Clustal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Clustal is a 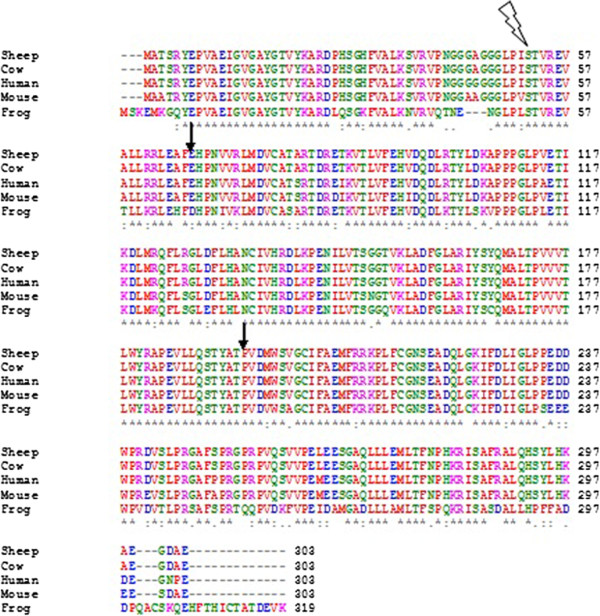
clustalv nameoffile.seq or clustalv /infile=nameoffile.seq
and the program will determine what type of sequence it is analyzing. When the program is completed, the output of the multiple sequence alignment as well as the dendrogram go to files with .aln and .dnd extensions respectively. The command line interface uses the default parameters, and doesn't allow for other options.
 ClustalW, like other Clustal versions, is used for aligning multiple nucleotide or protein sequences efficiently. It uses progressive alignment methods, which prioritize sequences for alignment based on similarity until a global alignment is returned. ClustalW is a matrix-based algorithm, whereas tools like
ClustalW, like other Clustal versions, is used for aligning multiple nucleotide or protein sequences efficiently. It uses progressive alignment methods, which prioritize sequences for alignment based on similarity until a global alignment is returned. ClustalW is a matrix-based algorithm, whereas tools like
LALIGN
should be used.
-clustering=UPGMA
As an approximate example, while a 10,000 sequences input would take over an hour for neighbor-joining, UPGMA would complete in less than a minute.
ClustalW2 also added an iterative alignment accuracy. This option does not increase efficiency, but it does offer the ability to increase alignment accuracy. This can be especially useful for small datasets.
The following flags activate iterative alignment:
-Iteration=Alignment
-Iteration=Tree
-numiters
The first option refines the final alignment. The second option incorporates the scheme in the progressive alignment step. The third specifies the number of iteration cycles, where the default value is set to 3.
 ClustalΩ (alternatively written as Clustal O and Clustal Omega) is a fast and
ClustalΩ (alternatively written as Clustal O and Clustal Omega) is a fast and
 Clustal Omega has five main steps in order to generate the
Clustal Omega has five main steps in order to generate the
Clustal2
is the packaged release of both the command-line ClustalW and graphical Clustal X. Neither are new tools, but are updated and improved versions of the previous implementations seen above. Both downloads come pre-compiled for many operating systems like Linux, Mac OS X and Windows (both XP and Vista). This release was designed to make the website more organized and user friendly, as well as updating the source codes to their most recent versions. Clustal2 is version 2 of both ClustalW and ClustalX, which is where it gets its name. Past versions can still be found on the website, however, every pre-compilation is now up to date.
Clustal Homepage
(free Unix/Linux, Mac, and Windows download)
Clustal Omega mirror at the EBI
{{Bioinformatics Phylogenetics software
computer program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to Execution (computing), execute. It is one component of software, which also includes software documentation, documentation and other intangibl ...
used for multiple sequence alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis an ...
in bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, ...
. The software and its algorithms have gone through several iterations, with ClustalΩ (Omega) being the latest version . It is available as standalone software, via a web interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
, and through a server hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) is an intergovernmental organization (IGO) which, as part of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) family, focuses on research and services in bioinformatics. It is located on the Wel ...
.
Clustal has been an important bioinformatic software, with two of its academic publications amongst the top 100 papers cited of all time, according to Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
in 2014.

History
Version history
* Clustal: The original software for multiple sequence alignments, created by Des Higgins in 1988, was based on deriving a guide tree from pairwise sequences ofamino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
or nucleotides
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
.
* ClustalV: The second generation of Clustal, released in 1992. It introduced the ability to create new alignments from existing alignments in a process known as phylogenetic tree reconstruction. ClustalV also added the option to create trees
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only p ...
using the neighbor joining
In bioinformatics, neighbor joining is a bottom-up (agglomerative) clustering method for the creation of phylogenetic trees, created by Naruya Saitou and Masatoshi Nei in 1987. Usually based on DNA or protein sequence data, the algorithm require ...
method.
*ClustalW: The third generation, released in 1994. It improved upon the progressive alignment algorithm, including sequence weighting
The process of frequency weighting involves emphasizing the contribution of particular aspects of a phenomenon (or of a set of data) over others to an outcome or result; thereby highlighting those aspects in comparison to others in the analy ...
options based on similarity and divergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the rate that the vector field alters the volume in an infinitesimal neighborhood of each point. (In 2D this "volume" refers to ...
. Additionally, it added the option to run Clustal in batch mode
Batch may refer to:
Food and drink
* Batch (alcohol), an alcoholic fruit beverage
* Batch loaf, a type of bread popular in Ireland
* A dialect term for a bread roll used in North Warwickshire, Nuneaton and Coventry, as well as on the Wirral, ...
from the command line
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user ...
.
*ClustalX: Released in 1997, this was the first version to have a graphical user interface.
*Clustal2: This updated both ClustalW and ClustalX with higher accuracy and efficiency in 2007.
*ClustalΩ (Omega): The current version, released in 2011.
Name origin
The guide tree in the initial versions of Clustal was constructed via aUPGMA
UPGMA (unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean) is a simple agglomerative (bottom-up) hierarchical clustering method. It also has a weighted variant, WPGMA, and they are generally attributed to Sokal and Michener.
Note that the unwei ...
cluster analysis of the pairwise alignments, hence the name CLUSTAL.Des Higgins, presentation at the SMBE 2012 conference in Dublin.cf. The first four versions of Clustal were numbered using Arabic numerals (1 to 4), whereas the fifth version uses the Roman numeral V.cf. The next two versions proceed alphabetically using the Latin alphabet, with W standing for weighted and X for X Window
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.
X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been a ...
to represent the changes introduced.cf. The name Omega was chosen to mark a change from the previous iterations.
Function
Clustal aligns sequences using aheuristic
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', '' mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless ...
that progressively builds a multiple sequence alignment from a set of pairwise alignments. This method works by analyzing the sequences as a whole and using the UPGMA/neighbor-joining method to generate a distance matrix
In mathematics, computer science and especially graph theory, a distance matrix is a square matrix (two-dimensional array) containing the distances, taken pairwise, between the elements of a set. Depending upon the application involved, the ''dist ...
. A guide tree is calculated from the scores of the sequences in the matrix, then subsequently used to build the multiple sequence alignment by progressively aligning the sequences in order of similarity.
Clustal creates multiple sequence alignments through three main steps:
#Complete a pairwise alignment using the progressive alignment method.
#Create a guide tree (or use a user-defined tree).
#Use the guide tree to carry out a multiple alignment.
These steps are carried out automatically by the function "Do Complete Alignment". Other options are "Do Alignment from guide tree and phylogeny" and "Produce guide tree only".
Input/Output
This program accepts a wide range of input formats, including NBRF/ PIR,FASTA
FASTA is a DNA and protein sequence alignment software package first described by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985. Its legacy is the FASTA format which is now ubiquitous in bioinformatics.
History
The original FASTA program ...
, EMBL/Swiss-Prot
UniProt is a freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from ...
, Clustal, GCC/MSF, GCG9 RSF, and GDE.
The output format can be one or many of the following: Clustal, NBRF/ PIR, GCG/MSF, PHYLIP, GDE, or NEXUS.
The same symbols are shown for both DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
/RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
alignments and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
alignments, so while * (asterisk) symbols are useful for both, the other consensus symbols should be ignored for DNA/RNA alignments.
Settings
The gap opening penalty and gap extension penalty parameters can be adjusted by the user.Clustal and ClustalV
Brief summary
The original Clustal software was developed in 1988 as a computational method for generating multiple sequence alignments onpersonal computers
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
. ClustalV was released 4 years later and greatly improved upon the original software, adding and altering few key features. It was a full re-write, written in C instead of Fortran.
Algorithm
Both versions use the same fast approximate algorithm to calculate the similarity scores between sequences, which in turn produces the pairwise alignments. The algorithm works by calculating the similarity scores as the number of k-tuple matches between two sequences, accounting for a set penalty for gaps. The more similar the sequences, the higher the score. Once the sequences are scored, adendrogram
A dendrogram is a diagram representing a Tree (graph theory), tree graph. This diagrammatic representation is frequently used in different contexts:
* in hierarchical clustering, it illustrates the arrangement of the clusters produced by ...
is generated through the UPGMA to generate an ordering of the multiple sequence alignment. Sequences are aligned in descending order by set order. This algorithm allows for very large data sets and is fast. However, the speed is dependent on the range of k-tuple matches selected for the particular sequence type.
Notable ClustalV improvements
Some of the most notable additions in ClustalV are profile alignments, and full command line interface options. The ability to use profile alignments allows the user to align two or more previous alignments or sequences to a new alignment and move misaligned sequences (low scored) further down the alignment order. This gives the user the option to gradually and methodically create multiple sequence alignments with more control than the basic option. The option to run from the command line expedites the multiple sequence alignment process. Sequences can be run with a simple command,ClustalW
Brief summary
T-Coffee
T-Coffee (Tree-based Consistency Objective Function for Alignment Evaluation) is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment. It can al ...
and Dialign are consistency-based. ClustalW is efficient, with competitive in comparison with similar software. This program requires three or more sequences in order to calculate a global alignment. For binary sequence alignment, other tools such as EMBOSS
EMBOSS is a free c software analysis package developed for the needs of the molecular biology and bioinformatics user community. The software automatically copes with data in a variety of formats and even allows transparent retrieval of sequence ...
oLALIGN
should be used.

Algorithm
ClustalW uses progressive alignment algorithms. In these, sequences are aligned in most-to-least alignment score order. This heuristic is necessary to restrict the time- and memory-complexity required to find the globally optimal solution. First, the algorithm computes a pairwise distance matrix between all pairs of sequences ( pairwise sequence alignment). Next, a neighbor-joining method uses midpoint rooting to create an overall guide tree. A diagram of this method is illustrated to the right. Finally, the guide tree is used as an approximate template to generate a global alignment.Time complexity
ClustalW has a time complexity of because of its use of the neighbor-joining method. ClustalW2 added an option to use UPGMA instead which is faster for large input sizes. The command line flag in order to use it instead of neighbor-joining is:Accuracy and Results
The algorithm ClustalW uses is nearly optimal. It is most effective for datasets with a large degree of variance. On such datasets, the process of generating a guide tree is less sensitive to noise. ClustalW was one of the first multiple sequence alignment algorithms to combine pairwise alignment and global alignment to increase speed, but this decision reduces result accuracy. When multiple sequence alignment algorithms were compared in 2014, ClustalW was one of the fastest that was able to produce results at the desired level of accuracy. However, it was not as accurate as consistency-based competitors such as T-Coffee. Out of MAFFT, T-Coffee, and Clustal Omega, ClustalW has the lowest accuracy for full-length sequences, but its accuracy is still considered acceptable. Additionally, ClustalW was the most memory-efficient algorithm of those studied. Continued updates to the software have made ClustalW2 more accurate while maintaining this speed.Clustal Omega
Brief summary
scalable
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system.
In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that ...
program written in C and C++ used for multiple sequence alignment. It uses seeded guide trees and a new HMM engine that focuses on two profiles to generate these alignments. The program requires three or more sequences in order to calculate the multiple sequence alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis an ...
. Clustal Omega is consistency-based and is widely viewed as one of the fastest online implementations of all multiple sequence alignment tools and still ranks high in accuracy, among both consistency-based and matrix-based algorithms.
Algorithm
 Clustal Omega has five main steps in order to generate the
Clustal Omega has five main steps in order to generate the multiple sequence alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis an ...
.
# A pairwise alignment is produced using the k-tuple method.This is a heuristic method that isn't guaranteed to find an optimal solution, but is more efficient than using dynamic programming.
# Sequences are clustered using the modified mBed method. The mBed method calculates pairwise distance using sequence embedding.
# The k-means clustering method is applied.
# A guide tree is constructed using the UPGMA method. In the figure to the right, this is shown as multiple guide tree steps leading into one final guide tree construction because of the agglomerative nature of UPGMA. At each step (diamonds in the flowchart), the nearest two clusters are combined. This is repeated until a final, global tree can be assessed.
# The final multiple sequence alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis an ...
is produced with the HHAlign package from the HH-Suite using two profile HMM's. A profile HMM is a linear state machine consisting of a series of nodes, each of which corresponds roughly to a position (column) in the alignment from which it was built.
Time complexity
The time complexity of exactly computing an optimal alignment of sequences of length is which is prohibitive for even a small number of sequences. To manage this, Clustal Omega uses a modified version of mBed which has a complexity of , and produces guide trees that are as accurate as those from conventional methods. The speed and accuracy of the guide trees in Clustal Omega is attributed to the implementation of a modified mBed algorithm. It also reduces the computational time and memory requirements to complete alignments on large datasets.Accuracy and results
The accuracy of Clustal Omega on a small number of sequences is, on average, very similar to what are considered high quality sequence aligners. On extremely large datasets with hundreds of thousands of input sequences, Clustal Omega outperforms all other algorithms in time, memory, and accuracy of results. It is capable of running 100,000+ sequences on one processor in a few hours. Clustal Omega uses the HHAlign package of the HH-Suite, which aligns two profile Hidden Markov Models instead of a profile-profile comparison. This improves the quality of the sensitivity and alignment significantly. This, combined with the mBed method, gives Clustal Omega its advantage over other sequence aligners. On data sets with non-conserved terminal bases, Clustal Omega can be more accurate than Probcons orT-Coffee
T-Coffee (Tree-based Consistency Objective Function for Alignment Evaluation) is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment. It can al ...
, despite the fact that both are consistency-based algorithms. On an efficiency test with programs that produce high accuracy scores, MAFFT
In bioinformatics, MAFFT (multiple alignment using fast Fourier transform) is a program used to create multiple sequence alignments of amino acid or nucleotide sequences. Published in 2002, the first version used an algorithm based on multiple seq ...
was the fastest, closely followed by Clustal Omega. Both were faster than T-Coffee, however MAFFT
In bioinformatics, MAFFT (multiple alignment using fast Fourier transform) is a program used to create multiple sequence alignments of amino acid or nucleotide sequences. Published in 2002, the first version used an algorithm based on multiple seq ...
and Clustal Omega required more memory to run.
Clustal2 (ClustalW/ClustalX)
Clustal2
is the packaged release of both the command-line ClustalW and graphical Clustal X. Neither are new tools, but are updated and improved versions of the previous implementations seen above. Both downloads come pre-compiled for many operating systems like Linux, Mac OS X and Windows (both XP and Vista). This release was designed to make the website more organized and user friendly, as well as updating the source codes to their most recent versions. Clustal2 is version 2 of both ClustalW and ClustalX, which is where it gets its name. Past versions can still be found on the website, however, every pre-compilation is now up to date.
See also
*Sequence alignment software
This list of sequence alignment software is a compilation of software tools and web portals used in pairwise sequence alignment and multiple sequence alignment. See structural alignment software for structural alignment of proteins.
Database searc ...
* Sequence mining
Sequential pattern mining is a topic of data mining concerned with finding statistically relevant patterns between data examples where the values are delivered in a sequence. It is usually presumed that the values are discrete, and thus time serie ...
* T-Coffee
T-Coffee (Tree-based Consistency Objective Function for Alignment Evaluation) is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment. It can al ...
* Align-m
* DIALIGN-T
DIALIGN-TX is a multiple sequence alignment program written by Amarendran R. Subramanian and is substantial improvement of DIALIGN-T by combining greedy and progressive alignment strategies in a new algorithm.
The original DIALIGN-T is a reimpl ...
* DIALIGN-TX
DIALIGN-TX is a multiple sequence alignment program written by Amarendran R. Subramanian and is substantial improvement of DIALIGN-T by combining greedy and progressive alignment strategies in a new algorithm.
The original DIALIGN-T is a reimpl ...
* JAligner
* MAFFT
In bioinformatics, MAFFT (multiple alignment using fast Fourier transform) is a program used to create multiple sequence alignments of amino acid or nucleotide sequences. Published in 2002, the first version used an algorithm based on multiple seq ...
* MAVID
* MUSCLE
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
* ProbCons
References
External links
Clustal Homepage
(free Unix/Linux, Mac, and Windows download)
Clustal Omega mirror at the EBI
{{Bioinformatics Phylogenetics software