Principality of Novgorod on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of
 In 882, Rurik's successor,
In 882, Rurik's successor,
 In 1259,
In 1259,
 At the time of annexation, Novgorod became the third largest city under Muscovy and then the
At the time of annexation, Novgorod became the third largest city under Muscovy and then the
 The city is known for the variety and age of its medieval monuments. The foremost among these is the St. Sophia Cathedral, built between 1045 and 1050 under the patronage of Vladimir Yaroslavich, the son of
The city is known for the variety and age of its medieval monuments. The foremost among these is the St. Sophia Cathedral, built between 1045 and 1050 under the patronage of Vladimir Yaroslavich, the son of  Outside the Kremlin walls, there are three large churches constructed during the reign of Mstislav the Great. St. Nicholas Cathedral (1113–1123), containing frescoes of Mstislav's family, graces
Outside the Kremlin walls, there are three large churches constructed during the reign of Mstislav the Great. St. Nicholas Cathedral (1113–1123), containing frescoes of Mstislav's family, graces
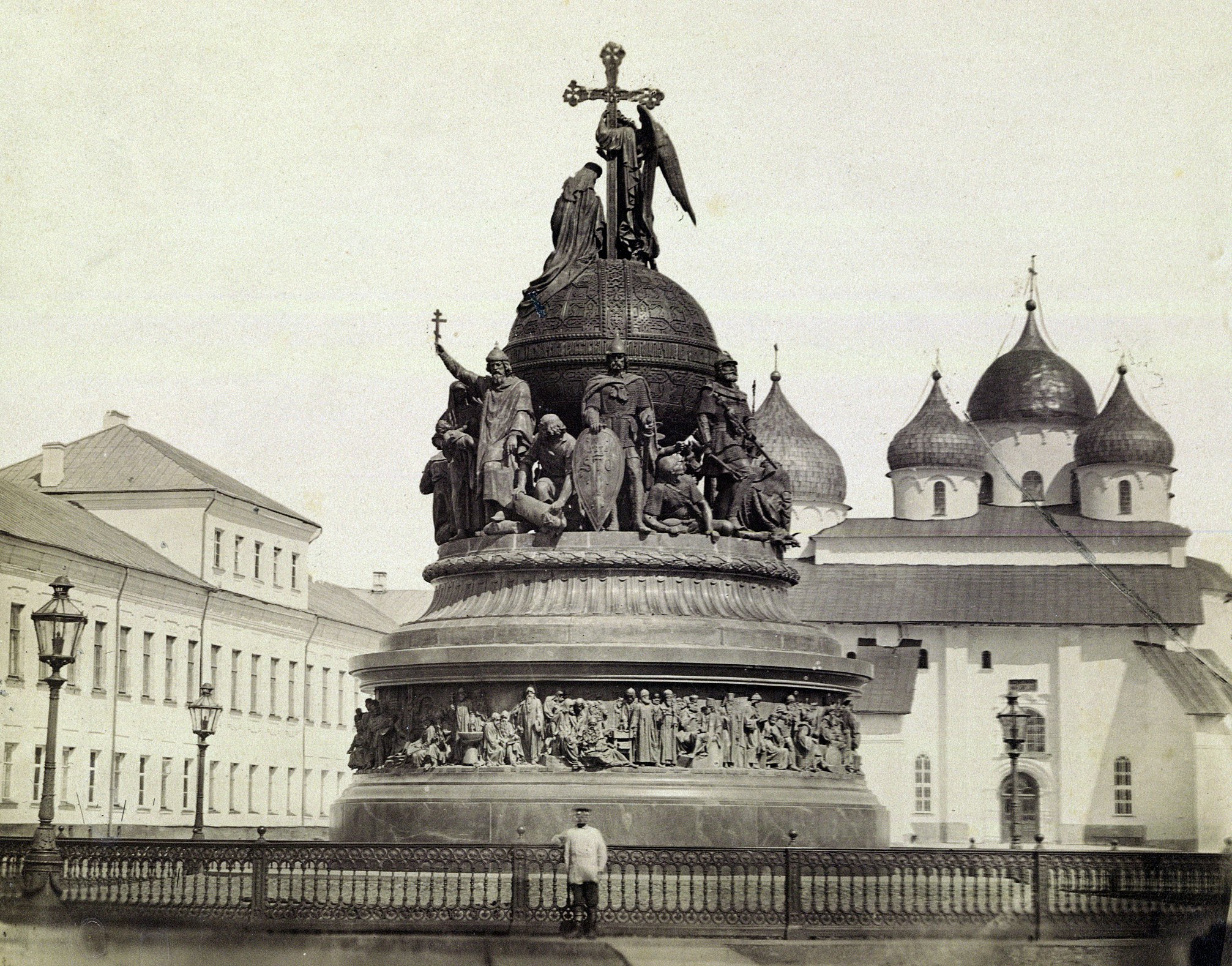
File:Nowgorod 2005 Millenium Monument.jpg, Bronze monument to the
 Novgorod has connections to
Novgorod has connections to
File:15 050528a.JPG, trolleybus Skoda-VMZ-14Tr
File:Novgorod - Trolleys and a bus at main station.jpg, Trolleybuses
Official website of Veliky Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod City PortalVeliky Novgorod for touristsThe Faceted Palace of the Kremlin in Novgorod the Great site
* * * * {{Authority control Archaeological sites in Russia Rus' settlements Capitals of former nations Trading posts of the Hanseatic League Novgorodsky Uyezd World Heritage Sites in Russia
Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast (russian: Новгоро́дская о́бласть, ''Novgorodskaya oblast'') is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Veliky Novgorod. Some of the oldest Russian cities, includin ...
, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the Volkhov River
The Volkhov (russian: Во́лхов) is a river in Novgorodsky and Chudovsky Districts of Novgorod Oblast and Kirishsky and Volkhovsky Districts of Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia. It connects Lake Ilmen and Lake Ladoga and forms pa ...
just downstream from its outflow from Lake Ilmen and is situated on the M10 federal highway connecting Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
and Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
. UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
recognized Novgorod as a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 1992. The city has a population of
At its peak during the 14th century, the city was the capital of the Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of mod ...
and was one of Europe's largest cities. The "Veliky" ("great") part was added to the city's name in 1999.
History
Early developments
TheSofia First Chronicle
The Sofia First Chronicle (Софийская первая летопись) is a Russian chronicle associated with the St. Sophia Cathedral, Novgorod, Russia. Its copies exist in two versions: Early Redaction (''starshy izvod''), which ends by 1 ...
makes initial mention of it in 859, while the Novgorod First Chronicle
The Novgorod First Chronicle (russian: Новгородская первая летопись) or The Chronicle of Novgorod, 1016–1471 is the most ancient extant Old Russian chronicle of the Novgorodian Rus'. It reflects a tradition different ...
first mentions it in 862, when it was purportedly already a major Baltics
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
-to- Byzantium station on the trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks
The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks was a medieval trade route that connected Scandinavia, Kievan Rus' and the Eastern Roman Empire. The route allowed merchants along its length to establish a direct prosperous trade with the Empir ...
. The Charter of Veliky Novgorod recognizes 859 as the year when the city was first mentioned.Charter of Veliky Novgorod, Article 1 Novgorod is traditionally considered to be a cradle of Russian statehood.
The oldest archaeological excavations in the middle to late 20th century, however, have found cultural layers dating back to the late 10th century, the time of the Christianization of Rus'
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
and a century after it was allegedly founded. Archaeological dating is fairly easy and accurate to within 15–25 years, as the streets were paved with wood, and most of the houses made of wood, allowing tree ring dating.
The Varangian
The Varangians (; non, Væringjar; gkm, Βάραγγοι, ''Várangoi'';Varangian
" Online Etymo ...
name of the city or ( or ) is mentioned in " Online Etymo ...
Norse Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, from the Super NES to the Pl ...
s as existing at a yet earlier stage, but the correlation of this reference with the actual city is uncertain. Originally, referred to the stronghold, now only to the south of the center of the present-day city, Rurikovo Gorodische (named in comparatively modern times after the Varangian chieftain Rurik, who supposedly made it his "capital" around 860). Archaeological data suggests that the Gorodishche, the residence of the Knyaz (prince), dates from the mid-9th century, whereas the town itself dates only from the end of the 10th century; hence the name Novgorod, "new city", from Old East Slavic and ( and ); the Old Norse term is a calque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language w ...
of an Old Russian word. First mention of this Norse etymology to the name of the city of Novgorod (and that of other cities within the territory of the then Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
) occurs in the 10th-century policy manual by Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
emperor Constantine VII.
Princely state within Kievan Rus'
 In 882, Rurik's successor,
In 882, Rurik's successor, Oleg of Novgorod
Oleg ( orv, Ѡлегъ, Ольгъ; non, Helgi; died 912), also known as Oleg the Wise (russian: Олег Вещий, lit=Oleg the Prophet; uk, Олег Віщий), was a Varangian prince of the Rus' who was ruler of Novgorod. He later con ...
, conquered Kiev and founded the state of Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
. Novgorod's size as well as its political, economic, and cultural influence made it the second most important city in Kievan Rus'. According to a custom, the elder son and heir of the ruling Kievan monarch was sent to rule Novgorod even as a minor. When the ruling monarch had no such son, Novgorod was governed by posadnik
Posadnik (Cyrillic: посадник, (literally: по-садник - ''pre-sident'') was the mayor in some East Slavic cities or towns. Most notably, the posadnik (equivalent to a stadtholder, burgomeister, or podestà in the medieval west) was ...
s, such as the legendary Gostomysl
Gostomysl depicted on the first plate of the book ''Illustrated Karamzin'' (1836), depicting the history of Russia.
Gostomysl () is a legendary 9th-century prince or posadnik of Novgorod who was introduced into the historiography by Vasily Tati ...
, Dobrynya Dobrynya (russian: Добрыня, uk, Добриня) was Vladimir the Great's maternal uncle and tutor. He was the historical prototype of the invincible bogatyr Dobrynya Nikitich in Kievan Rus folklore.
Dobrynya's life and extent of his inf ...
, Konstantin
The first name Konstantin () is a derivation from the Latin name ''Constantinus'' ( Constantine) in some European languages, such as Russian and German. As a Christian given name, it refers to the memory of the Roman emperor Constantine the Great ...
, and Ostromir Ostromir (''Остромир'' in Russian; Christian name - Joseph) (died c. 1057) was a statesman, voivod and posadnik of Novgorod in 1054-1057 and probably for some decades previous.
Ostromir is known from the first Russian dated book, the Ost ...
.
Of all their princes, Novgorodians most cherished the memory of Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was al ...
, who sat as Prince of Novgorod from 1010 to 1019, while his father, Vladimir the Great
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych ( orv, Володимѣръ Свѧтославичь, ''Volodiměrъ Svętoslavičь'';, ''Uladzimir'', russian: Владимир, ''Vladimir'', uk, Володимир, ''Volodymyr''. Se ...
, was a prince in Kiev. Yaroslav promulgated the first written code of laws (later incorporated into Russkaya Pravda
The ''Russkaya Pravda'' (Rus' Justice, Rus' Truth, or Russian Justice; orv, Правда роусьскаꙗ, ''Pravda Rusĭskaya'' (13th century, 1280), Правда Руськая, ''Pravda Rus'kaya'' (second half of the 15th century); russian: ...
) among the Eastern Slavs and is said to have granted the city a number of freedoms or privileges, which they often referred to in later centuries as precedents in their relations with other princes. His son, Vladimir
Vladimir may refer to:
Names
* Vladimir (name) for the Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Macedonian, Romanian, Russian, Serbian, Slovak and Slovenian spellings of a Slavic name
* Uladzimir for the Belarusian version of the name
* Volodymyr for the Ukr ...
, sponsored construction of the great St. Sophia Cathedral, more accurately translated as the Cathedral of Holy Wisdom, which stands to this day.
Early foreign ties
InNorse saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, from the Super NES to the Pl ...
s the city is mentioned as the capital of Gardariki. Many Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
kings and yarls came to Novgorod seeking refuge or employment, including Olaf I of Norway, Olaf II of Norway
Olaf II Haraldsson ( – 29 July 1030), later known as Saint Olaf (and traditionally as St. Olave), was King of Norway from 1015 to 1028. Son of Harald Grenske, a petty king in Vestfold, Norway, he was posthumously given the title '' Rex Per ...
, Magnus I of Norway
Magnus Olafsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Óláfsson''; Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus Olavsson''; – 25 October 1047), better known as Magnus the Good (Old Norse: ''Magnús góði'', Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus den gode''), was King of Norway ...
, and Harald Hardrada. No more than a few decades after the 1030 death and subsequent canonization of Olaf II of Norway, the city's community had erected in his memory Saint Olaf's Church in Novgorod.
The Gotland town of Visby
Visby () is an urban area in Sweden and the seat of Gotland Municipality in Gotland County on the island of Gotland with 24,330 inhabitants . Visby is also the episcopal see for the Diocese of Visby. The Hanseatic city of Visby is arguably th ...
functioned as the leading trading center in the Baltic before the Hansa League. At Novgorod in 1080, Visby merchants established a trading post which they named Gutagard (also known as Gotenhof). Later, in the first half of the 13th century, merchants from northern Germany also established their own trading station in Novgorod, known as Peterhof. At about the same time, in 1229, German merchants at Novgorod were granted certain privileges, which made their position more secure.
Novgorod Republic
In 1136, the Novgorodians dismissed their prince Vsevolod Mstislavich. The year is seen as the traditional beginning of theNovgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of mod ...
. The city was able to invite and dismiss a number of princes over the next two centuries, but the princely office was never abolished and powerful princes, such as Alexander Nevsky, could assert their will in the city regardless of what Novgorodians said. The city state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
controlled most of Europe's northeast, from lands east of today's Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
to the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, making it one of the largest states in medieval Europe, although much of the territory north and east of Lakes Ladoga and Onega was sparsely populated and never organized politically.
One of the most important local figures in Novgorod was the , or mayor, an official elected by the public assembly (called the ) from among the city's boyars
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgaria, Russia, Wallachia and Moldavia, and later Romania, Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. Boyars wer ...
, or aristocracy. The , or "thousandman", originally the head of the town militia but later a commercial and judicial official, was also elected by the . Another important local official was the Archbishop of Novgorod
The Diocese of Novgorod (russian: Новгородская епархия) is one of the oldest offices in the Russian Orthodox Church. The medieval archbishops of Novgorod were among the most important figures in medieval Russian history and cul ...
who shared power with the boyars. Archbishops were elected by the or by the drawing of lots, and after their election, were sent to the metropolitan for consecration.
While a basic outline of the various officials and the can be drawn up, the city-state's exact political constitution remains unknown. The boyars and the archbishop ruled the city together, although where one official's power ended and another's began is uncertain. The prince, although his power was reduced from around the middle of the 12th century, was represented by his , or lieutenant, and still played important roles as a military commander, legislator and jurist. The exact composition of the , too, is uncertain, with some historians, such as Vasily Klyuchevsky
Vasily Osipovich Klyuchevsky (russian: Василий Осипович Ключевский; in Voskresnskoye Village, Penza Governorate, Russia – , Moscow) was a leading Russian Imperial historian of the late imperial period. Also, he addres ...
, claiming it was democratic in nature, while later scholars, such as Marxists Valentin Ianin and Aleksandr Khoroshev, see it as a "sham democracy" controlled by the ruling elite.
In the 13th century, Novgorod, while not a member of the Hanseatic League, was the easternmost kontor
A ''kontor'' () was a foreign trading post of the Hanseatic League.
In addition to the major ''kontore'' in London (the Steelyard), Bruges, Bergen (Bryggen), and Novgorod (Peterhof), some ports had a representative merchant and a warehouse.
E ...
, or entrepôt
An ''entrepôt'' (; ) or transshipment port is a port, city, or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored, or traded, usually to be exported again. Such cities often sprang up and such ports and trading posts often developed into c ...
, of the league, being the source of enormous quantities of luxury ( sable, ermine, fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
, marmot
Marmots are large ground squirrels in the genus ''Marmota'', with 15 species living in Asia, Europe, and North America. These herbivores are active during the summer, when they can often be found in groups, but are not seen during the winter, ...
) and non-luxury furs (squirrel pelts).
Throughout the Middle Ages, the city thrived culturally. A large number of birch bark letters have been unearthed in excavations, perhaps suggesting widespread literacy. It was in Novgorod that the Novgorod Codex
The Novgorod Codex (russian: Новгородский кодекс) is the oldest book of the Rus’, unearthed on July 13, 2000 in Novgorod. It is a palimpsest consisting of three bound wooden tablets containing four pages filled with wax, on w ...
, the oldest Slavic book written north of Bulgaria, and the oldest inscription in a Finnic language ( Birch bark letter no. 292) were unearthed. Some of the most ancient Russian chronicles (Novgorod First Chronicle
The Novgorod First Chronicle (russian: Новгородская первая летопись) or The Chronicle of Novgorod, 1016–1471 is the most ancient extant Old Russian chronicle of the Novgorodian Rus'. It reflects a tradition different ...
) were written in the scriptorium of the archbishops who also promoted iconography and patronized church construction. The Novgorod merchant Sadko
Sadko (russian: Садко) is the principal character in a Russian medieval epic '' bylina''. He was an adventurer, merchant, and '' gusli'' musician from Novgorod.
Textual notes
"Sadko" is a version of the tale translated by Arthur Ransome ...
became a popular hero of Russian folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging ...
.
Novgorod was never conquered by the Mongols during the Mongol invasion of Rus
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered Kievan Rus' in the 13th century, destroying numerous southern cities, including the largest cities, Kiev (50,000 inhabitants) and Chernihiv (30,000 inhabitants), with the only major cities escaping de ...
. The Mongol army turned back about from the city, not because of the city's strength, but probably because the Mongol commanders did not want to get bogged down in the marshlands surrounding the city. However, the grand princes of Moscow, who acted as tax collectors for the khans of the Golden Horde, did collect tribute in Novgorod, most notably Yury Danilovich and his brother, Ivan Kalita
Iván I Danilovich Kalitá ( Russian: Ива́н I Данилович Калита́; 1 November 1288 – 31 March 1340 or 1341Basil Dmytryshyn, ''Medieval Russia:A source book, 850-1700'', (Academic International Press, 2000), 194.) was Grand D ...
.
 In 1259,
In 1259, Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
tax-collectors and census-takers arrived in the city, leading to political disturbances and forcing Alexander Nevsky to punish a number of town officials (he cut off their noses) for defying him as Grand Prince of Vladimir
The grand duke of Vladimir was the ruler of a principality during the era of Kievan Rus' and after its collapse. It ruled territory approximately bounded by three rivers, the Volga, the Oka and the Northern Dvina. From 1157 to 1238 its capital was ...
(soon to be the khan's tax-collector in Russia) and his Mongol overlords. In the 14th century, raids by Novgorod pirate
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
s, or , sowed fear as far as Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering an ...
and Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the ...
, assisting Novgorod in wars with the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
During the era of Old Rus' State, Novgorod was a trade hub at the northern end of both the Volga trade route
In the Middle Ages, the Volga trade route connected Northern Europe and Northwestern Russia with the Caspian Sea and the Sasanian Empire, via the Volga River. The Rus used this route to trade with Muslim countries on the southern shores of the ...
and the " route from the Varangians to the Greeks" along the Dnieper river
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
system. A vast array of goods were transported along these routes and exchanged with local Novgorod merchants and other traders. The farmers of Gotland retained the Saint Olof trading house well into the 12th century. Later German merchantmen also established tradinghouses in Novgorod. Scandinavian royalty would intermarry with Russian princes and princesses.
After the great schism, Novgorod struggled from the beginning of the 13th century against Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
, Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
, and German crusaders. During the Swedish-Novgorodian Wars, the Swedes invaded lands where some of the population had earlier paid tribute to Novgorod. The Germans had been trying to conquer the Baltic region since the late 12th century. Novgorod went to war 26 times with Sweden and 11 times with the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword ( la, Fratres militiæ Christi Livoniae, german: Schwertbrüderorden) was a Catholic military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theoderi ...
. The German knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Gr ...
s, along with Danish and Swedish feudal lords, launched a series of uncoordinated attacks in 1240–1242. Novgorodian sources mention that a Swedish army was defeated in the Battle of the Neva in 1240. The Baltic German campaigns ended in failure after the Battle on the Ice
The Battle on the Ice (german: Schlacht auf dem Eise; russian: Ледовое побоище, ''Ledovoye poboishche''; et, Jäälahing), alternatively known as the Battle of Lake Peipus (german: Schlacht auf dem Peipussee), took place on 5 Apr ...
in 1242. After the foundation of the castle of Viborg in 1293 the Swedes gained a foothold in Karelia. On August 12, 1323, Sweden and Novgorod signed the Treaty of Nöteborg
The Treaty of Nöteborg, also known as the ''Treaty of Oreshek'' ( sv, Freden i Nöteborg, Russian: ''Ореховский мир,'' fi, Pähkinäsaaren rauha), is a conventional name for the peace treaty signed at Oreshek ( sv, Nöteborg, fi, ...
, regulating their border for the first time.
The city's downfall occurred partially as a result of its inability to feed its large population, making it dependent on the Vladimir-Suzdal
Vladimir-Suzdal (russian: Владимирско-Су́здальская, ''Vladimirsko-Suzdal'skaya''), also Vladimir-Suzdalian Rus', formally known as the Grand Duchy of Vladimir (1157–1331) (russian: Владимиро-Су́здальс ...
region for grain. The main cities in the area, Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
and Tver
Tver ( rus, Тверь, p=tvʲerʲ) is a city and the administrative centre of Tver Oblast, Russia. It is northwest of Moscow. Population:
Tver was formerly the capital of a powerful medieval state and a model provincial town in the Russian ...
, used this dependence to gain control over Novgorod. Eventually Ivan III forcibly annexed the city to the Grand Duchy of Moscow in 1478. The was dissolved and a significant part of Novgorod's aristocracy, merchants and smaller landholding families was deported to central Russia. The Hanseatic League kontor was closed in 1494 and the goods stored there were seized by Muscovite forces.
Tsardom of Russia
 At the time of annexation, Novgorod became the third largest city under Muscovy and then the
At the time of annexation, Novgorod became the third largest city under Muscovy and then the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
(with 5,300 homesteads and 25–30 thousand inhabitants in the 1550s) and remained so until the famine of the 1560s and the Massacre of Novgorod in 1570. In the Massacre, Ivan the Terrible sacked the city, slaughtered thousands of its inhabitants, and deported the city's merchant elite and nobility to Moscow, Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl ( rus, Ярослáвль, p=jɪrɐˈsɫavlʲ) is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historic part of the city is a World Heritage Site, and is located at the confluenc ...
and elsewhere. The last decade of the 16th century was a comparatively favourable period for the city as Boris Godunov restored trade privileges and raised the status of Novgorod bishop. The German trading post was reestablished in 1603. Even after the incorporation into the Russian state Novgorod land retained its distinct identity and institutions, including the customs policy and administrative division. Certain elective offices were quickly restored after having been abolished by Ivan III.
During the Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles (russian: Смутное время, ), or Smuta (russian: Смута), was a period of political crisis during the Tsardom of Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Fyodor I (Fyodor Ivanovich, the last of the Rurik dy ...
, Novgorodians submitted to Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
troops led by Jacob De la Gardie
Field Marshal and Count Jacob Pontusson De la Gardie ( Reval, 20 June 1583 – Stockholm, 22 August 1652) was a statesman and a soldier of the Swedish Empire, and a Marshal from 1620 onward.
He was Privy Councilor from 1613 onward, Governo ...
in the summer of 1611. The city was restituted to Muscovy six years later by the Treaty of Stolbovo
The Treaty of Stolbovo () was a peace treaty that ended the Ingrian War (), which had been fought between the Swedish Empire and the Russian Tsardom between 1610 and 1617.
History
After nearly two months of negotiations, representatives from Sw ...
. The conflict led to further depopulation: the number of homesteads in the city decreased from 1158 in 1607 to only 493 in 1617, with the Sofia side described as 'deserted'. Novgorod only regained a measure of its former prosperity towards the end of the century, when such ambitious buildings as the Cathedral of the Sign and the Vyazhischi Monastery were constructed. The most famous of Muscovite patriarchs, Nikon
(, ; ), also known just as Nikon, is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, specializing in optics and imaging products. The companies held by Nikon form the Nikon Group.
Nikon's products include cameras, camera ...
, was active in Novgorod between 1648 and 1652. The Novgorod Land became one of the Old Believers' strongholds after the Schism. The city remained an important trade centre even though it was now eclipsed by Archangelsk, Novgorodian merchants were trading in the Baltic cities and Stockholm while Swedish merchants came to Novgorod where they had their own trading post since 1627. Novgorod continued to be a major centre of crafts which employed the majority of its population. There were more than 200 distinct professions in 16th century. Bells, cannons and other arms were produced in Novgorod; its silversmiths were famous for the skan' technique used for religious items and jewellery. Novgorod chests were in widespread use all across Russia, including the Tsar's household and the northern monasteries.
Russian Empire
In 1727, Novgorod was made the administrative center ofNovgorod Governorate
Novgorod Governorate (Pre-reformed rus, Новгоро́дская губе́рнія, r=Novgorodskaya guberniya, p=ˈnofɡərətskəjə ɡʊˈbʲernʲɪjə, t=Government of Novgorod), was an administrative division (a '' guberniya'') of the Ru ...
of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, which was detached from Saint Petersburg Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate (russian: Санкт-Петербу́ргская губе́рния, ''Sankt-Peterburgskaya guberniya''), or Government of Saint Petersburg, was an administrative division (a '' guberniya'') of the Tsardom of Russia ...
(see Administrative divisions of Russia in 1727–1728). This administrative division existed until 1927. Between 1927 and 1944, the city was a part of Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast ( rus, Ленинградская область, Leningradskaya oblast’, lʲɪnʲɪnˈgratskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, , ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 194 ...
, and then became the administrative center of the newly formed Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast (russian: Новгоро́дская о́бласть, ''Novgorodskaya oblast'') is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Veliky Novgorod. Some of the oldest Russian cities, includin ...
.
Modern era
On August 15, 1941, duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the city was occupied by the German Army. Its historic monuments were systematically obliterated. The Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
liberated the city on January 19, 1944. Out of 2,536 stone buildings, fewer than forty remained standing. After the war, thanks to plans laid down by Alexey Shchusev
Alexey Victorovich Shchusev (academic spelling), german: Schtschussew, french: Chtchoussev, pl, Szchusiew. (russian: Алексе́й Ви́кторович Щу́сев; – 24 May 1949) was a Russian and Soviet architect who was successf ...
, the central part was gradually restored. In 1992, the chief monuments of the city and the surrounding area were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
list as the Historic Monuments of Novgorod and Surroundings
Historic Monuments of Novgorod and Surroundings is a composite World Heritage Site which includes a number of medieval monuments in and around Veliky Novgorod, Russia. The site was inscribed in 1992.
History
Novgorod between the 9th and the 15th c ...
. In 1999, the city was officially renamed Veliky Novgorod (literally, Great Novgorod), thus partly reverting to its medieval title "Lord Novgorod the Great". This reduced the temptation to confuse Veliky Novgorod with Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gork ...
, a larger city the other side of Moscow which, between 1932 and 1990, had been renamed Gorky, in honour of Maxim Gorky
Alexei Maximovich Peshkov (russian: link=no, Алексе́й Макси́мович Пешко́в; – 18 June 1936), popularly known as Maxim Gorky (russian: Макси́м Го́рький, link=no), was a Russian writer and social ...
.
Administrative and municipal status
Veliky Novgorod is theadministrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
of the oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdo ...
and, within the framework of administrative divisions, it also serves as the administrative center of Novgorodsky District
Novgorodsky District (russian: Новгородский район) is an administrativeLaw #559-OZ and municipalLaw #400-OZ district (raion), one of the twenty-one in Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is located in the southwest of the oblast and borde ...
, even though it is not a part of it.Law #559-OZ As an administrative division, it is incorporated separately as the city of oblast significance of Veliky Novgorod—an administrative unit with status equal to that of the districts. As a municipal division, the city of oblast significance of Veliky Novgorod is incorporated as Veliky Novgorod Urban Okrug.Oblast Law #284-OZ
Sights
 The city is known for the variety and age of its medieval monuments. The foremost among these is the St. Sophia Cathedral, built between 1045 and 1050 under the patronage of Vladimir Yaroslavich, the son of
The city is known for the variety and age of its medieval monuments. The foremost among these is the St. Sophia Cathedral, built between 1045 and 1050 under the patronage of Vladimir Yaroslavich, the son of Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was al ...
; Vladimir and his mother, Anna Porphyrogenita, are buried in the cathedral. It is one of the best preserved churches from the 11th century. It is also probably the oldest structure still in use in Russia and the first one to represent original features of Russian architecture (austere stone walls, five helmet-like domes). Its frescoes were painted in the 12th century originally on the orders of Bishop Nikita (died 1108) (the "porches" or side chapels were painted in 1144 under Archbishop Nifont) and renovated several times over the centuries, most recently in the nineteenth century. The cathedral features famous bronze gates, which now hang in the west entrance, allegedly made in Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; nds, label=Low Saxon, Meideborg ) is the capital and second-largest city of the German state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is situated at the Elbe river.
Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archdiocese of Magdebu ...
in 1156 (other sources see them originating from Płock
Płock (pronounced ) is a city in central Poland, on the Vistula river, in the Masovian Voivodeship. According to the data provided by GUS on 31 December 2021, there were 116,962 inhabitants in the city. Its full ceremonial name, according to th ...
in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
) and reportedly snatched by Novgorodians from the Swedish town of Sigtuna
Sigtuna () is a locality situated in Sigtuna Municipality, Stockholm County, Sweden with 8,444 inhabitants in 2010. It is the namesake of the municipality even though the seat is in Märsta.
Sigtuna is for historical reasons often still referr ...
in 1187. More recent scholarship has determined that the gates were most likely purchased in the mid-15th century, apparently at the behest of Archbishop Euthymius II (1429–1458), a lover of Western art and architectural styles.
The Novgorod Kremlin
The Novgorod Detinets (russian: Новгородский детинец, Novgorodskiy detinets), also known as the Novgorod Kremlin (, ''Novgorodskiy kreml' ''), is a fortified complex (detinets) in Veliky Novgorod, Russia. It stands on the le ...
, traditionally known as the ''Detinets'', also contains the oldest palace in Russia (the so-called Chamber of the Facets, 1433), which served as the main meeting hall of the archbishops; the oldest Russian bell tower (mid-15th century), and the oldest Russian clock tower (1673). The Palace of Facets, the bell tower, and the clock tower were originally built on the orders of Archbishop Euphimius II, although the clock tower collapsed in the 17th century and had to be rebuilt and much of the palace of Euphimius II is no longer standing. Among later structures, the most remarkable are a royal palace (1771) and a bronze monument to the Millennium of Russia
The Millennium of Russia (russian: Тысячелетие России, Tysyacheletiye Rossii) is a bronze monument in the Novgorod Kremlin. It was erected in 1862 to celebrate the millennium of Rurik's arrival to Novgorod, an event tradition ...
, representing the most important figures from the country's history (unveiled in 1862).
Yaroslav's Court
Yaroslav's Court (russian: Ярославово Дворище, ''Yaroslavovo Dvorishche'') was the princely compound in the city of Novgorod the Great. Today it is roughly the area around the Trade Mart, the St. Nicholas Cathedral, the Church of ...
(formerly the chief square of Novgorod). The Yuriev Monastery
The St. George's (Yuriev) Monastery (russian: Юрьев монастырь) is usually cited as Russia's oldest monastery. It stands in 5 kilometers south of Novgorod on the left bank of the Volkhov River near where it flows out of Lake Ilmen. T ...
(one of the oldest in Russia, 1030) contains a tall, three-domed cathedral from 1119 (built by Mstislav's son, Vsevolod, and Kyurik, the head of the monastery). A similar three-domed cathedral (1117), probably designed by the same masters, stands in the Antoniev Monastery, built on the orders of Antony, the founder of that monastery.
There are now some fifty medieval and early modern churches scattered throughout the city and its surrounding areas. Some of them were blown up by the Nazis and subsequently restored. The most ancient pattern is represented by those dedicated to Saints Pyotr and Pavel (on the Swallow's Hill, 1185–1192), to Annunciation (in Myachino, 1179), to Assumption (on Volotovo Field, 1180s) and to St. Paraskeva-Piatnitsa (at Yaroslav's Court
Yaroslav's Court (russian: Ярославово Дворище, ''Yaroslavovo Dvorishche'') was the princely compound in the city of Novgorod the Great. Today it is roughly the area around the Trade Mart, the St. Nicholas Cathedral, the Church of ...
, 1207). The greatest masterpiece of early Novgorod architecture is the Savior church at Nereditsa (1198).
In the 13th century, tiny churches of the three-paddled design were in vogue. These are represented by a small chapel at the Peryn Monastery (1230s) and St. Nicholas' on the Lipnya Islet (1292, also notable for its 14th-century frescoes). The next century saw the development of two original church designs, one of them culminating in St Theodor's church (1360–1361, fine frescoes from 1380s), and another one leading to the Savior church on Ilyina street (1374, painted in 1378 by Feofan Grek). The Savior' church in Kovalevo (1345) was originally frescoed by Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
n masters, but the church was destroyed during the war. While the church has since been rebuilt, the frescoes have not been restored.
During the last century of the republican government, some new churches were consecrated to Saints Peter and Paul (on Slavna, 1367; in Kozhevniki, 1406), to Christ's Nativity (at the Cemetery, 1387), to St. John the Apostle's (1384), to the Twelve Apostles (1455), to St Demetrius (1467), to St. Simeon (1462), and other saints. Generally, they are not thought to be as innovative as the churches from the previous period. Several shrines from the 12th century (i.e., in Opoki) were demolished brick by brick and then reconstructed exactly as they used to be, several of them in the mid-fifteenth century, again under Archbishop Yevfimy II (Euthymius II), perhaps one of the greatest patrons of architecture in medieval Novgorod.
Novgorod's conquest by Ivan III in 1478 decisively changed the character of local architecture. Large commissions were thenceforth executed by Muscovite masters and patterned after cathedrals of Moscow Kremlin: e.g., the Savior Cathedral of Khutyn Monastery
Khutyn Monastery of Saviour's Transfiguration and of St. Varlaam (russian: Хутынский Спасо-Преображенский Варлаамиев монастырь) is an Orthodox monastery situated on the right bank of the Volkhov River ...
(1515), the Cathedral of the Mother of God of the Sign (1688), the St. Nicholas Cathedral of Vyaschizhy Monastery (1685). Nevertheless, the styles of some parochial churches were still in keeping with local traditions: e.g., the churches of Myrrh-bearing Women (1510) and of Saints Boris and Gleb
Boris and Gleb ( orv, Борисъ и Глѣбъ, ''Borisŭ i Glěbŭ''; russian: Борис и Глеб, ''Boris i Gleb''; ua, Борис і Гліб, ''Borys i Hlib''), Christian names Roman and David, respectively ( orv, Романъ, Да� ...
(1586).
In Vitoslavlitsy, along the Volkhov River
The Volkhov (russian: Во́лхов) is a river in Novgorodsky and Chudovsky Districts of Novgorod Oblast and Kirishsky and Volkhovsky Districts of Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia. It connects Lake Ilmen and Lake Ladoga and forms pa ...
and the Myachino Lake, close to the Yuriev Monastery
The St. George's (Yuriev) Monastery (russian: Юрьев монастырь) is usually cited as Russia's oldest monastery. It stands in 5 kilometers south of Novgorod on the left bank of the Volkhov River near where it flows out of Lake Ilmen. T ...
, a museum of wooden architecture was established in 1964. Over twenty wooden buildings (churches, houses and mills) dating from the 14th to the 19th century were transported there from all around the Novgorod region.
11400 graves of the German 1st Luftwaffe Field Division are found at the war cemetery in Novgorod. Also 1900 soldiers of the Spanish Blue Division
The Blue Division ( es, División Azul, german: Blaue Division) was a unit of volunteers from Francoist Spain within the German Army (''Wehrmacht'') on the Eastern Front during World War II. It was officially designated the Spanish Volunteer ...
are buried there.
Millennium of Russia
The Millennium of Russia (russian: Тысячелетие России, Tysyacheletiye Rossii) is a bronze monument in the Novgorod Kremlin. It was erected in 1862 to celebrate the millennium of Rurik's arrival to Novgorod, an event tradition ...
(1862)
File:Nowgorod 2005 w.jpg, Walls of the Novgorod Kremlin
File:VNovgorod WWIIMemoral 4211.JPG, War Memorial
File:Yaroslavovo Dvorische 01.jpg, View of the Yaroslav's Court
Yaroslav's Court (russian: Ярославово Дворище, ''Yaroslavovo Dvorishche'') was the princely compound in the city of Novgorod the Great. Today it is roughly the area around the Trade Mart, the St. Nicholas Cathedral, the Church of ...
File:Novgorod - Oblast Duma and Administration.jpg, Government Building
Transportation
Intercity transport
 Novgorod has connections to
Novgorod has connections to Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
(531 km) and St. Petersburg (189 km) by the federal highway M10. There are public buses to Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
and other destinations.
The city has direct railway passenger connections with Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
(Leningradsky Rail Terminal
Moscow Leningradsky railway terminal (russian: Ленинградский вокзал, ''Leningradsky vokzal'') also known as Moscow Passazhirskaya station (russian: Москва-Главная-Пассажирская) is the oldest of Mosc ...
, by night trains), St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
( Moscow Rail Terminal and Vitebsk Rail Terminal
St Petersburg-Vitebsky (russian: Ви́тебский вокза́л) is a railway station terminal in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Formerly known as ''St Petersburg-Tsarskoselsky'' station because its first line led to the suburban royal residence ...
, by suburban train
Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting commuters to a central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Generally commuter rail systems are consi ...
s), Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
(Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
) ( Minsk Passazhirsky railway station, by night trains) and Murmansk
Murmansk (Russian: ''Мурманск'' lit. "Norwegian coast"; Finnish: ''Murmansk'', sometimes ''Muurmanski'', previously ''Muurmanni''; Norwegian: ''Norskekysten;'' Northern Sámi: ''Murmánska;'' Kildin Sámi: ''Мурман ланнҍ'') ...
.
The city's former commercial airport Yurievo was decommissioned in 2006, and the area has now been redeveloped into a residential neighbourhood. The still existing Krechevitsy Airport
Krechevitsy is a functioning civil airfield, formerly Russian Airforce base located 11 km northeast of Veliky Novgorod, Russia (near Krechevitsy). It contains 30 large revetments in a sprawling taxiway pattern, suitable for large transports. ...
does not serve any regular flights since mid-1990s although there is a plan to turn Krechevitsy
Krechevitsy (russian: Кречевицы) is a microdistrict (since 2004) of the city of Veliky Novgorod, Russia. It is located remotely (some 15 km north-east) from the city centre, on the left bank of the Volkhov River. Population: 3,363 ( ...
into a new operational airport by 2025. The nearest international airport is St. Petersburg's Pulkovo Pulkovo may refer to:
*Pulkovo Heights marking the southern limit of Saint Petersburg, Russia
*Pulkovo Airport serving Saint Petersburg, Russia
*Pulkovo Aviation Enterprise
Pulkovo Federal State Unified Aviation Service Company (ФГУАП “� ...
, some north of the city.
Local transportation
Local transportation consists of a network of buses andtrolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or trol ...
es. The trolleybus network, which currently consists of five routes, started operating in 1995 and is the first trolley system opened in Russia after the fall of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
.
ZiU-9
ZiU-9, or ZIU-9 (Cyrillic: ЗиУ-9) is a Soviet (and later Russian) trolleybus. Other names for the ZiU-9 are ZiU-682 and HTI-682 (Cyrillic: ЗиУ-682 and ХТИ-682). The ZiU acronym stands for ''Zavod imeni Uritskogo'', which is a plant nam ...
File:Novgorod - Bus at main station 02.jpg, Bus LiAZ-5256
Honours
Aminor planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''mino ...
, 3799 Novgorod, discovered by the Soviet astronomer Nikolai Stepanovich Chernykh in 1979, is named after the city.
Twin towns – sister cities
Veliky Novgorod is twinned with: *Bielefeld
Bielefeld () is a city in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe Region in the north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population of 341,755, it is also the most populous city in the administrative region (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Detmold and the ...
, Germany
* Kohtla-Järve
Kohtla-Järve is a city and municipality in northeastern Estonia, founded in 1924 and incorporated as a town in 1946. The city is highly industrial, and is both a processor of oil shales and is a large producer of various petrochemical products ...
, Estonia
* Moss, Norway
* Nanterre
Nanterre (, ) is the prefecture of the Hauts-de-Seine department in the western suburbs of Paris. It is located some northwest of the centre of Paris. In 2018, the commune had a population of 96,807.
The eastern part of Nanterre, bordering t ...
, France
* Örebro
Örebro ( , ) is the sixth-largest city in Sweden, the seat of Örebro Municipality, and capital of the Örebro County. It is situated by the Närke Plain, near the lake Hjälmaren, a few kilometers inland along the small river Svartån, and ...
, Sweden
* Rochester, New York
Rochester () is a city in the U.S. state of New York, the seat of Monroe County, and the fourth-most populous in the state after New York City, Buffalo, and Yonkers, with a population of 211,328 at the 2020 United States census. Located in W ...
, USA
* Uusikaupunki
Uusikaupunki (; sv, Nystad, ) is a town and municipality of Finland. It is located in the Southwest Finland region, northwest of Turku and south of Pori. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is inland wate ...
, Finland
* Watford
Watford () is a town and borough in Hertfordshire, England, 15 miles northwest of Central London, on the River Colne.
Initially a small market town, the Grand Junction Canal encouraged the construction of paper-making mills, print works, and ...
, UK
* Zibo
Zibo (, ) is a prefecture-level city in central Shandong province, China. It borders the provincial capital Jinan to the west, Tai'an to the southwest, Linyi to the south, Weifang to the east, Dongying to the northeast, and Binzhou to the ...
, China
See also
*Old Novgorod dialect
Old Novgorod dialect (russian: древненовгородский диалект, translit=drevnenovgorodskij dialekt; also translated as Old Novgorodian or Ancient Novgorod dialect) is a term introduced by Andrey Zaliznyak to describe the dia ...
* Novgorod uprising of 1650
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * *William Craft Brumfield. A History of Russian Architecture (Seattle: Univ. of Washington Press, 2004) *Peter Bogucki. Novgorod (in Lost Cities; 50 Discoveries in World Archaeology, edited by Paul G. Bahn: Barnes & Noble, Inc., 1997)External links
*Official website of Veliky Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod City Portal
* * * * {{Authority control Archaeological sites in Russia Rus' settlements Capitals of former nations Trading posts of the Hanseatic League Novgorodsky Uyezd World Heritage Sites in Russia