Indigenous Californian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of
The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of
 Evidence of human occupation of California dates from at least 19,000 years ago. Prior to European contact, indigenous Californians had 500 distinct sub-tribes or groups, each consisting of 50 to 500 individual members. The size of California tribes today are small compared to tribes in other regions of the United States. Prior to contact with Europeans, the California region contained the highest Native American population density north of what is now
Evidence of human occupation of California dates from at least 19,000 years ago. Prior to European contact, indigenous Californians had 500 distinct sub-tribes or groups, each consisting of 50 to 500 individual members. The size of California tribes today are small compared to tribes in other regions of the United States. Prior to contact with Europeans, the California region contained the highest Native American population density north of what is now
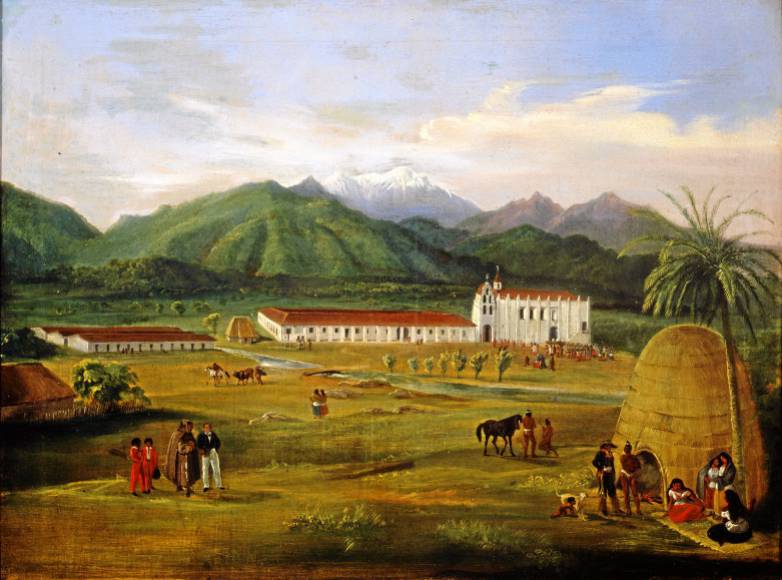 At the time of the establishment of the first Spanish Mission in 1769, the most widely accepted estimates say that California's indigenous population was around 340,000 people and possibly more. The indigenous peoples of California were extremely diverse and made up of ten different linguistic families with at least 78 distinct languages. These are further broken down into many dialects, while the people were organized into sedentary and semi-sedentary villages of 400-500 micro-tribes.
The Spanish began their long-term occupation in California in 1769 with the founding of
At the time of the establishment of the first Spanish Mission in 1769, the most widely accepted estimates say that California's indigenous population was around 340,000 people and possibly more. The indigenous peoples of California were extremely diverse and made up of ten different linguistic families with at least 78 distinct languages. These are further broken down into many dialects, while the people were organized into sedentary and semi-sedentary villages of 400-500 micro-tribes.
The Spanish began their long-term occupation in California in 1769 with the founding of
"California Indian History."
''California Native American Heritage Association.'' (retrieved 10 Sept 2010) From 1769 to 1832, an estimated total of 87,787 baptisms and 24,529 marriages had been conducted at the missions. In that same period, 63,789 deaths at the missions were recorded, indicating the immense death rate. This massive drop in population has been attributed to the introduction of diseases, which rapidly spread while native people were forced into close quarters at the missions, as well as torture, overworking, and malnourishment at the missions. The missions also introduced European
 The
The

 During the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century, the government attempted to force the indigenous peoples to break the ties with their native culture and tribalism and assimilate with the white society. In California, the federal government established such forms of education as the reservation day schools and
During the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century, the government attempted to force the indigenous peoples to break the ties with their native culture and tribalism and assimilate with the white society. In California, the federal government established such forms of education as the reservation day schools and
 California has the largest population of Native Americans out of any state in the United States, with 723,000 identifying an "American Indian or Alaska Native" tribe as a component of their race (14% of the nation-wide total). This population grew by 15% between 2000 and 2010, much less than the nation-wide growth rate of 27%, but higher than the population growth rate for all races, which was about 10% in California over that decade. Over 50,000 indigenous people live in Los Angeles alone.
According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, there are currently over one hundred federally recognized native groups or tribes in California including those that spread to several states. Federal recognition officially grants the Indian tribes access to services and funding from the
California has the largest population of Native Americans out of any state in the United States, with 723,000 identifying an "American Indian or Alaska Native" tribe as a component of their race (14% of the nation-wide total). This population grew by 15% between 2000 and 2010, much less than the nation-wide growth rate of 27%, but higher than the population growth rate for all races, which was about 10% in California over that decade. Over 50,000 indigenous people live in Los Angeles alone.
According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, there are currently over one hundred federally recognized native groups or tribes in California including those that spread to several states. Federal recognition officially grants the Indian tribes access to services and funding from the
File:Yokut Indian woman basket maker, Tule River Reservation near Porterville, California, ca.1900 (CHS-3803).jpg, alt=Woman weaving a wide, shallow, patterned basket while sitting on the ground, Yokut woman basket maker,
 There were two types of marine mammals important as food sources, large migratory species such as northern elephant seals and
There were two types of marine mammals important as food sources, large migratory species such as northern elephant seals and

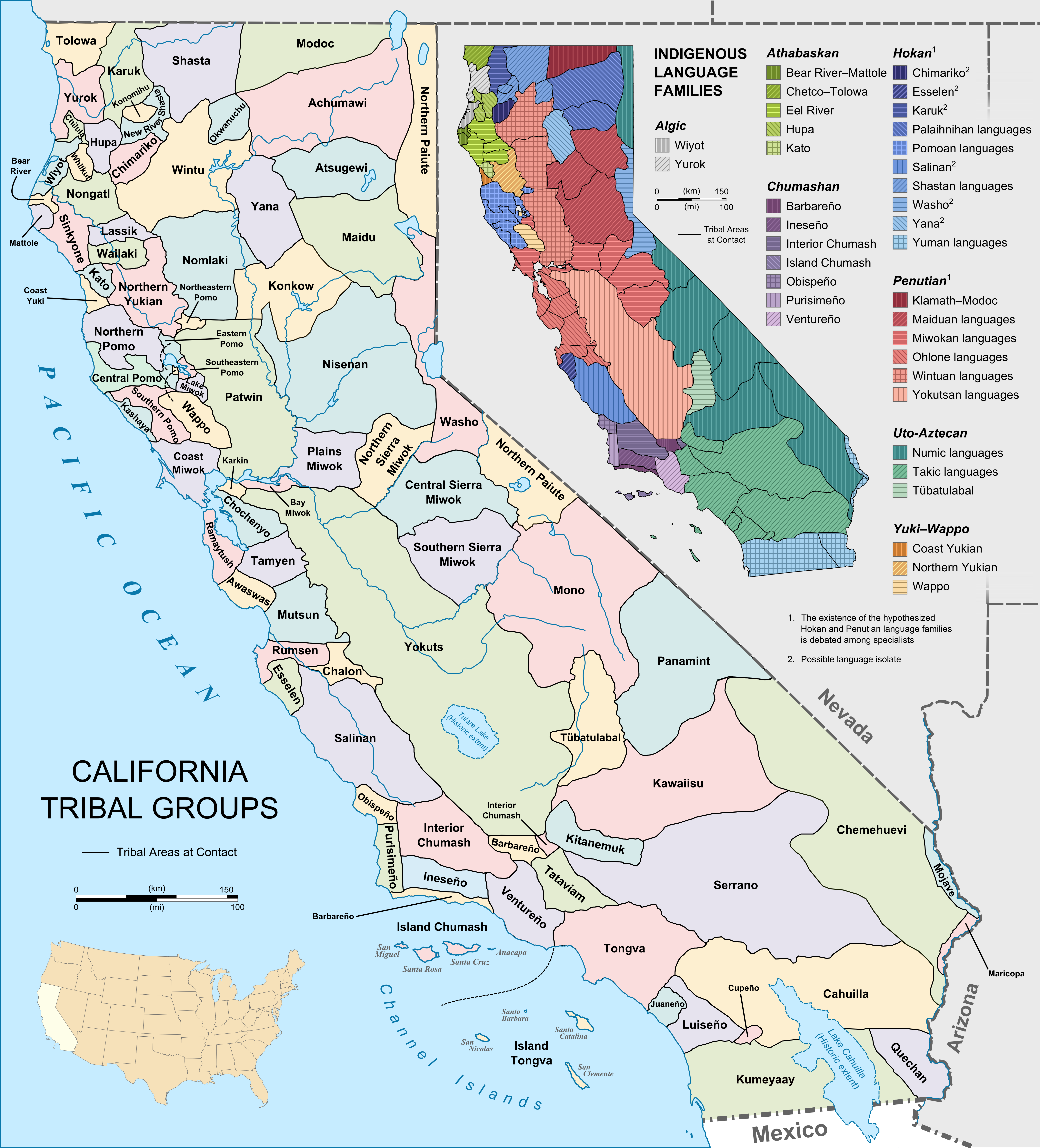 Before European contact, native Californians spoke over 300 dialects of approximately 100 distinct languages. The large number of languages has been related to the ecological diversity of California, and to a sociopolitical organization into small tribelets (usually 100 individuals or fewer) with a shared "ideology that defined language boundaries as unalterable natural features inherent in the land". Together, the area had more linguistic diversity than all of Europe combined.
"The majority of California Indian languages belong either to highly localized language families with two or three members (e.g. Yukian,
Before European contact, native Californians spoke over 300 dialects of approximately 100 distinct languages. The large number of languages has been related to the ecological diversity of California, and to a sociopolitical organization into small tribelets (usually 100 individuals or fewer) with a shared "ideology that defined language boundaries as unalterable natural features inherent in the land". Together, the area had more linguistic diversity than all of Europe combined.
"The majority of California Indian languages belong either to highly localized language families with two or three members (e.g. Yukian,
"Information About California Tribes"
Northern California Indian Development Council
Advocates for Indigenous California Language SurvivalCalifornia Indian Museum and Cultural Center
Santa Rosa
California Native American Heritage Association
"California Indians,"
SDSU Library and Information Access
Society for California Archaeology
California State University San Marcos, Oct. 5–6, 2012 * {{DEFAULTSORT:Indigenous peoples of California Indigenous peoples

 The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of
The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
before and after the arrival of Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) ...
. With over forty groups seeking to be federally recognized tribes
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States of America. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United ...
, California has the second-largest Native American population in the United States. The California cultural area does not conform exactly to the state of California's boundaries. Many tribes on the eastern border with Nevada are classified as Great Basin tribes
The Indigenous peoples of the Great Basin are Native Americans of the northern Great Basin, Snake River Plain, and upper Colorado River basin. The "Great Basin" is a cultural classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas and a cultural re ...
, and some tribes on the Oregon border are classified as Plateau tribes
Indigenous peoples of the Northwest Plateau, also referred to by the phrase Indigenous peoples of the Plateau, and historically called the Plateau Indians (though comprising many groups) are indigenous peoples of the Interior of British Columbia ...
. Tribes in Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
who do not cross into California are classified as indigenous peoples of Mexico
Indigenous peoples of Mexico ( es, gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans ( es, nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans ( es, pueblos originarios de México, lit=Original peoples of Mexico), are those ...
.
History
Pre-contact
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. Because of the temperate climate and easy access to food sources, approximately one-third of all Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United State ...
were living in the area of California.
Early Native Californians were hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s, with seed collection becoming widespread around 9,000 BCE. Due to the local abundance of food, tribes never developed agriculture or tilled the soil. Two early southern California cultural traditions include the La Jolla complex and the Pauma Complex, both dating from c. 6050–1000 BCE. From 3000 to 2000 BCE, regional diversity developed, with the peoples making fine-tuned adaptations to local environments. Traits recognizable to historic tribes were developed by approximately 500 BCE.
The indigenous people practiced various forms of sophisticated forest gardening
Forest gardening is a low-maintenance, Sustainable gardening, sustainable, plant-based food production and agroforestry system based on woodland ecosystems, incorporating fruit and Nut (fruit), nut trees, shrubs, herbs, vines and perennial vegeta ...
in the forests, grasslands, mixed woodlands, and wetlands to ensure availability of food and medicine plants. They controlled fire on a regional scale to create a low-intensity fire ecology
Fire ecology is a scientific discipline concerned with natural processes involving fire in an ecosystem and the ecological effects, the interactions between fire and the abiotic and biotic components of an ecosystem, and the role as an ecosystem p ...
; this prevented larger, catastrophic fires and sustained a low-density "wild" agriculture in loose rotation. By burning underbrush and grass, the natives revitalized patches of land and provided fresh shoots to attract food animals. A form of fire-stick farming
Fire-stick farming, also known as cultural burning and cool burning, is the practice of Aboriginal Australians regularly using fire to burn vegetation, which has been practised for thousands of years. There are a number of purposes for doing this ...
was used to clear areas of old growth to encourage new in a repeated cycle; a permaculture
Permaculture is an approach to land management and settlement design that adopts arrangements observed in flourishing natural ecosystems. It includes a set of design principles derived using whole-systems thinking. It applies these principle ...
.
Contact with Europeans
Different tribes encountered non-native European explorers and settlers at widely different times. The southern and central coastal tribes encountered European explorers in the mid-16th century. Tribes such as theQuechan
The Quechan (or Yuma) (Quechan: ''Kwatsáan'' 'those who descended') are a Native American tribe who live on the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation on the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California just north of the Mexican border. Despite the ...
or Yuman Indians
The Quechan (or Yuma) (Quechan: ''Kwatsáan'' 'those who descended') are a Native American tribe who live on the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation on the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California just north of the Mexican border. Despite the ...
in present-day southeast California and southwest Arizona first encountered Spanish explorers in the 1760s and 1770s. Tribes on the coast of northwest California, like the Miwok
The Miwok (also spelled Miwuk, Mi-Wuk, or Me-Wuk) are members of four linguistically related Native American groups indigenous to what is now Northern California, who traditionally spoke one of the Miwok languages in the Utian family. The word ' ...
, Yurok
The Yurok (Karuk language: Yurúkvaarar / Yuru Kyara - "downriver Indian; i.e. Yurok Indian") are an Indigenous people from along the Klamath River and Pacific coast, whose homelands are located in present-day California stretching from Trinidad ...
, and Yokut, had contact with Russian explorers and seafarers in the late 18th century. In remote interior regions, some tribes did not meet non-natives until the mid-19th century.
Mission era
 At the time of the establishment of the first Spanish Mission in 1769, the most widely accepted estimates say that California's indigenous population was around 340,000 people and possibly more. The indigenous peoples of California were extremely diverse and made up of ten different linguistic families with at least 78 distinct languages. These are further broken down into many dialects, while the people were organized into sedentary and semi-sedentary villages of 400-500 micro-tribes.
The Spanish began their long-term occupation in California in 1769 with the founding of
At the time of the establishment of the first Spanish Mission in 1769, the most widely accepted estimates say that California's indigenous population was around 340,000 people and possibly more. The indigenous peoples of California were extremely diverse and made up of ten different linguistic families with at least 78 distinct languages. These are further broken down into many dialects, while the people were organized into sedentary and semi-sedentary villages of 400-500 micro-tribes.
The Spanish began their long-term occupation in California in 1769 with the founding of Mission San Diego de Alcalá
Mission Basilica San Diego de Alcalá ( es, Misión San Diego de Alcalá) was the second Franciscan founded mission in The Californias (after San Fernando de Velicata), a province of New Spain. Located in present-day San Diego, California, it w ...
in San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the List of United States cities by population, eigh ...
. The Spanish built 20 additional missions in California.Castillo, Edward D"California Indian History."
''California Native American Heritage Association.'' (retrieved 10 Sept 2010) From 1769 to 1832, an estimated total of 87,787 baptisms and 24,529 marriages had been conducted at the missions. In that same period, 63,789 deaths at the missions were recorded, indicating the immense death rate. This massive drop in population has been attributed to the introduction of diseases, which rapidly spread while native people were forced into close quarters at the missions, as well as torture, overworking, and malnourishment at the missions. The missions also introduced European
invasive plant species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species ad ...
as well as cattle grazing
Pastoral farming (also known in some regions as ranching, livestock farming or grazing) is aimed at producing livestock, rather than growing crops. Examples include dairy farming, raising beef cattle, and raising sheep for wool. In contrast, ar ...
practices that significantly transformed the California landscape, altering native people's relationship to the land as well as key plant and animal species that had been integral to their ways of life and worldviews for thousands of years. The missions further perpetuated cultural genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines ...
against native people through enforced conversion to Christianity
Conversion to Christianity is the religious conversion of a previously non-Christian person to Christianity. Different Christian denominations may perform various different kinds of rituals or ceremonies initiation into their community of believ ...
and the prohibition of numerous cultural practices under threat of violence and torture, which were commonplace at the missions.
19th century
 The
The population of Native California
The population of Native California refers to the population of Indigenous peoples of California. Estimates prior to and after European contact have varied substantially. Pre-contact estimates range from 133,000 to 705,000 with some recent schol ...
was reduced by 90% during the 19th century—from more than 200,000 in the early 19th century to approximately 15,000 at the end of the century, mostly due to disease. Epidemics
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious d ...
swept through California Indian Country, such as the 1833 malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
epidemic.
Early to mid 19th Century, coastal tribes of northwest California had multiple contacts with Russian explorers due to Russian colonization of the Americas
The Russian colonization of North America covers the period from 1732 to 1867, when the Russian Empire laid claim to northern Pacific Coast territories in the Americas. Russian colonial possessions in the Americas are collectively known as Russi ...
. At that time period, Russian exploration of California and contacts with local population were usually associated with the activity of the Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty (russian: Под высочайшим Его Императорского Величества покровительством Российская-Американс� ...
. A Russian explorer, Baron Ferdinand von Wrangell, visited California in 1818, 1833, and 1835. Looking for a potential site for a new outpost of the company in California in place of Fort Ross
Fort Ross (Russian: Форт-Росс, Kashaya ''mé·ṭiʔni''), originally Fortress Ross ( pre-reformed Russian: Крѣпость Россъ, tr. ''Krepostʹ Ross''), is a former Russian establishment on the west coast of North America in ...
, Wrangell's expedition encountered the Indians north of San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
and visited their village. In his notes Wrangell remarked that local women, used to physical labor, seemed to be of stronger constitution than men, whose main activity was hunting. Local provision consisted primarily of fish and products made of seeds and grains: usually ground acorns and wild rye. Wrangell surmised his impressions of the California Indians as a people with a natural propensity for independence, inventive spirit, and a unique sense of the beautiful.
Another notable Russian expedition to California was the 13 months long visit of the scientist Ilya Voznesensky
Ilya Gavrilovich Voznesensky (russian: Илья́ Гаври́лович Вознесе́нский, also romanized as Ilia or Il'ia Voznesenskii or Wosnesenski, June 19, 1816 – May 18, 1871) was a Russian explorer and naturalist associated with ...
in 1840–1841. Voznesensky's goal was to gather some ethnographic, biological, and geological materials for the collection of the Imperial Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across t ...
. He described the locals that he met on his trip to Cape Mendocino as "the untamed Indian tribes of New Albion, who roam like animals and, protected by impenetrable vegetation, keep from being enslaved by the Spanish".
In 1834 Mexico secularized the Church's missions and confiscated their properties. But the new government did not return their lands to tribes but made land grants to settlers of at least partial European ancestry. Many landless Indians found wage labor on ranches. Following the United States victory in the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, it took control of California in 1848 with the signing of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
. Its administrators worked to honor Mexican land grant title but did not honor aboriginal land title.
California Gold Rush (1848–1855)
The negative impact of the California Gold Rush on both the local indigenous inhabitants and the environment were substantial, decimating the populations still remaining. Miners took land both for their camps and to farm and supply food for the camps. The surging mining population resulted in the disappearance of many food sources. In addition, the toxic waste from their operations killed fish and destroyed habitats. Miners also viewed indigenous people as competitors for gold, so they also actively went into villages where they raped the women and killed the men.
Conflicts and genocide
Most of inland California including California deserts and the Central Valley was in possession of the local tribes until the acquisition ofAlta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
by the United States. As the wave of migrants from the United States started to settle inland California during the Gold Rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New Z ...
, conflicts between the Native Californians and the settlers started to arise. The series of massacres, battles, and wars between the United States and the indigenous peoples of California lasting from 1850 to 1880 is referred to as the California Indian Wars
The California Indian Wars were a series of wars, battles, and massacres between the United States Army (or often the California State Militia, especially during the early 1850s), and the Indigenous peoples of California. The wars lasted from 18 ...
.
After guns and horses were introduced to the indigenous peoples of California in the beginning of the 19th century, the tensions between the neighboring tribes started to increase, and in combination with mass migration, caused dramatic changes. When in 1846 the Applegate Trail
The Applegate Trail was an emigrant trail through the present-day U.S. states of Idaho, Nevada, California, and Oregon used in the mid-19th century by emigrants on the American frontier. It was originally intended as a less dangerous alternative ...
cut through the Modoc
Modoc may refer to:
Ethnic groups
*Modoc people, a Native American/First Nations people
** Modoc language
**Modoc Tribe of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe of Modoc
*Modoc War, the last armed resistance of the Modoc people in 1873
*The "Mo ...
territory, the migrants and their livestock damaged the ecosystem that the locals were dependent on.
Some anthropologists insist that the indigenous resistance is often used to camouflage genocide in colonial history. For instance, the final stage of the Modoc Campaign was triggered when Modoc men led by Kintpuash (AKA Captain Jack) murdered General Canby at the peace tent in 1873. However, it's not widely known that between 1851 and 1872 the Modoc population decreased by 75 to 88% as a result of seven anti-Modoc campaigns started by the whites. There is evidence that the first massacre of the Modocs by non natives took place as early as 1840. According to the story told by a chief of the Achumawi tribe (neighboring to Modocs), a group of trappers from the north stopped by the Tule lake
Tule Lake ( ) is an intermittent lake covering an area of , long and across, in northeastern Siskiyou County and northwestern Modoc County in California, along the border with Oregon.
Geography
Tule Lake is fed by the Lost River. The elevat ...
around the year 1840 and invited the Modocs to a feast. As they sat down to eat, the cannon was fired and many Indians were killed. The father of Captain Jack was among the survivors of that attack. Since then the Modocs resisted the intruders notoriously.
20th century
 During the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century, the government attempted to force the indigenous peoples to break the ties with their native culture and tribalism and assimilate with the white society. In California, the federal government established such forms of education as the reservation day schools and
During the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century, the government attempted to force the indigenous peoples to break the ties with their native culture and tribalism and assimilate with the white society. In California, the federal government established such forms of education as the reservation day schools and American Indian boarding schools
American Indian boarding schools, also known more recently as American Indian residential schools, were established in the United States from the mid 17th to the early 20th centuries with a primary objective of "civilizing" or assimilating Na ...
. Some public schools would allow Indians to attend as well. Poor ventilation and nutrition (due to limited funding), and diseases were typical problems at schools for American Indians. In addition to that, most parents disagreed with the idea of their children being raised as whites: at boarding schools, the students were forced to wear European style clothes and haircuts, were given European names, and were strictly forbidden to speak indigenous languages. The Native American community recognized the American Indian boarding schools to have oppressed their native culture and demanded the right for their children to access public schools. In 1935 the restrictions that forbid the Native Americans from attending public schools were officially removed.
Since the 1920s, various Indian activist groups were demanding that the federal government fulfil the conditions of the 18 treaties of 1851–1852 that were never ratified and apparently, were classified. In 1944 and in 1946 the native peoples brought claims for reimbursements asking for compensations for the lands affected by treaties and Mexican land grants. They won $17.5 million and $46 million, respectively.
Throughout the 20th century, the population of indigenous peoples of California gradually rose
21st century
 California has the largest population of Native Americans out of any state in the United States, with 723,000 identifying an "American Indian or Alaska Native" tribe as a component of their race (14% of the nation-wide total). This population grew by 15% between 2000 and 2010, much less than the nation-wide growth rate of 27%, but higher than the population growth rate for all races, which was about 10% in California over that decade. Over 50,000 indigenous people live in Los Angeles alone.
According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, there are currently over one hundred federally recognized native groups or tribes in California including those that spread to several states. Federal recognition officially grants the Indian tribes access to services and funding from the
California has the largest population of Native Americans out of any state in the United States, with 723,000 identifying an "American Indian or Alaska Native" tribe as a component of their race (14% of the nation-wide total). This population grew by 15% between 2000 and 2010, much less than the nation-wide growth rate of 27%, but higher than the population growth rate for all races, which was about 10% in California over that decade. Over 50,000 indigenous people live in Los Angeles alone.
According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, there are currently over one hundred federally recognized native groups or tribes in California including those that spread to several states. Federal recognition officially grants the Indian tribes access to services and funding from the Bureau of Indian Affairs
The Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA), also known as Indian Affairs (IA), is a United States federal agency within the Department of the Interior. It is responsible for implementing federal laws and policies related to American Indians and A ...
, and Federal and State funding for Tribal TANF/CalWORKs programs.
Material culture
Basket weaving
Basket making was an important part of Native American Californian culture. Baskets were both beautiful and functional, made oftwine
Twine is a strong Thread (yarn), thread, light String (cord), string or cord composed of two or more thinner strands twisted, and then twisted together (Plying, plied). The strands are plied in the opposite direction to that of their twist, whic ...
, woven tight enough that they could hold water for cooking. Tribes made baskets in a wide variety of shapes and sizes to fulfill different daily functions, including "baby baskets, collecting vessels, food bowls, cooking items, ceremonial items" and wearable basket caps for both men and women. The watertight cooking baskets were often used for making acorn soup by placing fire-heated stones in the baskets with food mixtures, which were then stirred until cooked.
Baskets were generally made by women. Girls learned about the process from an early age, not just the act of weaving, but also how to tend, harvest, and prepare the plants for weaving.Tule River Reservation
''Schoenoplectus acutus'' ( syn. ''Scirpus acutus, Schoenoplectus lacustris, Scirpus lacustris'' subsp. ''acutus''), called tule , common tule, hardstem tule, tule rush, hardstem bulrush, or viscid bulrush, is a giant species of sedge in the pl ...
ca. 1900
File:Pomo Indian baskets and their makers (1902) (14595874320).jpg, alt=Stack of four baskets with zigzag pattern and conical shape, Pomo
The Pomo are an Indigenous people of California. Historical Pomo territory in Northern California was large, bordered by the Pacific Coast to the west, extending inland to Clear Lake, and mainly between Cleone and Duncans Point. One small grou ...
baskets, chuset weave
File:Pomo Indian baskets and their makers (1902) (14596080597).jpg, alt=Five baskets in various states of completeness, Basket materials and foundations
File:Collection of 19 Indian baskets on display, ca.1900 (CHS-3297).jpg, alt=A collection of 19 unidentified Indian baskets on display, photographed ca.1900. They are displayed on two tiers covered with a cloth and displayed hanging from a blanket backdrop. They mostly have the shape of a round bowl with a narrow neck and mouth. They have differing woven patterns including stripes, zig-zags, diamonds, steps, human figures and more. Many of them have tassels around the widest part of their bulge., Indigenous baskets of California, photographed ca. 1900
Foods
The indigenous peoples of California had a rich and diverse resource base, with access to hundreds of types of edible plants, both terrestrial and marine mammals, birds and insects. The diversity of the food supply was particularly important and sets California apart from other areas, where if the primary food supply diminished for any reason it could be devastating for the people in that region. In California, the variety meant that if one supply failed there were hundreds of others to fall back on. Despite this abundance, there were still 20-30 primary food resources which native peoples were dependent on. Different tribes' diets included fish, shellfish, insects, deer, elk, antelope, and plants such as buckeye, sage seed, and yampah (''Perideridia gairdneri
''Perideridia gairdneri'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae known by the common names common yampah, Gardner's yampah and Squaw root. It is native to western North America from southwestern Canada to California to New Mexico, ...
'').
Plant-based foods
Acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and borne ...
s of the California Live Oak, Quercus agrifolia
''Quercus agrifolia'', the California live oak, or coast live oak, is a highly variable, often evergreen oak tree, a type of live oak, native to the California Floristic Province. It may be shrubby, depending on age and growing location, but is g ...
were a primary traditional food throughout much of California. The acorns were ground into meal, and then either boiled into mush or baked in ashes to make bread. Acorns contain large amounts of tannic acid, so turning them into a food source required a discovery of how to remove this acid and significant amounts of labor to process them. Grinding in the mortal and pestle, then boiling allows for the tannins to be leached out in the water. There was also the need to harvest and store acorns like crops since they were only available in the fall. Acorns were stored in large granaries within villages, "providing a reliable food source through the winter and spring."
Native American tribes also used the berries of the Manzanita
Manzanita is a common name for many species of the genus ''Arctostaphylos''. They are evergreen shrubs or small trees present in the chaparral biome of western North America, where they occur from Southern British Columbia and Washington to Or ...
as a staple food source. The ripe berries were eaten raw, cooked or made into jellies. The pulp of the berries could also be dried and crushed to make a cider, while the dry seeds were sometimes ground to make flour. The bark was also used to make a tea, which would help the bladder and kidneys.
Native Americans also made extensive use of the California juniper
''Juniperus californica'', the California juniper, is a species of juniper native to southwestern North America.
Description
''Juniperus californica'' is a shrub or small tree reaching , but rarely up to tall. The bark is ashy gray, typically t ...
for medicinal purposes and as a food.
The Ohlone
The Ohlone, formerly known as Costanoans (from Spanish meaning 'coast dweller'), are a Native American people of the Northern California coast. When Spanish explorers and missionaries arrived in the late 18th century, the Ohlone inhabited the ...
and the Kumeyaay
The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai or by their historical Spanish name Diegueño, is a tribe of Indigenous peoples of the Americas who live at the northern border of Baja California in Mexico and the southern border of California in the Unit ...
brewed a tea made from juniper leaves to use as a painkiller and to help remedy a hangover. They also picked the berries for eating, either fresh or dried and pulverised. The ripe berries of the California huckleberry were also collected and eaten by many peoples in the region.
Marine life
California sea lions
The California sea lion (''Zalophus californianus'') is a coastal eared seal native to western North America. It is one of six species of sea lions. Its natural habitat ranges from southeast Alaska to central Mexico, including the Gulf of Califo ...
and non-migratory, such as harbor seals
The harbor (or harbour) seal (''Phoca vitulina''), also known as the common seal, is a true seal found along temperate and Arctic marine coastlines of the Northern Hemisphere. The most widely distributed species of pinniped (walruses, eared sea ...
and sea otters
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smalle ...
. Marine mammals were hunted for their meat and blubber, but even more importantly for their furs. Otter pelts in particular were important both for trade and as symbols of status.
A large quantity and variety of marine fish lived along the west coast of California, providing shoreline communities with food. Tribes living along the coast did mostly shore-based fishing.
Anadromous fish
Anadromous fish
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousan ...
live half their life the in the sea and the other half in the river where they come to spawn
Spawn or spawning may refer to:
* Spawn (biology), the eggs and sperm of aquatic animals
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Spawn (character), a fictional character in the comic series of the same name and in the associated franchise
** '' Spawn: ...
. Large rivers such as the Klamath Klamath may refer to:
Ethnic groups
*Klamath people, a Native American people of California and Oregon
**Klamath Tribes, a federally recognized group of tribes in Oregon
*Klamath language, spoken by the Klamath people
Places in the United States
* ...
and Sacramento
)
, image_map = Sacramento County California Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Sacramento Highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 250x200px
, map_caption = Location within Sacramento ...
"provided abundant fish along hundreds of miles during the spawning season." Pacific salmon
''Oncorhynchus'' is a genus of fish in the family Salmonidae; it contains the Pacific salmon and Pacific trout. The name of the genus is derived from the Greek ὄγκος (ónkos, “lump, bend”) + ῥύγχος (rhúnkhos, “snout”), in r ...
in particular were very important in the Californian Native American diet. Pacific salmon ran in Californian coastal rivers and streams from the Oregon line down to Baja California. For northwestern groups like Yurok
The Yurok (Karuk language: Yurúkvaarar / Yuru Kyara - "downriver Indian; i.e. Yurok Indian") are an Indigenous people from along the Klamath River and Pacific coast, whose homelands are located in present-day California stretching from Trinidad ...
and Karuk
The Karuk people are an indigenous people of California, and the Karuk Tribe is one of the largest tribes in California. Karuks are also enrolled in two other federally recognized tribes, the Cher-Ae Heights Indian Community of the Trinidad Ran ...
, Salmon was the defining food. For example, more than half of the diet of the Karuk people consisted of acorns and salmon from the Klamath River. This combination of fish with acorns distinguished them from some societies in the north which focused solely on fishing.
In contrast to acorns, fish required sophisticated equipment such as dip nets and harpoons
A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument and tool used in fishing, whaling, sealing, and other marine hunting to catch and injure large fish or marine mammals such as seals and whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the target animal ...
and they could only be caught during a brief seasonal window. During this time, salmon would be harvested, dried and stored in large quantities for later consumption.
Society and culture
Many tribes inCentral California
Central California is generally thought of as the middle third of the state, north of Southern California, which includes Los Angeles, and south of Northern California, which includes San Francisco. It includes the northern portion of the San J ...
and Northern California
Northern California (colloquially known as NorCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. Spanning the state's northernmost 48 counties, its main population centers incl ...
practised the Kuksu religion
Kuksu, was a religion in Northern California practiced by members within several Indigenous peoples of California before and during contact with the arriving European settlers. The religious belief system was held by several tribes in Central Ca ...
, especially the Nisenan, Maidu
The Maidu are a Native American people of northern California. They reside in the central Sierra Nevada, in the watershed area of the Feather and American rivers. They also reside in Humbug Valley. In Maiduan languages, ''Maidu'' means "man."
...
, Pomo
The Pomo are an Indigenous people of California. Historical Pomo territory in Northern California was large, bordered by the Pacific Coast to the west, extending inland to Clear Lake, and mainly between Cleone and Duncans Point. One small grou ...
and Patwin
The Patwin (also Patween, Southern Wintu) are a band of Wintun people native to the area of Northern California. The Patwin comprise the southern branch of the Wintun group, native inhabitants of California since approximately 500 AD.
The Patwi ...
tribes. The practice of Kuksu included elaborate narrative ceremonial dances and specific regalia. A male secret society
A secret society is a club or an organization whose activities, events, inner functioning, or membership are concealed. The society may or may not attempt to conceal its existence. The term usually excludes covert groups, such as intelligence a ...
met in underground dance rooms and danced in disguises at the public dances.Kroeber, Alfred L. ''The Religion of the Indians of California'', 1907.
In Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most po ...
the Toloache religion was dominant among tribes such as the Luiseño
The Luiseño or Payómkawichum are an indigenous people of California who, at the time of the first contacts with the Spanish in the 16th century, inhabited the coastal area of southern California, ranging from the present-day southern part of L ...
and Diegueño
The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai or by their historical Spanish name Diegueño, is a tribe of Indigenous peoples of the Americas who live at the northern border of Baja California in Mexico and the southern border of California in the Unit ...
. Ceremonies were performed after consuming a hallucinogenic drink made of the jimsonweed or Toloache plant (Datura meteloides
''Datura innoxia'' (often spelled ''inoxia''), known as pricklyburr, recurved thorn-apple, downy thorn-apple, Indian-apple, lovache, moonflower, nacazcul, toloatzin, toloaxihuitl, tolguache or toloache, is a species of flowering plant in the fami ...
), which put devotees in a trance and gave them access to supernatural knowledge.
Native American culture in California was also noted for its rock art
In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also ...
, especially among the Chumash Chumash may refer to:
*Chumash (Judaism), a Hebrew word for the Pentateuch, used in Judaism
*Chumash people, a Native American people of southern California
*Chumashan languages, indigenous languages of California
See also
* Chumash traditional ...
of southern California. The rock art, or pictograph
A pictogram, also called a pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto, and in computer usage an icon, is a graphic symbol that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and gr ...
s were brightly colored paintings of humans, animals and abstract designs, and were thought to have had religious significance.
Reservations
Reservations with over 500 people:List of peoples
*Achomawi
Achomawi (also Achumawi, Ajumawi and Ahjumawi), are the northerly nine (out of eleven) bands of the Pit River tribe of Palaihnihan Native Americans who live in what is now northeastern California in the United States. These 5 autonomous bands ...
, Achumawi, Pit River tribe
The Pit River Tribe is a federally recognized tribe of eleven bands of indigenous peoples of California. They primarily live along the Pit River in the northeast corner of California.Atsugewi
The Atsugewi are Native Americans residing in northeastern California, United States. Their traditional lands are near Mount Shasta, specifically the Pit River drainage on Burney, Hat, and Dixie Valley or Horse Creeks. They are closely related ...
, northeastern California
* Chemehuevi, eastern California
*Chumash Chumash may refer to:
*Chumash (Judaism), a Hebrew word for the Pentateuch, used in Judaism
*Chumash people, a Native American people of southern California
*Chumashan languages, indigenous languages of California
See also
* Chumash traditional ...
, coastal southern California
**" Barbareño", Coast Central Chumash
**" Cruzeño, Isleño", Island Chumash
**" Emigdiano", Tecuya, Interior Central Chumash
**"Interior", Cuyama, Interior Northwestern Chumash
**" Inezeño", "Ineseño
The Santa Ynez Band of Chumash Mission Indians is a federally recognized tribe of Chumash, an indigenous people of California, in Santa Barbara.Pritzker 122 Their name for themselves is Samala. The locality of Santa Ynez is referred to as ''� ...
", Samala, Inland Central Chumash
**" Obispeño", Yak-tityu-tityu-yak-tilhini, Northern Chumash
**" Purisimeño", Kagismuwas, Northern Chumash
**" Ventureño", Alliklik – Castac, Southern Chumash
* Chilula, northwestern California
* Chimariko, extinct, northwestern California
* Kuneste, "Eel River Athapaskan peoples
The Eel River Athabaskans include the Wailaki, Lassik, Nongatl, and Sinkyone (Sinkine) groups of Native Americans that traditionally live in present-day Mendocino, Trinity, and Humboldt counties on or near the Eel River and Van Duzen River o ...
"
** Lassik, northwestern California
**Mattole
The Mattole, including the Bear River Indians, are a group of Native Americans in California. Their traditional lands are along the Mattole and Bear Rivers near Cape Mendocino in Humboldt County, California. A notable difference between the Ma ...
( Bear River), northwestern California
**Nongatl
The Eel River Athabaskans include the Wailaki, Lassik, Nongatl, and Sinkyone (Sinkine) groups of Native Americans that traditionally live in present-day Mendocino, Trinity, and Humboldt counties on or near the Eel River and Van Duzen River o ...
, northwestern California
**Sinkyone
The Eel River Athabaskans include the Wailaki, Lassik, Nongatl, and Sinkyone (Sinkine) groups of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans that traditionally live in present-day Mendocino, Trinity, and Humboldt counties on or nea ...
, northwestern California
**Wailaki
The Eel River Athabaskans include the Wailaki, Lassik, Nongatl, and Sinkyone (Sinkine) groups of Native Americans that traditionally live in present-day Mendocino, Trinity, and Humboldt counties on or near the Eel River and Van Duzen River o ...
, Wai-lakki
The Eel River Athabaskans include the Wailaki, Lassik, Nongatl, and Sinkyone (Sinkine) groups of Native Americans that traditionally live in present-day Mendocino, Trinity, and Humboldt counties on or near the Eel River and Van Duzen River o ...
, northwestern California
*Esselen
The Esselen are a Native American people belonging to a linguistic group in the hypothetical Hokan language family, who are indigenous to the Santa Lucia Mountains of a region south of the Big Sur River in Big Sur, Monterey County, Californi ...
, west-central California
*Hupa
Hupa (Yurok language term: Huep'oola' / Huep'oolaa = "Hupa people") are a Native American people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group in northwestern California. Their endonym is Natinixwe, also spelled Natinook-wa, meaning "Peopl ...
, northwestern California
**Tsnungwe
The Tsnungwe (current Hupa-language orthography, own name: - "Tse:ning-din (Ironside Mountain) People") or ''Tsanunghwa'' are a Native American people indigenous to the modern areas of the lower South Fork Trinity River (), Willow Creek (), ...
*Karok
The Karuk people are an indigenous people of California, and the Karuk Tribe is one of the largest tribes in California. Karuks are also enrolled in two other federally recognized tribes, the Cher-Ae Heights Indian Community of the Trinidad Ran ...
, northwestern California
* Kato, Cahto
The Cahto (also spelled Kato, especially in anthropological and linguistic contexts) are an indigenous Californian group of Native Americans. Today most descendants are enrolled as the federally recognized tribe, the Cahto Indian Tribe of the ...
, northwestern California
*Kawaiisu
The Kawaiisu (pronounced: ″ka-wai-ah-soo″) are a Native Californian ethnic group in the United States who live in the Tehachapi Valley and to the north across the Tehachapi Pass in the southern Sierra Nevada, toward Lake Isabella and Walker P ...
, southeast-central California
*Konkow
The Maidu are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people of northern California. They reside in the central Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada, in the watershed area of the Feather River, Feather and American River, American ...
, northern-central California
*Kumeyaay
The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai or by their historical Spanish name Diegueño, is a tribe of Indigenous peoples of the Americas who live at the northern border of Baja California in Mexico and the southern border of California in the Unit ...
, Diegueño
The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai or by their historical Spanish name Diegueño, is a tribe of Indigenous peoples of the Americas who live at the northern border of Baja California in Mexico and the southern border of California in the Unit ...
, Kumiai
**Ipai
The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai or by their historical Spanish name Diegueño, is a tribe of Indigenous peoples of the Americas who live at the northern border of Baja California in Mexico and the southern border of California in the Unit ...
, southwestern California
*** Jamul, southwestern California
**Tipai
The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai or by their historical Spanish name Diegueño, is a tribe of Indigenous peoples of the Americas who live at the northern border of Baja California in Mexico and the southern border of California in the Unit ...
, southwestern California and northwestern Mexico
* La Jolla complex, southern California, c. 6050–1000 BCE
*Maidu
The Maidu are a Native American people of northern California. They reside in the central Sierra Nevada, in the watershed area of the Feather and American rivers. They also reside in Humbug Valley. In Maiduan languages, ''Maidu'' means "man."
...
, northeastern California
**Konkow
The Maidu are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people of northern California. They reside in the central Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada, in the watershed area of the Feather River, Feather and American River, American ...
, northern California
** Yamani, Mechoopda
The Mechoopda are a tribe of Maidu people, an indigenous peoples of California. They are enrolled in the Mechoopda Indian Tribe of Chico Rancheria, a federally recognized tribe. Historically, the tribe has spoken Konkow, a language related to the ...
, northern California
**Nisenan
The Nisenan are a group of Native Americans and an Indigenous people of California from the Yuba River and American River watersheds in Northern California and the California Central Valley. The Nisenan people are classified as part of the large ...
, Southern Maidu, northern California
*Miwok
The Miwok (also spelled Miwuk, Mi-Wuk, or Me-Wuk) are members of four linguistically related Native American groups indigenous to what is now Northern California, who traditionally spoke one of the Miwok languages in the Utian family. The word ' ...
, Me-wuk
The Miwok (also spelled Miwuk, Mi-Wuk, or Me-Wuk) are members of four linguistically related Native American groups indigenous to what is now Northern California, who traditionally spoke one of the Miwok languages in the Utian family. The word ' ...
, central California
**Bay Miwok
The Bay Miwok are a cultural and linguistic group of Miwok, a Native American people in Northern California who live in Contra Costa County. They joined the Franciscan mission system during the early nineteenth century, suffered a devastating p ...
, west-central California
**Coast Miwok
Coast Miwok are an indigenous people that was the second-largest group of Miwok people. Coast Miwok inhabited the general area of modern Marin County and southern Sonoma County in Northern California, from the Golden Gate north to Duncans Point ...
, west-central California
**Lake Miwok
The Lake Miwok are a branch of the Miwok, a Native American people of Northern California. The Lake Miwok lived in the Clear Lake basin of what is now called Lake County.
Culture
The Lake Miwok spoke their own Lake language in the Utian li ...
, west-central California
**Valley and Sierra Miwok
The Plains and Sierra Miwok were once the largest group of California Indian Miwok people, indigenous to California. Their homeland included regions of the Sacramento Valley, San Joaquin Valley, and the Sierra Nevada.
Geography
The Plains and ...
*Monache
The Mono ( ) are a Native American people who traditionally live in the central Sierra Nevada, the Eastern Sierra (generally south of Bridgeport), the Mono Basin, and adjacent areas of the Great Basin. The Eastern mono is often grouped under t ...
, Western Mono
The Mono ( ) are a Native American people who traditionally live in the central Sierra Nevada, the Eastern Sierra (generally south of Bridgeport), the Mono Basin, and adjacent areas of the Great Basin. The Eastern mono is often grouped under t ...
, central California
* Mohave, southeastern California
*Nisenan
The Nisenan are a group of Native Americans and an Indigenous people of California from the Yuba River and American River watersheds in Northern California and the California Central Valley. The Nisenan people are classified as part of the large ...
, eastern-central California
*Nomlaki
The Nomlaki (also Noamlakee, Central Wintu, Nomelaki) are a Wintun people native to the area of the Sacramento Valley, extending westward to the Coast Range in Northern California. Today some Nomlaki people are enrolled in the federally recogniz ...
, northwestern California
*Ohlone
The Ohlone, formerly known as Costanoans (from Spanish meaning 'coast dweller'), are a Native American people of the Northern California coast. When Spanish explorers and missionaries arrived in the late 18th century, the Ohlone inhabited the ...
, Costanoan, west-central California
** Awaswas
**Chalon Chalon may refer to:
Culture
* Chalon people, a Native American tribe of California
* Chalon language, an Ohlone language spoken by the Chalon people
Places
* Chalon, Isère, formerly Châlons, in France's Isère ''département''
* Le Chalon, in ...
** Chochenyo
** Karkin
**Mutsun
Mutsun (also known as San Juan Bautista Costanoan) is a Utian language spoken in Northern California. It was the primary language of a division of the Ohlone people living in the Mission San Juan Bautista area. The Tamien Nation and band is cu ...
**Ramaytush
The Ramaytush or Rammay-tuš people are a linguistic subdivision of the Ohlone people of Northern California. The term Ramaytush was first applied to them in the 1970s, but the modern Ohlone people of the peninsula have claimed it as their ethn ...
** Rumsen
**Tamyen
The Tamien people (also spelled as ''Tamyen'', ''Thamien'') are one of eight linguistic divisions of the Ohlone (Costanoan) people groups of Native Americans who lived in Northern California. The Tamien traditionally lived throughout the Santa ...
**Yelamu
The Yelamu are a local tribe of Ohlone people from the San Francisco Bay Area in Northern California. The Yelamu speak a language called Ramaytush. The moderAssociation of Ramaytush Ohlone (ARO)are the descendants of the Ramaytush.
Randall Milli ...
*Patwin
The Patwin (also Patween, Southern Wintu) are a band of Wintun people native to the area of Northern California. The Patwin comprise the southern branch of the Wintun group, native inhabitants of California since approximately 500 AD.
The Patwi ...
, central California
** Suisun, Southern Patwin
The Patwin (also Patween, Southern Wintu) are a band of Wintun people native to the area of Northern California. The Patwin comprise the southern branch of the Wintun group, native inhabitants of California since approximately 500 AD.
The Patwi ...
, central California
* Pauma Complex, southern California, c. 6050–1000 BCE
*Pomo
The Pomo are an Indigenous people of California. Historical Pomo territory in Northern California was large, bordered by the Pacific Coast to the west, extending inland to Clear Lake, and mainly between Cleone and Duncans Point. One small grou ...
, northwestern and central-western California
*Quechan
The Quechan (or Yuma) (Quechan: ''Kwatsáan'' 'those who descended') are a Native American tribe who live on the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation on the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California just north of the Mexican border. Despite the ...
, Yuman
The Quechan (or Yuma) (Quechan: ''Kwatsáan'' 'those who descended') are a Native American tribe who live on the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation on the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California just north of the Mexican border. Despite th ...
, southeastern California
* Te'po'ta'ahl, ("Salinan
The Salinan are a Native American tribe whose ancestral territory is in the southern Salinas Valley and the Santa Lucia Range in the Central Coast of California. Today, the Salinan governments are now working toward federal tribal recognition f ...
"), coastal central California
**" Antoniaño"
**" Migueleño"
**" Playano"
* Shasta northwestern California
** Konomihu, northwestern California
**Okwanuchu
The Okwanuchu were one of a number of small Shastan-speaking tribes of Native Americans in Northern California, who were closely related to the adjacent larger Shasta tribe.
Geography
The Okwanuchu occupied territory south, southwest, and south ...
, northwestern California
*Tolowa
The Tolowa people or Taa-laa-wa Dee-ni’ are a Native American people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethno-linguistic group. Two rancherias (Smith River and Elk Valley) still reside in their traditional territory in northwestern California. Tho ...
, northwestern California
*Takic
The Takic languages are a putative group of Uto-Aztecan languages historically spoken by a number of Indigenous peoples of California, Indigenous peoples of Southern California. Takic is grouped with the Tübatulabal language, Tubatulabal, Hopi la ...
**Acjachemem
The Acjachemen (, alternate spelling: Acagchemem) are an Indigenous people of California. They historically lived south of what is known as Aliso Creek and north of the Las Pulgas Canyon in what are now the southern areas of Orange County and t ...
, ("Juaneño
The Acjachemen (, alternate spelling: Acagchemem) are an Indigenous people of California. They historically lived south of what is known as Aliso Creek and north of the Las Pulgas Canyon in what are now the southern areas of Orange County and t ...
"), Takic, southwestern California
** Iívil̃uqaletem, Iviatim, ("Cahuilla
The Cahuilla , also known as ʔívil̃uqaletem or Ivilyuqaletem, are a Native American people of the various tribes of the Cahuilla Nation, living in the inland areas of southern California.Kitanemuk
The Kitanemuk are an indigenous people of California. They traditionally lived in the Tehachapi Mountains and the Antelope Valley area of the western Mojave Desert of southern California, United States. Today some Kitanemuk people are enrolled in ...
, (" Tejon") Takic, south-central California
** Kuupangaxwichem, ("Cupeño
The Cupeño (or Kuupangaxwichem) are a Native American tribe of Southern California.
They traditionally lived about inland and north of the modern day Mexico–United States border in the Peninsular Range of Southern California. Today their ...
"), southern California
** Payómkawichum, ("Luiseño
The Luiseño or Payómkawichum are an indigenous people of California who, at the time of the first contacts with the Spanish in the 16th century, inhabited the coastal area of southern California, ranging from the present-day southern part of L ...
"), Takic, southwestern California
**Tataviam
The Tataviam (Kitanemuk: ''people on the south slope'') are a Native American group in Southern California. The ancestral land of the Tataviam people includes northwest present-day Los Angeles County and southern Ventura County, primarily in th ...
, Allilik Takic ("Fernandeño
The Tongva language (also known as Gabrielino or Gabrieleño) is an extinct Uto-Aztecan language formerly spoken by the Tongva, a Native American people who live in and around Los Angeles, California. It has not been a language of everyday conve ...
"), southern California
**Tongva
The Tongva ( ) are an Indigenous people of California from the Los Angeles Basin and the Southern Channel Islands, an area covering approximately . Some descendants of the people prefer Kizh as an endonym that, they argue, is more historically ...
, ("Gabrieleño
The Tongva ( ) are an Indigenous people of California from the Los Angeles Basin and the Southern Channel Islands, an area covering approximately . Some descendants of the people prefer Kizh as an endonym that, they argue, is more historically ...
"), ("Fernandeño
The Tongva language (also known as Gabrielino or Gabrieleño) is an extinct Uto-Aztecan language formerly spoken by the Tongva, a Native American people who live in and around Los Angeles, California. It has not been a language of everyday conve ...
"), ("Nicoleño
The Nicoleño were an Uto-Aztecan people who lived on San Nicolas Island in California. Its population was "left devastated by a massacre in 1811 by sea otter hunters". Its last surviving member was given the name Juana Maria, who was born befor ...
"), " San Clemente tribe" Takic, coastal southern California
**Yuhaviatam
The Yuhaaviatam of San Manuel Nation is a federally recognized tribe of Serrano people in San Bernardino County, California.
Morongo
The Morongo Band of Mission Indians is a federally recognized tribe in California, United States. The main tribal groups are Cahuilla and Serrano. Tribal members also include Cupeño, Luiseño, and Chemehuevi Indians. Although many tribes in C ...
, Vanyume
The Vanyume or Desert Serrano are an Indigenous people of Southern California. Traditional Vanyume territory extended along the Mojave River from the Eastern Mojave Desert to present day Victorville and may have included portions of southern ...
Mohineyam (" Serrano"), southern California
* Tubatulabal, south-central California
** Bankalachi, Toloim, south-central California
** Pahkanapil, south-central California
**Palagewan
The Washoe or Wašišiw ("people from here", or transliterated in older literature as ''Wa She Shu'') are a Great Basin tribe of Native Americans, living near Lake Tahoe at the border between California and Nevada. The name "Washoe" or "Washo ...
, south-central California
*Wappo
The Wappo (endonym: ''Micewal'') are an indigenous people of northern California. Their traditional homelands are in Napa Valley, the south shore of Clear Lake, Alexander Valley, and Russian River valley. They are distantly related to the Yuki ...
, north-central California
*Whilkut
The Whilkut (variants: ''Whiylqit, Hwil'-kut, Hoilkut, Hoilkut-hoi'') also known as "(Upper) Redwood Creek Indians" or "Mad River Indians" were a Pacific Coast Athabaskan tribe speaking a dialect similar to the Hupa to the northeast and Chilula ...
, northwestern California
*Wintu
The Wintu (also Northern Wintun) are Native Americans who live in what is now Northern California. They are part of a loose association of peoples known collectively as the Wintun (or Wintuan). Others are the Nomlaki and the Patwin. The Wintu ...
, northwestern California
*Wiyot
The Wiyot ( Wiyot: Wíyot, Chetco-Tolowa: Wee-’at xee-she or Wee-yan’ Xee-she’, Euchre Creek Tututni: Wii-yat-dv-ne - "Mad River People“, Yurok: Weyet) are an indigenous people of California living near Humboldt Bay, California and a s ...
, northwestern California
*Yana
Yana may refer to:
Locations
*Yana, Burma, a village in Hkamti Township in Hkamti District in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Burma
*Yana, India, a village in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, India
* Yana, Nigeria, an administrative ca ...
, northern-central California
**Yahi
The Yana were a group of Native Americans indigenous to Northern California in the central Sierra Nevada, on the western side of the range. Their lands, prior to encroachment by white settlers, bordered the Pit and Feather rivers. They were ...
*Yokuts
The Yokuts (previously known as MariposasPowell, 1891:90–91.) are an ethnic group of Native Americans native to central California. Before European contact, the Yokuts consisted of up to 60 tribes speaking several related languages. ''Yokuts ...
, central and southern California
** Chukchansi, Foothill Yokuts, central California
** Northern Valley Yokuts, central California
**Tachi tribe
Santa Rosa Rancheria is the reservation of the Santa Rosa Indian Community of the Santa Rosa Rancheria. It is located southeast of Lemoore, California. Established in 1934 on about , the Santa Rosa Rancheria belongs to the federally recogniz ...
, Southern Valley Yokuts
Southern Valley Yokuts is a dialect network within the Valley Yokuts division of the Yokutsan languages spoken in the Central Valley of California.
Among the dialects grouped under the label Southern Valley Yokuts are Wechihi, Tachi, Telamni, ...
, south-central California
*Timbisha
The Timbisha ("rock paint", Timbisha language: Nümü Tümpisattsi) are a Native American tribe federally recognized as the Death Valley Timbisha Shoshone Band of California. They are known as the Timbisha Shoshone Tribe and are located in sout ...
, eastern California
* Yuki, Ukomno'm
The Yuki (also known as Yukiah) are an indigenous people of California, whose traditional territory is around Round Valley, Mendocino County. Today they are enrolled members of the Round Valley Indian Tribes of the Round Valley Reservation. Befor ...
, northwestern California
** Huchnom, northwestern California
*Yurok
The Yurok (Karuk language: Yurúkvaarar / Yuru Kyara - "downriver Indian; i.e. Yurok Indian") are an Indigenous people from along the Klamath River and Pacific coast, whose homelands are located in present-day California stretching from Trinidad ...
, northwestern California
Languages
 Before European contact, native Californians spoke over 300 dialects of approximately 100 distinct languages. The large number of languages has been related to the ecological diversity of California, and to a sociopolitical organization into small tribelets (usually 100 individuals or fewer) with a shared "ideology that defined language boundaries as unalterable natural features inherent in the land". Together, the area had more linguistic diversity than all of Europe combined.
"The majority of California Indian languages belong either to highly localized language families with two or three members (e.g. Yukian,
Before European contact, native Californians spoke over 300 dialects of approximately 100 distinct languages. The large number of languages has been related to the ecological diversity of California, and to a sociopolitical organization into small tribelets (usually 100 individuals or fewer) with a shared "ideology that defined language boundaries as unalterable natural features inherent in the land". Together, the area had more linguistic diversity than all of Europe combined.
"The majority of California Indian languages belong either to highly localized language families with two or three members (e.g. Yukian, Maiduan
Maiduan (also Maidun, Pujunan) is a small endangered language, endangered language family of northeastern California.
Family division
The Maiduan consists of 4 languages:
# Maidu language, Maidu ''†'' (also known as Maidu proper, Northeaste ...
) or are language isolates (e.g. Karuk
The Karuk people are an indigenous people of California, and the Karuk Tribe is one of the largest tribes in California. Karuks are also enrolled in two other federally recognized tribes, the Cher-Ae Heights Indian Community of the Trinidad Ran ...
, Esselen
The Esselen are a Native American people belonging to a linguistic group in the hypothetical Hokan language family, who are indigenous to the Santa Lucia Mountains of a region south of the Big Sur River in Big Sur, Monterey County, Californi ...
)." Of the remainder, most are Uto-Aztecan
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
or Athapaskan languages
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific Co ...
. Larger groupings have been proposed. The Hokan
The Hokan language family is a hypothetical grouping of a dozen small language families that were spoken mainly in California, Arizona and Baja California.
Etymology
The name ''Hokan'' is loosely based on the word for "two" in the various Hokan ...
superstock has the greatest time depth and has been most difficult to demonstrate; Penutian
Penutian is a proposed grouping of language families that includes many Native American languages of western North America, predominantly spoken at one time in British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and California. The existence of a Penutian s ...
is somewhat less controversial.
There is evidence suggestive that speakers of the Chumashan languages
Chumashan was a family of languages that were spoken on the southern California coast by Native American Chumash people, from the Coastal plains and valleys of San Luis Obispo to Malibu, neighboring inland and Transverse Ranges valleys and ca ...
and Yukian languages, and possibly languages of southern Baja California such as Waikuri, were in California prior to the arrival of Penutian
Penutian is a proposed grouping of language families that includes many Native American languages of western North America, predominantly spoken at one time in British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and California. The existence of a Penutian s ...
languages from the north and Uto-Aztecan
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
from the east, perhaps predating even the Hokan
The Hokan language family is a hypothetical grouping of a dozen small language families that were spoken mainly in California, Arizona and Baja California.
Etymology
The name ''Hokan'' is loosely based on the word for "two" in the various Hokan ...
languages. Wiyot
The Wiyot ( Wiyot: Wíyot, Chetco-Tolowa: Wee-’at xee-she or Wee-yan’ Xee-she’, Euchre Creek Tututni: Wii-yat-dv-ne - "Mad River People“, Yurok: Weyet) are an indigenous people of California living near Humboldt Bay, California and a s ...
and Yurok
The Yurok (Karuk language: Yurúkvaarar / Yuru Kyara - "downriver Indian; i.e. Yurok Indian") are an Indigenous people from along the Klamath River and Pacific coast, whose homelands are located in present-day California stretching from Trinidad ...
are distantly related to Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic languages, Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language f ...
in a larger grouping called Algic
The Algic languages (also Algonquian–Wiyot–Yurok or Algonquian–Ritwan) are an indigenous language family of North America. Most Algic languages belong to the Algonquian subfamily, dispersed over a broad area from the Rocky Mountains to ...
. The several Athapaskan languages
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific Co ...
are relatively recent arrivals, having arrived about 2000 years ago.
See also
*Aboriginal title in California
Aboriginal title in California refers to the aboriginal title land rights of the indigenous peoples of California. The state is unique in that no Native American tribe in California is the counterparty to a ratified federal treaty. Therefore, al ...
*California State Indian Museum
The California State Indian Museum is a museum in the state park system of California, United States, interpreting the diverse cultures of the indigenous peoples of California. It is located in Midtown Sacramento at 2618 K Street. The museum exh ...
*Indigenous peoples of Mexico
Indigenous peoples of Mexico ( es, gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans ( es, nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans ( es, pueblos originarios de México, lit=Original peoples of Mexico), are those ...
* List of federally recognized tribes by state#California
*Martis people
Martis is the name given by scientists to the group of Native Americans who lived in Northern California on both the eastern and western sides of the Sierra Nevada. The Martis complex lasted from 2000 BCE to 500 CE, during the Middle Archaic era ...
*Mission Indians
Mission Indians are the indigenous peoples of California who lived in Southern California and were forcibly relocated from their traditional dwellings, villages, and homelands to live and work at 15 Franciscan missions in Southern California and ...
*Population of Native California
The population of Native California refers to the population of Indigenous peoples of California. Estimates prior to and after European contact have varied substantially. Pre-contact estimates range from 133,000 to 705,000 with some recent schol ...
*Survey of California and Other Indian Languages
The Survey of California and Other Indian Languages (originally the Survey of California Indian Languages) at the University of California at Berkeley documents, catalogs, and archives the indigenous languages of the Americas. The survey also hosts ...
References
Further reading
* Hinton, Leanne (1994). ''Flutes of Fire: Essays on California Indian Languages.'' Berkeley: Heyday Books. . * * Lightfoot, Kent G. and Otis Parrish (2009). ''California Indians and Their Environment: An Introduction.'' Berkeley: University of California Press. .External links
"Information About California Tribes"
Northern California Indian Development Council
Advocates for Indigenous California Language Survival
Santa Rosa
California Native American Heritage Association
"California Indians,"
SDSU Library and Information Access
Society for California Archaeology
California State University San Marcos, Oct. 5–6, 2012 * {{DEFAULTSORT:Indigenous peoples of California Indigenous peoples
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...