|
Percolation
Percolation (from Latin ''percolare'', "to filter" or "trickle through"), in physics, chemistry and materials science, refers to the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials. It is described by Darcy's law. Broader applications have since been developed that cover connectivity of many systems modeled as lattices or graphs, analogous to connectivity of lattice components in the filtration problem that modulates capacity for percolation. Background During the last decades, percolation theory, the mathematical study of percolation, has brought new understanding and techniques to a broad range of topics in physics, materials science, complex networks, epidemiology, and other fields. For example, in geology, percolation refers to filtration of water through soil and permeable rocks. The water flows to recharge the groundwater in the water table and aquifers. In places where infiltration basins or septic drain fields are planned to dispose of substantial amounts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percolation Threshold
The percolation threshold is a mathematical concept in percolation theory that describes the formation of long-range connectivity in random systems. Below the threshold a giant connected component does not exist; while above it, there exists a giant component of the order of system size. In engineering and coffee making, percolation represents the flow of fluids through porous media, but in the mathematics and physics worlds it generally refers to simplified lattice models of random systems or networks (graphs), and the nature of the connectivity in them. The percolation threshold is the critical value of the occupation probability ''p'', or more generally a critical surface for a group of parameters ''p''1, ''p''2, ..., such that infinite connectivity (''percolation'') first occurs. Percolation models The most common percolation model is to take a regular lattice, like a square lattice, and make it into a random network by randomly "occupying" sites (vertices) or bonds (edges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percolation Theory
In statistical physics and mathematics, percolation theory describes the behavior of a network when nodes or links are added. This is a geometric type of phase transition, since at a critical fraction of addition the network of small, disconnected clusters merge into significantly larger connected, so-called spanning clusters. The applications of percolation theory to materials science and in many other disciplines are discussed here and in the articles network theory and percolation. Introduction A representative question (and the source of the name) is as follows. Assume that some liquid is poured on top of some porous material. Will the liquid be able to make its way from hole to hole and reach the bottom? This physical question is modelled mathematically as a three-dimensional network of vertices, usually called "sites", in which the edge or "bonds" between each two neighbors may be open (allowing the liquid through) with probability , or closed with probability , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percolation
Percolation (from Latin ''percolare'', "to filter" or "trickle through"), in physics, chemistry and materials science, refers to the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials. It is described by Darcy's law. Broader applications have since been developed that cover connectivity of many systems modeled as lattices or graphs, analogous to connectivity of lattice components in the filtration problem that modulates capacity for percolation. Background During the last decades, percolation theory, the mathematical study of percolation, has brought new understanding and techniques to a broad range of topics in physics, materials science, complex networks, epidemiology, and other fields. For example, in geology, percolation refers to filtration of water through soil and permeable rocks. The water flows to recharge the groundwater in the water table and aquifers. In places where infiltration basins or septic drain fields are planned to dispose of substantial amounts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percolation Test
A percolation test (colloquially called a perc test) is a test to determine the water absorption rate of soil (that is, its capacity for percolation) in preparation for the building of a septic drain field (leach field) or infiltration basin. The results of a percolation test are required to properly design a septic system. In its broadest terms, percolation testing is simply observing how quickly a known volume of water dissipates into the subsoil of a drilled hole of known surface area. While every jurisdiction will have its own laws regarding the exact calculations for the length of line, depth of pit, etc., the testing procedures are the same. In general, sandy soil will absorb more water than soil with a high concentration of clay or where the water table is close to the surface. Testing method A percolation test consists of digging one or more holes in the soil of the proposed leach field to a specified depth, presoaking the holes by maintaining a high water level in the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percolation Test
A percolation test (colloquially called a perc test) is a test to determine the water absorption rate of soil (that is, its capacity for percolation) in preparation for the building of a septic drain field (leach field) or infiltration basin. The results of a percolation test are required to properly design a septic system. In its broadest terms, percolation testing is simply observing how quickly a known volume of water dissipates into the subsoil of a drilled hole of known surface area. While every jurisdiction will have its own laws regarding the exact calculations for the length of line, depth of pit, etc., the testing procedures are the same. In general, sandy soil will absorb more water than soil with a high concentration of clay or where the water table is close to the surface. Testing method A percolation test consists of digging one or more holes in the soil of the proposed leach field to a specified depth, presoaking the holes by maintaining a high water level in the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
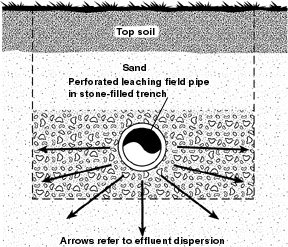
Septic Drain Field
Septic drain fields, also called leach fields or leach drains, are subsurface wastewater disposal facilities used to remove contaminants and impurities from the liquid that emerges after anaerobic digestion in a septic tank. Organic materials in the liquid are catabolized by a microbial ecosystem. A septic drain field, a septic tank, and associated piping compose a septic system. The drain field typically consists of an arrangement of trenches containing perforated pipes and porous material (often gravel) covered by a layer of soil to prevent animals (and surface runoff) from reaching the wastewater distributed within those trenches. Primary design considerations are both ''hydraulic'' for the volume of wastewater requiring disposal and ''catabolic'' for the long-term biochemical oxygen demand of that wastewater. The land area that is set aside for the septic drain field may be called a septic reserve area (SRA). Sewage farms similarly dispose of wastewater through a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septic Drain Field
Septic drain fields, also called leach fields or leach drains, are subsurface wastewater disposal facilities used to remove contaminants and impurities from the liquid that emerges after anaerobic digestion in a septic tank. Organic materials in the liquid are catabolized by a microbial ecosystem. A septic drain field, a septic tank, and associated piping compose a septic system. The drain field typically consists of an arrangement of trenches containing perforated pipes and porous material (often gravel) covered by a layer of soil to prevent animals (and surface runoff) from reaching the wastewater distributed within those trenches. Primary design considerations are both ''hydraulic'' for the volume of wastewater requiring disposal and ''catabolic'' for the long-term biochemical oxygen demand of that wastewater. The land area that is set aside for the septic drain field may be called a septic reserve area (SRA). Sewage farms similarly dispose of wastewater through a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater Recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs in the vadose zone below plant roots and is often expressed as a flux to the water table surface. Groundwater recharge also encompasses water moving away from the water table farther into the saturated zone. Recharge occurs both naturally (through the water cycle) and through anthropogenic processes (i.e., "artificial groundwater recharge"), where rainwater and or reclaimed water is routed to the subsurface. Processes Water is recharged naturally by rain and snow melt and to a smaller extent by surface water (rivers and lakes). Recharge may be impeded somewhat by human activities including paving, development, or logging. These activities can result in loss of topsoil resulting in reduced water infiltration, enhanced surface runo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition At the phase transition point for a substance, for instance the boiling point, the two phases involved - liquid and vapor, have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater is recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology. Typically, groundwater is thought of as water flowing through shallow aquifers, but, in the technical sense, it can also contain soil moisture, per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infiltration Basin
An infiltration basin (or recharge basin) is a form of engineered sump or percolation pond that is used to manage stormwater runoff, prevent flooding and downstream erosion, and improve water quality in an adjacent river, stream, lake or bay. It is essentially a shallow artificial pond that is designed to infiltrate stormwater through permeable soils into the groundwater aquifer. Infiltration basins do not release water except by infiltration, evaporation or emergency overflow during flood conditions. It is distinguished from a detention basin, sometimes called a dry pond, which is designed to discharge to a downstream water body (although it may incidentally infiltrate some of its volume to groundwater); and from a retention basin, which is designed to include a permanent pool of water. Design considerations Infiltration basins must be carefully designed to infiltrate the soil on a given site at a rate that will not cause flooding. They may be less effective in areas with: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). Likewise, if the radius of a filled s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(29856364125).jpg)
