Geology of Minnesota on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The geology of Minnesota comprises the

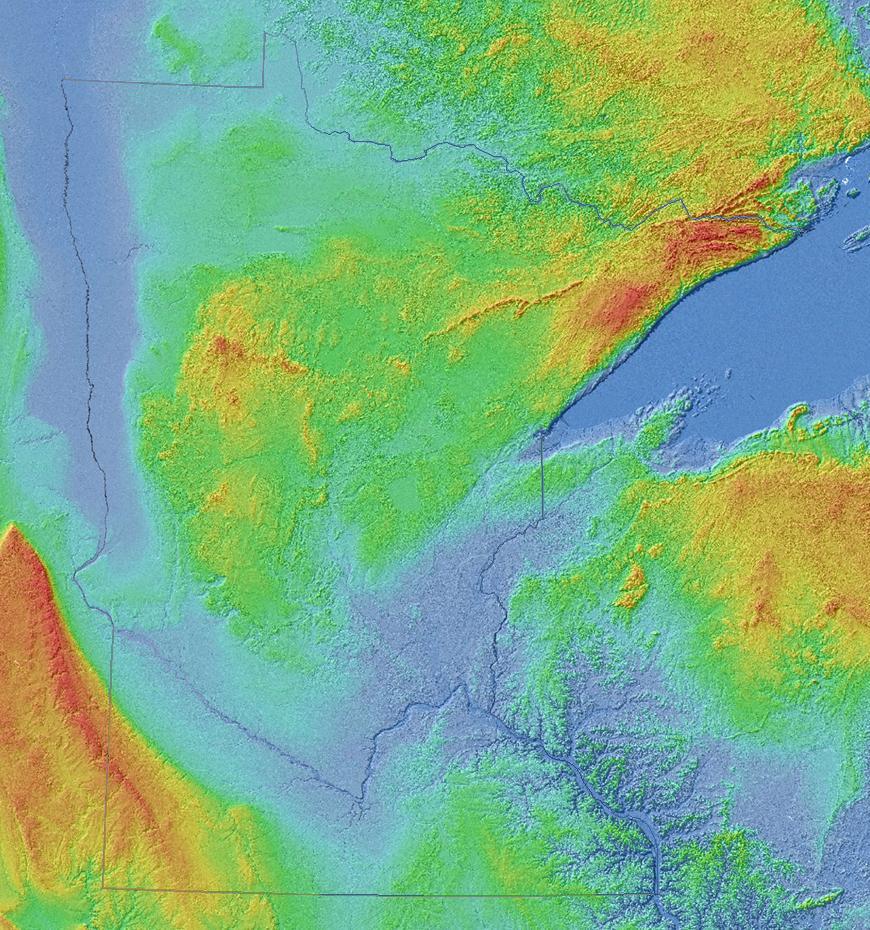 Minnesota contains some of the oldest rocks on Earth, granitic
Minnesota contains some of the oldest rocks on Earth, granitic
 In the
In the
 Contemporary Minnesota is much quieter geologically than in the past. Outcroppings of lava flows and magma intrusions are the only remaining traces of the volcanism that ended over 1,100 mya. Landlocked within the continent, the state is far from the seas that once covered it, and the continental glacier has receded entirely from North America. Minnesota's landscape is a relatively flat
Contemporary Minnesota is much quieter geologically than in the past. Outcroppings of lava flows and magma intrusions are the only remaining traces of the volcanism that ended over 1,100 mya. Landlocked within the continent, the state is far from the seas that once covered it, and the continental glacier has receded entirely from North America. Minnesota's landscape is a relatively flat
 Known as the
Known as the
 ''Southwestern Minnesota'' is in the watersheds of the
''Southwestern Minnesota'' is in the watersheds of the

 ''Southeastern Minnesota'' is separated from Southwestern Minnesota by the ''Owatonna Moraine'', the eastern branch of the Bemis Moraine, a
''Southeastern Minnesota'' is separated from Southwestern Minnesota by the ''Owatonna Moraine'', the eastern branch of the Bemis Moraine, a
 ''Central Minnesota'' is composed of (1) the
''Central Minnesota'' is composed of (1) the
 The subregion of ''East Central Minnesota'' is that part of Central Minnesota near the junction of three of the state's great rivers. Included are
The subregion of ''East Central Minnesota'' is that part of Central Minnesota near the junction of three of the state's great rivers. Included are
''Geologic History of Minnesota Rivers''
Minnesota Geological Survey, Educational Series 7. St. Paul: University of Minnesota. ISSN 0544-3083. {{Geology of the United States by political division
rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
, minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
, and soils
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former term ...
of the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sover ...
of Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
, including their formation, development, distribution, and condition.
The state's geologic history can be divided into three periods. The first period was a lengthy period of geologic instability from the origin of the planet until roughly 1,100 million years ago. During this time, the state's Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
bedrock was formed by volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called ...
and the deposition of sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
and then modified by processes such as faulting
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
, folding
Fold, folding or foldable may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Fold'' (album), the debut release by Australian rock band Epicure
* Fold (poker), in the game of poker, to discard one's hand and forfeit interest in the current pot
*Abov ...
and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
. In the second period, many layers of sedimentary rock were formed by deposition and lithification
Lithification (from the Ancient Greek word ''lithos'' meaning 'rock' and the Latin-derived suffix ''-ific'') is the process in which sediments compact under pressure, expel connate fluids, and gradually become solid rock. Essentially, lithificati ...
of successive layers of sediment from runoff and repeated incursions of the sea. In the third and most recent period starting about 1.8 million years ago, glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
eroded previous rock formations and deposited deep layers of glacial till
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
over most of the state, and created the beds and valleys of modern lakes and rivers.
Minnesota's geologic resources have been the historical foundation of the state's economy. Precambrian bedrock has been mined for metallic minerals, including iron ore, on which the economy of Northeast Minnesota was built. Archaen granites and gneisses, and later limestones and sandstones, are quarried for structural stone and monuments. Glacial deposits are mined for aggregates, glacial till and lacustrine deposits formed the parent soil for the state's farmlands, and glacial lakes are the backbone of Minnesota's tourist industry. These economic assets have in turn dictated the state's history and settlement patterns, and the trade and supply routes along the waterways, valleys and plains have become the state's state's transportation corridors.
Geological history
Precambrian bedrock

 Minnesota contains some of the oldest rocks on Earth, granitic
Minnesota contains some of the oldest rocks on Earth, granitic gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures an ...
es that formed some 3,600 mya (million years ago) — roughly 80% the age of the planet. About 2,700 mya, the first volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
rocks that would later underlie Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
began to rise up out of an ancient ocean, forming the Superior craton. This craton later assembled into the Canadian shield
The Canadian Shield (french: Bouclier canadien ), also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the anc ...
, which became part of the North American craton
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' is ...
. Much of the underlying gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures an ...
rock of today's state had already formed nearly a billion years earlier, but lay underneath the sea. Except for an area where islands appeared in what is now the northern part of the state, most of the region remained underwater.
In Middle Precambrian time, about 2,000 mya, the land rose above the water. Heavy mineral deposits containing iron had collected on the shores of the receding sea to form the Mesabi
The Mesabi Iron Range is a mining district in northeastern Minnesota following an elongate trend containing large deposits of iron ore. It is the largest of four major iron ranges in the region collectively known as the Iron Range of Minnesota ...
, Cuyuna, Vermilion
Vermilion (sometimes vermillion) is a color, color family, and pigment most often made, since ancient history, antiquity until the 19th century, from the powdered mineral cinnabar (a form of mercury sulfide, which is toxic) and its correspondi ...
, and Gunflint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fires ...
iron range
The term Iron Range refers collectively or individually to a number of elongated iron-ore mining districts around Lake Superior in the United States and Canada. Much of the ore-bearing region lies alongside the range of granite hills formed by ...
s from the center of the state north into Northwestern Ontario
Northwestern Ontario is a secondary region of Northern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north and west of Lake Superior and west of Hudson Bay and James Bay. It includes most of subarctic Ontario. Its western boundary is the ...
, Canada. These regions also showed the first signs of life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energ ...
as algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
grew in the shallow waters.
Over 1,100 mya, a rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
formed and lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
emerged from cracks along the edges of the rift valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear dep ...
. This Midcontinent Rift System
The Midcontinent Rift System (MRS) or Keweenawan Rift is a long geological rift in the center of the North American continent and south-central part of the North American plate. It formed when the continent's core, the North American craton, ...
extended from the lower peninsula of Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
north to the current Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
, southwest through the lake to the Duluth
, settlement_type = City
, nicknames = Twin Ports (with Superior), Zenith City
, motto =
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top: urban Duluth skyline; Minnesota ...
area, and south through eastern Minnesota down into what is now Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
. The rifting stopped before the land could become two separate continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
s. About 100 million years later, the last volcano went quiet.
Late Precambrian and Paleozoic sedimentary rock
The mountain-building and rifting events left areas of high relief above the low basin of the Midcontinent rift. Over the next 1,100 million years, the uplands were worn down and the rift filled with sediments, forming rock ranging in thickness from several hundred meters near Lake Superior to thousands of meters further south. While the crustal tectonic plates continued their slow drift over the surface of the planet, meeting and separating in the successive collision and sundering of continents, the North American craton remained stable. Although now free of folding and faulting caused byplate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
, the region continued to experience gradual subsidence and uplift.
Five hundred fifty million years ago, the state was repeatedly inundated with water of a shallow sea that grew and receded through several cycles. The land mass of what is now North America ran along the equator, and Minnesota had a tropical climate. Small marine creatures such as trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the At ...
s, coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
, and snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gastro ...
s lived in the sea. The shells of the tiny animals sank to the bottom, and are preserved in limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
s, sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
s, and shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
s from this era. Later, creatures resembling crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to inclu ...
s and shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimo ...
s slid through the water, and fossil shark teeth have been found on the uplands of the Mesabi Range
The Mesabi Iron Range is a mining district in northeastern Minnesota following an elongate trend containing large deposits of iron ore. It is the largest of four major iron ranges in the region collectively known as the Iron Range of Minnesota. ...
. During the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
and Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
eras other land animals followed as the dinosaurs disappeared, but much of the physical evidence from this era has been scraped away or buried by recent glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
. The rock units that remain in Minnesota from this time period are of Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
and Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start ...
age, from the Mount Simon Sandstone
The Mount Simon Sandstone is the basal sandstone of the Potsdam Sandstone. It was deposited in a nearshore environment, unconformably overlying Precambrian basement.
It is overlain by the Eau Claire Formation or Ordovician strata. It is presume ...
at the bottom of the sequence of sedimentary rocks to the Maquoketa Group
The Maquoketa Group is an assemblage of several geologic formations. It is Upper Ordovician in age and named for the Maquoketa River in Iowa. It exists in Missouri, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, and Indiana. It is equivalent to the all but the bas ...
at the top.
Ice ages
 In the
In the Quaternary Period
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three period (geology), periods of the Cenozoic era (geology), Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spa ...
starting about two million years ago, glaciers expanded and retreated across the region. The ice retreated for the last time about 12,500 years ago. Melting glaciers formed many of the state's lakes and etched its river valleys. They also formed a number of proglacial lakes
In geology, a proglacial lake is a lake formed either by the damming action of a moraine during the retreat of a melting glacier, a glacial ice dam, or by meltwater trapped against an ice sheet due to isostatic depression of the crust around the ...
, which contributed to the state's topography and soils. Principal among these lakes was Lake Agassiz
Lake Agassiz was a large glacial lake in central North America. Fed by glacial meltwater at the end of the last glacial period, its area was larger than all of the modern Great Lakes combined.
First postulated in 1823 by William H. Keating, it ...
, a massive lake with a volume rivaling that of all the present Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
combined. Dammed by the northern ice sheet, this lake's immense flow found an outlet in glacial River Warren
Glacial River Warren, also known as River Warren, was a prehistoric river that drained Lake Agassiz in central North America between about 13,500 and 10,650 BP calibrated (11,700 and 9,400 14C uncalibrated) years ago. A part of the uppermost porti ...
, which drained south across the Traverse Gap
The Traverse Gap is an ancient river channel occupied by Lake Traverse, Big Stone Lake and the valley connecting them at Browns Valley, Minnesota. It is located on the border of the U.S. states of Minnesota and South Dakota. Traverse Gap has an ...
through the valleys now occupied by the Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
and Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
s. Eventually, the ice sheet melted, and the Red River gave Lake Agassiz a northern outlet toward Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
. As the lake drained away its bed became peatlands
A mire, peatland, or quagmire is a wetland area dominated by living peat-forming plants. Mires arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to water-logging and subsequent anoxia. All types ...
and a fertile plain. Similarly, Glacial Lake Duluth
Lake Duluth was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Superior drainage basin as the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated.
, in the basin of Lake Superior, was dammed by a glacier; it drained down the ancient course of the Midcontinental Rift to the St. Croix River and the Mississippi. When the glaciers receded, the lake was able to drain through the Great Lakes to the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connectin ...
.
Giant animals roamed the area. Beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers ar ...
s were the size of bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
s, and mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks and, ...
s were 14 feet (4.3 m) high at the shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder mak ...
and weighed 10 ton
Ton is the name of any one of several units of measure. It has a long history and has acquired several meanings and uses.
Mainly it describes units of weight. Confusion can arise because ''ton'' can mean
* the long ton, which is 2,240 pounds
...
s. Even buffalo were much larger than today. The glaciers continued to retreat and the climate became warmer over the next few millennia; the giant creatures died out about 9,000 years ago.
This glaciation has drastically remodeled most of Minnesota, and all but two of the state's regions are covered with deep layers of glacial till. The driftless area
The Driftless Area, a topographical and cultural region in the American Midwest, comprises southwestern Wisconsin, southeastern Minnesota, northeastern Iowa, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois.
Never covered by ice during the last ...
of Southeastern Minnesota was untouched by the most recent glaciation. In the absence of glacial scouring
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
and drift
Drift or Drifts may refer to:
Geography
* Drift or ford (crossing) of a river
* Drift, Kentucky, unincorporated community in the United States
* In Cornwall, England:
** Drift, Cornwall, village
** Drift Reservoir, associated with the village
...
, this region presents a widespread highly dissected aspect absent from other parts of the state. Northeastern Minnesota was subject to glaciation and its effects, but its hard Archaen and Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
rocks were more resistant to glacial erosion than the sedimentary bedrock first encountered in many other regions, and glacial till is relatively sparse. While the effects of glacial erosion are clearly present and there are some areas of glacial till, older rocks and landforms remain unburied and exposed across much of the region.
Contemporary features
peneplain
390px, Sketch of a hypothetical peneplain formation after an orogeny.
In geomorphology and geology, a peneplain is a low-relief plain formed by protracted erosion. This is the definition in the broadest of terms, albeit with frequency the usage ...
; its highest and lowest points are separated by only of elevation.
While the state no longer has true mountain ranges or oceans, there is a fair amount of regional diversity in landforms
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, m ...
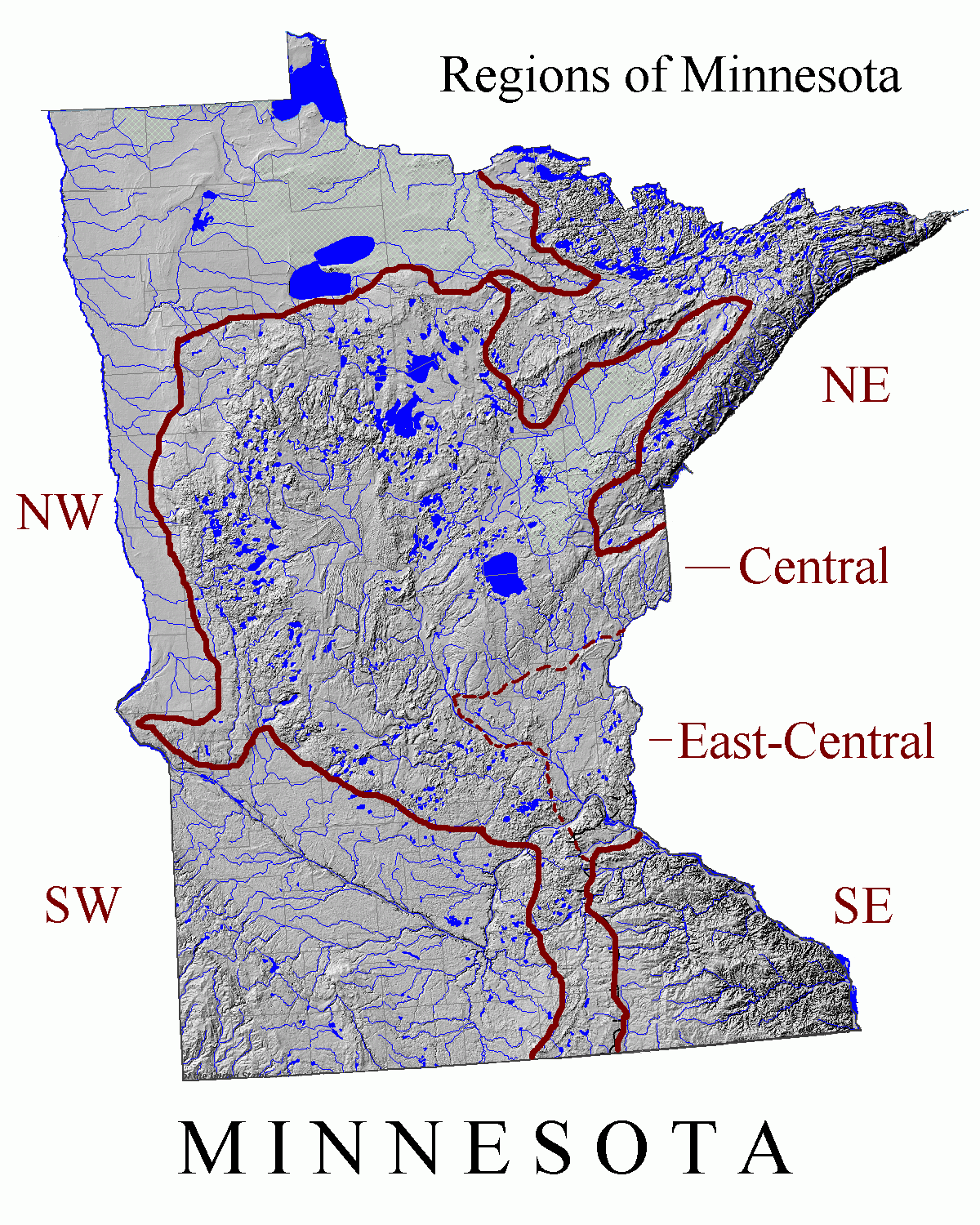
and geological history, which in turn has affected Minnesota's settlement patterns, human history, and economic development. These diverse geological regions can be classified several ways. The classification used here principally derives from Sansome's ''Minnesota Underfoot - A Field Guide to Minnesota's Geology'', but is also influenced by ''Minnesota's Geology'' by Ojakangas and Matsch. These authorities generally agree on areal borders, but the regions as defined by Ojakangas and Matsch are more geographical in their approximations of areas of similar geology, while Sansome's divisions are more irregular in shape in order to include within a region all areas of similar geology, with particular emphasis on the effects of recent glaciation. As glaciation and its residue has largely dictated regional surface geology and topography, Sansome's divisions are often coextensive with ecological provinces, sections, and subsections.
Northeastern Minnesota: ancient bedrock
''Northeastern Minnesota'' is an irregularly-shaped region composed of the northeasternmost part of the state north of Lake Superior, the area aroundJay Cooke State Park
Jay Cooke State Park is a state park of Minnesota, United States, protecting the lower reaches of the Saint Louis River. The park is located about southwest of Duluth and is one of the ten most visited state parks in Minnesota. The western ...
and the Nemadji River
The Nemadji River is a river rising in Pine County, Minnesota, United States, which flows through Carlton County, Minnesota, and Douglas County, Wisconsin, to Lake Superior. The river is long measured from its source in Maheu Lake in Pine Count ...
basin southwest of Duluth, and much of the area east of U.S. Highway 53 that runs between Duluth and International Falls
International Falls (sometimes referred to as I-Falls) is a city in and the county seat of Koochiching County, Minnesota. The population was 5,802 at the time of the 2020 census.
International Falls is located on the Rainy River directly acro ...
. Excluded are parts of the beds of glacial lakes
A glacial lake is a body of water with origins from glacier activity. They are formed when a glacier erodes the land and then melts, filling the depression created by the glacier.
Formation
Near the end of the last glacial period, roughly 10,0 ...
Agassiz and Upham, the latter now occupied by the upper valley of the Saint Louis River and its tributary the Cloquet. This area is coextensive with the Northern Superior Uplands Section of the Laurentian Mixed Forest.
 Known as the
Known as the Arrowhead
An arrowhead or point is the usually sharpened and hardened tip of an arrow, which contributes a majority of the projectile mass and is responsible for impacting and penetrating a target, as well as to fulfill some special purposes such as sign ...
for its shape, this region shows the most visible evidence of the state's violent past. There are surface exposures of rocks first formed in volcanic activity some 2,700 mya during construction of the Archaen-Superior province, including Ely greenstone, metamorphosed and highly folded volcanics once thought to be the oldest exposed rock on earth; Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
formations created about 1,900 mya that gave the area most of its mineral riches; and more recent intrusive gabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is che ...
and extrusive
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff. In contras ...
basalts
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
and rhyolites
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral ...
of the Duluth Complex
The Duluth Complex, the related Beaver Bay Complex, and the associated North Shore Volcanic Group are rock formations which comprise much of the basement bedrock of the northeastern part of the U.S. state of Minnesota in central North America. The ...
and North Shore Volcanic Group, created by magma and lava which upwelled and hardened about 1,100 mya during the Midcontinent Rift
The Midcontinent Rift System (MRS) or Keweenawan Rift is a long geological rift in the center of the North America, North American continent and south-central part of the North American plate. It formed when the continent's core, the North Amer ...
. The Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid Rock (geology), rock that lies under loose material (regolith) within the crust (geology), crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface mater ...
formed by this activity has been eroded but remains at or close to the surface over much of the area.
The entire area is the raw southern edge of the Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield (french: Bouclier canadien ), also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the anc ...
. Topsoils are thin and poor and their parent soils derived from the rock beneath or nearby rather than from glacial till, which is sparse. Many of this region's lakes are located in depressions formed by the differential erosion of tilted layers of bedded rock of the Canadian Shield; the crevasses thereby formed have filled with water to create many of the thousands of lakes and swamps of the Superior National Forest
Superior National Forest, part of the United States National Forest system, is located in the Arrowhead Region of the state of Minnesota between the Canada–United States border and the north shore of Lake Superior. The area is part of the grea ...
.
In post-glacial times Northeastern Minnesota was covered by forest broken only by these interconnected lakes and wetlands. Much of the area has been little changed by human activity, as there are substantial forest and wilderness preserves, most notably the Boundary Waters Canoe Area
The Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness (BWCAW or BWCA) is a wilderness area within the Superior National Forest in the northeastern part of the US state of Minnesota under the administration of the U.S. Forest Service. A mixture of forests, ...
and Voyageurs National Park
Voyageurs National Park is an American national park in northern Minnesota near the city of International Falls established in 1975. The park's name commemorates the ''voyageurs''—French-Canadian fur traders who were the first European settle ...
. In the remainder of the region, lakes provide recreation, forests are managed for pulpwood, and the underlying bedrock is mined for valuable ores deposited in Precambrian times. While copper and nickel ores have been mined, the principal metallic mineral is iron. Three of Minnesota's four iron ranges are in the region, including the Mesabi Range
The Mesabi Iron Range is a mining district in northeastern Minnesota following an elongate trend containing large deposits of iron ore. It is the largest of four major iron ranges in the region collectively known as the Iron Range of Minnesota. ...
, which has supplied over 90% of the state's historic output, including most of the natural ores pure enough to be fed directly into furnaces. The state's iron mines have produced over three and a half billion metric tons of ore. While high-grade ores have now been exhausted, lower-grade taconite
Taconite () is a variety of iron formation, an iron-bearing (over 15% iron) sedimentary rock, in which the iron minerals are interlayered with quartz, chert, or carbonate. The name "taconyte" was coined by Horace Vaughn Winchell (1865–1923) � ...
continues to supply a large proportion of the nation's needs.
Northwestern Minnesota: glacial lakebed
''Northwestern Minnesota'' is a vast plain in the bed of Glacial Lake Agassiz. This plain extends north and northwest from the Big Stone Moraine, beyond Minnesota's borders into Canada andNorth Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the Native Americans in the United States, indigenous Dakota people, Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north a ...
. In the northeast, the Glacial Lake Agassiz plain transitions into the forests of the Arrowhead. The region includes the lowland portions of the Red River watershed and the western half of the Rainy River watershed within the state, at approximately the level of Lake Agassiz’ Herman Beach
Herman Beach is one of several beaches delimiting the shorelines of the prehistoric glacial Lake Agassiz.Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
, with small areas of Lower Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
and Upper Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
s along the western border. By late Wisconsinan
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cor ...
times this bedrock had been covered by clayey glacial drift scoured and transported south from sedimentary rocks in Manitoba. The bottomland is undissected and essentially flat, but imperceptibly declines from about 400 meters at the southern beaches of Lake Agassiz to 335 meters along the Rainy River. There is almost no relief, except for benches or beaches where Glacial Lake Agassiz stabilized for a time before it receded to a lower level. In contrast to the lakebed, these beaches ''rise'' from the south to the north and east at a gradient of approximately 1:5000; this rise resulted from the isostatic rebound
Post-glacial rebound (also called isostatic rebound or crustal rebound) is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound a ...
of the land after recession of the last ice sheet. In the western part of the region in the Red River Valley, fine-grained glacial lake deposits and decayed organic materials up to 50 meters in depth form rich, well-textured, and moisture-retentive, yet well-drained soils (mollisols
Mollisol is a soil type which has deep, high organic matter, nutrient-enriched surface soil (a horizon), typically between 60 and 80 cm in depth. This fertile surface horizon, called a mollic epipedon, is the defining diagnostic feature of M ...
), which are ideal for agriculture. To the north and east, much of the land is poorly drained peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
, often organized in rare and distinctive patterns known as ''patterned peatland''.
At marginally higher elevations within these wetlands are areas of black spruce, tamarack, and other water-tolerant species.
Southwestern Minnesota: glacial river and glacial till
 ''Southwestern Minnesota'' is in the watersheds of the
''Southwestern Minnesota'' is in the watersheds of the Minnesota River
The Minnesota River ( dak, Mnísota Wakpá) is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately 332 miles (534 km) long, in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It drains a watershed of in Minnesota and about in South Dakota and Iowa.
It ris ...
, the Missouri River, and the Des Moines River
The Des Moines River () is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the upper Midwestern United States that is approximately long from its farther headwaters.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe Na ...
. The Minnesota River lies in the bed of the glacial River Warren
Glacial River Warren, also known as River Warren, was a prehistoric river that drained Lake Agassiz in central North America between about 13,500 and 10,650 BP calibrated (11,700 and 9,400 14C uncalibrated) years ago. A part of the uppermost porti ...
, a much larger torrent that drained Lake Agassiz while outlets to the north were blocked by glaciers. The Coteau des Prairies
The Coteau des Prairies is a plateau approximately 200 miles in length and 100 miles in width (320 by 160 km), rising from the prairie flatlands in eastern South Dakota, southwestern Minnesota, and northwestern Iowa in the United States. ...
divides the Minnesota and Missouri River valleys, and is a striking landform created by the bifurcation of different lobes of glacial advance. On the Minnesota side of the coteau is a feature known as Buffalo Ridge
Buffalo Ridge is a large expanse of rolling hills in the southeastern part of the larger Coteau des Prairies. It stands 1,995 feet (608 m) above sea level. The Buffalo Ridge is long and runs through Lincoln, Pipestone, Murray, Nobles, ...
, where wind speeds average 16 mph (26 km/h). This windy plateau is being developed for commercial wind power
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to electricity generation, generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable energy, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller Environmental impact of wi ...
, contributing to the state's ranking as third in the nation for wind-generated electricity.
Between the river and the plateau are flat prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
s atop varying depths of glacial till. In the extreme southwest portion of the state, bedrock outcroppings of Sioux Quartzite
The Sioux Quartzite is a Proterozoic quartzite that is found in the region around the intersection of Minnesota, South Dakota, and Iowa, and correlates with other rock units throughout the upper midwestern and southwestern United States. It was ...
are common, with less common interbedded outcrops of an associated metamorphosed mudstone named catlinite
Catlinite, also called pipestone, is a type of argillite (metamorphosed mudstone), usually brownish-red in color, which occurs in a matrix of Sioux Quartzite. Because it is fine-grained and easily worked, it is prized by Native Americans, prim ...
. Pipestone, Minnesota
Pipestone is a city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Pipestone County. The population was 4,215 at the 2020 census. The city is also the site of the Pipestone National Monument.
History
Pipestone was platted in October, 187 ...
is the site of historic Native American quarries of catlinite, which is more commonly known as "pipestone". Another notable outcrop in the region is the Jeffers Petroglyphs
The Jeffers Petroglyphs site is an outcrop in southwestern Minnesota with pre-contact Native American petroglyphs. The petroglyphs are pecked into rock of the Red Rock Ridge, a -long Sioux quartzite outcrop that extends from Watonwan County, Min ...
, a Sioux Quartzite outcropping with numerous petroglyphs which may be up to 7000–9000 years old.
Drier than most of the rest of the state, the region is a transition zone between the prairies and the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
. Once rich in wetlands known as prairie potholes, 90%, or some three million acres (12,000 km²), have been drained for agriculture in the Minnesota River basin. Most of the prairies are now farm fields. Due to the quaternary and bedrock geology of the region, as well as the reduced precipitation in the region, groundwater resources are neither plentiful, nor widely distributed, unlike most other areas of the state. Given these constraints, this rural area hosts a vast network of water pipelines which transports groundwater from the few localized areas with productive groundwater wells to much of the region's population.
Southeastern Minnesota: bluffs, caves and sinkholes

 ''Southeastern Minnesota'' is separated from Southwestern Minnesota by the ''Owatonna Moraine'', the eastern branch of the Bemis Moraine, a
''Southeastern Minnesota'' is separated from Southwestern Minnesota by the ''Owatonna Moraine'', the eastern branch of the Bemis Moraine, a terminal moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed by the front edge ...
of the Des Moines lobe from the last Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cor ...
. Ojakangas and Matsch extend the region west past the moraine to a line running north from the Iowa border between Mankato
Mankato ( ) is a city in Blue Earth, Nicollet, and Le Sueur counties in the state of Minnesota. The population was 44,488 according to the 2020 census, making it the 21st-largest city in Minnesota, and the 5th-largest outside of the Minnea ...
and New Ulm to the latitude of the Twin Cities
Twin cities are a special case of two neighboring cities or urban centres that grow into a single conurbation – or narrowly separated urban areas – over time. There are no formal criteria, but twin cities are generally comparable in statu ...
, then encompassing the latter metropolis with a broad arc east to the St. Croix River. This moraine runs south from the Twin Cities in the general area of Minnesota State Highway 13
Minnesota State Highway 13 (MN 13) is a highway in Minnesota that runs from its intersection with U.S. Highway 65 in Albert Lea to its northern terminus at its intersection with State Highway 149 at the West St. Paul / Saint Paul city boundar ...
and Interstate 35
Interstate 35 (I-35) is a major Interstate Highway in the central United States. As with most primary Interstates that end in a five, it is a major cross-country, north–south route. It stretches from Laredo, Texas, near the Mexican border ...
. Sansome attaches this moraine to her description of West-Central Minnesota, given its similarity in glacial features to that region. Under Sansome's classification (followed here), Southeastern Minnesota is generally coterminous with the Paleozoic Plateau Section of the Eastern Broadleaf Forest Province.
The bedrock here is lower Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
sedimentary rocks, with limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
and dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
especially prevalent near the surface. It is highly dissected, and local tributaries of the Mississippi have cut deep valleys into the bedrock. It is an area of karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
topography, with thin topsoils lying atop porous limestones, leading to formation of caverns and sinkholes
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
. The last glaciation did not cover this region (halting at the Des Moines terminal lobe mentioned above), so there is no glacial drift to form subsoils, giving the region the name of the Driftless area
The Driftless Area, a topographical and cultural region in the American Midwest, comprises southwestern Wisconsin, southeastern Minnesota, northeastern Iowa, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois.
Never covered by ice during the last ...
. As the topsoils are shallower and poorer than those to the west, dairy farming
Dairy farming is a class of agriculture for long-term production of milk, which is processed (either on the farm or at a dairy plant, either of which may be called a dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting or ...
rather than cash crops is the principal agricultural activity.
Central Minnesota: knob and kettle country
 ''Central Minnesota'' is composed of (1) the
''Central Minnesota'' is composed of (1) the drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, t ...
of the St. Croix River (2) the basin of the Mississippi River above its confluence with the Minnesota, (3) those parts of the Minnesota and Red River basins on the glacial uplands forming the divides of those two basins with that of the Mississippi, (4) the Owatonna Moraine atop a strip of land running from western Hennepin County
Hennepin County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of Minnesota. Its county seat is Minneapolis, the state's most populous city. The county is named in honor of the 17th-century explorer Father Louis Hennepin. The county extends from Minneapol ...
south to the Iowa border, and (5) the upper valley of the Saint Louis River and the valley of its principal tributary the Cloquet River
The Cloquet River is a , accessed May 7, 2012 river in Minnesota, United States. It is the main tributary of the Saint Louis River.
Name
Cloquet ( ) River is known in the Ojibwe language as the ''Gaa-biitootigweyaag-ziibi'' ("River that parallel ...
which once drained to the Mississippi before they were captured by stream piracy and their waters were redirected through the lower Saint Louis River to Lake Superior. Glacial landforms
Glacial landforms are landforms created by the action of glaciers. Most of today's glacial landforms were created by the movement of large ice sheets during the Quaternary glaciations. Some areas, like Fennoscandia and the southern Andes, have ...
are the common characteristics of this gerrymander
In representative democracies, gerrymandering (, originally ) is the political manipulation of electoral district boundaries with the intent to create undue advantage for a party, group, or socioeconomic class within the constituency. The m ...
-like region.
The bedrock ranges in age from Archean granites to Upper Mesozoic Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
sediments, and underlying the eastern part of the region (and the southerly extension to Iowa) are the Late Precambrian Keweenawan volcanics of the Midcontinent Rift, overlaid by thousands of meters of sedimentary rocks.
At the surface, the entire region is "Moraine terrain", with the glacial landforms
Glacial landforms are landforms created by the action of glaciers. Most of today's glacial landforms were created by the movement of large ice sheets during the Quaternary glaciations. Some areas, like Fennoscandia and the southern Andes, have ...
of moraines
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
, drumlins
A drumlin, from the Irish Gaelic, Irish word ''droimnín'' ("littlest ridge"), first recorded in 1833, in the classical sense is an elongated hill in the shape of an inverted spoon or half-buried egg formed by glacier, glacial ice acting on und ...
, esker
An esker, eskar, eschar, or os, sometimes called an ''asar'', ''osar'', or ''serpent kame'', is a long, winding ridge of stratified sand and gravel, examples of which occur in glaciated and formerly glaciated regions of Europe and North Amer ...
s, kame
A kame, or ''knob'', is a glacial landform, an irregularly shaped hill or mound composed of sand, gravel and till that accumulates in a depression on a retreating glacier, and is then deposited on the land surface with further melting of the g ...
s, outwash plain
An outwash plain, also called a sandur (plural: ''sandurs''), sandr or sandar, is a plain formed of glaciofluvial deposits due to meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier. As it flows, the glacier grinds the underlying rock surface and ca ...
s and till plain
Till plains are an extensive flat plain of glacial till that forms when a sheet of ice becomes detached from the main body of a glacier and melts in place, depositing the sediments it carried. Ground moraines are formed with melts out of the glacie ...
s, all relics from recent glaciation. In the multitude of glacier-formed depressions are wetlands and many of the state's "10,000 lakes", which make the area prime vacation territory. The glacial deposits are a source of aggregate, and underneath the glacial till are high-quality granites which are quarried for buildings and monuments.
East Central Minnesota: bedrock valleys and outwash plain
 The subregion of ''East Central Minnesota'' is that part of Central Minnesota near the junction of three of the state's great rivers. Included are
The subregion of ''East Central Minnesota'' is that part of Central Minnesota near the junction of three of the state's great rivers. Included are Dakota County Dakota County may refer to:
*Dakota County, Minnesota in the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area of east-central Minnesota
*Dakota County, Nebraska
Dakota County is a county in the U.S. state of Nebraska. As of th2020 United States Census the populati ...
, eastern Hennepin County
Hennepin County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of Minnesota. Its county seat is Minneapolis, the state's most populous city. The county is named in honor of the 17th-century explorer Father Louis Hennepin. The county extends from Minneapol ...
, and the region north of the Mississippi but south of an east-west line from Saint Cloud to the St. Croix River on the Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
border. It includes much of the Twin Cities
Twin cities are a special case of two neighboring cities or urban centres that grow into a single conurbation – or narrowly separated urban areas – over time. There are no formal criteria, but twin cities are generally comparable in statu ...
metropolitan area. The region has the same types of glacial landforms as the remainder of Central Minnesota, but is distinguished by its bedrock valleys, both active and buried.
The valleys now hold three of Minnesota's largest rivers, which join here. The St. Croix joins the Mississippi at Prescott, Wisconsin. Upstream, the Mississippi is joined by the Minnesota River at historic Fort Snelling
Fort Snelling is a former military fortification and National Historic Landmark in the U.S. state of Minnesota on the bluffs overlooking the confluence of the Minnesota and Mississippi Rivers. The military site was initially named Fort Saint Anth ...
. When River Warren Falls
The River Warren Falls was a massive waterfall on the glacial River Warren initially located in present-day Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. The waterfall was 2700 feet (823 m) across and 175 feet (53 m) high.
Geologic ...
receded past the confluence of the much smaller Upper Mississippi River
The Upper Mississippi River is the portion of the Mississippi River upstream of St. Louis, Missouri, United States, at the confluence of its main tributary, the Missouri River.
History
In terms of geologic and hydrographic history, the Upper ...
, a new waterfall was created where that river entered the much-lower River Warren. The new falls receded upstream on the Mississippi, migrating eight miles (13 km) over 9600 years to where Louis Hennepin
Father Louis Hennepin, O.F.M. baptized Antoine, (; 12 May 1626 – 5 December 1704) was a Belgian Roman Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Recollet order (French: ''Récollets'') and an explorer of the interior of North Amer ...
first saw it and named St. Anthony Falls
Saint Anthony Falls, or the Falls of Saint Anthony ( dak, italics=no, Owámniyomni, ) located at the northeastern edge of downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota, is the only natural major waterfall on the Mississippi River. Throughout the mid-to-late 1 ...
in 1680. Due to its value as a power source, this waterfall determined the location of Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. Minneapolis has its origins ...
. One tributary of the river coming from the west, Minnehaha Creek
Minnehaha Creek ( dak, Mniȟáȟa Wakpádaŋ) is a 22-mile-long (35 km) tributary of the Mississippi River that flows east from Gray's Bay Dam on Lake Minnetonka through the suburban cities of Minnetonka, Hopkins, Saint Louis Park, and Edin ...
, receded only a few hundred yards from one of the channels of the Mississippi. Minnehaha Falls
Minnehaha Park is a city park in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States, and home to Minnehaha Falls and the lower reaches of Minnehaha Creek. Officially named Minnehaha Regional Park, it is part of the Minneapolis Park and Recreation Board syst ...
remains as a picturesque and informative relic of River Warren Falls, and the limestone-over-sandstone construction is readily apparent in its small gorge. At St. Anthony Falls, the Mississippi dropped over a limestone ledge; these waterfalls were used to drive the flour mills
A gristmill (also: grist mill, corn mill, flour mill, feed mill or feedmill) grinds cereal grain into flour and middlings. The term can refer to either the grinding mechanism or the building that holds it. Grist is grain that has been separat ...
that were the foundation for the city's 19th century growth.
Other bedrock tunnel valley
A tunnel valley is a U-shaped valley originally cut under the glacial ice near the margin of continental ice sheets such as that now covering Antarctica and formerly covering portions of all continents during past glacial ages. They can be as lo ...
s lie deep beneath till deposited by the glaciers which created them, but can be traced in many places by the Chain of Lakes in Minneapolis and lakes and dry valleys in St. Paul.Ojakangas and Matsch, ''Minnesota’s Geology'', p. 236
North of the metropolitan area is the ''Anoka Sandplain'', a flat area of sandy outwash
An outwash plain, also called a sandur (plural: ''sandurs''), sandr or sandar, is a plain formed of glaciofluvial deposits due to meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier. As it flows, the glacier grinds the underlying rock surface and ca ...
from the last ice age. Along the eastern edge of the region are the Dalles of the St. Croix River, a deep gorge cut by runoff from Glacial Lake Duluth
Lake Duluth was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Superior drainage basin as the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated.
into ancient bedrock. Interstate Park
Interstate Park comprises two adjacent state parks on the Minnesota–Wisconsin border, both named Interstate State Park. They straddle ''the Dalles'' of the St. Croix River, a deep basalt gorge with glacial potholes and other rock formations. ...
here contains the southernmost surface exposure of the Precambrian lava flows of the Midcontinent Rift
The Midcontinent Rift System (MRS) or Keweenawan Rift is a long geological rift in the center of the North America, North American continent and south-central part of the North American plate. It formed when the continent's core, the North Amer ...
, providing a glimpse of Minnesota's volcanic past.
References
Notes
Sources
* (Date of webpage - 2005-04-01.) * * * (Date of webpage: 2005-04-29) * * * * Jirsa, Mark and Southwick, David. * (Date of webpage = 2005-04-01.) * * (Date of webpage: 2003-01-26.) * Date of webpage: (2007-03-31.) * * (Date of webpage: 2007.) * * * * (Date of photograph: 1991-04-25.) * * * * * * (Date of webpage: 2004-11-15.) * (Date of map: April 2007.) * Wright, W. E. (1990)''Geologic History of Minnesota Rivers''
Minnesota Geological Survey, Educational Series 7. St. Paul: University of Minnesota. ISSN 0544-3083. {{Geology of the United States by political division
Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
Natural history of Minnesota