|
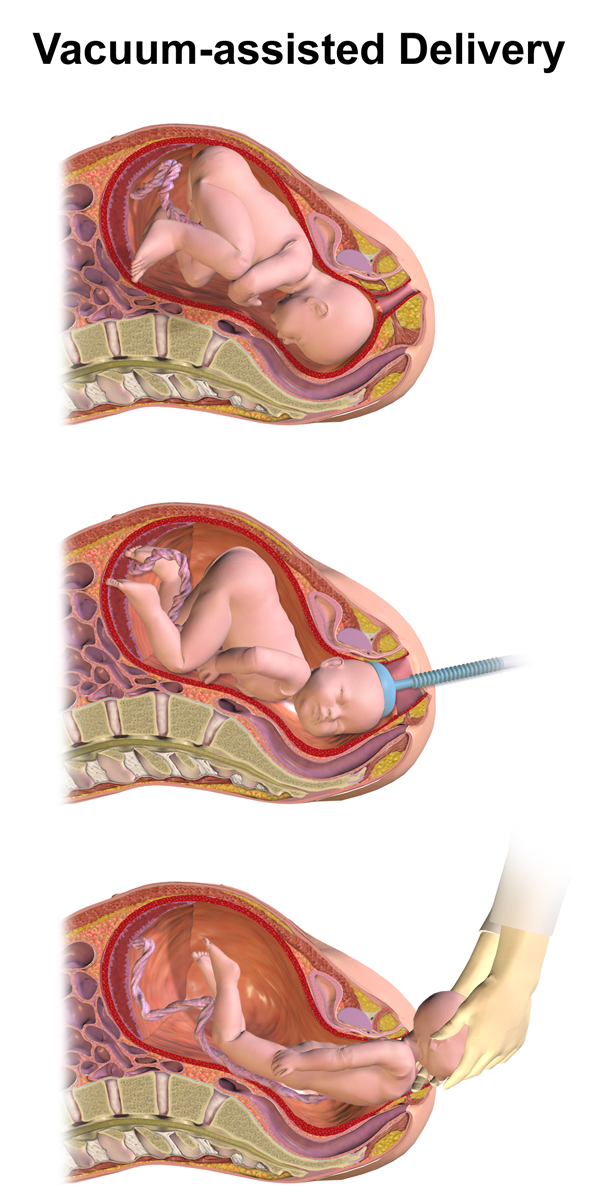
Vacuum Extraction
Vacuum extraction (VE), also known as ventouse, is a method to assist delivery of a baby using a vacuum device. It is used in the second stage of labor if it has not progressed adequately. It may be an alternative to a forceps delivery and caesarean section. It cannot be used when the baby is in the breech position or for premature births. The use of VE is generally safe, but it can occasionally have negative effects on either the mother or the child. The term comes from the French word for "suction cup". Medical uses There are several indications to use a vacuum extraction to aid delivery: * Maternal exhaustion * Prolonged second stage of labor * Foetal distress in the second stage of labor, generally indicated by changes in the foetal heart-rate (usually measured on a CTG) * Maternal illness where prolonged "bearing down" or pushing efforts would be risky (e.g. cardiac conditions, blood pressure, aneurysm, glaucoma). If these conditions are known about before the birth, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chignon (medical Term)
A chignon is a temporary swelling left on an infant's head after a ventouse suction cap has been used to deliver her or him. It is not a sign of serious injury and may take as little as two hours or as long as two weeks to disappear. See also * Caput succedaneum * Cephalohematoma A cephalohaematoma is a hemorrhage of blood between the skull and the periosteum of any age human, including a newborn baby secondary to rupture of blood vessels crossing the periosteum. Because the swelling is subperiosteal, its boundaries are ... References External links Childbirth Birth trauma Neonatology {{Pediatrics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
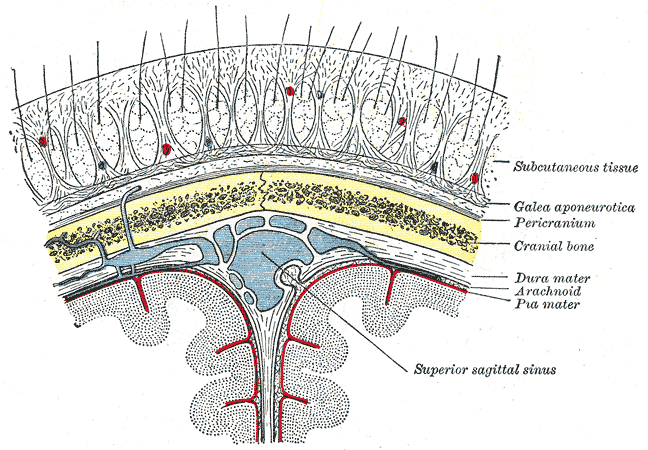
Scalp Sampling
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. Structure The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic: * S: The skin on the head from which head hair grows. It contains numerous sebaceous glands and hair follicles. * C: Connective tissue. A dense subcutaneous layer of fat and fibrous tissue that lies beneath the skin, containing the nerves and vessels of the scalp. * A: The aponeurosis called epicranial aponeurosis (or galea aponeurotica) is the next layer. It is a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue which runs from the frontalis muscle anteriorly to the occipitalis posteriorly. * L: The loose areolar connective tissue layer provides an easy plane of separation between the upper three layers and the pericranium. In scalping the scalp is torn off through this layer. It also provides a plane of access in craniofacial surgery and neurosurgery. This laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the shortening and opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the postpartum. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes. Contractions gradually becomes stronger and closer together. Since the pain of childbirth correlates with contractions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odón Device
Odón device is a medical device that assists during a difficult birth. The device consists of a plastic sleeve that is inflated around the baby's head and is used to gently pull and ease the head of the infant through the birth canal.McNeil, Donald G, Jr"Car Mechanic Dreams Up a Tool to Ease Births" ''The New York Times'', November 13, 2013. Accessed November 14, 2013. Need Worldwide, more than 13 million births each year face serious complications, and every day about 800 women die from preventable causes related to pregnancy and childbirth (about 300,000 annually). The use of forceps and other mechanical devices in the extraction of a baby in a difficult delivery can cause internal bleeding in the mother or may result in injuries to the baby's head or spine. The Odón device has the potential to allow for vaginal delivery in complicated pregnancies in which common medical practice would have led to a cesarean section, the use of forceps to extract the newborn or the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgaleal Hemorrhage
Subgaleal hemorrhage, also known as subgaleal hematoma, is bleeding in the potential space between the skull periosteum and the scalp galea aponeurosis. Symptoms The diagnosis is generally clinical, with a fluctuant boggy mass developing over the scalp (especially over the occiput) with superficial skin bruising. The swelling develops gradually 12–72 hours after delivery, although it may be noted immediately after delivery in severe cases. Subgaleal hematoma growth is insidious, as it spreads across the whole calvaria and may not be recognized for hours to days. If enough blood accumulates, a visible fluid wave may be seen. Patients may develop periorbital ecchymosis ("raccoon eyes"). Patients with subgaleal hematoma may present with hemorrhagic shock given the volume of blood that can be lost into the potential space between the skull periosteum and the scalp galea aponeurosis, which has been found to be as high as 20-40% of the neonatal blood volume in some studies. The swel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalohematoma
A cephalohaematoma is a hemorrhage of blood between the skull and the periosteum of any age human, including a newborn baby secondary to rupture of blood vessels crossing the periosteum. Because the swelling is subperiosteal, its boundaries are limited by the individual bones, in contrast to a caput succedaneum. Symptoms and signs Swelling appears after 2-3 days after birth. If severe the child may develop jaundice, anemia or hypotension. In some cases it may be an indication of a linear skull fracture or be at risk of an infection leading to osteomyelitis or meningitis. The swelling of a cephalohematoma takes weeks to resolve as the blood clot is slowly absorbed from the periphery towards the centre. In time the swelling hardens (calcification) leaving a relatively softer centre so that it appears as a 'depressed fracture'. Cephalohematoma should be distinguished from another scalp bleeding called subgaleal hemorrhage (also called subaponeurotic hemorrhage), which is blood betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chignon (medical Term)
A chignon is a temporary swelling left on an infant's head after a ventouse suction cap has been used to deliver her or him. It is not a sign of serious injury and may take as little as two hours or as long as two weeks to disappear. See also * Caput succedaneum * Cephalohematoma A cephalohaematoma is a hemorrhage of blood between the skull and the periosteum of any age human, including a newborn baby secondary to rupture of blood vessels crossing the periosteum. Because the swelling is subperiosteal, its boundaries are ... References External links Childbirth Birth trauma Neonatology {{Pediatrics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
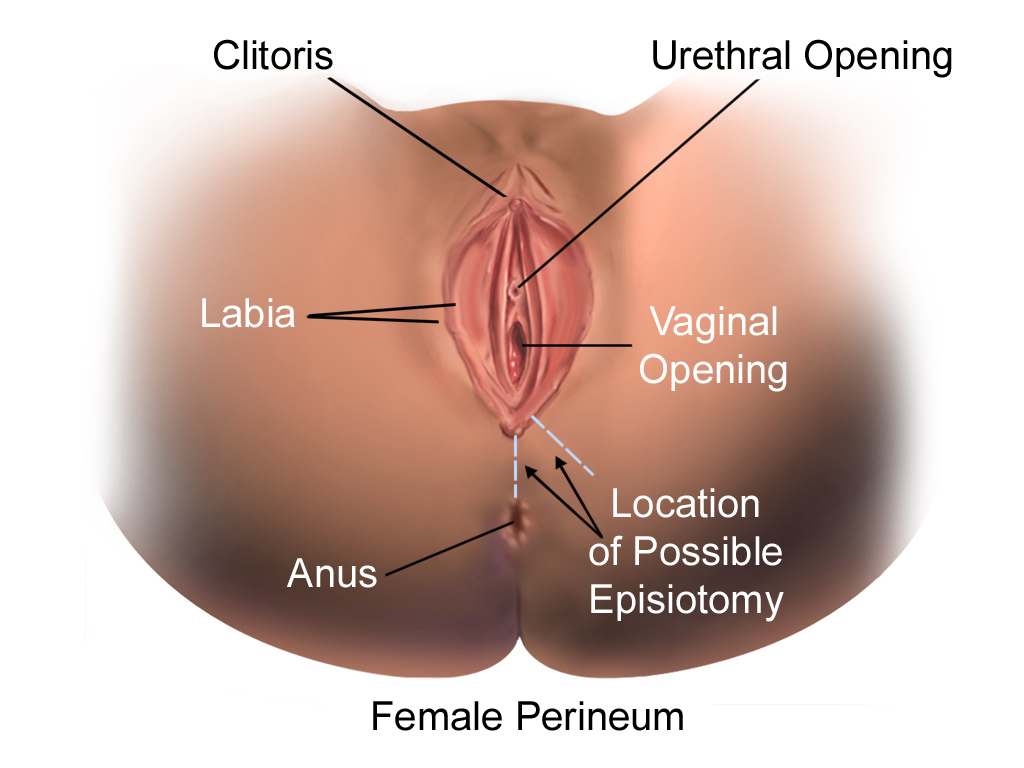
Episiotomy
Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by a midwife or obstetrician. Episiotomy is usually performed during second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the opening for the baby to pass through. The incision, which can be done from the posterior midline of the vulva straight toward the anus or at an angle to the right or left (medio-lateral episiotomy), is performed under local anesthetic (pudendal anesthesia), and is sutured after delivery. Its routine use is no longer recommended, as perineal massage is an alternative painless method of enlarging the opening for baby. Despite this, it is one of the most common surgical procedures specific to women. In the United States, as of 2012, it was performed in 12% of vaginal births. It is still widely practiced in many parts of the world, including Korea, Japan, Taiwan, China, and Spain. Uses Vaginal tears can occur during childbirth, most often at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, HChlorine, Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to PTFE. It is also a precursor to various refrigerants. It is trihalomethane. It is a powerful anesthetic, euphoriant, anxiolytic, and sedative when inhaled or ingested. Structure The molecule adopts a tetrahedral molecular geometry with C3v symmetry group, symmetry. Natural occurrence The total global flux of chloroform through the environment is approximately tonnes per year, and about 90% of emissions are natural in origin. Many kinds of seaweed produce chloroform, and fungi are believed to produce chloroform in soil. Abiotic processes are also believed to contribute to natural chloroform productions in soils although the mechanism is still unclear. Chloroform volatilizes readily from soil and surface water and undergoes degradation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Young Simpson
Sir James Young Simpson, 1st Baronet, (7 June 1811 – 6 May 1870) was a Scottish obstetrician and a significant figure in the history of medicine. He was the first physician to demonstrate the anaesthetic properties of chloroform on humans and helped to popularise its use in medicine. Simpson's intellectual interests ranged from archaeology to an almost taboo subject at the time: hermaphroditism. He was an early advocate of the use of midwives in the hospital environment. Many prominent women also consulted him for their gynaecological problems. Simpson wrote ''Homœopathy, its Tenets and Tendencies'' refuting the ideas put forward by Hahnemann. His services as an early founder of gynaecology and proponent of hospital reform were rewarded with a knighthood and by 1847 he had been appointed as physician to the Queen in Scotland. Simpson was a close friend of Sir David Brewster, and was present at his deathbed. His contribution to the understanding of the anaesthetic proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |