Newberry Volcano on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Newberry Volcano is a large
 The center of Newberry Volcano lies to the south of the city of Bend, at the intersection of Deschutes, Klamath and
The center of Newberry Volcano lies to the south of the city of Bend, at the intersection of Deschutes, Klamath and  The volcano has two crater lakes, Paulina Lake and East Lake, which are filled by precipitation and
The volcano has two crater lakes, Paulina Lake and East Lake, which are filled by precipitation and
 Overlapping with the northwestern corner of the
Overlapping with the northwestern corner of the
active
Active may refer to:
Music
* ''Active'' (album), a 1992 album by Casiopea
* Active Records, a record label
Ships
* ''Active'' (ship), several commercial ships by that name
* HMS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the British Royal ...
shield-shaped stratovolcano located about south of Bend, Oregon, United States, east of the major crest of the Cascade Range, within the Newberry National Volcanic Monument. Its highest point is Paulina Peak. The largest volcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc
The Cascade Volcanoes (also known as the Cascade Volcanic Arc or the Cascade Arc) are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern Calif ...
, Newberry has an area of when its lava flows are taken into account. From north to south, the volcano has a length of , with a width of and a total volume of approximately . It was named for the geologist and surgeon John Strong Newberry
John Strong Newberry (December 22, 1822 – December 7, 1892) was an American physician, geologist and paleontologist. He participated as a naturalist and surgeon on three expeditions to explore and survey the western United States. During the C ...
, who explored central Oregon for the Pacific Railroad Surveys
The Pacific Railroad Surveys (1853–1855) were of a series of explorations of the American West designed to find and document possible routes for a transcontinental railroad across North America. The expeditions included surveyors, scientists, and ...
in 1855. The surrounding area has been inhabited by Native American populations for more than 10,000 years.
The volcano contains a large caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
, in diameter, known as the Newberry Caldera. Within the caldera are two lakes: Paulina Lake and East Lake. The volcano and its vicinity include many pyroclastic cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and s ...
s, lava flows and lava domes; Newberry has more than 400 vents, the most of any volcano in the contiguous United States. Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s may have once been present at the volcano, though this remains contested. The area has a dry climate with low precipitation levels and little surface runoff.
The origin of the volcano remains somewhat unclear; while some scientists believe it originated from an independent hotspot, most evidence indicates that it formed from the subduction of the oceanic Juan de Fuca
Juan de Fuca (10 June 1536, Cefalonia 23 July 1602, Cefalonia)Greek Consulate of Vancouver,Greek Pioneers: Juan de Fuca. was a Greek pilot who served PhilipII of Spain. He is best known for his claim to have explored the Strait of Aniánnow k ...
and Gorda tectonic plates under the continental North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacif ...
. Eruptive activity at Newberry Volcano began about 600,000 years ago and has continued into the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
, the last eruption taking place 1,300 years ago. Unlike other shield-shaped volcanoes, which often erupt basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
ic lavas only, Newberry Volcano has also erupted andesitic
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomin ...
and rhyolitic
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral ...
lavas. A popular destination for hiking, fishing, boating, and other recreational activities, the volcano lies within of 16,400 people and within of nearly 200,000 people, and it continues to pose a threat to life. Still considered an active volcano, it could erupt and produce lava flows, pyroclastic flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of b ...
s, lahars (volcanically induced mudslides, landslides, and debris flows), ashfall, earthquakes, avalanches, and floods. To track this threat, the volcano and its surroundings are closely monitored with sensors by the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
.
Geography
 The center of Newberry Volcano lies to the south of the city of Bend, at the intersection of Deschutes, Klamath and
The center of Newberry Volcano lies to the south of the city of Bend, at the intersection of Deschutes, Klamath and Lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
counties in Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
, where it is one of the most accessible volcanoes in the state. It is the largest volcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc
The Cascade Volcanoes (also known as the Cascade Volcanic Arc or the Cascade Arc) are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern Calif ...
at , and has roughly the same area as the state of Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area and the seventh-least populous, with slightly fewer than 1.1 million residents as of 2020, but it ...
at if its lava flows are included. Newberry lies east of the major crest of the Cascade Range in the High Lava Plains region, rising above its surroundings. From north to south, the volcano runs for a length of , with a width of and a total volume of about . Because of its enormous size and topographic prominence, it is often confused for an entire mountain range.
Newberry Volcano has an extremely dry climate due to its location in the rain shadow of the Cascade Range. Climate data for the Newberry National Volcanic Monument are collected at the Lava Butte
Lava Butte is a cinder cone in central Oregon, United States, just west of U.S. Route 97 between the towns of Bend, and Sunriver in Deschutes County. It is part of a system of small cinder cones on the northwest flank of Newberry Volcano, a ...
cinder cone, which had an average annual precipitation of from 2002 to 2012. Summer temperatures average from , dipping to average minimum and maximum temperatures of during the winter season. Spring has average temperatures of , while fall temperatures average . Each year, total precipitation consisting of winter snow and summer rain varies from in the highest parts of the region, and surface runoff rarely occurs even during heavy rain showers. Only one stream appears on Newberry's entire surface, and it remains unclear whether the volcano has ever been able to support glaciers on its slopes, since the mountain lacks cirques (amphitheater-like valleys formed by glacial erosion) or evidence of contact between lava and ice. However, displaced glacial erratics have been found far from their native areas, moraine sediment has been deposited on the eastern and northeastern slopes of the volcano, and the mountain's various cone features have "boat" shapes that indicate glacial alteration. The precise history of glaciers on the volcano is debated, but dry channels and dry waterfalls on the eastern and western slopes are evidence that the volcano once held water.
 The volcano has two crater lakes, Paulina Lake and East Lake, which are filled by precipitation and
The volcano has two crater lakes, Paulina Lake and East Lake, which are filled by precipitation and percolation
Percolation (from Latin ''percolare'', "to filter" or "trickle through"), in physics, chemistry and materials science, refers to the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials.
It is described by Darcy's law.
Broader applicatio ...
of ground water. Paulina Lake occupies an area of and reaches a maximum depth of , and it is separated from East Lake by a narrow isthmus
An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus ...
(a piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated), which is composed of rhyolite lava. East Lake has a smaller area of with a maximum depth of . The lakes have historically flooded channels surrounding the volcano. A large flood between 4,000 and 2,300 years ago released up to 12,000 acre feet (0.0148 km3) in volume from Paulina Lake, filling the valley floor above the Paulina Prairie, which surrounds the lake. It was possibly caused by the failure of a rock ledge in height, rather than eruptive activity. Another flood took place in 1909 on the Deschutes River Deschutes River may refer to:
*Deschutes River (Oregon)
The Deschutes River in central Oregon is a major tributary of the Columbia River. The river provides much of the drainage on the eastern side of the Cascade Range in Oregon, gathering many ...
downstream from where it meets its tributary the Little Deschutes River
The Little Deschutes River is a tributary of the Deschutes River in the central part of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is about long, with a drainage basin of . It drains a rural area on the east side of the Cascade Range south of Bend. The Littl ...
.
Ecology
The Newberry National Volcanic Monument forms part of the northern section of the Mazama Ecological Province, which has soil comprised by aeolianpumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular v ...
and volcanic products over basalt bedrock. Flora within the Newberry Volcano area includes forests of juniper, whitebark pine
''Pinus albicaulis'', known by the common names whitebark pine, white bark pine, white pine, pitch pine, scrub pine, and creeping pine, is a conifer tree native to the mountains of the western United States and Canada, specifically subalpine ...
, ponderosa pine
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the ...
(including Oregon's largest ponderosa pine tree), lodgepole pine
''Pinus contorta'', with the common names lodgepole pine and shore pine, and also known as twisted pine, and contorta pine, is a common tree in western North America. It is common near the ocean shore and in dry montane forests to the subalpin ...
, jack pine
Jack pine (''Pinus banksiana'') is an eastern North American pine. Its native range in Canada is east of the Rocky Mountains from the Mackenzie River in the Northwest Territories to Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, and the north-central and ...
, and white fir
''Abies concolor'', the white fir, is a coniferous tree in the pine family Pinaceae. This tree is native to the mountains of western North America, including the Cascade Range and southern Rocky Mountains, and into the isolated mountain ranges ...
, in addition to other plants like Indian paintbrush, purple penstemon
''Penstemon'' , the beardtongues, is a large genus of roughly 250 species of flowering plants native mostly to the Nearctic, but with a few species also found in the North American portion of the Neotropics. It is the largest genus of flowering ...
, bitterbrush, manzanita
Manzanita is a common name for many species of the genus ''Arctostaphylos''. They are evergreen shrubs or small trees present in the chaparral biome of western North America, where they occur from Southern British Columbia and Washington to Or ...
, and snowbrush. Infestations by mountain pine beetle
The mountain pine beetle (''Dendroctonus ponderosae'') is a species of bark beetle native to the forests of western North America from Mexico to central British Columbia. It has a hard black exoskeleton, and measures approximately , about the siz ...
s have killed many lodgepole pines in the area. Animals near Newberry Volcano include burrowing owl
The burrowing owl (''Athene cunicularia''), also called the shoco, is a small, long-legged owl found throughout open landscapes of North and South America. Burrowing owls can be found in grasslands, rangelands, agricultural areas, deserts, or an ...
s, kangaroo rat
Kangaroo rats, small mostly nocturnal rodents of genus ''Dipodomys'', are native to arid areas of western North America. The common name derives from their bipedal form. They hop in a manner similar to the much larger kangaroo, but developed t ...
s, lizards, bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
s, rattlesnakes, eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
s, porcupines, otters, bobcats, mule deer
The mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') is a deer indigenous to western North America; it is named for its ears, which are large like those of the mule. Two subspecies of mule deer are grouped into the black-tailed deer.
Unlike the related whi ...
, Roosevelt elk
The Roosevelt elk (''Cervus canadensis roosevelti)'', also known commonly as the Olympic elk and Roosevelt's wapiti, is the largest of the four surviving subspecies of elk (''Cervus canadensis'') in North America by body mass (although by antl ...
, duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
s, and American pika
The American pika (''Ochotona princeps''), a diurnal species of pika, is found in the mountains of western North America, usually in boulder fields at or above the tree line. They are herbivorous, smaller relatives of rabbits and hares. Pikas ...
.
Lava flows from Newberry display varied vegetation cover, and there are variable levels of flora between flows, though the level of vegetation and species diversity
Species diversity is the number of different species that are represented in a given community (a dataset). The effective number of species refers to the number of equally abundant species needed to obtain the same mean proportional species abundan ...
generally increase with elevation. Dominant plant species on lava flows include oceanspray and wax currant, with rabbitbrush
Rabbitbrush is a common name for shrubs, principally of the western United States, in three related genera of the family Asteraceae:
* '' Chrysothamnus'' — about seven species in the United States, including Greene's rabbitbrush
* ''Ericame ...
also common. Though forb
A forb or phorb is an herbaceous flowering plant that is not a graminoid (grass, sedge, or rush). The term is used in biology and in vegetation ecology, especially in relation to grasslands and understory. Typically these are dicots without woo ...
s are not widespread on the lava flows, where they do occur Davidson's penstemon
Davidson's is a Roanoke, Virginia-based chain of menswear stores. The company was founded in 1910. Its downtown location is at 412 S. Jefferson St., in a former S&W Cafeteria, that it has occupied since 1964. In 2008, the location underwent a $ ...
and hotrock penstemon dominate. Above elevations of , roundleaf alumroot is common, particularly near the edges of lava flows. All lava flows support patches of grasses such as Idaho fescue
''Festuca idahoensis'' is a species of grass known by the common names Idaho fescue and blue bunchgrass. It is native to western North America, where it is widespread and common. It can be found in many ecosystems, from shady forests to open plai ...
, especially on north-facing slopes. One lava flow at Lava Butte is barren except for scattered, dense patches of greenleaf manzanita.
The Lava Cast Forest is a group of trees molded by lava from an eruption 6,000 years ago. Today, the surrounding site lies within the Newberry National Volcanic Monument and includes 11 kīpukas, plots of land surrounded by one or more younger lava flows. These habitat islands range from in area and sustain forests that have not been significantly altered by humans other than nearby fire suppression and land management efforts. Consisting of pure and mixed forest stands, these forests include ponderosa pine, lodgepole pine, and grand fir
''Abies grandis'' (grand fir, giant fir, lowland white fir, great silver fir, western white fir, Vancouver fir, or Oregon fir) is a fir native to the Pacific Northwest and Northern California of North America, occurring at altitudes of sea leve ...
/white fir hybrid trees, which are supported by young soils derived from Mazama pumice.
Geology
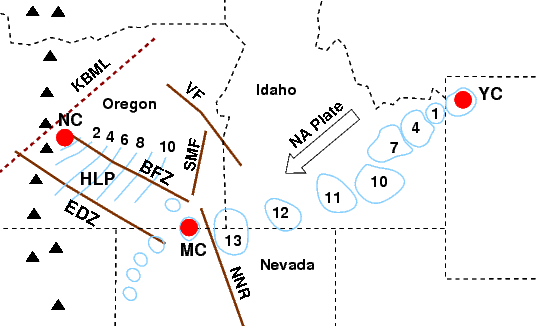
 Overlapping with the northwestern corner of the
Overlapping with the northwestern corner of the Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating ...
, also known as the High Lava Plains, Newberry Volcano lies within a Cenozoic highland marked by normal faults known as the Brothers Fault Zone
The Brothers Fault Zone (BFZ) is the most notable of a set of northwest-trending fault zones including the Eugene–Denio, McLoughlin, and Vale zones that dominate the Geology of Oregon, geological structure of most of Oregon. These are also ...
. It is situated at the intersection of the Brothers Fault Zone with the north–northwest-trending Sisters and northeast-trending Walker Rim fault zones. In the mantle under Newberry Volcano, P and S seismic wave
A seismic wave is a wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth. It can result from an earthquake, volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide, and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy ...
s exhibit an unusually low wave velocity. The Earth's crust thins from at the nearby Three Sisters volcano complex to near Newberry, where it has a high Poisson's ratio
In materials science and solid mechanics, Poisson's ratio \nu ( nu) is a measure of the Poisson effect, the deformation (expansion or contraction) of a material in directions perpendicular to the specific direction of loading. The value of Po ...
.
The oldest rocks in this region include silicic
Silicic is an adjective to describe magma or igneous rock rich in silica. The amount of silica that constitutes a silicic rock is usually defined as at least 63 percent. Granite and rhyolite are the most common silicic rocks.
Silicic is the grou ...
(rich in silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
) lava domes from the late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
or early Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58hotspot, but overwhelming evidence suggests that it is part of the Cascades Arc and was produced by the subduction of the oceanic
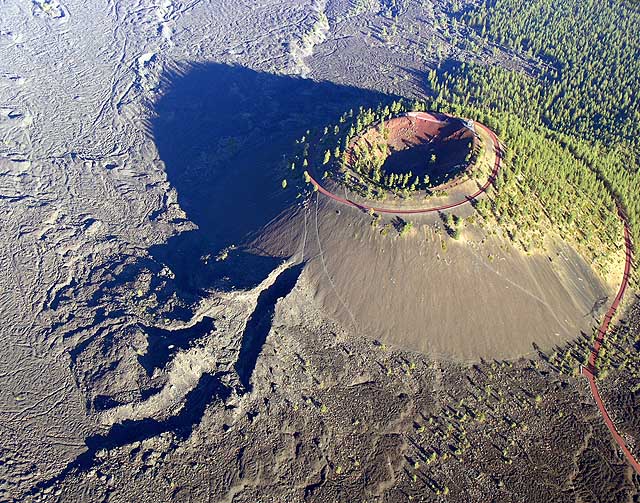 Vents at the volcano follow north-east and north-west trends influenced by extension of the Basin and Range Province. With more than 400 vents, Newberry has more individual subfeatures than any other volcano in the contiguous United States. These include cinder cones, lava domes, and various other lava edifices, with at least 25 vents on the volcano's flanks and summits becoming active within the past 10,000 years. Most of the cinder cones on the volcano's edifice vary from in elevation, though a number of them reach heights above with diameters greater than . Most of these exhibit saucer-like summit depression landforms, with notable exceptions at Lava Top and North Kawak Buttes, which have craters that are in depth. Basaltic and basaltic andesite lava flows have penetrated the bases of many of these cinder cones, forming a matrix of connected flows, and a veneer of pāhoehoe and ʻaʻā lavas can be found on Newberry volcano's northern and southern sides. The northern flank holds three distinct lava tube systems that formed out of pāhoehoe lava: the Horse Lava Tube System (also known as the Horse System),
Vents at the volcano follow north-east and north-west trends influenced by extension of the Basin and Range Province. With more than 400 vents, Newberry has more individual subfeatures than any other volcano in the contiguous United States. These include cinder cones, lava domes, and various other lava edifices, with at least 25 vents on the volcano's flanks and summits becoming active within the past 10,000 years. Most of the cinder cones on the volcano's edifice vary from in elevation, though a number of them reach heights above with diameters greater than . Most of these exhibit saucer-like summit depression landforms, with notable exceptions at Lava Top and North Kawak Buttes, which have craters that are in depth. Basaltic and basaltic andesite lava flows have penetrated the bases of many of these cinder cones, forming a matrix of connected flows, and a veneer of pāhoehoe and ʻaʻā lavas can be found on Newberry volcano's northern and southern sides. The northern flank holds three distinct lava tube systems that formed out of pāhoehoe lava: the Horse Lava Tube System (also known as the Horse System),
 During the late
During the late
 The area around Newberry Volcano has been inhabited by Native American peoples for more than 10,000 years, though only intermittently as a result of eruptive activity at the volcano and in the surrounding area. During an archaeological excavation near Paulina Lake in 1992, researchers discovered remnants of a central hearth and a housing structure with support posts and linear rock arrangements with dimensions of . Radiocarbon dating of charcoal samples from the site were dated to 11,000 years ago. The mountain's caldera was used to harvest obsidian, which they used to sharpen arrowheads and tools and traded throughout the Pacific Coast region for several thousand years.
The first recorded European to visit the volcano was Peter Skene Ogden, a trapper who reached the crater in 1826. In 1855, the volcano's namesake,
The area around Newberry Volcano has been inhabited by Native American peoples for more than 10,000 years, though only intermittently as a result of eruptive activity at the volcano and in the surrounding area. During an archaeological excavation near Paulina Lake in 1992, researchers discovered remnants of a central hearth and a housing structure with support posts and linear rock arrangements with dimensions of . Radiocarbon dating of charcoal samples from the site were dated to 11,000 years ago. The mountain's caldera was used to harvest obsidian, which they used to sharpen arrowheads and tools and traded throughout the Pacific Coast region for several thousand years.
The first recorded European to visit the volcano was Peter Skene Ogden, a trapper who reached the crater in 1826. In 1855, the volcano's namesake,
 Newberry Volcano is visited by 250,000 people each year, who come to go
Newberry Volcano is visited by 250,000 people each year, who come to go
Database for the Geologic Map of Newberry Volcano, Deschutes, Klamath, and Lake Counties, Oregon
– United States Geological Survey {{authority control Calderas of Oregon Cascade Volcanoes Volcanic crater lakes Fissure vents Geology of Oregon Hotspot volcanoes Lava domes Lava tubes Mountains of Deschutes County, Oregon Mountains of Klamath County, Oregon Mountains of Lake County, Oregon Mountains of Oregon National Natural Landmarks in Oregon Newberry National Volcanic Monument Polygenetic shield volcanoes Pyroclastic cones Potentially active volcanoes Shield volcanoes of the United States Subduction volcanoes Volcanoes of Deschutes County, Oregon Volcanoes of Klamath County, Oregon Volcanoes of Oregon
Juan de Fuca
Juan de Fuca (10 June 1536, Cefalonia 23 July 1602, Cefalonia)Greek Consulate of Vancouver,Greek Pioneers: Juan de Fuca. was a Greek pilot who served PhilipII of Spain. He is best known for his claim to have explored the Strait of Aniánnow k ...
and Gorda tectonic plates under the continental North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacif ...
. However, Newberry Volcano has been transformed by tectonic processes, possibly related to subductive mechanisms that enhance melting of the Juan de Fuca tectonic plate. The High Lava Plains Trend, or the Newberry Trend, moves at an oblique angle to the underlying North American tectonic plate, for which subduction counterflow, gravitational flow along the lithosphere's base, faulting, and extension of the Basin and Range Province have all been proposed as possible mechanisms. At Newberry, the subducting plate has a depth that is shallower than elsewhere in the major crest of the Cascades, accounting for its unique magmas. Newberry Volcano is likely fed by a magma chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it up ...
under the large, cauldron-like caldera at its summit. This caldera has dimensions of and formed about 75,000 years ago.
Newberry Volcano first formed about 600,000 years ago and has since been built up by several thousand eruptions. About 500,000 years ago, Mount Newberry attained an elevation of . The caldera-forming event occurred about 75,000 years ago from a major explosive eruption. It formed the crater lakes and Paulina Peak—which is the highest point on the volcano, at .
As a result of its caldera-forming eruption, Newberry has a horizontal profile, which is typical of a shield volcano. However, it is also considered a composite
Composite or compositing may refer to:
Materials
* Composite material, a material that is made from several different substances
** Metal matrix composite, composed of metal and other parts
** Cermet, a composite of ceramic and metallic materials
...
volcano, made up of a matrix of lava flows and pyroclastic deposits. Unlike more typical composite volcanoes in the Cascades, it formed from several eruption types including more traditional explosive eruptions and more fluid effusive events; thus it is usually classified as a "shield-shaped composite volcano", or shield-shaped stratovolcano. The volcano has a caldera at its summit, which has a diameter of and features two crater lakes: Paulina Lake and East Lake. This caldera, known as the Newberry Crater, is forested, with small parts of its surface covered with lava flows and pumice deposits. Before the caldera's creation, the mountain's summit was greater in height than its current elevation. The caldera has reformed several times throughout the volcano's history, burying the caldera floor to a depth of and creating concentric calderas, each smaller than its predecessor. The first caldera—the volcano's largest caldera, forming approximately 300,000 years ago—was produced by the eruption of of pyroclastic ejecta, which created the Tepee Draw tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
and ash deposits that cover the volcano's eastern flank. The last crater formed after an explosive eruption about 80,000 years ago, which ejected up to of pyroclastic materials. Throughout this progression, the volcano shifted from rhyodacitic
Rhyodacite is a volcanic rock intermediate in composition between dacite and rhyolite. It is the extrusive equivalent of those plutonic rocks that are intermediate in composition between monzogranite and granodiorite. Rhyodacites form from rapid ...
pumice to basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
ic ash flows, the latter producing the Black Lapilli tuff that covers the western side of the volcano. Since the last caldera-forming eruption 80,000 years ago, the volcano has undergone silicic eruptions at the caldera and produced basaltic and basaltic andesite
Basaltic andesite is a volcanic rock that is intermediate in composition between basalt and andesite. It is composed predominantly of augite and plagioclase. Basaltic andesite can be found in volcanoes around the world, including in Central Amer ...
lava flows that extended down its outer flanks. The tephra and ash from the Black Lapilli tuff by the caldera formed agglutinates around its rim. Newberry Volcano is cut by several fault scarp
A fault scarp is a small step or offset on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved vertically with respect to the other. It is the topographic expression of faulting attributed to the displacement of the land surface by movement a ...
s, small step offsets on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved vertically with respect to the other.
At the center of the isthmus that separates Newberry Volcano's two crater lakes is the central volcanic cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and ...
, named Central Pumice cone, which reaches above East Lake. With a broad, flat top, it formed during an explosive eruption about 7,000 years ago, and sits in the center of the caldera.
Compositionally, lava from the Newberry Volcano has varied from primitive basalts with high magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
levels to more evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
tholeiitic
The tholeiitic magma series is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma ...
and calc-alkaline
The calc-alkaline magma series is one of two main subdivisions of the subalkaline magma series, the other subalkaline magma series being the tholeiitic series. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic m ...
deposits (based on the major element characteristics of the lavas). Primitive lavas exhibit high abundances of chromium and nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
as well as variable concentrations of fluid-mobile elements like barium and strontium. Tholeiitic and calc-alkaline lavas display overlap in magnesium, calcium oxide
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ...
, and aluminum oxide levels but differ in that the tholeiites have lower contents of silica and potassium oxide
Potassium oxide ( K O) is an ionic compound of potassium and oxygen. It is a base. This pale yellow solid is the simplest oxide of potassium. It is a highly reactive compound that is rarely encountered. Some industrial materials, such as fertili ...
and higher iron(II) oxide
Iron(II) oxide or ferrous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula FeO. Its mineral form is known as wüstite. One of several iron oxides, it is a black-colored powder that is sometimes confused with rust, the latter of which consists ...
, titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insolub ...
, and sodium oxide
Sodium oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2 O. It is used in ceramics and glasses. It is a white solid but the compound is rarely encountered. Instead "sodium oxide" is used to describe components of various materials such as glass ...
. There is also much overlap in isotopic composition, though the tholeiitic lavas mark the low point for 87Sr/86Sr and the high point for 143Nd/144Nd and 176Hf/177Hf. Examination of Newberry lavas with olivine-plagioclase hygrometry
Psychrometrics (or psychrometry, ; also called hygrometry) is the field of engineering concerned with the physical and thermodynamic properties of gas-vapor mixtures.
Common applications
Although the principles of psychrometry apply to any p ...
shows that tholeiites are anhydrous (less than ) and thus distinct from calc-alkaline deposits (); both have different fractional crystallization sequences that derive from primitive magmas, which had their compositions influenced by equilibrium with peridotite in the mantle. By volume, basaltic andesite is the principal lava type at Newberry Volcano, with large volumes of silicic lava among older ash flow tuff deposits.
Subfeatures
 Vents at the volcano follow north-east and north-west trends influenced by extension of the Basin and Range Province. With more than 400 vents, Newberry has more individual subfeatures than any other volcano in the contiguous United States. These include cinder cones, lava domes, and various other lava edifices, with at least 25 vents on the volcano's flanks and summits becoming active within the past 10,000 years. Most of the cinder cones on the volcano's edifice vary from in elevation, though a number of them reach heights above with diameters greater than . Most of these exhibit saucer-like summit depression landforms, with notable exceptions at Lava Top and North Kawak Buttes, which have craters that are in depth. Basaltic and basaltic andesite lava flows have penetrated the bases of many of these cinder cones, forming a matrix of connected flows, and a veneer of pāhoehoe and ʻaʻā lavas can be found on Newberry volcano's northern and southern sides. The northern flank holds three distinct lava tube systems that formed out of pāhoehoe lava: the Horse Lava Tube System (also known as the Horse System),
Vents at the volcano follow north-east and north-west trends influenced by extension of the Basin and Range Province. With more than 400 vents, Newberry has more individual subfeatures than any other volcano in the contiguous United States. These include cinder cones, lava domes, and various other lava edifices, with at least 25 vents on the volcano's flanks and summits becoming active within the past 10,000 years. Most of the cinder cones on the volcano's edifice vary from in elevation, though a number of them reach heights above with diameters greater than . Most of these exhibit saucer-like summit depression landforms, with notable exceptions at Lava Top and North Kawak Buttes, which have craters that are in depth. Basaltic and basaltic andesite lava flows have penetrated the bases of many of these cinder cones, forming a matrix of connected flows, and a veneer of pāhoehoe and ʻaʻā lavas can be found on Newberry volcano's northern and southern sides. The northern flank holds three distinct lava tube systems that formed out of pāhoehoe lava: the Horse Lava Tube System (also known as the Horse System), Arnold Lava Tube System
The Arnold Lava Tube System (or Arnold system) is series of lava tubes in Deschutes County, Oregon, Deschutes County, Oregon, in the United States. It is located several miles southeast of the city of Bend, Oregon, Bend. The system starts in the D ...
, and the Lava Top Butte basalt.
About 7,000 years ago, at Newberry's Northwest Rift Zone, lava fountains erupted from a fissure with a length of , yielding basaltic and andesitic lava flows. Strombolian eruptions (which eject incandescent cinder, lapilli, and lava bombs) produced tephra that formed Lava Butte, a cinder cone near Newberry with a height of , a base diameter of , and a crater depth of . With a lopsided shape where the northeastern rim is taller than the southwestern counterpart, this cinder cone sits south of Bend.
The nearby Badlands shield volcano, which formed out of a rootless vent to produce a large basaltic lava flow at Newberry, has a diameter of . It has pāhoehoe lava throughout its surface, with tumuli
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
(mounds of earth and stones) and a pit crater
A pit crater (also called a subsidence crater or collapse crater) is a depression formed by a sinking or collapse of the surface lying above a void or empty chamber, rather than by the eruption of a volcano or lava vent. Pit craters are found ...
.
Dacite and rhyodacite domes can be found on the middle and upper flanks, and Newberry also features twenty rhyolitic lava domes and lava flows among its western, eastern, and southern flanks. These include East Butte and China Hat at the eastern base of the volcano, which date to 850,000 and 780,000 years ago, and therefore predate Newberry. The McKay Butte, found on the volcano's western side, formed 580,000 years ago. Other Holocene eruptions have produced rhyolite lava that remained close to the summit, including Paulina Peak, which has a width of one mile and reaches within of the wall of the caldera.
Hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by c ...
s can be found at Paulina Lake and East Lake, along with one fumarole
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcani ...
gas vent at Lost Lake, located near the Big Obsidian lava flow. These discharge gases like water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
and give off a rotten smell, though the composition has few noxious components.
Eruptive history
 During the late
During the late Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
, Newberry Volcano produced a number of voluminous lava flows, made of basalt, which originated from several vents on its northern flank and reached the modern areas of Bend and Redmond. They filled canyons that served as precursors for the Deschutes and Crooked rivers–since eroded–and extended tens of miles from the volcano. Lava from the last of these eruptions about 78,000 years ago covered the Bend area, surrounded the Pilot Butte cinder cone, and filled the Deschutes River bed.
In addition to its production of large lava flows, Newberry Volcano has also produced a number of Plinian eruptions similar to the eruption of Vesuvius
Of the many eruptions of Mount Vesuvius, a major stratovolcano in southern Italy, the best-known is its eruption in 79 AD, which was one of the deadliest in European history. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD is one of the best-known in h ...
that destroyed Pompeii and Peléan eruption
Peléan eruptions are a type of volcanic eruption. They can occur when viscous magma, typically of rhyolitic or andesitic type, is involved, and share some similarities with Vulcanian eruptions. The most important characteristic of a Peléan erupt ...
s like the 1902 explosion of Mount Pelée
Mount Pelée or Mont Pelée ( ; french: Montagne Pelée, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Montann Pèlé, meaning "bald mountain" or "peeled mountain") is an active volcano at the northern end of Martinique, an island and French overseas departmen ...
. These include a number of caldera-forming eruptions, producing ash flow deposits including the Tepee Draw tuff and Black Lapilli tuff, and rising or more into the stratosphere. The last of these eruptions covered tens of thousands of square miles with ash, extending to the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Go ...
in California nearly to the southwest. Here, it reaches a thickness of one centimeter. Additionally, Newberry has produced multiple, voluminous explosive eruptions, with certain studies estimating up to 60 eruptive events of rhyolite and dacite
Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyolite ...
tephra that reach Idaho, Utah, and northern California. These include the eruption that produced the Paulina Creek tephra between 55,000 and 50,000 years ago, and the eruption from 20,000 years ago responsible for the Wono tephra, which extends into western Nevada and east-central California. As a result of compositional zoning within the magma chamber that feeds the volcano, its ash deposits may show different chemical and mineralogical makeups. The last of these tephra eruptions yielded the Newberry pumice just before 1,300 years ago, reaching several hundred miles to the east.
Between the last Ice Age about 12,000 years ago and 7,700 years ago, the volcano erupted at least 12 times. Mount Mazama
Mount Mazama (''Giiwas'' in the Native American language Klamath) is a complex volcano in the state of Oregon, United States, in a segment of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and Cascade Range. Most of the mountain collapsed following a major erupt ...
erupted 7,700 years ago, producing volcanic ash and pumice that accumulated to a thickness of up to on the Newberry Volcano, covering many of the lava flows on its slopes. During three eruptive periods at Newberry over the past 7,500 years, the caldera has seen rhyolitic eruptions from seven individual vents. About 7,000 years ago, eruptions occurred along the rift zone northwest of Newberry Volcano's caldera, yielding 12 lava flows that encompassed an area of . At about the same time, the Central Pumice cone was produced by eruptions that also formed the Interlake and Game Hut obsidian flows from a vent on the cone's southern flank. An eruption from a fissure zone at East Lake, 3,500 years ago, yielded tephra and formed the East Lake obsidian lava flows.
The volcano underwent its most recent eruptions 1,300 years ago, producing the Big Obsidian flow. A silicic deposit, it is made up of rhyolite and features a number of lava blocks. Although it is frequently cited as the largest Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
obsidian formation in the United States, its area of and volume of actually place it fifth in the nation. The eruptions, which were both explosive and effusive, began with a Plinian explosion of pumice and tephra that covered the caldera's eastern half and reached several hundred miles to the east. This deposit, called the Newberry pumice, reaches a thickness of up to from the vent that produced it, which is located at the southern flank of the caldera, and a thickness of up to from the volcano. Because of strong westerly winds, tephra reached as far east as Idaho. This eruption also produced pyroclastic flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of b ...
s that left volcanic bomb
A volcanic bomb or lava bomb is a mass of partially molten rock (tephra) larger than 64 mm (2.5 inches) in diameter, formed when a volcano ejects viscous fragments of lava during an eruption. Because volcanic bombs cool after they l ...
s in Paulina Lake.
Recent activity and current threats
Though Newberry Volcano is currently quiet, theUnited States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
considers it an active volcano
An active volcano is a volcano which is either erupting or is likely to erupt in the future. An active volcano which is not currently erupting is known as a dormant volcano.
Overview
Tlocene Epoch. Most volcanoes are situated on the Pacific Ri ...
with a "very high" threat level. Hot springs within the caldera remain active, and small earthquakes have occurred within recent local history. Any future eruptions would likely show similar characteristics to eruptions from the past 15,000 years, ranging from effusive production of lava flows to explosive eruptions ejecting pumice and ash. If future lava flows from Newberry Volcano are of comparable size to its late Pleistocene eruptions, they would bury settlements throughout the Central Oregon
Central Oregon is a geographic region in the U.S. state of Oregon and is traditionally considered to be made up of Deschutes, Jefferson, and Crook counties. Other definitions include larger areas, often encompassing areas to the north towards ...
region. They would also likely destroy segments of U.S. Route 97, disabling transportation in the area, in addition to likely ruining gas pipelines and power lines that extend electricity to California, both of which would be accompanied by serious economic consequences.
Flank lava flows, which would likely be basaltic in origin, might form lava fountains that could scatter cinders and lava for several thousand meters, building cinder cones or initiating forest fires
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif ...
. While the flows themselves move at rates of per minute, and thus could be escaped by animals and humans, they would destroy stationary structures in their paths. Pyroclastic flows, on the other hand, travel at speeds of , and their violent force could incinerate or pulverize objects in their path, or asphyxiate living things.
If another caldera-forming eruption of similar magnitude to previous ones at the volcano occurred, pyroclastic flows could devastate the area surrounding the volcano for up to . However, pyroclastic flows have been rare at Newberry. Tephra from explosive eruptions would short-circuit electric transformers and power lines, clog engine filters, produce clouds that might yield lightning, and pose a hazard to aircraft overhead. It would also pose health hazards because ash particles can irritate eyes, and when ingested, lungs, among other health issues. Because of water from the two crater lakes, eruptions at Newberry Volcano may become more explosive and more likely to produce pyroclastic flows. Moreover, if pyroclastic flows mix with snow or water overflowing from the crater lakes, they could spawn lahars, volcanically induced mudslides, landslides, and debris flow
Debris flows are geological phenomena in which water-laden masses of soil and fragmented rock rush down mountainsides, funnel into stream channels, entrain objects in their paths, and form thick, muddy deposits on valley floors. They generally ...
s that could devastate the Paulina Creek valley and reach the La Pine valley within 30 minutes. Threats from the volcano pose hazards to about 16,400 people who live within and more than 180,000 people living within .
In addition to threats from volcanic activity, at least one flood has taken place at Newberry Volcano in the past, though it may not have been a result of eruptive activity. If lava flows from an eruption blocked the Deschutes River, they might generate floods upstream by increasing water level and downstream once the blockage clears. Earthquakes unrelated to volcanic activity also take place in Oregon, though they are usually less than 2.5 on the Richter magnitude scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 ...
. Volcanoes can also cause earthquakes reaching magnitudes up to 5 on the Richter scale, which sometimes occur as swarms. These clusters of tremors cause shaking of houses, walls, and windows and can crack plaster or walls in older buildings but rarely cause major damage. Powerful earthquakes close to magnitude 7 would cause damage independently, but they would not cause Newberry Volcano to erupt unless it were already on the verge of activity. Additional threats exist for rockfalls and avalanche
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a slope, such as a hill or mountain.
Avalanches can be set off spontaneously, by such factors as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, animals, and eart ...
s.
If Newberry Volcano were to erupt, it should be possible to detect increased seismic activity, while increased production of volcanic gas would likely kill trees near the volcano, which scientists would quickly recognize before notifying emergency management agencies. Before 2011, Newberry was monitored by just one seismic station that had been installed in 1987 and had only detected seven earthquakes within of the volcano. In 2011, scientists from the Cascades Volcano Observatory
The David A. Johnston Cascades Volcano Observatory (CVO) is a volcano observatory in the US that monitors volcanoes in the northern Cascade Range. It was established in the summer of 1980, after the eruption of Mount St. Helens.deformation
Deformation can refer to:
* Deformation (engineering), changes in an object's shape or form due to the application of a force or forces.
** Deformation (physics), such changes considered and analyzed as displacements of continuum bodies.
* Defor ...
monitors in the volcano's vicinity, which has seen the number of detectable earthquakes rise to 10–15 per year. The volcano continues to be closely monitored by the United States Geological Survey, which monitors a seismometer
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The outpu ...
network with the geophysics program at the University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seattl ...
and regularly conducts leveling surveys to check for deformation that could suggest impending activity, in addition to sampling geothermal areas. There are GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
instruments installed within the volcano's vicinity to monitor any swelling that occurs as a result of underground movement of magma. Despite historical uplift at the volcano, deformation has remained continuously low in recent years.
Human history
 The area around Newberry Volcano has been inhabited by Native American peoples for more than 10,000 years, though only intermittently as a result of eruptive activity at the volcano and in the surrounding area. During an archaeological excavation near Paulina Lake in 1992, researchers discovered remnants of a central hearth and a housing structure with support posts and linear rock arrangements with dimensions of . Radiocarbon dating of charcoal samples from the site were dated to 11,000 years ago. The mountain's caldera was used to harvest obsidian, which they used to sharpen arrowheads and tools and traded throughout the Pacific Coast region for several thousand years.
The first recorded European to visit the volcano was Peter Skene Ogden, a trapper who reached the crater in 1826. In 1855, the volcano's namesake,
The area around Newberry Volcano has been inhabited by Native American peoples for more than 10,000 years, though only intermittently as a result of eruptive activity at the volcano and in the surrounding area. During an archaeological excavation near Paulina Lake in 1992, researchers discovered remnants of a central hearth and a housing structure with support posts and linear rock arrangements with dimensions of . Radiocarbon dating of charcoal samples from the site were dated to 11,000 years ago. The mountain's caldera was used to harvest obsidian, which they used to sharpen arrowheads and tools and traded throughout the Pacific Coast region for several thousand years.
The first recorded European to visit the volcano was Peter Skene Ogden, a trapper who reached the crater in 1826. In 1855, the volcano's namesake, John Strong Newberry
John Strong Newberry (December 22, 1822 – December 7, 1892) was an American physician, geologist and paleontologist. He participated as a naturalist and surgeon on three expeditions to explore and survey the western United States. During the C ...
, a surgeon and geologist for the Williamson and Abbot survey party, visited central Oregon while mapping the local area for the Pacific Railroad
The Pacific Railroad (not to be confused with Union Pacific Railroad) was a railroad based in Missouri. It was a predecessor of both the Missouri Pacific Railroad and St. Louis-San Francisco Railway.
The Pacific was chartered by Missouri in 1849 ...
, but never visited the volcano. Paulina Lake, Paulina Creek, and Paulina Peak are named after Paulina, a Snake Indian chief who headed raiding parties against whites during the 1850s and 1860s before he was pursued and shot by settler Howard Maupin. Near the end of the 19th century, the Lava River Cave was used by the hunter Leander Dillman to store perishable foods. The name Mount Newberry was proposed by Israel Russell, who visited the area in 1903, though the name did not come into use. Instead, it was known as Newberry Crater until it was renamed to the Newberry Volcano in the 1930s by geologist Howel Williams
Howel Williams (October 12, 1898 – January 12, 1980) was a noted American geologist and volcanologist.
Early life
He was born of Welsh parents in Liverpool, England, on October 12, 1898. He received a BA in geography in 1923 and an MA in ar ...
, a name which was formally accepted in 2003 when geologist Larry Chitwood supported it through the official geographic naming process.
Because of the efforts of Hollis Dole, head of the Oregon Department of Geology, to promote the area, in 1963 NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
scientists became interested in using lava fields at Newberry to prepare for the United States' first moon landing
A Moon landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon. This includes both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was the Soviet Union's Luna 2, on 13 September 1959.
The United S ...
. NASA used the area in October 1964 and July 1966 to geologically train the Apollo Astronauts
As part of the Apollo program by NASA, 24 astronauts flew 9 missions to the Moon between December 1968 and December 1972. During six successful two-man landing missions, 12 men walked on the lunar surface, six of whom drove Lunar Roving Vehicl ...
in recognizing volcanic features, such as cinder and pumice cones, lava flows, ash and obsidian flows, and a lava tube. Astronauts who would use this training on the Moon included Apollo 11
Apollo 11 (July 16–24, 1969) was the American spaceflight that first landed humans on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and lunar module pilot Buzz Aldrin landed the Apollo Lunar Module ''Eagle'' on July 20, 1969, at 20:17 UTC, ...
's Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin
Buzz Aldrin (; born Edwin Eugene Aldrin Jr.; January 20, 1930) is an American former astronaut, engineer and fighter pilot. He made three spacewalks as pilot of the 1966 Gemini 12 mission. As the Lunar Module ''Eagle'' pilot on the 1969 A ...
, Apollo 12's Alan Bean
Alan LaVern Bean (March 15, 1932 – May 26, 2018) was an American naval officer and aviator, aeronautical engineer, test pilot, NASA astronaut and painter; he was the fourth person to walk on the Moon. He was selected to become an astron ...
, Apollo 14's Edgar Mitchell, Apollo 15's James Irwin
James Benson Irwin (March 17, 1930 – August 8, 1991) was an American astronaut, aeronautical engineer, test pilot, and a United States Air Force pilot. He served as Apollo Lunar Module pilot for Apollo 15, the fourth human lunar landi ...
, and Apollo 16's Charlie Duke. Notable geologist instructors included Aaron Waters.
The Newberry National Volcanic Monument was established in November 1990 by the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
. With an area of more than , it forms a near-circular shape around the summit caldera and then a long corridor from the mountain's northwestern side to the Deschutes River that includes a rift zone
A rift zone is a feature of some volcanoes, especially shield volcanoes, in which a set of linear cracks (or rifts) develops in a volcanic edifice, typically forming into two or three well-defined regions along the flanks of the vent. Believed t ...
. The Monument lies within the Deschutes National Forest
The Deschutes National Forest is a United States National Forest located in parts of Deschutes, Klamath, Lake, and Jefferson counties in central Oregon. It comprises along the east side of the Cascade Range. In 1908, the Deschutes National F ...
, which is managed by the United States Forest Service
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 national forests and 20 national grasslands. The Forest Service manages of land. Major divisions of the agency in ...
. As of 1997, the caldera area of Newberry holds seven campgrounds, two resort areas, and six summer houses.
Mining and geothermal energy
Because Newberry has had recent eruptive activity, has remained active for a long time, and has a shallow heat source feeding hot springs, it represents a source of geothermal energy. An investigation conducted by the United States Geological Survey in 1981 drilled a well in depth at a location to the east of the Big Obsidian flow, finding temperatures of under the surface there. An energy company drilled two holes with a depth of in 1995 and 1996, but they were unable to find fluids, so they lacked a mechanism to drive turbines and opted to end the project at Newberry. According to many scientists, Newberry Volcano represents the best geothermal energy candidate in thePacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Tho ...
; in 2012, a deep well was built to determine whether water directed into the hole might be heated and returned to the surface in order to yield energy.
Recreation
 Newberry Volcano is visited by 250,000 people each year, who come to go
Newberry Volcano is visited by 250,000 people each year, who come to go fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
for trout in East Lake, to camp on Paulina Lake, or go mountain biking around the loop that surrounds the crater. The lakes are also popular for boating. At the Newberry National Volcanic Monument, camping, fishing, and hiking are popular, including on the Trail of the Molten Land, which follows a 7,000-year-old lava flow from Lava Butte, and the Trail of the Whispering Pines, which traverses a ponderosa pine forest. Horse riding
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, driving, and vaulting. This broad description includes the ...
is also possible in a section of the Peter Skene Ogden Trail, long, which runs through the monument area; snowmobiling
A snowmobile, also known as a Ski-Doo, snowmachine, sled, motor sled, motor sledge, skimobile, or snow scooter, is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow. It is designed to be operated on snow and ice and does not ...
and cross-country skiing are also popular.
The Lava Lands Visitor Center within the Monument has an exhibit on the area's geology and culture and offers a paved path that runs for . A shuttle leaves from the center every 20 minutes during the peak season from Memorial Day through Labor Day, costing $2 per traveler. The area can also be accessed by personal motorized vehicles during off season with a permit from the visitor center, and the center's parking area remains open year-round. The area offers eight campgrounds operated by the United States Forest Service.
The last lava flow from Newberry during the Pleistocene formed the Lava River Cave
The Lava River Cave near Bend, Oregon, is part of the Newberry National Volcanic Monument, which is managed by the United States Forest Service. At in length, the northwest section of the cave is the longest continuous lava tube in Oregon. W ...
, to the south of Bend. This feature is the state's longest continuous lava tube, which can be hiked for more than one mile to the north and west and has an arching ceiling with a thickness of . This trail represents the monument's most popular attraction and can be hiked between May and mid-September with a recreation day pass that costs $5. Jackets are recommended, as the temperature within the cave is usually . The Lava Cast Forest, a group of trees molded by lava from an eruption 6,000 years ago, covers an area of and can be observed from a paved, narrow, and steep one-mile trail. The area was designated as the Lava Cast Forest Geological Area in April 1942 by the United States Forest Service, which included of land in the region. Known to the American public since 1928, by the mid-1940s the Lava Cast Forest was visited by thousands of tourists each year. In the mid-1970s, the region had 150,000 tourist visitors annually, with the Lava Lands Visitors Center built by the Forest Service in September 1975.
The trail to the volcano's summit at Paulina Peak lasts from Highway 97, with an easy paved road to the caldera and four rest stops, though it grows steep and twisty near the end. The winding trail near the end is made of gravel and lasts for three miles, offering views of Mount Hood, Mount McLoughlin, and the Three Sisters volcanoes.
Notes
* Other sources list the elevation of Paulina Peak as or . * At a depth of under Newberry, p- ands-wave
__NOTOC__
In seismology and other areas involving elastic waves, S waves, secondary waves, or shear waves (sometimes called elastic S waves) are a type of elastic wave and are one of the two main types of elastic body waves, so named because th ...
velocities increase, which has been interpreted via tomography
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, astrophysics, ...
as the top of the subducting Juan de Fuca tectonic plate. This differs from earthquake data suggesting the surface of the plate lies at a depth of .
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * . * * . * * * * *External links
* *Database for the Geologic Map of Newberry Volcano, Deschutes, Klamath, and Lake Counties, Oregon
– United States Geological Survey {{authority control Calderas of Oregon Cascade Volcanoes Volcanic crater lakes Fissure vents Geology of Oregon Hotspot volcanoes Lava domes Lava tubes Mountains of Deschutes County, Oregon Mountains of Klamath County, Oregon Mountains of Lake County, Oregon Mountains of Oregon National Natural Landmarks in Oregon Newberry National Volcanic Monument Polygenetic shield volcanoes Pyroclastic cones Potentially active volcanoes Shield volcanoes of the United States Subduction volcanoes Volcanoes of Deschutes County, Oregon Volcanoes of Klamath County, Oregon Volcanoes of Oregon