. A gymnasium was also built in the 1830s including a courtyard for Fives
Fives is an English sport believed to derive from the same origins as many racquet sports. In fives, a ball is propelled against the walls of a 3- or 4-sided special court, using a gloved or bare hand as though it were a racquet, similar to ...
, and three barrel vaulted rooms on the first floor and a terrace roof.
The seminary was closed in 1856 after a fire which, in 1836, had resulted in extensive damage and renovation and brought about financial insolvency. It was bought in 1867 by Bishop Clifford who founded a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
Grammar School in the mansion. Prior Park operated as a grammar school until 1904. During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
the site was occupied by the army and used for officer cadet training. Following the war, several tenants occupied the site. In 1921, the Christian Brothers acquired the building and opened a boarding school for boys in 1924, which continues today as a mixed public school
Public school may refer to:
* State school (known as a public school in many countries), a no-fee school, publicly funded and operated by the government
* Public school (United Kingdom), certain elite fee-charging independent schools in England an ...
.
The main building (the Mansion) has been badly burnt twice. The 1836 fire left visible damage to some stonework. The 1991 fire gutted the interior, except for parts of the basement. Unusually, the blaze started on the top floor, and spread downwards. Rebuilding took approximately three years.
Architecture
 The house described by Pevsner as "the most ambitious and most complete re-creation of Palladio's villas on English soil" was designed by John Wood the Elder, however, Wood and his patron, Allen, quarrelled and completion of the project was overseen by Richard Jones, the clerk-of-works.
The plan consists of a
The house described by Pevsner as "the most ambitious and most complete re-creation of Palladio's villas on English soil" was designed by John Wood the Elder, however, Wood and his patron, Allen, quarrelled and completion of the project was overseen by Richard Jones, the clerk-of-works.
The plan consists of a corps de logis
In architecture, a ''corps de logis'' () is the principal block of a large, (usually Classical architecture, classical), mansion or palace. It contains the principal rooms, state apartments and an entry.Curl, James Stevens (2006). ''Oxford Dict ...
flanked by two pavilions connected to the corps de logis by segmented single storey arcades. The northern façade (or garden façade) of the corps de logis is of 15 bays, the central 5 bays carry a prostyle
Prostyle is an architectural term designating temples (especially Greek and Roman) featuring a row of columns on the front. The term is often used as an adjective when referring to the portico of a classical building, which projects from the m ...
portico of six Corinthian Corinthian or Corinthians may refer to:
*Several Pauline epistles, books of the New Testament of the Bible:
**First Epistle to the Corinthians
**Second Epistle to the Corinthians
**Third Epistle to the Corinthians (Orthodox)
*A demonym relating to ...
columns. The southern façade is more sombre in its embellishment, but has at its centre, six ionic columns surmounted by a pediment. The terminating pavilions have been much altered from their original design by Wood; he originally envisaged two pavilions at each end of the range; an unusual composition which was ignored by Jones who terminated the range with a single pavilion as is the more conventional Palladian concept. The East Wing was altered around 1830 when it was converted into a school, having included a brewhouse previously when a pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape.
Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds.
A pedimen ...
ed three-bay second floor was added by John Pensiston. Around 1834 Goodridge altered the West Wing to include a theatre, which was damaged by bombs during the Bath Blitz
The term Bath Blitz refers to the air raids by the German ''Luftwaffe'' on the British city of Bath, Somerset, during World War II.
The city was bombed in April 1942 as part of the so-called "Baedeker raids", in which targets were chosen for th ...
of 1942. The central flight of steps and urns, in Baroque style, which front the north portico were added by Goodridge in 1836.
In the 1830s Goodridge put forward plans for a large cathedral to be built in the grounds. However this was never proceeded with and instead was replaced by a plan for a small chapel to be incorporated in the west wing of the mansion. In 1844 Joseph John Scoles
Joseph John Scoles (1798–1863) was an English Gothic Revival architect, who designed many Roman Catholic churches.
Early life and education
Scoles was born in London on 27 June 1798, the son of Roman Catholic parents Matthew Scoles, a joiner, ...
created the Church of St Paul which, along with the remainder of the west wing, is Grade I listed.
The total length of the principal elevation is between and in length. Of that, the corps de logis occupies . The two-storey building with attics and a basement is topped with a Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
slate roof.
Gardens
 The first park on the site was set out by
The first park on the site was set out by John of Tours
John of Tours or John de Villula (died 1122) was a medieval Bishop of Wells in England who moved the diocese seat to Bath. He was a native of Tours and was King William I of England's doctor before becoming a bishop. After his consecration ...
the Bishop of Bath and Wells
The Bishop of Bath and Wells heads the Church of England Diocese of Bath and Wells in the Province of Canterbury in England.
The present diocese covers the overwhelmingly greater part of the (ceremonial) county of Somerset and a small area of Do ...
around 1100, as part of a deer park, and subsequently sold to Humphrey Colles and then Matthew Colhurst. It is set in a small valley with steep sides, from which there are views of the city of Bath. Prior Park's landscape garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a sty ...
was laid out by the poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral or writte ...
Alexander Pope
Alexander Pope (21 May 1688 O.S. – 30 May 1744) was an English poet, translator, and satirist of the Enlightenment era who is considered one of the most prominent English poets of the early 18th century. An exponent of Augustan literature, ...
between the construction of the house and 1764. During 1737, at least 55,200 trees, mostly elm and Scots pine, were planted, along the sides and top of the valley. No trees were planted on the valley floor. Water was channeled into fish ponds at the bottom of the valley.
Later work, during the 1750s and 1760s, was undertaken by the landscape gardener Capability Brown
Lancelot Brown (born c. 1715–16, baptised 30 August 1716 – 6 February 1783), more commonly known as Capability Brown, was an English gardener and landscape architect, who remains the most famous figure in the history of the English la ...
. This included extending the gardens to the north and removing the central cascade making the combe into a single sweep. The garden, as it was originally laid out, influenced other designers and contributed to defining the style of garden thought of as the English garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a sty ...
in continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
.
 The features in the gardens include a
The features in the gardens include a Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
bridge (one of only 4 left in the world), Gothic temple, gravel cabinet, Mrs Allen's Grotto, ice house, lodge and three pools with curtain walls plus a serpentine lake. The Palladian bridge, which is a copy of the one at Wilton House
Wilton House is an English country house at Wilton near Salisbury in Wiltshire, which has been the country seat of the Earls of Pembroke for over 400 years. It was built on the site of the medieval Wilton Abbey. Following the dissolution o ...
, was built by Richard Jones, and has been designated as a Grade I listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
and Scheduled Ancient Monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
. It was repaired in 1936.
The rusticated stone piers on either side of the main entrance gates are surmounted by entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and ...
s and large ornamental vases, while those at the drive entrance have ornamental carved finial
A finial (from '' la, finis'', end) or hip-knob is an element marking the top or end of some object, often formed to be a decorative feature.
In architecture, it is a small decorative device, employed to emphasize the Apex (geometry), apex of a d ...
s. The porter's lodge was built along with the main house to designs by John Wood the Elder.
In 1993, the National Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
obtained the park and pleasure grounds. In November 2006, the large-scale restoration project began on the cascade, serpentine lake and Gothic temple in the Wilderness area (as shown in special episode 28 of the Time Team
''Time Team'' is a British television programme that originally aired on Channel 4 from 16 January 1994 to 7 September 2014. It returned online in 2022 for two episodes released on YouTube. Created by television producer Tim ...
). Extensive planting also took place in 2007. The Palladian Bridge is also featured on the cover of the album ''Morningrise
''Morningrise'' is the second studio album by Swedish progressive metal band Opeth. It was released on 24 June 1996 in Europe by Candlelight Records and on 24 June 1997 in the United States by Century Black. The recording sessions took place at ...
'' by Swedish progressive metal band Opeth
Opeth is a Swedish progressive metal/rock band from Stockholm, formed in 1990 by lead vocalist David Isberg. The group has been through several personnel changes, including the replacement of every original member; notably Isberg in 1992. Mikael ...
released in 1996.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * Hart, Vaughan (1989). ‘One View of a Town. Prior Park and the City of Bath’, ''RES: Journal of Anthropology and Aesthetics'', pp. 140–157. * * * * *External links
{{good article Houses completed in 1743 Grade I listed buildings in Bath, Somerset Palladian architecture in England Grade I listed houses Country houses in Somerset Combe Down