|
Prairie Pothole Region
The Prairie Pothole Region (PPR; french: Région des cuvettes/fondrières des prairies) is an expansive area of the northern Great Plains that contains thousands of shallow wetlands known as potholes. These potholes are the result of glacier activity in the Wisconsin glaciation, which ended about 10,000 years ago. The decaying ice sheet left behind depressions formed by the uneven deposition of till in ground moraines. These depressions are called potholes, glacial potholes, kettles, or kettle lakes. They fill with water in the spring, creating wetlands, which range in duration from temporary to semi-permanent. The region covers an area of about 800,000 sq. km and expands across three Canadian provinces (Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Alberta) and five U.S. states (Minnesota, Iowa, North and South Dakota, and Montana). The hydrology of the wetlands is variable, which results in long term productivity and biodiversity. The PPR is a prime spot during breeding and nesting season for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large portion of the population with nine reservations currently in the state and have historically dominated the territory. South Dakota is the seventeenth largest by area, but the 5th least populous, and the 5th least densely populated of the 50 United States. As the southern part of the former Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with North Dakota. They are the 39th and 40th states admitted to the union; President Benjamin Harrison shuffled the statehood papers before signing them so that no one could tell which became a state first. Pierre is the state capital, and Sioux Falls, with a population of about 192,200, is South Dakota's largest city. South Dakota is bordered by the states of No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygonum
''Polygonum'' is a genus of about 130 species of flowering plant in the buckwheat and knotweed family Polygonaceae. Common names include knotweed and knotgrass (though the common names may refer more broadly to plants from Polygonaceae). In the Middle English glossary of herbs ''Alphita'' ( 1400–1425), it was known as ars-smerte. There have been various opinions about how broadly the genus should be defined. For example, buckwheat (''Fagopyrum esculentum'') has sometimes been included in the genus as ''Polygonum fagopyrum''. Former genera such as ''Polygonella'' have been subsumed into ''Polygonum''; other genera have been split off. The genus primarily grows in northern temperate regions. The species are very diverse, ranging from prostrate herbaceous Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody stems above ground. This broad category of plants includes many perennials, and nearly all annuals and biennials. Definitions of "herb" and "herb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
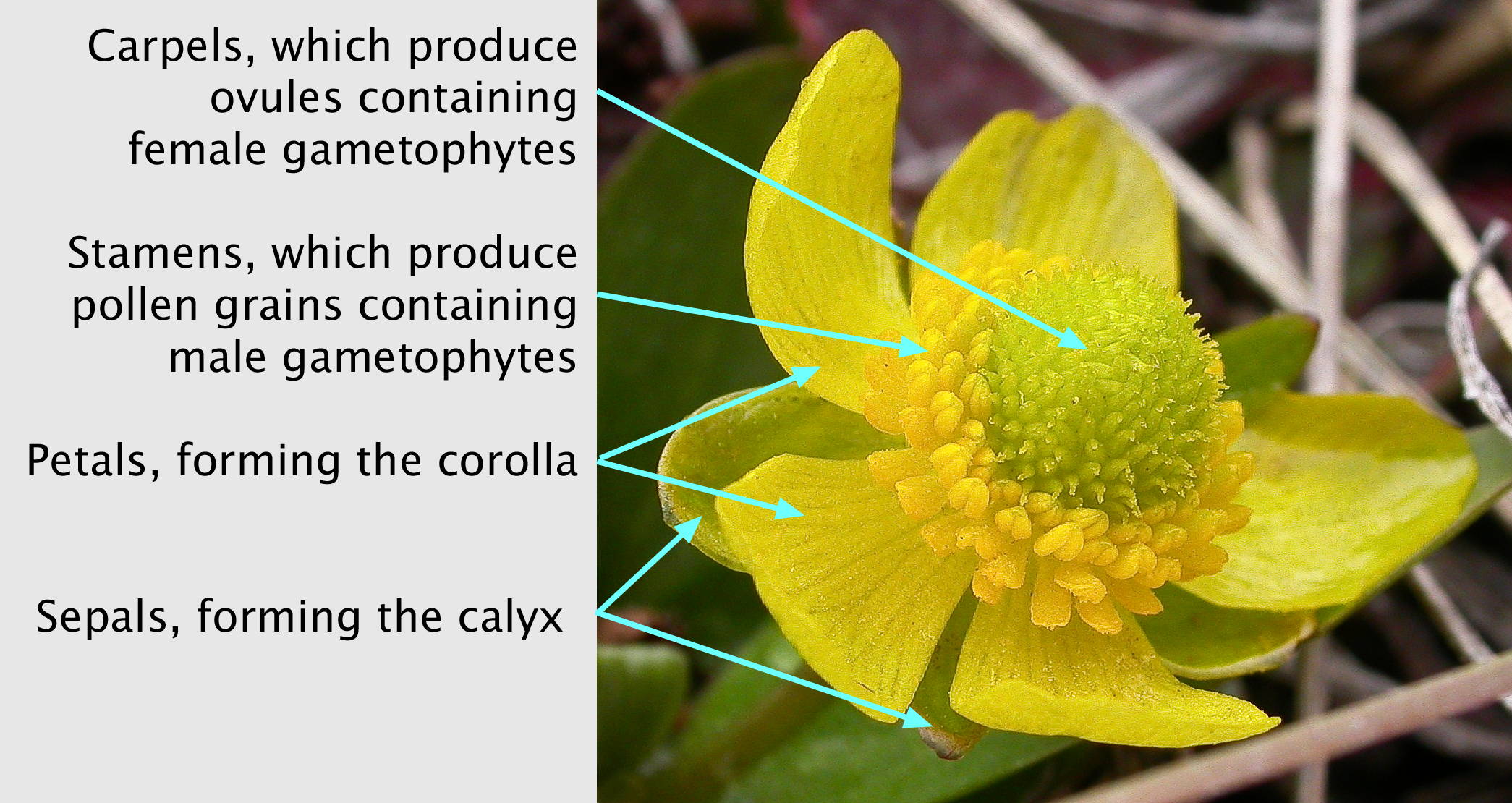
Ranunculus
''Ranunculus'' is a large genus of about almost 1700 to more than 1800 species of flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae. Members of the genus are known as buttercups, spearworts and water crowfoots. The genus is distributed in Europe, North America and South America. The familiar and widespread buttercup of gardens throughout Northern Europe (and introduced elsewhere) is the creeping buttercup ''Ranunculus repens'', which has extremely tough and tenacious roots. Two other species are also widespread, the bulbous buttercup ''Ranunculus bulbosus'' and the much taller meadow buttercup ''Ranunculus acris''. In ornamental gardens, all three are often regarded as weeds. Buttercups usually flower in the spring, but flowers may be found throughout the summer, especially where the plants are growing as opportunistic colonizers, as in the case of garden weeds. The water crowfoots (''Ranunculus'' subgenus ''Batrachium''), which grow in still or running water, are sometimes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pondweed
Pondweed refers to many species and genera of aquatic plants and green algae: *''Potamogeton'', a diverse and worldwide genus *''Elodea'', found in North America *''Aponogeton'', in Africa, Asia and Australasia *''Groenlandia ''Groenlandia'' is a monotypic genus of aquatic plants (pondweed) of the family Potamogetonaceae. The only species in the genus is ''Groenlandia densa''. Opposite-leaved pondweed is a common name for this plant. It is native to much of Europe, ...'', a genus of aquatic plants *'' Stuckenia'', a genus of aquatic plants * Charales, an order of green algae {{Plant common name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemnoideae
Lemnoideae is a subfamily of flowering aquatic plants, known as duckweeds, water lentils, or water lenses. They float on or just beneath the surface of still or slow-moving bodies of fresh water and wetlands. Also known as bayroot, they arose from within the arum or aroid family (Araceae), so often are classified as the subfamily Lemnoideae within the family Araceae. Other classifications, particularly those created prior to the end of the twentieth century, place them as a separate family, Lemnaceae. These plants have a simple structure, lacking an obvious stem or leaves. The greater part of each plant is a small organized "thallus" or "frond" structure only a few cells thick, often with air pockets (aerenchyma) that allow it to float on or just under the water surface. Depending on the species, each plant may have no root or may have one or more simple rootlets. Reproduction is mostly by asexual budding (vegetative reproduction), which occurs from a meristem enclosed at the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoenoplectus Pungens
''Schoenoplectus pungens'' is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family known as common threesquare, common three-square bulrush and sharp club-rush. It is a herbaceous emergent plant that is widespread across much of North and South America as well as Europe, New Zealand and Australia.Acevedo-Rodríguez, P. & Strong, M.T. (2012). Catalogue of seed plants of the West Indies. Smithsonian Contributions to Botany 98: 1-1192. Habitat Threesquare is found in open, sun-lit marshes and along the shores of lakes and ponds, in water up to deep. It is resistant to fire. Description ''Schoenoplectus pungens'' is a long-lived perennial herb up to tall. The foliage is dark green, rough and dense. The small flowers are grouped in dense spikelets, with of 1–7 spikelets on each stem. The seeds are brown. It is closely related to ''S. americanus,'' and many ''S. pungens'' specimens have long been misidentified as ''S. americanus.'' File:Schoenoplectus spp Sturm11.jpg, Painting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoenoplectus Tabernaemontani
''Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani'' ( syn. ''Scirpus validus'') is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family known by the common names softstem bulrush, grey club-rush, and great bulrush. It can be found throughout much of the world; it has been reported from every state in the United States (including Hawaii), and from every province and territory in Canada except Nunavut. It grows in moist and wet habitat, and sometimes in shallow water. ''Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani'' is quite variable in appearance, thus explaining the long list of synonyms that have been created over the years. It is a perennial herb producing dense stands of many narrow erect stems reaching 1–3 m (33–100 inches) in height. It grows from a long rhizome system. The leaves are mostly basal and have wide sheaths around the stems. The inflorescence is generally a panicle of spikelets on long, thin branches which spread, arch, or droop. The spikelets vary in color. There is usually a long, stiff brac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoenoplectus Acutus
''Schoenoplectus acutus'' ( syn. ''Scirpus acutus, Schoenoplectus lacustris, Scirpus lacustris'' subsp. ''acutus''), called tule , common tule, hardstem tule, tule rush, hardstem bulrush, or viscid bulrush, is a giant species of sedge in the plant family Cyperaceae, native to freshwater marshes all over North America. The common name derives from the Nāhuatl word ''tōllin'' , and it was first applied by the early settlers from New Spain who recognized the marsh plants in the Central Valley of California as similar to those in the marshes around Mexico City. Tules once lined the shores of Tulare Lake in California, formerly the largest freshwater lake in the western United States. It was drained by land speculators in the 20th century. The expression "out in the tules" is still common, deriving from the dialect of old Californian families and meaning "where no one would want to live", with a touch of irony. The phrase is comparable to "out in the boondocks". ''Schoenoplectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments ( saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that grows in or near water and is either emergent, submergent, or floating. In lakes and rivers macrophytes provide cover for fish, substrate for aquatic invertebrates, produce oxygen, and act as food for some fish and wildlife. Macrophytes are primary producers and are the basis of the food web for many organisms. They have a significant effect on soil chemistry and light levels as they slow down the flow of water and capture pollutants and trap sediments. Excess sediment will settle into the benthos aided by the reduction of flow rates caused by the presence of plant stems, leaves and roots. Some plants have the capability of absorbing pollutants into their tissue. Seaweeds are multicellular marine algae and, although their ecological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater Recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs in the vadose zone below plant roots and is often expressed as a flux to the water table surface. Groundwater recharge also encompasses water moving away from the water table farther into the saturated zone. Recharge occurs both naturally (through the water cycle) and through anthropogenic processes (i.e., "artificial groundwater recharge"), where rainwater and or reclaimed water is routed to the subsurface. Processes Water is recharged naturally by rain and snow melt and to a smaller extent by surface water (rivers and lakes). Recharge may be impeded somewhat by human activities including paving, development, or logging. These activities can result in loss of topsoil resulting in reduced water infiltration, enhanced surface r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater is Groundwater recharge, recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at spring (hydrosphere), springs and Seep (hydrology), seeps, and can form oasis, oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agriculture, agricultural, city, municipal, and Industrial sector, industrial use by constructing and operating extraction water well, wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology. Typically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |