|
Jay Cooke State Park
Jay Cooke State Park is a state park of Minnesota, United States, protecting the lower reaches of the Saint Louis River. The park is located about southwest of Duluth and is one of the ten most visited state parks in Minnesota. The western half of the park contains part of a rocky, gorge. This was a major barrier to Native Americans and early Europeans traveling by canoe, which they bypassed with the challenging Grand Portage of the St. Louis River. The river was a vital link connecting the Mississippi waterways to the west with the Great Lakes to the east. Today Minnesota State Highway 210 runs through Jay Cooke State Park. The of the route between Carlton and Highway 23—which include the park—are designated the Rushing Rapids Parkway, a state scenic byway. The park is named for Pennsylvania financier Jay Cooke, who had developed a nearby power plant, which is still in use. The Grand Portage trail and three districts of 1930s park structures are listed on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
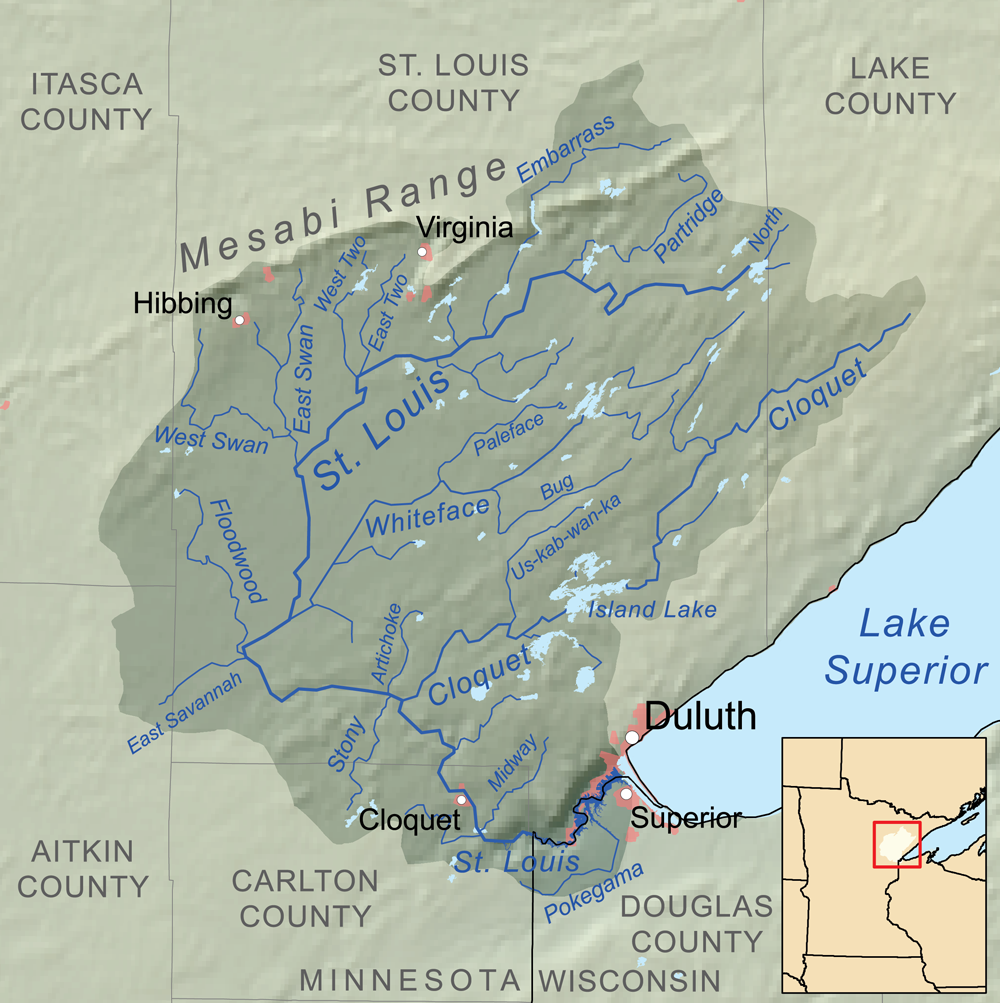
Saint Louis River (Lake Superior Tributary)
The Saint Louis River (abbreviated St. Louis River) is a river in the U.S. states of Minnesota and Wisconsin that flows into Lake Superior. The largest U.S. river to flow into the lake, it is in lengthU.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed May 1, 2012 and starts east of Hoyt Lakes, Minnesota. The river's watershed covers . Near the Twin Ports of Duluth, Minnesota and Superior, Wisconsin, the river becomes a freshwater estuary. History According to Warren Upham, the Ojibwe name of the river is ''Gichigami-ziibi'' (Great-lake River). He notes: "The river was probably so named by Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye (1685–1749), who was a very active explorer, in the years 1731 and onward. Shortly before his death the king of France in 1749 conferred on him the cross of Saint Louis as a recognition of the importance of his discoveries, and thence the name of the Saint Louis River appears to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jay Cooke
Jay Cooke (August 10, 1821 – February 16, 1905) was an American financier who helped finance the Union war effort during the American Civil War and the postwar development of railroads in the northwestern United States. He is generally acknowledged as the first major investment banker in the United States and creator of the first wire house firm. Early life Cooke was born at Sandusky, Ohio, the son of Eleutheros Cooke and Martha Carswell Cooke. Eleutheros Cooke was a pioneer Ohio lawyer and Whig, a member of the Ohio General Assembly, and a member of Congress from Ohio from 1831 to 1833. Financier of the Civil War In 1838, Cooke went to Philadelphia, where he entered the banking house of E. W. Clark & Co. as a clerk, and became a partner in 1842. He left this firm in 1858. On January 1, 1861, just months before the start of the American Civil War, Cooke opened the private banking house of Jay Cooke & Company in Philadelphia. Soon after the war began, the state of Pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coureur Des Bois
A coureur des bois (; ) or coureur de bois (; plural: coureurs de(s) bois) was an independent entrepreneurial French-Canadian trader who travelled in New France and the interior of North America, usually to trade with First Nations peoples by exchanging various European items for furs. Some learned the trades and practices of the indigenous peoples. These expeditions were part of the beginning of the fur trade in the North American interior. Initially they traded for beaver coats and furs. However, as the market grew, ''coureurs de bois'' were trapping and trading prime beavers whose skins were to be felted in Europe. Evolution While French settlers had lived and traded alongside Indigenous people since the earliest days of New France, coureurs des bois reached their apex during the second half of the 17th century. After 1681, the independent coureur des bois was gradually replaced by state-sponsored voyageurs, who were workers associated with licensed fur traders. They trave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Fur Trade
The North American fur trade is the commercial trade in furs in North America. Various Indigenous peoples of the Americas traded furs with other tribes during the pre-Columbian era. Europeans started their participation in the North American fur trade from the initial period of their colonization of the Americas onward, extending the trade's reach to Europe. European merchants from France, England and the Dutch Republic established trading posts and forts in various regions of North America to conduct the trade with local Indigenous communities. The trade reached the peak of its economic importance in the 19th century, by which time it relied upon elaborately developed trade networks. The trade soon became one of the main economic drivers in North America, attracting competition amongst European nations which maintained trade interests in the Americas. The United States sought to remove the substantial British control over the North American fur trade during the first decades of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
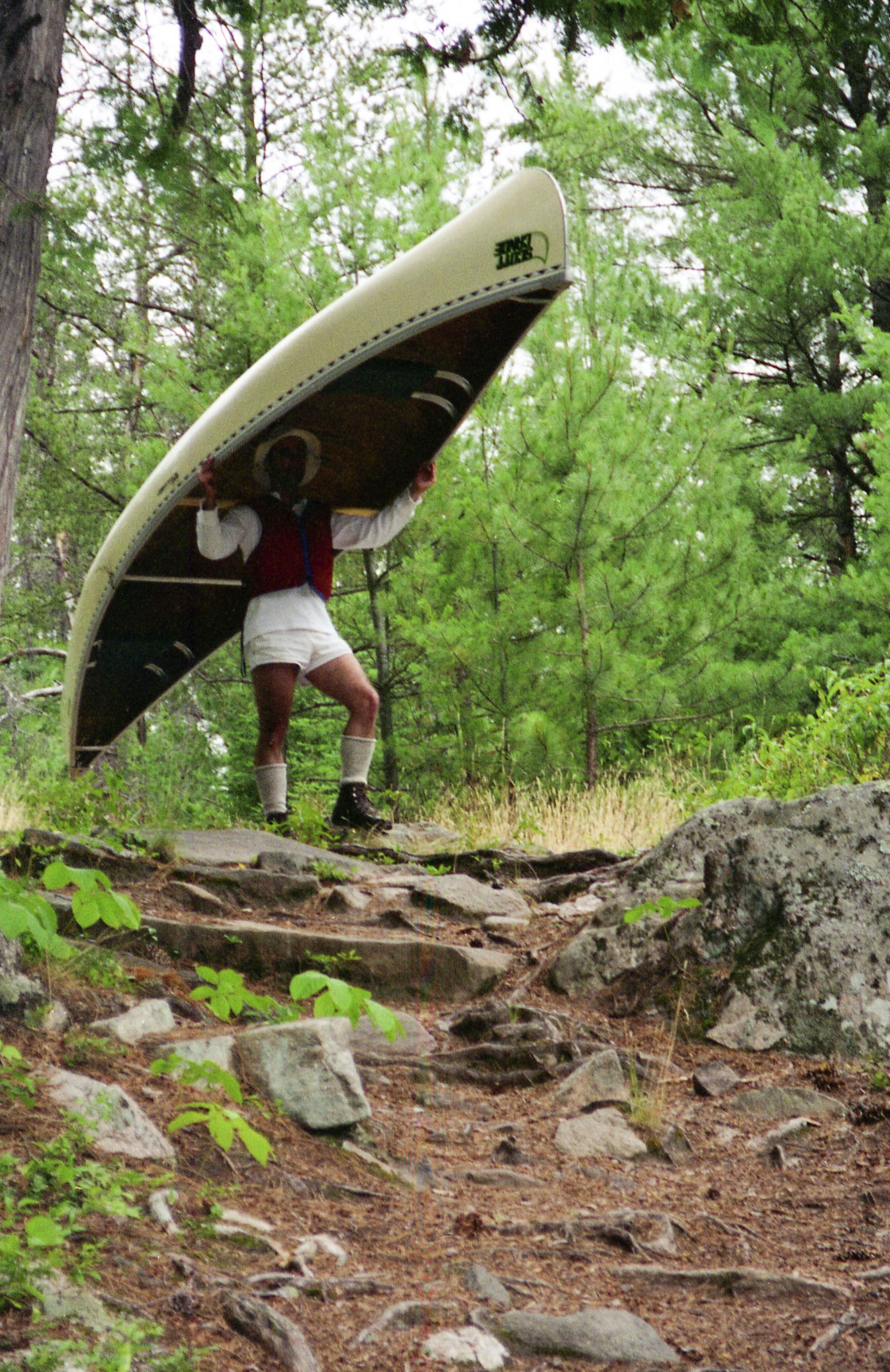
Voyageur Canoe
The voyageurs (; ) were 18th and 19th century French Canadians who engaged in the transporting of furs via canoe during the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including the ''Pays d'en Haut'' and the ''Pays des Illinois'') and times where transportation of materials was mainly over long distances. The voyageurs were regarded as legendary. They were heroes celebrated in folklore and music. For reasons of promised celebrity status and wealth, this position was coveted. Despite the fame surrounding the voyageur, their life was one of toil and not nearly as glorious as folk tales make it out to be. For example, they had to be able to carry two bundles of fur over portages. Some carried up to four or five, and there is a report of a voyageur carrying seven bundles for half of a mile.Mike Hillman, "La Bonga: The Greatest Voyageur" Boundary Waters Journal Magazine, Summer 2010 Issue, pp 20–25 Hernias were common a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shooting The Rapids 1879
Shooting is the act or process of discharging a projectile from a ranged weapon (such as a gun, Bow and arrow, bow, crossbow, slingshot, or Blowgun, blowpipe). Even the acts of launching Flamethrower, flame, artillery, Dart (missile), darts, harpoons, grenades, rockets, and guided missiles can be considered acts of shooting. When using a firearm, the act of shooting is often called firing as it involves initiating a combustion (deflagration) of chemical propellants. Shooting can take place in a shooting range or in the field, in shooting sports, hunting, or in combat. The person involved in the shooting activity is called a shooter. A skilled, accurate shooter is a ''marksman'' or ''sharpshooter'', and a person's level of shooting proficiency is referred to as their ''marksmanship''. Competitive shooting Shooting has inspired competition, and in several countries rifle clubs started to form in the 19th century. Soon international shooting events evolved, including Shooting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ''portage.'' The term comes from French, where means "to carry," as in "portable". In Canada, the term "carrying-place" was sometimes used. Early French explorers in New France and French Louisiana encountered many rapids and cascades. The Native Americans carried their canoes over land to avoid river obstacles. Over time, important portages were sometimes provided with canals with locks, and even portage railways. Primitive portaging generally involves carrying the vessel and its contents across the portage in multiple trips. Small canoes can be portaged by carrying them inverted over one's shoulders and the center strut may be designed in the style of a yoke to facilitate this. Historically, voyageurs often employed tump lines on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is , of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. Native Americans have lived along the Mississippi River and its tributaries for thousands of years. Most were hunter-ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: baie d'Hudson), sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. Although not geographically apparent, it is for climatic reasons considered to be a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It Hudson Bay drainage basin, drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay. The Cree language, Eastern Cree name for Hudson an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic District
A historic district or heritage district is a section of a city which contains older buildings considered valuable for historical or architectural reasons. In some countries or jurisdictions, historic districts receive legal protection from certain types of development. Historic districts may or may not also be the center of the city. They may be coterminous with the commercial district, administrative district, or arts district, or separate from all of these. Historical districts are often parts of a larger urban setting, but they can also be parts or all of small towns, or a rural areas with historic agriculture-related properties, or even a physically disconnected series of related structures throughout the region. Much criticism has arisen of historic districts and the effect protective zoning and historic designation status laws have on the housing supply. When an area of a city is designated as part of a 'historic district', new housing development is artificially re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
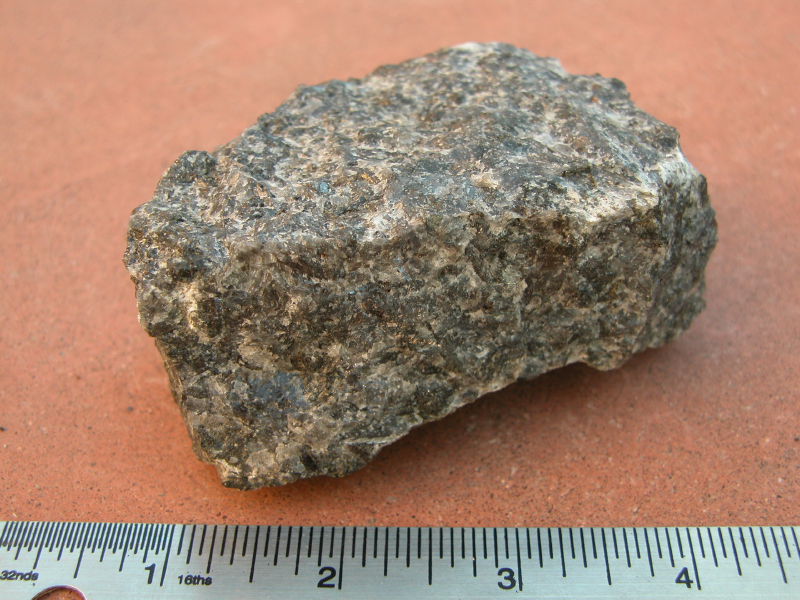
Gabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is chemically equivalent to rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt. Much of the Earth's oceanic crust is made of gabbro, formed at mid-ocean ridges. Gabbro is also found as plutons associated with continental volcanism. Due to its variant nature, the term ''gabbro'' may be applied loosely to a wide range of intrusive rocks, many of which are merely "gabbroic". By rough analogy, gabbro is to basalt as granite is to rhyolite. Etymology The term "gabbro" was used in the 1760s to name a set of rock types that were found in the ophiolites of the Apennine Mountains in Italy. It was named after Gabbro, a hamlet near Rosignano Marittimo in Tuscany. Then, in 1809, the German geologist Christian Leopold von Buch used the term more restrictively in his descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |