Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of
pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
where one or more
babies
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
exits the internal environment of the
mother
]
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of ges ...
via
vaginal delivery or
caesarean section.
In 2019, there were about 140.11 million
birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
s globally. In the
developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
most are
home birth
A home birth is a birth that takes place in a residence rather than in a hospital or a birthing center. They may be attended by a midwife, or lay attendant with experience in managing home births. Home birth was, until the advent of modern medic ...
s.
The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery.
It involves four
stages of labour
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globall ...
: the
shortening
Shortening is any fat that is a solid at room temperature and used to make crumbly pastry and other food products. Although butter is solid at room temperature and is frequently used in making pastry, the term ''shortening'' seldom refers to b ...
and
opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the
placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the
postpartum
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within 6 weeks as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium, puerperal pe ...
. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes.
Contractions gradually becomes stronger and closer together.
Since the pain of childbirth correlates with contractions, the pain becomes more frequent and strong as the labour progresses. The second stage ends when the infant is fully expelled. The third stage is the delivery of the placenta.
The fourth stage of labour involves the recovery of the mother,
delayed clamping of the umbilical cord, and monitoring of the neonate.
all major health organizations advise that immediately following a
live birth, regardless of the delivery method, that the infant be placed on the mother's chest (termed
skin-to-skin contact
Kangaroo care also called skin-to-skin contact (SSC), is a technique of newborn care where babies are kept chest-to-chest and skin-to-skin with a parent, typically their mother (occasionally their father).
Kangaroo care, named for the similarity ...
), and to delay neonate procedures for at least one to two hours or until the baby has had its first breastfeeding.
A vaginal delivery is recommended over a cesarean section due to increased risk for complications of a cesarean section and natural benefits of a vaginal delivery in both mother and baby. Various methods may help with pain, such as
relaxation techniques,
opioids, and
spinal blocks.
It is best practice to limit the amount of interventions that occur during labour and delivery such as an elective cesarean section, however in some cases a scheduled cesarean section must be planned for a successful delivery and recovery of the mother. An emergency cesarean section may be recommended if unexpected complications occur or little to no progression through the birthing canal is observed in a vaginal delivery.
Each year, complications from pregnancy and childbirth result in about 500,000
birthing deaths, seven million women have serious long-term problems, and 50 million women giving birth have negative health outcomes following delivery, most of which occur in the
developing world.
Complications in the mother include
obstructed labour
Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is the baby not exiting the pelvis because it is physically block during childbirth although the uterus contracts normally. Complications for the baby include not getting enough oxygen which may ...
,
postpartum bleeding
Postpartum bleeding or postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is often defined as the loss of more than 500 ml or 1,000 ml of blood following childbirth. Some have added the requirement that there also be signs or symptoms of low blood volume fo ...
,
eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is one of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in ...
, and
postpartum infection.
Complications in the baby include
lack of oxygen at birth,
birth trauma, and
prematurity.
Signs and symptoms
The most prominent sign of labour is strong repetitive
uterine contractions. Pain in contractions has been described as feeling similar to very strong
menstrual cramps
Dysmenorrhea, also known as period pain, painful periods or menstrual cramps, is pain during menstruation. Its usual onset occurs around the time that menstruation begins. Symptoms typically last less than three days. The pain is usually in th ...
. Women giving birth are often encouraged to refrain from screaming. However, moaning and grunting may be encouraged to help lessen pain. Crowning may be experienced as an intense stretching and burning.
Back labour is a term for specific pain occurring in the lower back, just above the
tailbone, during childbirth.
[Harms, Rogert W]
Does back labor really happen?
, mayoclinic.com, Retrieved 8 September 2014
Another prominent sign of labour is the
rupture of membranes Rupture of membranes (ROM) or amniorrhexis is a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac. Normally, it occurs spontaneously at full term either during or at the beginning of labor. Rupture of the membranes is known col ...
, commonly known as "water breaking". This is the leaking of fluid from the amniotic sac that surrounds a fetus in the uterus and helps provide cushion and thermoregulation. However, it is common for water to break long before contractions begin and in which case it is not a sign of immediate labour and hospitalization is generally required for monitoring the fetus and prevention of preterm birth.
Psychological
During the later stages of gestation there is an increase in abundance of
oxytocin, a hormone that is known to evoke feelings of contentment, reductions in anxiety, and feelings of calmness and security around the mate.
Oxytocin is further released during labour when the fetus stimulates the cervix and vagina, and it is believed that it plays a major role in the bonding of a mother to her infant and in the establishment of maternal behavior. The act of
nursing
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ...
a child also causes a release of oxytocin to help the baby get milk more easily from the nipple.
Vaginal birth

Station refers to the relationship of the fetal presenting part to the level of the
ischial spine
The ischial spine is part of the posterior border of the body of the ischium bone of the pelvis. It is a thin and pointed triangular eminence, more or less elongated in different subjects.
Structure
The pudendal nerve travels close to the ischia ...
s. When the presenting part is at the ischial spines the station is 0 (synonymous with engagement). If the presenting fetal part is above the spines, the distance is measured and described as minus stations, which range from −1 to −4
cm. If the presenting part is below the ischial spines, the distance is stated as plus stations ( +1 to +4 cm). At +3 and +4 the presenting part is at the perineum and can be seen.
The fetal head may temporarily change shape (becoming more elongated or cone shaped) as it moves through the birth canal. This change in the shape of the fetal head is called ''molding'' and is much more prominent in women having their first vaginal delivery.
Cervical ripening is the physical and chemical changes in the cervix to prepare it for the stretching that will take place as the fetus moves out of the uterus and into the birth canal. A scoring system called a
Bishop score can be used to judge the degree of cervical ripening in order to predict the timing of labour and delivery of the infant or for women at risk for preterm labour. It is also used to judge when a woman will respond to
induction of labour for a postdate pregnancy or other medical reasons. There are several methods of inducing cervical ripening which will allow the uterine contractions to effectively dilate the cervix.
Vaginal delivery involves four stages of labour: the
shortening
Shortening is any fat that is a solid at room temperature and used to make crumbly pastry and other food products. Although butter is solid at room temperature and is frequently used in making pastry, the term ''shortening'' seldom refers to b ...
and
opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the
placenta during the third, and the 4th stage of recovery which lasts until two hours after the delivery. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts around half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes.
The contractions (and pain) gradually becomes stronger and closer together.
The second stage ends when the infant is fully expelled. In the third stage, the delivery of the placenta.
The fourth stage of labour involves recovery, the uterus beginning to contract to pre-pregnancy state,
delayed clamping of the umbilical cord, and monitoring of the neonatal tone and vitals.
all major health organizations advise that immediately following a
live birth, regardless of the delivery method, that the infant be placed on the mother's chest, termed
skin-to-skin contact
Kangaroo care also called skin-to-skin contact (SSC), is a technique of newborn care where babies are kept chest-to-chest and skin-to-skin with a parent, typically their mother (occasionally their father).
Kangaroo care, named for the similarity ...
, and delaying routine procedures for at least one to two hours or until the baby has had its first breastfeeding.
Onset of labour

Definitions of the onset of labour include:
* Regular uterine contractions at least every six minutes with evidence of change in
cervical dilation Cervical dilation (or cervical dilatation) is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery. Cervical dilation may occur naturally, or may be induced surgically o ...
or
cervical effacement Cervical effacement or cervical ripening refers to a thinning of the cervix.
Background
Cervical effacement is a component of the Bishop score and can be expressed as a percentage.
Prior to effacement, the cervix is like a long bottleneck, usu ...
between consecutive digital examinations.
* Regular contractions occurring less than 10 minutes apart and progressive cervical dilation or cervical effacement.
* At least three painful regular uterine contractions during a 10-minute period, each lasting more than 45 seconds.
Many women are known to experience what has been termed the "nesting instinct". Women report a spurt of energy shortly before going into labour.
Common signs that labour is about to begin may include what is known as ''lightening'', which is the process of the baby moving down from the rib cage with the head of the baby engaging deep in the pelvis. The pregnant woman may then find breathing easier, since her lungs have more room for expansion, but pressure on her bladder may cause more frequent need to void (urinate). Lightening may occur a few weeks or a few hours before labour begins, or even not until labour has begun.
Some women also experience an increase in vaginal discharge several days before labour begins when the "mucus plug", a thick plug of
mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
that blocks the opening to the uterus, is pushed out into the vagina. The mucus plug may become dislodged days before labour begins or not until the start of labour.
While inside the uterus the baby is enclosed in a fluid-filled membrane called the
amniotic sac. Shortly before, at the beginning of, or during labour the
sac ruptures. Once the sac ruptures, termed "the water breaks", the baby is at risk for infection and the mother's medical team will assess the need to
induce labour if it has not started within the time they believe to be safe for the infant.
Stages of labour
First stage
The first stage of labour is divided into latent and active phases, where the latent phase is sometimes included in the definition of labour, and sometimes not.
The latent phase is generally defined as beginning at the point at which the woman perceives regular
uterine contraction
Uterine contractions are muscle contractions of the uterine smooth muscle that occur during the menstrual cycle and labour. Uterine contractions occur throughout the menstrual cycle in the non-pregnant state and throughout gestation.
Throughout ...
s. In contrast,
Braxton Hicks contractions
Braxton Hicks contractions, also known as practice contractions or false labor, are sporadic uterine contractions that may start around six weeks into a pregnancy. However, they are usually felt in the second or third trimester of pregnancy.
...
, which are contractions that may start around 26 weeks gestation and are sometimes called "false labour", are infrequent, irregular, and involve only mild cramping.
Cervical effacement Cervical effacement or cervical ripening refers to a thinning of the cervix.
Background
Cervical effacement is a component of the Bishop score and can be expressed as a percentage.
Prior to effacement, the cervix is like a long bottleneck, usu ...
, which is the thinning and stretching of the
cervix, and
cervical dilation Cervical dilation (or cervical dilatation) is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery. Cervical dilation may occur naturally, or may be induced surgically o ...
occur during the closing weeks of
pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
. Effacement is usually complete or near-complete and dilation is about 5 cm by the end of the latent phase.
The degree of cervical effacement and dilation may be felt during a vaginal examination.
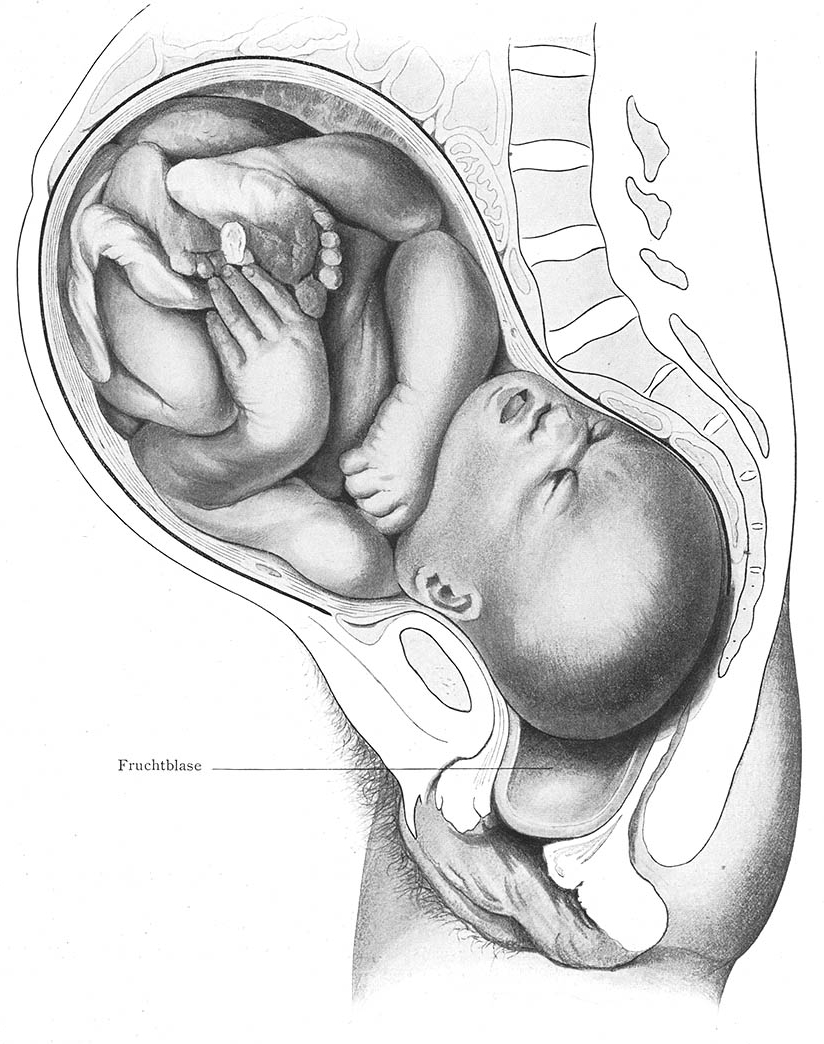
The active phase of labour has geographically differing definitions. The World Health Organization describes the active first stage as "a period of time characterized by regular painful uterine contractions, a substantial degree of cervical effacement and more rapid cervical dilatation from 5 cm until full dilatation for first and subsequent labours. In the US, the definition of active labour was changed from 3 to 4 cm, to 5 cm of
cervical dilation Cervical dilation (or cervical dilatation) is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery. Cervical dilation may occur naturally, or may be induced surgically o ...
for multiparous women, mothers who had given birth previously, and at 6 cm for nulliparous women, those who had not given birth before. This was done in an effort to increase the rates of vaginal delivery.
Health care providers may assess the mother's progress in labour by performing a cervical exam to evaluate the cervical dilation, effacement, and station. These factors form the
Bishop score. The Bishop score can also be used as a means to predict the success of an
induction of labour.
During effacement, the cervix becomes incorporated into the lower segment of the uterus. During a contraction, uterine muscles contract causing shortening of the upper segment and drawing upwards of the lower segment, in a gradual expulsive motion. The presenting fetal part then is permitted to descend. Full dilation is reached when the cervix has widened enough to allow passage of the baby's head, around 10 cm dilation for a term baby.
A standard duration of the latent first stage has not been established and can vary widely from one woman to another. However, the duration of active first stage (from 5 cm until full cervical dilatation) usually does not extend beyond 12 hours in the first labour("primiparae"), and usually does not extend beyond 10 hours in subsequent labours ("multiparae").
Dystocia of labour, also called "dysfunctional labour" or "failure to progress", is difficult labour or abnormally slow progress of labour, involving progressive cervical dilatation or lack of descent of the fetus. Friedman's Curve, developed in 1955, was for many years used to determine labour dystocia. However, more recent medical research suggests that the Friedman curve may not be currently applicable.
Second stage: fetal expulsion

The expulsion stage begins when the cervix is fully dilated, and ends when the baby is born. As pressure on the cervix increases, a sensation of pelvic pressure is experienced, and, with it, an urge to begin pushing. At the beginning of the normal second stage, the head is fully engaged in the pelvis; the widest diameter of the head has passed below the level of the
pelvic inlet
The pelvic inlet or superior aperture of the pelvis is a planar surface which defines the boundary between the pelvic cavity and the abdominal cavity (or, according to some authors, between two parts of the pelvic cavity, called lesser pelvis an ...
. The fetal head then continues descent into the pelvis, below the pubic arch and out through the
vaginal opening. This is assisted by the additional maternal efforts of pushing, or bearing down, similar to
defecation. The appearance of the fetal head at the vaginal opening is termed crowning. At this point, the mother will feel an intense burning or stinging sensation.
When the
amniotic sac has not
ruptured during labour or pushing, the infant can be born with the membranes intact. This is referred to as "delivery en
caul
A caul or cowl ( la, Caput galeatum, literally, "helmeted head") is a piece of membrane that can cover a newborn's head and face. Birth with a caul is rare, occurring in fewer than 1 in 80,000 births. The caul is harmless and is immediately remov ...
".
Complete expulsion of the baby signals the successful completion of the second stage of labour. Some babies, especially preterm infants, are born covered with a waxy or cheese-like white substance called
vernix
Vernix caseosa, also known as vernix or birthing custard, is the waxy white substance found coating the skin of newborn human babies. It is produced by dedicated cells and is thought to have some protective roles during fetal development and for ...
. It is thought to have some protective roles during fetal development and for a few hours after birth.
The second stage varies from one woman to another. In first labours, birth is usually completed within three hours whereas in subsequent
labours, birth is usually completed within two hours. Second-stage labours longer than three hours are associated with declining rates of spontaneous vaginal delivery and increasing rates of infection,
perineal tears, and obstetric haemorrhage, as well as the need for intensive care of the neonate.
Third stage: placenta delivery
The period from just after the fetus is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the ''third stage of labour'' or the ''involution stage''.
Placental expulsion begins as a physiological separation from the wall of the uterus. The average time from delivery of the baby until complete expulsion of the placenta is estimated to be 10–12 minutes dependent on whether active or expectant management is employed. In as many as 3% of all vaginal deliveries, the duration of the third stage is longer than 30 minutes and raises concern for
retained placenta.
Placental expulsion can be managed actively or it can be managed expectantly, allowing the placenta to be expelled without medical assistance. Active management is the administration of a
uterotonic drug within one minute of fetal delivery, controlled traction of the umbilical cord and
fundal massage after delivery of the placenta, followed by performance of uterine massage every 15 minutes for two hours. In a joint statement,
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
, the
International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics
The International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, usually just FIGO ("fee'go") as the acronym of its French name Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique, is a worldwide non-governmental organisation representing ...
and the
International Confederation of Midwives recommend active management of the third stage of labour in all vaginal deliveries to help to prevent
postpartum haemorrhage.
Delaying the clamping of the
umbilical cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologi ...
for at least one minute or until it ceases to pulsate, which may take several minutes, improves outcomes as long as there is the ability to treat
jaundice if it occurs. For many years it was believed that late cord cutting led to a mother's risk of experiencing significant bleeding after giving birth, called
postpartum bleeding
Postpartum bleeding or postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is often defined as the loss of more than 500 ml or 1,000 ml of blood following childbirth. Some have added the requirement that there also be signs or symptoms of low blood volume fo ...
. However a recent review found that delayed cord cutting in healthy full-term infants resulted in early
haemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
concentration and higher birthweight and increased iron reserves up to six months after birth with no change in the rate of postpartum bleeding.
Fourth stage:postpartum
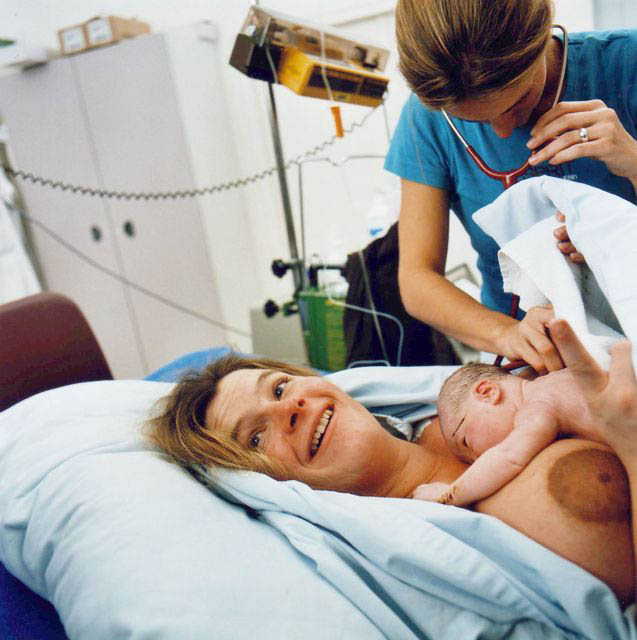
The fourth stage of labour is the period beginning immediately after childbirth, and extends for about six weeks. The terms ''
postpartum
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within 6 weeks as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium, puerperal pe ...
'' and ''postnatal'' are often used for this period.
The woman's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, return to a non-pregnant state and the newborn adjusts to life outside the mother's body. The
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO) describes the postnatal period as the most critical and yet the most neglected phase in the lives of mothers and babies; most deaths occur during the postnatal period.
Following the birth, if the mother had an
episiotomy
Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by a midwife or obstetrician. Episiotomy is usually performed during second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the opening ...
or a tearing of the
perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), includi ...
, it is stitched. This is also an optimal time for uptake of
long-acting reversible contraception
Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARC) are methods of birth control that provide effective contraception for an extended period without requiring user action. They include injections, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and subdermal contraceptiv ...
(LARC), such as the
contraceptive implant
A contraceptive implant is an implantable medical device used for the purpose of birth control. The implant may depend on the timed release of hormones to hinder ovulation or sperm development, the ability of copper to act as a natural spermici ...
or
intrauterine device (IUD), both of which can be inserted immediately after delivery while the woman is still in the delivery room. The mother has regular assessments for uterine contraction and
fundal height
Fundal height, or McDonald's rule, is a measure of the size of the uterus used to assess fetal growth and development during pregnancy. It is measured from the top of the mother's uterus to the top of the mother's pubic symphysis. Fundal height, ...
,
vaginal bleeding, heart rate and blood pressure, and temperature, for the first 24 hours after birth. Some women may experience an uncontrolled episode of shivering or
postpartum chills following the birth. The first passing of urine should be documented within six hours.
Afterpains (pains similar to menstrual cramps), contractions of the uterus to prevent excessive blood flow, continue for several days. Vaginal discharge, termed "lochia", can be expected to continue for several weeks; initially bright red, it gradually becomes pink, changing to brown, and finally to yellow or white.
At one time babies born in hospitals were removed from their mothers shortly after birth and brought to the mother only at feeding times. Mothers were told that their newborn would be safer in the nursery and that the separation would offer the mother more time to rest. As attitudes began to change, some hospitals offered a "rooming in" option wherein after a period of routine hospital procedures and observation, the infant could be allowed to share the mother's room. As of 2020,
rooming in has increasingly become standard practice in maternity wards.
Cardinal movements of birth
Humans are bipedal with an erect stance. The erect posture causes the weight of the abdominal contents to thrust on the
pelvic floor
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. The pelvic diaphragm is a muscular partition formed by the lev ...
, a complex structure which must not only support this weight but allow, in women, three channels to pass through it: the
urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra c ...
, the
vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
and the
rectum. The infant's head and shoulders must go through a specific sequence of maneuvers in order to pass through the ring of the mother's pelvis. Range of motion and ambulation are typically unaffected during labour and it is encouraged that the mother move to help facilitate progression of labour. The vagina is called a 'birth canal' when the baby enters this passage. Six phases of a typical vertex or
cephalic
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals m ...
(head-first presentation) delivery:
# Engagement of the
fetal head
The fetal head, from an obstetrical viewpoint, and in particular its size, is important because an essential feature of labor is the adaptation between the fetal head and the maternal bony pelvis. Only a comparatively small part of the head at ter ...
in the transverse position. The baby's head is facing across the pelvis at one or other of the mother's hips.
# Descent and
flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
of the fetal head. The baby's head moves down the birthing canal and tucks its chin on its chest so that the back or crown of its head leads the way through the birth canal.
# Internal rotation. The fetal head rotates 90 degrees to the
occipito-anterior position so that the baby's face is towards the mother's rectum.
# Delivery by extension. The back of the neck presses against the pubic bone and its chin leaves its chest, extending the neck – as if to look up, and the rest of its head passes out of the birth canal.
# Restitution. The fetal head turns through 45 degrees to restore its normal relationship with the shoulders, which are still at an angle.
# External rotation. The shoulders repeat the corkscrew movements of the head, which can be seen in the final movements of the fetal head.
Failure to complete the cardinal movements of birth in the correct order may result in complications of labour and birth injuries.
Early skin-to-skin contact
Skin-to-skin contact
Kangaroo care also called skin-to-skin contact (SSC), is a technique of newborn care where babies are kept chest-to-chest and skin-to-skin with a parent, typically their mother (occasionally their father).
Kangaroo care, named for the similarity ...
(SSC), sometimes also called
kangaroo care
Kangaroo care also called skin-to-skin contact (SSC), is a technique of newborn care where babies are kept chest-to-chest and skin-to-skin with a parent, typically their mother (occasionally their father).
Kangaroo care, named for the similarity ...
, is a technique of newborn care where babies are kept chest-to-chest and skin-to-skin with a parent, typically their mother, though more recently (2022) their father as well. This means without the shirt or undergarments on the chest of both the baby and parent. A 2011 medical review found that early skin-to-skin contact resulted in a decrease in infant crying, improved cardio-respiratory stability and blood glucose levels, and improved breastfeeding duration.
A 2016
Cochrane review
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health profes ...
also found that SSC at birth promotes the likelihood and effectiveness of breastfeeding.
As of 2014, early postpartum SSC is endorsed by all major organizations that are responsible for the well-being of infants, including the
American Academy of Pediatrics.
The
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO) states that "the process of
childbirth is not finished until the baby has safely transferred from placental to mammary nutrition." It is advised that the newborn be placed skin-to-skin with the mother following vaginal birth, or as soon as the mother is alert and responsive after a Caesarean section, postponing any routine procedures for at least one to two hours. The baby's father or other support person may also choose to hold the baby SSC until the mother recovers from the anesthetic.
The WHO suggests that any initial observations of the infant can be done while the infant remains close to the mother, saying that even a brief separation before the baby has had its first feed can disturb the bonding process. They further advise frequent skin-to-skin contact as much as possible during the first days after delivery, especially if it was interrupted for some reason after the delivery.
La Leche League
La Leche League International (LLLI) () is a non-governmental, nonprofit organization that organizes advocacy, education, and training related to breastfeeding. It is present in about 89 countries.
The aim of the charity is to provide mother to ...
advises women to have a delivery team which includes a support person who will advocate to assure that:
:* The mother and her baby are not separated unnecessarily
:*The baby will receive only her milk
:*The baby will receive no supplementation without a medical reason
:* All testing, bathing or other procedures are done in the parent's room
It has long been known that a mother's level of the hormone
oxytocin elevates in a mother when she interacts with her infant. In 2019, a large review of the effects of oxytocin found that the oxytocin level in fathers that engage in SSC is increased as well. Two studies found that "when the infant is clothed only in a diaper and placed in between the mother or father's breasts, chest-to-chest
levated paternal oxytocin levels wereshown to reduce stress and anxiety in parents after interaction."
Discharge
For births that occur in hospitals the WHO recommends a hospital stay of at least 24 hours following an uncomplicated vaginal delivery and 96 hours for a Cesarean section. Looking at length of stay (in 2016) for an uncomplicated delivery around the world shows an average of less that 1 day in Egypt to 6 days in (pre-war) Ukraine. Averages for Australia are 2.8 days and 1.5 days in the UK.
While this number is low, two-thirds of women in the UK have midwife-assisted births and in some cases the mother may choose a hospital setting for birth to be closer to the wide range of assistance available for an emergency situation. However, women with midwife care may leave the hospital shortly after birth and her midwife will continue her care at her home.
In the U.S. the average length of stay has gradually dropped from 4.1 days in 1970 to a current stay of 2 days. The CDC attributed the drop to the rise in health care costs, saying people could not afford to stay in the hospital any longer. To keep it from dropping any lower, in 1996 congress passed the
Newborns' and Mothers' Health Protection Act that requires insurers to cover at least 48 hours for uncomplicated delivery.
Labour induction and Caesarean section
In many cases and with increasing frequency, childbirth is achieved through
labour induction
Labor induction is the process or treatment that stimulates childbirth and delivery. Inducing (starting) labor can be accomplished with pharmaceutical or non-pharmaceutical methods. In Western countries, it is estimated that one-quarter of pregnan ...
or
caesarean section. Labour induction is the process or treatment that stimulates childbirth and delivery. Inducing labour can be accomplished with pharmaceutical or non-pharmaceutical methods. Inductions are most often performed either with
prostaglandin drug treatment alone, or with a combination of prostaglandin and intravenous
oxytocin treatment.
Caesarean section is the removal of the
neonate
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
through a surgical incision in the abdomen, rather than through vaginal birth.
Childbirth by C-sections increased 50% in the US from 1996 to 2006. In 2012, about 23 million deliveries occurred by Caesarean section.
Induced births and elective cesarean before 39 weeks can be harmful to the neonate as well as harmful or without benefit to the mother. Therefore, many guidelines recommend against non-medically required induced births and elective cesarean before 39 weeks.
The 2012 rate of labour induction in the United States was 23.3 per cent, and had more than doubled from 1990 to 2010.
By 2022 it had climbed to 32%.
The
American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines recommend a full evaluation of the maternal-fetal status, the status of the cervix, and at least a 39 completed weeks (full term) of gestation for optimal health of the newborn when considering elective induction of labour. Per these guidelines, indications for induction may include:
*
Abruptio placentae
*
Chorioamnionitis
* Fetal compromise such as isoimmunisation leading to
haemolytic disease of the newborn or
oligohydramnios
* Fetal demise
*
Gestational hypertension
Gestational hypertension or pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is the development of new hypertension in a pregnant woman after 20 weeks' gestation without the presence of protein in the urine or other signs of pre-eclampsia. Gestational hyperte ...
* Maternal conditions such as
gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and of ...
or
chronic kidney disease
*
Preeclampsia or
eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is one of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in ...
*
Premature rupture of membranes
* Post-term pregnancy
Induction is also considered for logistical reasons, such as the distance from hospital or psychosocial conditions, but in these instances gestational age confirmation must be done, and the maturity of the fetal lung must be confirmed by testing. The ACOG also note that contraindications for induced labour are the same as for spontaneous vaginal delivery, including
vasa previa, complete
placenta praevia
Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in a position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated ...
,
umbilical cord prolapse
Umbilical cord prolapse is when the umbilical cord comes out of the uterus with or before the presenting part of the baby. The concern with cord prolapse is that pressure on the cord from the baby will compromise blood flow to the baby. It usual ...
or active
genital herpes simplex infection.
A Caesarean section, also called a C section, can be the safest option for delivery in some pregnancies. During a C section, the patient is usually numbed with an epidural or a spinal block, but general anesthesia can be used as well. A cut is made in the patient’s abdomen and then in the uterus to remove the baby. A C section may be the best option when the small size or shape of the mother's pelvis makes delivery of the baby impossible, or the lie or presentation of the baby as it prepares to enter the birth canal is dangerous. Other medical reasons for C section are placenta previa (the placenta blocks the baby’s path to the birth canal), uterine rupture, or fetal distress, like due to endangerment of the baby’s oxygen supply. Before the 1970s, once a patient delivered one baby via C section, it was recommended that all of her future babies be delivered by C section, but that recommendation has changed. Unless there is some other indication, mothers can attempt a trial of labour and most are able to have a vaginal birth after C section (VBAC).
Like any procedure, a C section is not without risks. Having a C section puts the mother at greater risk for uterine rupture and abnormal attachment of the placenta to the uterus in future pregnancies (placenta accreta spectrum). The rate of deliveries occurring via C section instead of vaginal deliveries has been increasing since the 1970s. The WHO recommends a C section rate of between 10 to 15 percent because C sections rates higher than 10 percent are not associated with a decrease in morbidity and mortality.
Management

Obstetric care frequently subjects women to institutional routines, which may have adverse effects on the progress of labour. Supportive care during labour may involve emotional support, comfort measures, and information and advocacy which may promote the physical process of labour as well as women's feelings of control and competence, thus reducing the need for obstetric intervention. The continuous support may be provided either by hospital staff such as nurses or midwives,
doula
A doula () is a trained professional who provides expert guidance for the service of others and who supports another person (the doula's client) through a significant health-related experience, such as childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion or ...
s, or by companions of the woman's choice from her social network.There is increasing evidence to show that the participation of the child's father in the birth leads to a better birth and also post-birth outcomes, providing the father does not exhibit excessive anxiety.
Continuous labour support may help women to give birth spontaneously, that is, without caesarean or vacuum or forceps, with slightly shorter labours, and to have more positive feelings regarding their experience of giving birth. Continuous labour support may also reduce women's use of pain medication during labour and reduce the risk of babies having low five-minute Agpar scores.
Preparation
Eating or drinking during labour is an area of ongoing debate. While some have argued that eating in labour has no harmful effects on outcomes, others continue to have concern regarding the increased possibility of an aspiration event (choking on recently eaten foods) in the event of an emergency delivery due to the increased relaxation of the esophagus in pregnancy, upward pressure of the uterus on the stomach, and the possibility of general anaesthetic in the event of an emergency cesarean. A 2013
Cochrane review
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health profes ...
found that with good obstetrical anaesthesia there is no change in harms from allowing eating and drinking during labour in those who are unlikely to need surgery. They additionally acknowledge that not eating does not mean there is an empty stomach or that its contents are not as acidic. They therefore conclude that "women should be free to eat and drink in labour, or not, as they wish."
At one time shaving of the
area around the vagina, was common practice due to the belief that hair removal reduced the risk of infection, made an
episiotomy
Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by a midwife or obstetrician. Episiotomy is usually performed during second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the opening ...
(a surgical cut to enlarge the vaginal entrance) easier, and helped with instrumental deliveries. It is currently less common, though it is still a routine procedure in some countries even though a systematic review found no evidence to recommend shaving. Side effects appear later, including irritation, redness, and multiple superficial scratches from the razor. Another effort to prevent infection has been the use of the antiseptic
chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine (CHX) (commonly known by the salt forms chlorhexidine gluconate and chlorhexidine digluconate (CHG) or chlorhexidine acetate) is a disinfectant and antiseptic that is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to sterilize surgi ...
or
providone-iodine solution
Povidone-iodine (PVP-I), also known as iodopovidone, is an antiseptic used for skin disinfection before and after surgery. It may be used both to disinfect the hands of healthcare providers and the skin of the person they are caring for. It may a ...
in the vagina. Evidence of benefit with chlorhexidine is lacking. A decreased risk is found with providone-iodine when a cesarean section is to be performed.
Forceps or vacuum assisted delivery
An assisted delivery is used in about 1 in 8 births, and may be needed if either mother or infant appears to be at risk during a vaginal delivery. The methods used are termed
obstetrical forceps
Obstetrical forceps are a medical instrument used in childbirth. Their use can serve as an alternative to the ventouse (vacuum extraction) method.
Medical uses
Forceps births, like all assisted births, should only be undertaken to help pr ...
extraction and
vacuum extraction
Vacuum extraction (VE), also known as ventouse, is a method to assist delivery of a baby using a vacuum device. It is used in the second stage of labor if it has not progressed adequately. It may be an alternative to a forceps delivery and caes ...
, also called ventouse extraction. Done properly, they are both safe with some preference for forceps rather than vacuum, and both are seen as preferable to an unexpected C-section. While considered safe, some risks for the mother include vaginal tearing, including a higher chance of having a more major vaginal tear that involves the muscle or wall of the anus or rectum. For women undergoing operative vaginal delivery with vacuum extraction or forceps, there is strong evidence that
prophylactic antibiotics help to reduce the risk of infection. There is a higher risk of blood clots forming in the legs or pelvis – anti-clot stockings or medication may be ordered to avoid clots.
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. It has been identified as an important issue in geri ...
is not unusual after childbirth but it is more common after an instrument delivery. Certain exercises and physiotherapy will help the condition to improve.
Pain control
Non pharmaceutical
Some women prefer to avoid
analgesic medication during childbirth. Psychological preparation may be beneficial. Relaxation techniques, immersion in water, massage, and
acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
may provide pain relief. Acupuncture and relaxation were found to decrease the number of caesarean sections required.
Immersion in water has been found to relieve pain during the first stage of labour and to reduce the need for anaesthesia and shorten the duration of labour, however the safety and efficacy of immersion during birth,
water birth
Water birth is labor and sometimes delivery that occurs in water, usually a birthing pool. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists does not recommend birthing in water as the safety has not been determined. Proponents believe ch ...
, has not been established or associated with maternal or fetal benefit.
Most women like to have someone to support them during labour and birth; such as a midwife, nurse, or
doula
A doula () is a trained professional who provides expert guidance for the service of others and who supports another person (the doula's client) through a significant health-related experience, such as childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion or ...
; or a lay person such as the father of the baby, a family member, or a close friend. Studies have found that continuous support during labour and delivery reduce the need for medication and a caesarean or operative vaginal delivery, and result in an improved
Apgar score for the infant.
Pharmaceutical
Different measures for pain control have varying degrees of success and side effects to the woman and her baby. In some countries of Europe, doctors commonly prescribe inhaled
nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has ...
gas for pain control, especially as 53% nitrous oxide, 47% oxygen, known as
Entonox
Nitrous oxide, is an inhaled gas used as a pain medication and together with other medications for anesthesia. Common uses include during childbirth, following trauma, and as part of end-of-life care. Onset of effect is typically within half a m ...
; in the UK, midwives may use this gas without a doctor's prescription.
Opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use ...
s such as
fentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocain ...
may be used, but if given too close to birth there is a risk of respiratory depression in the infant.
Popular medical pain control in hospitals include the regional anaesthetics
epidural
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, , upon" + ''dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians an ...
s (EDA), and
spinal anaesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia (or spinal anesthesia), also called spinal block, subarachnoid block, intradural block and intrathecal block, is a form of neuraxial regional anaesthesia involving the injection of a local anaesthetic or opioid into the subar ...
. Epidural analgesia is a generally safe and effective method of relieving pain in labour, but has been associated with longer labour, more operative intervention (particularly instrument delivery), and increases in cost. However, a more recent (2017) Cochrane review suggests that the new epidural techniques have no effect on labour time and the use of instruments or the need for C-section deliveries.
Generally, pain and stress hormones rise throughout labour for women without epidurals, while pain, fear, and stress hormones decrease upon administration of epidural analgesia, but rise again later.
Medicine administered via epidural can cross the placenta and enter the bloodstream of the fetus. Epidural analgesia has no statistically significant impact on the risk of caesarean section, and does not appear to have an immediate effect on neonatal status as determined by Apgar scores.
Augmentation

Augmentation is the process of stimulating the uterus to increase the intensity and duration of contractions after labour has begun. Several methods of augmentation are commonly been used to treat slow progress of labour (dystocia) when uterine contractions are assessed to be too weak.
Oxytocin is the most common method used to increase the rate of vaginal delivery. The World Health Organization recommends its use either alone or with
amniotomy
Artificial rupture of membranes (AROM), also known as an amniotomy, is performed by a midwife or obstetrician and was once thought to be an effective means to induce or accelerate labor. The membranes can be ruptured using a specialized tool, suc ...
(rupture of the amniotic membrane) but advises that it must be used only after it has been correctly confirmed that labour is not proceeding properly if harm is to be avoided. The WHO does not recommend the use of
antispasmodic
An antispasmodic (synonym: spasmolytic) is a pharmaceutical drug or other agent that suppresses muscle spasms.
Smooth muscle spasm
One type of antispasmodics is used for smooth muscle relaxation, especially in tubular organs of the gastrointest ...
agents for prevention of delay in labour.
Episiotomy
For years an
episiotomy
Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by a midwife or obstetrician. Episiotomy is usually performed during second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the opening ...
was thought to help prevent more extensive vaginal tears and heal better than a natural tear.
Perineal tears can occur at the vaginal opening as the baby's head passes through, especially if the baby descends quickly. Tears can involve the
perineal skin or extend to the muscles and the anal sphincter and anus. Once common, they are now recognised as generally not needed.
[ When needed, the midwife or obstetrician makes a surgical cut in the perineum to prevent severe tears that can be difficult to repair. A 2017 Cochrane review compared episiotomy as needed (restrictive) with routine episiotomy to determine the possible benefits and harms for mother and baby. The review found that restrictive episiotomy policies appeared to give a number of benefits compared with using routine episiotomy. Women experienced less severe perineal trauma, less posterior perineal trauma, less suturing and fewer healing complications at seven days with no difference in occurrence of pain, urinary incontinence, painful sex or severe vaginal/perineal trauma after birth.
]
Multiple births
In cases of a head first-presenting first twin, twins can often be delivered vaginally. In some cases twin delivery is done in a larger delivery room or in an operating theatre, in the event of complication e.g.
* Both twins born vaginally – this can occur both presented head first or where one comes head first and the other is breech and/or helped by a forceps/ventouse delivery
* One twin born vaginally and the other by caesarean section.
* If the twins are joined at any part of the body – called conjoined twins
Conjoined twins – sometimes popularly referred to as Siamese twins – are twins joined ''Uterus, in utero''. A very rare phenomenon, the occurrence is estimated to range from 1 in 49,000 births to 1 in 189,000 births, with a somewhat higher in ...
, delivery is mostly by caesarean section.
Fetal monitoring
For external monitoring of the fetus during childbirth, a simple pinard stethoscope or doppler fetal monitor
A Doppler fetal monitor is a hand-held ultrasound transducer used to detect the fetal heartbeat for prenatal care. It uses the Doppler effect to provide an audible simulation of the heart beat. Some models also display the heart rate in beats pe ...
("'' doptone''") can be used.
A method of external (noninvasive) fetal monitoring (EFM) during childbirth is cardiotocography
Cardiotocography (CTG) is a technique used to monitor the fetal heartbeat and the uterine contractions during pregnancy and labour. The machine used to perform the monitoring is called a cardiotocograph.
Fetal heart sounds was described as earl ...
(CTG), using a ''cardiotocograph'' that consists of two sensors: The ''heart'' (cardio) sensor is an ultrasonic sensor, similar to a Doppler fetal monitor
A Doppler fetal monitor is a hand-held ultrasound transducer used to detect the fetal heartbeat for prenatal care. It uses the Doppler effect to provide an audible simulation of the heart beat. Some models also display the heart rate in beats pe ...
, that continuously emits ultrasound and detects motion of the fetal heart by the characteristic of the reflected sound. The pressure-sensitive ''contraction'' transducer, called a ''tocodynamometer'' (toco) has a flat area that is fixated to the skin by a band around the belly. The pressure required to flatten a section of the wall correlates with the internal pressure, thereby providing an estimate of contraction.
Monitoring with a cardiotocograph can either be intermittent or continuous. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO) advises that for healthy women undergoing spontaneous labour continuous cardiotocography is not recommended for assessment of fetal well-being. The WHO states: "In countries and settings where continuous CTG is used defensively to protect against litigation, all stakeholders should be made aware that this practice is not evidence-based and does not improve birth outcomes."
A mother's water has to break before internal (invasive) monitoring can be used. More invasive monitoring can involve a fetal scalp electrode to give an additional measure of fetal heart activity, and/or intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC). It can also involve fetal scalp pH testing.
Complications

 Per figures retrieved in 2015, since 1990 there has been a 44 percent decline in the maternal death rate. However, according to 2015 figures 830 women die every day from causes related to pregnancy or childbirth and for every woman who dies, 20 or 30 encounter injuries, infections or disabilities. Most of these deaths and injuries are preventable.
Per figures retrieved in 2015, since 1990 there has been a 44 percent decline in the maternal death rate. However, according to 2015 figures 830 women die every day from causes related to pregnancy or childbirth and for every woman who dies, 20 or 30 encounter injuries, infections or disabilities. Most of these deaths and injuries are preventable.World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO) has urged midwife training to strengthen maternal and newborn health services. To support the upgrading of midwifery skills the WHO established a midwife training program, Action for Safe Motherhood.[
The rising maternal death rate in the US is of concern. In 1990 the US ranked 12th of the 14 developed countries that were analysed. However, since that time the rates of every country have steadily continued to improve while the US rate has spiked dramatically. While every other developed nation of the 14 analysed in 1990 shows a 2017 death rate of less than 10 deaths per every 100,000 live births, the US rate has risen to 26.4. By comparison, the United Kingdom ranks second highest at 9.2 and Finland is the safest at 3.8. Furthermore, for every one of the 700 to 900 US woman who die each year during pregnancy or childbirth, 70 experience significant complications such as haemorrhage and organ failure, totalling more than one per cent of all births.
Compared to other developed nations, the United States also has high infant mortality rates. The Trust for America's Health reports that as of 2011, about one-third of American births have some complications; many are directly related to the mother's health including increasing rates of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and physical inactivity. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has led an initiative to improve woman's health previous to conception in an effort to improve both neonatal and maternal death rates.
]
Labour and delivery complications
Obstructed labour
The second stage of labour may be delayed or lengthy due to poor or uncoordinated uterine action, an abnormal uterine position such as breech or shoulder dystocia
Shoulder dystocia is when, after vaginal delivery of the head, the baby's anterior shoulder gets caught above the mother's pubic bone. Signs include retraction of the baby's head back into the vagina, known as "turtle sign". Complications for th ...
, and cephalopelvic disproportion (a small pelvis or large infant). Prolonged labour may result in maternal exhaustion, fetal distress, and other complications including obstetric fistula.
Eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy in which there is high blood pressure and either large amounts of protein in the urine or other organ dysfunction. Pre-eclampsia is routinely screened for during prenatal care. Onset may be before, during, or rarely, after delivery. Around one per cent of women with eclampsia die.
Maternal complications
A puerperal disorder or postpartum disorder is a complication which presents primarily during the puerperium, or postpartum period. The postpartum period can be divided into three distinct stages; the initial or acute phase, six to 12 hours after childbirth; subacute postpartum period, which lasts two to six weeks, and the delayed postpartum period, which can last up to six months. In the subacute postpartum period, 87% to 94% of women report at least one health problem.
Postpartum bleeding
According to the WHO, hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal death worldwide accounting for approximately 27.1% of maternal deaths.Thrombin
Thrombin (, ''fibrinogenase'', ''thrombase'', ''thrombofort'', ''topical'', ''thrombin-C'', ''tropostasin'', ''activated blood-coagulation factor II'', ''blood-coagulation factor IIa'', ''factor IIa'', ''E thrombin'', ''beta-thrombin'', ''gamma- ...
, which is a molecule used in the human body’s blood clotting system, represents all coagulopathies.
Postpartum infections
Postpartum infections, also historically known as childbed fever and medically as puerperal fever, are any bacterial infections of the reproductive tract following childbirth or miscarriage. Signs and symptoms usually include a fever greater than 38.0 °C (100.4 °F), chills, lower abdominal pain, and possibly bad-smelling vaginal discharge. The infection usually occurs after the first 24 hours and within the first ten days following delivery. Infection remains a major cause of maternal deaths and morbidity in the developing world. The work of Ignaz Semmelweis
Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis (; hu, Semmelweis Ignác Fülöp ; 1 July 1818 – 13 August 1865) was a Hungarian physician and scientist, who was an early pioneer of antiseptic procedures. Described as the "saviour of mothers", he discovered that t ...
was seminal in the pathophysiology and treatment of childbed fever and his work saved many lives.
Psychological complications
Childbirth can be an intense event and strong emotions, both positive and negative, can be brought to the surface. Abnormal and persistent fear of childbirth is known as tokophobia
Tokophobia is a significant fear of childbirth. It is a common reason why some women request an elective cesarean section. The fear often includes fear of injury to the baby, genital tract, or death. Treatment may occur via counselling.
It is a ...
. The prevalence of fear of childbirth around the world ranges between 4–25%, with 3–7% of pregnant women having clinical fear of childbirth.Postpartum depression
Postpartum depression (PPD), also called postnatal depression, is a type of mood disorder associated with childbirth, which can affect both sexes. Symptoms may include extreme sadness, low energy, anxiety, crying episodes, irritability, and cha ...
is different from the "baby blues". With postpartum depression, feelings of sadness and anxiety can be extreme and might interfere with a woman's ability to care for herself or her family. Because of the severity of the symptoms, postpartum depression usually requires treatment. The condition, which occurs in nearly 15 percent of births, may begin shortly before or any time after childbirth, but commonly begins between a week and a month after delivery.Childbirth-related posttraumatic stress disorder
Childbirth-related post-traumatic stress disorder is a psychological disorder that can develop in women who have recently given birth. This disorder can also affect men or partners who have observed a difficult birth. Its symptoms are no ...
is a psychological disorder that can develop in women who have recently given birth.posttraumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that can develop because of exposure to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats ...
(PTSD). Many women who are experiencing symptoms of PTSD after childbirth are misdiagnosed with postpartum depression or adjustment disorder
Adjustment disorder is a maladaptive response to a psychosocial stressor. It is classified as a mental disorder. The maladaptive response usually involves otherwise normal emotional and behavioral reactions that manifest more intensely than usual ...
s. These diagnoses can lead to inadequate treatment.Postpartum psychosis
Postpartum psychosis, also known as puerperal psychosis, involves the abrupt onset of severe mental illness shortly following childbirth. While symptoms of postpartum psychosis have long been observed in mothers, the phenomenon eventually came t ...
is a rare psychiatric emergency in which symptoms of high mood and racing thoughts ( mania), depression, severe confusion, loss of inhibition, paranoia, hallucinations and delusions set in, beginning suddenly in the first two weeks after childbirth. The symptoms vary and can change quickly.[
]
Fetal complications
 Five causes make up about 80 per cent of newborn deaths globally: prematurity, low-birth-weight, infections, lack of oxygen at birth, and trauma during birth.
Five causes make up about 80 per cent of newborn deaths globally: prematurity, low-birth-weight, infections, lack of oxygen at birth, and trauma during birth.[
]
Stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
death at or after 20 to 28 weeks of pregnancy.[
Worldwide prevention of most stillbirths is possible with improved health systems.]developed world
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
.[ Otherwise depending on how far along the pregnancy is, medications may be used to start labour or a type of surgery known as ]dilation and evacuation
Dilation and evacuation (D&E) is the dilation of the cervix and surgical evacuation of the uterus (potentially including the fetus, placenta and other tissue) after the first trimester of pregnancy. It is a method of abortion as well as a common ...
may be carried out.South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
and Sub-Saharan Africa.[ Stillbirth rates have declined, though more slowly since the 2000s.]
Preterm birth
Preterm birth is the birth of an infant at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Su ...
. Globally, about 15 million infants were born before 37 weeks of gestation. Premature birth is the leading cause of death in children under five years of age though many that survive experience disabilities including learning defects and visual and hearing problems. Causes for early birth may be unknown or may be related to certain chronic conditions such as diabetes, infections, and other known causes. The World Health Organization has developed guidelines with recommendations to improve the chances of survival and health outcomes for preterm infants.tocolytics
Tocolytics (also called anti-contraction medications or labor suppressants) are medications used to suppress premature labor (from Greek τόκος ''tókos'', "childbirth", and λύσις ''lúsis'', "loosening"). Preterm birth accounts for 70% ...
. Tocolytics delay labour by inhibiting contractions of the uterine muscles that progress labor. The most widely used tocolytics include beta agonists, calcium channel blockers, and magnesium sulfate. The goal of administering tocolytics is not to delay delivery to the point that the child can be delivered at term, but instead to postponing delivery long enough for the administration of glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
which can help the fetal lungs to mature enough to reduce morbidity and mortality from infant respiratory distress syndrome.
Post-term birth
The term postterm pregnancy is used to discribe a condition in which a woman has not yet delivered her baby after 42 weeks of gestation, two weeks beyond the usual 40-week duration of pregnancy. Postmature births carry risks for both the mother and the baby, including meconium aspiration syndrome
Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) also known as neonatal aspiration of meconium is a medical condition affecting newborn infants. It describes the spectrum of disorders and pathophysiology of newborns born in meconium-stained amniotic fluid (MSAF ...
, fetal malnutrition, and stillbirths
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term ...
. The placenta, which supplies the baby with oxygen and nutrients, begins to age and will eventually fail after the 42nd week of gestation. Induced labor is indicated for postterm pregnancy.
Neonatal infection
Newborns are prone to infection in the first month of life. The pathogenic bacterium
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of t ...
''Streptococcus agalactiae
''Streptococcus agalactiae'' (also known as group B streptococcus or GBS) is a gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) with a tendency to form chains (as reflected by the genus name ''Streptococcus''). It is a beta- hemolytic, catalase-negative, ...
'' (a group B streptococcus) is most often the cause of these occasionally fatal infections. The baby contracts the infection from the mother during labour. In 2014 it was estimated that about one in 2000 newborn babies had a group B streptococcuss infection within the first week of life, usually evident as respiratory disease
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, bro ...
, general sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, or meningitis.
Untreated sexually transmitted infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral ...
(STIs) are associated with birth defect
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities ca ...
s, and infections in newborn babies, particularly in the areas where rates of infection remain high. The majority of STIs have no symptoms or only mild symptoms that may not be recognised. Mortality rates resulting from some infections may be high, for example the overall perinatal mortality rate associated with untreated syphilis is 30 per cent.
Perinatal asphyxia
Perinatal asphyxia
Perinatal asphyxia (also known as neonatal asphyxia or birth asphyxia) is the medical condition resulting from deprivation of oxygen to a newborn infant that lasts long enough during the birth process to cause physical harm, usually to the brain. ...
is the medical condition resulting from deprivation of oxygen to a newborn infant that lasts long enough during the birth process to cause physical harm.heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
, lungs, liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, gut, kidneys
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; bloo ...
), but brain damage is of most concern and perhaps the least likely to quickly or completely heal.cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sens ...
.
Mechanical fetal injury
Risk factors for fetal birth injury include fetal macrosomia (big baby), maternal obesity Maternal obesity refers to obesity (often including being overweight) of a woman during pregnancy. Parental obesity refers to obesity of either parent during pregnancy.
Maternal obesity has a significant impact on maternal metabolism and offspring ...
, the need for instrumental delivery, and an inexperienced attendant. Specific situations that can contribute to birth injury include breech presentation and shoulder dystocia
Shoulder dystocia is when, after vaginal delivery of the head, the baby's anterior shoulder gets caught above the mother's pubic bone. Signs include retraction of the baby's head back into the vagina, known as "turtle sign". Complications for th ...
. Most fetal birth injuries resolve without long term harm, but brachial plexus injury
A brachial plexus injury (BPI), also known as brachial plexus lesion, is an injury to the brachial plexus, the network of nerves that conducts signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm and hand. These nerves originate in the fifth, sixth, s ...
may lead to Erb's palsy
Erb's palsy is a paralysis of the arm caused by injury to the upper group of the arm's main nerves, specifically the severing of the upper trunk C5–C6 nerves. These form part of the brachial plexus, comprising the ventral rami of spinal ner ...
or Klumpke's paralysis.
History
Role of males
Historically, women have been attended and supported by other women during labour and birth. Midwife training in European cities began in the 1400s, but rural women were usually assisted by female family or friends.[Hutter Epstein, M.D., Randi (2011). ''Get Me Out: A History of Childbirth from the Garden of Eden to the Sperm Bank''. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, Inc.] However, it was not simply a ladies' social bonding event as some historians have portrayed – fear and pain often filled the atmosphere, as death during childbirth was a common occurrence.home birth
A home birth is a birth that takes place in a residence rather than in a hospital or a birthing center. They may be attended by a midwife, or lay attendant with experience in managing home births. Home birth was, until the advent of modern medic ...
; the father would be waiting downstairs or in another room in the home. If it was in a hospital, then the father would wait in the waiting room. Fathers were only permitted in the room if the life of the mother or baby was severely at-risk. In 1522, a German physician was sentenced to death for sneaking into a delivery room dressed as a woman.Soranus of Ephesus
Soranus of Ephesus ( grc-gre, Σωρανός ὁ Ἑφέσιος; 1st/2nd century AD) was a Greek physician. He was born in Ephesus but practiced in Alexandria and subsequently in Rome, and was one of the chief representatives of the Methodic ...
, wrote a book about obstetrics and gynaecology in the second century, which was referenced for the next thousand years. The book contained endless home remedies for pregnancy and childbirth, many of which would be considered heinous by modern women and medical professionals.Kangaroo care
Kangaroo care also called skin-to-skin contact (SSC), is a technique of newborn care where babies are kept chest-to-chest and skin-to-skin with a parent, typically their mother (occasionally their father).
Kangaroo care, named for the similarity ...
, immediately following birth and for the first few weeks of life. Some fathers have begun to hold their newborns skin to skin; the new baby is familiar with the father's voice and it is believed that contact with the father helps the infant to stabilise and promotes father to infant bonding. Looking at recent studies, a 2019 review found that the level of oxytocin was found to increase not only in mothers who had experienced early skin to skin attachment with their infants but in the fathers as well, suggesting a neurobiological connection.[
]
Hospitals
Historically, most women gave birth at home without emergency medical care available. In the early days of hospitalisation of childbirth, a 17th-century maternity ward in Paris was incredibly congested, with up to five pregnant women sharing one bed. At this hospital, one in five women died during the birthing process.Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, giving birth at home became more difficult due to congested living spaces and dirty living conditions. That drove urban and lower-class women to newly available hospitals, while wealthy and middle-class women continued to labour at home.[A natural process? Women, men and the medicalisation of childbirth". ''broughttolife.sciencemuseum.org.uk''. Retrieved 3 December 2018.] In the United States, the middle classes were especially receptive to the medicalisation of childbirth, which promised a safer and less painful labour.
Baby Friendly Hospitals
In 1991 the WHO launched a global program, the Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI), that encourages birthing centers and hospitals to institute procedures that encourage mother/baby bonding and breastfeeding. The Johns Hopkins Hospital describes the process of receiving the Baby Friendly designation:
Every major health organization, such as the CDC, supports the BFHI. As of 2019, 28% of hospitals in the US have been accredited by the WHO.
Medication
The use of pain medication in labour has been a controversial issue for hundreds of years. A Scottish woman was burned at the stake in 1591 for requesting pain relief in the delivery of twins. Medication became more acceptable in 1852, when Queen Victoria used chloroform as pain relief during labour. The use of morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
and scopolamine, also known as " twilight sleep", was first used in Germany and popularised by German physicians Bernard Kronig and Karl Gauss. This concoction offered minor pain relief but mostly allowed women to completely forget the entire delivery process. Under twilight sleep, mothers were often blindfolded and restrained as they experienced the immense pain of childbirth. The cocktail came with severe side effects, such as decreased uterine contractions and altered mental state. Additionally, babies delivered with the use of childbirth drugs often experienced temporarily-ceased breathing. The feminist movement in the United States openly and actively supported the use of twilight sleep, which was introduced to the country in 1914. Some physicians, many of whom had been using painkillers for the past fifty years, including opium, cocaine, and quinine, embraced the new drug. Others were rightfully hesitant.
Caesarean sections
There are many conflicting stories of the first successful cesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or ...
(or C-section) in which both mother and baby survived. It is, however, known that the procedure had been attempted for hundreds of years before it became accepted in the beginning of the twentieth century.caesarean delivery on maternal request
Caesarean delivery on maternal request (CDMR) is a caesarean section birth requested by the pregnant woman without a medical reason.
Background
The concept of "Caesarean delivery on maternal request" (CDMR) is not well-recognized in health care ...
is a medically unnecessary caesarean section, where the infant is born by a caesarean section requested by the parent even though there is not a medical indication to have the surgery.
Natural childbirth
The reemergence of "natural childbirth" began in Europe and was adopted by some in the US as early as the late 1940s. Early supporters believed that the drugs used during deliveries interfered with "happy childbirth" and could negatively impact the newborn's "emotional wellbeing". By the 1970s, the call for natural childbirth was spread nationwide, in conjunction with the second-wave of the feminist movement.home birth
A home birth is a birth that takes place in a residence rather than in a hospital or a birthing center. They may be attended by a midwife, or lay attendant with experience in managing home births. Home birth was, until the advent of modern medic ...
s have gained popularity.
Epidemiology
 The
The United Nations Population Fund
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), formerly the United Nations Fund for Population Activities, is a UN agency aimed at improving reproductive and maternal health worldwide. Its work includes developing national healthcare strategies a ...
estimated that 303,000 women died of pregnancy or childbirth related causes in 2015.obstructed labour
Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is the baby not exiting the pelvis because it is physically block during childbirth although the uterus contracts normally. Complications for the baby include not getting enough oxygen which may ...
,birth attendant A birth attendant, also known as skilled birth attendant, is a health professional who provides basic and emergency care to women and their newborns during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. A birth attendant, who may be a midwife, phy ...
s with backup emergency obstetric care, the global maternal mortality ratio has fallen from 385 maternal deaths per 100,000 live births in 1990 to 216 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2015, and it was reported in 2017 that many countries had halved their maternal death rates in the last 10 years.antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
were discovered in the 1930s, because of high rates of puerperal fever.
Society and culture
 Distress levels vary widely during pregnancy as well as during labour and delivery. They appear to be influenced by fear and anxiety levels, experience with prior childbirth, cultural ideas of childbirth pain, mobility during labour, and the support received during labour.
Distress levels vary widely during pregnancy as well as during labour and delivery. They appear to be influenced by fear and anxiety levels, experience with prior childbirth, cultural ideas of childbirth pain, mobility during labour, and the support received during labour.
 Personal expectations, the amount of support from caregivers, quality of the caregiver-patient relationship, and involvement in decision-making are more important in mother's overall satisfaction with the birthing experience than are other factors such as age, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, preparation, physical environment, pain, immobility, or medical interventions.
Personal expectations, the amount of support from caregivers, quality of the caregiver-patient relationship, and involvement in decision-making are more important in mother's overall satisfaction with the birthing experience than are other factors such as age, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, preparation, physical environment, pain, immobility, or medical interventions.
Costs
 According to a 2013 analysis performed commissioned by the New York Times and performed by Truven Healthcare Analytics, the cost of childbirth varies dramatically by country. In the United States the average amount actually paid by insurance companies or other payers in 2012 averaged $9,775 for an uncomplicated conventional delivery and $15,041 for a caesarean birth.
According to a 2013 analysis performed commissioned by the New York Times and performed by Truven Healthcare Analytics, the cost of childbirth varies dramatically by country. In the United States the average amount actually paid by insurance companies or other payers in 2012 averaged $9,775 for an uncomplicated conventional delivery and $15,041 for a caesarean birth.National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
began recommending that many women give birth at home under the care of a midwife rather than an obstetrician, citing lower expenses and better healthcare outcomes. The median cost associated with home birth was estimated to be about $1,500 vs. about $2,500 in hospital.
Location
Childbirth routinely occurs in hospitals in many developed countries. Before the 20th century and in some countries to the present day, such as the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, it has more typically occurred at home.Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
and Northern Manitoban communities in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
as well as Australian aboriginal
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait I ...
communities. There has been research considering the negative effects of maternal evacuation due to a lack of social support provided to these women. These negative effects include an increase in maternal newborn complications and postpartum depression, and decreased breastfeeding rates.
Facilities
Facilities for childbirth include:
* A ''labour ward'', also called a ''delivery ward'' or ''labour and delivery'', is generally a department of a hospital that focuses on providing health care to women and their children during childbirth. It is generally closely linked to the hospital's neonatal intensive care unit and/or obstetric surgery
Obstetrics and Gynaecology (also spelled as Obstetrics and Gynecology; abbreviated as Obs and Gynae, O&G, OB-GYN and OB/GYN) is the medical specialty that encompasses the two subspecialties of obstetrics (covering pregnancy, childbirth, and t ...
unit if present. A ''maternity ward'' or ''maternity unit'' may include facilities both for childbirth and for postpartum
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within 6 weeks as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium, puerperal pe ...
rest and observation of mothers in normal as well as complicated cases.
* A maternity hospital
A maternity hospital specializes in caring for women during pregnancy and childbirth. It also provides care for newborn infants, and may act as a centre for clinical training in midwifery and obstetrics. Formerly known as lying-in hospitals, most ...
is a hospital that specialises in caring for women while they are pregnant and during childbirth and provide care for newborn babies,
* A birthing center generally presents a simulated home-like environment. Birthing centers may be located on hospital grounds or "free standing" (that is, not affiliated with a hospital).
* A home birth
A home birth is a birth that takes place in a residence rather than in a hospital or a birthing center. They may be attended by a midwife, or lay attendant with experience in managing home births. Home birth was, until the advent of modern medic ...
is usually accomplished with the assist of a midwife. Some women choose to give birth at home without any professionals present, termed an unassisted childbirth.
Associated occupations
 Different categories of
Different categories of birth attendant A birth attendant, also known as skilled birth attendant, is a health professional who provides basic and emergency care to women and their newborns during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. A birth attendant, who may be a midwife, phy ...
s may provide support and care during pregnancy and childbirth, although there are important differences across categories based on professional training and skills, practice regulations, and the nature of care delivered. Many of these occupations are highly professionalised, but other roles exist on a less formal basis.
"Childbirth educators" are instructors who aim to teach pregnant women and their partners about the nature of pregnancy, labour signs and stages, techniques for giving birth, breastfeeding and newborn baby care. Training for this role can be found in hospital settings or through independent certifying organisations. Each organisation teaches its own curriculum and each emphasises different techniques. The Lamaze technique is one well-known example.
Doula
A doula () is a trained professional who provides expert guidance for the service of others and who supports another person (the doula's client) through a significant health-related experience, such as childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion or ...
s are assistants who support mothers during pregnancy, labour, birth, and postpartum. They are not medical attendants; rather, they provide emotional support and non-medical pain relief for women during labour. Like childbirth educators and other unlicensed assistive personnel
Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are paraprofessionals who assist individuals with physical disabilities, mental impairments, and other health care needs with their activities of daily living (ADLs). UAPs also provide bedside care—includ ...
, certification to become a doula is not compulsory, thus, anyone can call themself a doula or a childbirth educator.
Confinement nannies are individuals who are employed to provide assistance and stay with the mothers at their home after childbirth. They are usually experienced mothers who took courses on how to take care of mothers and newborn babies.
Midwives are autonomous practitioners who provide basic and emergency health care before, during and after pregnancy and childbirth, generally to women with low-risk pregnancies. Midwives are trained to assist during labour and birth, either through direct-entry or nurse-midwifery education programs. Jurisdictions where midwifery is a regulated profession will typically have a registering and disciplinary body for quality control, such as the American Midwifery Certification Board in the United States, the College of Midwives of British Columbia in Canada or the Nursing and Midwifery Council
The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) is the regulator for nursing and midwifery professions in the UK. The NMC maintains a register of all nurses, midwives and specialist community public health nurses and nursing associates eligible to pra ...
in the United Kingdom.
In the past, midwifery played a crucial role in childbirth throughout most indigenous societies. Although western civilisations attempted to assimilate their birthing technologies into certain indigenous societies, like Turtle Island, and get rid of the midwifery, the National Aboriginal Council of Midwives brought back the cultural ideas and midwifery that were once associated with indigenous birthing.obstetricians
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a sur ...
, family practitioners and general practitioners whose training, skills and practices include obstetrics, and in some contexts general surgeon
General surgery is a surgical specialty that focuses on alimentary canal and abdominal contents including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, appendix and bile ducts, and often the thyroid g ...
s. These physicians and surgeons variously provide care across the whole spectrum of normal and abnormal births and pathological labour conditions. Categorically specialised obstetricians are qualified surgeons, so they can undertake surgical procedures relating to childbirth. Some family practitioners or general practitioners also perform obstetrical surgery. Obstetrical procedures include cesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or ...
s, episiotomies, and assisted delivery. Categorical specialists in obstetrics are commonly trained in both obstetrics and gynaecology
Obstetrics and Gynaecology (also spelled as Obstetrics and Gynecology; abbreviated as Obs and Gynae, O&G, OB-GYN and OB/GYN) is the medical specialty that encompasses the two subspecialties of obstetrics (covering pregnancy, childbirth, and t ...
(OB/GYN), and may provide other medical and surgical gynaecological care, and may incorporate more general, well-woman, primary care
Primary care is the day-to-day healthcare given by a health care provider. Typically this provider acts as the first contact and principal point of continuing care for patients within a healthcare system, and coordinates other specialist care ...
elements in their practices. Maternal–fetal medicine specialists are obstetrician/gynecologists subspecialised in managing and treating high-risk pregnancy and delivery.
Anaesthetists or anesthesiologists are medical doctors who specialise in pain relief and the use of drugs to facilitate surgery and other painful procedures. They may contribute to the care of a woman in labour by performing an epidural
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, , upon" + ''dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians an ...
or by providing anaesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), a ...
(often spinal anaesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia (or spinal anesthesia), also called spinal block, subarachnoid block, intradural block and intrathecal block, is a form of neuraxial regional anaesthesia involving the injection of a local anaesthetic or opioid into the subar ...
) for Cesarean section or forceps delivery
Obstetrical forceps are a medical instrument used in childbirth. Their use can serve as an alternative to the ventouse (vacuum extraction) method.
Medical uses
Forceps births, like all assisted births, should only be undertaken to help prom ...
. They are experts in pain management during childbirth
Pain management during childbirth is the treatment or prevention of pain that a woman may experience during labor and delivery. The amount of pain a woman feels during labor depends partly on the size and position of her baby, the size of her p ...
.
Obstetric nurses assist midwives, doctors, women, and babies before, during, and after the birth process, in the hospital system. They hold various nursing certifications and typically undergo additional obstetric training in addition to standard nursing training.
Paramedic
A paramedic is a registered healthcare professional who works autonomously across a range of health and care settings and may specialise in clinical practice, as well as in education, leadership, and research.
Not all ambulance personnel are p ...
s are healthcare providers that are able to provide emergency care to both the mother and infant during and after delivery using a wide range of medications and tools on an ambulance. They are capable of delivering babies but can do very little for infants that become "stuck" and are unable to be delivered vaginally.
Lactation consultants assist the mother and newborn to breastfeed successfully. A health visitor comes to see the mother and baby at home, usually within 24 hours of discharge, and checks the infant's adaptation to extrauterine life and the mother's postpartum physiological changes.
Non-western communities
Cultural values, assumptions, and practices of pregnancy and childbirth vary across cultures. For example, some Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popul ...
women who work in agricultural fields of some rural communities will usually continue to work in a similar function to how they normally would throughout pregnancy, in some cases working until labour begins.umbilical cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologi ...
, it will cause for the child to go through clothes very quickly. In order to prevent this, a jagged ceramic tile is used to cut the umbilical cord.
Collecting stem cells
It is currently possible to collect two types of stem cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
during childbirth: amniotic stem cells Amniotic stem cells are the mixture of stem cells that can be obtained from the amniotic fluid as well as the amniotic membrane. They can develop into various tissue types including skin, cartilage, cardiac tissue, nerves, muscle, and bone. The cell ...
and umbilical cord blood
Cord blood (umbilical cord blood) is blood that remains in the placenta and in the attached umbilical cord after childbirth. Cord blood is collected because it contains stem cells, which can be used to treat hematopoietic and genetic disorders s ...
stem cells.[ They are being studied as possible treatments of a number of conditions.]
Placentophagy
Some animal mothers are known to eat their afterbirth, called placentophagy. In some cultures the placenta may be consumed as a nutritional boost, but it may also be seen as a special part of birth and eaten by the newborn's family ceremonially. In the developed world the placenta may be eaten believing that it reduces postpartum bleeding, increases milk supply, provides micronutrients such as iron, and improves mood and boosts energy. The CDC advises against this practice, saying it has not been shown to promote health but has been shown to possibly transmit disease organisms that were passed from the placenta into the mother's breastmilk and then infecting the baby.
See also
References
External links
Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery
Video by Merck Manual Professional Edition
Maternal Morbidity/Mortality in the Media
{{Authority control
Midwifery
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
 Station refers to the relationship of the fetal presenting part to the level of the
Station refers to the relationship of the fetal presenting part to the level of the  Definitions of the onset of labour include:
* Regular uterine contractions at least every six minutes with evidence of change in
Definitions of the onset of labour include:
* Regular uterine contractions at least every six minutes with evidence of change in  The active phase of labour has geographically differing definitions. The World Health Organization describes the active first stage as "a period of time characterized by regular painful uterine contractions, a substantial degree of cervical effacement and more rapid cervical dilatation from 5 cm until full dilatation for first and subsequent labours. In the US, the definition of active labour was changed from 3 to 4 cm, to 5 cm of
The active phase of labour has geographically differing definitions. The World Health Organization describes the active first stage as "a period of time characterized by regular painful uterine contractions, a substantial degree of cervical effacement and more rapid cervical dilatation from 5 cm until full dilatation for first and subsequent labours. In the US, the definition of active labour was changed from 3 to 4 cm, to 5 cm of  The expulsion stage begins when the cervix is fully dilated, and ends when the baby is born. As pressure on the cervix increases, a sensation of pelvic pressure is experienced, and, with it, an urge to begin pushing. At the beginning of the normal second stage, the head is fully engaged in the pelvis; the widest diameter of the head has passed below the level of the
The expulsion stage begins when the cervix is fully dilated, and ends when the baby is born. As pressure on the cervix increases, a sensation of pelvic pressure is experienced, and, with it, an urge to begin pushing. At the beginning of the normal second stage, the head is fully engaged in the pelvis; the widest diameter of the head has passed below the level of the  The fourth stage of labour is the period beginning immediately after childbirth, and extends for about six weeks. The terms ''
The fourth stage of labour is the period beginning immediately after childbirth, and extends for about six weeks. The terms '' Augmentation is the process of stimulating the uterus to increase the intensity and duration of contractions after labour has begun. Several methods of augmentation are commonly been used to treat slow progress of labour (dystocia) when uterine contractions are assessed to be too weak. Oxytocin is the most common method used to increase the rate of vaginal delivery. The World Health Organization recommends its use either alone or with
Augmentation is the process of stimulating the uterus to increase the intensity and duration of contractions after labour has begun. Several methods of augmentation are commonly been used to treat slow progress of labour (dystocia) when uterine contractions are assessed to be too weak. Oxytocin is the most common method used to increase the rate of vaginal delivery. The World Health Organization recommends its use either alone or with  Five causes make up about 80 per cent of newborn deaths globally: prematurity, low-birth-weight, infections, lack of oxygen at birth, and trauma during birth.
Five causes make up about 80 per cent of newborn deaths globally: prematurity, low-birth-weight, infections, lack of oxygen at birth, and trauma during birth.
 The
The  Distress levels vary widely during pregnancy as well as during labour and delivery. They appear to be influenced by fear and anxiety levels, experience with prior childbirth, cultural ideas of childbirth pain, mobility during labour, and the support received during labour.
Distress levels vary widely during pregnancy as well as during labour and delivery. They appear to be influenced by fear and anxiety levels, experience with prior childbirth, cultural ideas of childbirth pain, mobility during labour, and the support received during labour.
 Personal expectations, the amount of support from caregivers, quality of the caregiver-patient relationship, and involvement in decision-making are more important in mother's overall satisfaction with the birthing experience than are other factors such as age, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, preparation, physical environment, pain, immobility, or medical interventions.
Personal expectations, the amount of support from caregivers, quality of the caregiver-patient relationship, and involvement in decision-making are more important in mother's overall satisfaction with the birthing experience than are other factors such as age, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, preparation, physical environment, pain, immobility, or medical interventions.
 According to a 2013 analysis performed commissioned by the New York Times and performed by Truven Healthcare Analytics, the cost of childbirth varies dramatically by country. In the United States the average amount actually paid by insurance companies or other payers in 2012 averaged $9,775 for an uncomplicated conventional delivery and $15,041 for a caesarean birth. The aggregate charges of healthcare facilities for four million annual births in the United States was estimated at over $50 billion. The summed cost of prenatal care, childbirth, and newborn care came to $30,000 for a vaginal delivery and $50,000 for a caesarian section.
In the United States, childbirth hospital stays have some of the lowest ICU utilisations. Vaginal delivery with and without complicating diagnoses and caesarean section with and without comorbidities or major comorbidities account for four of the 15 types of hospital stays with low rates of ICU utilisation (where less than 20% of visits were admitted to the ICU). During stays with ICU services, approximately 20% of costs were attributable to the ICU.
A 2013 study found varying costs by facility for childbirth expenses in California, varying from $3,296 to $37,227 for a vaginal birth and from $8,312 to $70,908 for a caesarean birth.
Beginning in 2014, the
According to a 2013 analysis performed commissioned by the New York Times and performed by Truven Healthcare Analytics, the cost of childbirth varies dramatically by country. In the United States the average amount actually paid by insurance companies or other payers in 2012 averaged $9,775 for an uncomplicated conventional delivery and $15,041 for a caesarean birth. The aggregate charges of healthcare facilities for four million annual births in the United States was estimated at over $50 billion. The summed cost of prenatal care, childbirth, and newborn care came to $30,000 for a vaginal delivery and $50,000 for a caesarian section.
In the United States, childbirth hospital stays have some of the lowest ICU utilisations. Vaginal delivery with and without complicating diagnoses and caesarean section with and without comorbidities or major comorbidities account for four of the 15 types of hospital stays with low rates of ICU utilisation (where less than 20% of visits were admitted to the ICU). During stays with ICU services, approximately 20% of costs were attributable to the ICU.
A 2013 study found varying costs by facility for childbirth expenses in California, varying from $3,296 to $37,227 for a vaginal birth and from $8,312 to $70,908 for a caesarean birth.
Beginning in 2014, the  Different categories of
Different categories of