|
Neo-Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and the principles of formal classical architecture from ancient Greek and Roman traditions. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Palladio's interpretation of this classical architecture developed into the style known as Palladianism. Palladianism emerged in England in the early 17th century, led by Inigo Jones, whose Queen's House at Greenwich has been described as the first English Palladian building. Its development faltered at the onset of the English Civil War. After the Stuart Restoration, the architectural landscape was dominated by the more flamboyant English Baroque. Palladianism returned to fashion after a reaction against the Baroque in the early 18th century, fuelled by the publication of a number of architectural books, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitruvius Britannicus
Colen Campbell (15 June 1676 – 13 September 1729) was a pioneering Scottish architect and architectural writer, credited as a founder of the Georgian style. For most of his career, he resided in Italy and England. As well as his architectural designs he is known for ''Vitruvius Britannicus'', three volumes of high-quality engravings showing the great houses of the time. Early life A descendant of the Campbells of Cawdor Castle, he is believed to be the Colinus Campbell who graduated from the University of Edinburgh in July 1695.page 7, Catalogue of the Drawings Collection of the Royal Institute of British Architects: Colen Campbell, John Harris 1973, Gregg International Publishers Ltd He initially trained as a lawyer, being admitted to the Faculty of Advocates on 29 July 1702. He travelled in Italy between 1695 and 1702, and is believed to be the Colinus Campbell who signed the visitor's book at the University of Padua in 1697. He is believed to have trained in and studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colen Campbell
Colen Campbell (15 June 1676 – 13 September 1729) was a pioneering Scottish architect and architectural writer, credited as a founder of the Georgian style. For most of his career, he resided in Italy and England. As well as his architectural designs he is known for ''Vitruvius Britannicus'', three volumes of high-quality engravings showing the great houses of the time. Early life A descendant of the Campbells of Cawdor Castle, he is believed to be the Colinus Campbell who graduated from the University of Edinburgh in July 1695.page 7, Catalogue of the Drawings Collection of the Royal Institute of British Architects: Colen Campbell, John Harris 1973, Gregg International Publishers Ltd He initially trained as a lawyer, being admitted to the Faculty of Advocates on 29 July 1702. He travelled in Italy between 1695 and 1702, and is believed to be the Colinus Campbell who signed the visitor's book at the University of Padua in 1697. He is believed to have trained in and studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Palladio Fourth Book Image
Andrea is a given name which is common worldwide for both males and females, cognate to Andreas, Andrej and Andrew. Origin of the name The name derives from the Greek word ἀνήρ (''anēr''), genitive ἀνδρός (''andrós''), that refers to man as opposed to woman (whereas ''man'' in the sense of ''human being'' is ἄνθρωπος, ''ánthropos''). The original male Greek name, ''Andréas'', represents the hypocoristic, with endearment functions, of male Greek names composed with the ''andr-'' prefix, like Androgeos (''man of the earth''), Androcles (''man of glory''), Andronikos (''man of victory''). In the year 2006, it was the third most popular name in Italy with 3.1% of newborns. It is one of the Italian male names ending in ''a'', with others being Elia (Elias), Enea (Aeneas), Luca ( Lucas), Mattia (Matthias), Nicola (Nicholas), Tobia (Tobias). In recent and past times it has also been used on occasion as a female name in Italy and in Spain, where it is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Wenzeslaus Von Knobelsdorff
(Hans) Georg Wenzeslaus von Knobelsdorff (17 February 1699 – 16 September 1753) was a painter and architect in Prussia. Knobelsdorff was born in Kuckädel, now in Krosno Odrzańskie County. A soldier in the service of Prussia, he resigned his commission in 1729 as captain so that he could pursue his interest in architecture. In 1740 he travelled to Paris and Italy to study at the expense of the new king, Frederick II of Prussia. Knobelsdorff was influenced as an architect by French Baroque Classicism and by Palladian architecture. With his interior design and the backing of the king, he created the basis for the Frederician Rococo style at Rheinsberg, which was the residence of the crown prince and later monarch. Knobelsdorff was the head custodian of royal buildings and head of a privy council on financial matters. In 1746 he was dismissed by the king, and Johann Boumann finished all his projects, including Sanssouci. Knobelsdorff died in Berlin. His grave is preserved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick The Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Silesian wars, his re-organisation of the Prussian Army, the First Partition of Poland, and his patronage of the arts and the Enlightenment. Frederick was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled King in Prussia, declaring himself King of Prussia after annexing Polish Prussia from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1772. Prussia greatly increased its territories and became a major military power in Europe under his rule. He became known as Frederick the Great (german: links=no, Friedrich der Große) and was nicknamed "Old Fritz" (german: links=no, "Der Alte Fritz"). In his youth, Frederick was more interested in music and philosophy than in the art of war, which led to clashes with his authoritarian father, Frederick William I of Prus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Algarotti
Count Francesco Algarotti (11 December 1712 – 3 May 1764) was an Italian polymath, philosopher, poet, essayist, anglophile, art critic and art collector. He was a man of broad knowledge, an expert in Newtonianism, architecture and opera. He was a friend of Frederick the Great and leading authors of his times: Voltaire, Jean-Baptiste de Boyer, Marquis d'Argens, Pierre-Louis de Maupertuis and the atheist Julien Offray de La Mettrie. Lord Chesterfield, Thomas Gray, George Lyttelton, Thomas Hollis, Metastasio, Benedict XIV and Heinrich von Brühl were among his correspondents. Early life Algarotti was born in Venice as the son of a rich merchant. His father and uncle were art collectors. Unlike his older brother, Bonomo he did not step into the company, but decided to become an author. Francesco obtained a classical education; also studied natural sciences and mathematics in Rome. While the experimental physics and medicine at University of Bologna under Francesco Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a " Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Guards (building)
Horse Guards is a historic building in the City of Westminster, London, between Whitehall and Horse Guards Parade. It was built in the mid-18th century, replacing an earlier building, as a barracks and stables for the Household Cavalry. It was, between the early 18th century and 1858, the main military headquarters for the British Empire. Horse Guards originally formed the entrance to the Palace of Whitehall and later St James's Palace; for that reason it is still ceremonially defended by the King's Life Guard. Although still in military use, part of the building houses the Household Cavalry Museum which is open to the public. It also functions as a gateway between Whitehall and St James's Park. History The first Horse Guards building was commissioned by King Charles II in 1663,Tabor, p.18 on the site of a cavalry stables which had been built on the tiltyard of the Palace of Whitehall during the Commonwealth. Built of red brick and costing some £4,000, it comprised a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea, with The Wash to the north-west. The county town is the city of Norwich. With an area of and a population of 859,400, Norfolk is a largely rural county with a population density of 401 per square mile (155 per km2). Of the county's population, 40% live in four major built up areas: Norwich (213,000), Great Yarmouth (63,000), King's Lynn (46,000) and Thetford (25,000). The Broads is a network of rivers and lakes in the east of the county, extending south into Suffolk. The area is protected by the Broads Authority and has similar status to a national park. History The area that was to become Norfolk was settled in pre-Roman times, (there were Palaeolithic settlers as early as 950,000 years ago) with camps along the higher land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
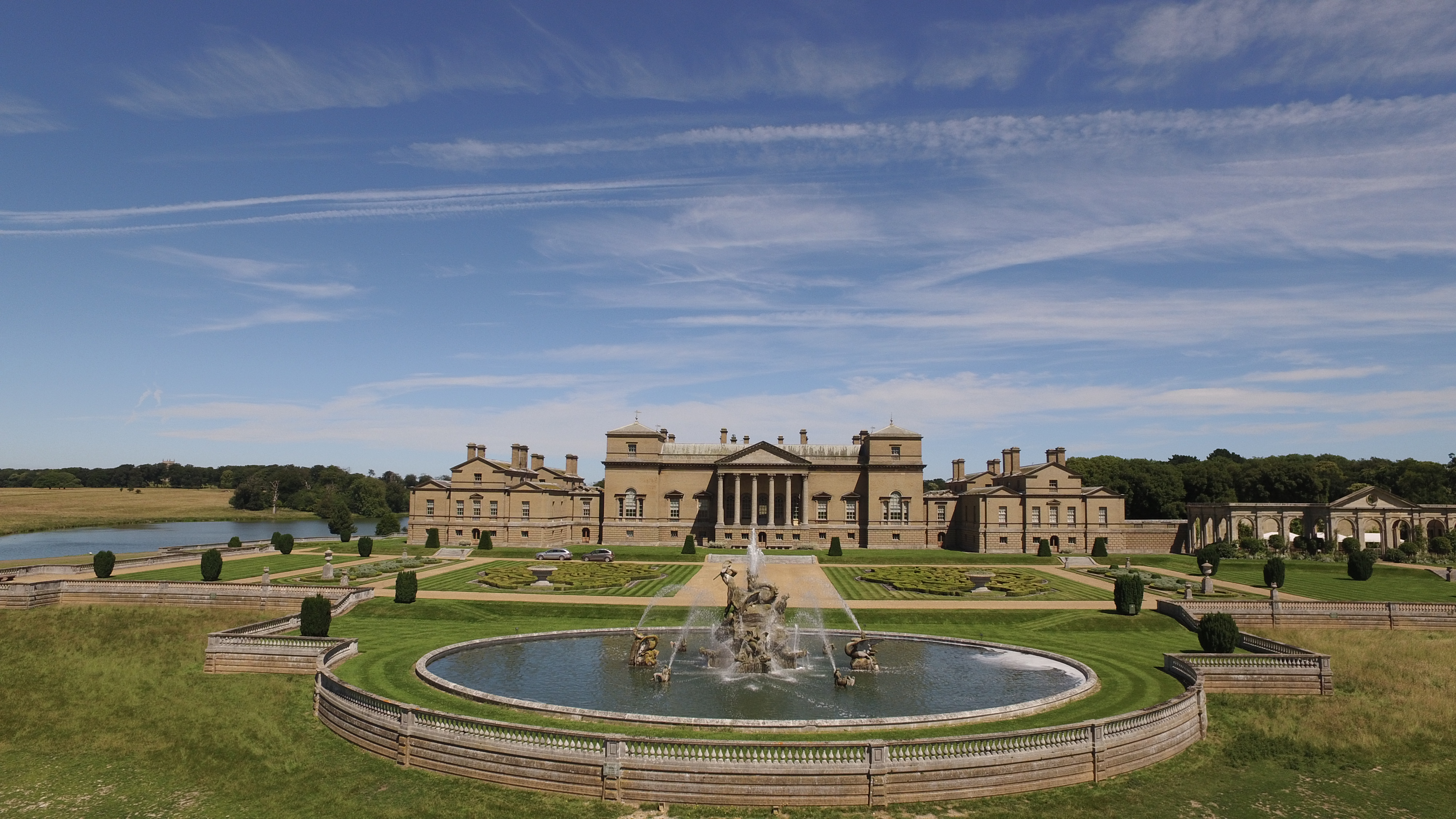
Holkham Hall
Holkham Hall ( or ) is an 18th-century country house near the village of Holkham, Norfolk, England, constructed in the Neo-Palladian style for the 1st Earl of Leicester,The Earldom of Leicester has been, to date, created seven times. Thomas Coke, the builder of Holkham, was the 1st Earl of the fifth creation. His grand nephew Thomas Coke was the 1st Earl of the seventh creation. by the architect William Kent, aided by Lord Burlington. Holkham Hall is one of England's finest examples of the Palladian revival style of architecture, and the severity of its design is closer to Palladio's ideals than many of the other numerous Palladian style houses of the period. The Holkham Estate was built up by Sir Edward Coke, the founder of his family's fortune. He bought Neales manor in 1609, though never lived there, and made many other purchases of land in Norfolk to endow to his six sons. His fourth son, John, inherited the land and married heiress Meriel Wheatley in 1612. They made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Kent
William Kent (c. 1685 – 12 April 1748) was an English architect, landscape architect, painter and furniture designer of the early 18th century. He began his career as a painter, and became Principal Painter in Ordinary or court painter, but his real talent was for design in various media. Kent introduced the Palladian style of architecture into England with the villa at Chiswick House, and also originated the 'natural' style of gardening known as the English landscape garden at Chiswick, Stowe Gardens in Buckinghamshire, and Rousham House in Oxfordshire. As a landscape gardener he revolutionised the layout of estates, but had limited knowledge of horticulture. He complemented his houses and gardens with stately furniture for major buildings including Hampton Court Palace, Chiswick House, Devonshire House and Rousham. Early life Kent was born in Bridlington, East Riding of Yorkshire, and baptised on 1 January 1686, as William Cant. His parents were William and Esther Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burlington House
Burlington House is a building on Piccadilly in Mayfair, London. It was originally a private Neo-Palladian mansion owned by the Earls of Burlington and was expanded in the mid-19th century after being purchased by the British government. Today, the Royal Academy and five learned societies occupy much of the building. History The house was one of the earliest of a number of very large private residences built on the north side of Piccadilly, previously a country lane, from the 1660s onwards. The first version was begun by Sir John Denham in about 1664. It was a red-brick double-pile hip-roofed mansion with a recessed centre, typical of the style of the time, or perhaps even a little old fashioned. Denham may have acted as his own architect, or he may have employed Hugh May, who certainly became involved in the construction after the house was sold in an incomplete state in 1667 to Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Burlington, from whom it derives its name. Burlington had the house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |