|
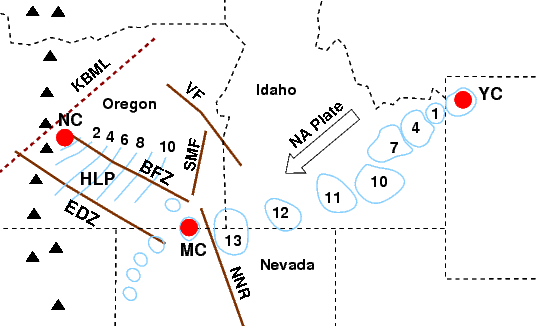
Brothers Fault Zone
The Brothers Fault Zone (BFZ) is the most notable of a set of northwest-trending fault zones including the Eugene–Denio, McLoughlin, and Vale zones that dominate the Geology of Oregon, geological structure of most of Oregon. These are also representative of a regional pattern of generally northwest-striking geological features ranging from Walker Lane on the California–Nevada border to the Olympic–Wallowa Lineament in Washington; these are generally associated with the regional extension and faulting of the Basin and Range Province, of which the BFZ is considered the northern boundary. The relationships with other features is complex. At the BFZ's eastern end, near the Steens Mountain fault, the zone of surface faulting turns slightly to the south-southeast (possibly due to rotation of Nevada), then follows the Northern Nevada Rift to form the Oregon–Nevada lineament, with a total length of over . Lavas associated with the Nevada Rift have been dated to 16.3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steens Mountain
Steens Mountain is in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Oregon, and is a large fault-block mountain. Located in Harney County, it stretches some north to south, and rises from the west side the Alvord Desert at elevation of about to a summit elevation of . Steens Mountain is not part of a mountain range but is properly a single mountain, the largest of Oregon's fault-block mountains.Conkling, C., Jackman, E. R., & Scharff, J. (1967)Steens Mountain in Oregon's high desert country Caxton Press. Retrieved April 25, 2022 The Steens Mountain Wilderness encompasses of Steens Mountain. of the Wilderness are protected from grazing and free of cattle. History The mountain was called the "Snowy Mountains" by John Work, one of the fur traders who were the first Europeans in the area. It was renamed in 1860 for United States Army Major Enoch Steen, who fought and drove members of the Paiute tribe off the mountain. American Indians used the Steens Mountain, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
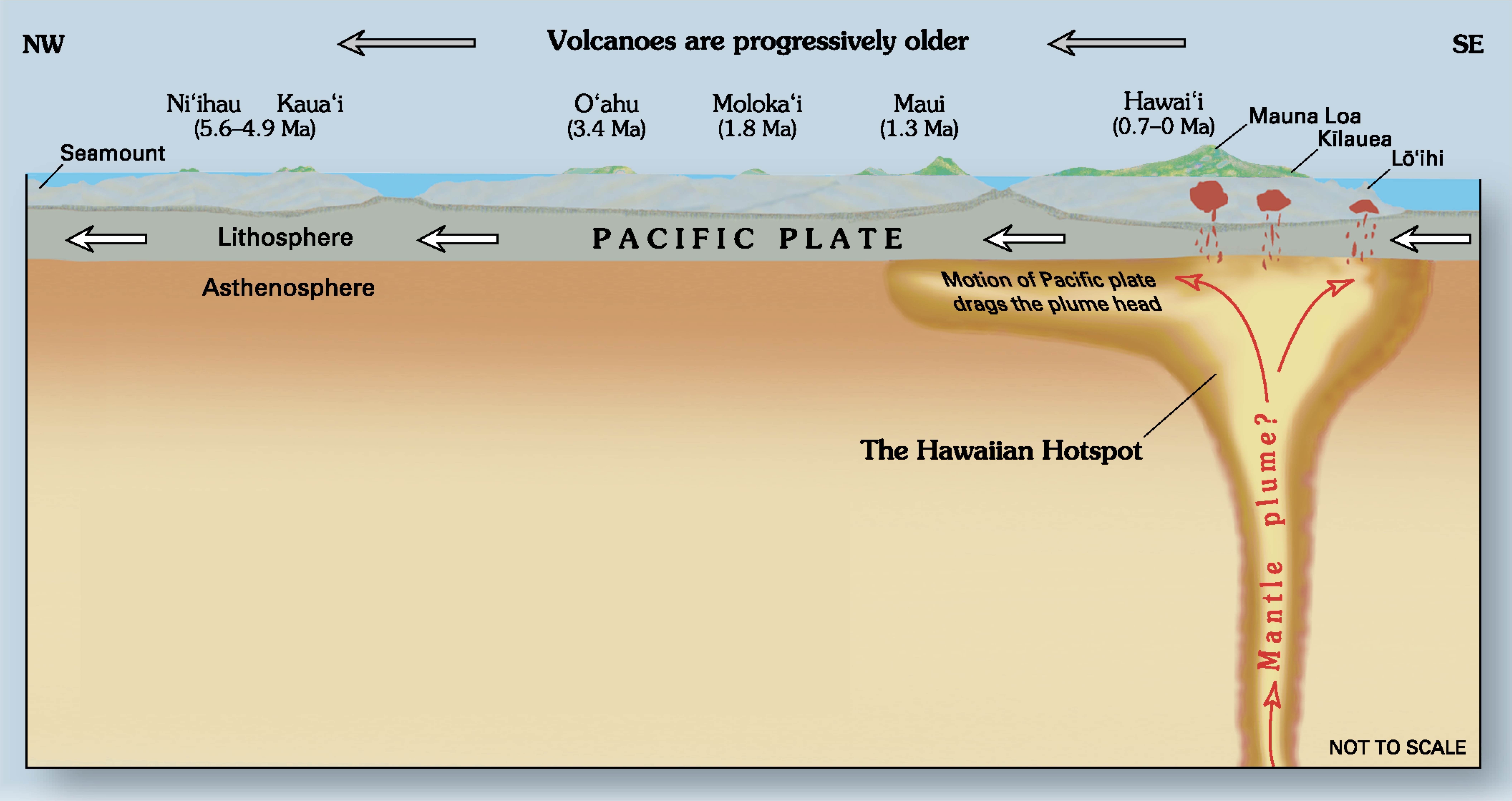
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated in 1963 that the formation of the Hawaiian Islands resulted from the slow movement of a te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates; the exceptions occur where geologically recent rifting events have separated cratons and created passive margins along their edges. Cratons are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots that extend as much as several hundred kilometres into Earth's mantle. Terminology The term ''craton'' is used to distinguish the stable portion of the continental crust from regions that are more geologically active and unstable. Cratons are composed of two layers: A continental '' shield'', in which the basement rock crops out at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia River Basalt Group
The Columbia River Basalt Group is the youngest, smallest and one of the best-preserved continental flood basalt province on Earth, covering over mainly eastern Oregon and Washington, western Idaho, and part of northern Nevada. The basalt group includes the Steens and Picture Gorge basalt formations. Introduction During the middle to late Miocene epoch, the Columbia River flood basalts engulfed about of the Pacific Northwest, forming a large igneous province with an estimated volume of . Eruptions were most vigorous 17–14 million years ago, when over 99 percent of the basalt was released. Less extensive eruptions continued 14–6 million years ago. Erosion resulting from the Missoula Floods has extensively exposed these lava flows, laying bare many layers of the basalt flows at Wallula Gap, the lower Palouse River, the Columbia River Gorge and throughout the Channeled Scablands. The Columbia River Basalt Group is thought to be a potential link to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steens Basalts
Steens may refer to: *Steens, Mississippi, an unincorporated community *Steens Mountain, a fault-block mountain in southeast Oregon state See also *Ron Steens Ronaldus "Ron" Franciscus Johannes Steens (born 18 June 1952) is a former field hockey player from The Netherlands, who was a member of the Dutch National Team that finished sixth in the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles, California. Eight yea ... (b. 1952), Dutch field hockey player * Steens Highway, Oregon Route 78 {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowstone Hotspot
The Yellowstone hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the United States responsible for large scale volcanism in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Wyoming, formed as the North American tectonic plate moved over it. It formed the eastern Snake River Plain through a succession of caldera-forming eruptions. The resulting calderas include the Island Park Caldera, Henry's Fork Caldera, and the Bruneau-Jarbidge caldera. The hotspot currently lies under the Yellowstone Caldera. The hotspot's most recent caldera-forming supereruption, known as the Lava Creek Eruption, took place 640,000 years ago and created the Lava Creek Tuff, and the most recent Yellowstone Caldera. The Yellowstone hotspot is one of a few volcanic hotspots underlying the North American tectonic plate; another example is the Anahim hotspot. Snake River Plain The eastern Snake River Plain is a topographic depression that cuts across Basin and Range Mountain structures, more or less parallel to North American plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly through California. It forms the tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is right-lateral strike-slip (horizontal). The fault divides into three segments, each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The slip rate along the fault ranges from /yr. It was formed by a transform boundary. The fault was identified in 1895 by Professor Andrew Lawson of UC Berkeley, who discovered the northern zone. It is often described as having been named after San Andreas Lake, a small body of water that was formed in a valley between the two plates. However, according to some of his reports from 1895 and 1908, Lawson actually named it after the surrounding San Andreas Valley. Following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, Lawson concluded that the fault extended all the way into southern California. In 1953, geologist Thomas Dibblee c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klamath Mountains
The Klamath Mountains are a rugged and lightly populated mountain range in northwestern California and southwestern Oregon in the western United States. As a mountain system within both the greater Pacific Coast Ranges and the California Coast Ranges, the Klamath Mountains have a varied geology, with substantial areas of serpentinite and marble, and a climate characterized by moderately cold winters with very heavy snowfall and warm, very dry summers with limited rainfall, especially in the south. As a consequence of the geology and soil types, the mountains harbor several endemic or near-endemic trees, forming one of the largest collections of conifers in the world. The mountains are also home to a diverse array of fish and animal species, including black bears, large cats, owls, eagles, and several species of Pacific salmon. Millions of acres in the mountains are managed by the United States Forest Service. The northernmost and largest sub-range of the Klamath Mountains are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terranes
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own distinctive geologic history, which is different from that of the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. Older usage of ''terrane'' simply described a series of related rock formations or an area having a preponderance of a particular rock or rock groups. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane is not necessarily an independent microplate in origin, since it may not contain the full thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago. The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic Era, and extended to the beginning of the Quaternary glaciation at the end of the Pliocene Epoch. The time span covered by the Tertiary has no exact equivalent in the current geologic time system, but it is essentially the merged Paleogene and Neogene periods, which are informally called the Early Tertiary and the Late Tertiary, respectively. The Tertiary established the Antarctic as an icy island continent. Historical use of the term The term Tertiary was first used by Giovanni Arduino during the mid-18th century. He classified geologic time into primitive (or primary), secondary, and tertiary periods based on observations of geology in Northern Italy. Later a fourth period, the Quaternary, was applied. In the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)