Mark 15 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mark 15 is the fifteenth chapter of the
18:28–19:42


 The original text was written in
The original text was written in
Expositor's Greek Testament on Mark 15
accessed 10 April 2020 According to
JA18
4.2) All the other The priests however convince the crowd to ask for the release of Barabbas, a prisoner. Mark says he was in prison chained "with" insurrectionists who had committed murder during a recent στασισ (''stasis'', a riot), probably "one of ... numerous insurrections against the Roman power" Maclear, G. F.
The priests however convince the crowd to ask for the release of Barabbas, a prisoner. Mark says he was in prison chained "with" insurrectionists who had committed murder during a recent στασισ (''stasis'', a riot), probably "one of ... numerous insurrections against the Roman power" Maclear, G. F.
Cambridge Bible for Schools and Colleges on Mark 15
accessed 11 December 2017 Theologian John Gill says he was "at the head" of the rebels. Both Luke and John say he was a
 Mark says the soldiers took Jesus to the Praetorium, either
Mark says the soldiers took Jesus to the Praetorium, either



 On the way to their final destination the soldiers force a man passing by, Simon of Cyrene, to carry Jesus' cross for him, though Mark does not say why. Cyrene was in North
On the way to their final destination the soldiers force a man passing by, Simon of Cyrene, to carry Jesus' cross for him, though Mark does not say why. Cyrene was in North
14:57–58
The chief priests are also there and say that if he is really the
16
Mark might be stressing that if one follows Jesus, who Mark believes is the messiah, then one can expect help from God, such as Jesus' miracles, but one will not be saved from the pains of this world, and indeed in some way they are necessary to achieve a greater goal as Jesus' death is necessary for his role as the messiah.
6:3
She could also be another Mary, perhaps another relative. Salome was James' and John's mother. The fact the Mark has not explicitly related any of Jesus' interaction with them shows that Mark has left out many of the events of the life of the " Historical Jesus" and only related events he deems necessary to make his points about Jesus. John says the soldiers were told to take down the bodies for the Sabbath and broke the other two men's legs but stabbed Jesus with a spear to make sure he was dead. John claims this is eyewitness testimony.
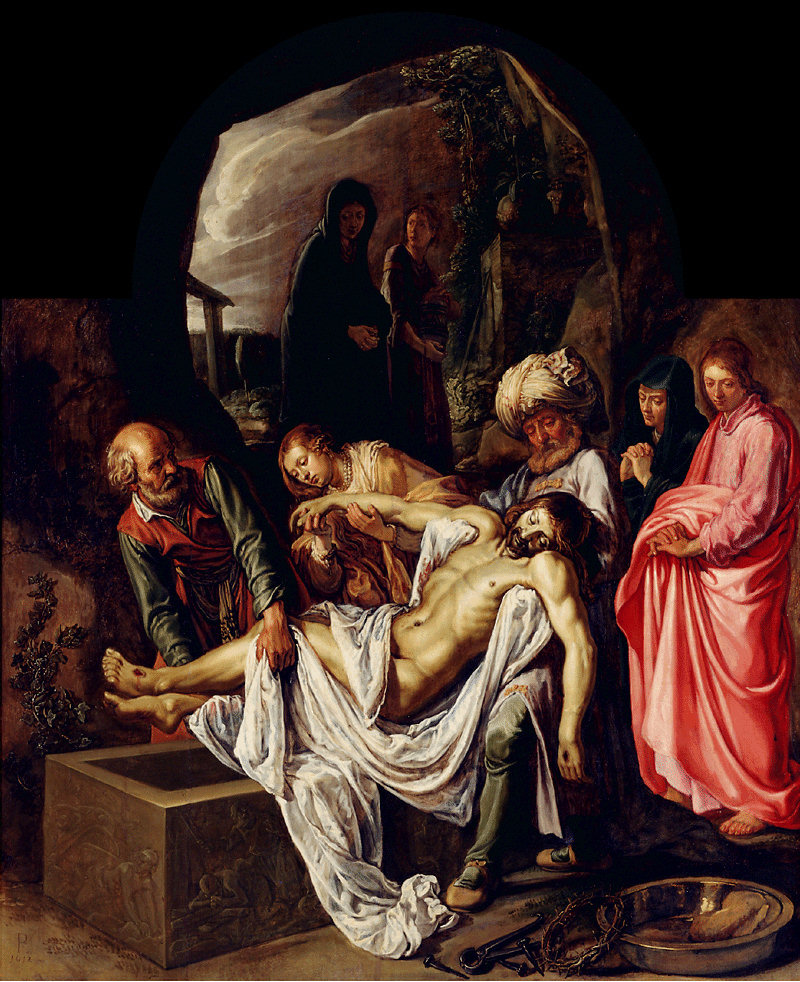 Evening is approaching and Joseph of Arimathea, a member of the
Evening is approaching and Joseph of Arimathea, a member of the
English Translation with Parallel Latin Vulgate''Online Bible'' at GospelHall.org
(ESV, KJV, Darby, American Standard Version, Bible in Basic English)
Multiple bible versions at ''Bible Gateway''
(NKJV, NIV, NRSV etc.) {{Gospel of Mark Gospel of Mark chapters Crucifixion of Jesus Pontius Pilate Calvary Barabbas
Gospel of Mark
The Gospel of Mark), or simply Mark (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). is the second of the four canonical gospels and of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells of the ministry of Jesus from his baptism by John the Baptist to h ...
in the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
of the Christian Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
. This chapter records the narrative of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
' passion, including his trial before Pontius Pilate and then his crucifixion, death and entombment
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
. Jesus' trial before Pilate and his crucifixion, death, and burial are also recorded in Matthew 27, Luke 23, and Joh18:28–19:42
Text


 The original text was written in
The original text was written in Koine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
. This chapter is divided into 47 verses.
Textual witnesses
Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter are: *Codex Vaticanus
The Codex Vaticanus ( The Vatican, Bibl. Vat., Vat. gr. 1209), designated by siglum B or 03 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), δ 1 ( von Soden), is a fourth-century Christian manuscript of a Greek Bible, containing the majority of the Greek Old ...
(~325–350)
*Codex Sinaiticus
The Codex Sinaiticus ( Shelfmark: London, British Library, Add MS 43725), designated by siglum [Aleph] or 01 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 2 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscript ...
(~330–360)
* Codex Bezae (~400)
* Codex Washingtonianus (~400)
*Codex Alexandrinus
The Codex Alexandrinus (London, British Library, Royal MS 1. D. V-VIII), designated by the siglum A or 02 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 4 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscripts), is a manu ...
(~400–440)
* Codex Ephraemi Rescriptus (~450; complete)
Old Testament references
* : Psalm * : Psalm * : Psalm * : PsalmNew Testament references
*: ; ; *: ; *: ; ; *: ; ; *: ; ;Trial before Pilate
Verse 1
:''Immediately, in the morning, the chief priests held a consultation with the elders and scribes and the whole council; and they bound Jesus, led Him away, and delivered Him to Pilate.'' In the previous chapter, Mark has stressed that "all the chief priests, the elders, and the scribes", "all the council", had taken part in the overnight trial of Jesus. Early the next morning the council or Sanhedrin reaches a decision, and agrees to hand Jesus over toPontius Pilate
Pontius Pilate (; grc-gre, Πόντιος Πιλᾶτος, ) was the fifth governor of the Roman province of Judaea, serving under Emperor Tiberius from 26/27 to 36/37 AD. He is best known for being the official who presided over the trial of ...
. Pilate was the Roman Prefect
Prefect (from the Latin ''praefectus'', substantive adjectival form of ''praeficere'': "put in front", meaning in charge) is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area.
A prefect's ...
(governor) of Iudaea Province from 26 to 36, which was the Roman combination of Idumea
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east ...
, Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous so ...
and Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first ...
and did not include Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Gali ...
, which was under the jurisdiction of Herod Antipas
Herod Antipas ( el, Ἡρῴδης Ἀντίπας, ''Hērǭdēs Antipas''; born before 20 BC – died after 39 AD), was a 1st-century ruler of Galilee and Perea, who bore the title of tetrarch ("ruler of a quarter") and is referred to as both ...
. William Robertson Nicoll suggests that the "consultation" should be understood as the "resolution" resulting from the consultation, given that the whole council had been involved in the trial.Nicoll, W. R.Expositor's Greek Testament on Mark 15
accessed 10 April 2020 According to
Matthew
Matthew may refer to:
* Matthew (given name)
* Matthew (surname)
* ''Matthew'' (ship), the replica of the ship sailed by John Cabot in 1497
* ''Matthew'' (album), a 2000 album by rapper Kool Keith
* Matthew (elm cultivar), a cultivar of the Chi ...
, the Sanhedrin had decided to execute Jesus. Only the Romans were allowed to execute someone, not the local officials, according to John 18:31, yet records the Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin ( Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as " rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temp ...
ordering the stoning of Saint Stephen
Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ''Stéphanos'', meaning "wreath, crown" and by extension "reward, honor, renown, fame", often given as a title rather than as a name; c. 5 – c. 34 AD) is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first ...
and also James the Just according to Antiquities of the Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' ( la, Antiquitates Iudaicae; el, Ἰουδαϊκὴ ἀρχαιολογία, ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by historian Flavius Josephus in the 13th year of the ...
(20.9.1), resulting in a rebuke from the Roman authority.
Verse 2
: ''Pilate asked him, 'Are you the King of the Jews?' :: ''He answered him, 'You say so.' ''(NRSV) The Greek Textus Receptus/Majority Text
In the textual criticism of the New Testament, the Byzantine text-type (also called Majority Text, Traditional Text, Ecclesiastical Text, Constantinopolitan Text, Antiocheian Text, or Syrian Text) is one of the main text types. It is the form fo ...
reads:
: καὶ ἐπηρώτησεν αὐτὸν ὁ Πιλάτος, Σὺ εἶ ὁ βασιλεὺς τῶν Ἰουδαίων;
:: ὁ δὲ ἀποκριθεὶς εἶπεν αὐτῷ, Σὺ λέγεις.
Cross references: Matthew 27:11; Luke 23:3; John 18:37
An interpretation is that Pilate is asking Jesus if he is the messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
, just as the high priest
The term "high priest" usually refers either to an individual who holds the office of ruler-priest, or to one who is the head of a religious caste.
Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, a high priest was the chief priest of any of the many gods rev ...
before in , only with an explicit emphasis on the Messiah's political role, that of Jewish King.Brown ''et al.'' 627 According to John's gospel
The Gospel of John ( grc, Εὐαγγέλιον κατὰ Ἰωάννην, translit=Euangélion katà Iōánnēn) is the fourth of the four canonical gospels. It contains a highly schematic account of the ministry of Jesus, with seven "si ...
, in response to Pilate's question Jesus has a short conversation with Pilate and then answers, "You are right in saying I am a king. In fact, for this reason I was born, and for this I came into the world, to testify to the truth. Everyone on the side of truth listens to me." Historically
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
it is likely that perceived insurrection against Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
was for what Pilate executed Jesus. According to , however, Jesus said one should pay the Roman tax and was thus not a revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective, to refer to something that has a major, sudden impact on society or on some aspect of human endeavor.
...
.
The 1985 Jesus Seminar
The Jesus Seminar was a group of about 50 critical biblical scholars and 100 laymen founded in 1985 by Robert Funk that originated under the auspices of the Westar Institute.''Making Sense of the New Testament'' by Craig Blomberg (Mar 1, 2004) ...
reached the conclusion that the temple incident was the cause of the crucifixion.
Verse 3
:''And the chief priests accused Him of many things, but He answered nothing.'' The chief priests remain in attendance before Pilate and make several further, unspecified, allegations, "heaping accusations on Him". Nicoll surmises that the single accusation, that Jesus had declared himself king, was not sufficient to convince Pilate of any wrongdoing. Some manuscripts state here that Jesus gives no reply. Pilate pushes him for one but he still remains silent, which amazes or surprises Pilate. According to Luke, Pilate at this point sent Jesus toHerod Antipas
Herod Antipas ( el, Ἡρῴδης Ἀντίπας, ''Hērǭdēs Antipas''; born before 20 BC – died after 39 AD), was a 1st-century ruler of Galilee and Perea, who bore the title of tetrarch ("ruler of a quarter") and is referred to as both ...
because Jesus, as a Galilean, was under Herod's jurisdiction. Herod was excited to see Jesus at first, but ended up mocking him and sending him back to Pilate.
Release of Barabbas
According to Mark's account, it was a custom to release a prisoner atPassover
Passover, also called Pesach (; ), is a major Jewish holiday that celebrates the Biblical story of the Israelites escape from slavery in Egypt, which occurs on the 15th day of the Hebrew month of Nisan, the first month of Aviv, or spring. ...
, which was a celebration of freedom. No other historical record of the time records Pilate doing this, and he is known to have been cruel, for which he was eventually expelled from his post.JA18
4.2) All the other
Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
s however also agree with Mark on this tradition. Some theologians suggest that Pilate did this once or a few times or that the Gospels accurately record this tradition even though other sources fail to mention. The Jesus Seminar
The Jesus Seminar was a group of about 50 critical biblical scholars and 100 laymen founded in 1985 by Robert Funk that originated under the auspices of the Westar Institute.''Making Sense of the New Testament'' by Craig Blomberg (Mar 1, 2004) ...
argued doing this during a volatile situation like this would have been unlikely.
According to Matthew, Pilate received a message from his wife that she believed Jesus was innocent because of a disturbing dream she had just had. He asks the crowd if they want the King of the Jews released to them because, according to Mark, Pilate knew the priests were envious
Envy is an emotion which occurs when a person lacks another's quality, skill, achievement, or possession and either desires it or wishes that the other lacked it.
Aristotle defined envy as pain at the sight of another's good fortune, stirred ...
of Jesus and so presumably wanted to free him without a fight with them.
 The priests however convince the crowd to ask for the release of Barabbas, a prisoner. Mark says he was in prison chained "with" insurrectionists who had committed murder during a recent στασισ (''stasis'', a riot), probably "one of ... numerous insurrections against the Roman power" Maclear, G. F.
The priests however convince the crowd to ask for the release of Barabbas, a prisoner. Mark says he was in prison chained "with" insurrectionists who had committed murder during a recent στασισ (''stasis'', a riot), probably "one of ... numerous insurrections against the Roman power" Maclear, G. F.Cambridge Bible for Schools and Colleges on Mark 15
accessed 11 December 2017 Theologian John Gill says he was "at the head" of the rebels. Both Luke and John say he was a
revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective, to refer to something that has a major, sudden impact on society or on some aspect of human endeavor.
...
. Jesus seems to have already been declared guilty as this seems a choice between releasing two prisoners.
Pilate then asks what should be done with Jesus. They say he should be crucified, but Pilate asks what he is guilty of. They still demand he be crucified so Pilate turns Barabbas over to the crowd and has Jesus flogged
Flagellation (Latin , 'whip'), flogging or whipping is the act of beating the human body with special implements such as whips, rods, switches, the cat o' nine tails, the sjambok, the knout, etc. Typically, flogging has been imposed on ...
and then sent out to be crucified. Matthew has Pilate washing his hands and declaring the crowd responsible, which the crowd accepts.
For his flogging Jesus would have been tied to a pillar, and hit with bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
or metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
studded whips.Brown ''et al.'' 628 Crucifixion was a particularly shameful form of death, with a stigma put onto even the condemned's family.
Roman magistrates had wide discretion in executing their tasks, and some question whether Pilate would have been so captive to the demands of the crowd. Summarily executing someone to calm the situation however would have been a tool a Roman governor would have used.
The soldiers mock Jesus
 Mark says the soldiers took Jesus to the Praetorium, either
Mark says the soldiers took Jesus to the Praetorium, either Herod's palace Herod’s Palace may refer to any of several palace-fortresses built (or rebuilt from previous fortresses) during the reign of Herod the Great, King of Judea from 37 BC to 4 BC. Mostly in ruins today, several have been excavated.
* Herod's Palace ( ...
or the Fortress Antonia. They gather together all the other soldiers. These were probably mostly recruits from the area of Palestine or Syria.
The soldiers put a purple
Purple is any of a variety of colors with hue between red and blue. In the RGB color model used in computer and television screens, purples are produced by mixing red and blue light. In the RYB color model historically used by painters ...
robe on Jesus and put a crown of thorns on his head and mockingly hail him as the King of the Jews. They hit him in the head with a staff and pay fake homage
Homage (Old English) or Hommage (French) may refer to:
History
*Homage (feudal) /ˈhɒmɪdʒ/, the medieval oath of allegiance
*Commendation ceremony, medieval homage ceremony Arts
*Homage (arts) /oʊˈmɑʒ/, an allusion or imitation by one arti ...
to him. According to Matthew they put the staff in his hand first before beating him with it. They dress him in his own clothes and take him out to be crucified. According to John they left his purple robe and crown on.
Jesus is given the trappings of a King. Purple is a royal color. He wears a crown and is hit with a staff, also a royal symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
. This whole scene is colored with divine
Divinity or the divine are things that are either related to, devoted to, or proceeding from a deity.divine< ...
irony, as everything the soldiers do to mock Jesus' claim of being a King is used by Mark to show this, at the height of the Passion, as Jesus' crowning as messiah according to God's plan.
According to John after the flogging Pilate brought Jesus back a second time and tried to convince the crowd that he was innocent but the crowd still demanded Jesus' death and so then Pilate had him crucified. Luke has no account of the soldiers beating Jesus.
Jesus' crucifixion


 On the way to their final destination the soldiers force a man passing by, Simon of Cyrene, to carry Jesus' cross for him, though Mark does not say why. Cyrene was in North
On the way to their final destination the soldiers force a man passing by, Simon of Cyrene, to carry Jesus' cross for him, though Mark does not say why. Cyrene was in North Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and Simon would have moved from there or would have been visiting. Mark lists his children, Alexander and Rufus.
Verse 21
:''Then they compelled a certain man, Simon a Cyrenian, the father of Alexander and Rufus, as he was coming out of the country and passing by, to bear His cross.'' That Mark takes the time to list only Alexander and Rufus as the names of Simon's children suggests they might have beenEarly Christians
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewis ...
known to Mark's intended audience. Paul also lists a Rufus in Romans . A burial cave in the Kidron Valley discovered in 1941 by E. L. Sukenik, belonging to Cyrenian Jews and dating before AD 70, was found to have an ossuary inscribed twice in Greek "Alexander son of Simon." It cannot, however, be certain that this refers to the same person.
Luke has Jesus talking to some of his women followers along the way.
They arrive at Golgotha
Calvary ( la, Calvariae or ) or Golgotha ( grc-gre, Γολγοθᾶ, ''Golgothâ'') was a site immediately outside Jerusalem's walls where Jesus was said to have been crucified according to the canonical Gospels. Since at least the early medie ...
, which Mark says means the place of the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
. This was probably an exhausted rock quarry whose remaining rock had been damaged in an earthquake.
They offer Jesus wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
laced with myrrh
Myrrh (; from Semitic, but see '' § Etymology'') is a gum-resin extracted from a number of small, thorny tree species of the genus '' Commiphora''. Myrrh resin has been used throughout history as a perfume, incense and medicine. Myrrh m ...
to lessen the pain, but he refuses. Mark then simply says they crucified him. They then take his clothes and draw lots to distribute them. George Maclear suggests that they are "unconsciously fulfilling" the words of , which John actually quotes as a fulfillment of prophecy
In religion, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a ''prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain divine will or law, or p ...
.
According to Mark, it was the "third hour" when Jesus was crucified. This would be the third hour of daylight, or about 9:00 am. John however says Jesus was condemned to death around the sixth hour, or noon. The charge listed on Jesus' cross is "THE KING OF THE JEWS" (INRI
In the New Testament, Jesus is referred to as the King of the Jews, both at the beginning of his life and at the end. In the Koine Greek of the New Testament, e.g., in John 19:3, this is written as ''Basileus ton Ioudaion'' ().
Both uses of th ...
) According to John, the chief priests complained to Pilate about this but he refused to change the charge.
Two robbers
Robbery is the crime of taking or attempting to take anything of value by force, threat of force, or by use of fear. According to common law, robbery is defined as taking the property of another, with the intent to permanently deprive the per ...
were also crucified, one on each side of him, and according to Mark, both of them mocked Jesus, even when they were in their processes of death. Luke reports the robbers' conversation with Jesus. People come by and insult Jesus and mock him for claiming he would destroy and then rebuild Herod's Temple in three days, which Jesus has not said so far in Mark but was falsely accused of claiming to destroy the "man-made" Temple and rebuilt it in three days in Mar14:57–58
The chief priests are also there and say that if he is really the
Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
then he should be able to come down from the cross and save himself as he had saved others, a reference to his many miracles earlier in Mark.
Mark relates these two mockings to perhaps highlight the question of why, if Jesus is indeed the messiah, can he not save himself from being put to death. Mark refutes these two charges later when Jesus rebuilds the Temple of his body and not only overcomes the cross but death itself in Mar16
Mark might be stressing that if one follows Jesus, who Mark believes is the messiah, then one can expect help from God, such as Jesus' miracles, but one will not be saved from the pains of this world, and indeed in some way they are necessary to achieve a greater goal as Jesus' death is necessary for his role as the messiah.
The death of Jesus
According to Mark:Verses 33–39
:''And when the sixth hour was come, there was darkness over the whole land until the ninth hour. And at the ninth hour Jesus cried with a loud voice, saying, Eloi, Eloi, lama sabachthani? which is, being interpreted, My God, my God, why hast thou forsaken me? And some of them that stood by, when heard it, said, Behold, he calleth Elias. And one ran and filled a spunge full of vinegar, and put it on a reed, and gave him to drink, saying, Let alone; let us see whether Elias will come to take him down. And Jesus cried with a loud voice, and gave up theghost
A ghost is the soul or spirit of a dead person or animal that is believed to be able to appear to the living. In ghostlore, descriptions of ghosts vary widely from an invisible presence to translucent or barely visible wispy shapes, to re ...
. And the veil of the temple was rent in twain from the top to the bottom. And when the centurion
A centurion (; la, centurio , . la, centuriones, label=none; grc-gre, κεντυρίων, kentyríōn, or ) was a position in the Roman army during classical antiquity, nominally the commander of a century (), a military unit of around 80 ...
, which stood over against him, saw that he so cried out, and gave up the ghost, he said, Truly this man was the Son of God.''
The soldier might be recognizing something that no one else could and thus vindicating Jesus,Brown 147 or he might be saying this sarcastically. This statement may bring the Gospel full circle to Mark 1:1 where Jesus is identified by the writer as "the Son of God" (only in some versions, see Mark 1 for details). Luke records that he said that Jesus was a righteous man. Matthew adds that at the moment of Jesus' death tombs in Jerusalem were opened and many bodies of "the saints" were raised from the dead. They were seen subsequently in the "holy city," Jerusalem, by many ( Matthew 27:53– 54).
The veil of the Temple was the barrier between the inner Temple, thought to be God's place on Earth, and the rest. Its destruction is a vindication of Jesus. This might be a metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide (or obscure) clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are often compared wi ...
for God now no longer being separated but free for all the world. Given the imagery of the temple veil (there were cherubim woven into it, like the cherub set as guard over the entrance to Eden after Adam and Eve were cast out) as a symbol of the barrier between the Holy God and sinful men, the rending of the veil indicates a propitiation of God's wrath.
According to John, Jesus' mother Mary and her sister Mary were there with the disciple whom Jesus loved and Jesus told the disciple to take Mary into his home.
It is notable that, according to Mark, it is only Jesus' women followers who are now still with him:
Verses 40–41
:''There were also women looking on from afar, among whom wereMary Magdalene
Mary Magdalene (sometimes called Mary of Magdala, or simply the Magdalene or the Madeleine) was a woman who, according to the four canonical gospels, traveled with Jesus as one of his followers and was a witness to his crucifixion and
resurre ...
, Mary the mother of James the Less and of Joses, and Salome
Salome (; he, שְלוֹמִית, Shlomit, related to , "peace"; el, Σαλώμη), also known as Salome III, was a Jewish princess, the daughter of Herod II, son of Herod the Great, and princess Herodias, granddaughter of Herod the Great, a ...
, who also followed Him and ministered to Him when He was in Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Gali ...
, and many other women who came up with Him to Jerusalem.''
Mary Magdalene has not been mentioned so far in Mark, and the other Mary is perhaps Jesus' mother Mary as she is also mentioned as James' mother in Mar6:3
She could also be another Mary, perhaps another relative. Salome was James' and John's mother. The fact the Mark has not explicitly related any of Jesus' interaction with them shows that Mark has left out many of the events of the life of the " Historical Jesus" and only related events he deems necessary to make his points about Jesus. John says the soldiers were told to take down the bodies for the Sabbath and broke the other two men's legs but stabbed Jesus with a spear to make sure he was dead. John claims this is eyewitness testimony.
Jesus' entombment
''For the subject in art, see Entombment of Christ'' Evening is approaching and Joseph of Arimathea, a member of the
Evening is approaching and Joseph of Arimathea, a member of the sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin ( Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as " rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temp ...
, who was also waiting for the "Kingdom of God
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms Kingdom of God and Kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" ...
," goes to Pilate and asks for Jesus' body. The Scholars Version notes this as "unexpected .. Is Joseph in effect bringing Jesus into his family?" As the next day was the Sabbath Jesus would have to have been buried before sundown or then not until the next night. According to Mosaic law (), if someone was hanged on a tree they were not to remain there at night. Pilate is surprised that Jesus has died so soon and asks for confirmation, and then gives Jesus' body to Joseph.
Joseph wraps it in linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
and puts it in a sepulchre, rolls a stone over the entrance, and leaves. According to John, he was assisted by the Pharisee Nicodemus. The two Marys witness the burial, or at any rate the location where Jesus' body was buried: German biblical commentators Meyer and Weiss infer from the Greek perfect tense
The perfect tense or aspect (abbreviated or ) is a verb form that indicates that an action or circumstance occurred earlier than the time under consideration, often focusing attention on the resulting state rather than on the occurrence itself. ...
τέθειται (''tetheitai'', he was laid) that "the women were not present at the burial, but simply approached and took note where Jesus lay after burial". Bodies were normally anointed, but there seems to be no time here. John however says Nicodemus wrapped up Jesus' body with spices, which seems to indicate an anointing. The tomb, one of many around Jerusalem, was a limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
and Jesus' body would have been laid on a pre-cut shelf, and then most bodies would have been left for a year.
Verse 47
:''And Mary Magdalene and Mary the mother of Joses observed where He was laid.'' NKJV Maclear suggests reading this verse as "observed carefully".See also
*Crucifixion of Jesus
The crucifixion and death of Jesus occurred in 1st-century Judea, most likely in AD 30 or AD 33. It is described in the four canonical gospels, referred to in the New Testament epistles, attested to by other ancient sources, and consider ...
* Pilate's court
In the canonical gospels, Pilate's court refers to the trial of Jesus in praetorium before Pontius Pilate, preceded by the Sanhedrin Trial. In the Gospel of Luke, Pilate finds that Jesus, being from Galilee, belonged to Herod Antipas' juri ...
* Rufus (biblical figure)
* Stephaton
Stephaton, or Steven, is the name given in medieval Christian traditions to the Roman soldier or bystander, unnamed in the Bible, who offered Jesus a sponge soaked in vinegar wine at the Crucifixion. In later depictions of the Crucifixion, Ste ...
* Related Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
parts: Matthew 27, Luke 23, John 18
John 18 is the eighteenth chapter of the Gospel of John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. This chapter records the events on the day of the Crucifixion of Jesus, starting with the arrest of Jesus the evening before (in Judaic calculat ...
, John 19
John 19 is the nineteenth chapter of the Gospel of John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. The book containing this chapter is anonymous, but early Christian tradition uniformly affirmed that John composed this Gospel.Holman Illustrate ...
, Romans 16
Romans 16 is the sixteenth (and the last) chapter of the Epistle to the Romans in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It is authored by Paul the Apostle, while Paul was in Corinth in the mid 50s AD, with the help of a secretary (amanuen ...
References
Sources
*Brown, Raymond E. ''An Introduction to the New Testament'' Doubleday 1997 *Brown, Raymond E. ''et al.'' ''The New Jerome Biblical Commentary'' Prentice Hall 1990 *Kilgallen, John J. ''A Brief Commentary on the Gospel of Mark'' Paulist Press 1989 * *Miller, Robert J. Editor ''The Complete Gospels'' Polebridge Press 1994External links
* King James Bible - WikisourceEnglish Translation with Parallel Latin Vulgate
(ESV, KJV, Darby, American Standard Version, Bible in Basic English)
Multiple bible versions at ''Bible Gateway''
(NKJV, NIV, NRSV etc.) {{Gospel of Mark Gospel of Mark chapters Crucifixion of Jesus Pontius Pilate Calvary Barabbas