Cooper T40 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
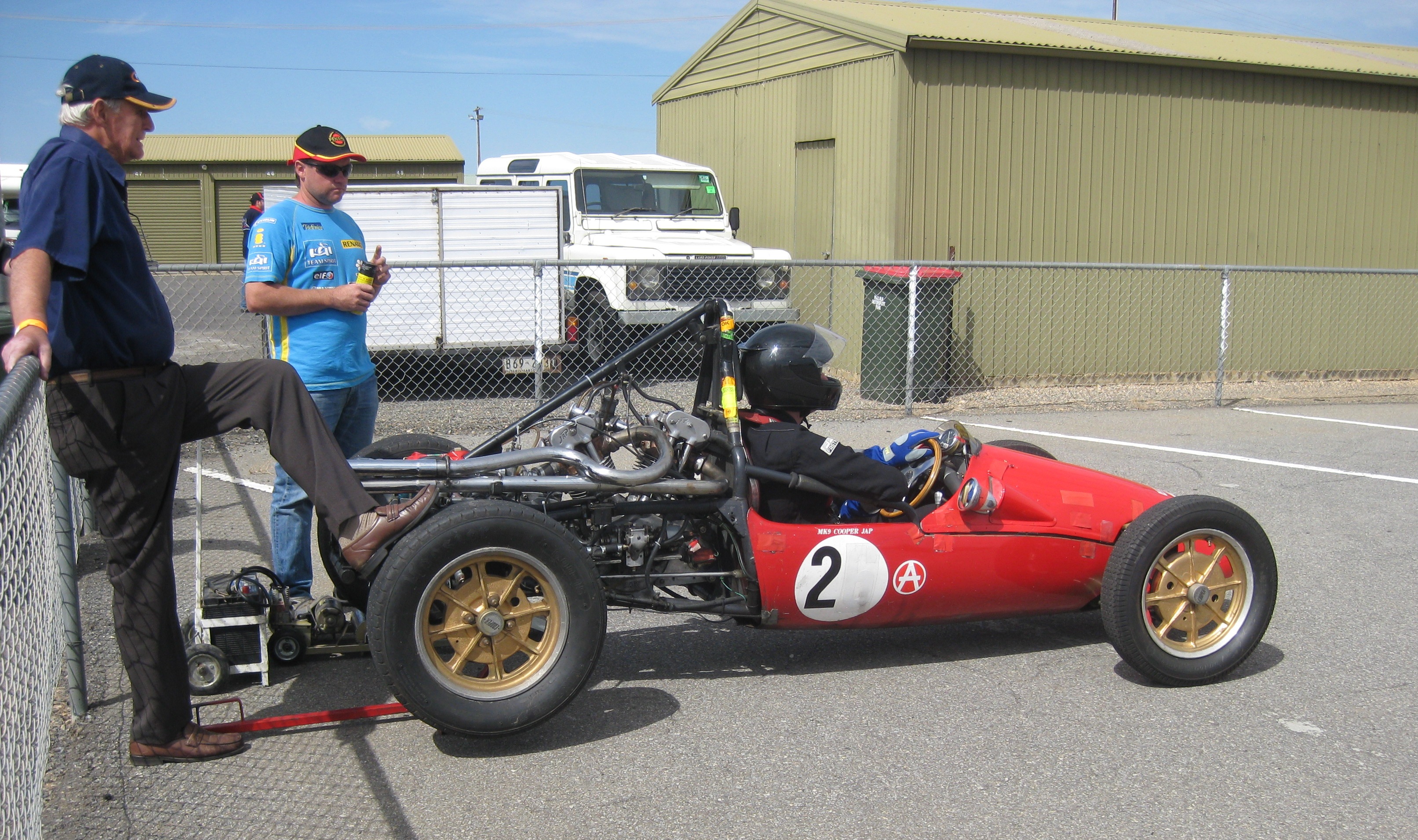

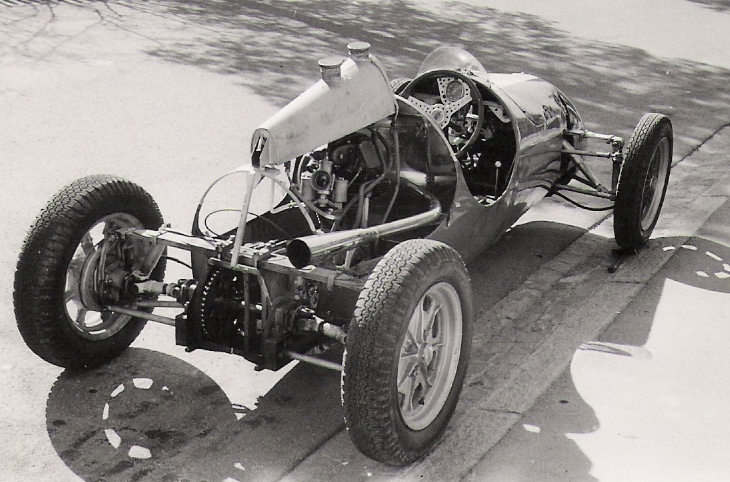


 The Cooper Car Company is a British car manufacturer founded in December 1947 by Charles Cooper and his son John Cooper. Together with John's boyhood friend,
The Cooper Car Company is a British car manufacturer founded in December 1947 by Charles Cooper and his son John Cooper. Together with John's boyhood friend,
 The first cars built by the Coopers were single-seat 500-cc
The first cars built by the Coopers were single-seat 500-cc
 After the death of his father, John Cooper sold the Cooper Formula One team to the Chipstead Motor Group in April 1965. The same year, the Formula One team moved from Surbiton to a modern factory unit at Canada Road, Oyster Lane in Byfleet, just along the road from Brabham in New Haw and close to
After the death of his father, John Cooper sold the Cooper Formula One team to the Chipstead Motor Group in April 1965. The same year, the Formula One team moved from Surbiton to a modern factory unit at Canada Road, Oyster Lane in Byfleet, just along the road from Brabham in New Haw and close to
TNF Tourist Guide to Former Premises to the Metropolitan Police and the local Traffic Division (V Victor) moved in. They would stay there for the next 25 years and 'TDV' would become one of the busier police garages. In August 1968, they were supplied with two Mini Coopers, index numbers PYT767F and PYT768F. The centre boss of the steering wheel was replaced by a speaker and microphone and a PTT transmitter switch, was added to the steering column. The vehicles were trialled for a number of months, but no orders were placed for other garages. The police subsequently moved out, and the building became a Porsche dealership.
John Cooper Works
* John Cooper (1977). ''The Grand Prix Carpetbaggers: The Autobiography of John Cooper''. Doubleday. * ''Cooper Cars'', by Doug Nye, 1983, Osprey Publishing, 2003, Motorbooks International * Wright, Terry; ''Power Without Glory: Racing the Big-twin Cooper'', Loose Fillings Sydney 2015. See also www.loosefillings.com
{{Authority control Formula One constructors Formula One entrants 1947 establishments in England 1969 disestablishments in England Car manufacturers of the United Kingdom British auto racing teams British racecar constructors Formula Two constructors Auto racing teams established in 1947 Auto racing teams disestablished in 1969 Formula One World Constructors' Champions British Touring Car Championship teams 24 Hours of Le Mans teams


 The Cooper Car Company is a British car manufacturer founded in December 1947 by Charles Cooper and his son John Cooper. Together with John's boyhood friend,
The Cooper Car Company is a British car manufacturer founded in December 1947 by Charles Cooper and his son John Cooper. Together with John's boyhood friend, Eric Brandon
Eric Brandon (18 July 1920 in East Ham, Essex – 8 August 1982 in Gosport, Hampshire) was a motor racing driver and businessman. He was closely associated with the Cooper Car Company, and was instrumental in the early development of the company. ...
, they began by building racing cars in Charles's small garage in Surbiton, Surrey, England, in 1946. Through the 1950s and early 1960s they reached motor racing
Motorsport, motorsports or motor sport is a global term used to encompass the group of competitive sporting events which primarily involve the use of motorized vehicles. The terminology can also be used to describe forms of competition of tw ...
's highest levels as their mid-engined, single-seat cars competed in both Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, ...
and the Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly called the Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at Indianapolis Motor Speedway (IMS) in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indi ...
, and their Mini Cooper Mini Cooper may refer to:
*Cars of the original Mini series called the "Mini Cooper", made by the British Motor Corporation and its successors 1961–1971, and 1990–2000
*Cars of the Mini (marque), including a number of different models produced ...
dominated rally racing. The Cooper name lives on in the Cooper versions of the Mini
The Mini is a small, two-door, four-seat car, developed as ADO15, and produced by the British Motor Corporation (BMC) and its successors, from 1959 through 2000. Minus a brief hiatus, original Minis were built for four decades and sold during ...
production cars that are built in England, but is now owned and marketed by BMW.
Origins

 The first cars built by the Coopers were single-seat 500-cc
The first cars built by the Coopers were single-seat 500-cc Formula Three
Formula Three, also called Formula 3, abbreviated as F3, is a third-tier class of open-wheel formula racing. The various championships held in Europe, Australia, South America and Asia form an important step for many prospective Formula One dri ...
racing cars driven by John Cooper and Eric Brandon, and powered by a JAP motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising ...
engine. Since materials were in short supply immediately after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the prototypes were constructed by joining two old Fiat Topolino
''Topolino'' (from the Italian name for Mickey Mouse) is an Italian digest-sized comic series featuring Disney comics. The series has had a long running history, first appearing in 1932 as a comics magazine. It is currently published by Panin ...
front-ends together. According to John Cooper, the stroke of genius that would make the Coopers an automotive legend—the location of the engine behind the driver—was merely a practical matter at the time. As the car was powered by a motorcycle engine, they believed it was more convenient to have the engine in the back, driving a chain. In fact there was nothing new about 'mid' engined racing cars but there is no doubt Coopers led the way in popularising what was to become the dominant arrangement for racing cars.
Called the Cooper 500, this car's success in hillclimbs and on track, including Eric winning the 500 race at one of the first postwar meetings at Gransden Lodge Airfield
Gransden Lodge Airfield is a former wartime airfield located west of Cambridge, Cambridgeshire, England.
The Cambridge University Gliding Club (now Cambridge Gliding Centre) moved to Gransden Lodge in October 1991, having previously shared ...
, quickly created demand from other drivers (including, over the years, Stirling Moss, Peter Collins, Jim Russell, Ivor Bueb
Ivor Léon John Bueb (6 June 1923 – 1 August 1959) was a British professional sports car racing and Formula One driver from England.
Career
Born in East Ham, Essex east of London, Bueb started racing seriously in a Formula Three 500cc Cooper ...
, Ken Tyrrell
Robert Kenneth Tyrrell (3 May 1924 – 25 August 2001) was a British Formula Two racing driver and the founder of the Tyrrell Formula One constructor.Setright, L. J. K. "Tyrrell: A Shrewd Talent-spotter", in Northey, Tom, ed. ''World of Autom ...
, and Bernie Ecclestone) and led to the establishment of the Cooper Car Company to build more. The business grew by providing an inexpensive entry to motorsport for seemingly every aspiring young British driver, and the company became the world's first and largest postwar, specialist manufacturer of racing cars for sale to privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s.
Cooper built up to 300 single-and twin-cylinder cars during the 1940s and 1950s, and dominated the F3 category, winning 64 of 78 major races between 1951 and 1954. This volume of construction was unique and enabled the company to grow into the senior categories; With a modified Cooper 500 chassis, a T12 model, Cooper had its first taste of top-tier racing when Harry Schell
Henry O'Reilly "Harry" Schell (June 29, 1921 – May 13, 1960) was an American Grand Prix motor racing driver. He was the first American driver to start a Formula One Grand Prix.
Early life
Schell was born in Paris, France, the son of expatri ...
qualified for the 1950 Monaco Grand Prix
The 1950 Monaco Grand Prix, formally titled the ''Prix de Monte-Carlo et XI Grand Prix Automobile'', was a Formula One motor race held on 21 May 1950 at Monaco. It was race two of seven in the 1950 World Championship of Drivers. The 100-lap race ...
. Though Schell retired in the first lap, this marked the first appearance of a rear-engined racer at a Grand Prix event since the end of WWII.
The front-engined Formula Two
Formula Two (F2 or Formula 2) is a type of open-wheel formula racing category first codified in 1948. It was replaced in 1985 by Formula 3000, but revived by the FIA from 2009– 2012 in the form of the FIA Formula Two Championship. The name ...
Cooper Bristol model was introduced in 1952. Various iterations of this design were driven by a number of legendary drivers – among them Juan Manuel Fangio and Mike Hawthorn
John Michael Hawthorn (10 April 1929 – 22 January 1959) was a British racing driver. He became the United Kingdom's first Formula One World Champion driver in 1958, whereupon he announced his retirement, having been profoundly affected by the ...
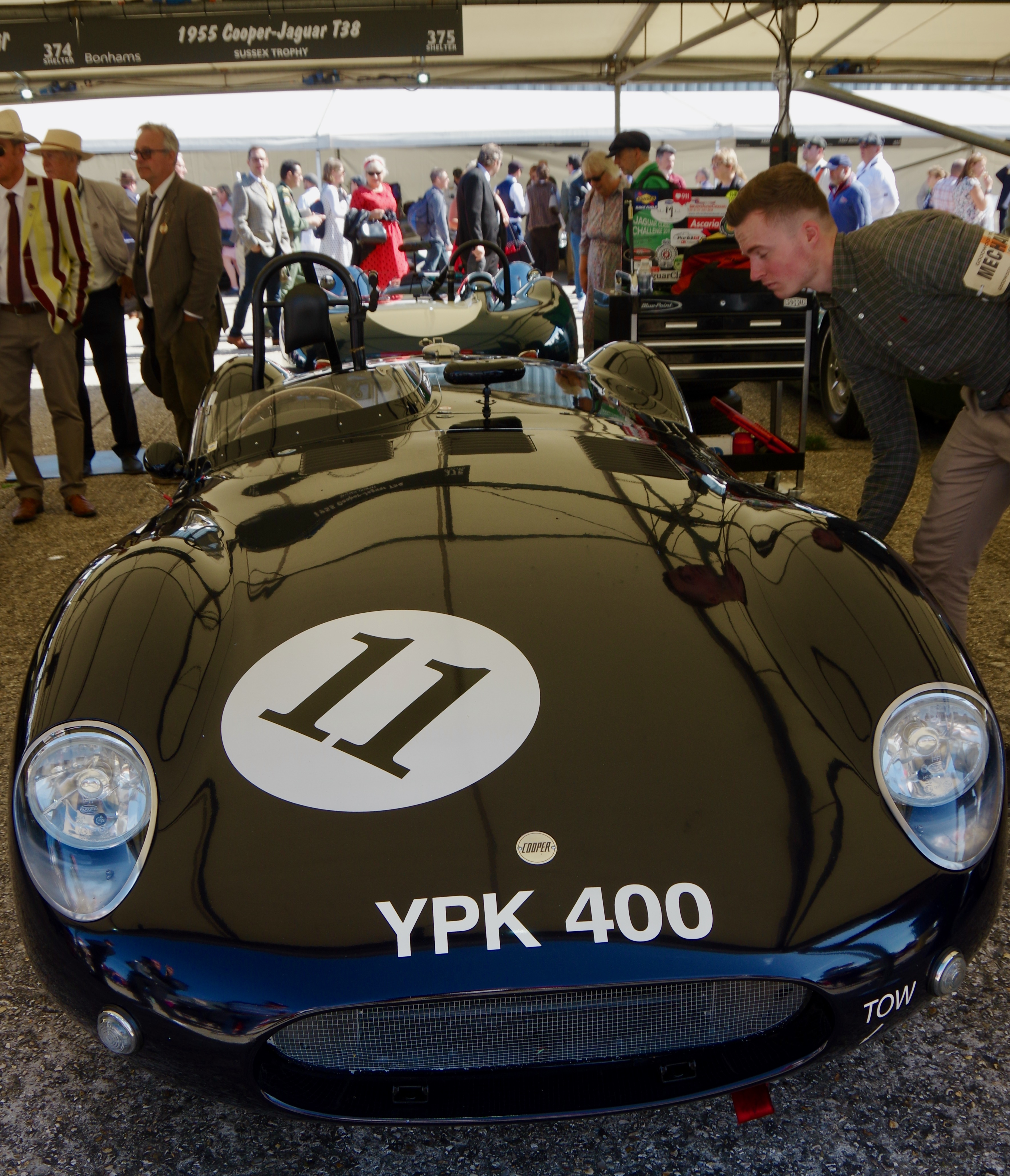
– and furthered the company's growing reputation by appearing in Grand Prix races, which at the time were run to F2 regulations. Until the company began building rear-engined sports cars
A sports car is a car designed with an emphasis on dynamic performance, such as handling, acceleration, top speed, the thrill of driving and racing capability. Sports cars originated in Europe in the early 1900s and are currently produced by ...
in 1955, they really had not become aware of the benefits of having the engine behind the driver. Based on the 500-cc cars and powered by a modified Coventry Climax
Coventry Climax was a British forklift truck, fire pump, racing, and other specialty engine manufacturer.
History
Pre WW1
The company was started in 1903 as Lee Stroyer, but two years later, following the departure of Stroyer, it was reloca ...
fire-pump engine, these cars were called "Bobtails". With the centre of gravity closer to the middle of the car, they found it was less liable to spins and much more effective at putting the power down to the road, so they decided to build a single-seater version and began entering it in Formula 2 races.
Rear-engined revolution
Jack Brabham
Sir John Arthur Brabham (2 April 1926 – 19 May 2014) was an Australian racing driver who was Formula One World Champion in , , and . He was a founder of the Brabham racing team and race car constructor that bore his name.
Brabham was a R ...
raised some eyebrows when he took sixth place at the 1957 Monaco Grand Prix
The 1957 Monaco Grand Prix was a Formula One motor race held on 19 May 1957 at Monaco. It was race 2 of 8 in the 1957 World Championship of Drivers.
Race report
Despite a hesitant start, Moss led away on the first lap from Collins, Fangio, ...
in a rear-engined Formula 1 Cooper. When Stirling Moss won the 1958 Argentine Grand Prix in Rob Walker's privately entered Cooper and Maurice Trintignant
Maurice Bienvenu Jean Paul Trintignant (30 October 1917 – 13 February 2005) was a motor racing driver and vintner from France. He competed in the Formula One World Championship for fourteen years, between 1950 and 1964, one of the longest care ...
duplicated the feat in the next race at Monaco, the racing world was stunned and a rear-engined revolution had begun. The next year, , Brabham and the Cooper works team became the first to win the Formula One World Championship in a rear-engined car. Both team and driver repeated the feat in , and every World Champion since has been sitting in front of the engine.
The little-known designer behind the car was Owen Maddock, who was employed by Cooper Car Company. Maddock was known as 'The Beard' by his workmates, and 'Whiskers' to Charles Cooper. Maddock was a familiar figure in the drivers' paddock of the 1950s in open-neck shirt and woolly jumper and a prime force behind the rise of British racing cars to their dominant position in the 1960s.
Describing how the revolutionary rear-engined Cooper chassis came to be, Maddock explained, "I'd done various schemes for the new car which I'd shown to Charlie Cooper. He kept saying 'Nah, Whiskers, that's not it, try again.' Finally, I got so fed up I sketched a frame in which every tube was bent, meant just as a joke. I showed it to Charlie and to my astonishment he grabbed it and said: 'That's it!' "
Maddock later pioneered one of the first designs for a honeycomb monocoque stressed skin composite chassis, and helped develop Cooper's C5S racing gearbox.
Brabham took one of the championship-winning Cooper T53 "Lowlines" to Indianapolis Motor Speedway for a test in 1960, then entered the famous 500-mile race in a larger, longer, and offset car based on the 1960 F1 design, the unique Type T54. Arriving at the Speedway 5 May 1961, the "funny" little car from Europe was mocked by the other teams, but it ran as high as third and finished ninth. It took a few years, but the Indianapolis establishment gradually realized the writing was on the wall and the days of their front-engined roadsters were numbered. Beginning with Jim Clark, who drove a rear-engined Lotus in 1965, every winner of the Indianapolis 500 since has had the engine in the back. The revolution begun by the little chain-driven Cooper 500 was complete.
Once every Formula car manufacturer began building mid-engined racers, the practicality and intelligent construction of Cooper's single-seaters was overtaken by more sophisticated technology from Lola
Lola may refer to:
Places
* Lolá, a or subdistrict of Panama
* Lola Township, Cherokee County, Kansas, United States
* Lola Prefecture, Guinea
* Lola, Guinea, a town in Lola Prefecture
* Lola Island, in the Solomon Islands
People
* Lola ...
, Lotus, BRM, and Ferrari. The Cooper team's decline was accelerated when John Cooper was seriously injured in a road accident in 1963 driving a twin-engined Mini, and Charles Cooper died in 1964.
Final years
 After the death of his father, John Cooper sold the Cooper Formula One team to the Chipstead Motor Group in April 1965. The same year, the Formula One team moved from Surbiton to a modern factory unit at Canada Road, Oyster Lane in Byfleet, just along the road from Brabham in New Haw and close to
After the death of his father, John Cooper sold the Cooper Formula One team to the Chipstead Motor Group in April 1965. The same year, the Formula One team moved from Surbiton to a modern factory unit at Canada Road, Oyster Lane in Byfleet, just along the road from Brabham in New Haw and close to Alan Mann Racing
Alan Mann Racing was a British motor racing team organised by Alan Mann (22 August 1936 – 21 March 2012), who was a part-time racing driver and team manager. The team ran a substantial part of the Ford works racing effort in Europe from 1964 t ...
. Cooper's 1965 season petered out and at the end of the year, number one driver Bruce McLaren
Bruce Leslie McLaren (30 August 1937 – 2 June 1970) was a New Zealand racing car designer, driver, engineer, and inventor.
His name lives on in the McLaren team which has been one of the most successful in Formula One championship history, ...
left to build his own F1 car for the new for 1966 3-litre formula. Cooper's new owners held the Maserati concession for the UK and arrangements were made for Cooper to build a new 3-litre Cooper-Maserati car which would be available for sale as well being raced by the works team. The Maserati engine was an updated and enlarged version of the 2.5-litre V-12 which had made sporadic appearances in the works 250Fs in 1957. It was an old design, heavy and thirsty and the new Cooper T81
The Cooper T81 is a Formula One car produced by the Cooper Car Company for the 1966 Formula One season. It represented something of a comeback for Cooper's fortunes, winning two races and enabling Cooper to finish third in the Constructors' Ch ...
chassis built to take it was necessarily on the large side, in spite of which the bulky V-12 always looked as though it was spilling out of the back. Three cars were sold to private owners, one each to Rob Walker for Jo Siffert
Joseph Siffert (; 7 July 1936 – 24 October 1971) was a Swiss racing driver.
Affectionately known as "Seppi" to his family and friends, Siffert was born in Fribourg, Switzerland, the son of a dairy owner. He initially made his name in racing ...
to drive, Jo Bonnier
Joakim Bonnier (31 January 1930 – 11 June 1972) was a Swedish sportscar racing and Formula One driver who raced for various teams. He was the first Swede to both enter and win a Formula One Grand Prix.
Early life
Jo Bonnier was born in Stockh ...
's Anglo Swiss Racing Team, and French privateer Guy Ligier
Guy Camille Ligier (12 July 1930 – 23 August 2015) was a French racing driver and team owner. He maintained many varied and successful careers over the course of his life, including rugby player, butcher, racing driver and Formula One team owner ...
. None of these cars achieved much success.
Jochen Rindt
Jochen is a given name. Notable people with the name include:
*Jochen Asche, East German luger, competed during the 1960s
*Jochen Böhler (born 1969), German historian, specializing in the history of World War II
*Jochen Babock (born 1953), East G ...
was entering the second year of his three-year contract, but with the departure of McLaren, Cooper had a seat to fill in the second car and with the team's recent lack of success, understandably, a large queue of potential drivers was not forming at Canada Road. In the circumstances, Cooper were fortunate to acquire the services of Honda's Richie Ginther, who was temporarily unemployed due to the Japanese company's late development of their new 3-litre car. After a couple of races, Ginther was recalled by Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a producti ...
to commence testing of their new car and the American was no doubt more than somewhat chagrined to discover that it was even bigger and heavier than the Cooper. After making a one-off arrangement with Chris Amon
Christopher Arthur Amon (20 July 1943 – 3 August 2016) was a New Zealand motor racing driver. He was active in Formula One racing in the 1960s and 1970s, and is widely regarded as one of the best F1 drivers never to win a championship Grand ...
(unemployed due to the McLaren team's engine problems) to drive in the French Grand Prix
The French Grand Prix (french: Grand Prix de France), formerly known as the Grand Prix de l'ACF (Automobile Club de France), is an auto race held as part of the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile's annual Formula One World Championsh ...
, Cooper had an enormous stroke of luck when John Surtees
John Surtees, (11 February 1934 – 10 March 2017) was a British Grand Prix motorcycle road racer and Formula One driver. On his way to become a seven-time Grand Prix motorcycle World Champion, he won his first title in 1956, and followed with ...
became available after falling out with Ferrari. Once conflicting fuel contract issues were resolved (Surtees was with Shell, Cooper with BP), Surtees joined the team. Cooper honoured its commitment to Amon, so three cars were run in the French GP. Subsequently, the team reverted to two entries for Surtees and Rindt and with the former Ferrari driver's development skills and a switch to Firestone tyres, the car was improved to the point that Surtees was able to win the final race of the year in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
.
Surtees left to join Honda for 1967 and Pedro Rodríguez joined Rindt in the team and immediately won the opening race of 1967 in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
in an unlikely Cooper one-two. This was a fortuitous win for Rodríguez, as he was being outpaced by Rhodesian John Love in his three-year-old ex McLaren Tasman Cooper powered by a 2.7-litre Coventry Climax
Coventry Climax was a British forklift truck, fire pump, racing, and other specialty engine manufacturer.
History
Pre WW1
The company was started in 1903 as Lee Stroyer, but two years later, following the departure of Stroyer, it was reloca ...
FPF. Unfortunately, Love had to make a late pit stop for fuel and could only finish second. This was to be Cooper's last Grand Prix victory. The rest of the 1967 season had the team's fortunes steadily decline and the midseason appearance of the lighter and slimmer T86 chassis failed to improve things. Rindt, impatiently seeing out his Cooper contract, deliberately blew up his increasingly antiquated Maserati engine in the US Grand Prix
The United States Grand Prix is a motor racing event that has been held on and off since 1908, when it was known as the American Grand Prize. The Grand Prix later became part of the Formula One World Championship. , the Grand Prix has been held ...
and was fired before the season finale in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
.
For 1968, Cooper would have liked to have joined the queue for the Cosworth-Ford DFV, but felt that its connections to British Leyland
British Leyland was an automotive engineering and manufacturing conglomerate formed in the United Kingdom in 1968 as British Leyland Motor Corporation Ltd (BLMC), following the merger of Leyland Motors and British Motor Holdings. It was partl ...
with the Mini-Coopers made this inadvisable. Instead, a deal was done with BRM for the use of its 3-litre V-12, originally conceived as a sports car unit, but which BRM themselves would be using in 1968. A slightly modified version of the T86 was built for the new engine, dubbed T86B and Italian ex-Ferrari driver Ludovico Scarfiotti
Ludovico Scarfiotti (18 October 1933 – 8 June 1968) was a Formula One and sports car driver from Italy. Just prior to entering Formula One, he won the 1963 24 Hours of Le Mans for Ferrari. He later participated in 12 World Championship F ...
and young Englishman Brian Redman
Brian Herman Thomas Redman (born 9 March 1937 in Burnley, Lancashire and educated at Rossall School, Fleetwood, Lancashire), is a retired British racing driver.
Racing for Carl Haas and Jim Hall's Chaparral Cars, Brian Redman won the 1974, '75 ...
were employed to drive it. The cars managed three-four finishes in the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
and Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Lig ...
Grands Prix, largely thanks to the unreliability of the competition, but then Scarfiotti was killed driving a Porsche in the Rossfeld hill climb and Redman had a big accident in the Belgian Grand Prix
The Belgian Grand Prix (French: ''Grand Prix de Belgique''; Dutch: ''Grote Prijs van België''; German: ''Großer Preis von Belgien'') is a motor racing event which forms part of the Formula One World Championship.
The first national race of ...
which put him out of action for several months. Cooper continued the season with a motley collection of drivers, none of whom could make anything of the outclassed T86B. During the season, Cooper built a modified chassis, the T86C, intended to take an Alfa Romeo
Alfa Romeo Automobiles S.p.A. () is an Italian luxury car manufacturer and a subsidiary of Stellantis. The company was founded on 24 June 1910, in Milan, Italy. "Alfa" is an acronym of its founding name, "Anonima Lombarda Fabbrica Automobili." "A ...
3-litre V-8 but the project was stillborn.
The beginning of the end for the Cooper Car Company was in 1969, as it tried, and failed, to find sponsorship for a new Cosworth DFV
The DFV is an internal combustion engine that was originally produced by Cosworth for Formula One motor racing. The name is an abbreviation of ''Double Four Valve'', the engine being a V8 development of the earlier four-cylinder FVA, which had fo ...
-powered car and there were many redundancies. Frank Boyles was the last to leave, since he was in charge of building customer cars and it had been hoped that some more F2 cars would be sold. Frank went on to design and build a Formula Ford car called the Oscar and also a series of Oval Circuit cars known as Fireballs. Driving the rear-engine version of this car, Frank won more than 200 races during a period up until 1975 in a car he had designed and raced himself. This record is believed to have never been beaten.
In all, Coopers participated in 129 Formula One World Championship events in nine years, winning 16 races.
Besides Formula One cars, Cooper offered a series of Formula Junior
Formula Junior is an open wheel formula racing class first adopted in October 1958 by the CSI (''International Sporting Commission'', the part of the FIA that then regulated motorsports). The class was intended to provide an entry level class ...
cars. These were the T52, T56, T59, and T67 models. Ken Tyrrell
Robert Kenneth Tyrrell (3 May 1924 – 25 August 2001) was a British Formula Two racing driver and the founder of the Tyrrell Formula One constructor.Setright, L. J. K. "Tyrrell: A Shrewd Talent-spotter", in Northey, Tom, ed. ''World of Autom ...
ran a very successful team with John Love and Tony Maggs
Anthony Francis O'Connell Maggs (9 February 1937 in Pretoria, South Africa – 2 June 2009) was a racing driver from South Africa. He participated in 27 Formula One World Championship Grands Prix, debuting on 15 July 1961. He achieved three pod ...
as his drivers. Following the demise of Formula Junior, Ken Tyrrell tested Jackie Stewart
Sir John Young Stewart (born 11 June 1939), known as Jackie Stewart, is a British former Formula One racing driver from Scotland. Nicknamed the "Flying Scot", he competed in Formula One between 1965 and 1973, winning three World Drivers' Cha ...
in a Formula Three
Formula Three, also called Formula 3, abbreviated as F3, is a third-tier class of open-wheel formula racing. The various championships held in Europe, Australia, South America and Asia form an important step for many prospective Formula One dri ...
car, a Cooper T72. This test at the Goodwood Circuit marked the start of partnership which dominated motorsport later on.
John Cooper retired to the Sussex coast, where in 1971, he founded the garage business at Ferring, near Worthing. The garage sold Mini Cooper engine-tuning kits and performance parts.
The garage was sold to Honda in 1986 and the business was moved to East Preston to convert Mini Coopers into race cars.
In October 2009, Mike Cooper, the son of John Cooper, launched Cooper Bikes, the bicycle division of the Cooper Car Company.
Formula One results
Mini legacy
As the company's fortunes in Formula One declined, however, the John Cooper-conceivedMini
The Mini is a small, two-door, four-seat car, developed as ADO15, and produced by the British Motor Corporation (BMC) and its successors, from 1959 through 2000. Minus a brief hiatus, original Minis were built for four decades and sold during ...
– introduced in 1961 as a development of the Alec Issigonis
Sir Alexander Arnold Constantine Issigonis (18 November 1906 – 2 October 1988) was a British-Greek automotive designer. He designed the Mini, launched by the British Motor Corporation in 1959, and voted the second most influential car of t ...
-designed British Motor Corporation Mini
The Mini is a small, two-door, four-seat car, developed as ADO15, and produced by the British Motor Corporation (BMC) and its successors, from 1959 through 2000. Minus a brief hiatus, original Minis were built for four decades and sold during ...
with a more powerful engine, new brakes, and a distinctive livery – continued to dominate in saloon car
A sedan or saloon (British English) is a passenger car in a three-box configuration with separate compartments for an engine, passengers, and cargo.
The first recorded use of the word "sedan" in reference to an automobile body occurred in 19 ...
and rally races throughout the 1960s, winning many championships and the 1964, 1965, and 1967 Monte Carlo rallies.
Several different Cooper-marked versions of the Mini and various Cooper conversion kits have been, and continue to be, marketed by various companies. The current BMW MINI
Mini (stylised as MINI) is a British automotive marque founded in 1969, owned by German automotive company BMW since 2000, and used by them for a range of small cars assembled in the United Kingdom, Austria and the Netherlands. The word Mi ...
, in production since 2001, has Cooper and Cooper S models and a number of John Cooper Works
John Cooper Works (JCW) is an English car brand now owned by BMW and used on its Mini vehicles. It was founded in 2002 by Michael Cooper, son of John Cooper, the racing car maker and tuner responsible for the original Mini Cooper.
In 2007, Ge ...
tuner packages.
Cooper garage
On 1 April 1968, John Cooper leased the building, 243 Ewell Road,TNF Tourist Guide to Former Premises to the Metropolitan Police and the local Traffic Division (V Victor) moved in. They would stay there for the next 25 years and 'TDV' would become one of the busier police garages. In August 1968, they were supplied with two Mini Coopers, index numbers PYT767F and PYT768F. The centre boss of the steering wheel was replaced by a speaker and microphone and a PTT transmitter switch, was added to the steering column. The vehicles were trialled for a number of months, but no orders were placed for other garages. The police subsequently moved out, and the building became a Porsche dealership.
References
;Footnotes ;SourcesJohn Cooper Works
* John Cooper (1977). ''The Grand Prix Carpetbaggers: The Autobiography of John Cooper''. Doubleday. * ''Cooper Cars'', by Doug Nye, 1983, Osprey Publishing, 2003, Motorbooks International * Wright, Terry; ''Power Without Glory: Racing the Big-twin Cooper'', Loose Fillings Sydney 2015. See also www.loosefillings.com
External links
{{Authority control Formula One constructors Formula One entrants 1947 establishments in England 1969 disestablishments in England Car manufacturers of the United Kingdom British auto racing teams British racecar constructors Formula Two constructors Auto racing teams established in 1947 Auto racing teams disestablished in 1969 Formula One World Constructors' Champions British Touring Car Championship teams 24 Hours of Le Mans teams